Abstract
A series of novel ligustrazine-oleanolic acid (TOA) derivatives were designed, and synthesized by conjugating amino acids to the 3-hydroxy group of TOA by ester bonds. Their cytotoxicity was evaluated on four cancer cell lines (HepG2, HT-29, Hela and BGC-823) by standard MTT assays. The ClogP values were calculated by means of computer simulation, and logP values of both 3β-glycine ester olean-12-en-28-oic acid-3,5,6-trimethylpyrazin-2-methyl ester (6a) and TOA were determined using a shake flask-ultraviolet spectrophotometry method. It was found that 6a and the 3β-l-lysine ester-6g not only displayed good cytotoxicity (IC50 < 3.5 μM) but also possessed better hydrophilicity than TOA. Moreover, 6a (IC50 = 4.884 μM) had lower nephrotoxicity than both 6g (IC50 = 2.310 μM) and cisplatin (CDDP, IC50 = 3.691 μM) on MDCK cells. Combining Giemsa and DAPI staining, it was further verified that 6a could induce HepG2 apoptosis via nuclei fragmentation and had lower nephrotoxicity. In addition, the structure-activity relationships of these derivatives are briefly discussed.
1. Introduction
Based on the principle of chemical combination, the attempt to discover lead compounds from Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCMs) has drawn considerable attentions [1,2,3,4,5,6]. There are potential advantages in having such agents with complementary pharmacological activities in the form of a single chemical entity [2]. In the earlier studies in this field, several ligustrazine derivatives had been designed, synthesized and biologically evaluated [3,4,5,6]. Thereafter, a novel anticancer lead compound 3β-hydroxyolea-12-en-28-oic acid-3,5,6-trimethylpyrazin-2-methyl ester (TOA, C38H58O3N2, Figure 1) was screened [6,7,8,9,10,11]. TOA was synthesized by conjugating the effective antitumor ingredients ligustrazine (TMP) and oleanolic acid (OA). It exhibited promising anticancer effects in vitro [6] and prevented the expression of nuclear transcription factor NF-κB/p65 and COX-2 in S180 mice [7]. In addition, the acute toxicity tests verified that the LD50 value of TOA exceeded 6.0 g/kg via gavage in mice. However, the shortcoming of TOA’s poor hydrophilicity limited its oral bioavailability. In our previous study, solid dispersions and microemulsion systems of TOA were developed to enhance the bioactivity of TOA, and they displayed favorable pharmacokinetic profiles in vivo. The TOA microemulsion formulation showed 28-fold and 4-fold higher maximum concentration (Cmax) than the pure drug and solid dispersion, respectively [10,11].
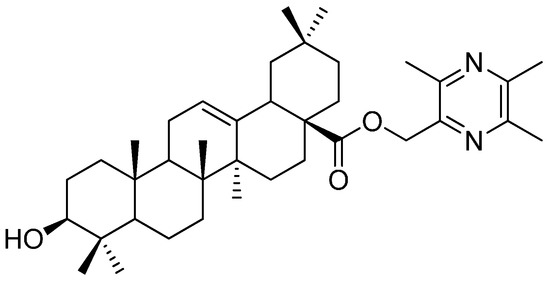
Figure 1.
The structure of the anticancer lead compound TOA.
As essential nutrients of the human body, amino acids have favorable hydrophilicity. Numerous studies have showed that by introducing amino acid groups into the structures of insoluble drugs, the hydrophilicity and the bioactivity could be enhanced [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. In addition, some studies have indicated that low aqueous-solubility drugs conjugated with amino acids or dipeptides could be selectively identified and taken up by certain transporters, thus significantly improving their membrane permeability and cytotoxicity [22,23].
In this paper, twelve different amino acids were selected for conjugation to the 3-hydroxy moiety of TOA by ester bond formation. Their cytotoxicity was then evaluated on four cancer cell lines, including the human hepatoma cell line HepG2, human colorectal cancer cell line HT-29, human cervical cancer cell line Hela and human gastric cancer cell lines BGC-823, by standard thiazolyl blue (MTT) assays. In the study, the antineoplastic drug cisplatin (CDDP) was selected as the positive control. Due to its nephrotoxicity in clinical use, the Madin-Darby canine kidney cell line (MDCK) was used to test the toxicity of the TOA-amino acid derivatives and CDDP. The ClogP values were calculated by means of computer simulation. logP values of both 6a and TOA were determined using a shake flask-ultraviolet spectrophotometry method. Model cellular morphological and nuclear damage studies were carried out by Giemsa and DAPI staining, respectively. In addition, the structure-activity relationships of the new TOA-amino acid derivatives are briefly discussed.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
Compound 3 (TMP-Br) was synthesized by the treatment of anhydrous tetramethylpyrazine (TMP) with N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) [24]. The product was used in the next step without further purification. Compound 4 (TOA) was obtained through the formation of an ester bond between compound 3 and OA after stirring for 1.5 h at room temperature under alkaline conditions in dry tetrahydrofuran (THF) (Scheme 1).
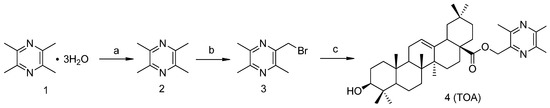
Scheme 1.
Synthesis route to TOA.
To avoid the formation of by-products, the amino acid groups were protected with t-butyloxy- carbonyl (Boc-) or benzoyloxycarbonyl groups (Cbz-). The general synthesis of compounds 6a–6l was conducted according to Scheme 2. Ester condensation reactions were catalyzed by 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDCI) and 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP). The removal of the Boc- groups was conducted in 3 M HCl/ethyl acetate solution, and Cbz- groups were de-protected with H2, Pd/C (or Pd(OH)2/C). Before esterification with TOA, the hydroxyl group of Cbz-L-serine was protected with TBDMS-Cl; the TBDMS group of the intermediate was de-protected with TBAF to produce 6l. The structures of the new compounds that had not been reported previously were elucidated by HRMS and NMR spectroscopy.
2.2. Biological Activities
The cytotoxicity of TOA-amino acid derivatives was evaluated on HepG2, HT-29, Hela and BGC-823 cancer cells using the MTT assay. In addition their toxicity evaluation was carried out on MDCK cells. As shown in Table 1, most of the synthesized compounds exhibited preferable cytotoxicity. Compounds 6a, 6b, 6c, 6g and 6l demonstrated much better cytotoxicity (IC50 < 8.0 μM) than TOA on all cancer cell lines. In particular, 6a and 6g showed much better cytotoxicity (IC50 < 3.5 μM) against the four cell lines than the others. Moreover, 6a (IC50 = 4.884 μM) had lower nephrotoxicity than both 6g (IC50 = 2.310 μM) and CDDP (IC50 = 3.691 μM) on MDCK cells.
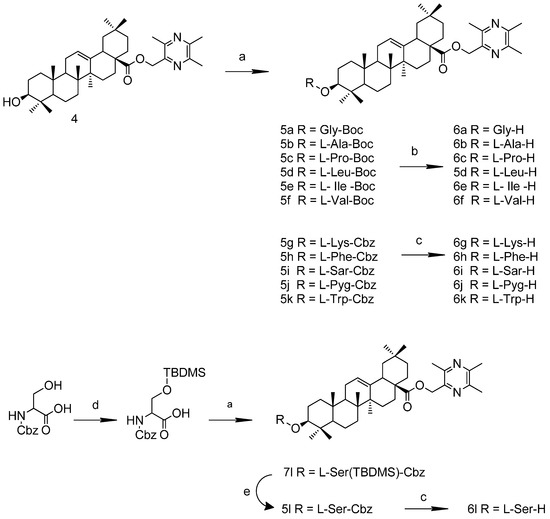
Scheme 2.
