Contributions of NMR to the Understanding of the Coordination Chemistry and DNA Interactions of Metallo-Bleomycins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
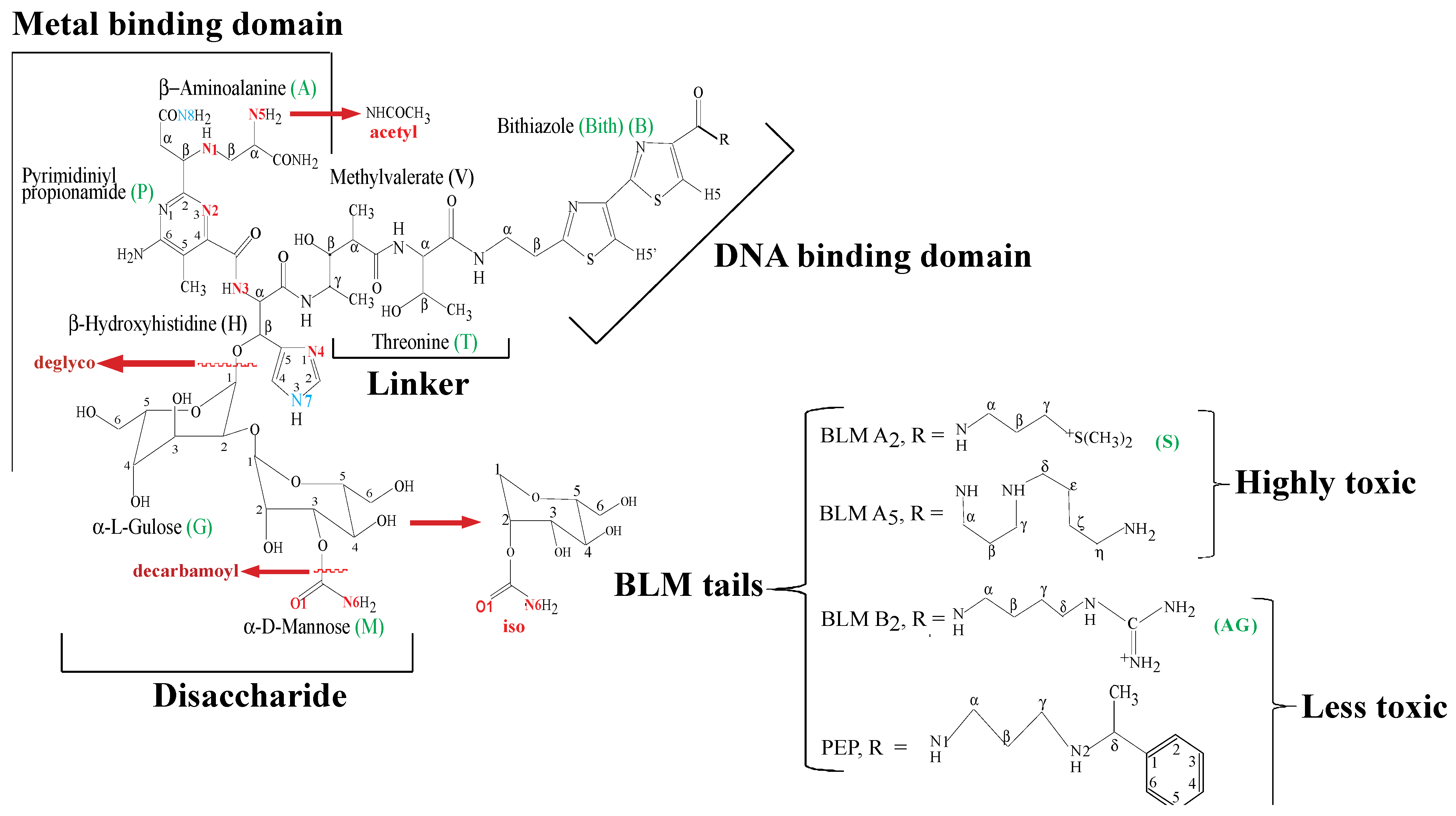
2. Apo-BLMs
3. Metallo-BLMs
3.1. Zn(II)BLM Complexes
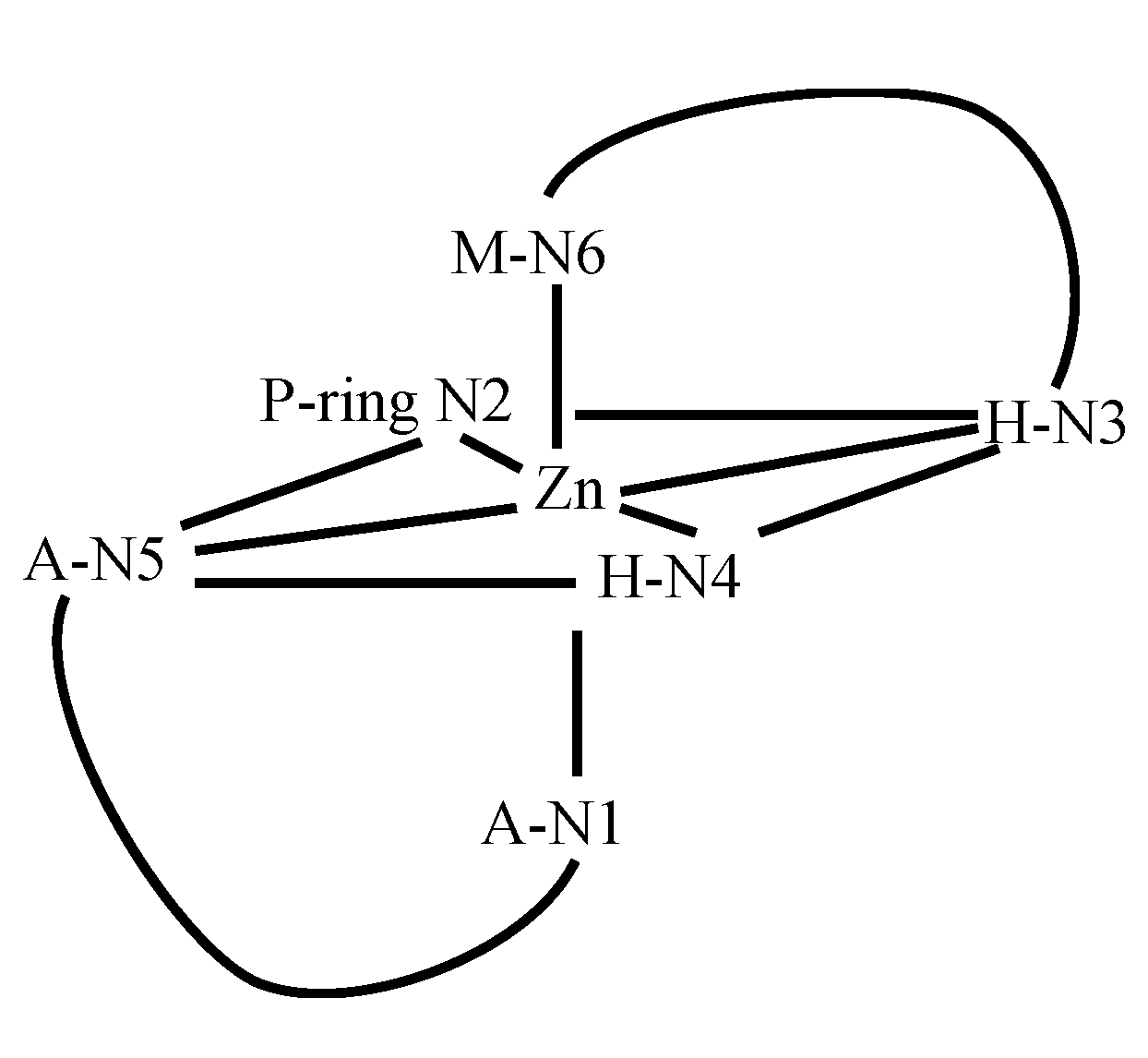
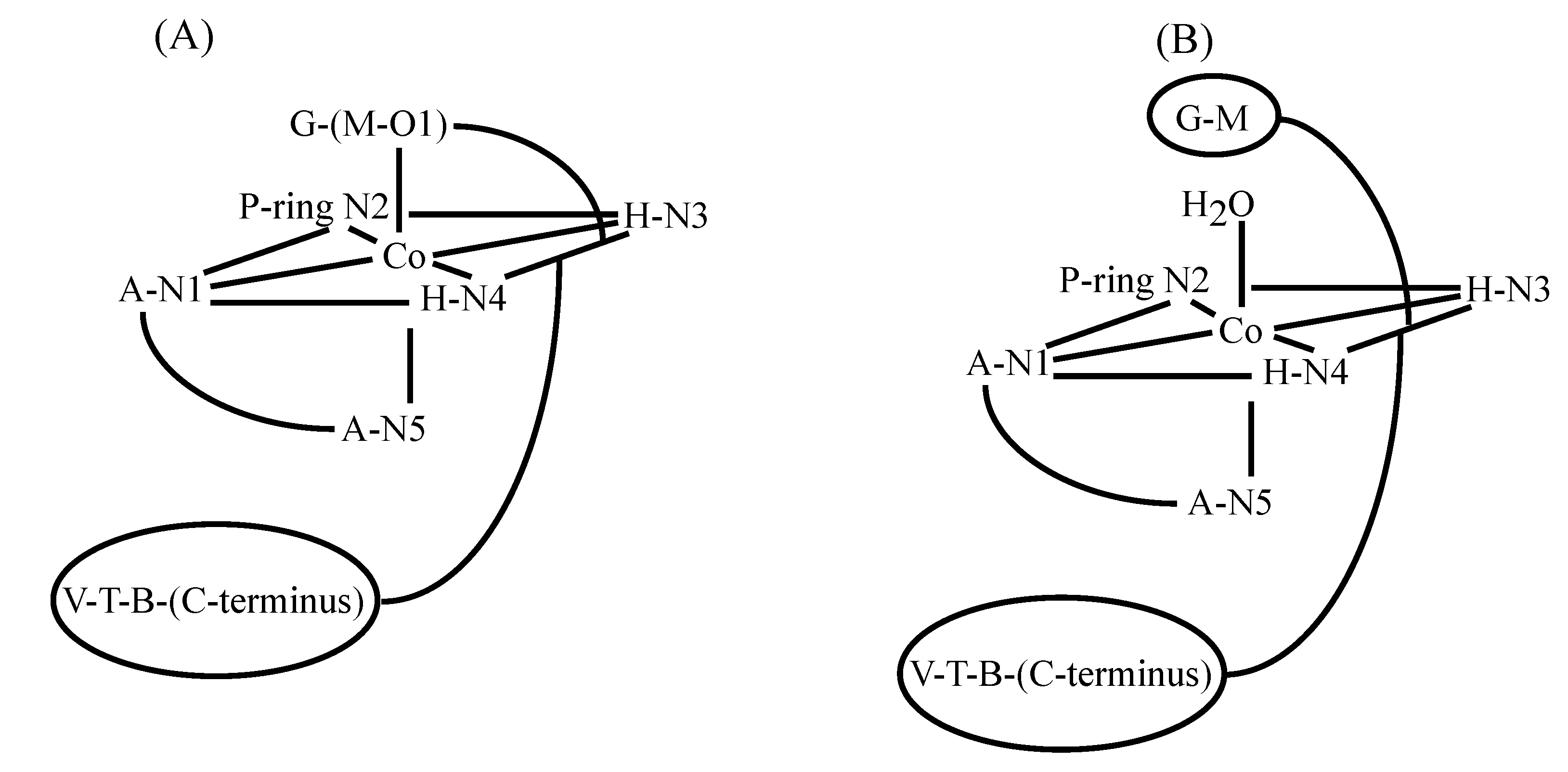
3.2. CoBLM Complexes

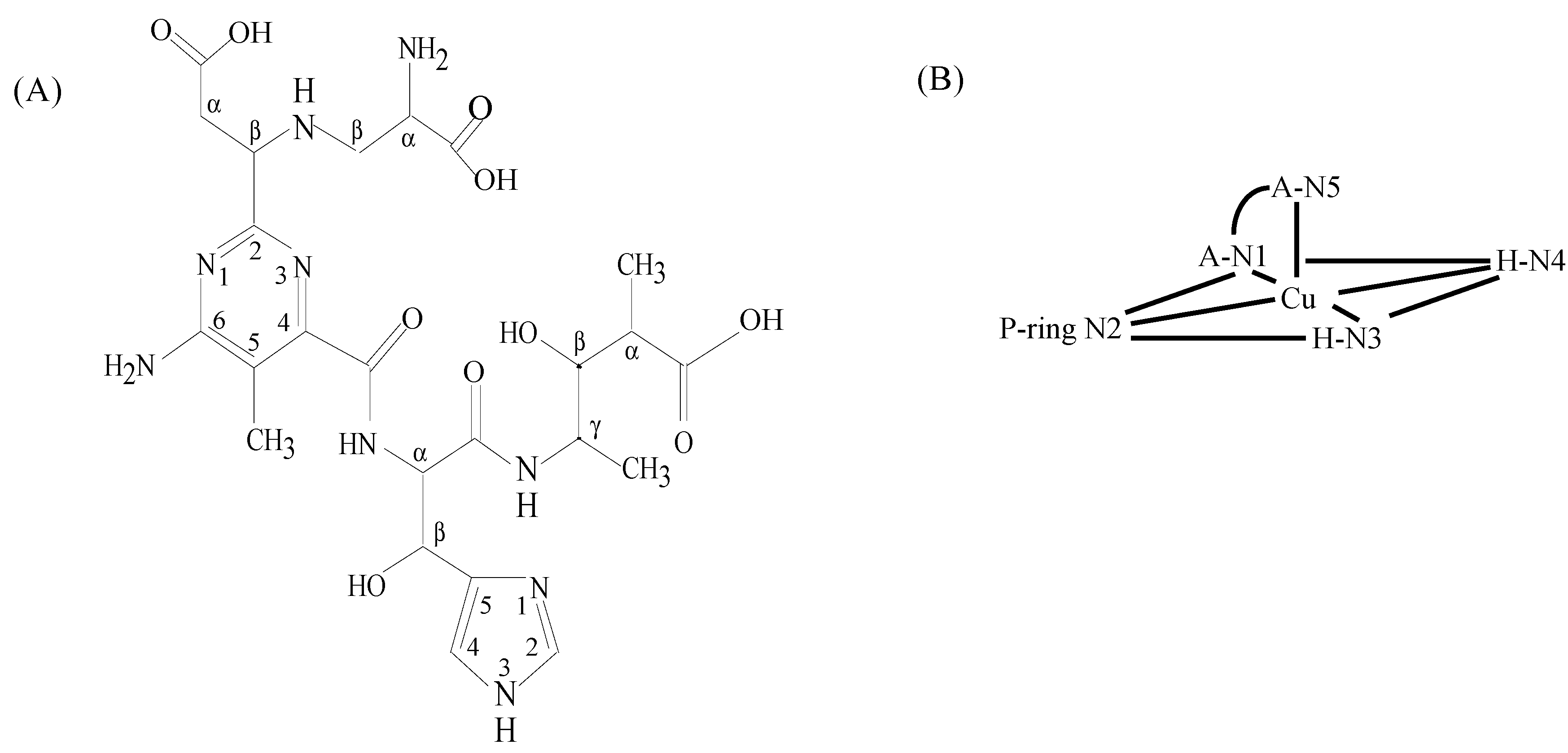
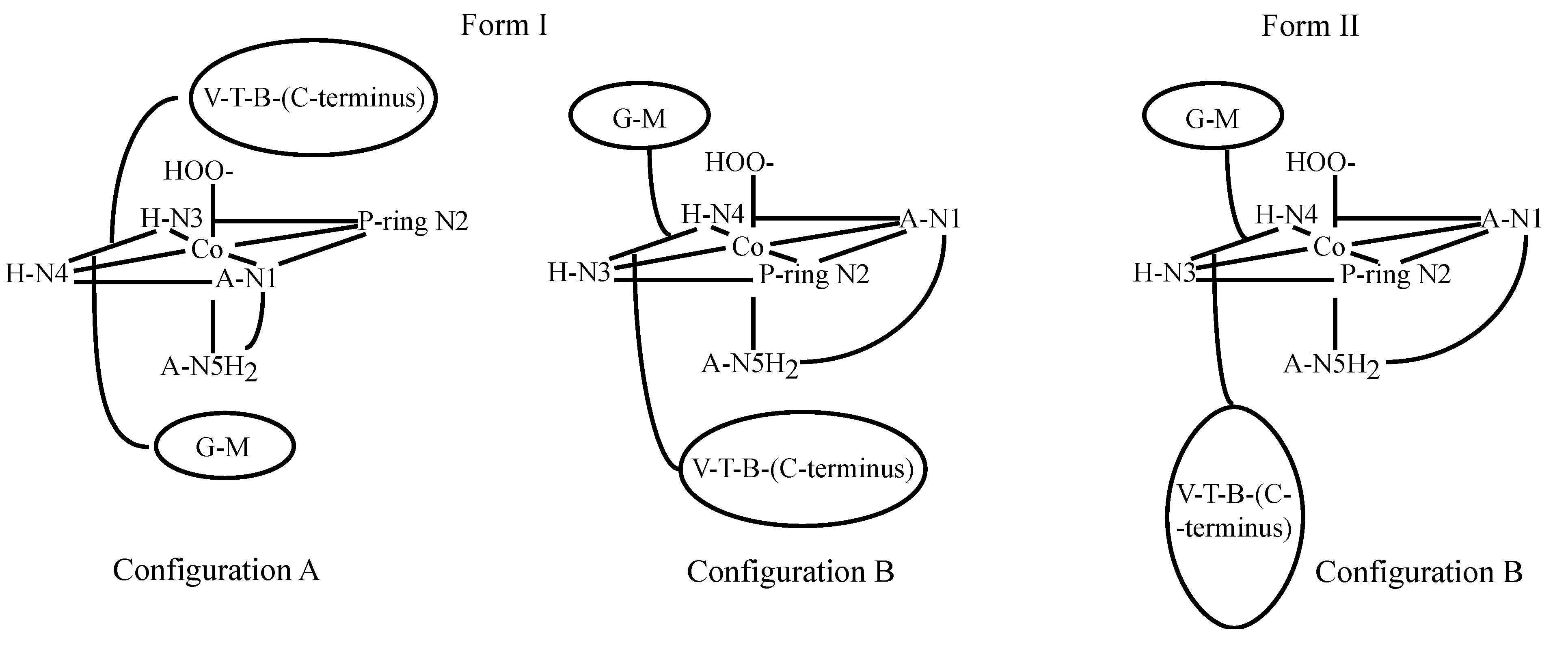
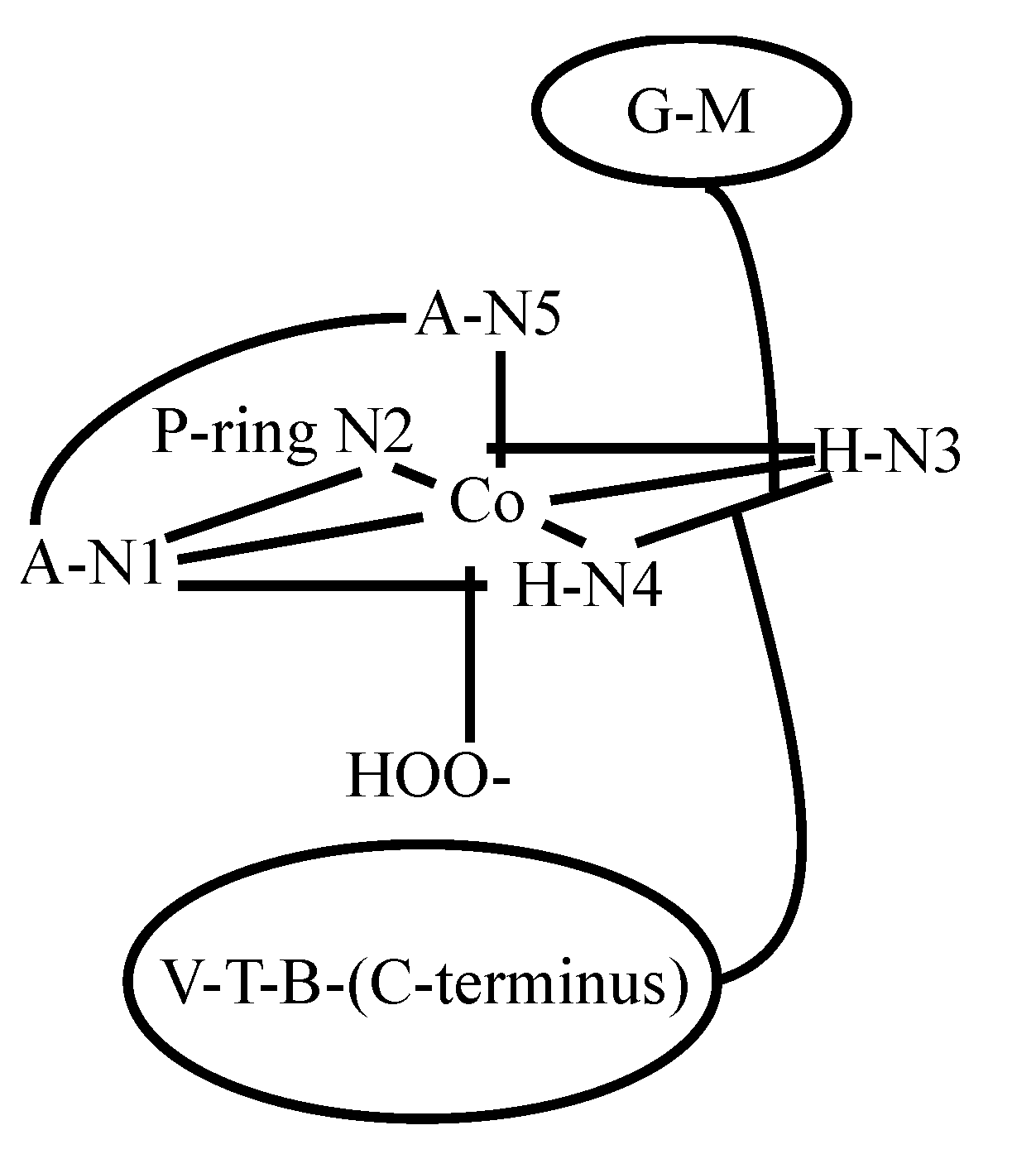
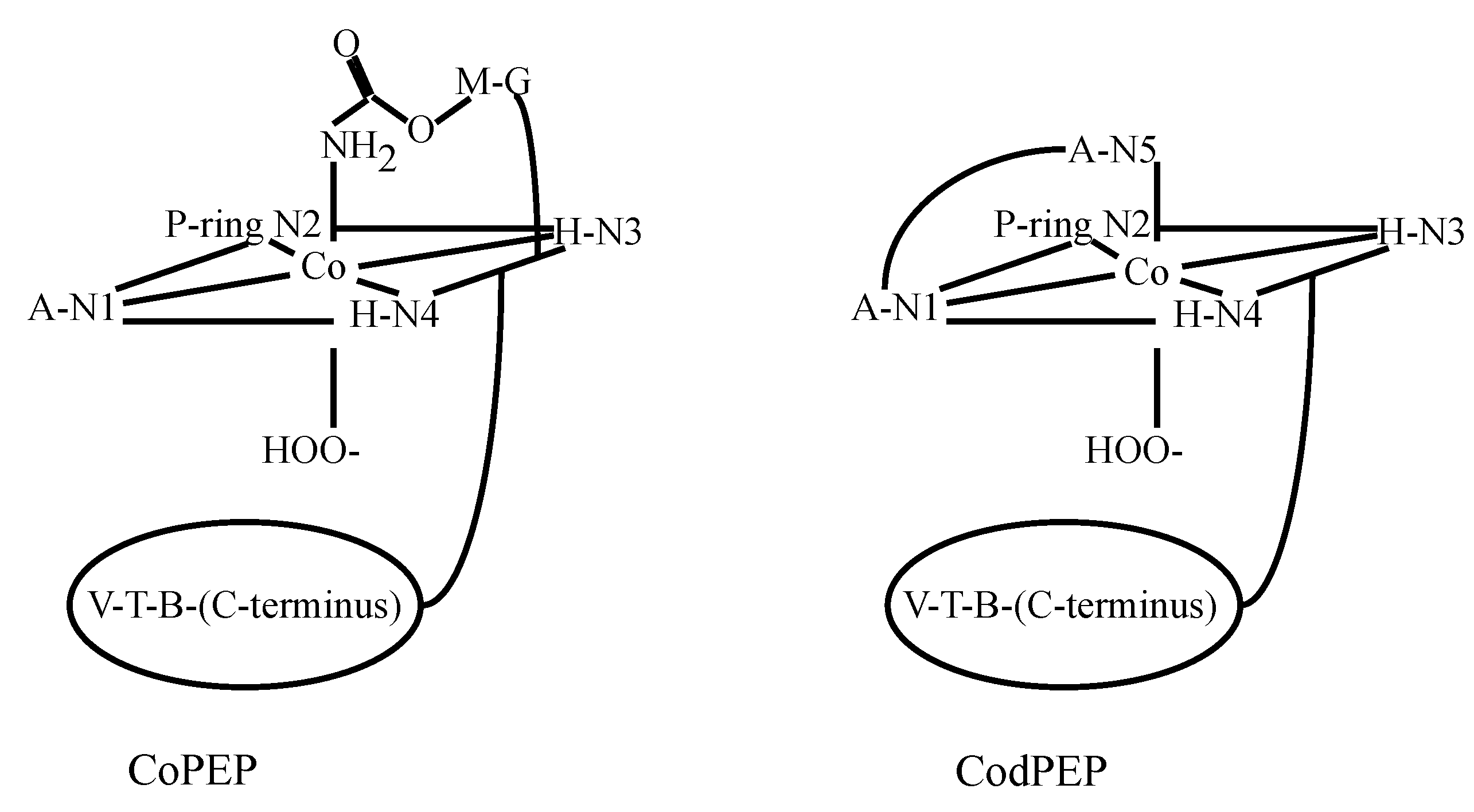
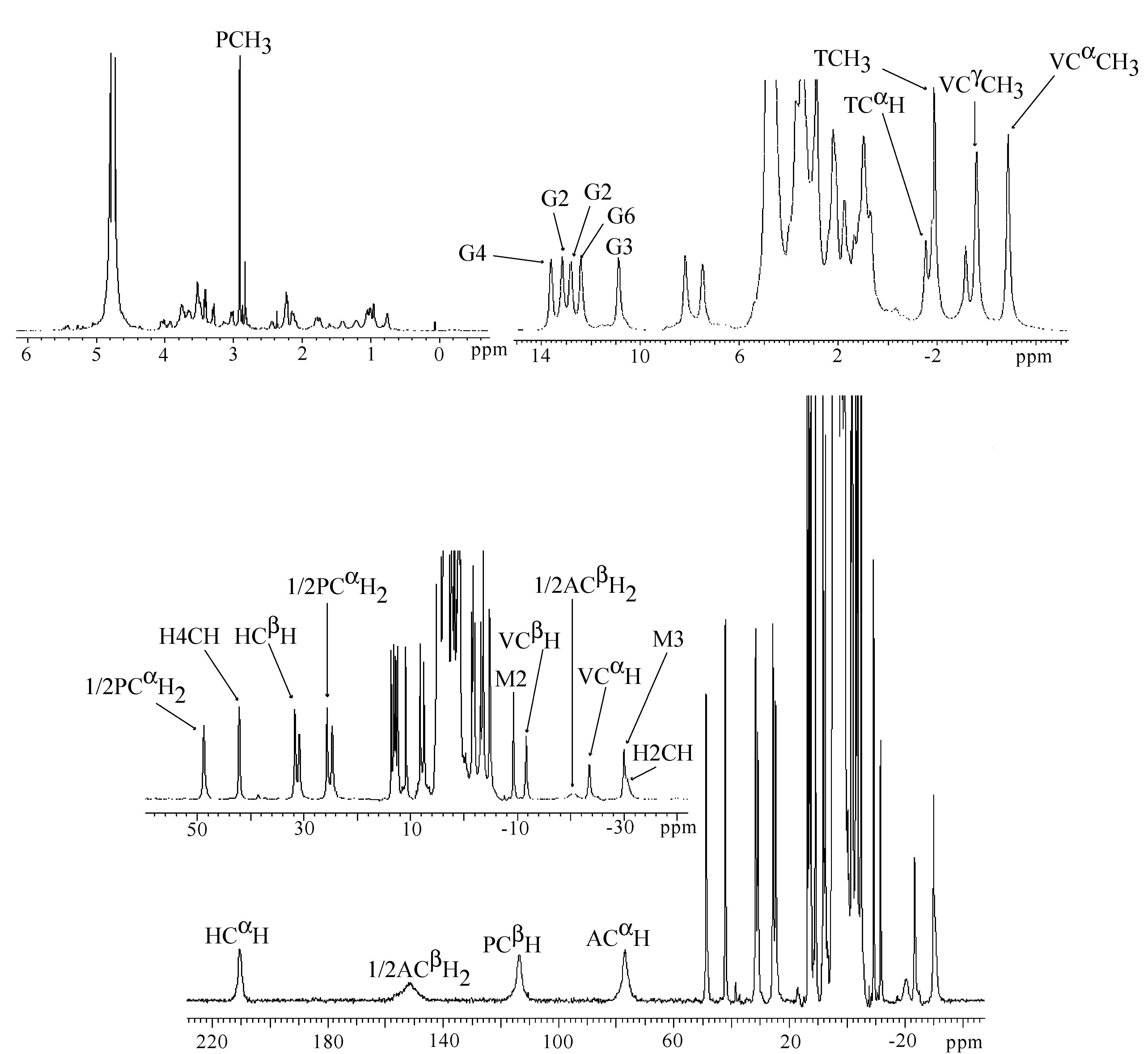
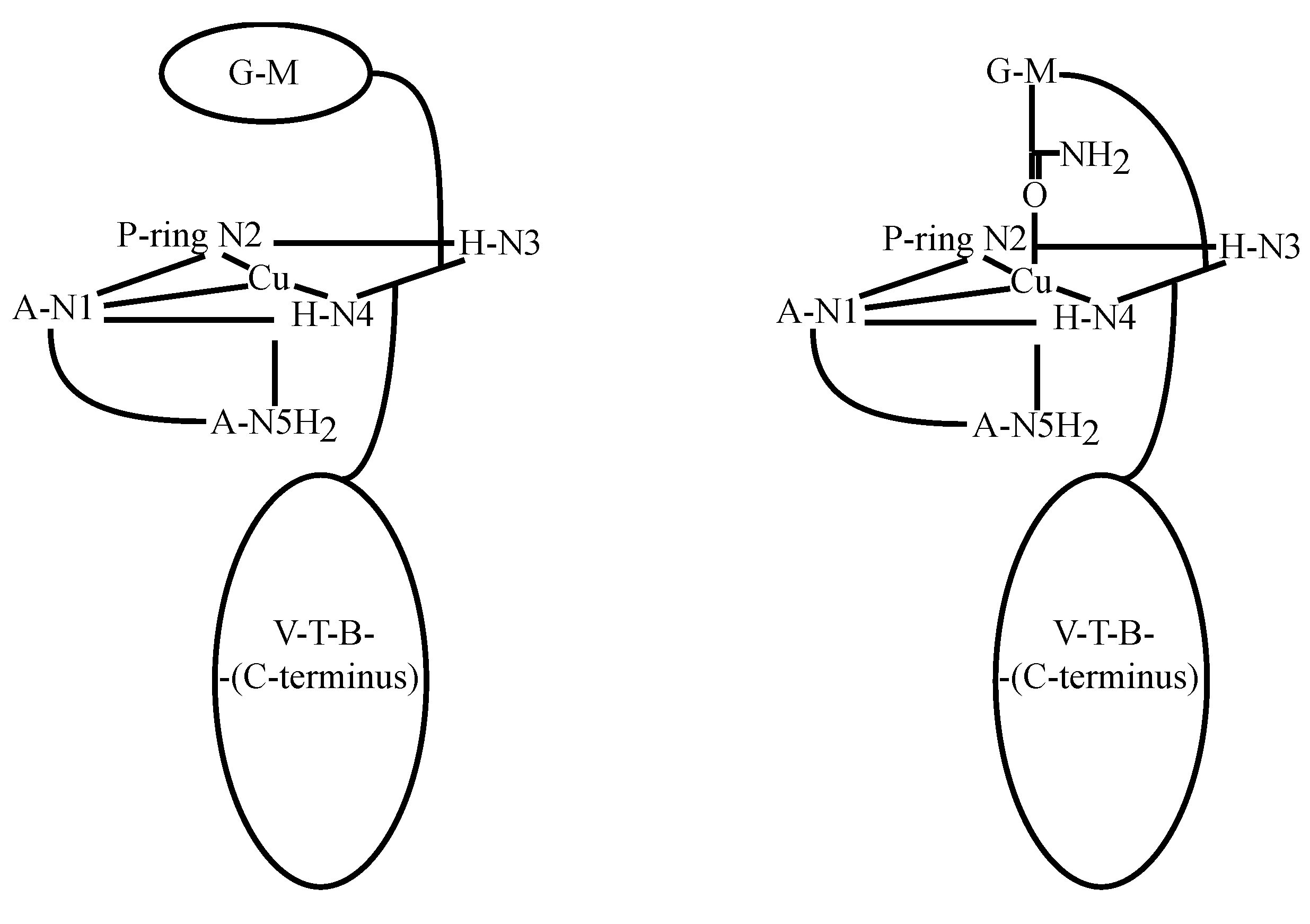
3.3. CuBLM Complexes
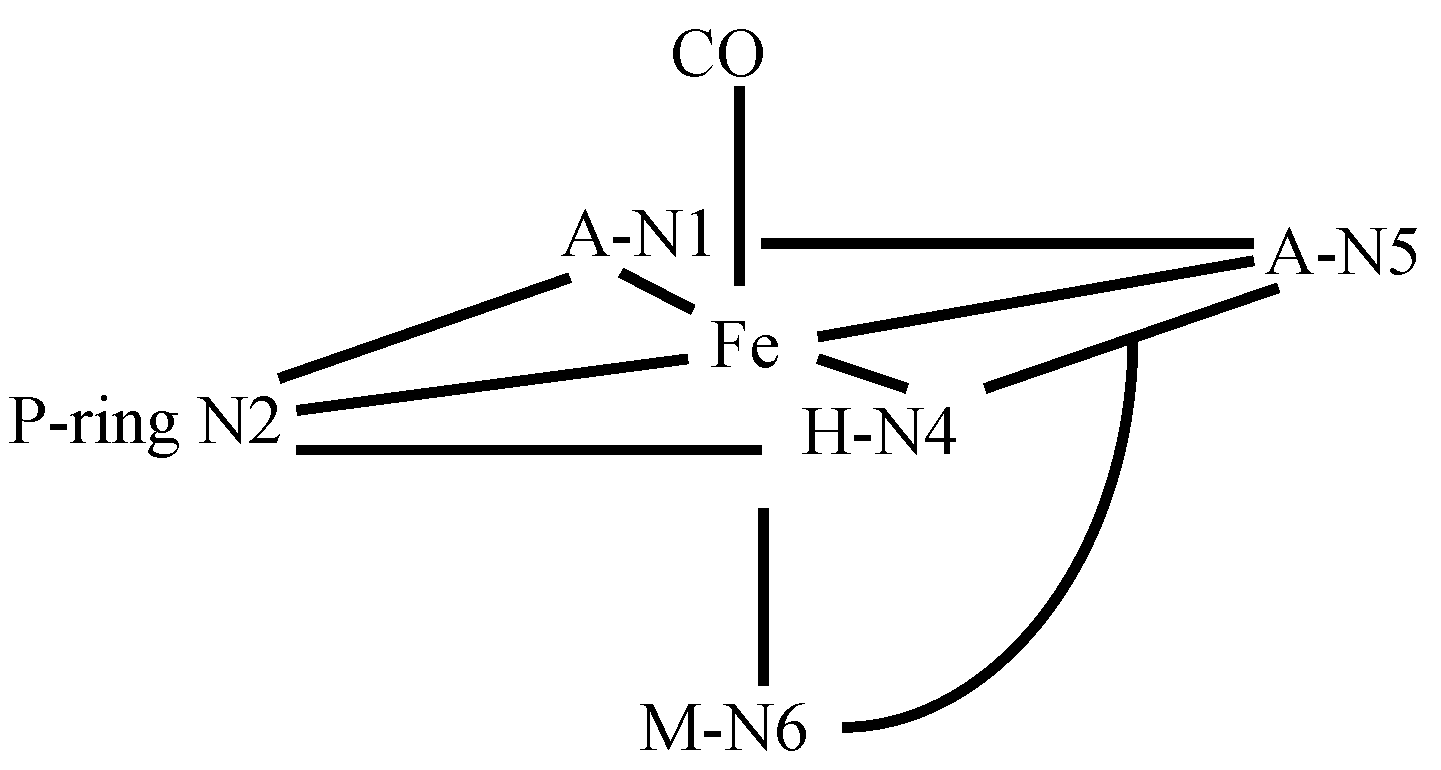
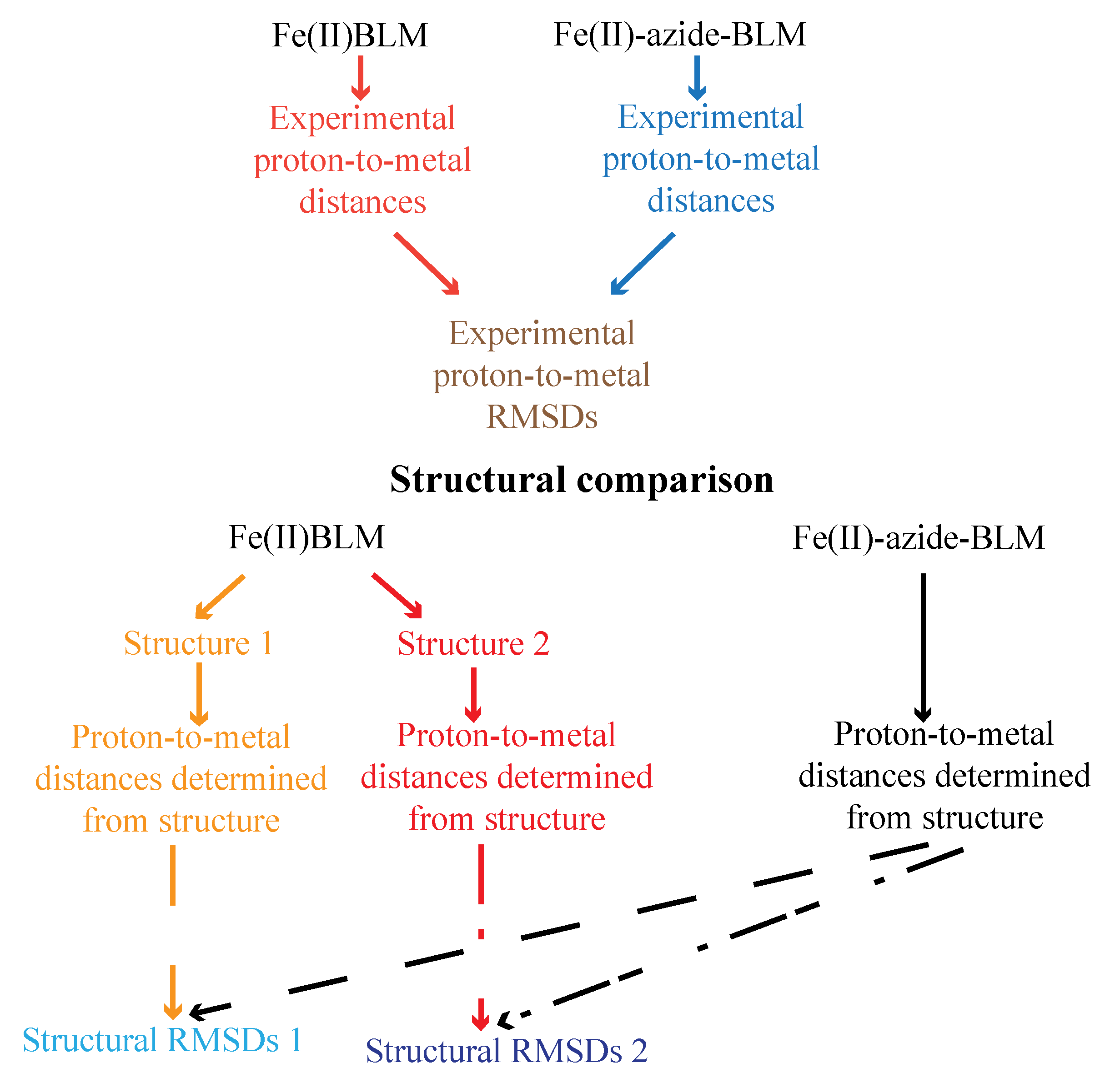
3.4. FeBLM Complexes
| Peak position (ppm) | Relaxation time T1 (ms) | Assignment |
|---|---|---|
| β-hydroxyhistidine | ||
| 206 | 1.2 | CαH |
| 121 | <0.8 | C2H |
| 66.5 | - | N3H |
| 42.3 | 10.0 | C4H |
| −17.3 | 3.1 | CβH |
| β-aminoalanine | ||
| 204 | 2.8 | CβH2 |
| 108 | 0.8 | CβH2 |
| 127 | 1.5 | CαH |
| Pyrimidinilpropionamide | ||
| 153 | <0.8 | CβH |
| 44.9 | 7.9 | CαH2 |
| 32.1 | 5.8 | CαH2 |
| 2.1 | - | CH3 |
| 14.0 | - | CONH2 |
| 10.1 | - | CONH2 |
| Methylvalerate | ||
| 12.9 | 32.8 | VALCαCH3 |
| 37.8 | 3.1 | CαH |
| 24.8 | 7.6 | CβH |
| 20.9 | 18.2 | CγH |
| 8.1 | 23.5 | CγCH3 |
| Threonine | ||
| 6.2 | 110.2 | CαH |
| 5.2 | 210.1 | CβH |
| 2.3 | - | CH3 |
| 15.0 | - | NH |
| Gulose | ||
| −7.5 | 16.0 | C1 |
| −4.7 | 59.4 | C2 |
| −2.36 | - | C3 |
| 3.6 | - | C4 |
| −5.4 | 15.3 | C5 |
| 1.5 | 106.0 | C6 |
| 2.3 | 115.0 | C6 |
| Mannose | ||
| −1.38 | 78.8 | C1 |
| −2.10 | 90.9 | C2 or C3 |
| −2.40 | 106.5 | C2 or C3 |
| −2.48 | 111.8 | C4 |
| −12.5 | 22.1 | C5 |
| −2.23 | 141.0 | C6 |
| −2.68 | 133.3 | C6 |
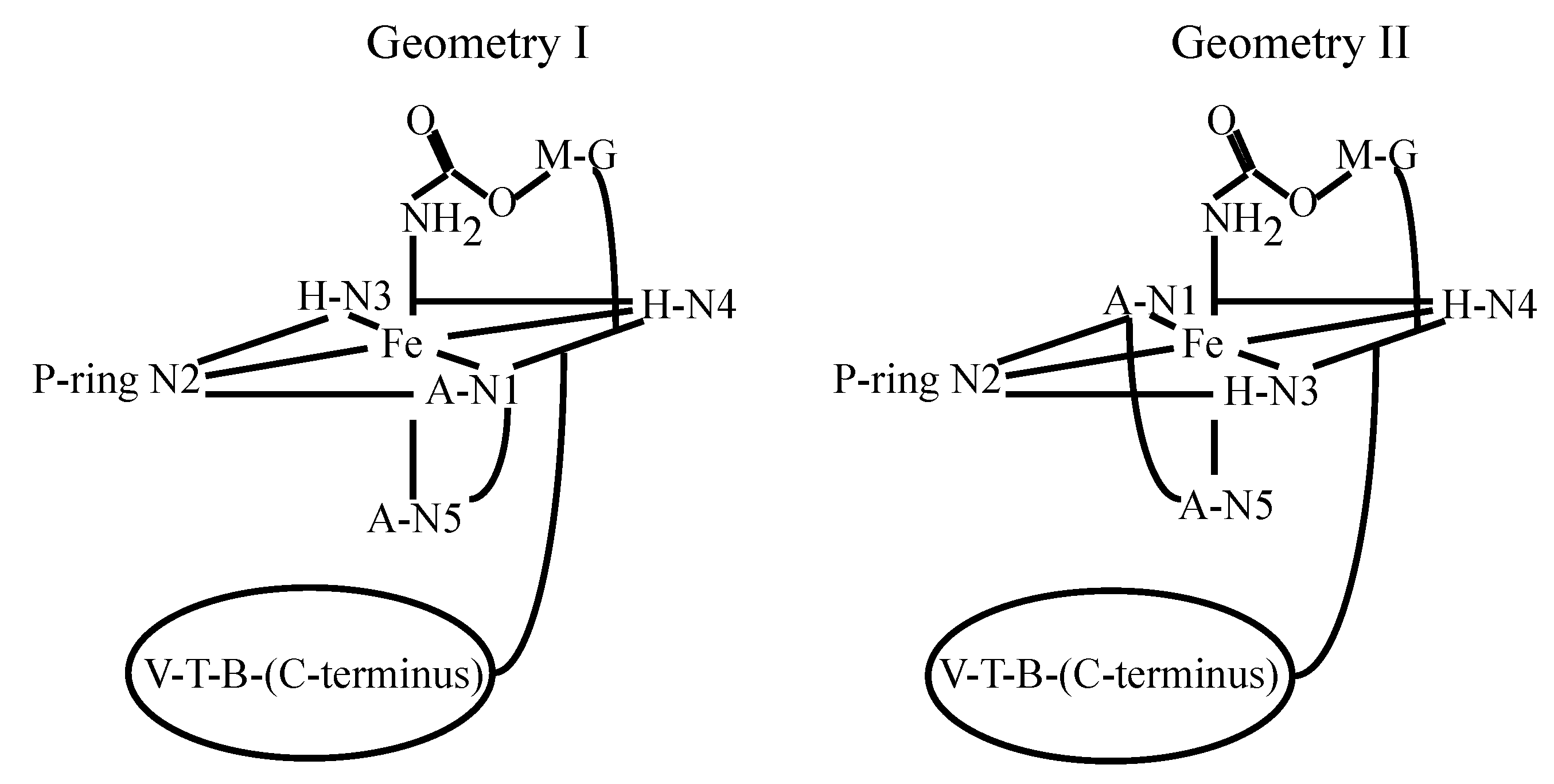
4. Metallo-BLM Interactions with DNA
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bennett, J.M.; Reich, S.D. Bleomycin. Ann. Inter. Med. 1979, 90, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.W.; Sikic, B.I.; Turbow, M.M.; Ballon, S.C. Combination cisplatin, vinblastine, and bleomycin chemotherapy (pvb) for malignant germ-cell tumors of the ovary. J. Clin. Oncol. 1983, 1, 645–651. [Google Scholar]
- Sikic, B.I.; Rozencweig, M.; Carter, S.K. Bleomycin Chemotherapy; Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Einhorn, L.H.; Donohue, J. Cis-diamminedichloroplatinum, vinblastine, and bleomycin combination chemotherapy in disseminated testicular cancer. Ann. Inter. Med. 1977, 87, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sausville, E.A.; Peisach, J.; Horwitz, S.B. Role for ferrous ion and oxygen in degradation of DNA by bleomycin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1976, 73, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, S.M. RNA degradation by bleomycin, a naturally-occurring bioconjugate. Bioconjugate Chem. 1994, 5, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, S.A.; Hecht, S.M. Polynucleotide recognition and degradation by bleomycin. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 1994, 49, 313–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, S.M. Bleomycin: New perspectives on the mechanism of action. