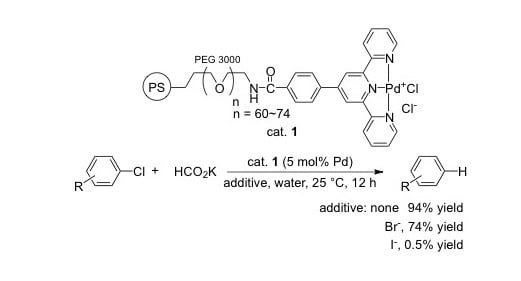
Reactivity of Aryl Halides for Reductive Dehalogenation in (Sea)water Using Polymer-Supported Terpyridine Palladium Catalyst
Abstract
:1. Introduction
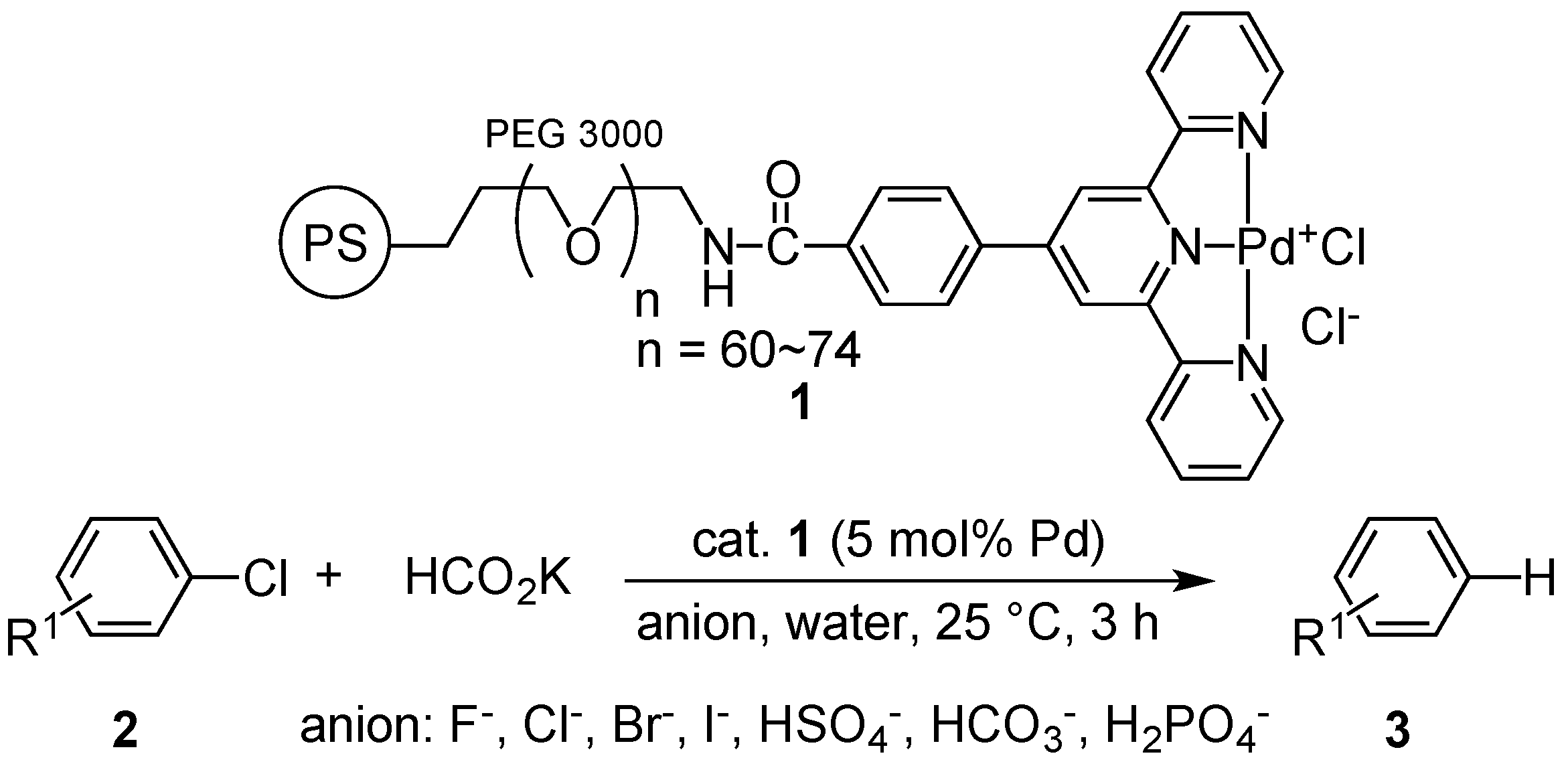
2. Results and Discussion
| Run | R1:2 | R1:3 | Yield (%) (Water) | Yield (%) (Seawater) | Yield (%) (Seawater) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | p-Ac:2a | Ac:3a | 94 | 56 | 94 c |
| 2 | m-Ac:2b | 3a | 96 | 65 | 95 c |
| 3 | o-Ac:2c | 3a | 95 | 44 | 91 c |
| 4 b | p-B:2d | Bz:3b | 94 | 52 | 87 c |
| 5 b | m-Bz:2e | 3b | 94 | 84 | 84 c |
| 6 b | o-Bz:2f | 3b | 93 | 68 | 68 c |
| 7 b | p-NH2:2g | NH2:3c | 93 | 9 | 94 c |
| 8 | m-NH2:2h | 3c | 95 | 44 | 95 c |
| 9 | o-NH2:2i | 3c | 96 | 33 | 95 c |
| 10 | p-OH:2j | OH:3d | 94 | 90 | 94 c |
| 11 | m-OH:2k | 3d | 94 | 77 | 94 c |
| 12 | o-OH:2l | 3d | 94 | 59 | 94 c |
| 13 | Ac, 2,5-Cl:2m | 3a | 90 | 21 | 58 c |
| 14 d | Ac, 2,3,5-Cl:2n | 3a | 96 e | 43 | 90 e |
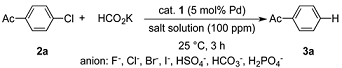
| Run | Salts | Amount of Salts (mol) 100 ppm | Yield (%) a |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | none | --- | 94 |
| 2 | NaF | 3.57 × 10−6 | 94 |
| 3 | NaCl | 2.57 × 10−6 | 95 |
| 4 | NaBr | 1.46 × 10−6 | 63 |
| 5 | NaI | 1.00 × 10−6 | 60 |
| 6 | Na2SO4·10H2O | 0.47 × 10−6 | 96 |
| 7 | Na2CO3 | 1.42 × 10−6 | 95 |
| 8 | NaH2PO4·2H2O | 0.96 × 10−6 | 95 |
| 9 | AgNO3 | 1.59 × 10−6 | 92 |
| 10 | AgNO3, NaBr | 1.50 × 10−6 | 96 |
| 11 b | AgNO3 | 1.59 × 10−6 | 0 |
| 12 b,c | None | --- | 94 |
| Entry | Aryl Halide | Yield (%) a |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4-Cl-acetophenone 2a | quant. |
| 2 b | 4-Br-acetophenone 2o | 74 |
| 3 b | 4-I-acetophenone 2p | 0.5 |

3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Methods
3.2. Materials
3.3. Synthesis of Polymer-Supported Ligand
3.4. Preparation of PS–PEG Resin-Supported Terpyridine Palladium Complex 1
3.5. Hydrodechlorination of Aryl Chlorides
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Hites, R.A. Environmental behavior of chlorinated dioxins and furans. Acc. Chem. Res. 1990, 23, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blais, J.M.; Schindler, D.W.; Muir, D.C.G.; Kimpe, L.E.; Donald, D.B.; Rosemberg, B. Accumulation of persistent organochlorine compounds in mountains of western Canada. Nature 1988, 395, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, D.; Muller, J.; Carter, S. Pesticide and herbicide residues in sediments and seagrasses from the Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area and Queensland Coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 41, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, K.; Bengtson, N.S.; Eaglesham, G.; Negri, A. Herbicide contamination and the potential impact to seagrass meadows in Hervey Bay, Queensland, Australia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negri, A.; Humpherey, C.; Heyward, A.; Jones, R.; Eaglesham, G.; Fabricius, K. Effects of the herbicide diuron on the early life history stages of coral. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakugawa, H.; Tahara, K.; Aoki, K.; Arai, N.; Nakatani, N.; Takeda, K. Studies on concentration, decomposition rate, half-life time and degradation products of herbicide diuron in river waters of Hiroshima prefecture, Japan. Geochemistry 2010, 44, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuka, T.; Sato, Y.; Ogihara, K. Transfer Reduction of Aryl Chlorides with Potassium Formate in Seawater Using Polymer-Supported Terpyridine Palladium Complex. Trans. Mater. Res. Soc. Jpn. 2014, 39, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüth, C.; Reinhard, M. Hydrodechlorination and hydrogenation of aromatic compounds over palladium on alumina in hydrogen-saturated water. App. Catal. B 1998, 18, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramendia, M.A.; Borau, V.; Garcia, I.M.; Jimenez, C.; Lafont, F.; Marians, A.; Marinaas, J.M.; Urbano, F.J. Liquid-phase hydrodechlorination of chlorobenzene over palladium-supported catalysts—Influence of HCl formation and NaOH addition. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2002, 184, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, R.; Narasimha Rao, K.; Sai Prasad, P.S.; Madhavendra, S.S.; Nayaranam, S.; Vivekanadam, G. Hydrodechlorination of chlorobenzene on Nb2O5-supported Pd catalysts: Influence of microwave irradiation during preparation on the stability of the catalyst. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2002, 181, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murena, F.; Gioia, F. Catalytic hydrodechlorination of decachlorobiphenyl. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2002, 38, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menini, C.; Park, C.; Shin, E.J.; Tavoularis, G.; Keane, M.A. Catalytic hydrodehalogenation as a detoxification methodology. Catal. Today 2000, 62, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcadi, A.; Cerichelli, G.; Chiarini, M.; Vico, R.; Zorzan, D. Pd/C-catalyzed transfer reduction of aryl chlorides with sodium formate in water. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 2004, 3404–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, R.; Rhee, H.; Uozumi, Y. Hydrogenation and dehalogenation under aqueous conditions with an amphiphilic-polymer-supported nanopalladium catalyst. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, T.; Atake, I.; Ohishi, Y.; Shishido, T.; Tian, Y.; Takaki, K.; Takehira, T. Liquid phase catalytic hydrodechlorination of aryl chlorides over Pd-Al-MCM-41 catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 66, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutt, M.O.; Heck, K.N.; Alvarez, P.; Wong, M.S. Improved Pd-on-Au bimetallic nanoparticle catalysts for aqueous-phase trichloroethene hydrodechlorination. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 69, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parshetti, G.K.; Doong, R.A. Immobilization of bimetallic nanoparticles on microfiltration membranes for trichloroethylene dechlorination. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 1629–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Lin, S.; Chen, Z.L.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Dechlorination of p-chlorophenol from aqueous solution using bentonite supported Fe/Pd nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and kinetics. Desalination 2011, 280, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Bacik, D.B.; Roberts, C.B.; Zhao, D.Y. Catalytic hydrodechlorination of trichloroethylene in water with supported CMC-stabilized palladium nanoparticles. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3706–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, E.; Mohedano, A.F.; Casas, J.A.; Calvo, L.; Gilarranz, M.