Synthesis routes to TOA-amino acid derivatives.
In addition, it was observed that introducing different types of amino acids on the 3-hydroxy group of TOA significantly different cytotoxicity resulted. It was worth noting that cytotoxicity showed a negative correlation with the length of amino acids’ branched carbon chain, in the order 6a > 6b > 6f > 6e > 6d. The cytotoxicity of cyclic secondary amines was better than that of cyclic acylamino derivatives, such as 6c > 6j. Increasing the number of amino groups might enhance the activity. For instance, 6g containing two amino groups had strong cytotoxicity (IC50 < 2.5 μM) on both cancer and MDCK cells.

Table 1.
Anti-proliferative effects and ClogP values of TOA-amino acid derivatives.
| Compound | IC50 Values (μM) | ClogP | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HepG2 | HT-29 | Hela | BGC-823 | MDCK | ||
| CDDP | 2.856 | 6.112 | 9.838 | 6.819 | 3.691 | -b |
| TOA | 21.45 | -a | 8.683 | - | - | 8.125 |
| 6a | 1.999 | 2.498 | 3.256 | 3.062 | 4.884 | 7.433 |
| 6b | 2.322 | 4.770 | 7.690 | 4.474 | 5.125 | 7.835 |
| 6c | 2.391 | 3.213 | 6.754 | 4.976 | 5.034 | 8.590 |
| 6d | - | - | - | - | - | 8.763 |
| 6e | 5.969 | 9.830 | - | - | - | 8.750 |
| 6f | 4.257 | 5.956 | - | 9.522 | 9.785 | 8.479 |
| 6g | 2.270 | 2.347 | 2.383 | 2.481 | 2.310 | 7.343 |
| 6h | 8.216 | 9.503 | - | - | 8.119 | 8.831 |
| 6i | 10.22 | 16.85 | 12.61 | 16.04 | 15.78 | 8.346 |
| 6j | 5.785 | 5.480 | 11.47 | 10.73 | 12.62 | 8.117 |
| 6k | 11.44 | - | - | 10.01 | 10.82 | 8.895 |
| 6l | 4.783 | 4.829 | 5.217 | 4.898 | 3.122 | 6.860 |
The derivatives were evaluated on human hepatoma cell lines (HepG2), human colorectal cancer cell lines (HT-29), women cervical cancer cell lines (Hela) and human gastric cancer cell lines (BGC-823) using MTT assay, as well as their toxicity evaluation was carried out on Madin-Darby canine kidney cell lines (MDCK). -a meant IC50 > 25 μM, the compounds’ effects were considered to be weaker than TOA and not evaluated. Data are derived from three independent experiments. -b means the ClogP value was not calculated, due to structural differences between CDDP and others.
2.3. Computer Simulation of ClogP and Determination of logP
Lipophilicity (ClogP) is used in rational drug design as a key factor related to the cell transmembrane transport or other biological processes [25,26,27]. ClogP values can either be calculated experimentally [28,29,30] or predicted by means of commercially available programs [31,32,33,34,35]. In this work, ClogP values of the TOA-amino acid derivatives were predicted using Sybyl-X 2.0 (Tripos, Certara Inc., St. Louis, MO, USA) [5]. As shown in Table 1, 6a, 6b, 6g, 6j and 6l possessed lower values compared to the ClogP value of TOA. It found that smaller amino acids, and polar or basic amino acids could decrease the derivatives’ ClogP values. To determine the octanol-water partition coefficient (logP), a shake flask-ultraviolet spectrophotometry method [36] was used to determine the concentration of 6a and TOA in the water phase and organic phase at pH 6.8 with n-caprylic alcohol-water as the simulation system. It determined that the logP values of 6a and TOA were 4.30 and 6.11, respectively. This indicated that by conjugating amino acids the logP value could be decreased and the hydrophilicity improved, which was in accordance with previous studies [12,13,21,22]. However, the better activity connected with the increases of these amino acid conjugates’ solubility is worthy of further study.
2.4. Changes in Cellular Morphologies [37]
Apoptosis has been considered a major mechanism of chemotherapy-induced cell death, and the drug cytotoxicity often elicits cellular morphology changes [38], including loss of intercellular contacts, membrane damage and nuclear fragmentation. These characteristic changes are usually considered as the hallmarks of apoptosis [39].
2.4.1. Geimsa Staining
To confirm the apoptopic morphological changes induced by 6a, HepG2 cells were treated with 0, 1, 2 and 4 μM of 6a for 72 h and then Giemsa staining was performed. The morphology changes observed in treated cells compared to control cells under inverted phase-contrast microscope at a magnification of 400×, included loss of intercellular contacts, lysis of nuclei, increased cell debris and membrane damage (marked by arrows in Figure 2). Meanwhile, we could clearly observe that the morphological changes of HepG2 cells significantly increased with increasing concentration of 6a. There was no complete cell morphology when cells were treated with 2 and 4 μM of 6a.
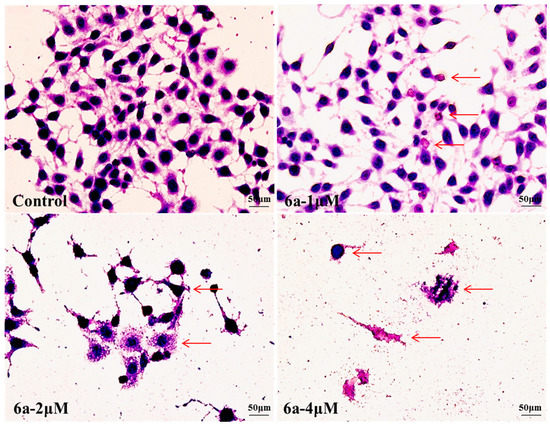
Figure 2.
Morphological changes of HepG2 cells after treatment with 0, 1, 2 and 4 μM of 6a was observed under inverted phase-contrast microscope at a magnification of 400×. Cells showed changes in cell morphology, included loss of intercellular contacts, lysis of nuclei, increased cell debris and membrane damage (arrows) with increasing doses of 6a when compared to the control cells. Data were derived from three independent experiments.
To test the agents’ nephrotoxicity, MDCK cells were exposed to 2 μM of compound 6a and CDDP for 72 h. Then Giemsa staining was performed on model cells. Changes were observed in the CDDP- treated groups under inverted phase-contrast microscope at a magnification of 200×, including less density, larger volume, lighter nuclear staining and cellular atypia. However, no significant morphological changes were observed in cells treated with 6a and control cells (Figure 3). By combining Giemsa staining, we found that 6a could induce HepG2 apoptosis and had lower nephrotoxicity than CDDP.
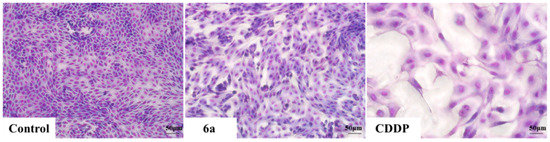
Figure 3.
Morphology of MDCK cells after treatment with 6a and CDDP was observed under a microscope in the same multiples (200×). Data were derived from three independent experiments.
