Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Apigenin Derivatives as Antibacterial and Antiproliferative Agents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
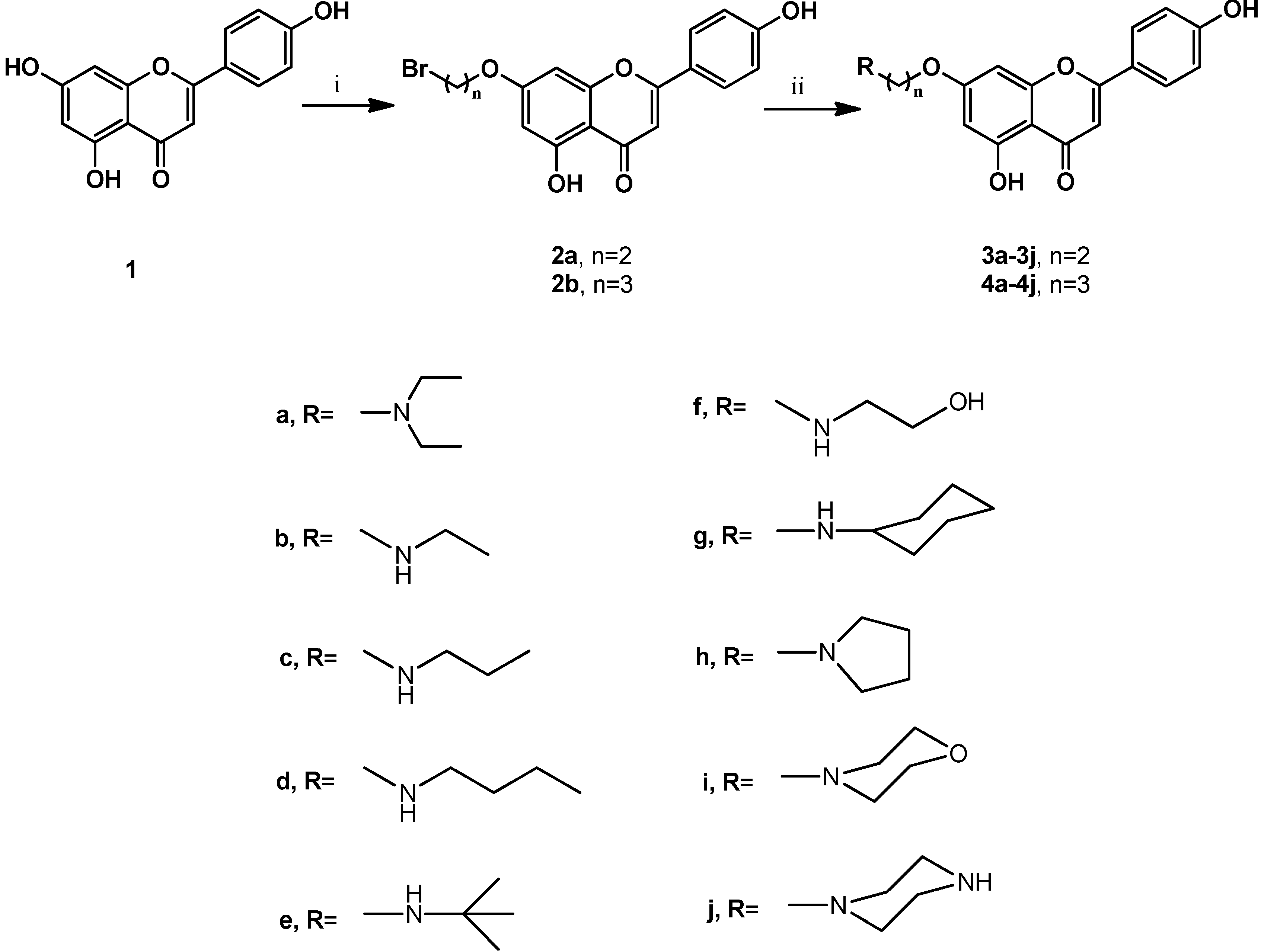
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Antibacterial Activity
| Compounds | S. aureus | B. subtilis | E. coli | P. aeruginosa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATCC 25923 | ATCC 6633 | ATCC 25922 | ATCC 27853 | |
| Apigenin (1) | 11.1 ± 0.3 | 11.0 ± 1.0 | 10.1 ± 0.3 | 10.3 ± 0.2 |
| 2a | 11.8 ± 0.2 | 11.2 ± 0.3 | 10.2 ± 0.1 | 10.5 ± 0.2 |
| 2b | 11.5 ± 0.1 | 11.3 ± 0.5 | 11.8 ± 0.3 | 11.9 ± 0.2 |
| 3a | 17.0 ± 0.9 | 17.5 ± 0.4 | 12.5 ± 0.2 | 14.0 ± 0.3 |
| 3b | 17.3 ± 0.3 | 16.5 ± 0.5 | 15.5 ± 0.4 | 14.8 ± 0.4 |
| 3c | 17.1 ± 0.5 | 17.5 ± 0.3 | 17.0 ± 0.3 | 19.5 ± 0.5 |
| 3d | 17.3 ± 0.1 | 17.5 ± 0.2 | 16.0 ± 0.3 | 17.5 ± 0.3 |
| 3e | 17.5 ± 0.7 | 19.0 ± 0.8 | 16.5 ± 0.5 | 15.5 ± 0.2 |
| 3f | 17.2 ± 0.4 | 17.5 ± 0.5 | 14.5 ± 0.4 | 15.0 ± 0.3 |
| 3g | 21.0 ± 0.2 | 21.5 ± 0.7 | 15.5 ± 0.4 | 17.5 ± 0.4 |
| 3h | 21.4 ± 0.8 | 21.6 ± 0.9 | 15.0 ± 0.6 | 17.2 ± 0.5 |
| 3i | 21.7 ± 1.0 | 21.8 ± 1.0 | 19.0 ± 0.6 | 18.5 ± 0.6 |
| 3j | 21.2 ± 0.5 | 21.0 ± 0.6 | 16.5 ± 0.2 | 17.5 ± 0.4 |
| 4a | 21.0 ± 0.4 | 20.0 ± 0.4 | 15.0 ± 0.3 | 15.0 ± 0.3 |
| 4b | 18.5 ± 0.3 | 19.0 ± 0.4 | 16.0 ± 0.1 | 17.5 ± 0.5 |
| 4c | 21.1 ± 0.6 | 21.8 ± 0.5 | 18.0 ± 0.4 | 19.0 ± 0.6 |
| 4d | 22.0 ± 0.8 | 20.0 ± 0.3 | 18.0 ± 0.3 | 21.0 ± 0.8 |
| 4e | 18.1 ± 0.2 | 21.0 ± 0.2 | 17.5 ± 0.3 | 15.5 ± 0.7 |
| 4f | 21.0 ± 0.7 | 17.5 ± 0.3 | 18.0 ± 0.5 | 17.5 ± 0.5 |
| 4g | 21.9 ± 0.9 | 18.0 ± 0.2 | 18.5 ± 0.6 | 18.7 ± 0.9 |
| 4h | 21.6 ± 1.0 | 19.0 ± 0.5 | 17.0 ± 0.4 | 17.6 ± 0.6 |
| 4i | 24.8 ± 1.0 | 22.0 ± 0.7 | 21.0 ± 0.3 | 21.3 ± 1.0 |
| 4j | 24.5 ± 0.8 | 21.5 ± 0.6 | 17.5 ± 0.3 | 18.0 ± 0.9 |
| Ampicillin | 37.3 ± 0.6 | 36.7 ± 1.5 | 28.9 ± 0.1 | 33.7 ± 0.5 |
| Tetracycline | 26.3 ± 0.5 | 21.0 ± 1.0 | 21.7 ± 1.1 | 24.3 ± 1.1 |
| Compounds | MIC (μg/mL) a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus ATCC 25923 | B. subtilis ATCC 6633 | E. coli ATCC 25922 | P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | |
| Apigenin (1) | 31.25 | 31.25 | 62.5 | 62.5 |
| 2a | 31.25 | 31.25 | 62.5 | 62.5 |
| 2b | 31.25 | 31.25 | 31.25 | 31.25 |
| 3a | 7.81 | 7.81 | 31.25 | 15.63 |
| 3b | 7.81 | 15.63 | 15.63 | 15.63 |
| 3c | 7.81 | 7.81 | 15.63 | 7.81 |
| 3d | 7.81 | 7.81 | 15.63 | 7.81 |
| 3e | 7.81 | 7.81 | 15.63 | 15.63 |
| 3f | 7.81 | 7.81 | 15.63 | 15.63 |
| 3g | 3.91 | 3.91 | 15.63 | 7.81 |
| 3h | 3.91 | 3.91 | 15.63 | 7.81 |