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iitaka, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Nakatani, T.; Muraoka, Y.; Fujii, A.; Takita, T.; Umezawa, H. Chemistry of bleomycin. XX. X-ray structure determination of P-3A Cu(II)-complex, a biosynthetic intermediate of bleomycin. J. Antibiot. 1978, 31, 1070–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, M.; Kumagai, T.; Hayashida, M.; Maruyama, M.; Matoba, Y. The 1.6-Å crystal structure of the copper(II)-bound bleomycin complexed with the bleomycin-binding protein from bleomycin-producing Streptomyces verticillus. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 2311–2320. [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin, K.D.; Lewis, M.A.; Long, E.C.; Georgiadis, M.M. Crystal structure of DNA-bound Co(III)-bleomycin B-2: Insights on intercalation and minor groove binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5052–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takita, T.; Muraoka, Y.; Yoshioka, T.; Fujii, A.; Maeda, K.; Umezawa, H. Chemistry of bleomycin .9. Structures of bleomycin and phleomycin. J. Antibiot. 1972, 25, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganawa, H.; Muraoka, Y.; Takita, T.; Umezawa, H. Chemistry of bleomycin. 18. C-13 NMR-studies. J. Antibiot. 1977, 30, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganawa, H.; Takita, T.; Umezawa, H.; Hull, W.E. Chemistry of bleomycin. 23. Natural abundance N-15-NMR spectroscopic evidence for the structure of bleomycin. J. Antibiot. 1979, 32, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umezawa, H. Structure and action of bleomycin. Prog. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1976, 11, 18–27. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Hawkins, B.L.; Glickson, J.D. Proton nuclear magnetic-resonance study of bleomycin in aqueous-solution-assignment of resonances. Biochemistry 1977, 16, 2731–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haasnoot, C.A.G.; Pandit, U.K.; Kruk, C.; Hilbers, C.W. Complete assignment of the 500 MHz H-1-NMR spectra of bleomycin A2 in H2O and D2O solution by means of two-dimensional NMR-spectroscopy. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 1984, 2, 449–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, W.; Takita, T. Pepleomycin-2nd generation bleomycin chemically derived from bleomycin A2. Heterocycles 1979, 13, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, S. A review of clinical-studies of peplomycin. Recent Res. Cancer 1980, 74, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, T.; Li, Y.; Armstrong, G.S. NMR study of peplomycin in aqueous solution. Assignment of resonances by means of two-dimensional spectroscopy. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64,, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowiak, J.C.; Greenaway, F.T.; Longo, W.E.; Vanhusen, M.; Crooke, S.T. Spectroscopic investigation of metal-binding site of bleomycin A-2-Cu(II) and Zn(II) derivatives. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1978, 517, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cass, A.E.G.; Galdes, A.; Hill, H.A.O.; Mcclelland, C.E. Binding of Zinc(II) to bleomycin-investigation using H-1 NMR-spectroscopy. FEBS Lett. 1978, 89, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowiak, J.C.; Greenaway, F.T.; Grulich, R. Transition-metal binding-site of bleomycin A2-C-13 nuclear magnetic-resonance study of Zinc(II) and Copper(II) derivatives. Biochemistry 1978, 17, 4090–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenkinski, R.E.; Dallas, J.L. An NMR investigation of the kinetics of dissociation of the Zinc(II) complex of bleomycin antibiotics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1979, 101, 5902–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer, N.J.; Rodriguez, L.O.; Hecht, S.M. Proton nuclear magnetic-resonance study of the structure of bleomycin and the Zinc-bleomycin complex. Biochemistry 1979, 18, 3439–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer, N.J.; Rodriguez, L.O.; Hecht, S.M. Metal-binding to modified bleomycins-zinc and ferrous complexes with an acetylated bleomycin. Biochemistry 1980, 19, 4096–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkerman, M.A.J.; Haasnoot, C.A.G.; Hilbers, C.W. Studies of the solution structure of the bleomycin-A2 zinc complex by means of two-dimensional NMR-spectroscopy and distance geometry calculations. Eur. J. Biochem. 1988, 173, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkerman, M.A.J.; Haasnoot, C.A.G.; Hilbers, C.W. Complete assignment of the C-13 NMR-spectra of bleomycin-A2 and its zinc complex by means of two-dimensional NMR-spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Chem. 1988, 26, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, D.; Mclennan, I.J.; Bax, A.; Gamcsik, M.P.; Glickson, J.D. Two-dimensional NMR-study of bleomycin and its zinc(II) complex-reassignment of C-13 resonances. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 1990, 8, 375–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calafat, A.M.; Won, H.; Marzilli, L.G. A new arrangement for the anticancer antibiotics tallysomycin and bleomycin when bound to zinc: An assessment of metal and ligand chirality by NMR and molecular dynamics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 3656–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulouse, K.P.; Watkins, A.E.; Reba, R.C.; Eckelman, W.C.; Goodyear, M. Cobalt-labeled bleomycin-new radiopharmaceutical for tumor localization-comparative clinical evaluation with gallium citrate. J. Nucl. Med. 1975, 16, 839–841. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.S.; Goodwin, D.A.; Kruse, S.L. Bleomycin as a TC-99M carrier in tumor visualization. J. Nucl. Med. 1974, 15, 338–342. [Google Scholar]
- De Reimer, L.H.; Meares, C.F.; Goodwin, D.A.; Diamanti, C.I. BLEDTA–tumor-localization by a bleomycin analog containing a metal-chelating group. J. Med. Chem. 1979, 22, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, Y. Bleomycin-iron complexes-electron-spin resonance study, ligand effect, and implication for action mechanism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 5208–5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereman, R.D.; Winkler, M.E. Coordination chemistry of the anti-tumor compound bleomycin-a spectral investigation of the cobalt complex. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1980, 42, 1797–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakinuma, J.; Orii, H. Preparation, isolation and identification of bleomycin Co-57 chelate with special reference to its chelate structure. J. Labelled Compd. Rad. 1979, 16, 200. [Google Scholar]