2.4.2. DAPI Staining
Apoptosis can be differentiated from necrosis by their characteristic nuclear changes. DAPI is a nuclear stain which is observed as blue fluorescence when excited under fluorescence microscope [39].
In our present study, HepG2 cells were treated with 0, 1, 2 and 4 μM of 6a for 72 h and then DAPI staining was performed. Control cells (0 μM) showed intact cell bodies with clear round nuclei, while treated cells clearly showed condensed chromatin, nuclear fragmentation and weak fluorescence compared to the control cells (Figure 4). Meanwhile, we could clearly observe that nuclear fragmentation of HepG2 cells increased significantly with increasing concentration of 6a. Thus, DAPI staining indicated that 6a could induce HepG2 apoptosis via nuclear fragmentation.
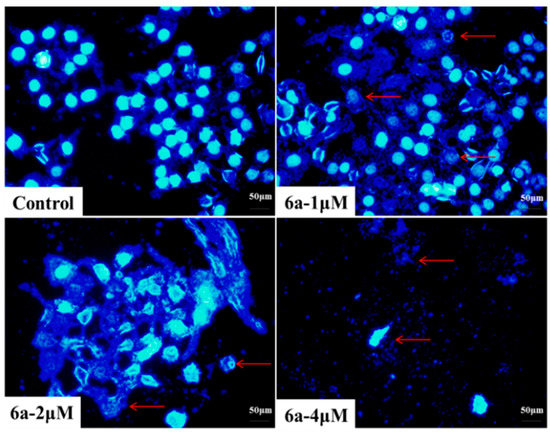
Figure 4.
Nuclear fragmentation of HepG2 cells induced by compound 6a with different doses (0, 1, 2 and 4 μM), which was observed using inverted phase-contrast microscope at a magnification of 400× with an excitation wavelength of 470 nm. Data were derived from three independent experiments.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Information
Reactions were monitored by TLC using silica gel coated aluminum sheets (Qingdao Haiyang Chemical Co., Qingdao, China) and visualized in UV light (254 nm). 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR assays were recorded on a Bruker AVANCE 500 NMR spectrometer (Fällanden, Switzerland) and chemical shifts are reported in form of δ (ppm). Deuterated chloroform or deuterated dimethylsulfoxide was served as the solvent (Beijing InnoChem Science and Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). HRMS spectra were performed on High-resolution ESI mass spectrum (Solarix 9.4T, Bruker, Germany). Samples were freeze-dried using the vacuum freeze dryer (Beijing Boyikang Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). Melting points were measured at a rate of 5 °C/min using an X-5 micro melting point apparatus (Beijing Tech Instrument Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). The specific rotation of the synthesized compounds was measured using P-1020 polarimeter (Jasco, Tokyo, Japan). DAHZ-300 versatile constant temperature bath oscillator (Taicang experimental plant, Jiangsu, China) and TU-1810 UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Beijing Purkinje General Instrument Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) were used in determination of the oil-water partition coefficients. Cellular morphologies were observed using an inverted fluorescence microscope (Olympus IX71, Tokyo, Japan). Silica-gel column chromatography was performed using 200–300 mesh silica gel. The yields were calculated based on the last step reaction. All solvents and chemicals used were analytical or high-performance liquid chromatography grade.
3.2. Chemistry
2-(Bromomethyl)-3,5,6-Trimethylpyrazine (3)
Compound 3 was prepared according to our previously reported method [24]. The crude product, with 70% purity, was not purified further because of its strong mucous membrane irritation.
3β-Hydroxyolea-12-en-28-oic acid-3,5,6-trimethylpyrazine-2-methyl Ester (TOA, 4)
The crude product was obtained according to a reported method [6]. After further purification by silica-gel column chromatography, the purity was improved to more than 95%, and the product could be used directly for the later reactions.
3.2.1. General Synthesis of the TOA-Amino Acid Derivatives 6a–6f
The corresponding t-butyloxycarbonyl-protected amino acids (0.38 mmol), EDCI (0.50 mmol) and DMAP (0.025 mmol) were dissolved in dry DCM, then compound 4 (0.25 mmol) was added and the reaction solution was stirred at room temperature overnight. The crude product was extracted with CH2Cl2. After drying the organic layer over anhydrous Na2SO4 and evaporating the solvent under vacuum, the crude product was purified by flash chromatography with dichloromethane-methanol (20:1) as eluent. The product was stirred in ethyl acetate with 3 M hydrochloric acid for 1 h. The reaction solution was then evaporated with vacuum at 30 °C. The crude products were neutralized with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution and extracted with dichloromethane. After separating by flash chromatography with dichloromethane-methanol (20:1) as eluent, the products were lyophilized.
3β-Glycine ester olean-12-en-28-oic acid-3,5,6-trimethylpyrazin-2-methyl ester (6a). White solid, m.p. 96.0–97.6 °C, = +63.8 (c 1.0, MeOH), yield: 64%. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 0.55, 0.85, 0.86, 0.89, 1.11 (s, 15H, 5×-CH3, methyl of OA), 0.90 (brs, 6H, 2×-CH3, methyl of OA), 2.24 (brs, 2H, -NH2), 1.00–2.50 (23H, methine- and methylene- of OA), 2.49, 2.51, 2.55 (s, each, 3H, 3×-CH3, methyl of TMP), 2.86 (m, 1H, -CH=CCH-), 3.48 (s, 2H,-NH2CH2-), 4.55 (m, 1H, -OCOCH-), 5.12, 5.19 (d, each, J = 10 Hz, 1H, -OCH2-), 5.24 (brs, 1H, -CH=C-). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 15.7, 16.8, 16.9, 18.2, 23.0, 23.4, 23.6, 25.8, 27.6, 28.1, 29.7, 30.7, 32.4, 32.6, 33.1, 33.8, 36.9, 37.8, 38.1, 39.2, 41.3, 41.6, 43.7 (-CH2NH2), 45.9, 47.5, 55.3, 64.9, 81.9 (-OCOCH-), 122.3 (-CH=C-), 143.6 (-CH=C-), 173.4 (-CO-), 177.2 (-CO-), pyrazine ring: 20.6 (-CH3), 21.4 (-CH3), 21.7 (-CH3), 64.9 (-COCH2-), 145.4, 148.8, 149.2, 151.0. HRMS (ESI) m/z: 648.47410 [M+H]+, calcd for C40H62N3O4: 648.4662.
3β-l-Alanine ester olean-12-en-28-oic acid-3,5,6-trimethylpyrazin-2-methyl ester (6b). White solid, m.p. 89.7–92.1 °C, = +30.5 (c 1.0, MeOH), yield: 56%. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 0.54, 0.89, 1.11 (s, each, 3H, 3×-CH3, methyl of OA), 0.87 (brs, 6H, 2×-CH3, methyl of OA), 0.91 (brs, 6H, 2×-CH3, methyl of OA), 1.00–2.50 (25H, methyl of L-alanine, methine- and methylene- of OA), 2.49, 2.51, 2.55 (s, each, 3H, 3×-CH3, methyl of TMP), 2.74 (brs, 2H, -NH2), 2.86 (m, 1H, -CH=CCH-), 3.58 (s, 1H, -NH2CH-), 4.53 (m, 1H, -OCOCH-), 5.12, 5.19 (d, each, J = 10 Hz, 1H, -OCH2-), 5.24 (brs, 1H, -CH=C-). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 15.7, 16.7, 16.8, 18.2, 23.0, 23.5, 23.7, 25.8, 27.6, 28.1, 28.2, 30.7, 32.4, 32.6, 33.1, 33.8, 36.9, 37.8, 38.0, 38.1, 39.2, 41.3, 41.6, 45.9, 46.9, 47.5, 55.3, 55.4 (-CHNH2), 81.9 (-OCOCH-), 122.3 (-CH=C-), 143.6 (-CH=C-), 173.4 (-CO-), 177.2 (-CO-), pyrazine ring: 20.6 (-CH3), 21.4 (-CH3), 21.7 (-CH3), 64.9 (-COCH2-), 145.4, 148.8, 149.2, 151.0. HRMS (ESI) m/z: 662.48967 [M+H]+, calcd for C41H64N3O4: 662.48186.
