Tetracycline-Containing MCM-41 Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Escherichia coli
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation of TC-Containing MCM-41 MSNs and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)

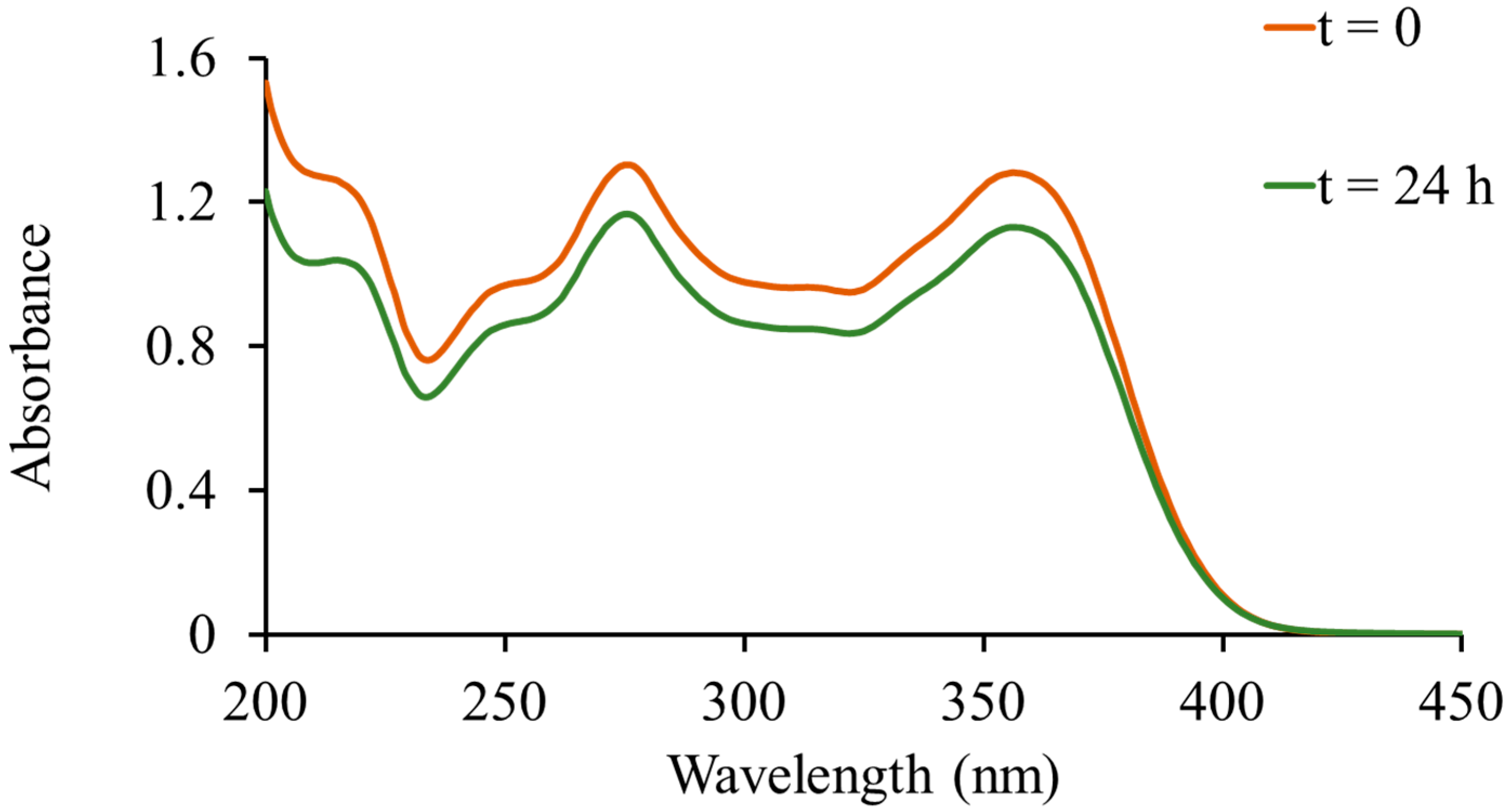
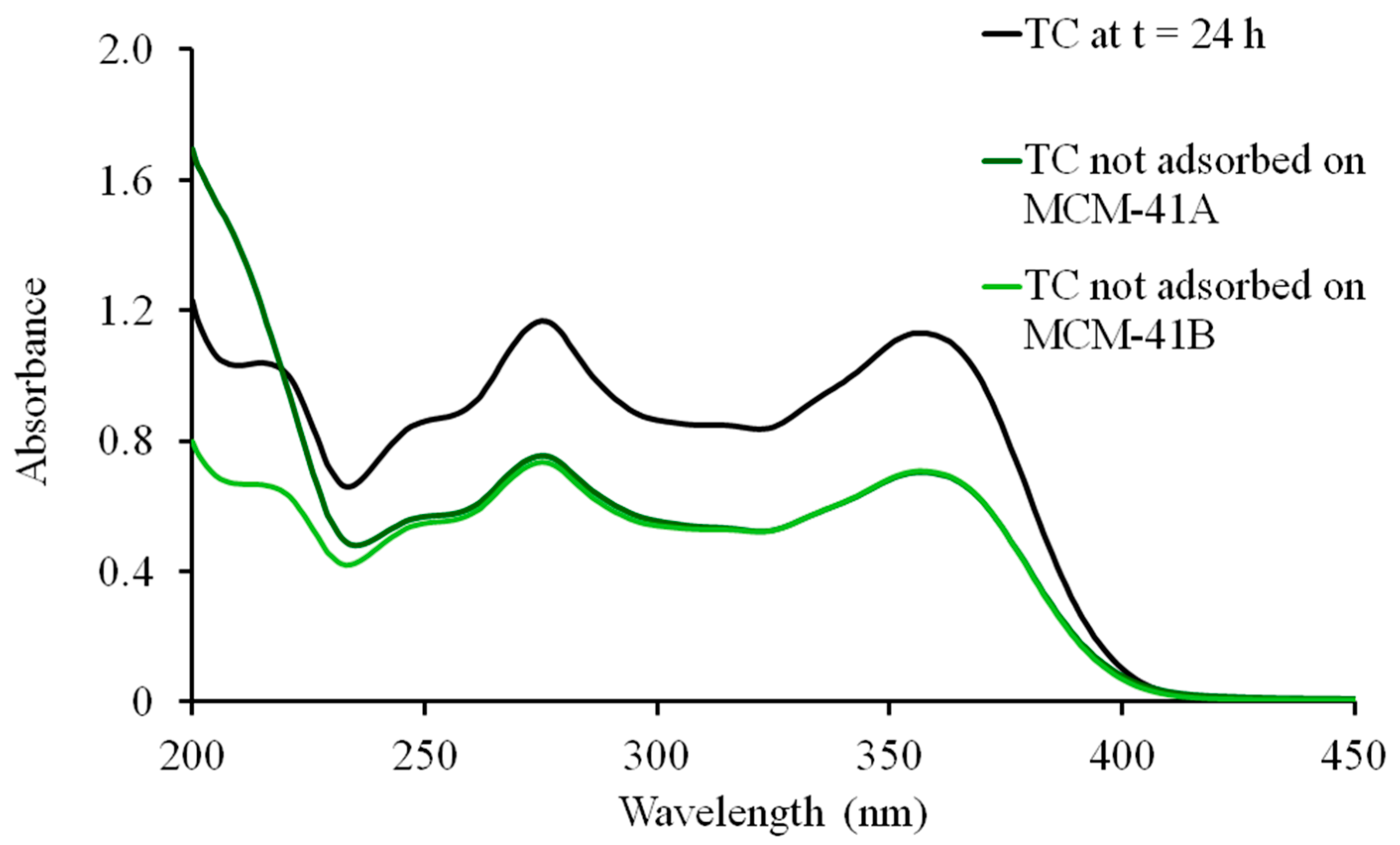
2.2. In Vitro Drug Release
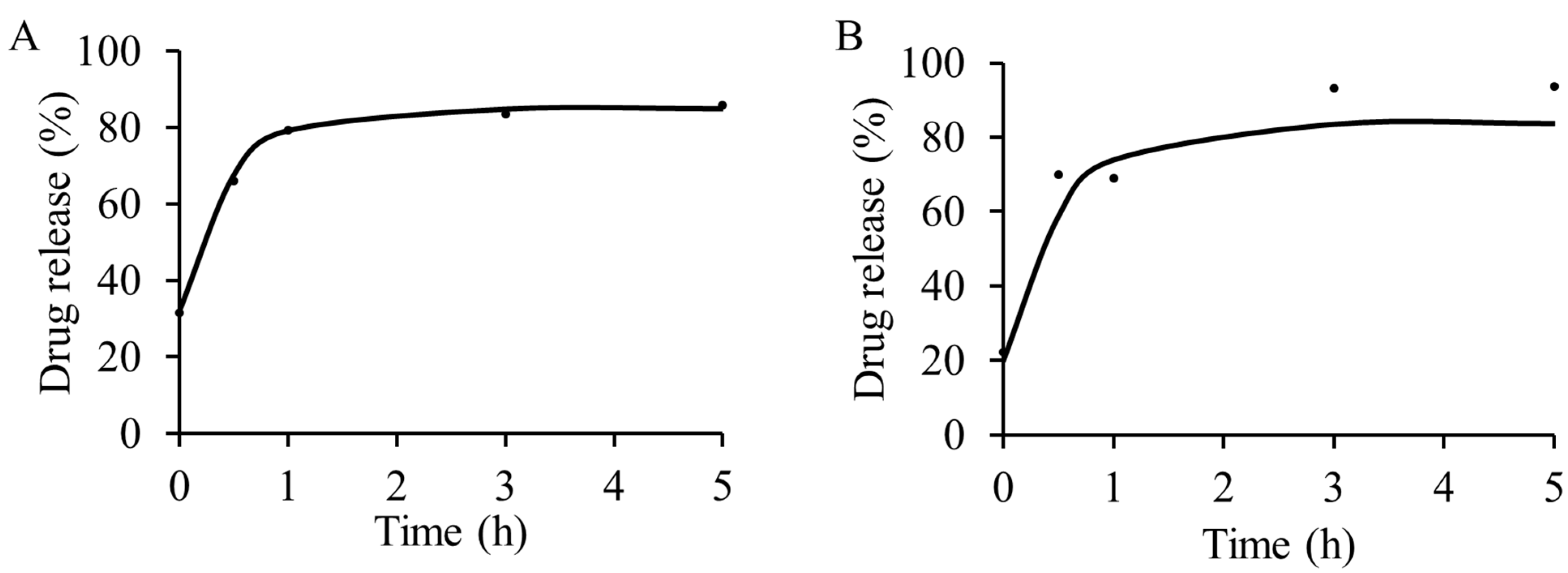
2.3. Antibacterial Activity against E. coli
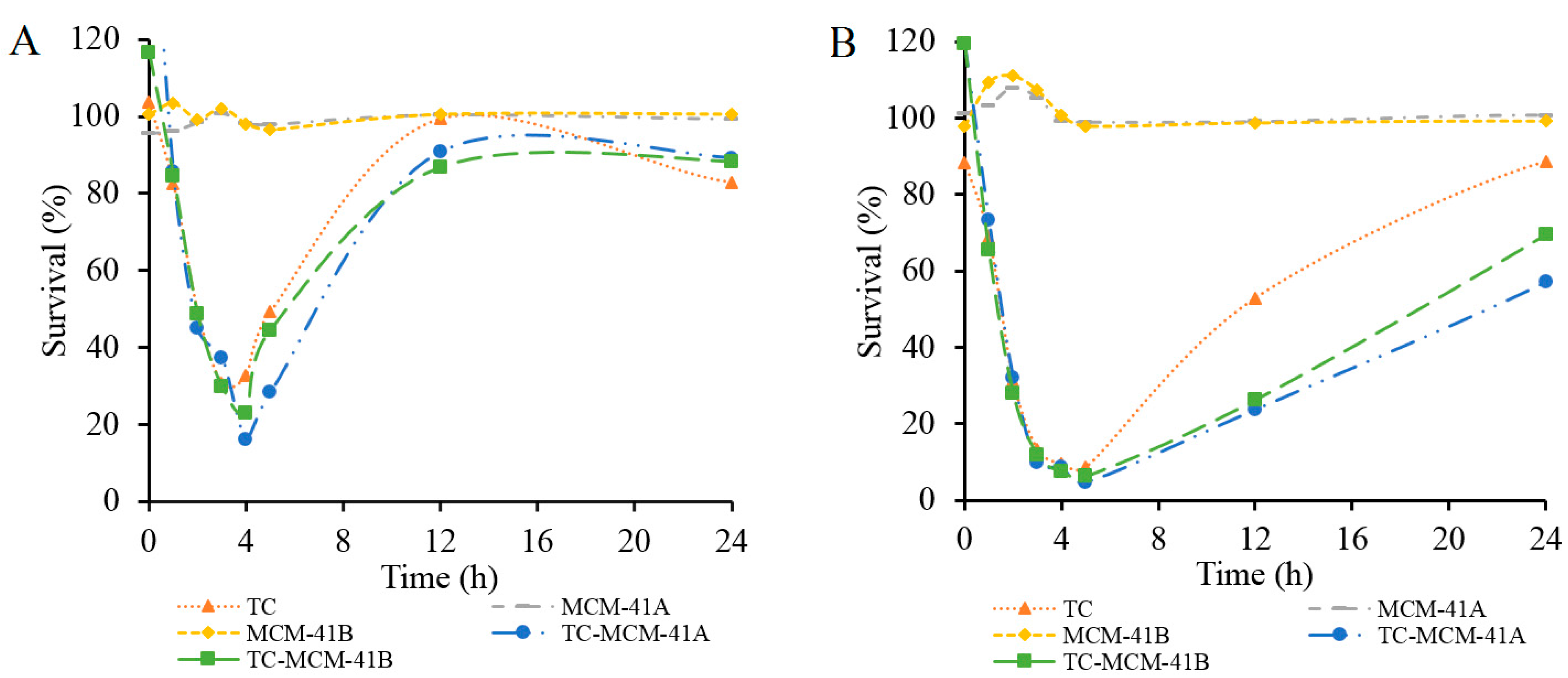
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Information
3.2. Synthesis of Tetracycline-Containing MCM-41 Nanoparticles
3.3. UV-Vis Spectroscopy
3.4. In Vitro Release Studies
3.5. Antibacterial Activity of TC-MCM-41A and TC-MCM-41B against E. coli
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duggar, B.M. Aureomycin; a product of the continuing search for new antibiotics. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1948, 51, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, M.O.; Fricovsky, E.; Ceballos, G.; Villarreal, F. Tetracyclines: A pleitropic family of compounds with promising therapeutic properties. Review of the literature. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2010, 299, C539–C548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Model Lists of Essential Medicines. Available online: http://www.who.int/selection_medicines/committees/expert/20/EML_2015_FINAL_amended_JUN2015.pdf?ua=1 (7/27/15) (accessed on 23 October 2015).
- Nelson, M.L.; Levy, S.B. The history of the tetracyclines. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1241, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalowicz, B.S.; Pihlstrom, B.L.; Drisko, C.L.; Cobb, C.M.; Killoy, W.J.; Caton, J.G.; Lowenguth, R.A.; Quinones, C.; Encarnacion, M.; Knowles, M.; et al. Evaluation of periodontal treatments using controlled-release tetracycline fibers: Maintenance response. J. Periodontol. 1995, 66, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zheng, T.; Lee, C.G.; Homer, R.J.; Elias, J.A. Tetracycline-controlled transcriptional regulation systems: Advances and application in transgenic animal modeling. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2002, 13, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenawy El, R.; Bowlin, G.L.; Mansfield, K.; Layman, J.; Simpson, D.G.; Sanders, E.H.; Wnek, G.E. Release of tetracycline hydrochloride from electrospun poly(ethylene-co-vinylacetate), poly(lactic acid), and a blend. J. Control. Release 2002, 81, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, S.; Pillay, V.; Chetty, D.J.; Essack, S.Y.; Dangor, C.M.; Govender, T. Optimisation and characterisation of bioadhesive controlled release tetracycline microspheres. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 306, 24–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luginbuehl, V.; Ruffieux, K.; Hess, C.; Reichardt, D.; von Rechenberg, B.; Nuss, K. Controlled release of tetracycline from biodegradable beta-tricalcium phosphate composites. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 92, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Slowing, I.I.; Trewyn, B.G.; Giri, S.; Lin, V.S.-Y. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery and biosensing applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pasqua, A.J.; Yuan, H.; Chung, Y.; Kim, J.K.; Huckle, J.E.; Li, C.; Sadgrove, M.; Tran, T.H.; Jay, M.; Lu, X. Neutron-activatable holmium-containing mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a potential radionuclide therapeutic agent for ovarian cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 54, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pasqua, A.J.; Wallner, S.; Kerwood, D.J.; Dabrowiak, J.C. Adsorption of the Pt(II) anticancer drug carboplatin by mesoporous silica. Chem. Biodivers. 2009, 6, 1343–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.Y.; Trewyn, B.G.; Jeftinija, D.M.; Jeftinija, K.; Xu, S.; Jeftinija, S.; Lin, V.S. A mesoporous silica nanosphere-based carrier system with chemically removable CdS nanoparticle caps for stimuli-responsive controlled release of neurotransmitters and drug molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 4451–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, J.S.; Vartuli, J.C.; Roth, W.J.