- Vos, C.M.; Westera, G.; Vanzanten, B. Different forms of the cobalt-bleomycin A2 complex. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1980, 12, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, C.M.; Westera, G.; Schipper, D. A C-13 NMR and electron-spin-resonance study on the structure of the different forms of the cobalt-bleomycin A2 complex. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1980, 13, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukayama, M.; Randall, C.R.; Santillo, F.S.; Dabrowiak, J.C. Transition-metal binding-site of bleomycin-Cobalt(III) bleomycin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowiak, J.C.; Tsukayama, M. Cobalt(III) complex of pseudotetrapeptide-A of bleomycin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 7543–7550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Antholine, W.E.; Petering, D.H. Reaction of Co(II)bleomycin with dioxygen. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 944–949. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.X.; Nettesheim, D.; Otvos, J.D.; Petering, D.H. NMR determination of the structures of peroxycobalt(III) bleomycin and cobalt(III) bleomycin, products of the aerobic oxidation of cobalt(II) bleomycin by dioxygen. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Vanderwall, D.E.; Lui, S.M.; Tang, X.J.; Turner, C.J.; Kozarich, J.W.; Stubbe, J. Studies of Co center dot bleomycin A2 green: Its detailed structural characterization by NMR and molecular modeling and its sequence-specific interaction with DNA oligonucleotides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 1268–1280. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, S.K.; Ultmann, J. Peplomycin. Cancer Treat. Rev. 1984, 11, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Ekimoto, H.; Aoyagi, S.; Koyu, A.; Kuramochi, H.; Yoshioka, O.; Matsuda, A.; Fujii, A.; Umezawa, H. Biological studies on the degradation products of 3-[(s)-1′-phenylethylamino]propylaminobleomycin-novel analog (pepleomycin). J. Antibiot. 1979, 32, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, A.; Yoshioka, O.; Ebihara, K.; Yashamita, T.; Umezawa, H. Bleomycin: Current Status and New Developments; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 299–331. [Google Scholar]
