Structural Elucidation of the DFG-Asp in and DFG-Asp out States of TAM Kinases and Insight into the Selectivity of Their Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Kinases as Therapeutic Targets
1.2. The TAM Family as Therapeutic Targets
1.3. Structure-Based Drug Design for Lead Identification and Optimization
1.4. Comprehension of Binding-Mode for the Design of Specific Enzyme Inhibitors
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Homology Modeling of the TAM Family
2.2. Validation of the TAM Kinase Models
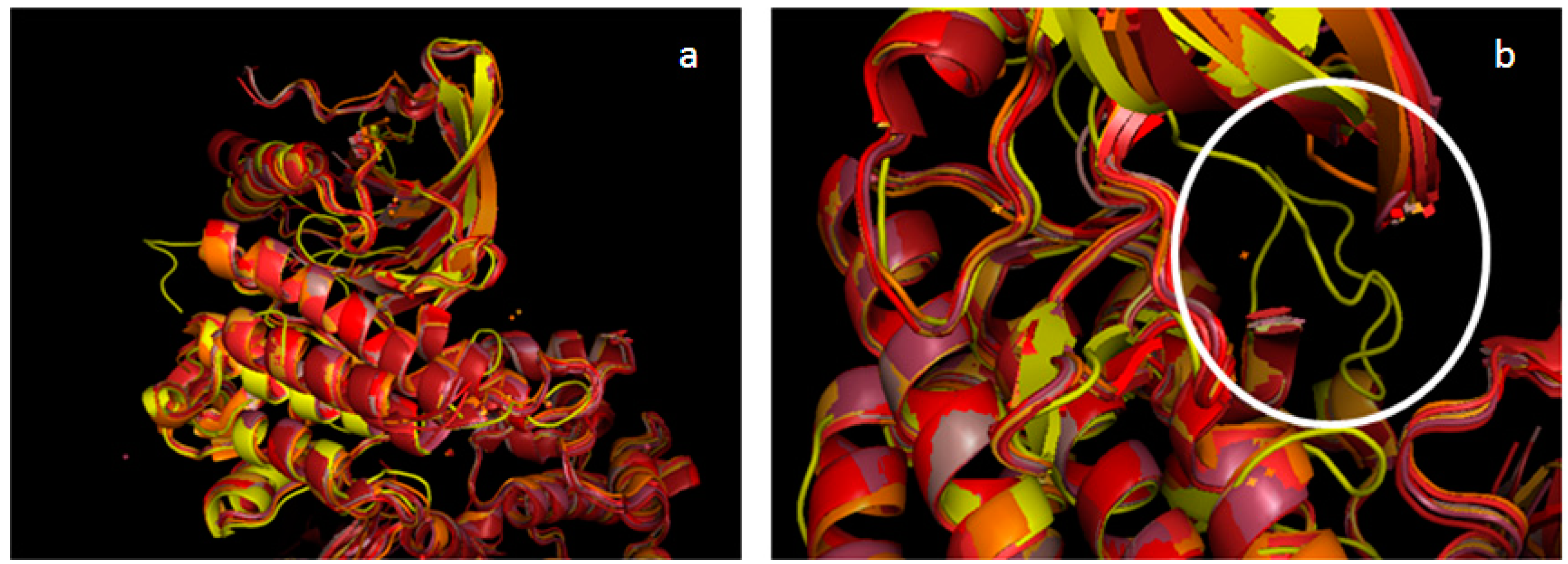
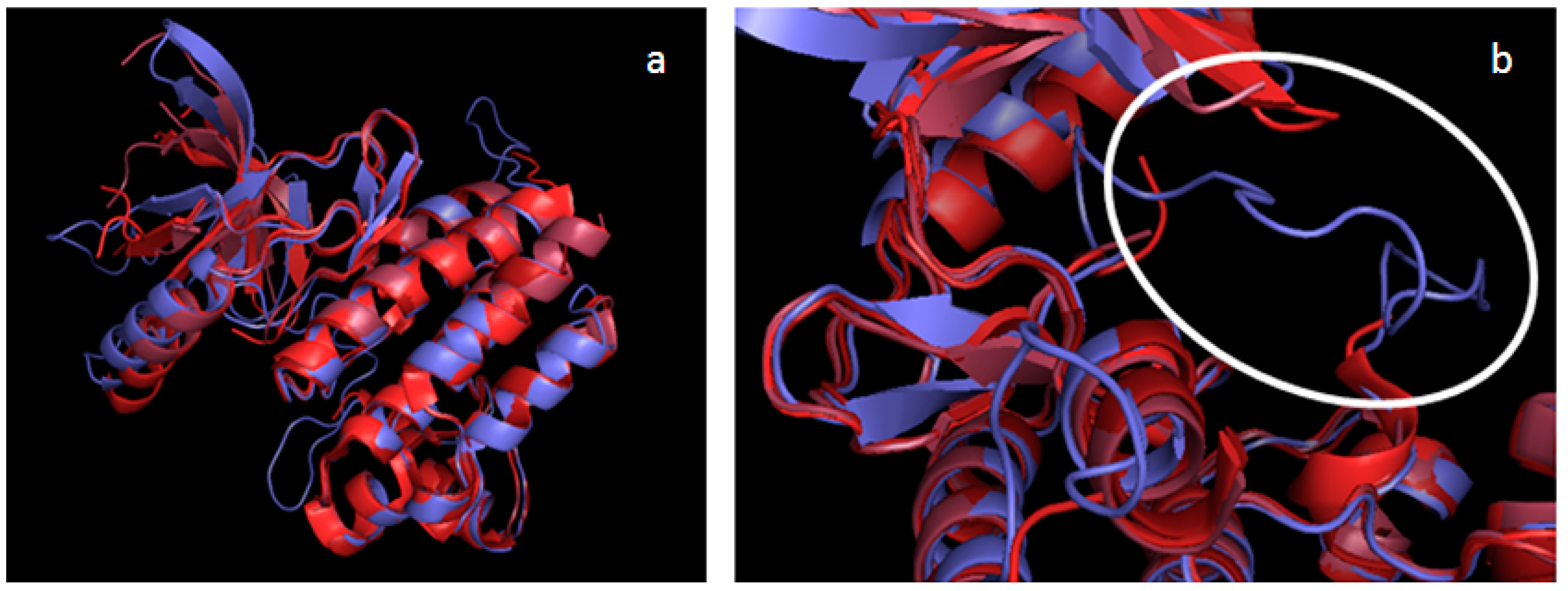
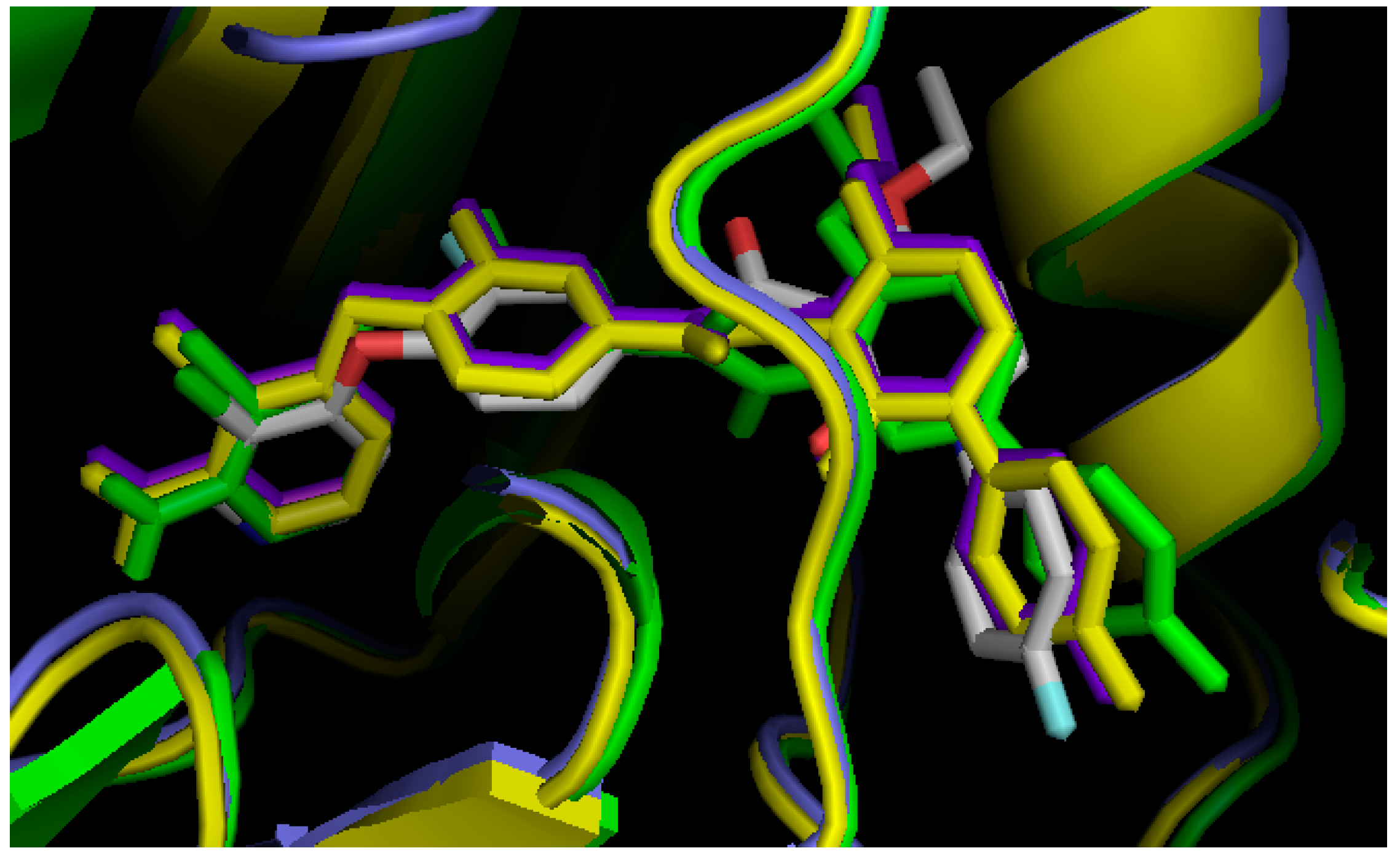
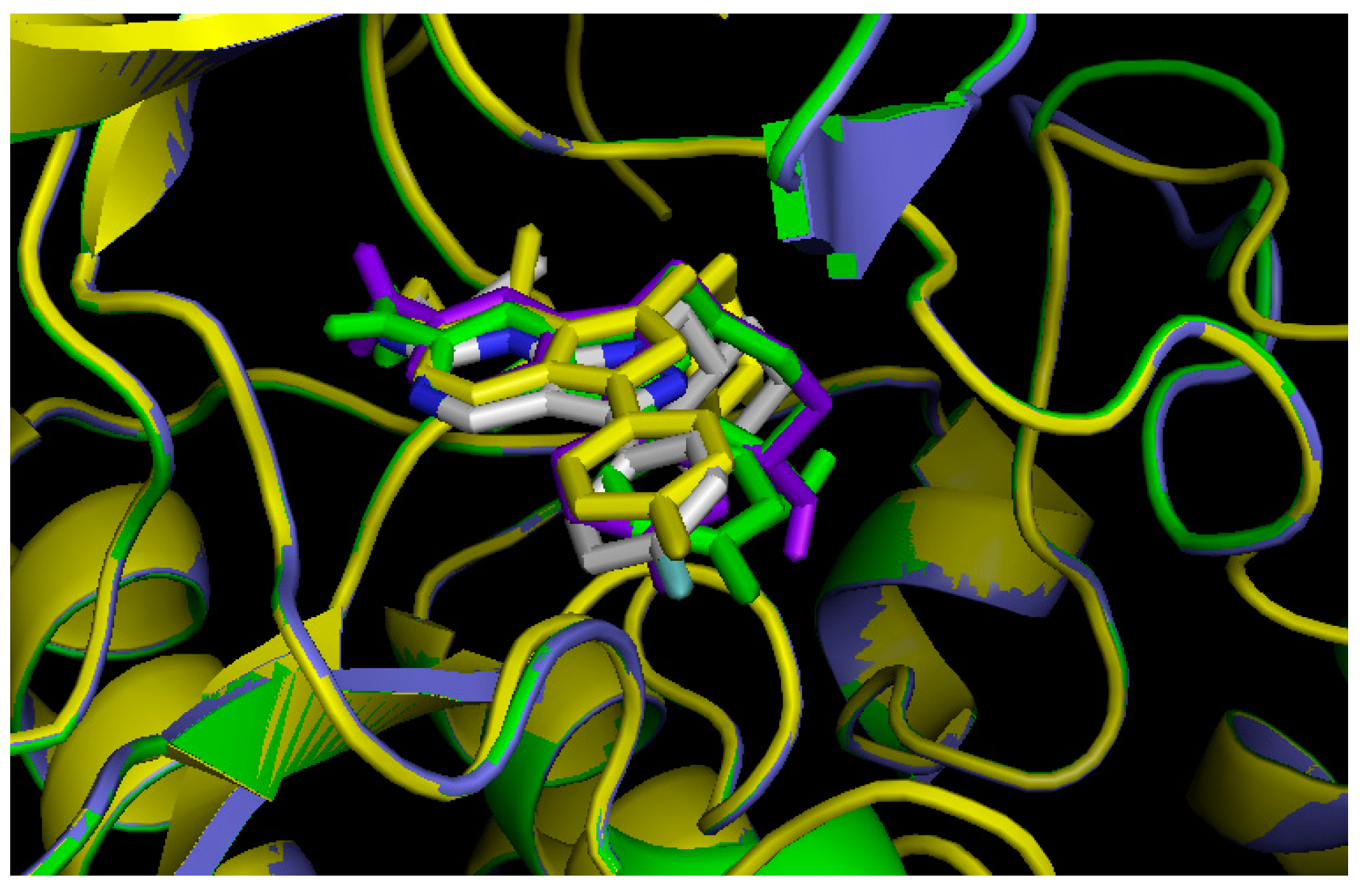
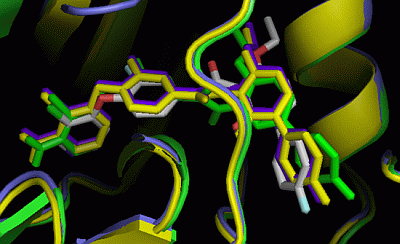
2.3. Comparison of Active Sites

2.4. Virtual Screening
2.5. Insight into Selectivity
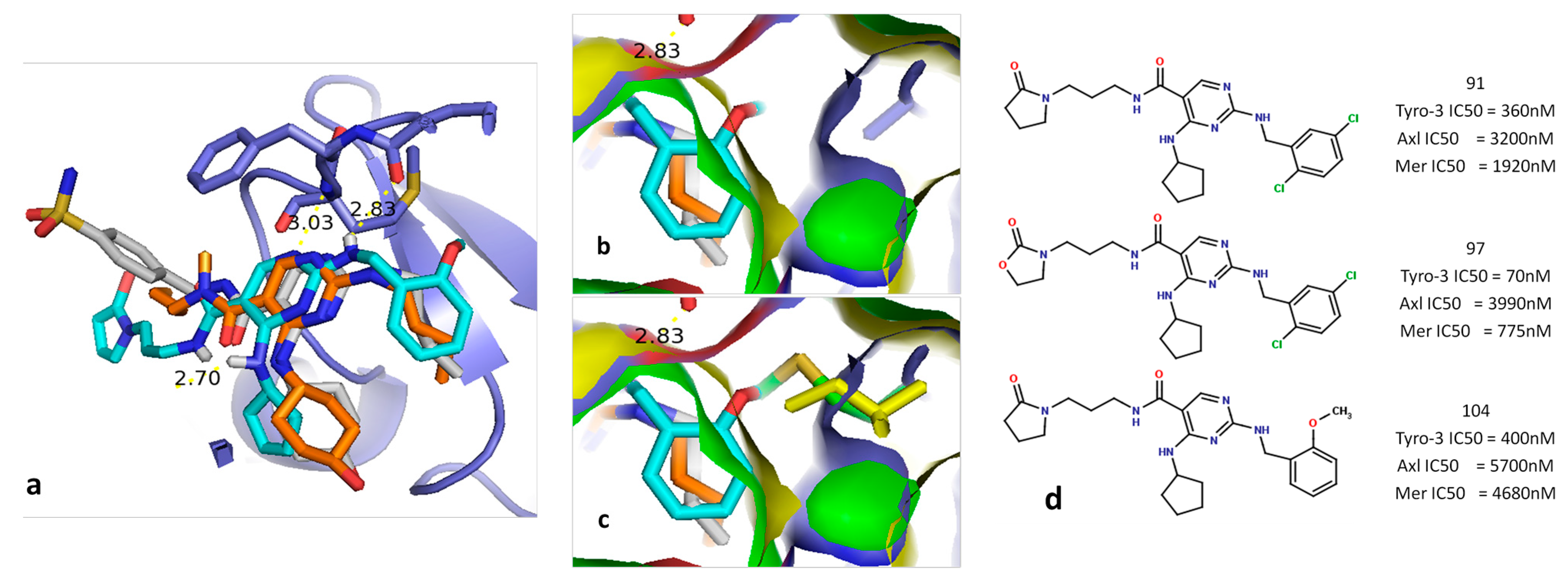
2.5.1. Diaminopyrimidine Scaffold
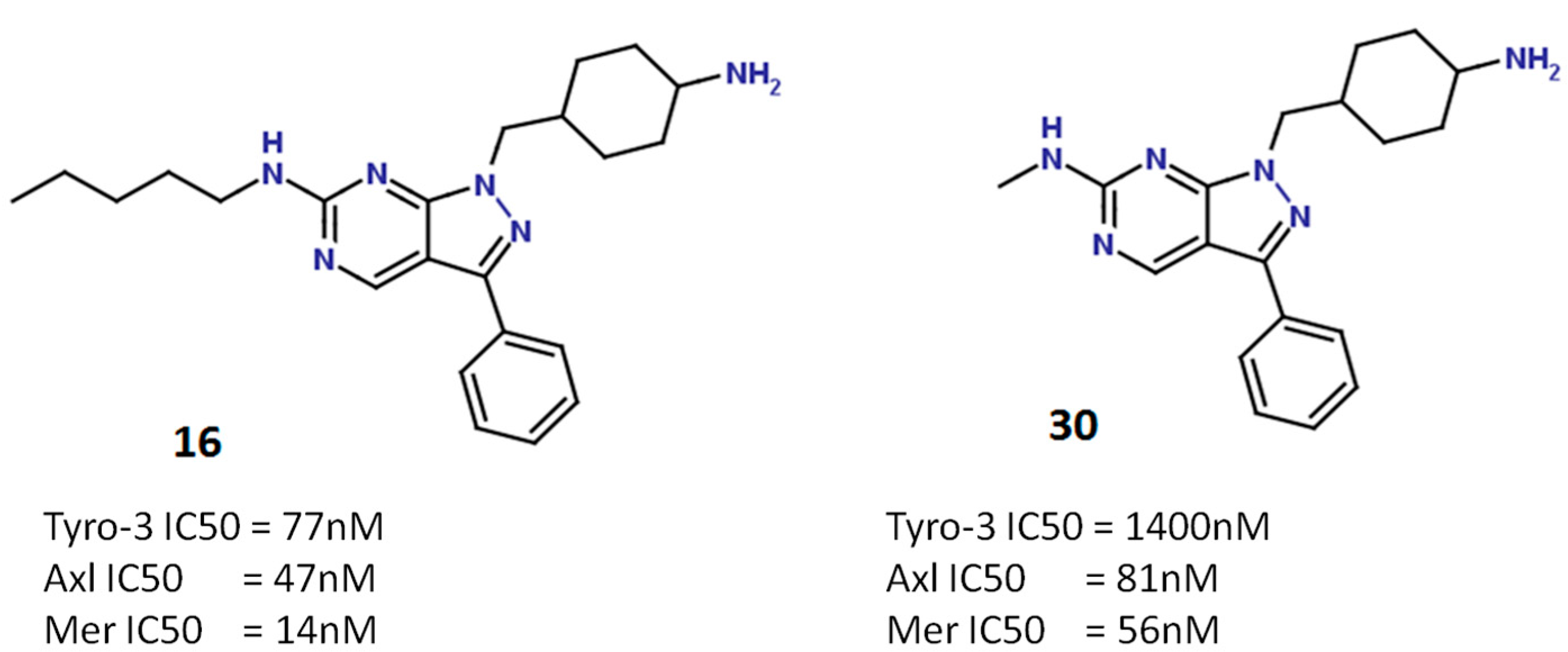
2.5.2. Pyrazolopyrimidine Scaffold
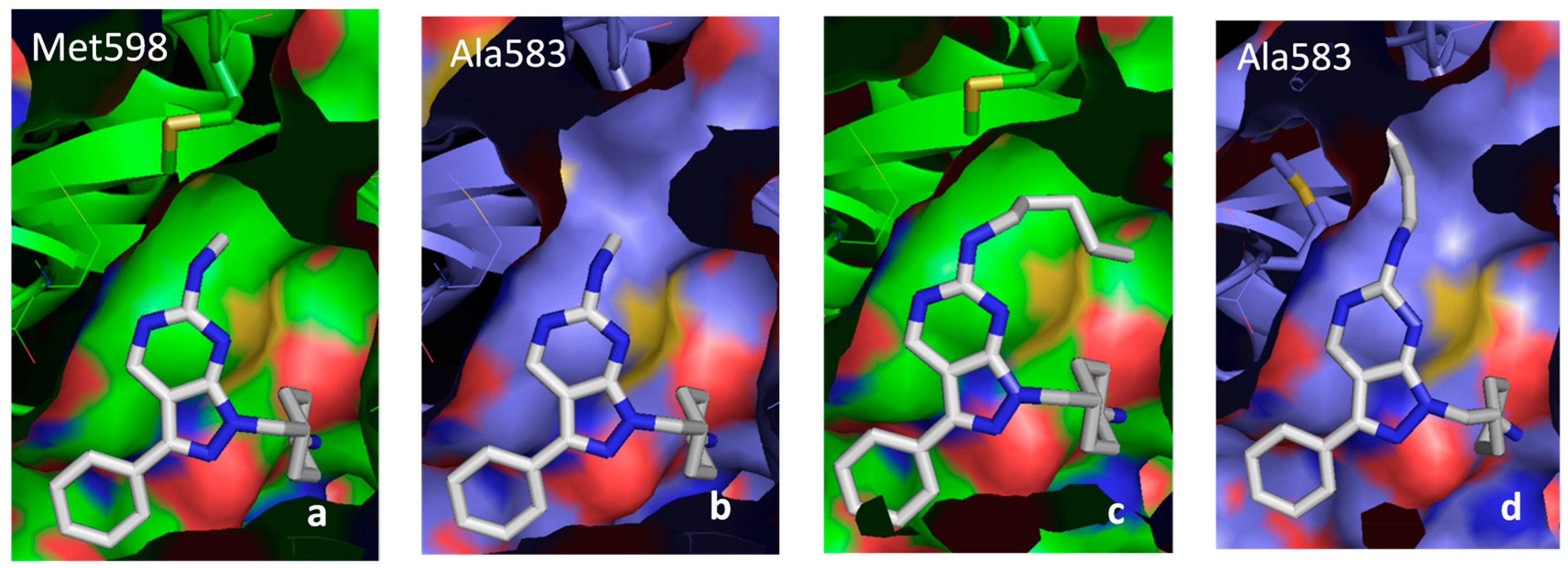
2.5.3. DFG-Asp out Docking Analysis
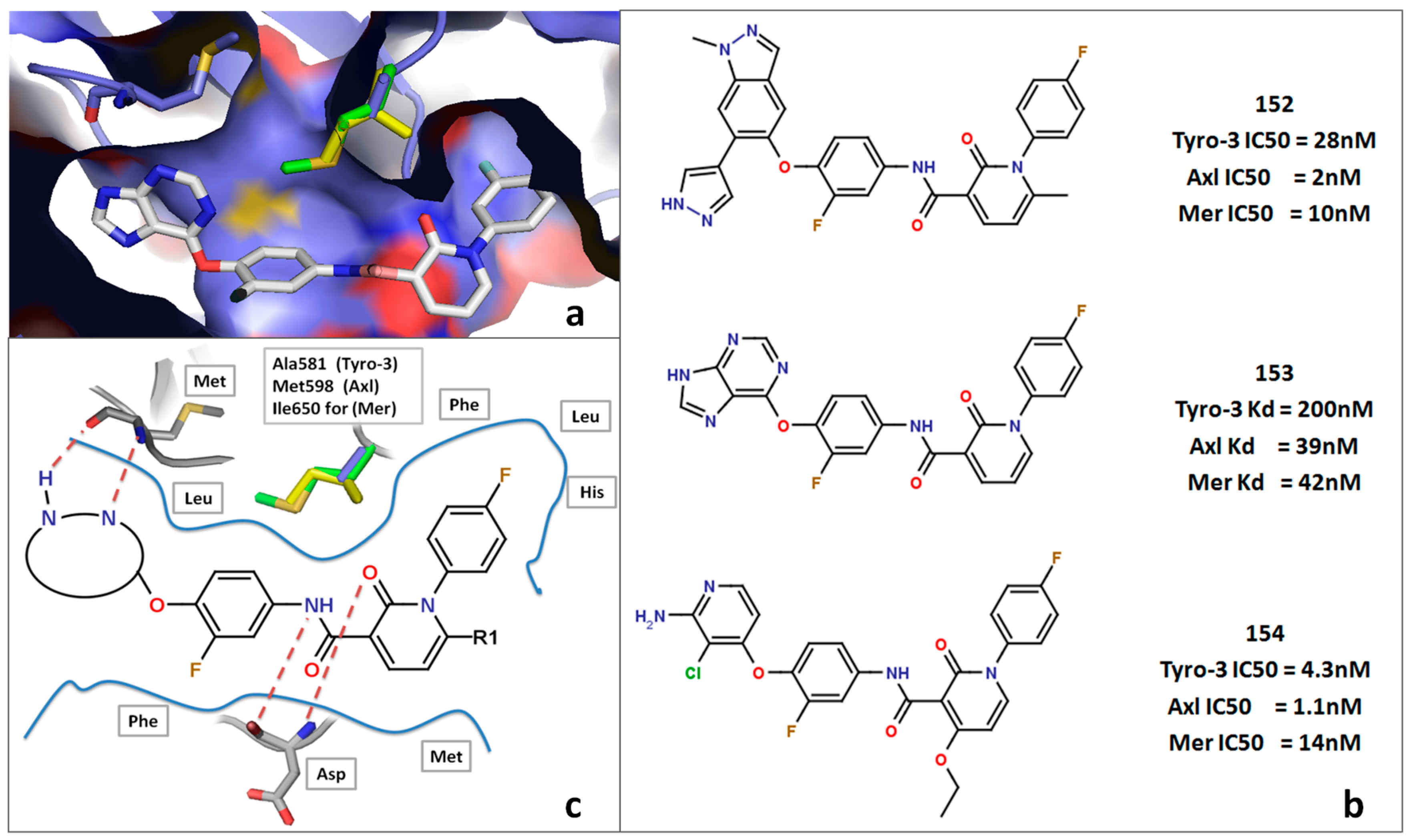
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Data Sources
3.2. Homology Modeling
3.3. Docking
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manning, G.; Whyte, D.B.; Martinez, R.; Hunter, T.; Sudarsanam, S. The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science 2002, 298, 1912–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varnum, B.C.; Young, C.; Elliott, G.; Garcia, A.; Bartley, T.D.; Fridell, Y.W.; Hunt, R.W.; Trail, G.; Clogston, C.; Toso, R.J. Axl receptor tyrosine kinase stimulated by the vitamin K-dependent protein encoded by growth-arrest-specific gene 6. Nature 1995, 373, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linger, R.M.A.; Keating, A.K.; Earp, H.S.; Graham, D.K. TAM receptor tyrosine kinases: Biologic functions, signaling, and potential therapeutic targeting in human cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2008, 100, 35–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, E.; Hjelle, B.; Bishop, J.M. Transforming genes in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 1952–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Bryan, J.P.; Frye, R.A.; Cogswell, P.C.; Neubauer, A.; Kitch, B.; Prokop, C.; Espinosa, R., 3rd; Le Beau, M.M.; Earp, H.S.; Liu, E.T. Axl, a transforming gene isolated from primary human myeloid leukemia cells, encodes a novel receptor tyrosine kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1991, 11, 5016–5031. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Neubauer, A.; Fiebeler, A.; Graham, D.K.; O’Bryan, J.P.; Schmidt, C.A.; Barckow, P.; Serke, S.; Siegert, W.; Snodgrass, H.R.; Huhn, D. Expression of axl, a transforming receptor tyrosine kinase, in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Blood 1994, 84, 1931–1941. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.K.; Bowman, G.W.; Dawson, T.L.; Stanford, W.L.; Earp, H.S.; Snodgrass, H.R. Cloning and developmental expression analysis of the murine c-mer tyrosine kinase. Oncogene 1995, 10, 2349–2359. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.S.; Fujimoto, J.; Tamaya, T. Coexpression of growth arrest-specific gene 6 and receptor tyrosine kinases Axl and Sky in human uterine endometrial cancers. Ann. Oncol. 2003, 14, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, B.I.; Malkowicz, S.B.; Nguyen, T.B.; Libertino, J.A.; McGarvey, T.W. Expression of the proto-oncogene Axl in renal cell carcinoma. DNA Cell Biol. 2003, 22, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, A.; Boström, A.-K.; Ljungberg, B.; Axelson, H.; Dahlbäck, B. Gas6 and the receptor tyrosine kinase Axl in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. PLoS One 2009, 4, e7575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.C.; Li, A.F.; Chi, C.W.; Chung, W.W.; Huang, C.L.; Lui, W.Y.; Kung, H.J.; Wu, C.W. Tie-1 protein tyrosine kinase: A novel independent prognostic marker for gastric cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 1999, 5, 1745–1751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-W.; Li, A.F.Y.; Chi, C.-W.; Lai, C.-H.; Huang, C.L.; Lo, S.-S.; Lui, W.-Y.; Lin, W.-C. Clinical significance of AXL kinase family in gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 2002, 22, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Craven, R.J.; Xu, L.H.; Weiner, T.M.; Fridell, Y.W.; Dent, G.A.; Srivastava, S.; Varnum, B.; Liu, E.T.; Cance, W.G. Receptor tyrosine kinases expressed in metastatic colon cancer. Int. J. Cancer 1995, 60, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, A.N.; Kalapurakal, J.; Davidson, W.R.; Kandpal, G.; Dunson, N.; Prashar, Y.; Kandpal, R.P. A receptor tyrosine kinase, UFO/Axl, and other genes isolated by a modified differential display PCR are overexpressed in metastatic prostatic carcinoma cell line DU145. Cancer Detect. Prev. 1999, 23, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, N.P.; Whang, Y.E.; Mohler, J.L.; Earp, H.S. Activated tyrosine kinase Ack1 promotes prostate tumorigenesis: Role of Ack1 in polyubiquitination of tumor suppressor Wwox. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 10514–10523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sainaghi, P.P.; Castello, L.; Bergamasco, L.; Galletti, M.; Bellosta, P.; Avanzi, G.C. Gas6 induces proliferation in prostate carcinoma cell lines expressing the Axl receptor. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005, 204, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-M.; Robinson, D.R.; Kung, H.-J. Signal pathways in up-regulation of chemokines by tyrosine kinase MER/NYK in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7311–7320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Nagayama, Y.; Nakano, T.; Takamura, N.; Namba, H.; Fukada, S.; Kuma, K.; Yamashita, S.; Niwa, M. Expression profile of receptor-type protein tyrosine kinase genes in the human thyroid. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Ito, M.; Naito, S.; Ohtsuru, A.; Nagayama, Y.; Kanematsu, T.; Yamashita, S.; Sekine, I. Expression of the Axl receptor tyrosine kinase in human thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid 1999, 9, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, M.; Nakashima, M.; Nakayama, T.; Ohtsuru, A.; Nagayama, Y.; Takamura, N.; Demedchik, E.P.; Sekine, I.; Yamashita, S. Expression of receptor-type tyrosine kinase, Axl, and its ligand, Gas6, in pediatric thyroid carcinomas around chernobyl. Thyroid 2002, 12, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shieh, Y.-S.; Lai, C.-Y.; Kao, Y.-R.; Shiah, S.-G.; Chu, Y.-W.; Lee, H.-S.; Wu, C.-W. Expression of axl in lung adenocarcinoma and correlation with tumor progression. Neoplasia 2005, 7, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wimmel, A.; Glitz, D.; Kraus, A.; Roeder, J.; Schuermann, M. Axl receptor tyrosine kinase expression in human lung cancer cell lines correlates with cellular adhesion. Eur. J. Cancer 2001, 37, 2264–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berclaz, G.; Altermatt, H.J.; Rohrbach, V.; Kieffer, I.; Dreher, E.; Andres, A.C. Estrogen dependent expression of the receptor tyrosine kinase axl in normal and malignant human breast. Ann. Oncol. 2001, 12, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavazoie, S.F.; Alarcón, C.; Oskarsson, T.; Padua, D.; Wang, Q.; Bos, P.D.; Gerald, W.L.; Massagué, J. Endogenous human microRNAs that suppress breast cancer metastasis. Nature 2008, 451, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zantek, N.D.; Walker-Daniels, J.; Stewart, J.; Hansen, R.K.; Robinson, D.; Miao, H.; Wang, B.; Kung, H.J.; Bissell, M.J.; Kinch, M.S. MCF-10A-NeoST: a new cell system for studying cell-ECM and cell-cell interactions in breast cancer. Clin. Cancer 2001, 7, 3640–3648. [Google Scholar]