3β-l-Proline ester olean-12-en-28-oic acid-3,5,6-trimethylpyrazin-2-methyl ester (6c). White solid, m.p. 89.6–91.3 °C, = +29.0 (c 1.0, MeOH), yield: 51%. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 0.54, 0.86, 0.87, 0.89, 1.11 (s, each, 3H, 5×-CH3, methyl of OA), 0.91 (brs, 6H, 2×-CH3, methyl of OA), 1.00–2.50 (26H, methylene- of l-proline, methine- and methylene- of OA), 2.49, 2.51, 2.55 (s, each, 3H, 3×-CH3, methyl of TMP), 2.86 (m, 1H, -CH=CCH-), 2.95, 3.10 (m, 2H, -NHCH2-), 3.74 (brs, 1H, -NH-), 3.81 (m, 1H, -NHCH-), 4.55 (m, 1H, -OCOCH-), 5.12, 5.19 (d, each, J = 10.0 Hz, 1H, -OCH2-), 5.24 (brs, 1H, -CH=C-). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 15.7, 16.9, 18.1, 23.0, 23.4, 23.6, 23.7, 25.4, 25.8, 27.6, 28.1, 29.7, 30.5, 30.7, 32.4, 32.6, 33.1, 33.8, 36.9, 37.8, 38.1, 39.2, 41.3, 41.6, 45.9, 46.9, 47.0 (-NHCH2-), 47.5, 55.3, 60.0 (-NHCH-), 81.9 (-OCOCH-), 122.3 (-CH=C-), 143.6 (-CH=C-), 174.7 (-CO-), 177.2 (-CO-), pyrazine ring: 20.6 (-CH3), 21.4 (-CH3), 21.7 (-CH3), 64.9 (-COCH2-), 145.4, 148.8, 149.2, 151.0. HRMS (ESI) m/z: 688.50525[M+H]+, calcd for C43H66N3O4: 688.49751.
3β-l-Leucine ester olean-12-en-28-oic acid-3,5,6-trimethylpyrazin-2-methyl ester (6d). White solid, m.p. 89.6–91.6 °C, = +42.0 (c 1.0, MeOH), yield: 49%. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 0.54, 0.89, 1.10 (s, each, 3H, 3×-CH3, methyl of OA), 0.87 (brs, 6H, 2×-CH3, methyl of OA), 0.91 (brs, 6H, 2×-CH3, methyl of OA), 0.96 (m, 6H, 2×-CH3, methyl of L-leucine), 1.00–2.50 (27H, methine- and methylene- of l-leucine and OA), 2.49, 2.51, 2.54 (s, each, 3H, 3×-CH3, methyl of TMP), 2.86 (m, 1H, -CH=CCH-), 3.51 (m, 1H, -CHNH2), 4.53 (m, 1H, -OCOCH-), 5.12, 5.19 (d, each, J = 10.0 Hz, 1H, -OCH2-), 5.24 (brs, 1H, -CH=C-). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 15.7, 16.8, 18.2, 21.8, 23.0, 23.1, 23.4, 23.5, 23.6, 24.8, 25.8, 27.6, 28.1, 29.7, 30.7, 32.4, 32.6, 33.1, 33.8, 36.9, 37.8, 38.1, 39.2, 41.3, 41.6, 43.7, 45.9, 46.9, 47.5, 53.3 (-CHNH2), 55.3, 81.9 (-OCOCH-), 122.3 (-CH=C-), 143.6 (-CH=C-), 173.4(-CO-), 177.2 (-CO-), pyrazine ring: 20.6 (-CH3), 21.4 (-CH3), 21.7 (-CH3), 64.9 (-COCH2-), 145.4, 148.8, 149.2, 151.0. HRMS (ESI) m/z: 704.53694 [M+H]+, calcd for C44H70N3 O4: 704.52881.
3β-l-Isoleucine ester olean-12-en-28-oic acid-3,5,6-trimethylpyrazin-2-methyl ester (6e). White solid, m.p. 89.8–90.7 °C, = +44.8 (c 1.0, MeOH), yield: 49%. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 0.55, 0.89, 1.11 (s, each, 3H, 3×-CH3, methyl of OA), 0.88 (brs, 6H, 2×-CH3, methyl of OA), 0.91 (brs, 6H, 2×-CH3, methyl of OA), 1.01 (m, 3H, -CH3, methyl of L-isoleucine), 1.00–2.50 (30H, methyl-, methine- and methylene- of l-isoleucine, methine- and methylene- of OA), 2.49, 2.51, 2.54 (s, each, 3H, 3×-CH3, methyl of TMP), 2.87 (m, 1H, -CH=CCH-), 3.42 (m, 1H, -CHNH2), 4.53 (m, 1H, -OCOCH-), 5.12, 5.19 (d, each, J = 10.0 Hz, 1H, -OCH2-), 5.24 (brs, 1H, -CH=C-). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 11.7, 15.3, 15.9, 16.8, 16.9, 18.2, 23.1, 23.4, 23.6, 23.8, 24.4, 25.8, 27.6, 28.1, 30.7, 32.4, 32.6, 33.1, 33.8, 36.9, 37.7, 38.1, 38.7, 39.2, 41.3, 41.6, 45.9, 46.9, 47.5, 55.3, 59.7 (-CHNH2), 81.9 (-OCOCH-), 122.3 (-CH=C-), 143.6 (-CH=C-), 173.5 (-CO-), 177.2 (-CO-), pyrazine ring: 20.6 (-CH3), 21.4 (-CH3), 21.7 (-CH3), 64.9 (-COCH2-), 145.4, 148.8, 149.4, 151.1. HRMS (ESI) m/z: 704.53668 [M+H]+, calcd for C44H70N3O4: 704.52881.