- Caceres-Cortes, J.; Sugiyama, H.; Ikudome, K.; Saito, I.; Wang, A.H.J. Structures of cobalt(III)-pepleomycin and cobalt(III)-deglycopepleomycin (green forms) determined by NMR studies. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 244, 818–828. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, T.E.; Serrano, M.L.; Que, L. Coordination chemistry of Co(II)-bleomycin: Its investigation through NMR and molecular dynamics. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 3886–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.W.; Forsterling, F.H.; Petering, D.H. Identification of the internal axial ligand of HO2-cobalt(III)-bleomycin: H-1{N-15} HSQC NMR investigation of bleomycin, deglycobleomycin, and their hydroperoxide-cobalt(III) complexes. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 6559–6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer, N.J.; Chang, C.; Rodriguez, L.O.; Hecht, S.M. Copper(I).bleomycin-a structurally unique oxidation-reduction active complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 1514–1517. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld, G.M.; Rodriguez, L.O.; Hecht, S.M.; Chang, C.; Basus, V.J.; Oppenheimer, N.J. Copper(I)-bleomycin-structurally unique complex that mediates oxidative DNA strand scission. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Yoshioka, O.; Matsuda, A.; Umezawa, H. Intracellular reduction of cupric ion of bleomycin copper complex and transfer of cuprous ion to a cellular protein. J. Antibiot. 1977, 30, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Kuwahara, J.; Sugiura, Y. Copper-bleomycin has no significant DNA cleavage activity. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 4719–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenfeld, G.M.; Shipley, J.B.; Heimbrook, D.C.; Sugiyama, H.; Long, E.C.; Vanboom, J.H.; Vandermarel, G.A.; Oppenheimer, N.J.; Hecht, S.M. Copper-dependent cleavage of DNA by bleomycin. Biochemistry 1987, 26, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, T.E. Structural study of copper(I)-bleomycin. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 9, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umezawa, H.; Maeda, K.; Takeuchi, T.; Okami, Y. New antibiotics bleomycin A and B. J. Antibiot. 1966, 19, 200–209. [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowiak, J.C.; Greenaway, F.T.; Santillo, F.S.; Crooke, S.T. The iron complexes of bleomycin and tallysomycin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1979, 91, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Ferretti, J.A.; Caspary, W.J. Location of iron in the Fe2+-bleomycin complex as observed by C-13 NMR-spectroscopy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1979, 89, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer, N.J.; Rodriguez, L.O.; Hecht, S.M. Structural studies of active complex of bleomycin-assignment of ligands to the ferrous ion in a ferrous-bleomycin carbon monoxide complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 5616–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, R.P.; Lenkinski, R.E.; Sakai, T.T.; Geckle, J.M.; Krishna, N.R.; Glickson, J.D. Proton NMR-study of iron(II)-bleomycin: Assignment of resonances by saturation transfer experiments. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1980, 96, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkerman, M.A.J.; Neijman, E.W.J.F.; Wijmenga, S.S.; Hilbers, C.W.; Bermel, W. Studies of the solution structure of the bleomycin-A2 iron(II) carbon-monoxide complex by means of 2-dimensional NMR-spectroscopy and distance geometry calculations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 7462–7474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, T.E.; Ming, L.J.; Rosen, M.E.; Que, L. NMR studies of the paramagnetic complex Fe(II)-bleomycin. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 2807–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeb, K.E.; Zaleski, J.M.; Hess, C.D.; Hecht, S.M.; Solomon, E.I. Spectroscopic investigation of the metal ligation and reactivity of the ferrous active sites of bleomycin and bleomycin derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, T.E. Molecular modeling of the three-dimensional structure of Fe(II)-bleomycin: Are the Co(II) and Fe(II) adducts isostructural? J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 7, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, T.E.; Li, Y. Possible structural role of the disaccharide unit in Fe-bleomycin before and after oxygen activation. J. Antibiot. 2012, 65, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, T.E.; Li, Y. Solution structure of Fe(II)-azide-bleomycin derived from NMR data: Transition from Fe(II)-bleomycin to Fe(II)-azide-bleomycin as derived from NMR data and structural calculations. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 17, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, T.; Li, Y. Coordination chemistry and solution structure of Fe(II)-peplomycon. Two possible coordination geometries. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2012, 111, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caceres-Cortes, J.; Sugiyama, H.; Ikudome, K.; Saito, I.; Wang, A.H.J. Interactions of deglycosylated cobalt(III)–pepleomycin (green form) with DNA based on NMR structural studies. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 9995–10005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoehn, S.T.; Junker, H.D.; Bunt, R.C.; Turner, C.J.; Stubbe, J. Solution structure of Co(III)-bleomycin- OOH bound to a phosphoglycolate lesion containing oligonucleotide: Implications for bleomycin- induced double-strand DNA cleavage. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 5894–5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, S.M.; Vanderwall, D.E.; Wu, W.; Tang, X.-J.; Turner, C.J.; Kozarich, J.W.; Stubbe, J. Structural characterization of Co.bleomycin A2 brown: Free and bound to d(CCAGGCCTGG). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 9603–9613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manderville, R.A.; Ellena, J.F.; Hecht, S.M. Interaction of Zn(II)·bleomycin with d(CGCTAGCG)(2)-a binding model-based on NMR experiments and restrained molecular-dynamics calculations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 7891–7903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderwall, D.E.; Lui, S.M.; Turner, C.J.; Kozarich, J.W.; Stubbe, J. A model of the structure of HOO-Co.bleomycin bound to d(CCAGTACTGG): Recognition of the d(GpT) site and implications for double-stranded DNA cleavage. Chem. Biol. 1997, 4, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Vaderwall, D.E.; Stubbe, J.; Kozarich, J.W.; Turner, C.J. Interaction of Co.bleomycin A2 (green) with d(CCAGGCCTGG)2: Evidence for intercalation using 2D NMR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 10843–10844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Vanderwall, D.E.; Turner, C.J.; Kozarich, J.W.; Stubbe, J. Solution structure of Co·bleomycin A2 green complexed with d(CCAGGCCTGG). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 1281–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Vanderwall, D.E.; Teramoto, S.; Lui, S.M.; Hoehn, S.T.; Tang, X.-J.; Turner, C.J.; Boger, D.L.; Kozarich, J.W.; Stubbe, J. NMR studies of Co.deglycobleomycin A2 green and its complexes with d(CCAGGCCTGG). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 2239–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Vanderwall, D.E.; Turner, C.J.; Hoehn, S.; Chen, J.Y.; Kozarich, J.W.; Stubbe, J. Solution structure of the hydroperoxide of Co(III) phleomycin complexed with d(CCAGGCCTGG)2: Evidence for binding by partial intercalation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 4881–4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.Q.; Xia, C.W.; Mao, Q.K.; Forsterling, H.; DeRose, E.; Antholine, W.E.; Subczynski, W.K.; Petering, D.H. Structures of HO2-Co(III)bleomycin A2 bound to d(GAGCTC)2 and d(GGAAGCTTCC)2: Structure-reactivity relationships of Co and Fe bleomycins. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2002, 91, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povirk, L.F.; Hogan, M.; Dattagupta, N. Binding of bleomycin to DNA: Intercalation of the bithiazole rings. Biochemistry 1979, 18, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urata, H.; Ueda, Y.; Usami, Y.; Akagi, M. Enantiospecific recognition of DNA by bleomycin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 7135–7138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glickson, J.D.; Pillai, R.P.; Sakai, T.T. Proton NMR studies of the Zn(II)-bleomycin-A2-poly (dA-dT) ternary complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 2967–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.M.; Sakai, T.T.; Glickson, J.D.; Patel, D.J. Bleomycin-A2 complexes with poly(dA-dT)-proton nuclear magnetic-resonance study of the non-exchangeable hydrogens. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1980, 92, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, T.E.; Sakai, T.T.; Glickson, J.D. Interaction of bleomycin-A2 with poly(deoxyadenylylthymidylic acid)-a proton nuclear magnetic-resonance study of the influence of temperature, pH, and ionic-strength. Biochemistry 1983, 22, 4211–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, T.T.; Riordan, J.M.; Glickson, J.D. Bleomycin interactions with DNA-studies on the role of the c-terminal cationic group of bleomycin-A2 in association with and degradation of DNA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1983, 758, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, M.; Grollman, A.P.; Horwitz, S.B. Bleomycin-DNA interactions: Fluorescence and proton magnetic resonance studies. Biochemistry 1977, 16, 2641–2647. [Google Scholar]
