Triterpenoids of Marine Origin as Anti-Cancer Agents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Triterpenoids from Marine Sponges
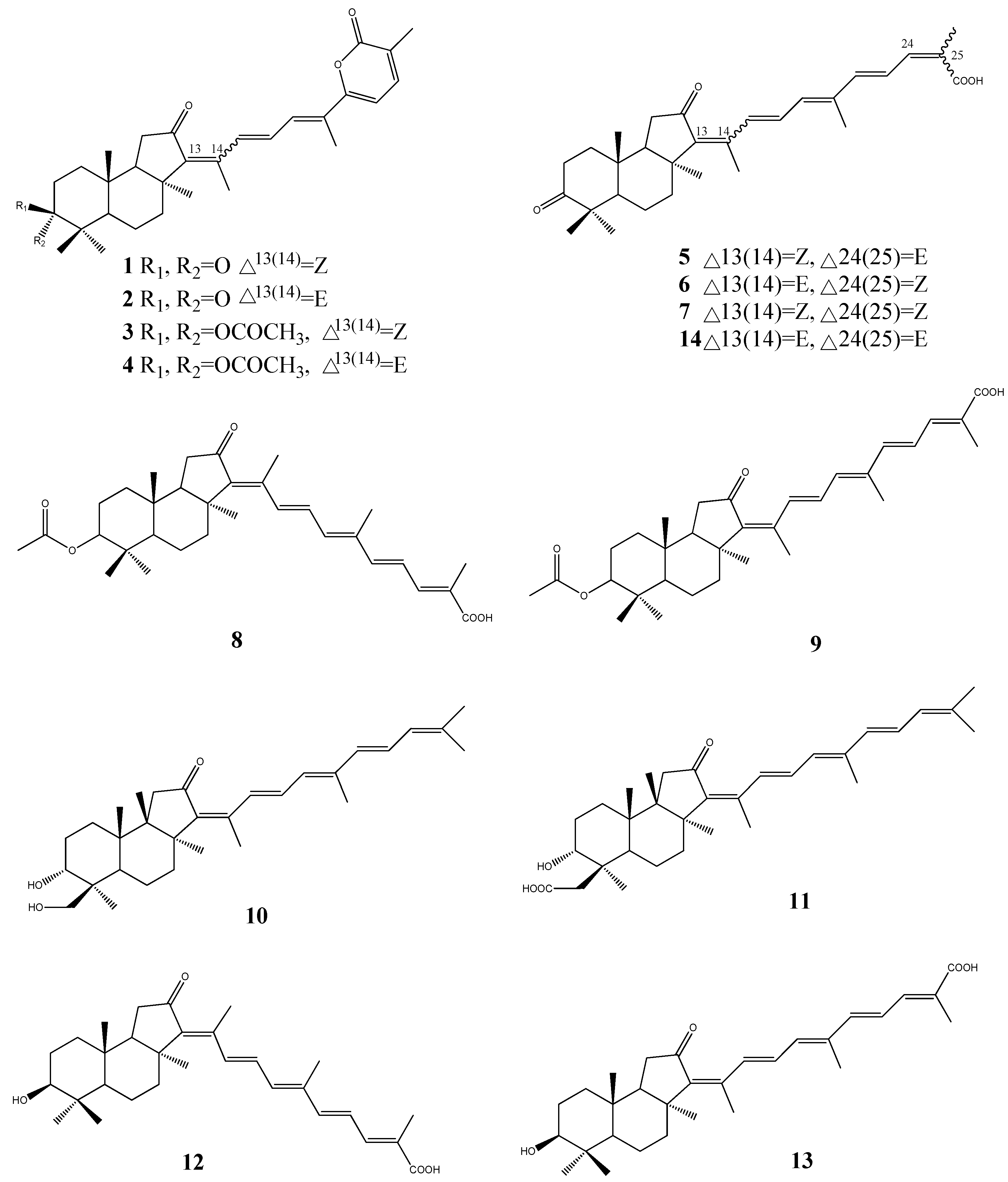
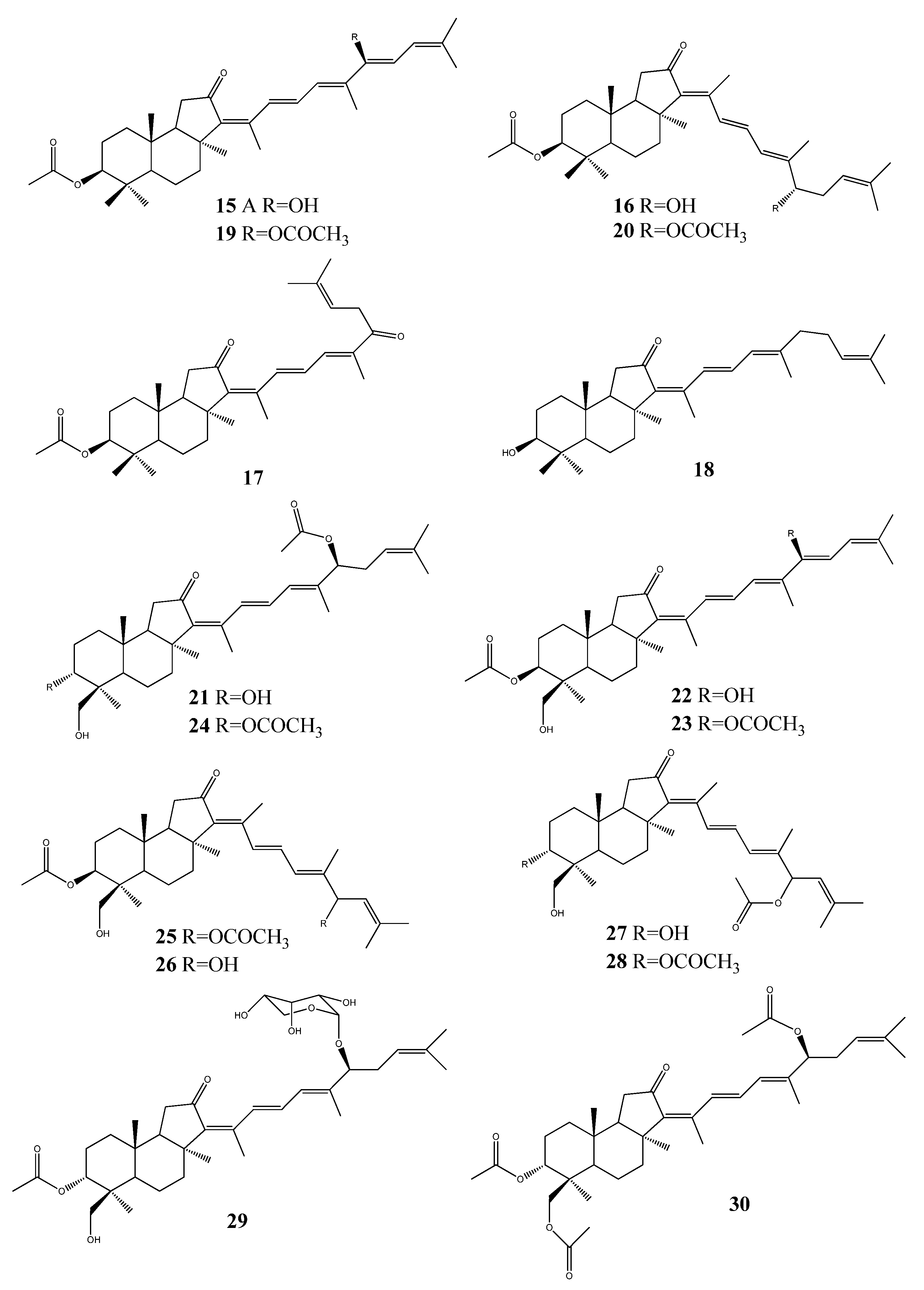
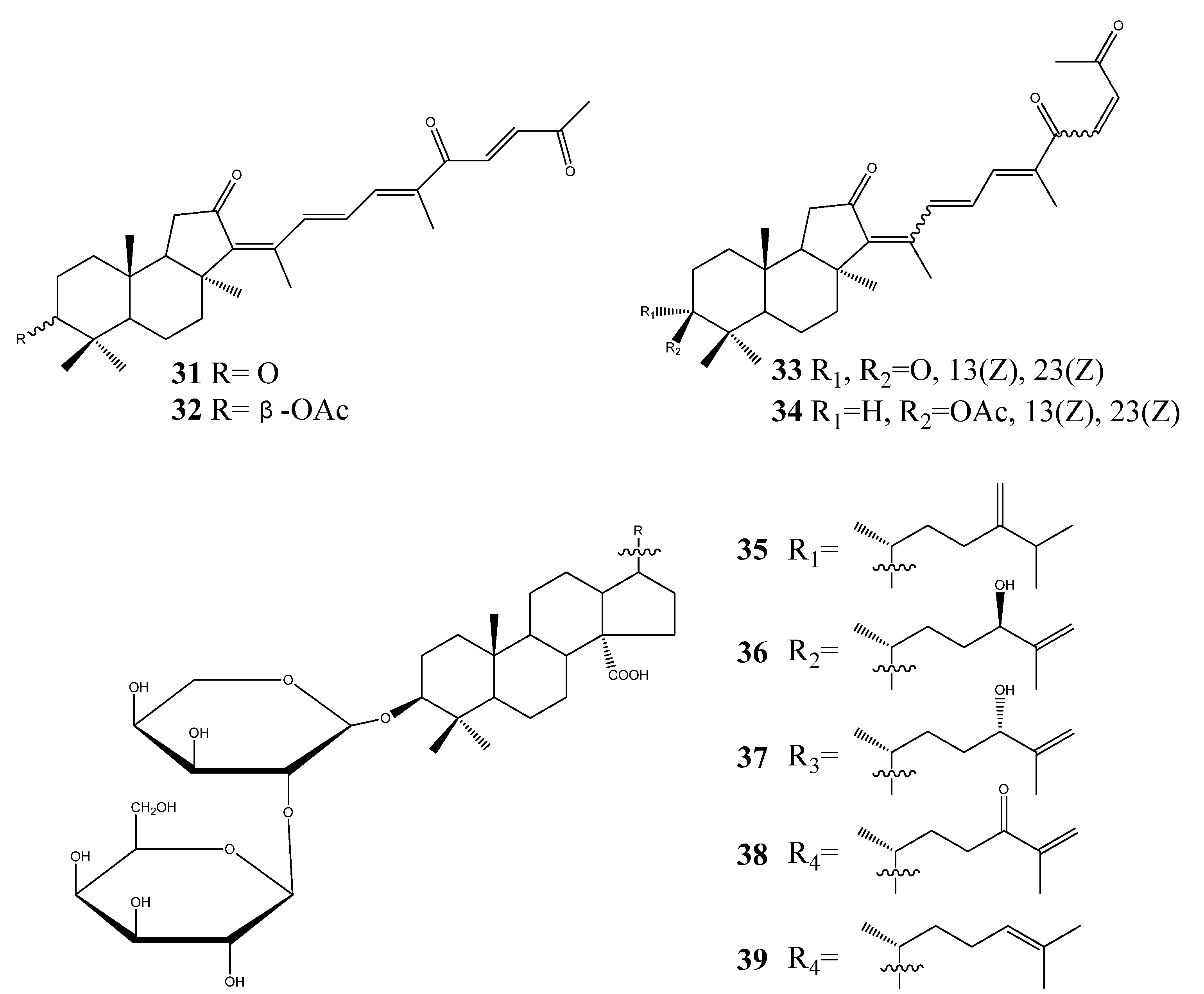
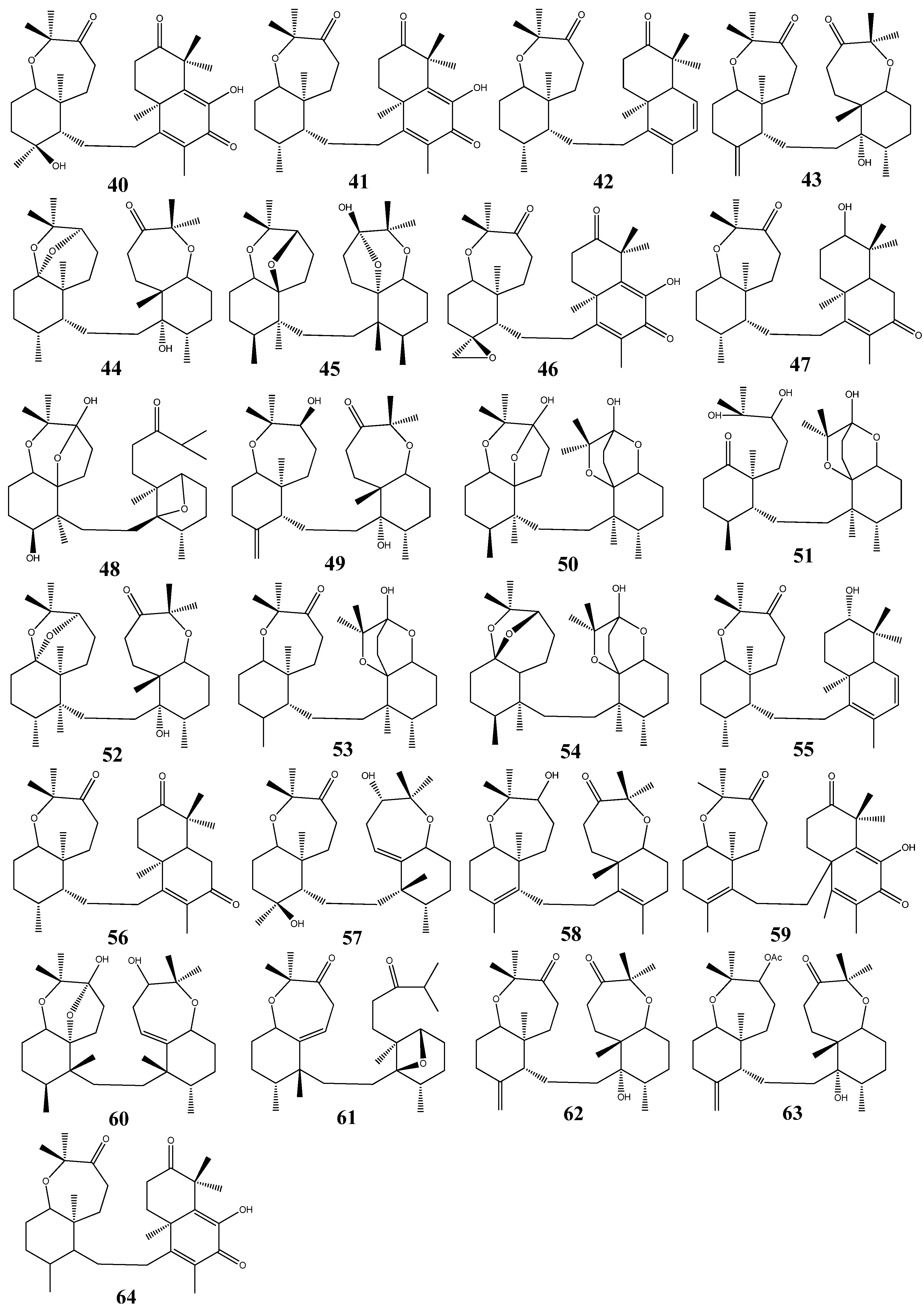
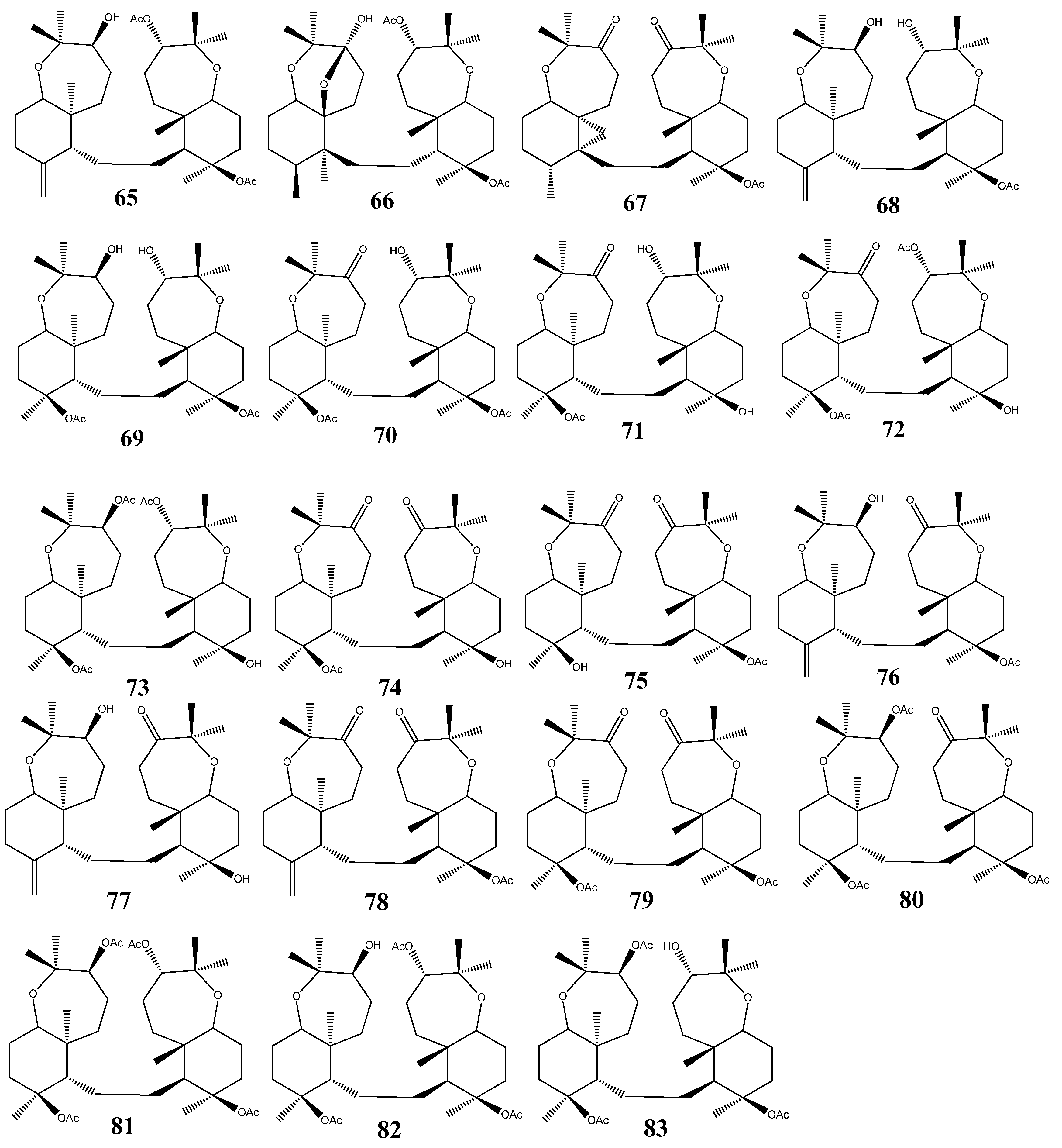
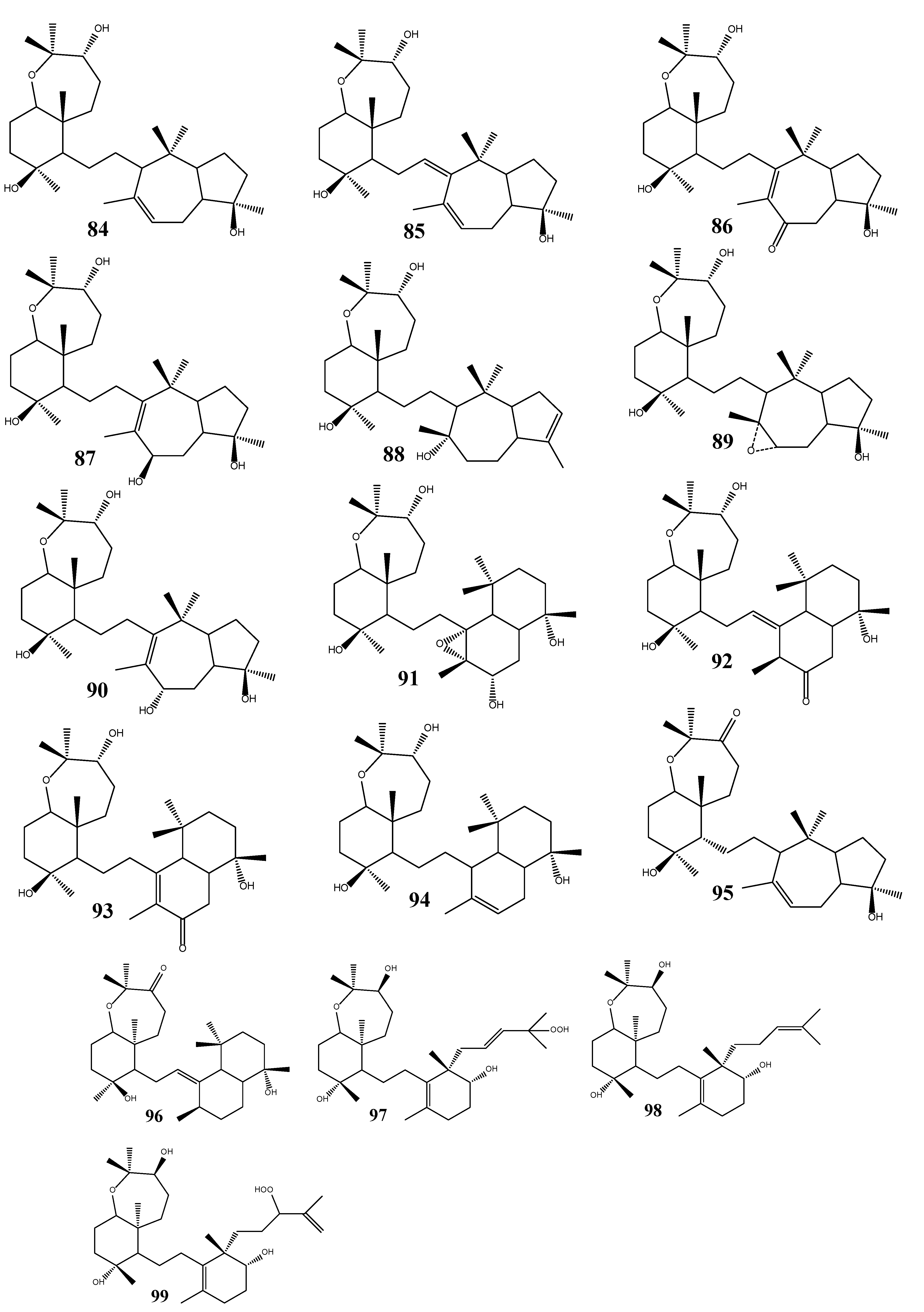
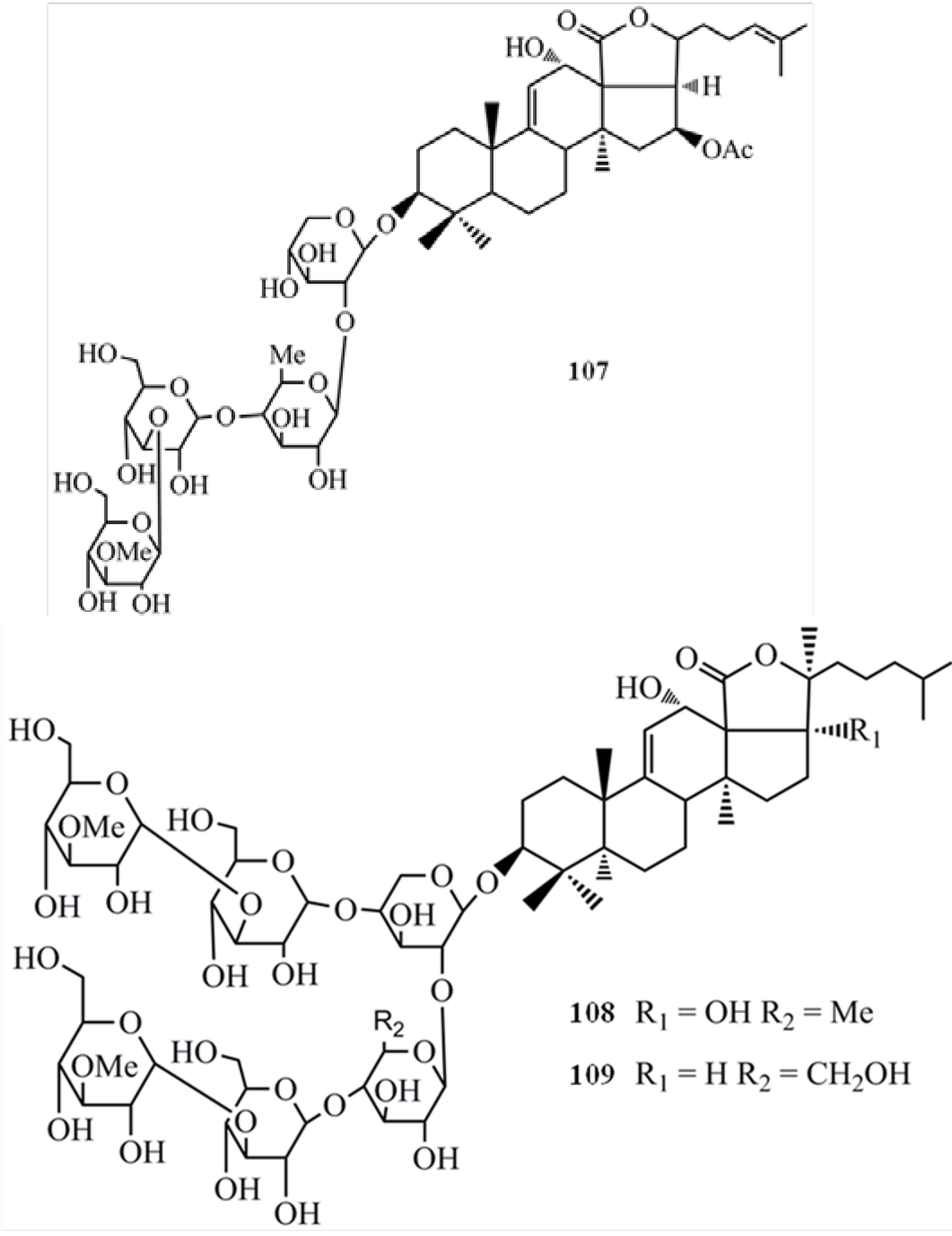
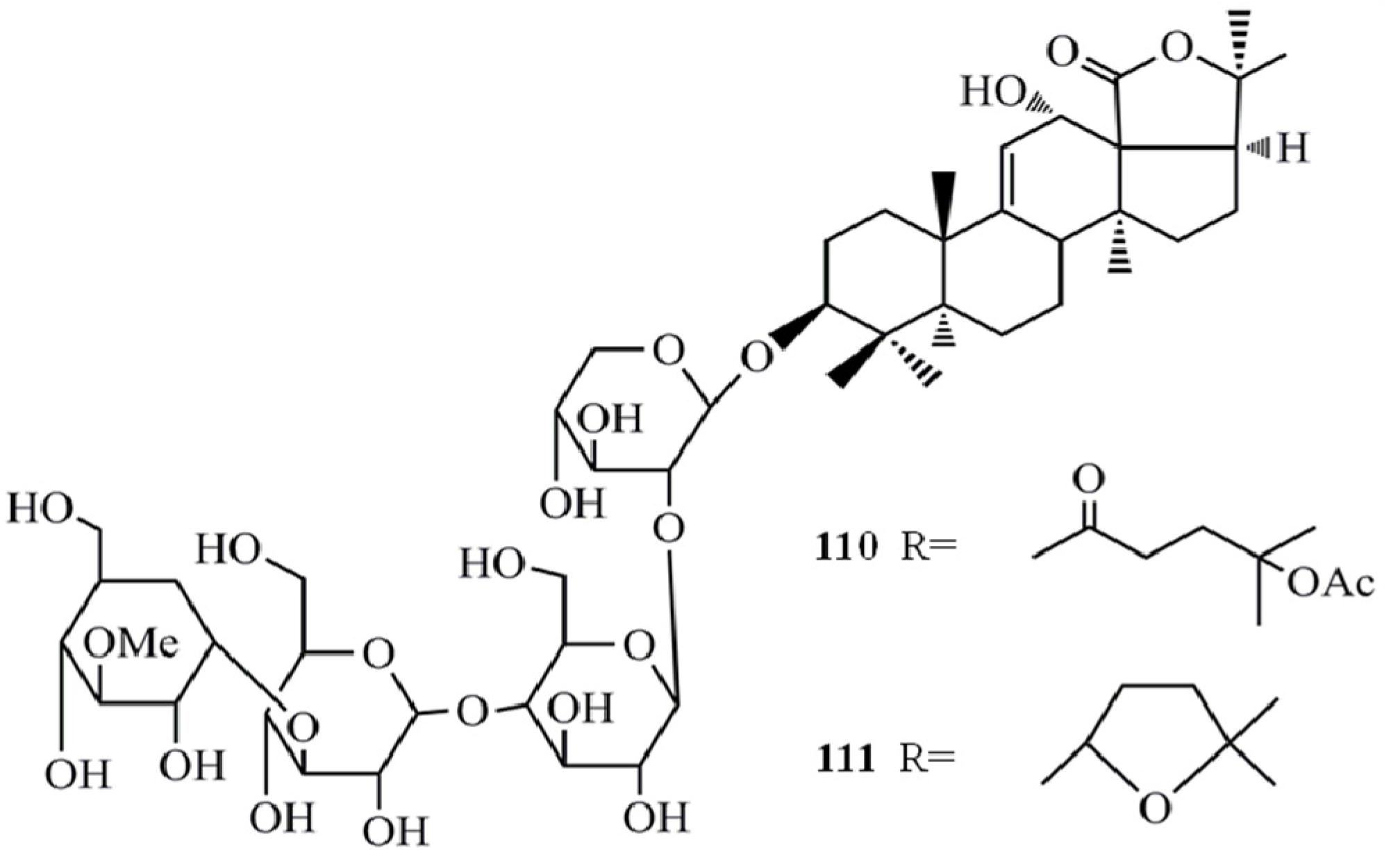
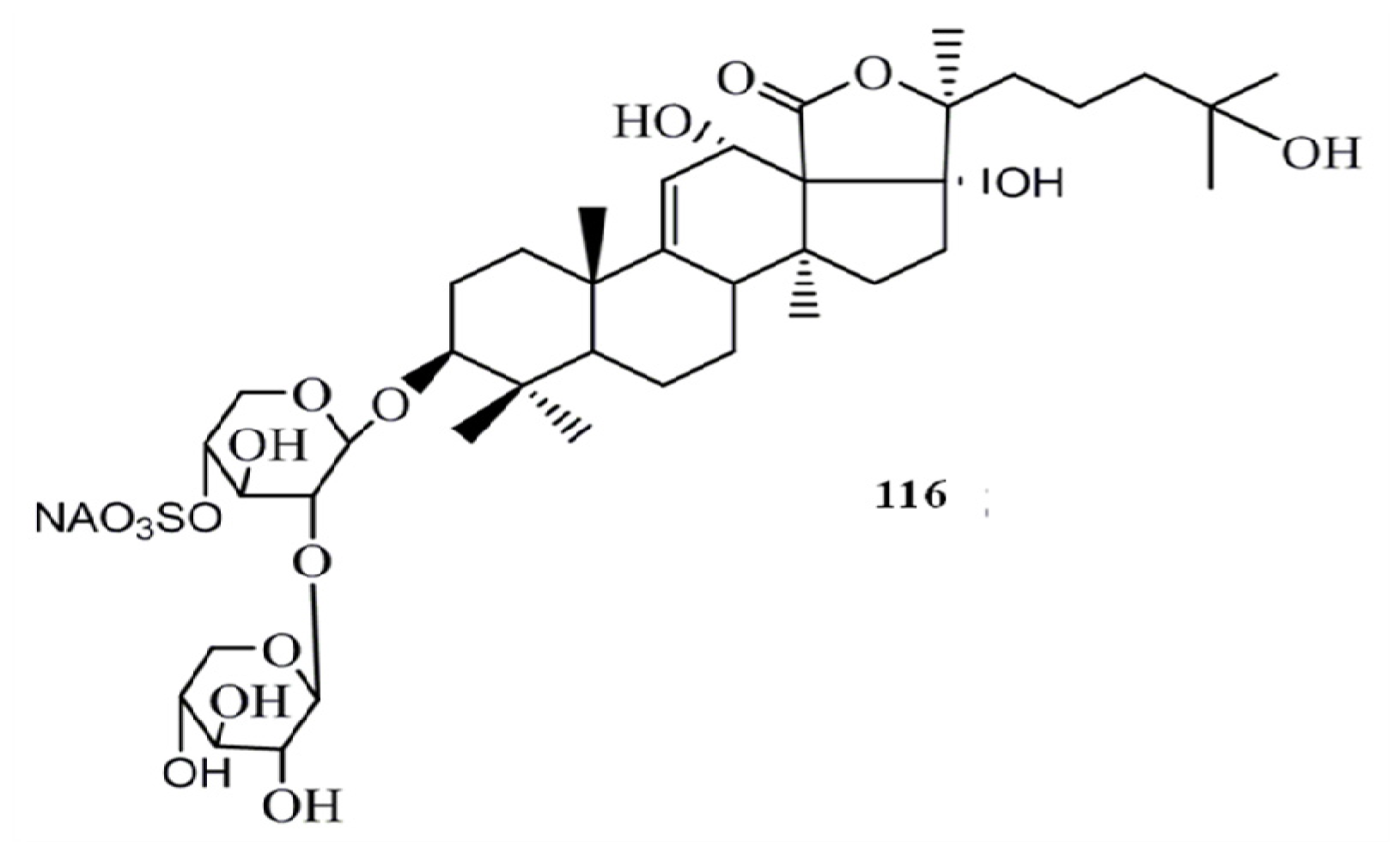
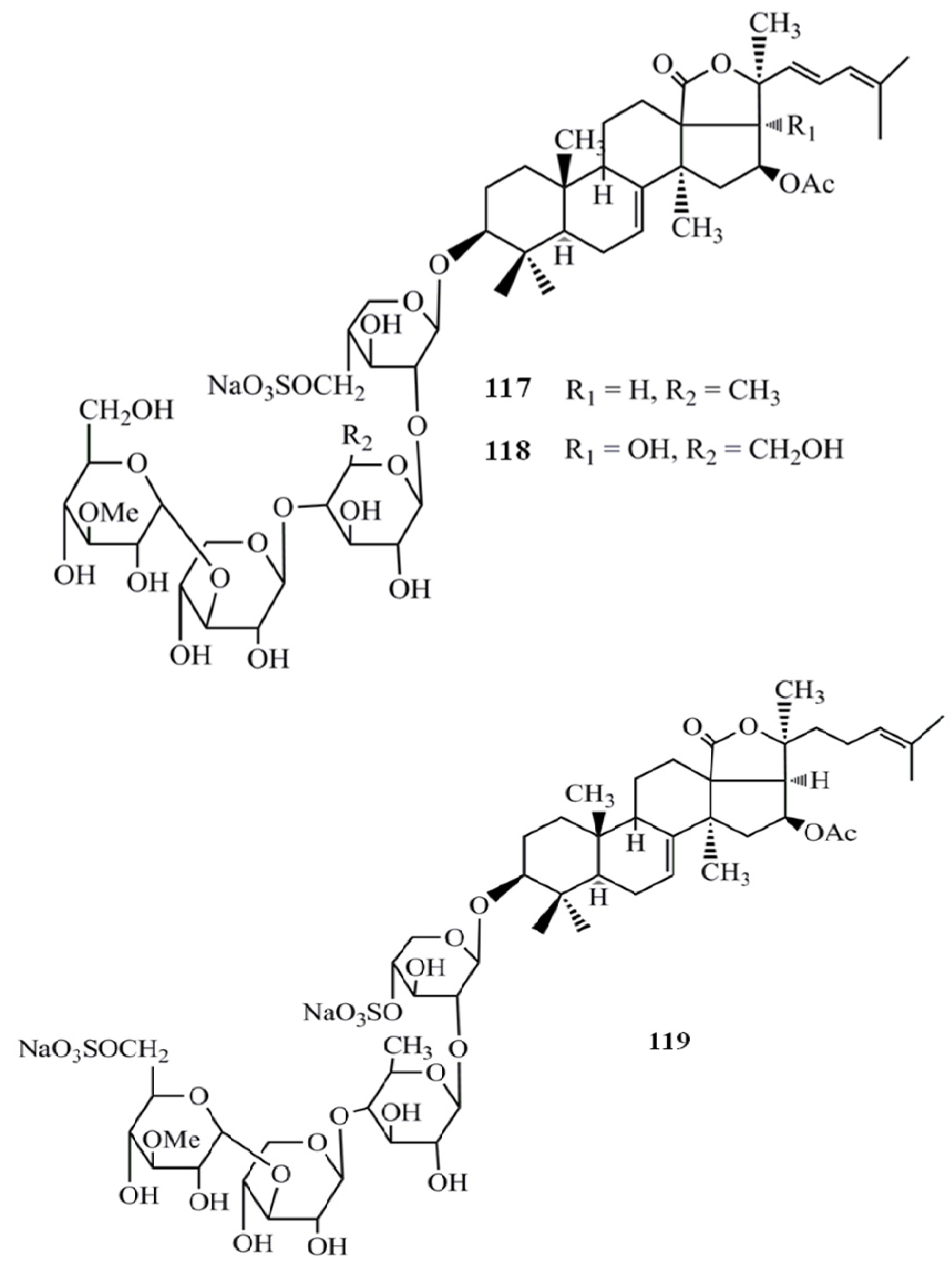
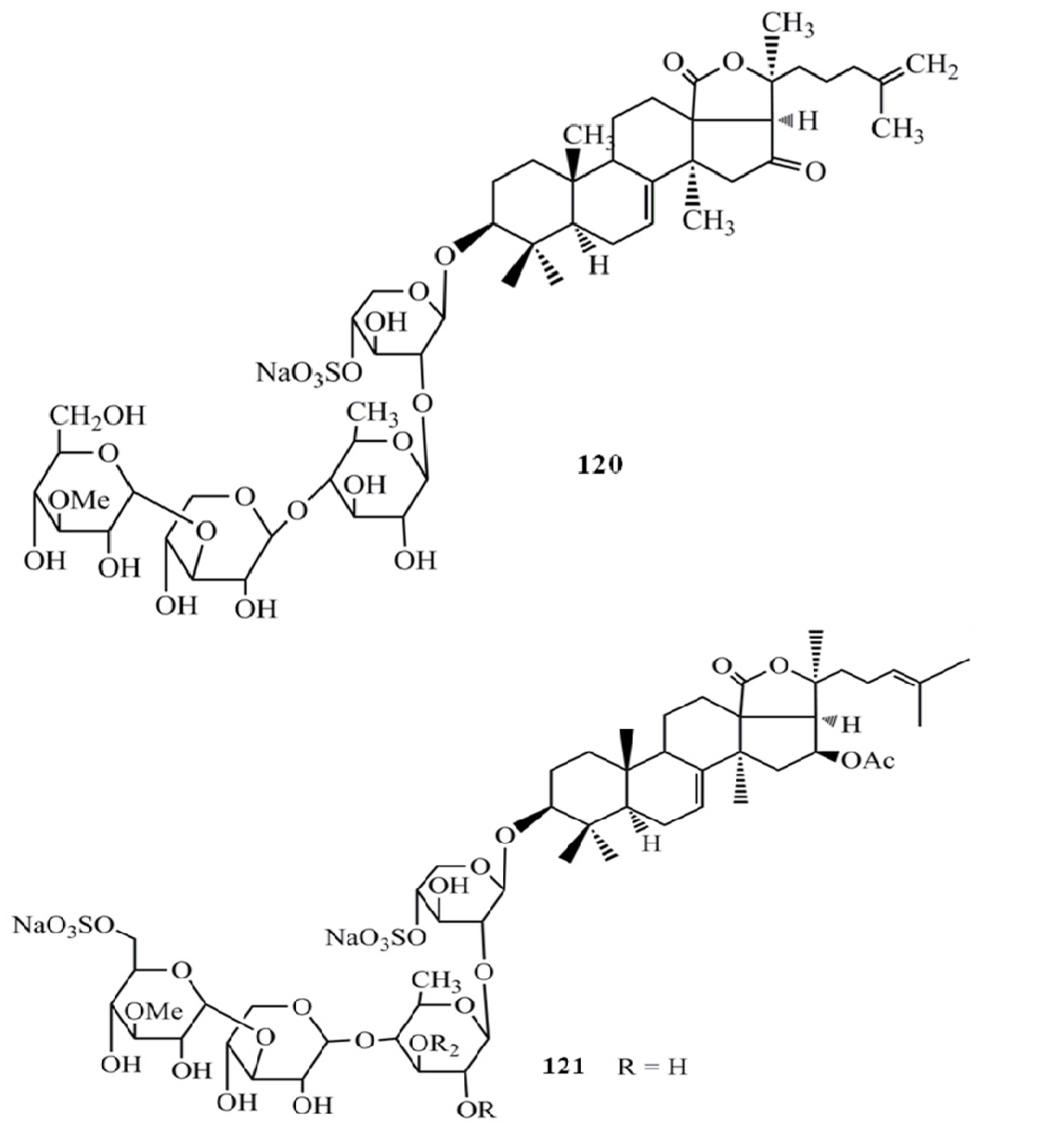
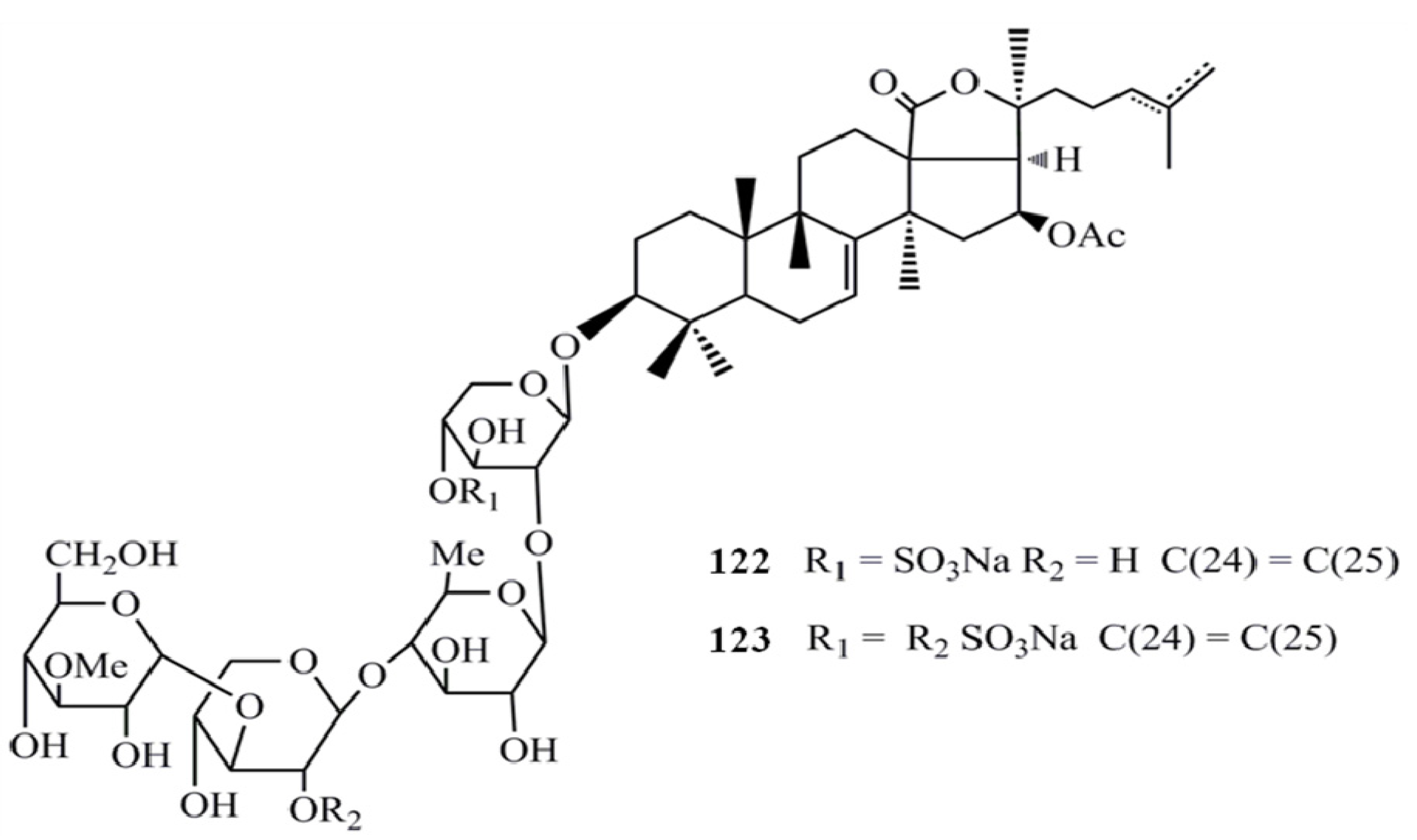
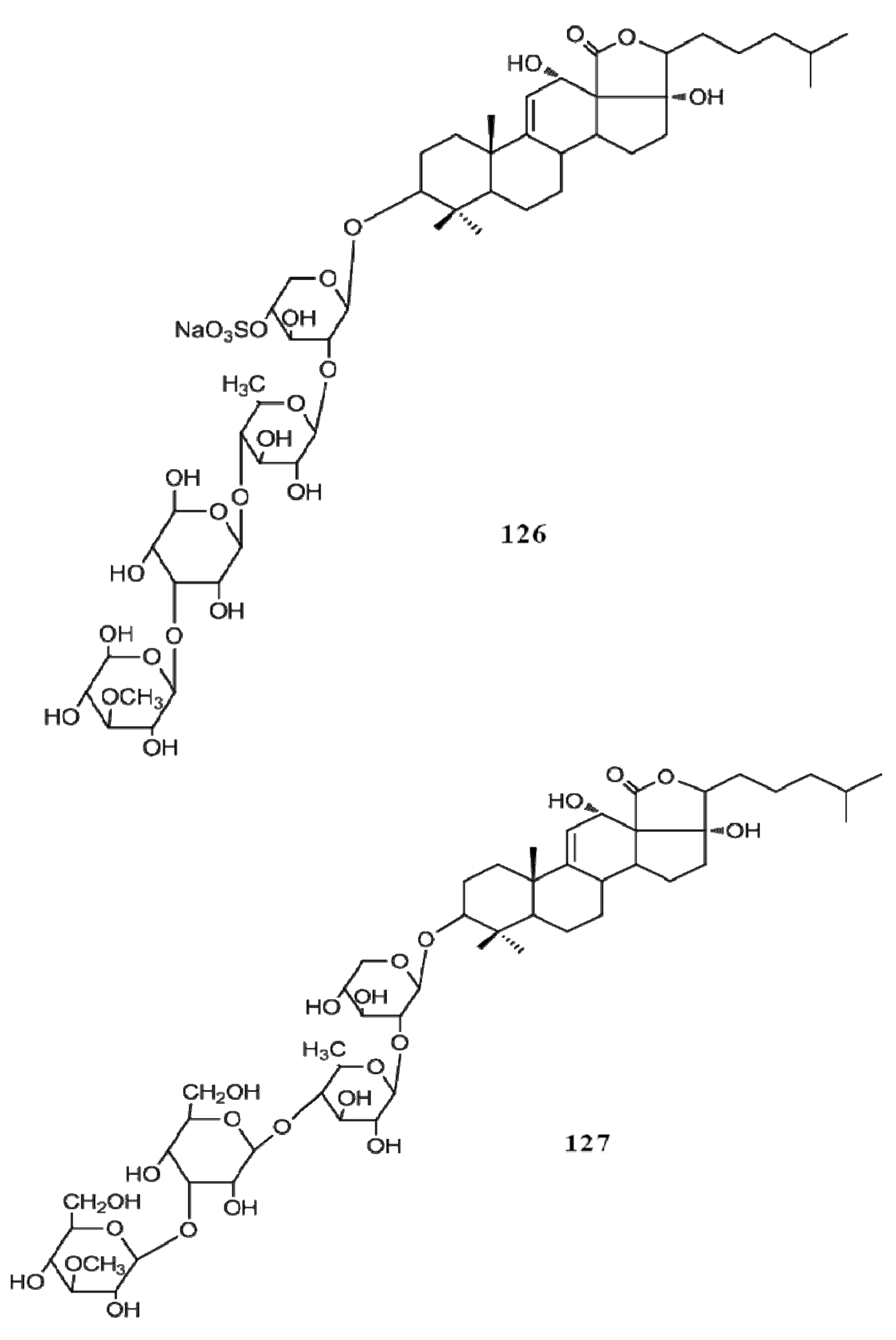
3. Triterpenoids from Sea Cucumbers
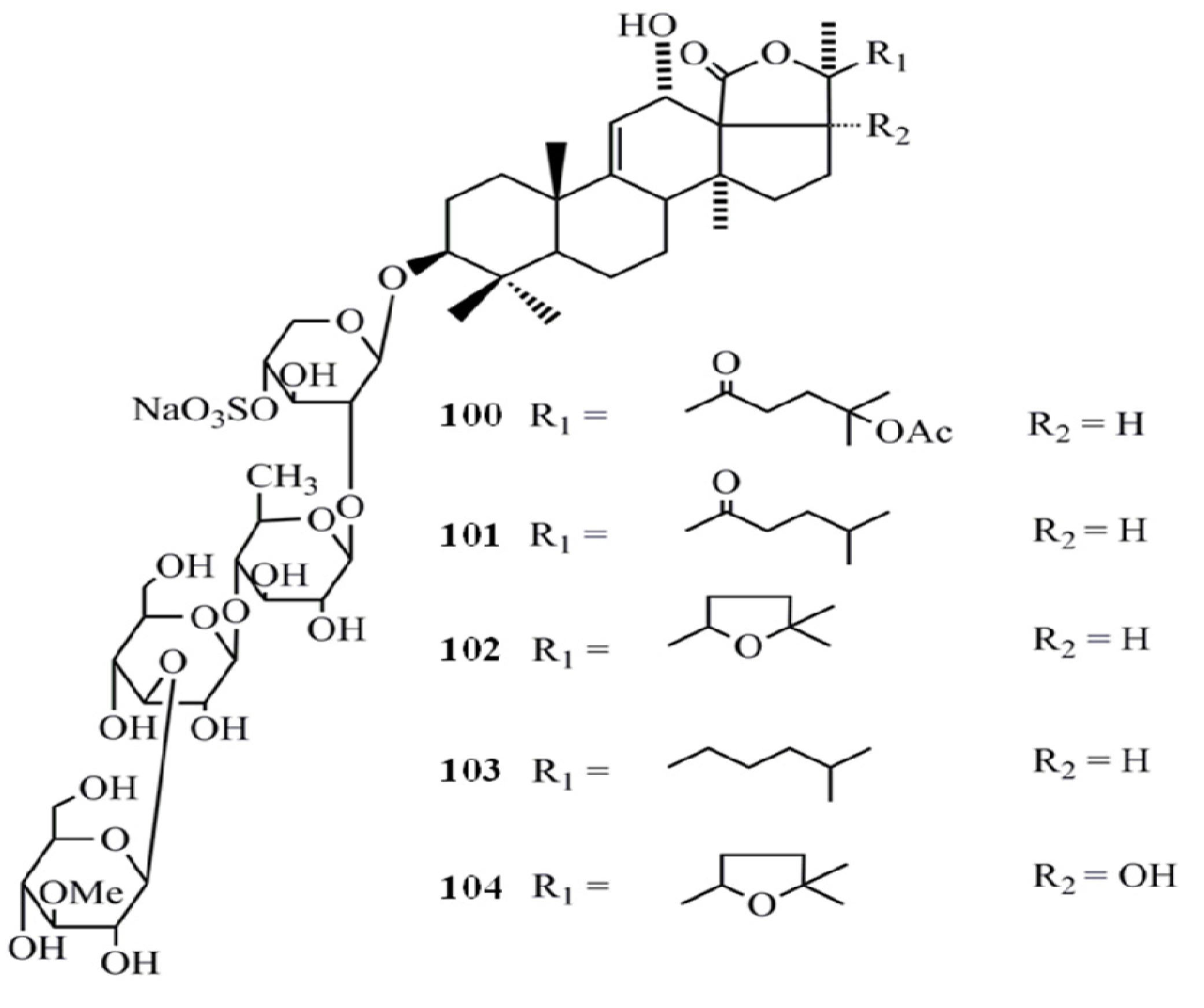
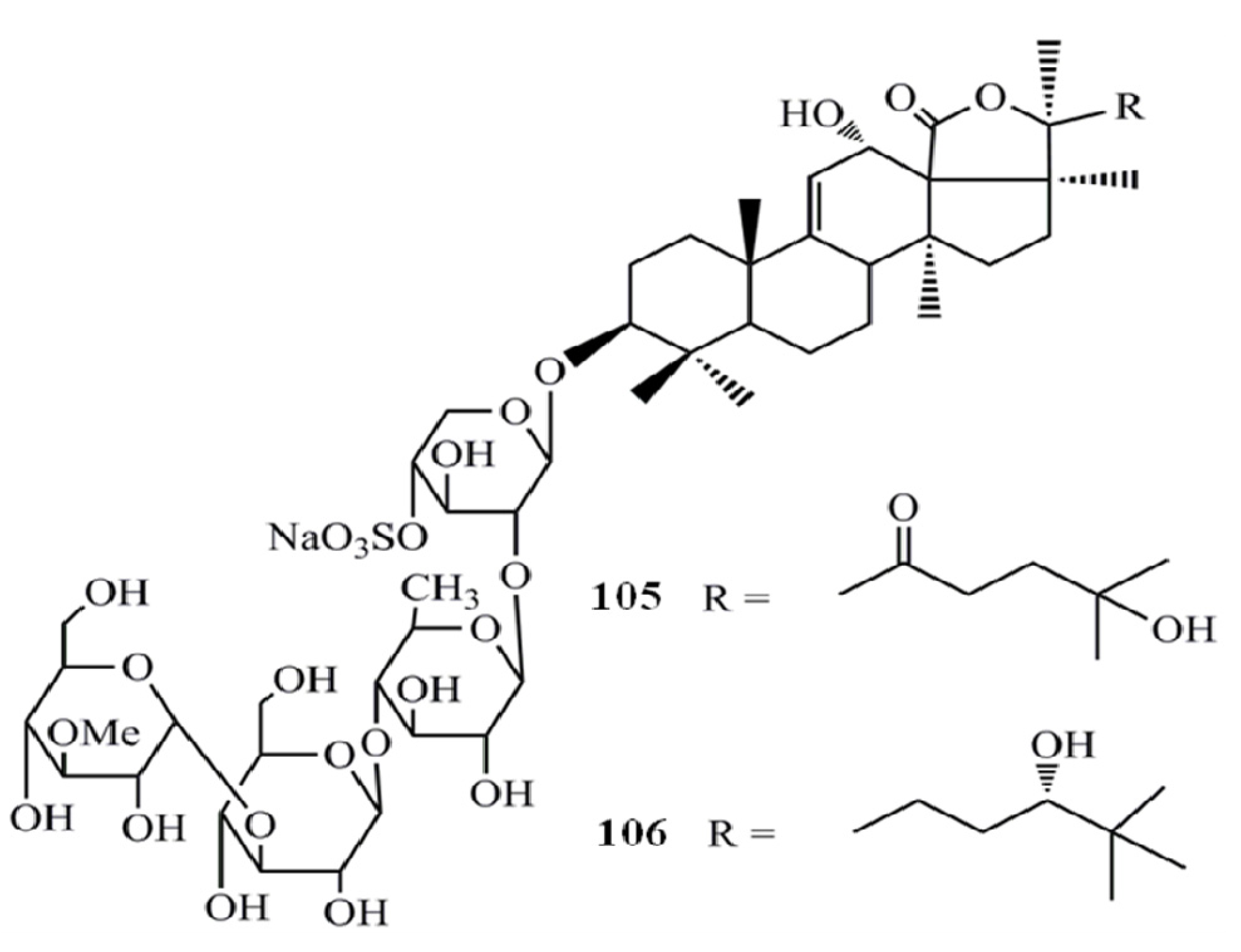


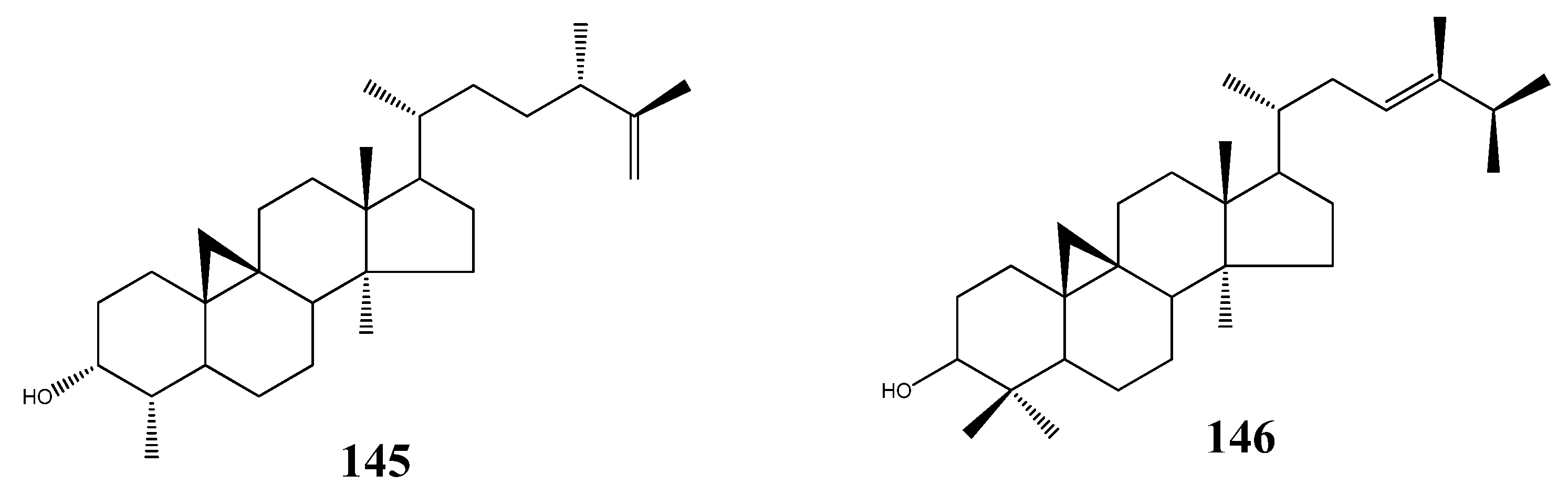
4. Triterpenoids from Marine Algae

5. Triterpenoids from Marine-Derived Fungi

6. Structure Activity Relationships
7. Addressing the Limitations of Using Anti-Cancer Tritepenoids as Therapeutics
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Connolly, J.D.; Hill, R.A. Triterpenoids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1997, 14, 661–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, J.D.; Hill, R.A. Triterpenoids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2002, 19, 494–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, B.N.; Wells, R.J. Malabaricane triterpenes from a fijian collection of the sponge Jaspis stellifera. J. Org. Chem. 1981, 46, 1998–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Z.G.; Deng, S.Z.; Wu, H.M.; Jiang, S.K. Rhabdastrellic acid-A, a novel triterpenoid from the marine sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 1163–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminin, D.L.; Koy, C.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Müller-Hilke, B.; Koczan, D.; Arbogast, B.; Silchenko, A.A.; Kalinin, V.I..; Avilov, S.A.; Stonik, V.A.; et al. Immunomodulatory effects of holothurian triterpene glycosides on mammalian splenocytes determined by mass spectrometric proteome analysis. J. Proteomics. 2009, 72, 886–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen-Pacheco, F.; Nordström, L.; Souto, M.L.; Martín, M.N.; Fernández, J.J.; Daranas, A.H. Studies on polyethers produced by red algae. