1,4-Naphthoquinones: From Oxidative Damage to Cellular and Inter-Cellular Signaling
Abstract
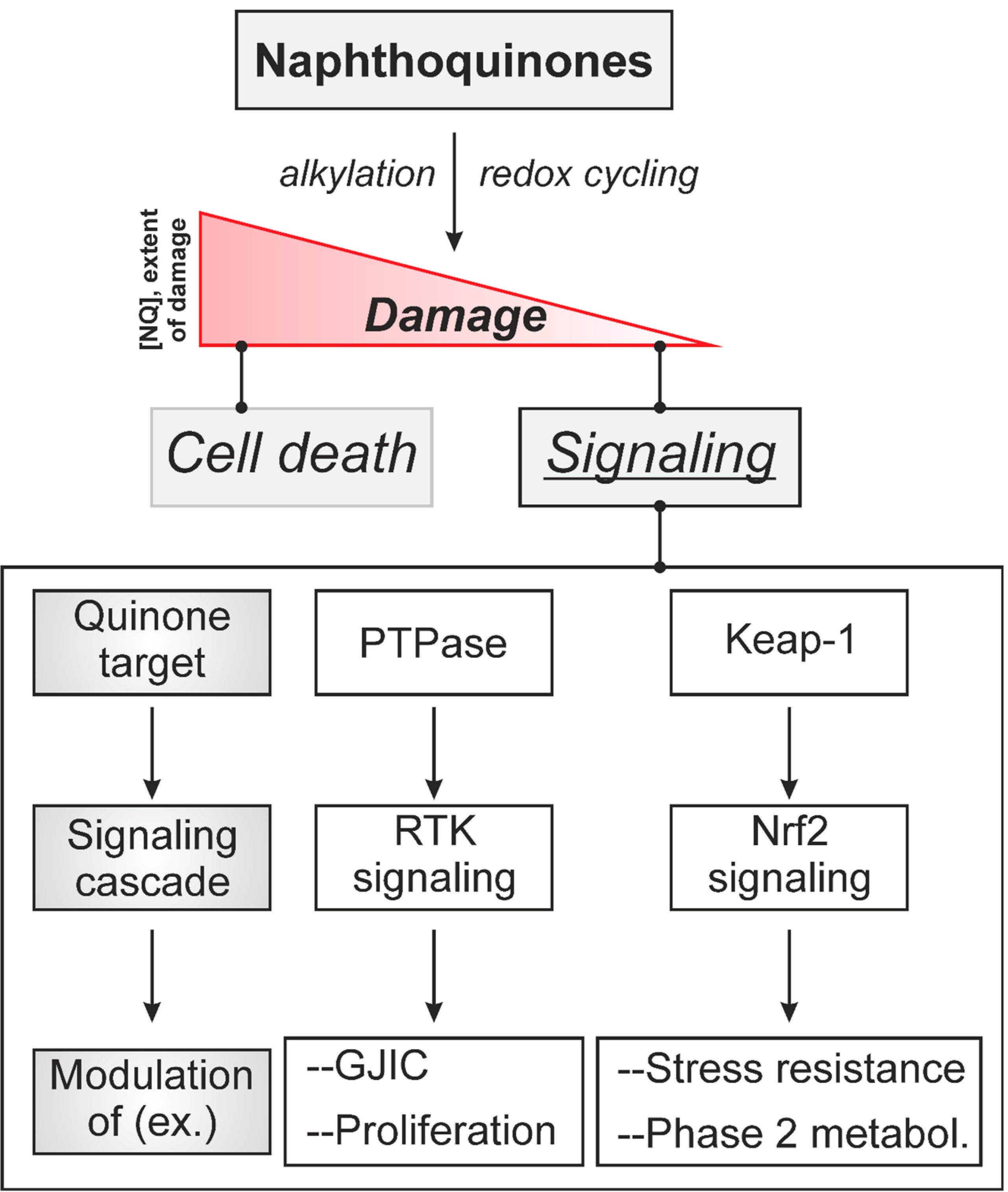
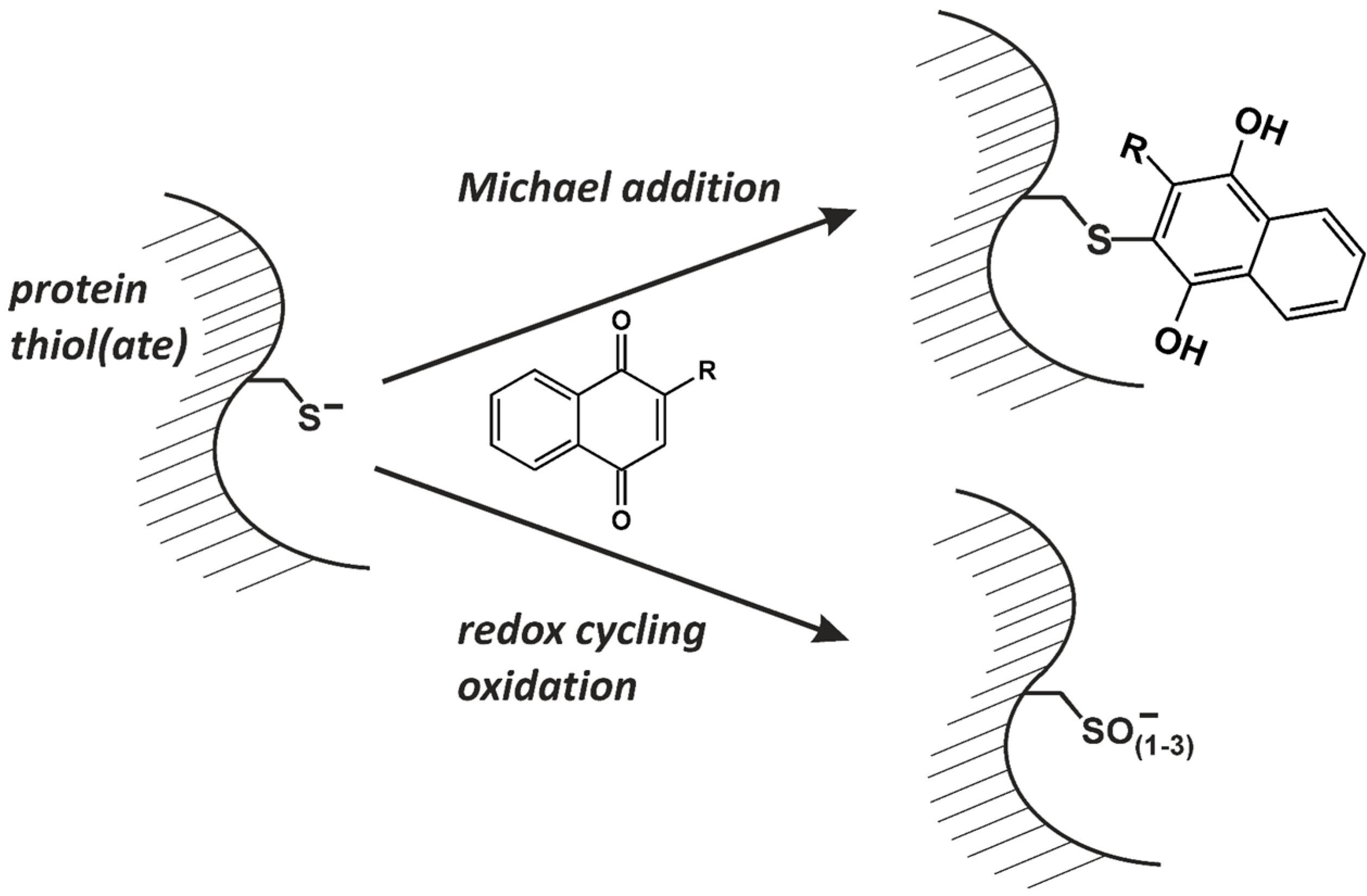
:1. Introduction: Naphthoquinones as Redox Cyclers and Alkylating Agents
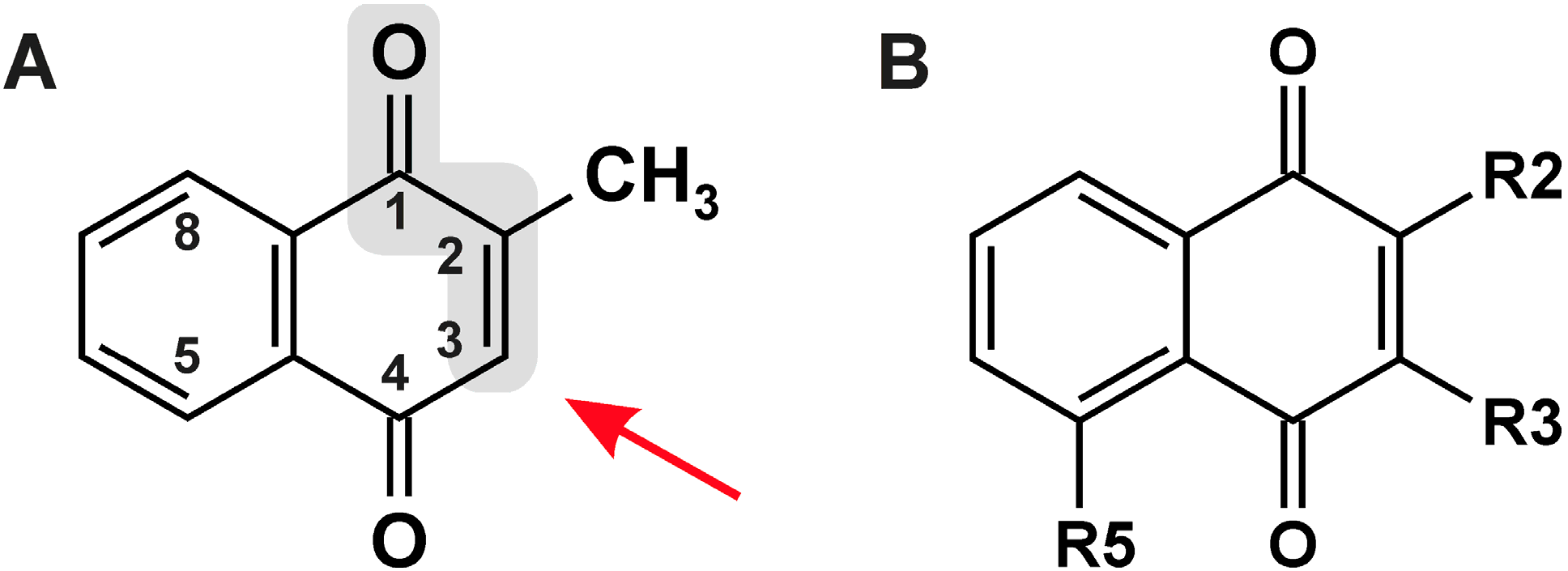
| # | R2 | R3 | R5 | Names/Acronyms Used |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | H | H | 1,4-Naphthoquinone |