3β-l-Valine ester olean-12-en-28-oic acid-3,5,6-trimethylpyrazin-2-methyl ester (6f). White solid, m.p. 89.5–91.0 °C, = +29.3 (c 1.0, MeOH), yield: 57%. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 0.55, 0.89, 1.11 (s, each, 3H, 3×-CH3, methyl of OA), 0.88 (brs, 6H, 2×-CH3, methyl of OA), 0.91 (brs, 6H, 2×-CH3, methyl of OA), 1.00–2.50 (31H, methyl- and methine- of l-valine, methine- and methylene- of OA), 2.49, 2.51, 2.54 (s, each, 3H, 3×-CH3, methyl of TMP), 2.87 (m, 1H, -CH=CCH-), 3.31 (m, 1H, -CHNH2), 4.53 (m, 1H, -OCOCH-), 5.12, 5.19 (d, each, J = 10.0 Hz, 1H, -OCH2-), 5.24 (brs, 1H, -CH=C-). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 15.3, 16.7, 16.8, 16.9, 18.2, 19.7, 23.1, 23.4, 23.6, 23.7, 25.8, 27.6, 28.1, 30.7, 31.7, 32.4, 32.6, 33.1, 33.8, 36.9, 37.7, 38.1, 39.2, 41.3, 41.6, 45.9, 46.9, 47.5, 55.3, 60.4(-CHNH2), 81.9 (-OCOCH-), 122.3 (-CH=C-), 143.6 (-CH=C-), 173.5(-CO-), 177.2 (-CO-), pyrazine ring: 20.6 (-CH3), 21.4 (-CH3), 21.7 (-CH3), 64.9 (-COCH2-), 145.4, 148.8, 149.4, 151.1. HRMS (ESI) m/z: 690.52101 [M+H]+, calcd for C43H68N3O4: 690.51316.
3.2.2. General Synthesis of the TOA-Amino Acid Derivatives 6g–6k
The corresponding benzoyloxycarbonyl-protected amino acids (0.38 mmol), EDCI (0.50 mmol) and DMAP (0.025 mmol) were dissolved in dry DCM, then compound 4 (0.25 mmol) was added and the reaction solution was stirred at room temperature overnight. The crude product was extracted with CH2Cl2. After drying the organic layer over anhydrous Na2SO4 and evaporating the solvent under vacuum, the crude product was purified by flash chromatography with dichloromethane-methanol (20:1) as eluent. The crude product and a little 10% Pd/C or Pd(OH)2/C were stirred in methanol under a hydrogen atmosphere overnight. The reaction solution was filtered and evaporated with vacuum. After separation by flash chromatography with dichloromethane-methanol (20:1) as eluent, the product was lyophilized.
3β-l-Lysine ester olean-12-en-28-oic acid-3,5,6-trimethylpyrazin-2-methyl ester (6g). White solid, m.p. 87.5–88.2 °C, = +156.0 (c 1.0, MeOH), yield: 69%. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 0.55, 0.89, 1.11 (s, each, 3H, 3×-CH3, methyl of OA), 0.88 (brs, 6H, 2×-CH3, methyl of OA), 0.91 (brs, 6H, 2×-CH3, methyl of OA), 1.00–2.50 (32H, methylene- of l-lysine, methine- and methylene- of OA), 2.49, 2.51, 2.54 (s, each, 3H, 3×-CH3, methyl of TMP), 2.75 (m, 2H, -CH2NH2), 2.87 (m, 1H, -CH=CCH-), 3.44 (m, 1H, -CHNH2), 4.52 (m, 1H, -OCOCH-), 5.12, 5.19 (d, each, J = 10.0 Hz, 1H, -OCH2-), 5.24 (brs, 1H, -CH=C-). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 15.3, 16.8, 16.9, 18.2, 22.9, 23.1, 23.4, 23.5, 23.6, 25.8, 27.6, 28.1, 30.7, 31.0, 32.4, 32.6, 33.1, 33.8, 34.4, 36.9, 37.7, 38.1, 39.2, 41.4, 41.6, 41.8, 45.9, 46.9, 47.5, 54.6 (-CHNH2), 55.3, 81.9 (-OCOCH-), 122.3 (-CH=C-), 143.6 (-CH=C-), 175.3 (-CO-), 177.2 (-CO-), pyrazine ring: 20.6 (-CH3), 21.4 (-CH3), 21.7 (-CH3), 64.9 (-OCOCH2-), 145.4, 148.8, 149.2, 151.0. HRMS (ESI) m/z: 719.54488 [M+H]+, calcd for C44H71N4O4: 719.53971.
3β-l-Phenylalanine ester olean-12-en-28-oic acid-3,5,6-trimethylpyrazin-2-methyl ester (6h). White solid, m.p. 82.4–83.8 °C, = +63.3 (c 1.0, MeOH), yield: 60%. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 0.54, 0.79, 0.84, 0.89, 0.90, 0.91, 1.11 (s, each, 3H, 7×-CH3, methyl of OA), 1.00–2.50 (24H, methine- and methylene- of OA), 2.49, 2.51, 2.54 (s, each, 3H, 3×-CH3, methyl of TMP), 2.87 (m, 1H, -CH=CCH-), 3.16 (m, 2H, -CH2CHNH2), 3.76 (m, 1H, -CHNH2), 4.53 (m, 1H, -OCOCH-), 5.12, 5.19 (d, each, J = 10.0 Hz, 1H, -OCH2-), 5.24 (brs, 1H, -CH=C-), 7.22, 7.23, 7.29, 7.30, 7.31 (m, 5H, -C6H5). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 15.3, 16.8, 16.9, 18.2, 23.1, 23.4, 23.5, 23.6, 25.9, 27.6, 28.1, 30.7, 32.4, 32.6, 33.1, 33.8, 36.9, 37.7, 38.1, 39.2, 41.0, 41.3, 41.7, 45.9, 46.9, 47.5, 55.3, 56.1 (-CHNH2), 81.6 (-OCOCH-), 122.3 (-CH=C-), 143.6 (-CH=C-), 175.3 (-CO-), 177.2 (-CO-), benzene ring: 126.8, 128.5, 128.6, 129.3, 129.4, 137.2, pyrazine ring: 20.6 (-CH3), 21.4 (-CH3), 21.7 (-CH3), 64.9 (-OCOCH2-), 145.4, 148.8, 149.2, 151.0. HRMS (ESI) m/z: 738.52094 [M+H]+, calcd for C47H68N3O4: 738.51316.
3β-l-Sarcosine ester olean-12-en-28-oic acid-3,5,6-trimethylpyrazin-2-methyl ester (6i). White solid, m.p. 81.9–82.5 °C, = +48.8 (c 1.0, MeOH), yield: 55%. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 0.55, 0.86, 0.87, 0.89, 1.11 (s, each, 3H, 5×-CH3, methyl of OA), 0.91 (brs, 6H, 2×-CH3, methyl of OA), 2.45 (s, 3H, -NHCH3), 1.00–2.50 (23H, methine- and methylene- of OA), 2.49, 2.51, 2.54 (s, each, 3H, 3×-CH3, methyl of TMP), 2.87 (m, 1H, -CH=CCH-), 3.37 (s, 2H, -CH2NH-), 4.57 (m, 1H, -OCOCH-), 5.12, 5.19 (d, each, J = 10.0 Hz, 1H, -OCH2-), 5.24 (brs, 1H, -CH=C-). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 15.4, 16.7, 16.8, 18.3, 23.1, 23.4, 23.6, 23.6, 25.8, 27.6, 28.1, 30.7, 32.4, 32.6, 33.1, 33.9, 36.0 (-NHCH3), 36.9, 37.7, 38.1, 39.2, 41.3, 41.6, 45.9, 46.9, 47.5, 52.9 (-CH2NH-), 55.3, 81.5 (-OCOCH-), 122.3 (-CH=C-), 143.6 (-CH=C-), 172.0(-CO-), 177.2 (-CO-), pyrazine ring: 20.6 (-CH3), 21.4 (-CH3), 21.7 (-CH3), 64.9 (-OCOCH2-), 145.4, 148.8, 149.2, 151.0. HRMS (ESI) m/z: 662.48967 [M+H]+, calcd for C41H64N3O4: 662.48186.