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Kresge, C.T.; Schmitt, K.D.; Chu, C.T.W.; Olson, D.H.; Sheppard, E.W. A new family of mesoporous molecular sieves prepared with liquid crystal templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10834–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regi, M.; Balas, F.; Arcos, D. Mesoporous materials for drug delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2007, 46, 7548–7558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halamová, D.; Zeleňák, V. NSAID naproxen in mesoporous matrix MCM-41: Drug uptake and release properties. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2012, 72, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.Z. Preparation and controlled release of mesoporous MCM-41/propranolol hydrochloride composite drug. J. Microencapsul. 2013, 30, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, F.; Zhu, G.; Huang, S.; Li, S.; Qiu, S. Effective controlled release of captopril by silylation of mesoporous MCM-41. Chemphyschem 2006, 7, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Doadrio, J.C.; Doadrio, A.L.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Pérez-Pariente, J. Hexagonal ordered mesoporous material as a matrix for the controlled release of amoxicillin. Solid State Ion. 2004, 172, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Singh, R.K.; Perez, R.A.; Neel, E.A.A.; Kim, H.W.; Chrzanowski, W. Silica-based mesoporous nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery. J. Tissue Eng. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, B.K.; Snisarenko, O.; Lee, H.S.; Shin, E.W. Adsorption of tetracycline on La-impregnated MCM-41 materials. Environ. Technol. 2010, 31, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Wu, L.; Lan, H.; Qu, J. Preparation of amino-Fe(III) functionalized mesoporous silica for synergistic adsorption of tetracycline and copper. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Hou, L.A.; Yu, S.; Xi, B.