- Meric, F.; Lee, W.-P.; Sahin, A.; Zhang, H.; Kung, H.-J.; Hung, M.-C. Expression profile of tyrosine kinases in breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Macleod, K.; Mullen, P.; Sewell, J.; Rabiasz, G.; Lawrie, S.; Miller, E.; Smyth, J.F.; Langdon, S.P. Altered ErbB receptor signaling and gene expression in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6789–6800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Fujimoto, J.; Tamaya, T. Coexpression of Gas6/Axl in human ovarian cancers. Oncology 2004, 66, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsou, A.P.; Wu, K.M.; Tsen, T.Y.; Chi, C.W.; Chiu, J.H.; Lui, W.Y.; Hu, C.P.; Chang, C.; Chou, C.K.; Tsai, S.F. Parallel hybridization analysis of multiple protein kinase genes: Identification of gene expression patterns characteristic of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Genomics 1998, 50, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vajkoczy, P.; Knyazev, P.; Kunkel, A.; Capelle, H.-H.; Behrndt, S.; von Tengg-Kobligk, H.; Kiessling, F.; Eichelsbacher, U.; Essig, M.; Read, T.-A.; et al. Dominant-negative inhibition of the Axl receptor tyrosine kinase suppresses brain tumor cell growth and invasion and prolongs survival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5799–5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quong, R.Y.; Bickford, S.T.; Ing, Y.L.; Terman, B.; Herlyn, M.; Lassam, N.J. Protein kinases in normal and transformed melanocytes. Melanoma Res. 1994, 4, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Györffy, B.; Lage, H. A Web-based data warehouse on gene expression in human malignant melanoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ginkel, P.R.; Gee, R.L.; Shearer, R.L.; Subramanian, L.; Walker, T.M.; Albert, D.M.; Meisner, L.F.; Varnum, B.C.; Polans, A.S. Expression of the receptor tyrosine kinase Axl promotes ocular melanoma cell survival. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, T.; Tani, M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Kimura, K.; Park, Y.-B.; Imaizumi, N.; Tsuda, H.; Aoyagi, K.; Sasaki, H.; Ohwada, S.; et al. Biological properties and gene expression associated with metastatic potential of human osteosarcoma. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2003, 20, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosier, P.S.; Hall, L.R.; Vitas, M.R.; Lewis, P.M.; Crosier, K.E. Identification of a novel receptor tyrosine kinase expressed in acute myeloid leukemic blasts. Leuk. Lymphoma 1995, 18, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challier, C.; Uphoff, C.C.; Janssen, J.W.; Drexler, H.G. Differential expression of the ufo/axl oncogene in human leukemia-lymphoma cell lines. Leukemia 1996, 10, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Vos, J.; Couderc, G.; Tarte, K.; Jourdan, M.; Requirand, G.; Delteil, M.C.; Rossi, J.F.; Mechti, N.; Klein, B. Identifying intercellular signaling genes expressed in malignant plasma cells by using complementary DNA arrays. Blood 2001, 98, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Lee, J.C.; Lin, L.; Olivas, V.; Au, V.; LaFramboise, T.; Abdel-Rahman, M.; Wang, X.; Levine, A.D.; Rho, J.K.; et al. Activation of the AXL kinase causes resistance to EGFR-targeted therapy in lung cancer. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadevan, D.; Cooke, L.; Riley, C.; Swart, R.; Simons, B.; Della Croce, K.; Wisner, L.; Iorio, M.; Shakalya, K.; Garewal, H.; et al. A novel tyrosine kinase switch is a mechanism of imatinib resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3909–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Greger, J.; Shi, H.; Liu, Y.; Greshock, J.; Annan, R.; Halsey, W.; Sathe, G.M.; Martin, A.-M.; Gilmer, T.M. Novel mechanism of lapatinib resistance in HER2-positive breast tumor cells: Activation of AXL. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6871–6878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, K.M.; Kalinowski, F.C.; Candy, P.A.; Epis, M.R.; Zhang, P.M.; Redfern, A.D.; Stuart, L.M.; Goodall, G.J.; Leedman, P.J. Axl mediates acquired resistance of head and neck cancer cells to the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor erlotinib. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 2541–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Wang, H.; Logsdon, C.D.; Rashid, A.; Fleming, J.B.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Gomez, H.F.; Evans, D.B.; Wang, H. Overexpression of receptor tyrosine kinase Axl promotes tumor cell invasion and survival in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer 2011, 117, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaldor, S.W.; Kalish, V.J.; Davies, J.F., 2nd; Shetty, B.V.; Fritz, J.E.; Appelt, K.; Burgess, J.A.; Campanale, K.M.; Chirgadze, N.Y.; Clawson, D.K.; et al. Viracept (nelfinavir mesylate, AG1343): A potent, orally bioavailable inhibitor of HIV-1 protease. J. Med. Chem. 1997, 40, 3979–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wlodawer, A.; Vondrasek, J. Inhibitors of HIV-1 protease: A major success of structure-assisted drug design. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1998, 27, 249–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.E.; Baker, C.T.; Dwyer, M.D.; Murcko, M.A.; Rao, B.G.; Tung, R.D.; Navia, M.A. Crystal structure of HIV-1 protease in complex with VX-478, a potent and orally bioavailable inhibitor of the enzyme. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 1181–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feneyrolles, C.; Spenlinhauer, A.; Guiet, L.; Fauvel, B.; Daydé-Cazals, B.; Warnault, P.; Chevé, G.; Yasri, A. Axl kinase as a key target for oncology: Focus on small molecule inhibitors. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 2141–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, G.M.; An, Y.; Cai, Z.-W.; Chen, X.-T.; Clark, C.; Cornelius, L.A.M.; Dai, J.; Gullo-Brown, J.; Gupta, A.; Henley, B.; et al. Discovery of N-(4-(2-amino-3-chloropyridin-4-yloxy)-3-fluorophenyl)-4-ethoxy-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridine-3-carboxamide (BMS-777607), a selective and orally efficacious inhibitor of the Met kinase superfamily. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 1251–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Finerty, P., Jr.; Walker, J.R.; Butler-Cole, C.; Vedadi, M.; Schapira, M.; Parker, S.A.; Turk, B.E.; Thompson, D.A.; Dhe-Paganon, S. Structural insights into the inhibited states of the Mer receptor tyrosine kinase. J. Struct. Biol. 2009, 165, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yang, C.; Simpson, C.; Deryckere, D.; van Deusen, A.; Miley, M.J.; Kireev, D.; Norris-Drouin, J.; Sather, S.; Hunter, D.; et al. Discovery of novel small molecule Mer kinase inhibitors for the treatment of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, N.A.; Hoffman, J.K.; Ciske, F.L.; Kaufman, M.D.; Kohrt, J.T.; Quin, J.; Sheehan, D.J.; Delaney, A.; Baxi, S.M.; Catana, C.; et al. Highly selective 2,4-diaminopyrimidine-5-carboxamide inhibitors of Sky kinase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 23, 1046–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, D.; Stashko, M.A.; DeRyckere, D.; Hunter, D.; Kireev, D.; Miley, M.J.; Cummings, C.; Lee, M.; Norris-Drouin, J.; et al. Pseudo-cyclization through intramolecular hydrogen bond enables discovery of pyridine substituted pyrimidines as new Mer kinase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9683–9692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, J.; Lumb, S.; Franklin, R.J.; Gascon-Simorte, J.M.; Calmiano, M.; Riche, K.L.; Lallemand, B.; Keyaerts, J.; Edwards, H.; Maloney, A.; et al. Discovery of 4-azaindoles as novel inhibitors of c-Met kinase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 2780–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christoph, S.; Deryckere, D.; Schlegel, J.; Frazer, J.K.; Batchelor, L.A.; Trakhimets, A.Y.; Sather, S.; Hunter, D.M.; Cummings, C.T.; Liu, J.; et al. UNC569, a novel small-molecule mer inhibitor with efficacy against acute lymphoblastic leukemia in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 2367–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez, R.M.; Chevot, F.; Cavagnino, A.; Saettel, N.; Radvanyi, F.; Piguel, S.; Bernard-Pierrot, I.; Stoven, V.; Legraverend, M. Inhibitors of the TAM subfamily of