- Hiroaki, H.; Nakayama, T.; Ikehara, M.; Uesugi, S. Interaction of bleomycin with deoxyribonucleic-acid oligomer-proton nuclear-magnetic-resonance titration study using novel bleomycin complexes with Ni-2+ and VO-3+. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1991, 39, 2780–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, Y.; Suzuki, T. Nucleotide sequence specificity of DNA cleavage by iron-bleomycin. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 10544–10546. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, K.; Kawanishi, S. Enhancement and alteration of bleomycin-catalyzed site-specific DNA cleavage by distamycin A and some minor groove binders. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 183, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Kuwahara, J.; Sugiura, Y. Nucleotide sequence cleavage of guanine-modified and DNA with aflatoxin B, dimethyl sulfate, and mitomycin C by bleomycin and deoxyribonuclease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1983, 117, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemsely, J.N.; Loeb, K.; Chow, M.S.; Decker, A.; Shishova, E.Y.; Wasinger, E.C.; Hedman, B.; Hodgson, K.O.; Solomon, E.I. Spectroscopic studies of the interaction of ferrous bleomycin with DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 10810–10821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbi, P.G.; Federico, M. What has happened to VBM (vinblastine, bleomycin, and methotrexate) chemotherapy for early-stage Hodgkin lymphoma? CRC Cr. Rev. Oncol-Hem. 2012, 82, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raisfeld, I.H. Pulmonary toxicity of bleomycin analogs. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 1980, 56, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raisfeld, I.H.; Chovan, J.P.; Frost, S. Bleomycin pulmonary toxicity-production of fibrosis by bithiazole-terminal amine and terminal amine moieties of bleomycin-A2. Life Sci. 1982, 30, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raisfeld, I.H.; Chu, P.; Hart, N.K.; Lane, A. A comparison of the pulmonary toxicity produced by metal-free and copper-complexed analogs of bleomycin and phleomycin. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 1982, 63, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Lehmann, T.; Topchiy, E. Contributions of NMR to the Understanding of the Coordination Chemistry and DNA Interactions of Metallo-Bleomycins. Molecules 2013, 18, 9253-9277. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18089253
Lehmann T, Topchiy E. Contributions of NMR to the Understanding of the Coordination Chemistry and DNA Interactions of Metallo-Bleomycins. Molecules. 2013; 18(8):9253-9277. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18089253
Chicago/Turabian StyleLehmann, Teresa, and Elena Topchiy. 2013. "Contributions of NMR to the Understanding of the Coordination Chemistry and DNA Interactions of Metallo-Bleomycins" Molecules 18, no. 8: 9253-9277. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18089253
APA StyleLehmann, T., & Topchiy, E. (2013). Contributions of NMR to the Understanding of the Coordination Chemistry and DNA Interactions of Metallo-Bleomycins. Molecules, 18(8), 9253-9277. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18089253