3β-l-Pyroglutamate ester olean-12-en-28-oic acid-3,5,6-trimethylpyrazin-2-methyl ester (6j). White solid, m.p. 124.6–125.8 °C, = +35.6 (c 1.0, MeOH), yield: 45%. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 0.55, 0.89, 1.11 (s, each, 3H, 3×-CH3, methyl of OA), 0.88 (brs, 6H, 2×-CH3, methyl of OA), 0.91 (brs, 6H, 2×-CH3, methyl of OA), 1.00–2.50 (27H, methylene- of l-pyroglutamate, methine- and methylene- of OA), 2.50, 2.52, 2.56 (s, each, 3H, 3×-CH3, methyl of TMP), 2.87 (m, 1H, -CH=CCH-), 4.25 (m, 1H, -CHNH-), 4.57 (m, 1H, -OCOCH-), 5.12, 5.19 (d, each, J = 10.0 Hz, 1H, -OCH2-), 5.24 (brs, 1H, -CH=C-). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 15.3, 16.8, 16.8, 18.2, 23.1, 23.4, 23.5, 23.8, 25.1, 25.9, 27.7, 28.1, 29.3, 30.7, 32.4, 32.6, 33.1, 33.9, 36.9, 37.9, 38.1, 39.2, 41.3, 41.9, 45.9, 46.9, 47.5, 55.3, 55.7 (-CHNH-), 82.5 (-OCOCH-), 122.3 (-CH=C-), 143.6 (-CH=C-), 171.7 (-CO-), 177.2 (-CO-), 177.7 (-CONH-), pyrazine ring: 20.6 (-CH3), 21.4 (-CH3), 21.7 (-CH3), 64.9 (-OCOCH2-), 145.4, 148.8, 149.2, 150.9. HRMS (ESI) m/z: 702.48461 [M+H]+, calcd for C43H64N3O5: 702.47677.
3β-l-Tryptophan ester olean-12-en-28-oic acid-3,5,6-trimethylpyrazin-2-methyl ester (6k). White solid, m.p. 206.9–207.7 °C, = +39.3 (c 1.0, MeOH), yield: 43%. 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ (ppm): 0.35, 0.60, 0.69, 0.81, 1.06 (s, each, 3H, 5×-CH3, methyl of OA), 0.87 (brs, 6H, 2×-CH3, methyl of OA), 2.40, 2.42, 2.46 (s, each, 3H, 3×-CH3, methyl of TMP), 1.00–2.50 (24H, methine- and methylene- of OA). 2.76 (m, 1H, -CH=CCH-), 2.96, 3.12 (m, 2H, -CH2CHNH2), 3.75 (m, 1H, -CHNH2), 4.35 (m, 1H, -OCOCH-), 5.09, 5.10, (d, each, J = 10.0 Hz, 1H, -OCH2-), 5.11 (brs, 1H, -CH=C-), indole ring: 6.97, 7.06 (m, each, 1H), 7.14 (brs, -CHNH-), 7.34, 7.53 (d, each, J = 10.0 Hz, 1H), 10.9 (s, 1H, -NH). 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ (ppm): 14.9, 16.3, 16.4, 17.6, 22.6, 22.8, 23.0, 23.3, 25.4, 26.9, 27.4, 30.1, 30.3, 32.0, 32.1, 32.7, 33.1, 36.3, 37.1, 37.4, 38.7, 40.9, 41.2, 45.4, 46.2, 46.7, 54.4, 54.9 (-CHNH2), 80.6 (-OCOCH-), 121.8 (-CH=C-), 143.2 (-CH=C-), 173.3 (-CO-), 176.1 (-CO-), indole ring: 109.2, 111.4, 118.2, 118.3, 120.9, 123.8, 127.1, 136.2, pyrazine ring: 20.1 (-CH3), 20.9 (-CH3), 21.2 (-CH3), 64.2 (-OCOCH2-), 145.0, 148.2, 148.7, 150.6. HRMS (ESI) m/z: 777.53162 [M+H]+, calcd for C49H69N4O4: 777.52406.
3.2.3. Synthesis of the TOA-Amino Acid Derivative 6l
Cbz-l-serine (1.0 mmol), TBDMS-Cl (1.2 mmol) and imidazole (2.0 mmol) were stirred in DMF at room temperature overnight. The crude product was extracted with CH2Cl2. After drying the organic layer over anhydrous Na2SO4 and evaporating the solvent under vacuum, the crude product was purified by flash chromatography with dichloromethane-methanol (20:1) as eluent. The crude product (0.50 mmol), EDCI (0.50 mmol) and DMAP (0.025 mmol) were dissolved in dry DCM, then compound 4 (0.25 mmol) was added and the reaction solution was stirred at room temperature overnight. The crude product was extracted with CH2Cl2. After drying the organic layer over anhydrous Na2SO4 and evaporating the solvent under vacuum, the crude product was purified by flash chromatography with dichloromethane-methanol (20:1) as eluent. The crude product and 1.5 equivalents of TBAF were stirred in THF for about 0.5 h in an ice-bath. The crude product was extracted with CH2Cl2. After drying the organic layer over anhydrous Na2SO4 and evaporating the solvent under vacuum, the crude product was purified by flash chromatography with dichloromethane-methanol (20:1) as eluent. The crude product and a little 10% Pd/C or Pd(OH)2/C were stirred in methanol under a hydrogen atmosphere overnight. The crude product was extracted with CH2Cl2. After drying the organic layer over anhydrous Na2SO4 and evaporating the solvent under vacuum, the crude product was purified by flash chromatography with dichloromethane-methanol (20:1) as eluent. The product was lyophilized.
3β-l-Serine ester olean-12-en-28-oic acid-3,5,6-trimethylpyrazin-2-methyl ester (6l). White solid, m.p. 107.1–108.5 °C, = +55.5 (c 1.0, MeOH), yield: 36%. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 0.55, 0.89, 1.11 (s, each, 3H, 3×-CH3), 0.87 (brs, 6H, 2×-CH3, methyl of OA), 0.91 (brs, 6H, 2×-CH3, methyl of OA), 2.17 (s, 1H, -OH), 1.00–2.50 (25H, methine- and methylene- of OA), 2.49, 2.51, 2.54 (s, each, 3H, 3×-CH3, methyl of TMP), 2.71 (m, 2H, -CH2OH), 2.87 (m, 1H, -CH=CCH-), 4.54 (m, 1H, -OCOCH-), 5.12, 5.19 (d, each, J = 10.0 Hz, 1H, -OCH2-), 5.24 (brs, 1H, -CH=C-). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 15.7, 16.8, 16.9, 18.2, 23.0, 23.5, 23.7, 23.8, 25.8, 27.6, 28.1, 30.7, 32.4, 32.6, 33.1, 33.8, 36.9, 37.8, 38.0, 39.2, 41.3, 41.6, 45.9, 46.9, 47.5, 55.3, 56.1 (-CHNH2), 63.7 (-CH2OH), 81.9 (-OCOCH-), 122.3 (-CH=C-), 143.6 (-CH=C-), 173.4 (-CO-), 177.2 (-CO-), pyrazine ring: 20.6 (-CH3), 21.4 (-CH3), 21.7 (-CH3), 64.9 (-OCOCH2-), 145.4, 148.8, 149.2, 151.0. HRMS (ESI) m/z: 678.48175 [M+H]+, calcd for C41H64N3O5: 678.47677.