tyrosine kinases: Synthesis and biological evaluation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 61, 2–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulusu, K.C.; Tym, J.E.; Coker, E.A.; Schierz, A.C.; Al-Lazikani, B. canSAR: Updated cancer research and drug discovery knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D1040–D1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Suzek, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; He, S.; Cheng, T.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Gindulyte, A.; Bryant, S.H. PubChem BioAssay: 2014 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D1075–D1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, D.; Yokota, K.; Gouda, M.; Narumi, Y.; Ohmoto, H.; Nishiwaki, E.; Akita, K.; Kirii, Y. Activity-based kinase profiling of approved tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Genes Cells 2013, 18, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-F.; Tian, X.-T.; Ohkoshi, E.; Qin, B.; Liu, Y.-N.; Wu, P.-C.; Hour, M.-J.; Hung, H.-Y.; Qian, K.; Huang, R.; et al. Design and synthesis of diarylamines and diarylethers as cytotoxic antitumor agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 6224–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, N.A.; Kohrt, J.T.; Filipski, K.J.; Kaufman, M.; Sheehan, D.; Edmunds, J.E.; Delaney, A.; Wang, Y.; Bourbonais, F.; Lee, D.-Y.; et al. Novel and selective spiroindoline-based inhibitors of Sky kinase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, C.S.; Kim, B.G.; Blazey, C.M.; Ma, S.; Johnson, H.W.B.; Anand, N.K.; Arcalas, A.; Baik, T.G.; Buhr, C.A.; Cannoy, J.; et al. Discovery of a novel class of highly potent, selective, ATP-competitive, and orally bioavailable inhibitors of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 2218–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Ai, J.; Liang, Z.; Li, C.; Peng, X.; Ji, Y.; Jiang, H.; Geng, M.; Luo, C.; Liu, H. Discovery of novel 2-aminopyridine-3-carboxamides as c-Met kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 5169–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; McIver, A.L.; Stashko, M.A.; DeRyckere, D.; Branchford, B.R.; Hunter, D.; Kireev, D.; Miley, M.J.; Norris-Drouin, J.; Stewart, W.M.; et al. Discovery of Mer specific tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment and prevention of thrombosis. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9693–9700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.B.; Peek, V.L.; Ajamie, R.; Buchanan, S.G.; Graff, J.R.; Heidler, S.A.; Hui, Y.