| 3i | 3.91 | 3.91 | 7.81 | 7.81 |
| 3j | 3.91 | 3.91 | 15.63 | 7.81 |
| 4a | 3.91 | 7.81 | 15.63 | 15.63 |
| 4b | 7.81 | 7.81 | 15.63 | 7.81 |
| 4c | 3.91 | 3.91 | 7.81 | 7.81 |
| 4d | 3.91 | 3.91 | 7.81 | 3.91 |
| 4e | 7.81 | 3.91 | 7.81 | 15.63 |
| 4f | 3.91 | 7.81 | 7.81 | 7.81 |
| 4g | 3.91 | 7.81 | 7.81 | 7.81 |
| 4h | 3.91 | 7.81 | 7.81 | 7.81 |
| 4i | 1.95 | 3.91 | 3.91 | 3.91 |
| 4j | 1.95 | 3.91 | 7.81 | 7.81 |
| Ampicillin | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.98 | 0.49 |
| Tetracycline | 1.95 | 3.91 | 3.91 | 3.91 |
2.3. Antiproliferative Activity
| Compounds | IC50 (μg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A549 | HeLa | HepG2 | MCF-7 | |
| Apigenin (1) | 1,740 ± 3.4 | 450 ± 2.0 | 460 ± 2.2 | >2,000 ± 3.6 |
| 2a | 643 ± 4.2 | 590 ± 4.1 | 408 ± 3.8 | 534 ± 3.4 |
| 2b | 251 ± 3.4 | 233 ± 2.2 | 176 ± 2.1 | 209 ± 2.8 |
| 3a | 101 ± 3.0 | 110 ± 2.0 | 116 ± 2.3 | 125 ± 2.2 |
| 3b | 94 ± 2.5 | 109 ± 1.9 | 103 ± 1.9 | 102 ± 2.1 |
| 3c | 87 ± 2.2 | 98 ± 1.5 | 105 ± 1.4 | 114 ± 1.9 |
| 3d | 80 ± 1.5 | 117 ± 2.1 | 112 ± 2.0 | 137 ± 2.6 |
| 3e | 78 ± 1.6 | 97 ± 1.8 | 92 ± 1.8 | 99 ± 2.0 |
| 3f | 83 ± 2.3 | 89 ± 1.4 | 96 ± 1.5 | 92 ± 2.0 |
| 3g | 42 ± 2.1 | 32 ± 1.2 | 33 ± 1.2 | 71 ± 1.2 |
| 3h | 45 ± 1.7 | 46 ± 1.0 | 43 ± 1.7 | 70 ± 1.8 |
| 3i | 39 ± 0.9 | 42 ± 0.9 | 36 ± 1.0 | 54 ± 1.1 |
| 3j | 26 ± 1.0 | 17 ± 0.8 | 29 ± 1.2 | 49 ± 1.4 |
| 4a | 91 ± 2.4 | 99 ± 2.3 | 100 ± 2.8 | 99 ± 2.1 |
| 4b | 85 ± 2.1 | 83 ± 1.7 | 94 ± 2.2 | 87 ± 2.3 |
| 4c | 72 ± 1.8 | 81 ± 1.3 | 82 ± 1.8 | 95 ± 2.8 |
| 4d | 63 ± 1.1 | 101 ± 2.6 | 83 ± 1.7 | 103 ± 3.1 |
| 4e | 62 ± 1.5 | 86 ± 2.0 | 90 ± 2.0 | 88 ± 2.9 |
| 4f | 70 ± 2.2 | 75 ± 1.3 | 89 ± 1.4 | 89 ± 3.3 |
| 4g | 32 ± 1.4 | 27 ± 1.1 | 31 ± 1.0 | 59 ± 2.0 |
| 4h | 35 ± 2.0 | 34 ± 1.5 | 44 ± 1.2 | 50 ± 2.3 |
| 4i | 27 ± 1.3 | 19 ± 1.0 | 28 ± 1.1 | 47 ± 1.9 |
| 4j | 16 ± 1.0 | 11 ± 1.1 | 25 ± 1.6 | 32 ± 1.8 |
3. Experimental
3.1. General
3.2. Synthesis of Compounds 2a, 2b, 3a–3j, and 4a–4j
3.3. Antibacterial Assay
3.4. Antiproliferative Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eckhardt, S. Recent progress in the development of anticancer agents. Curr. Med. Chem.-Anti-Cancer Agents 2002, 2, 419–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.W.; Hong, D.H.; Han, S.B.; Jung, S.H.; Kim, H.C.; Fine, R.L.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.M. A novel stereo-selective sulfonylurea, 1-[1-(4-aminobenzoyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-6-sulfonyl]-4-phenyl-imidazolidin-2-one, has antitumor efficacy in in vitro and in vivo tumor model. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 64, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, N.S.H.N.; Cerqueira, N.S.; Ramos, M.J.; Fernandes, P.A. Title QSAR analysis of 2-benzoxazolyl hydrazone derivatives for anticancer activity and its possible target prediction. Med. Chem. Res. 2012, 21, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, E.L. Drug discovery, CAM and natural products. Evid. Based Complement Altern. Med. 2004, 1, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesołowska, O. Interaction of phenothiazines, stilbenes and flavonoids with multidrug resistance-associated transporters, P-glycoprotein and MRP1. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2011, 58, 433–448. [Google Scholar]
- Kandaswami, C.; Lee, L.T.; Lee, P.P.H.; Hwang, J.J.; Ke, F.C.; Huang, Y.T.; Lee, M.T. The antitumor activities of flavonoids. In Vivo 2005, 19, 895–909. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Yi, T.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Chen, H.B. Quercetin induces apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway in KB and KBv200 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 2188–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdameri, G.; Gauthier, C.; Terreux, R.; Kachadourian, R.; Day, B.J.; Winnischofer, S.M.B.; Rocha, M.E.M.; Frachet, V.; Ronot, X.; Pietro, A.D.; et al. Investigation of chalcones as selective inhibitors of the breast cancer resistance protein: Critical role of methoxylation in both inhibition potency and cytotoxicity. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 3193–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egert, S.; Rimbach, G. Which sources of flavonoids: Complex diets or dietary supplements? Adv. Nutr. 2011, 2, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miean, K.H.; Mohamed, S. Flavonoid (myricetin, quercetin, kaempferol, luteolin, and apigenin) content of edible tropical plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 3106–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotsis, T.; Pepper, M.S.; Aktas, E.; Breit, S.; Rasku, S.; Adlercreutz, H.; Wahala, K.; Montesano, R.; Schweigerer, L. Flavonoids, dietary-derived inhibitors of cell proliferation and in vitro angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 2916–2921. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.C.; Chuang, Y.J.; Yu, C.C.; Yang, J.S.; Lu, C.C.; Chiang, J.H.; Lin, J.P.; Tang, N.Y.; Huang, A.C.; Chung, J.G. Apigenin induces apoptosis through mitochondrial dysfunction in U-2 OS human osteosarcoma cells and inhibits osteosarcoma xenograft tumor growth in vivo. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 11395–11402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, S.; Dwivedi, P.; Purwar, S. In vitro evaluation of antibacterial activities of crude extracts of Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) to bacterial pathogens. Asian J. Biotechnol. 2011, 3, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, G.; Radulovi, N.; Hashimoto, T.; Palic, R. In vitro antimicrobial activity of extracts of four Achillea species: The composition of Achillea clavennae L. (Asteraceae) extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 101, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.N.; Xiao, Z.P.; Ding, H.; Ge, H.M.; Xu, C.; Zhu, H.L.; Tan, R.X. Synthesis and cytotoxic evaluation of novel 7-O-modified genistein derivatives. Chem. Biodivers. 2007, 4, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Q.; Shi, L.; Li, Q.S.; Liu, P.G.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, H.L. Synthesis of C(7) modified chrysin derivatives designing to inhibit β-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthase III (FabH) as antibiotics. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 6264–6269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.C.; Li, H.Q.; Xue, J.Y.; Shi, L.; Zhu, H.L. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel luteolin derivatives as antibacterial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.G.; Kim, H.; Hur, H.G.; Lim, Y.; Ahn, J.H. Regioselectivity of 7-O-methyltransferase of poplar to flavones. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 126, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.G.; Jung, B.R.; Lee, Y.; Hur, H.G.; Lim, Y.; Ahn, J.H. Regiospecific flavonoid 7-O-methylation with Streptomyces avermitilis O-methyltransferase expressed in Escherichia coli. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, K.S.; Lee, C.; Chong, Y. Synthesis of a complete series of O-methyl analogues of naringenin and apigenin. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2007, 28, 2527–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabuseenivasan, S.; Jayakumar, M.; Ignacimuthu, S. In vitro antibacterial activity of some plant essential oils. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2006, 6, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhao, B.; Wang, D.E.; Yao, T.Y.; Pang, L.; Tu, Q.; Ahmed, S.M.; Liu, J.J.; Wang, J.J. Nitrogen-containing apigenin analogs: Preparation and biological activity. Molecules 2012, 17, 14748–14764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan Hilmy, K.M.; Khalifa, M.M.A.; Allah Hawata, M.A.; AboAlzeen Keshk, R.M.; El-Torgman, A.A. Synthesis of new pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives as antibacterial and antifungal agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 5243–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (NCCLS), Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests, 7th ed.; Approved standard, M2–A7; NCCLS: Wayne, PA, USA, 2000.
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (NCCLS), Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Document M100–S12; NCCLS: Wayne, PA, USA, 2002.
- Liu, J.Y.; Pang, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, P.; Huang, W.; Zhu, X.Y.; Yan, D.Y. Hyperbranched polydiselenide as a self assembling broad spectrum anticancer agent. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7765–7774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.H.; Liu, X.; Shen, M.Y.; Nie, S.P.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Gong, D.M.; Xie, M.Y. Purification, physicochemical characterisation and anticancer activity of a polysaccharide from Cyclocarya paliurus leaves. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1, 2a, 2b, 3a–3j, and 4a–4j are available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, R.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, M.; Zhou, J.; Tu, Q.; Liu, J.-J.; Wang, J. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Apigenin Derivatives as Antibacterial and Antiproliferative Agents. Molecules 2013, 18, 11496-11511. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules180911496
Liu R, Zhang H, Yuan M, Zhou J, Tu Q, Liu J-J, Wang J. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Apigenin Derivatives as Antibacterial and Antiproliferative Agents. Molecules. 2013; 18(9):11496-11511. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules180911496
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Rui, Hongchi Zhang, Maosen Yuan, Jiao Zhou, Qin Tu, Jian-Jun Liu, and Jinyi Wang. 2013. "Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Apigenin Derivatives as Antibacterial and Antiproliferative Agents" Molecules 18, no. 9: 11496-11511. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules180911496
APA StyleLiu, R., Zhang, H., Yuan, M., Zhou, J., Tu, Q., Liu, J.-J., & Wang, J. (2013). Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Apigenin Derivatives as Antibacterial and Antiproliferative Agents. Molecules, 18(9), 11496-11511. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules180911496