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1178–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, W.L.; Fang, Y.C.; Zhu, T.J.; Gu, Q.Q.; Zhu, W.M. Cytotoxic alkaloids and antibiotic nordammarane triterpenoids from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sydowi. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishayee, A.; Ahmed, S.; Brankov, N.; Perloff, M. Triterpenoids as potential agents for the chemoprevention and therapy of breast cancer. Front Biosci. 2011, 16, 980–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drag, M.; Surowiak, P.; Drag-Zalesinska, M.; Dietel, M.; Lage, H.; Oleksyszyn, J. Comparision of the cytotoxic effects of birch bark extract, betulin and betulinic acid towards human gastric carcinoma and pancreatic carcinoma drug-sensitive and drug-resistant cell lines. Molecules 2009, 14, 1639–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liby, K.T.; Yore, M.M.; Sporn, M.B. Triterpenoids and rexinoids as multifunctional agents for the prevention and treatment of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.A.; Connolly, J.D. Triterpenoids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 780–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen Kumar, D.R.; Shikha, S.; Cijo George, V.; Suresh, P.K.; Ashok Kumar, R. Anticancer and anti-metastatic activities of RHEUM EMODI rhizome chloroform extracts. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2012, 3, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Narang, A.S.; Desai, D.S. Anticancer drug development. In Pharmaceutical Perspectives of Cancer Therapeutics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 49–92. [Google Scholar]
- Petronelli, A.; Pannitteri, G.; Testa, U. Triterpenoids as new promising anticancer drugs. Anticancer Drugs 2009, 20, 880–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.A.; Deng, Z.W.; Li, J.; Fu, H.Z.; Pei, Y.H.; Zhang, S.; Lin, W.H. A new isomalabaricane triterpenoid from sponge Jaspis sp. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2005, 16, 353–355. [Google Scholar]
- McCormick, J.L.; McKee, T.C.; Cardellina, J.H.; Leid, M.; Boyd, M.R. Cytotoxic triterpenes from a marine sponge, Stelletta sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 1047–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, G.; Matsunaga, S.; Fusetani, N. Globostellatic acids A-D, new cytotoxic isomalabaricane triterpenes from the marine sponge Stelletta globostellata. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 512–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.W.; Wang, Z.L.; Wu, J.H; Shi, N.; Zhang, H.J; Chen, W.S.; Morris-Natschke, S.L.; Lin, A.S. Stellettins L and M, Cytotoxic isomalabaricane-type triterpenes, and sterols from the marine sponge Stelletta tenuis. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1114–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.; Deng, Z.W.; Li, J.; Fu, H.Z.; Soest, R.W.M.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W.H. Isomalabaricane-Type Compounds from the Marine Sponge Rhabdastrella aff. distincta. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 2033–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.Y.; Meng, Y.H.; Zen, L.M. Stelletttin A, a new triterpenoid pigment from the marine sponge Stelletta tenuzs. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 1450–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essack, M.; Bajic, V.B.; Archer, J.A.C. Recently confirmed apoptosis-inducing lead compounds isolated from marine sponge of potential relevance in cancer treatment. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1580–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebada, S.S.; Lin, W.H.; Proksch, P. Bioactive sesterterpenes and triterpenes from marine sponges: Occurrence and pharmacological significance. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 313–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasdemir, D.; Mangalindan, G.C.; Concepcion, G.P.; Verbitski, S.M.; Rabindran, S.; Miranda, M.; Greenstein, M.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Harper, M.K.; Ireland, C.M. Bioactive isomalabaricane triterpenes from the marine sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, J.A.; Li, M.; Hecht, S.M.; Kingston, D.G.I. Bioactive isomalabaricane triterpenoids from Rhabdastrella globostellata that stabilize the binding of DNA polymerase β to DNA. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Ishibashi, M.; Agemi, K.; Sasaki, T.; Kobayashi, J. Stelliferins A–F, new antineoplastic isomalabaricane triterpenes from the Okinawan marine sponge Jaspis stellifera. Tetrahedron 1991, 47, 2181–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meragelman, K.M.; McKee, T.C.; Boyd, M.R. New cytotoxic isomalabaricane triterpenes from the sponge Jaspis Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.K.; Ho, J.C.K.; Che, C.T. Apoptotic activity of isomalabaricane triterpenes on human promyelocytic leukemia HL60 cells. Cancer Letters 2005, 230, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonov, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Stonik, V.A.; Afiyatullov, S.S.; Aminin, D.L.