| 2 | H | H | OH | Juglone |
| 3 | CH3 | H | H | Menadione/MQ |
| 4 | CH3 | H | OH | Plumbagin |
| 5 | OH | H | H | Lawsone |
| 6 | OH | CH2-CH=C(CH3)2 | H | Lapachol |
| 7 | OCH3 | H | H | MeONQ |
| 8 | OCH3 | OCH3 | H | DMNQ |
| 9 | S-CH2-CH2-OH | S-CH2-CH2-OH | H | NSC 95397 |
2. Naphthoquinone-Induced Intra- and Intercellular Signaling
2.1. Menadione and “Menadione Reductase”: Naphthoquinones, Nrf2 Signaling and the Expression of Protective Genes
2.2. Stimulation of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling by Naphthoquinones—Consequences for Gap Junctional Intercellular Communication
| # | LC50 (µM) | DNA Damage | GSH | GSSG | Superoxide Formation | E1pH7 (mV) | Activation of EGFR/ErbB2 | Naphthoquinone |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15 | N.D. | ↓↓ | ↑ | ↑ | −140 | +++ | 1,4-Naphthoquinone |
| 2 | 6 | ↑ | ↓↓ | ↑ | ↑ | −93 | +++ | Juglone |
| 3 | 40 | ↑↑ | ↓ | ↑ | ↑↑↑ | −203 | ++ | Menadione |
| 4 | 5 | N.D. | ↓↓ | ↑ | ↑↑ | −156 | +++ | Plumbagin |
| 5 | >100 | → | → | → | ↑/→ | −415 | − | Lawsone |
| 6 | >100 | N.D. | → | → | → | − | Lapachol |
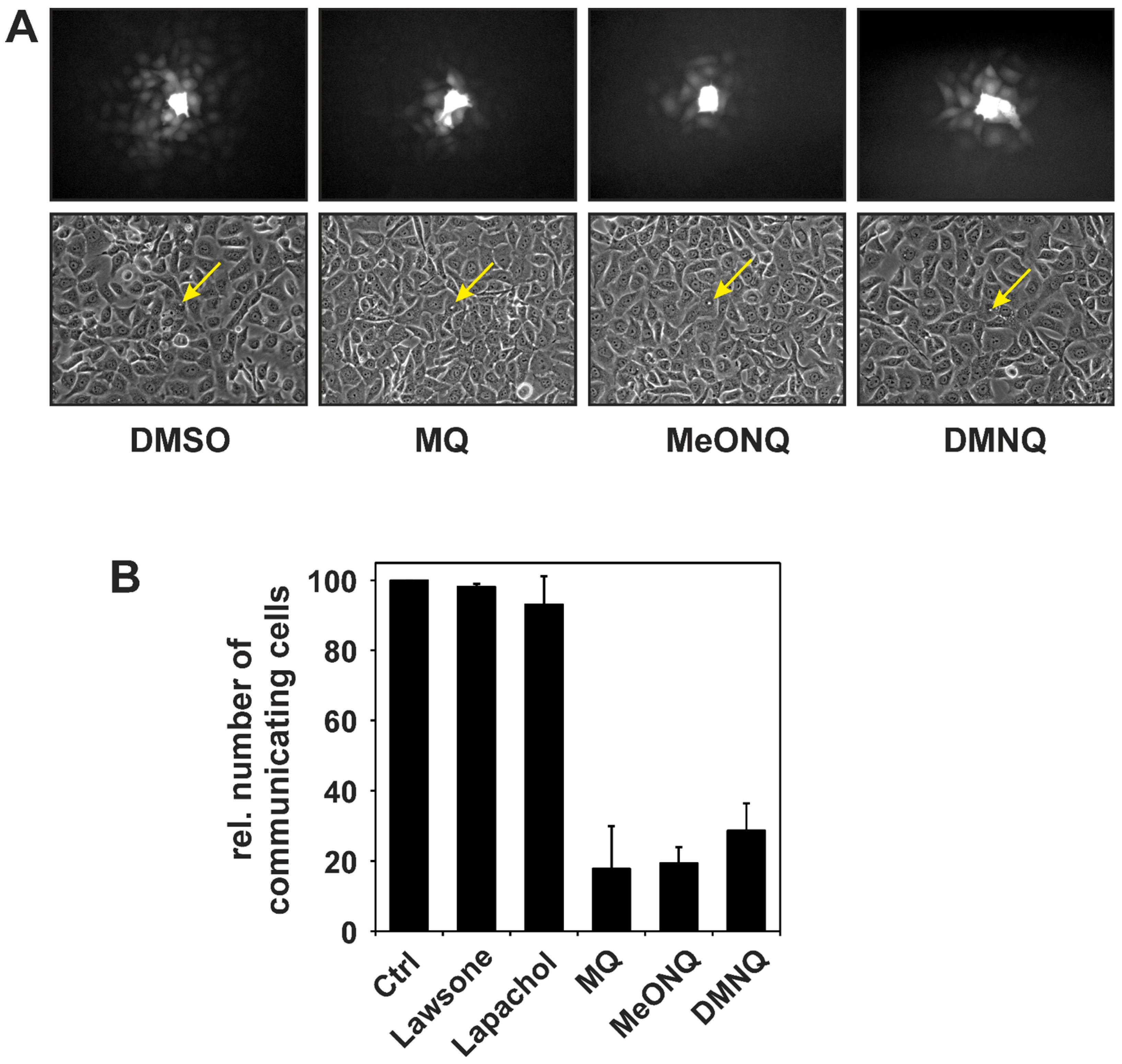
3. Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases as Targets in Naphthoquinone-Induced Signaling
