The Suppressive Activities of Six Sources of Medicinal Ferns Known as Gusuibu on Heat-Labile Enterotoxin-Induced Diarrhea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
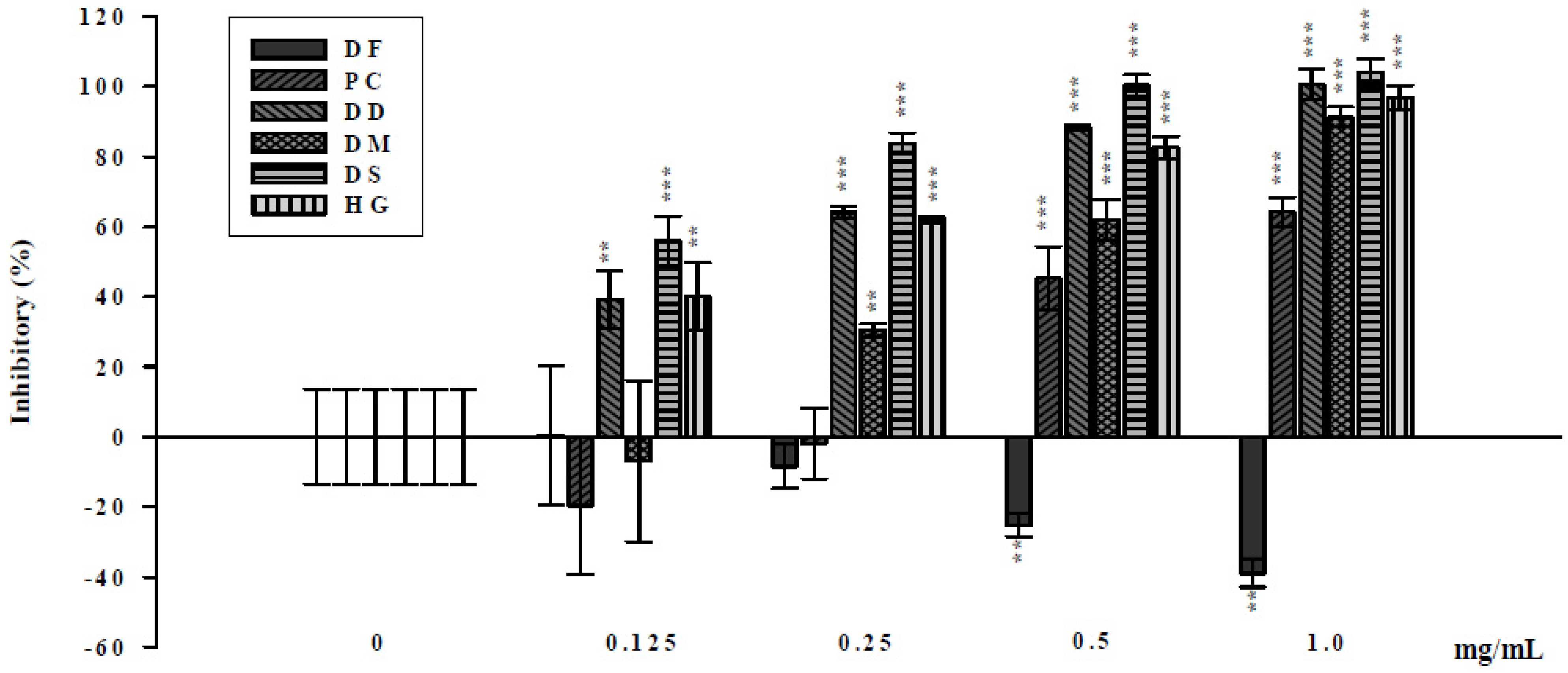
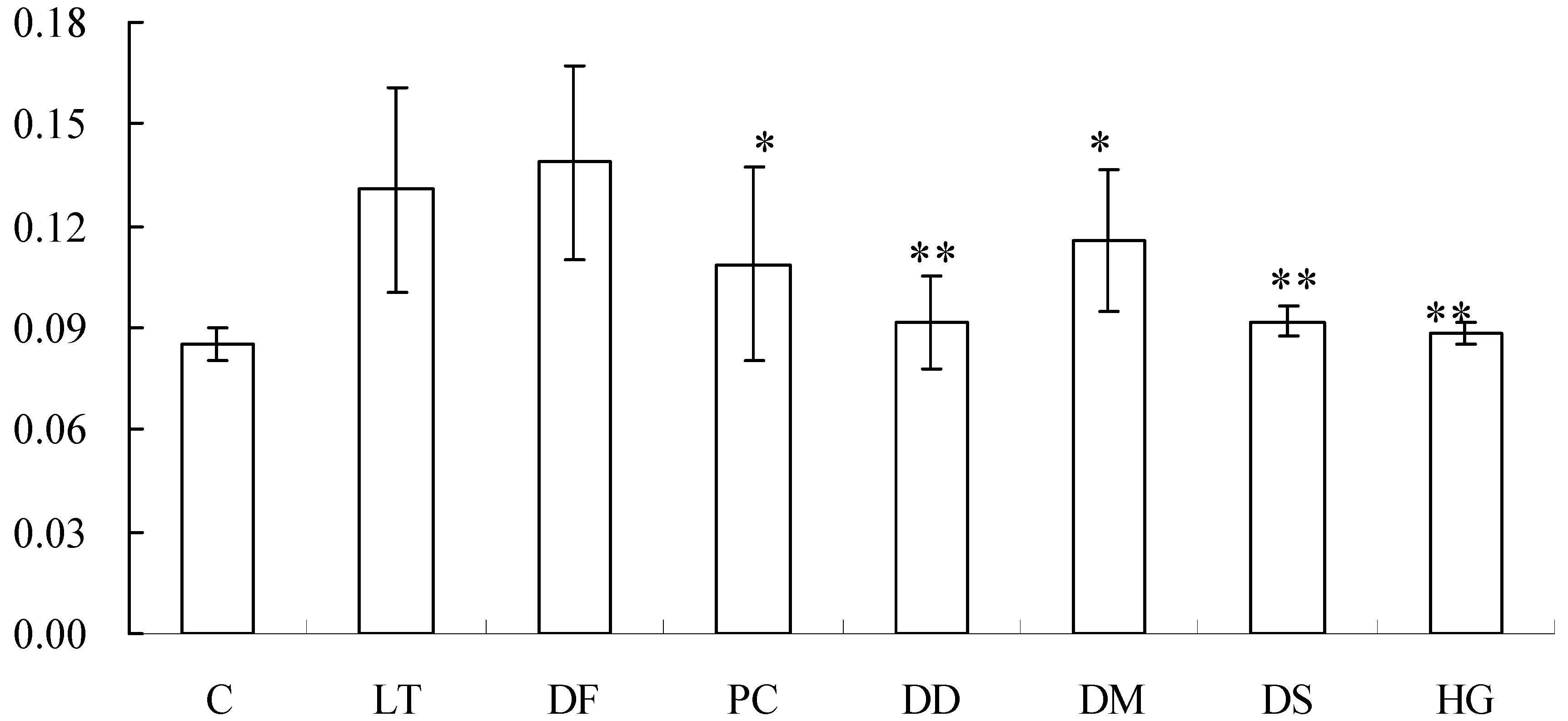
3. Experimental
3.1. Plant Materials
| Family Name | Botanic Name | Common Name | Voucher Number | Location | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polypodiaceae | Drynaria fortunei (Kze.) J.Sm. | Gusuibu | CMU-94-DF-01 | Hsinchu, Taichung | 11.2 |
| Pseudodrynaria coronans (Wall. ex Mett.) Ching | Gusuibu | CMU-94-PC-01 | Taichung, Nantou | 15.0 | |
| Davalliaceae | Davallia divaricata Bl. | Dayegusuibu | CMU-94-DD-01 | Nantou | 14.6 |
| Davallia mariesii Moore ex Bak | Haizhougusuibu | CMU-94-DM-01 | Nantou | 8.5 | |
| Davallia solida (Forst.) Sw. | Koyegusuibu | CMU-94-DS-01 | Taitung | 12.7 | |
| Humata griffithiana (Hk.) C.Chr. | Begaigusuibu | CMU-94-HG-01 | Taichung | 6.7 |
3.2. Extractions
3.3. The In Vitro and In Vivo Assay
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wiedermann, U.; Kollaritsch, H. Vaccines against traveler’s diarrhoea and rotavirus disease–a review. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2006, 118, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). State of the Art of New Vaccines: Research and Development. Diarrhoeal Diseases. Available online: http://www.medicina.ufba.br/educacao_medica/graduacao/dep_pediatria/disc_pediatria/disc_prev_social/roteiros/desidratacao/stateofart_excler%202003.pdf (accessed on 24 January 2014).
- World Health Organization (WHO) Expert Committee. WHO Technical Report Series on Enteric Infection. Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/40603/1/WHO_TRS_288.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 24 January 2014).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Ending Preventable Deaths from Pneumonia and Diarrhoea by 2025. Available online: http://www.who.int/maternal_child_adolescent/news_events/news/2013/gappd_launch/en/index.html (accessed on 24 January 2014).