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Mollo, E.; Cimino, G. Isolation and structures of erylosides from the Carribean sponge Erylus formosus. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudi, A.; Kashman, Y. Sodwanones A-F, new triterpenoids from the marine sponge Axinella weltneri. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 1416–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudi, A.; Goldberg, I.; Stein, Z.; Kashman, Y. Sodwanones G, H, and I, new cytotoxic triterpenes from a marine sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 1702–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudi, A.; Aknin, M.; Gaydou, E.M.; Kashman, Y. Sodwanones K, L, and M; new triterpenes from the marine sponge Axinella weltner. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 700–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bon, C.F.; Berrué, F.; Thomas, O.P.; Reyes, F.; Amade, P. Sodwanone S, a triterpene from the marine sponge Axinella weltneri. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1284–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.Q.; Fishback, J.A.; Zhou, Y.D.; Nagle, D.G. Sodwanone and yardenone triterpenes from a South African species of the marine sponge Axinella inhibit hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) activation in both breast and prostate tumor cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1715–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino, G.; Madaio, A.; Trivellone, E. Minor triterpenoids from the mediterranean sponge, Raspaciona aculeata. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino, G.; Crispino, A.; Madaio, A.; Trivellone, E. Raspacionin B, a further triterpenoid from the mediterranean sponge Raspaciona aculeata. J. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino, G.; Epifanio, R. D. A.; Madaio, A.; Puliti, R.; Trivellone, E. Absolute stereochemistry of raspacionin, the main triterpenoid from the marine sponge Raspaciona aculeata. J. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56, 1622–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Abraham, I.; Carvalho, P.; Kuang, Y.H.; Shaala, L.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Avery, M.A.; Chen, Z.S.; Sayed, K.E. Sipholane triterpenoids: Chemistry, reversal of ABCB1/P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance, and pharmacophore modeling. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Laphookhieo, S.; Shi, Z.; Fu, L.W.; Akiyama, S.; Chen, Z.S.; Youssef, D.T. A.; Soest, R.W.M.; Sayed, K.E. Reversal of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance by sipholane triterpenoids. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 928–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Jain, S.; Kim, I.W.; Peng, X.X.; Abraham, I.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Fu, L.W.; Sayed, K.E.; Ambudkar, S.V.; Chen, Z.S. Sipholenol A, a marine-derived sipholane triterpene, potently reverses P-glycoprotein (ABCB1)-mediated multidrug resistance in cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, I.; Jain, S.; Wu, C.P.; Khanfar, M.; Kuang, Y.H.; Dai, C.L.; Shi, Z.; Chen, X.; Fu, L.W.; Ambudkar, S.V.; Sayed, K.E.; Chen, Z.S. Marine sponge-derived sipholane triterpenoids reverse P-glycoprotein (ABCB1)-mediated multidrug resistance in cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yi, Y.; Tang, H.; Li, L.; Sun, P.; Wu, J. Two new bioactive triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Pseudocolochirus violaceus. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, N.H.; Thanh, N.V.; Kiem, P.V.; Huong, L.M.; Minh, C.V.; Kim, Y.H. Two new triterpene glycosides from the vietnamese sea cucumber Holothuria scabra. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2007, 30, 1387–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.S.; Yi, Y.H.; Li, L. Arguside A: A new cytotoxic triterpene glycoside from the sea cucumber Bohadschia argus Jaeger. Chem. Biodiver. 2007, 4, 2845–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.S.; Yi, Y.H.; Li, L. Argusides B and C, two new cytotoxic triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Bohadschia argus Jaeger. Chem. Biodiver. 2008, 5, 1288–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.S.; Yi, Y.H.; Yi, L.; et al. Argusides D and E, two new cytotoxic triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Bohadschia argus Jaeger. Chem. Biodiver. 2008, 5, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Liu, B.S.; Yi, Y.H. A new cytotoxic lanostane-type triterpene glycoside from the sea cucumber Holothuria impatiens. Chem. Biodiver. 