4. Conclusions: Naphthoquinones—Useful in a Clinical Setting?
4.1. Naphthoquinones and Cancer Cells: “Death by ROS”
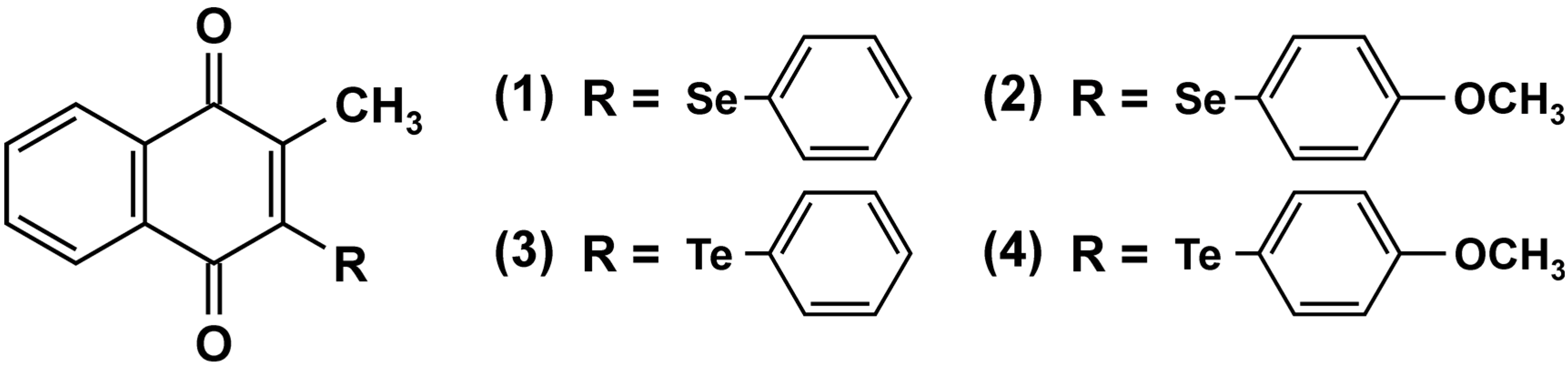
4.2. Naphthoquinones and PTPase Inhibition
4.3. Naphthoquinones and EGFR Activation—Alleviation of Side Effects?
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferland, G. The discovery of vitamin K and its clinical applications. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 61, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klaus, V.; Hartmann, T.; Gambini, J.; Graf, P.; Stahl, W.; Hartwig, A.; Klotz, L.O. 1,4-Naphthoquinones as inducers of oxidative damage and stress signaling in HaCaT human keratinocytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 496, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inbaraj, J.J.; Chignell, C.F. Cytotoxic action of juglone and plumbagin: A mechanistic study using HaCaT keratinocytes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2004, 17, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappus, H.; Sies, H. Toxic drug effects associated with oxygen metabolism: Redox cycling and lipid peroxidation. Experientia 1981, 37, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooseboom, M.; Commandeur, J.N.; Vermeulen, N.P. Enzyme-catalyzed activation of anticancer prodrugs. Pharmacol. Rev. 2004, 56, 53–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernster, L. DT Diaphorase: A historical review. Chem. Scr. 1987, 27A, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Thor, H.; Smith, M.T.; Hartzell, P.; Bellomo, G.; Jewell, S.A.; Orrenius, S. The metabolism of menadione (2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone) by isolated hepatocytes. A study of the implications of oxidative stress in intact cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 12419–12425. [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama, T.; Izawa, T.; Usami, M.; Ohnuma, T.; Ogura, K.; Hiratsuka, A. Cooperation of NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 and UDP-glucuronosyltransferases reduces menadione cytotoxicity in HEK293 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 394, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadenas, E. Antioxidant and prooxidant functions of DT-diaphorase in quinone metabolism. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995, 49, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Arcy Doherty, M.; Rodgers, A.; Cohen, G.M. Mechanisms of toxicity of 2- and 5-hydroxy-1, 4-naphthoquinone; absence of a role for redox cycling in the toxicity of 2-hydroxy-1, 4-naphthoquinone to isolated hepatocytes. J. Appl. Toxicol. 1987, 7, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmohsen, K.; Gerber, P.A.; von Montfort, C.; Sies, H.; Klotz, L.O. Epidermal growth factor receptor is a common mediator of quinone-induced signaling leading to phosphorylation of connexin-43—Role of glutathione and tyrosine phosphatases. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 38360–38367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmohsen, K.; Patak, P.; von Montfort, C.; Melchheier, I.; Sies, H.; Klotz, L.O. Signaling effects of menadione: From tyrosine phosphatase inactivation to connexin phosphorylation. Methods Enzymol. 2004, 378, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buffinton, G.D.; Öllinger, K.; Brunmark, A.; Cadenas, E. DT-diaphorase-catalysed reduction of 1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives and glutathionyl-quinone conjugates. Effect of substituents on autoxidation rates. Biochem. J. 1989, 257, 561–571. [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai, Y.; Shinkai, Y.; Miura, T.; Cho, A.K. The chemical biology of naphthoquinones and its environmental implications. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 52, 221–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Talalay, P. NAD(P)H:quinone acceptor oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1), a multifunctional antioxidant enzyme and exceptionally versatile cytoprotector. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 501, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Fahey, J.W.; Talalay, P. Chemical structures of inducers of nicotinamide quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1). Methods Enzymol. 2004, 382, 423–448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Talalay, P.; de Long, M.J.; Prochaska, H.J. Identification of a common chemical signal regulating the induction of enzymes that protect against chemical carcinogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 8261–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshinari, K.; Okino, N.; Sato, T.; Sugatani, J.; Miwa, M. Induction of detoxifying enzymes in rodent white adipose tissue by aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists and antioxidants. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2006, 34, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jaiswal, A.K. Regulation of human NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase gene. Role of AP1 binding site contained within human antioxidant response element. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 15097–15104. [Google Scholar]