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, X. MCM-41 impregnated with A zeolite precursor: Synthesis, characterization and tetracycline antibiotics removal from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 223, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.X.; Qiao, S.Z.; Yu, C.Z.; Ismadji, S.; Lu, G.Q. Periodic mesoporous silica and organosilica with controlled morphologies as carriers for drug release. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 117, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemikia, S.; Hemmatinejad, N.; Ahmadi, E.; Montazer, M. Optimization of tetracycline hydrochloride adsorption on amino modified SBA-15 using response surface methodology. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 443, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Wu, S.H.; Hung, Y.; Mou, C.Y. Size effect on cell uptake in well-suspended, uniform mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Small 2009, 5, 1408–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pasqua, A.J.; Miller, M.L.; Lu, X.L.; Peng, L.; Jay, M. Tumor accumulation of neutron-activatable holmium-containing mesoporous silica nanoparticles in an orthotopic non-small cell lung cancer mouse model. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2012, 393, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pasqua, A.J.; Sharma, K.K.; Shi, Y.L.; Toms, B.B.; Ouellette, W.; Dabrowiak, J.C.; Asefa, T. Cytotoxicity of mesoporous silica nanomaterials. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2008, 102, 1416–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Fassihi, R. Stability of metronidazole, tetracycline HCl and famotidine alone and in combination. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 290, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horcajada, P.; Rámila, A.; Perez-Pariente, J.; Vallet-Regi, M. Influence of pore size of MCM-41 matrices on drug delivery rate. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 68, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.Y.; Zhu, G.S.; Huang, S.Y.; Li, S.G.; Sun, J.Y.; Zhang, D.L.; Qiu, S.L. Controlled release of Captopril by regulating the pore size and morphology of ordered mesoporous silica. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 92, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, R.; Sahoo, S.K. Antibacterial activity of doxycycline-loaded nanoparticles. In Nanomedicine: Infectious Diseases, Immunotherapy, Diagnostics, Antifibrotics, Toxicology And Gene Medicine; Düzgüneş, N., Ed.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; Volume 509, pp. 61–85. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, J.A.; Curtis, B.S.; Curtis, W.R. Improving accuracy of cell and chromophore concentration measurements using optical density. BMC Biophys. 2013, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koneru, B.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Chavala, S.H.; Miller, M.L.; Holbert, B.; Conson, M.; Ni, A.; Di Pasqua, A.J. Tetracycline-Containing MCM-41 Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Escherichia coli. Molecules 2015, 20, 19690-19698. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201119650
Koneru B, Shi Y, Wang Y-C, Chavala SH, Miller ML, Holbert B, Conson M, Ni A, Di Pasqua AJ. Tetracycline-Containing MCM-41 Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Escherichia coli. Molecules. 2015; 20(11):19690-19698. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201119650
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoneru, Bhuvaneswari, Yi Shi, Yu-Chieh Wang, Sai H. Chavala, Michael L. Miller, Brittany Holbert, Maricar Conson, Aiguo Ni, and Anthony J. Di Pasqua. 2015. "Tetracycline-Containing MCM-41 Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Escherichia coli" Molecules 20, no. 11: 19690-19698. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201119650
APA StyleKoneru, B., Shi, Y., Wang, Y.-C., Chavala, S. H., Miller, M. L., Holbert, B., Conson, M., Ni, A., & Di Pasqua, A. J. (2015). Tetracycline-Containing MCM-41 Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Escherichia coli. Molecules, 20(11), 19690-19698. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201119650