2007, 4, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.Q.; Li, L.; Yi, Y.H.; Yuan, W.H.; Liua, B.S.; Weng, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Sun, P.; Wang, Z.L. Two new cytotoxic nonsulfated pentasaccharide holostane (=20-Hydroxylanostan-18-oic Acid γ-Lactone) glycosides from the sea cucumber Holothuria grisea. Helv. Chim. Acta 2008, 91, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yi, Y.H.; Tang, H.F.; Zou, Z.R.; Wu, H.M. Structure and cytotoxicity of a new lanostane-type triterpene glycoside from the sea cucumber Holothuria hilla. Chem. Biodivers 2006, 3, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.R.; Yi, Y.H.; Wu, H.M.; Wu, J.H.; Liaw, C.C.; Lee, K.H. Intercedensides A−C, three new cytotoxic triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Mensamaria intercedens Lampert. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Tang, H.F.; Yi, Y.H. Cytotoxic triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Pseudocolochirus violaceus. Fitoterapia 2007, 78, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.H.; Xu, Q.Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, S.L.; Wu, H.M.; Ding, J.; Tong, Y.G.; Tan, W.F.; Li, M.H.; Tian, F.; Wu, J.H.; Liaw, C.C.; Bastow, K.F.; Lee, K.H. Philinopsides A and B, two new sulfated triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Pentacta quadrangularis. Helv. Chim. Acta 2006, 89, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouqi, N.A.; Iratni, R.; Nemmar, A. Frondoside A inhibits human breast cancer cell survival, migration, invasion and the growth of breast tumor xenografts. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 668, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.O.; Shastina, V.V.; Shin, S.W. Differential effects of triterpene glycosides, frondoside A and cucumarioside A2–2 isolated from sea cucumbers on caspase activation and apoptosis of human leukemia cells. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Xue, Y.; Wang, J.F. In vitro and in vivo anti-tumour activities of echinoside A and ds-echinoside A from Pearsonothuria graeffei. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 9, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, N.Y.; Li, X.M.; Xie, H.; Ding, J.; Li, K.; Ding, L.P.; Wang, B.G. Highly oxygenated triterpenoids from the marine red alga Laurencia mariannensis (Rhodomelaceae). Helv. Chim. Acta 2008, 91, 1940–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norte, M.; Fernandez, J.J.; Souto, M.L.; Garcia-Gravalos, M.D. Two new antitumoral polyether squalene derivatives. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 15, 2671–2674. [Google Scholar]