- Kansanen, E.; Kuosmanen, S.M.; Leinonen, H.; Levonen, A.L. The Keap1-Nrf2 pathway: Mechanisms of activation and dysregulation in cancer. Redox Biol. 2013, 1, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, L.G.; Kelleher, M.O.; Eggleston, I.M.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Hayes, J.D. Transcription factor Nrf2 mediates an adaptive response to sulforaphane that protects fibroblasts in vitro against the cytotoxic effects of electrophiles, peroxides and redox-cycling agents. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 237, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, L.G.; Hayes, J.D. The cap'n'collar transcription factor Nrf2 mediates both intrinsic resistance to environmental stressors and an adaptive response elicited by chemopreventive agents that determines susceptibility to electrophilic xenobiotics. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2011, 192, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, T.; Shinkai, Y.; Jiang, H.Y.; Iwamoto, N.; Sumi, D.; Taguchi, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Jinno, H.; Tanaka-Kagawa, T.; Cho, A.K.; et al. Initial response and cellular protection through the Keap1/Nrf2 system during the exposure of primary mouse hepatocytes to 1,2-naphthoquinone. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiss, E.H.; Schachner, D.; Zimmermann, K.; Dirsch, V.M. Glucose availability is a decisive factor for Nrf2-mediated gene expression. Redox Biol. 2013, 1, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggler, A.L.; Liu, G.; Pezzuto, J.M.; van Breemen, R.B.; Mesecar, A.D. Modifying specific cysteines of the electrophile-sensing human Keap1 protein is insufficient to disrupt binding to the Nrf2 domain Neh2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10070–10075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, K.; Wakabayashi, N.; Katoh, Y.; Ishii, T.; O’Connor, T.; Yamamoto, M. Keap1 regulates both cytoplasmic-nuclear shuttling and degradation of Nrf2 in response to electrophiles. Genes Cells 2003, 8, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shay, K.P.; Shenvi, S.; Hagen, T.M. Lipoic acid as an inducer of Phase II detoxification enzymes through activation of Nrf2-dependent gene expression. In Lipoic Acid: Energy Production, Antioxidant Activity and Health Effects; Patel, M.S., Packer, L., Eds.; CRC Press; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 349–371. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, T.; Itoh, K.; Takahashi, S.; Sato, H.; Yanagawa, T.; Katoh, Y.; Bannai, S.; Yamamoto, M. Transcription factor Nrf2 coordinately regulates a group of oxidative stress-inducible genes in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 16023–16029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Cederbaum, A.I. Menadione cytotoxicity to Hep G2 cells and protection by activation of nuclear factor-kappaB. Mol. Pharmacol. 1997, 52, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Son, T.G.; Camandola, S.; Arumugam, T.V.; Cutler, R.G.; Telljohann, R.S.; Mughal, M.R.; Moore, T.A.; Luo, W.; Yu, Q.S.; Johnson, D.A.; et al. Plumbagin, a novel Nrf2/ARE activator, protects against cerebral ischemia. J. Neurochem. 2010, 112, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, T.G.; Kawamoto, E.M.; Yu, Q.S.; Greig, N.H.; Mattson, M.P.; Camandola, S. Naphthazarin protects against glutamate-induced neuronal death via activation of the Nrf2/ARE pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 433, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, P.R.; Son, T.G.; Wilson, M.A.; Yu, Q.S.; Wood, W.H.; Zhang, Y.; Becker, K.G.; Greig, N.H.; Mattson, M.P.; Camandola, S.; et al. Extension of lifespan in C. elegans by naphthoquinones that act through stress hormesis mechanisms. PLoS One 2011, 6, e21922. [Google Scholar]
- Heidler, T.; Hartwig, K.; Daniel, H.; Wenzel, U. Caenorhabditis elegans lifespan extension caused by treatment with an orally active ROS-generator is dependent on DAF-16 and SIR-2.1. Biogerontology 2010, 11, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, D.D. Phosphorylation of Nrf2 at multiple sites by MAP kinases has a limited contribution in modulating the Nrf2-dependent antioxidant response. PLoS One 2009, 4, e6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotz, L.O.; Patak, P.; Ale-Agha, N.; Buchczyk, D.P.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Gerber, P.A.; von Montfort, C.; Sies, H. 2-Methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone, vitamin K(3), decreases gap-junctional intercellular communication via activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor/extracellular signal-regulated kinase cascade. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 4922–4928. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beier, J.I.; von Montfort, C.; Sies, H.; Klotz, L.O. Activation of ErbB2 by 2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone (menadione) in human keratinocytes: Role of EGFR and protein tyrosine phosphatases. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 1859–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- llinger, K.; Brunmark, A. Effect of hydroxy substituent position on 1,4-naphthoquinone toxicity to rat hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 21496–21503. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O'Brien, P.J. Molecular mechanisms of quinone cytotoxicity. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1991, 80, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, S.G.; Jung, S.H.; Han, J.H.; Yang, S.Y.; Yun, E.; Song, G.Y.; Myung, C.S. 5,8-Dimethoxy-2-Nonylamino-Naphthalene-1,4-Dione Inhibits Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation by Blocking Autophosphorylation of PDGF-Receptor beta. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2013, 17, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.J.; Zhang, W.Y.; Yi, H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, I.S.; Shen, G.N.; Song, G.Y.; Myung, C.S. Anti-proliferative actions of 2-decylamino-5,8-dimethoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 411, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Han, J.H.; Yun, E.; Jung, S.H.; Lee, J.J.; Song, G.Y.; Myung, C.S. Inhibitory effect of a novel naphthoquinone derivative on proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells through suppression of platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta tyrosine kinase. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 733, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmohsen, K.; Sauerbier, E.; Ale-Agha, N.; Beier, J.I.; Walter, P.; Galban, S.; Stuhlmann, D.; Sies, H.; Klotz, L.O. Epidermal growth factor- and stress-induced loss of gap junctional communication is mediated by ERK-1/ERK-2 but not ERK-5 in rat liver epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 364, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melchheier, I.; von Montfort, C.; Stuhlmann, D.; Sies, H.; Klotz, L.O. Quinone-induced Cdc25A inhibition causes ERK-dependent connexin phosphorylation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 327, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazo, J.S.; Nemoto, K.; Pestell, K.E.; Cooley, K.; Southwick, E.C.; Mitchell, D.A.; Furey, W.; Gussio, R.; Zaharevitz, D.W.; Joo, B.; et al. Identification of a potent and selective pharmacophore for Cdc25 dual specificity phosphatase inhibitors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 61, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nemoto, K.; Vogt, A.; Oguri, T.; Lazo, J.S. Activation of the Raf-1/MEK/Erk kinase pathway by a novel Cdc25 inhibitor in human prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2004, 58, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakis, J.M.; Avruch, J. Mammalian MAPK signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation: A 10-year update. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 689–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laird, D.W. Life cycle of connexins in health and disease. Biochem. J. 2006, 394, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valiunas, V.; Polosina, Y.Y.; Miller, H.; Potapova, I.A.; Valiuniene, L.; Doronin, S.; Mathias, R.T.; Robinson, R.B.; Rosen, M.R.; Cohen, I.S.; et al. Connexin-specific cell-to-cell transfer of short interfering RNA by gap junctions. J. Physiol. 2005, 568, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampe, P.D.; Lau, A.F. The effects of connexin phosphorylation on gap junctional communication. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2004, 36, 1171–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warn-Cramer, B.J.; Lau, A.F. Regulation of gap junctions by tyrosine protein kinases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1662, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warn-Cramer, B.J.; Lampe, P.D.; Kurata, W.E.; Kanemitsu, M.Y.; Loo, L.W.; Eckhart, W.; Lau, A.F. Characterization of the mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation sites on the connexin-43 gap junction protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 3779–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warn-Cramer, B.J.; Cottrell, G.T.; Burt, J.M.; Lau, A.F. Regulation of connexin-43 gap junctional intercellular communication by mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 9188–9196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmohsen, K.; von Montfort, C.; Stuhlmann, D.; Gerber, P.A.; Decking, U.K.; Sies, H.; Klotz, L.O. Doxorubicin induces EGF receptor-dependent downregulation of gap junctional intercellular communication in rat liver epithelial cells. Biol. Chem. 2005, 386, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMillan, D.C.; Sarvate, S.D.; Oatis, J.E., Jr.; Jollow, D.J. Role of oxidant stress in lawsone-induced hemolytic anemia. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 82, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ale-Agha, N.; Albrecht, C.; Klotz, L.O. Loss of gap junctional intercellular communication in rat lung epithelial cells exposed to quartz particles. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 390, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ale-Agha, N.; Albrecht, C.; Klotz, L.O. Loss of gap junctional intercellular communication in rat lung epithelial cells exposed to carbon or silica-based nanoparticles. Biol. Chem. 2010, 391, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotz, L.O. Posttranscriptional regulation of connexin-43 expression. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 524, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ale-Agha, N.; Galban, S.; Sobieroy, C.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Gorospe, M.; Sies, H.; Klotz, L.O. HuR regulates gap junctional intercellular communication by controlling beta-catenin levels and adherens junction integrity. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Östman, A.; Frijhoff, J.; Sandin, A.; Böhmer, F.D. Regulation of protein tyrosine phosphatases by reversible oxidation. J. Biochem. 2011, 150, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, N.; Sumi, D.; Ishii, T.; Uchida, K.; Cho, A.K.; Froines, J.R.; Kumagai, Y. Chemical knockdown of protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B by 1,2-naphthoquinone through covalent modification causes persistent transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 33396–33404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padhye, S.; Dandawate, P.; Yusufi, M.; Ahmad, A.; Sarkar, F.H. Perspectives on medicinal properties of plumbagin and its analogs. Med. Res. Rev. 2012, 32, 1131–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aykin-Burns, N.; Ahmad, I.M.; Zhu, Y.; Oberley, L.W.; Spitz, D.R. Increased levels of superoxide and H2O2 mediate the differential susceptibility of cancer cells versus normal cells to glucose deprivation. Biochem. J. 2009, 418, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Kalen, A.L.; Smith, B.J.; Cullen, J.J.; Oberley, L.W. Enhancing the antitumor activity of adriamycin and ionizing radiation. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4294–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.G.; Weydert, C.J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.; Liu, J.; Spitz, D.R.; Cullen, J.J.; Oberley, L.W. Superoxide Enhances the Antitumor Combination of AdMnSOD Plus BCNU in Breast Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2010, 2, 68–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, F.H.; Holme, A.L.; Giles, N.M.; Giles, G.I.; Collins, C.; Holt, K.; Pariagh, S.; Gelbrich, T.; Hursthouse, M.B.; Gutowski, N.J.; et al. Multifunctional redox catalysts as selective enhancers of oxidative stress. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2005, 3, 2579–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döpp, F. Aktivierung der extrazellulär regulierten Kinasen (ERK) 1 und 2 durch selen- und tellurhaltige Naphthochinonderivate in Rattenleberepithelzellen. MD Thesis, Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf, Düsseldorf, Germany, December 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Donzelli, M.; Draetta, G.F. Regulating mammalian checkpoints through Cdc25 inactivation. EMBO Rep. 2003, 4, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynes, N.E.; Lane, H.A. ERBB receptors and cancer: The complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarden, Y.; Pines, G. The ERBB network: At last, cancer therapy meets systems biology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tebbutt, N.; Pedersen, M.W.; Johns, T.G. Targeting the ERBB family in cancer: Couples therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, P.A.; Buhren, B.A.; Kürle, S.; Homey, B. Therapie mit Inhibitoren des epidermalen Wachstumsfaktorrezeptors. Spektrum kutaner Nebenwirkungen. Spektrum kutaner Nebenwirkungen. Hautarzt 2010, 61, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potthoff, K.; Hofheinz, R.; Hassel, J.C.; Volkenandt, M.; Lordick, F.; Hartmann, J.T.; Karthaus, M.; Riess, H.; Lipp, H.P.; Hauschild, A.; et al. Interdisciplinary management of EGFR-inhibitor-induced skin reactions: a German expert opinion. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Soler, R.; Zou, Y.; Li, T.; Tornos, C.; Ling, Y. Topical vitamin K3 (Vit K3, Menadione) prevents erlotinib and cetuximab-induced EGFR inhibition in the skin. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 3036. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Klotz, L.-O.; Hou, X.; Jacob, C. 1,4-Naphthoquinones: From Oxidative Damage to Cellular and Inter-Cellular Signaling. Molecules 2014, 19, 14902-14918. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190914902
Klotz L-O, Hou X, Jacob C. 1,4-Naphthoquinones: From Oxidative Damage to Cellular and Inter-Cellular Signaling. Molecules. 2014; 19(9):14902-14918. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190914902
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlotz, Lars-Oliver, Xiaoqing Hou, and Claus Jacob. 2014. "1,4-Naphthoquinones: From Oxidative Damage to Cellular and Inter-Cellular Signaling" Molecules 19, no. 9: 14902-14918. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190914902
APA StyleKlotz, L.-O., Hou, X., & Jacob, C. (2014). 1,4-Naphthoquinones: From Oxidative Damage to Cellular and Inter-Cellular Signaling. Molecules, 19(9), 14902-14918. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190914902