3.3. Bio-Evaluation Methods
3.3.1. Cytotoxicity Evaluation
The cytotoxicity of these compounds was tested on five cells lines by the standard MTT assay. The human cancer cells lines (HepG2, HT-29, Hela, BGC-823) and MDCK cells were provided by the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Peking Union Medical College. The tumor cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum and 1% (v/v) penicillin-streptomycin (Thermo Technologies, New York, NY, USA) at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. The growing tumor cells at a density 3 × 103 cells/mL were exposed to various concentrations of the tested drugs and incubated in a 96-well microtiter plate for 72 h (37 °C, 5% CO2). After MTT solution (20 μL, 5 mg/mL) was added to each well, the plate was incubated for a further 4 h. Then the media was removed. Formazan crystals were dissolved with DMSO (150 μL). After mixing well, the absorbance was quantified at 490 nm with a BIORAD 550 spectrophotometer (Bio-rad Life Science Development Ltd., Beijing, China). Wells containing no drugs were used to be blanks. The IC50 values were defined as the concentration of compounds that produced a 50% reduction of surviving cells and calculated using the Logit-method. Tumor cell growth inhibitory rate was calculated in the following Equation (1):
% inhibition = (1 − Sample group OD/Control group OD) × 100%
3.3.2. Giemsa Staining [37]
HepG2 cells in logarithmic growth phase were cultured in 6-well plates for 24 h at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. And then each group was treated with different concentrations of compound 6a for 72 h. The cell culture medium was discarded. And the cells were washed twice with PBS, kept in PBS/ethanol (1:1) for 2 min, fixated in ethanol for 10 min. After removing the ethanol, the cells were stained with Giemsa stain for 2 min and observed under inverted phase-contrast microscope at a magnification of 400×. MDCK cells in logarithmic growth phase were cultured in 6-well plates for 24 h at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. The cells were treated with 2 μM of compound 6a and CDDP for 72 h. The same operation was experimented as described above, and the cells were observed under inverted phase-contrast microscope at a magnification of 200×.
3.3.3. DAPI Staining [40,41]
HepG2 cells in logarithmic growth phase were allowed to grow in 6-well plates for 24 h at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. And each group was treated with different concentrations of compound 6a for 72 h. Cell culture medium was discarded and the cells were washed twice with PBS. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (pH 7.4) for 15 min and then washed twice with PBS. With an excitation wavelength of 470 nm, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, 600 nM, Molecular Probes/Invitrogen Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) staining was then performed for 2 min and nuclear fragments were observed using inverted phase-contrast microscope at a magnification of 400×.
4. Conclusions
In summary, a series of novel TOA-amino acid derivatives were synthesized by conjugating amino acids to the 3-hydroxy group of TOA by ester bonds. The target products were characterized by spectroscopic data. Their cytotoxicity was evaluated on four cancer cell lines (HepG2, HT-29, Hela and BGC-823) by the standard MTT assay, and their nephrotoxicity was tested using MDCK cells. The ClogP values were calculated by means of computer simulation, and logP values of both 6a and TOA were determined using a shake flask-ultraviolet spectrophotometry method. Among the active compounds, 6a exhibited promising cytotoxicity, lower toxicity and better hydrophilicity. Combining Giemsa and DAPI staining, it was further verified that 6a could induce HepG2 apoptosis via nuclei fragmentation and had lower nephrotoxicity than CDDP. The results suggested that the attempt to introduce small, polar or basic amino acids into the hydroxy group of TOA could effectively enhance the hydrophilicity and biological activity. However, it is worthy of further study whether the better activity of TOA-amino acid derivatives is connected with a hydrophilicity increase of the amino acid conjugates, the positive charge, selective identification by membrane surface protein receptors or other ways. Our completed work lays the foundation for further research on the cytotoxicity mechanism, transmembrane transport and bioavailability of TOA-amino acid derivatives.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81173519 and No.81073017), the Innovation Team Project Foundation of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine (Lead Compound Discovering and Developing Innovation Team Project Foundation, 2011-CXTD-15) and the Graduate Independent Topics of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine (2014-JYBZZ-XS-118).
Author Contributions
F. Chu, X. Xu, P. Wang and H. Lei designed research. F. Chu, G. Li and K. Xu performed chemistry experiments and analyzed the data. F. Chu, Y. Gong, M. Wang and H. Zhang performed pharmacological experiments and analyzed the data. Y. Zhang analyzed pharmacological data and elaborated cell morphology. B. Xu predicted the ClogP values of the compounds on Computer Simulation. S. Gu measured specific rotation values. F. Chu and P. Wang wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, J.L.; Wang, H.; Pi, H.F.; Ruan, H.L.; Zhang, P.; Wu, J.Z. Structural analysis and antitussive evaluation of five novel esters of verticinone and bile acids. Steroids 2009, 74, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhosle, D.; Bharambe, S.; Gairola, N.; Dhaneshwar, S.S. Mutual prodrug concept: Fundamentals and applications. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 1994, 56, 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.L.; Cheng, Y.T.; Xu, K.; An, Y.W.; Wang, W.; Li, Q.S.; Han, Q.J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H.G.; Lei, H.M. Synthesis and anti-tumor evaluation of one novel tetramethylpyrazin-rhein derivative. Asian J. Chem. 2013, 25, 4885–4888. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.L.; Zhang, H.G.; Chu, F.H.; Xu, X.; Lin, J.X.; Chen, C.X.; Li, G.L.; Cheng, Y.T.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; et al. Synthesis and protective effect of new ligustrazine-benzoic acid derivatives against CoCl2-induced neurotoxicity in differentiated PC12 cells. Molecules 2013, 18, 13027–13042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Xu, X.; Chu, F.H.; Wang, M.N.; Wang, P.L.; Li, G.L.; Song, J.X.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Lei, H.M. Synthesis and biological evaluation of T-OA derivatives as cytotoxic agents. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2014, 1737, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.L.; She, G.M.; Yang, Y.N.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H.G.; Liu, J.; Cao, Y.Q.; Xu, X.; Lei, H.M. Synthesis and biological evaluation of new ligustrazine derivatives as anti-tumor agents. Molecules 2012, 17, 4972–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.L.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Xu, K.; Li, Q.S.; Zhang, H.G.; Guo, J.; Pang, D.D.; Cheng, Y.T.; Lei, H.M. A new ligustrazine derivative--pharmacokinetic evaluation and antitumor activity by suppression of NF-κB/p65 and COX-2 expression in S180 mice. Pharmazie 2013, 68, 782–789. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Gong, Y.; Xu, B.; Tian, Y.F.; Wang, M.X.; Zhang, H.Z.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Lei, H.M. Identification of metabolites of antitumor lead compound T-OA in rat urine by HPLC-HRMS. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2014, 39, 911–915. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Wang, P.L.; Xu, X.; Xu, S.X.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Lei, H.M. Equilibrium solubility and apparent oil/water partition coefficient of anticancer primer T-OA in various media. J. Beijing Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2013, 36, 554–557. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, P.; Ni, J.; Cao, S.L.; Lei, H.M.; Cai, Z.J.; Zhang, T.; Yu, F.; Tan, Q.Z. Preparation and evaluation of solid dispersions of a new antitumor compound based on early-stage preparation discovery concept. AAPS PharmSciTech 2013, 14, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, P.; Cao, S.L.; Ni, J.; Zhang, T.; Cai, Z.J.; Liu, J.J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.L.; Lei, H.M.; Liu, Y. In-vitro and in vivo comparison of T-OA microemulsions and solid dispersions based on EPDC. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.J.; Chai, H.B.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, D.S. Preparation of amino acid conjugates of betulinic acid with activity against human melanoma. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1999, 9, 1201–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drag-Zalesinska, M.; Kulbacka, J.; Saczko, J.; Wysocka, T.; Zabel, M.; Surowiak, P.; Drag, M. Esters of botulin and betulinic acid with amino acids have improved water solubility and are selectively cytotoxic toward cancer cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 4814–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.Q.; Liu, D.; Cai, L.L.; Chen, H.; Cao, B.; Wang, Y.Z. The synthesis of ursolic acid derivatives with cytotoxic activity and the investigation of their preliminary mechanism of action. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.F.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, M.M.; Li, X.F.; Li, J.X. Synthesis and evaluation of a novel series of heterocyclic oleanolic acid derivatives with anti-osteoclast formation activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 2796–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.X.; Zhao, J.W.; Wang, S.Z.; Pan, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Kadota, S. Synthesis and activity of oleanolic acid derivatives, a novel class of inhibitors of osteoclast formation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 1629–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.M.; Yi, H.W.; Xu, J.L.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.X.; Cao, S.X.; Xu, Q. A novel synthetic oleanolic acid derivative with amino acid conjugate suppresses tumour growth by inducing cell cycle arrest. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, A.; Rivas, F.; Lopez, P.E.; Garcia-Granados, A.; Martinez, A.; Albericio, F.; Marquez, N.; Muñoz, E. Solution- and solid- phase synthesis and anti-HIV activity of maslinic acid derivatives containing amino acids and peptides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, A.; Martin-Fonseca, S.; Rivas, F.; Reyes-Zurita, F.J.; Medina-O’Donnell, M.; Rufino-Palomares, E.E.; Martinez, A.; Garcia-Granados, A.; Lupiañez, J.A.; Albericio, F. Solid-phase library synthesis of bi-functional derivatives of oleanolic and maslinic acids and their cytotoxicity on three cancer cell lines. ACS Comb. Sci. 2014, 16, 428–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeda-Hirschmann, G.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Theoduloz, C.; Valderrama, J.A. Gastroprotective effect and cytotoxicity of labdeneamides with amino acids. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimi, A.; Hashizume, H.; Tamaki, S.; Tsuda, H.; Fukata, F.; Nishimura, K.; Yata, N. Importance of hydrolysis of amino acid moiety in water-soluble prodrugs of disodium cromoglycate for increased oral bioavailability. J. Pharmacobio-Dyn. 1992, 15, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Wang, M.; Gou, S.H.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, H.; Cao, F. Combination of amino acid/dipeptide with nitric oxide donating oleanolic acid derivatives as PepT1 targeting antitumor prodrugs. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landowski, C.P.; Vig, B.S.; Song, X.; Amidon, G.L. Targeted delivery to PEPT1- overexpressing cells: Acidic, basic, and secondary floxuridine amino acid ester prodrugs. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Wang, P.L.; Xu, X.; Han, Q.J.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Lei, H.M. Synthetic process optimization of the intermediate 2-bromomethyl-3,5,6-trimethylpyrazine. Anhui Med. Pharm. J. 2013, 17, 1467–1470. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.L.; Testa, B.; Fahr, A. Lipophilicity and its relationship with passive drug permeation. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 962–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waring, J.M. Lipophilicity in drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2010, 5, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Wang, R.; Komatsu, K.; Bonaz-Krause, P.; Zyrianov, Y.; McKenna, C.E.; Csipke, C.; Tokes, Z.A.; Lien, E.J. Synthesis, biological evaluation, and quantitative structure-activity relationship analysis of new schiff bases of hydroxysemicarbazide as potential antitumor agents. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servusová, B.; Eibinová, D.; Doležal, M.; Kubíček, V.; Paterová, P.; Peško, M.; Kráľová, K. Substituted N-benzylpyrazine-2-carboxamides: Synthesis and biological evaluation. Molecules 2012, 17, 13183–13198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, E.; Hansen, S.V.; Urban, C.; Hudson, B.D.; Wargent, E.T.; Grundmann, M.; Jenkins, L.; Zaibi, M.; Stocker, C.J.; Ullrich, S.; et al. Discovery of TUG-770: A highly potent free fatty acid receptor 1 (FFA1/GPR40) of agonist for treatment type 2 diabetes. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeter, T.S.; Schwaighofer, A.; Mika, S.; Ter Laak, A.; Suelzle, D.; Ganzer, U.; Heinrich, N.; Müller, K.R. Predicting lipophilicity of drug-discovery molecules using Gaussian process models. Chem. Med. Chem. 2007, 2, 1265–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penta, A.; Ganguly, S.; Murugesan, S. Design and synthesis of 3α,4,7,7α-tetrahydro-1H-isoindole-1, 3(2H)-diones as inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 5, 659–664. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, G.R.; Li, J.J.; Wang, G.L.; Dong, M.J.; Zhang, Q. Synthesis and cytotoxic activities of the amino Acid-conjugates of 10-hydroxycamptothecin. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 34, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.A.; Panda, S.S.; Birs, A.S.; Serrano, J.C.; Gonzalez, C.F.; Alamry, K.A.; Katritzky, A.R. Synthesis and antibacterial evaluation of amino acid-antibiotic conjugates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 1856–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozio, P.; Cerasa, L.S.; Laserra, S.; Cacciatore, I.; Cornacchia, C.; di Filippo, E.S.; Fulle, S.; Fontana, A.; di Crescenzo, A.; Grilli, M.; et al. Memantine-sulfur containing antioxidant conjugates as potential prodrugs to improve the treatmentof Alzheimer's disease. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 49, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Long, X.Y.; Ding, M.G.; Ye, X.F.; Liang, J.M.; Gu, J.H.; Li, Z.T.; Li, G.H. Determination of equilibrium solubility and apparent oil/water partition coefficient of silymarin. J. Guangdong Pharm. Univ. 2011, 27, 445–449. [Google Scholar]
- George, V.C.; Kumar, D.R.N.; Suresh, P.K.; Kumar, R.A. Oleanolic acid inhibit cell growth and induces apoptosis in A375 melanoma cells. Biomed. Prev. Nutr. 2014, 4, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, M.S.; Zong, W.X. Chemotherapeutic approaches for targeting cell death pathways. Oncologist 2006, 11, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.L.; Tang, H.M.; Mak, K.H.; Hu, S.; Wang, S.S.; Wong, K.M.; Wong, C.S.; Wu, H.Y.; Law, H.T.; Liu, K.; et al. Cell survival, DNA damage, and oncogenic transformation after a transient and reversible apoptotic response. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 2240–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajaniradje, S.; Mohankumar, K.; Pamidimukkala, R.; Subramanian, S.; Rajagopalan, R. Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of sesbania grandiflora leaves in human cancer cells. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.C.; Kuo, C.L.; Lee, M.H.; Lai, K.C.; Lin, J.P.; Yang, J.S.; Yu, C.S.; Lu, C.C.; Chiang, J.H.; Chueh, F.S.; et al. Wogonin triggers apoptosis in human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cells through the endoplasmic reticulum stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and caspase-3-dependent signaling pathways. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 39, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds aren’t available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).