- Pec, M.K.; Aguirre, A.; Moser-Their, K.; Fernandez, J.J.; Souto, M.L.; Dota, J.; Diaz-Gonzalez, F.; Villar, J. Induction of apoptosis in estrogen dependent and independent breast cancer cells by the marine terpenoid dehydrothyrsiferol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 65, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, F.C.; Villa-Pulgarin, J.A.; Mollinedo, F.; Martín, M.N.; Fernández, J.J.; Daranas, A.H. New polyether triterpenoids from laurencia viridis and their biological evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2220–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, M.L.; Manrı´quez, C. P.; Norte, M.; Leira, F.; Ferna´ndez, J. The inhibitory effects of squalene-derived triterpenes on protein phosphatase PP2A. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 1261–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norte, M.; Fernandez, J.J.; Saouto, M.L.; Gavin, J.A.; GarciaGravalos, M.D. Thyrsenols A and B two unusual polyether squalene derivatives. Tetrahedron 1997, 53, 3173–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Takeda, S.; Suzuki, M.; Kurosawa, E.; Kato, A.; Imanaka, Y. Constituents of marine plants. Part 67. Cytotoxic squalene-derived polyethers from the marine red alga Laurencia obtusa (Hudson) Lamouroux. Chem. Lett. 1987, 361–364. [Google Scholar]
- Gamal, A.A.E. Biological importance of marine algae. Saudi Pharm. J. 2010, 18, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.H.; liu, T.; Gu, C.X.; Shao, C.L.; Zhou, J.; Wang, C.Y. Steroids and triterpenoids from the brown alga Kjellmaniella crassifolia. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2012, 48, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Akihisa, T.; Tokuda, H.; Ukiya, M.; Watanabe, K.; Nishino, H. Cancer chemopreventive effects of cycloartane-type and related triterpenoids in in vitro and in vivo models. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 918–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebel, R. Terpenes from marine-derived fungi. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2340–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Lin, X.; Lu, C.H.; Shen, Y.M. Three new triterpenes from Xylarialean sp. A45, an endophytic fungus from Annona squamosa L. Helv. Chim. Acta 2011, 94, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinin, V.I. System-theoretical (Holistic) Approach to the modeling of structural functional relationships of biomolecules and their evolution: An example of triterpene glycosides from sea cucumbers (Echinodermata, Holothurioidea). J. Theor. Biol. 2000, 206, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinin, V.I.; Prkofieva, N. G.; Likhatskaya, G. N. Hemolytic activities of triterpene glycosides from the holothurian order Dendrochirotida: Some trends in the evolution of this group of toxins. Toxicon 1996, 34, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinin, V.I.; Volkova, O.V.; Likhatskaya, G. N. Hemolytic activity of triterpene glycosides from Cucumariidae family holothurians and evolution of this group of toxins. J. Nat. Toxins 1992, 1, 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Maltsev, I.I.; Stekhova, S.I.; Schentsova, E.B.; Anisimov, M.M.; Stonik, V.A. Antimicrobial activities of glycosides from the sea cucumbers of family. Stichopodidae. Khim-Pharm. Zhurn 1985, 1985, 54–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.K.; Himaya, S.W.A. Triterpene Glycosides from Sea Cucumbers and Their Biological Activities. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2012, 65, 297–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.M.; Cullis, P.R. Drug Delivery Systems: Entering the Mainstream. Science 2004, 303, 1818–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M. Cancer nanotechnology: Opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Wang, X.; Nie, S.; Chen, Z.; Shin, D.M. Therapeutic Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery in Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.-X.; Himaya, S.W.A.; Kim, S.-K. Triterpenoids of Marine Origin as Anti-Cancer Agents. Molecules 2013, 18, 7886-7909. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18077886
Li Y-X, Himaya SWA, Kim S-K. Triterpenoids of Marine Origin as Anti-Cancer Agents. Molecules. 2013; 18(7):7886-7909. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18077886
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yong-Xin, S. W. A. Himaya, and Se-Kwon Kim. 2013. "Triterpenoids of Marine Origin as Anti-Cancer Agents" Molecules 18, no. 7: 7886-7909. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18077886
APA StyleLi, Y.-X., Himaya, S. W. A., & Kim, S.-K. (2013). Triterpenoids of Marine Origin as Anti-Cancer Agents. Molecules, 18(7), 7886-7909. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18077886