-H.; Huss, K.L.; Konicek, B.W.; Manro, J.R.; et al. LY2801653 is an orally bioavailable multi-kinase inhibitor with potent activity against MET, MST1R, and other oncoproteins, and displays anti-tumor activities in mouse xenograft models. Investig. New Drugs 2013, 31, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consortium, T.U. Activities at the universal protein resource (UniProt). Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D191–D198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, K.; Bordoli, L.; Kopp, J.; Schwede, T. The SWISS-MODEL workspace: a web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinform. Oxf. Engl. 2006, 22, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: A program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guex, N.; Peitsch, M.C. SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: An environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 1997, 18, 2714–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. Automated docking of substrates to proteins by simulated annealing. Proteins 1990, 8, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Lai, L.; Wang, S. Further development and validation of empirical scoring functions for structure-based binding affinity prediction. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2002, 16, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The PyMol Molecular Graphics System; Version 0.99rc6; Schrodinger; Delano Scientific LLC: San Carlos, CA, USA, 2002.
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Messoussi, A.; Peyronnet, L.; Feneyrolles, C.; Chevé, G.; Bougrin, K.; Yasri, A. Structural Elucidation of the DFG-Asp in and DFG-Asp out States of TAM Kinases and Insight into the Selectivity of Their Inhibitors. Molecules 2014, 19, 16223-16239. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191016223
Messoussi A, Peyronnet L, Feneyrolles C, Chevé G, Bougrin K, Yasri A. Structural Elucidation of the DFG-Asp in and DFG-Asp out States of TAM Kinases and Insight into the Selectivity of Their Inhibitors. Molecules. 2014; 19(10):16223-16239. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191016223
Chicago/Turabian StyleMessoussi, Abdellah, Lucile Peyronnet, Clémence Feneyrolles, Gwénaël Chevé, Khalid Bougrin, and Aziz Yasri. 2014. "Structural Elucidation of the DFG-Asp in and DFG-Asp out States of TAM Kinases and Insight into the Selectivity of Their Inhibitors" Molecules 19, no. 10: 16223-16239. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191016223
APA StyleMessoussi, A., Peyronnet, L., Feneyrolles, C., Chevé, G., Bougrin, K., & Yasri, A. (2014). Structural Elucidation of the DFG-Asp in and DFG-Asp out States of TAM Kinases and Insight into the Selectivity of Their Inhibitors. Molecules, 19(10), 16223-16239. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191016223