- Lutterodt, G.D. Inhibition of gastrointestinal release of acetylcholine by quercetin as possible mode of action of Psidium guiana leaf extracts in the treatment of acute disease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1989, 25, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syder, J.D.; Merson, M.H. The magnitude of the global problem of acute diarrhoeal disease, a review of active surveillance data. Bull. World Health Organ. 1982, 60, 605–613. [Google Scholar]
- State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Zhong Hua Ben Cao (China Herbal); Shanghai Science and Technology Press: Shanghai, China, 1999; Chapter 2; pp. 25–270. [Google Scholar]
- Pharmacopoeia Commission of the People Republic of China (ChPC). Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2005; Chapter 1; pp. 179–180. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Jia, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. A review of the study on Drynaria fortunei. Zhong Yao Cai 1999, 22, 263–266. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.C.; Pang, W.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Mok, S.K.; Lai, W.P.; Chow, H.K.; Leung, P.C.; Yao, X.S.; Wong, M.S. Drynaria fortunei-derived total flavonoid fraction and isolated compounds exert estrogen-like protective effects in bone. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.S.; Chang, W.C.; Cheng, Y.H.; Chen, K.Y.; Chen, K.H.; Chang, T.L. The effects of Davallic acid from Davallia divaricata Blume on apoptosis induction in A549 lung cancer cells. Molecules 2012, 17, 12938–12949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.B.; Tezuka, Y.; Kikuchi, T.; Nakano, H.; Tamaoki, T.; Park, J.H. Davallin, a new tetrameric proanthocyanidin from the rhizomes of Davallia mariesii Moore. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1991, 39, 2179–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancon, S.; Chaboud, A.; Darbour, N.; Comte, G.; Bayet, C.; Simon, P.N.; Raynaud, J.; di Pietro, A.; Cabalion, P.; Barron, D. Natural and synthetic benzophenones: Interaction with the cytosolic binding domain of p-glycoprotein. Phytochemistry 2001, 57, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.; Ho, T.Y.; Chang, Y.S.; Wu, S.L.; Hsiang, C.Y. Anti-diarrheal effect of Galla Chinensis on the Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin and ganglioside interaction. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 103, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.; Ho, T.Y.; Chang, Y.S.; Wu, S.L.; Li, C.C.; Hsiang, C.Y. Identification of Escherichia coli enterotoxin inhibitors from traditional medicinal herbs by in silico, in vitro, and in vivo analyses. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 121, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmgren, J.; Svennerholm, A.M. Bacterial enteric infections and vaccine development. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 1992, 21, 283–302. [Google Scholar]
- Merritt, E.A.; Hol, W.G. AB5 toxins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1995, 5, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickens, J.C.; Merritt, E.A.; Ahn, M.; Verlinde, C.L.; Hol, W.G.; Fan, E. Anchor-based design of improved cholera toxin and E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin receptor binding antagonists that display multiple binding modes. Chem. Biol. 2002, 9, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spangler, B.D. Structure and function of cholera toxin and the related Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 56, 622–647. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, H.-C.; Chen, J.-C.; Yang, J.-L.; Tsay, H.-S.; Hsiang, C.-Y.; Ho, T.-Y. The Suppressive Activities of Six Sources of Medicinal Ferns Known as Gusuibu on Heat-Labile Enterotoxin-Induced Diarrhea. Molecules 2014, 19, 2114-2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19022114
Chang H-C, Chen J-C, Yang J-L, Tsay H-S, Hsiang C-Y, Ho T-Y. The Suppressive Activities of Six Sources of Medicinal Ferns Known as Gusuibu on Heat-Labile Enterotoxin-Induced Diarrhea. Molecules. 2014; 19(2):2114-2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19022114
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Hung-Chi, Jaw-Chyun Chen, Jiun-Long Yang, Hsin-Sheng Tsay, Chien-Yun Hsiang, and Tin-Yun Ho. 2014. "The Suppressive Activities of Six Sources of Medicinal Ferns Known as Gusuibu on Heat-Labile Enterotoxin-Induced Diarrhea" Molecules 19, no. 2: 2114-2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19022114
APA StyleChang, H.-C., Chen, J.-C., Yang, J.-L., Tsay, H.-S., Hsiang, C.-Y., & Ho, T.-Y. (2014). The Suppressive Activities of Six Sources of Medicinal Ferns Known as Gusuibu on Heat-Labile Enterotoxin-Induced Diarrhea. Molecules, 19(2), 2114-2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19022114