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Deactivation of a Pd/AC catalyst in the hydrodechlorination of chlorinated herbicides. Catal. Today 2015, 241, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helquist, P. Palladium hydrides in organic synthesis. Reduction of aryl bromides by sodium formate catalyzed by tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium. Tetrahedron Lett. 1978, 22, 1913–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuka, T.; Ogihara, K.; Higa, M. Transfer Reduction of Aryl Chlorides with Potassium Formate in Water Using Polymer-Supported Terpyridine Palladium Complex. Trans. Mater. Res. Soc. Jpn. 2014, 39, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramendia, M.A.; Borau, V.; Garcia, I.M.; Jimenez, C.; Lafont, F.; Marians, A.; Marinas, J.M.; Urbano, F.J. Liquid-phase Hydrodechlorination of Chlorobenzene Over Palladium-Supported Catalysts: Influence of HCl Formation and NaOH Addition. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2002, 184, 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Cesteros, Y.; Salagre, P.; Medina, F.; Sueiras, J.E.; Tichit, D.; Coq, P. Hydrodechlorination of 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene on nickel-based catalysts prepared from several Ni/Mg/Al hydrotalcite-like precursors. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2001, 32, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipshutz, B.C.; Tomioka, T.; Sato, K. Nickel-on-Charcoal-Catalyzed Reductions of Aryl Chlorides. Synlett 2001, 970–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañete, Á.F.; Salas, C.O.; Zacconi, F.C. Efficeint Indium-Mediated Dehalogenation of Aromatics in Ionic Liquid Media. Molecules 2013, 18, 398–407. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuka, T.; Adachi, M.; Yang, Z.-S.; Ogihara, K.; Higa, M. Use of Polymer-Supported Terpyridine Palladium Complex for Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reaction in Water and the Synthesis of 2,6-Disubstituted Pyrimidines. Trans. Mater. Res. Soc. Jpn. 2013, 38, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, E.C.; Dunphy, E.L.; Housecroft, C.E.; Neuburger, M.; Schaffner, S.; Schaper, F.; Batten, S.R. Expanded ligands: Bis(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine carboxylic acid) ruthenium(II) complexes as metallosupramolecular analogues of dicarboxylic acids. Dalton. Trans. 2007, 14, 4323–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- For a review of terpyridine metal complexes, see: Eryazici, I.; Moorefield, N.; Newkome, R. Square-Planar Pd(II), Pt(II), and Au(III) Terpyridine Complexes: Their Syntheses, Physical Properties, Supramolecular Constructs, and Biomedical Activities. Chem. Rev. 2010, 108, 1834–1895 and references therein. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suzuka, T.; Sueyoshi, H.; Maehara, S.; Ogasawara, H. Reactivity of Aryl Halides for Reductive Dehalogenation in (Sea)water Using Polymer-Supported Terpyridine Palladium Catalyst. Molecules 2015, 20, 9906-9914. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20069906
Suzuka T, Sueyoshi H, Maehara S, Ogasawara H. Reactivity of Aryl Halides for Reductive Dehalogenation in (Sea)water Using Polymer-Supported Terpyridine Palladium Catalyst. Molecules. 2015; 20(6):9906-9914. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20069906
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuzuka, Toshimasa, Hiromu Sueyoshi, Shohei Maehara, and Hiroaki Ogasawara. 2015. "Reactivity of Aryl Halides for Reductive Dehalogenation in (Sea)water Using Polymer-Supported Terpyridine Palladium Catalyst" Molecules 20, no. 6: 9906-9914. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20069906
APA StyleSuzuka, T., Sueyoshi, H., Maehara, S., & Ogasawara, H. (2015). Reactivity of Aryl Halides for Reductive Dehalogenation in (Sea)water Using Polymer-Supported Terpyridine Palladium Catalyst. Molecules, 20(6), 9906-9914. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20069906