Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Allergic Activities of Pentaherb Formula, Moutan Cortex (Danpi) and Gallic Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of PHF, Danpi and GA on Cell Surface Expression of Adhesion Molecule
2.2. Effect of PHF, DP and GA on Inflammation-Related Chemokines CCL2, CCL5 and CXCL8 Production from IL-33-Activated KU812 Cells
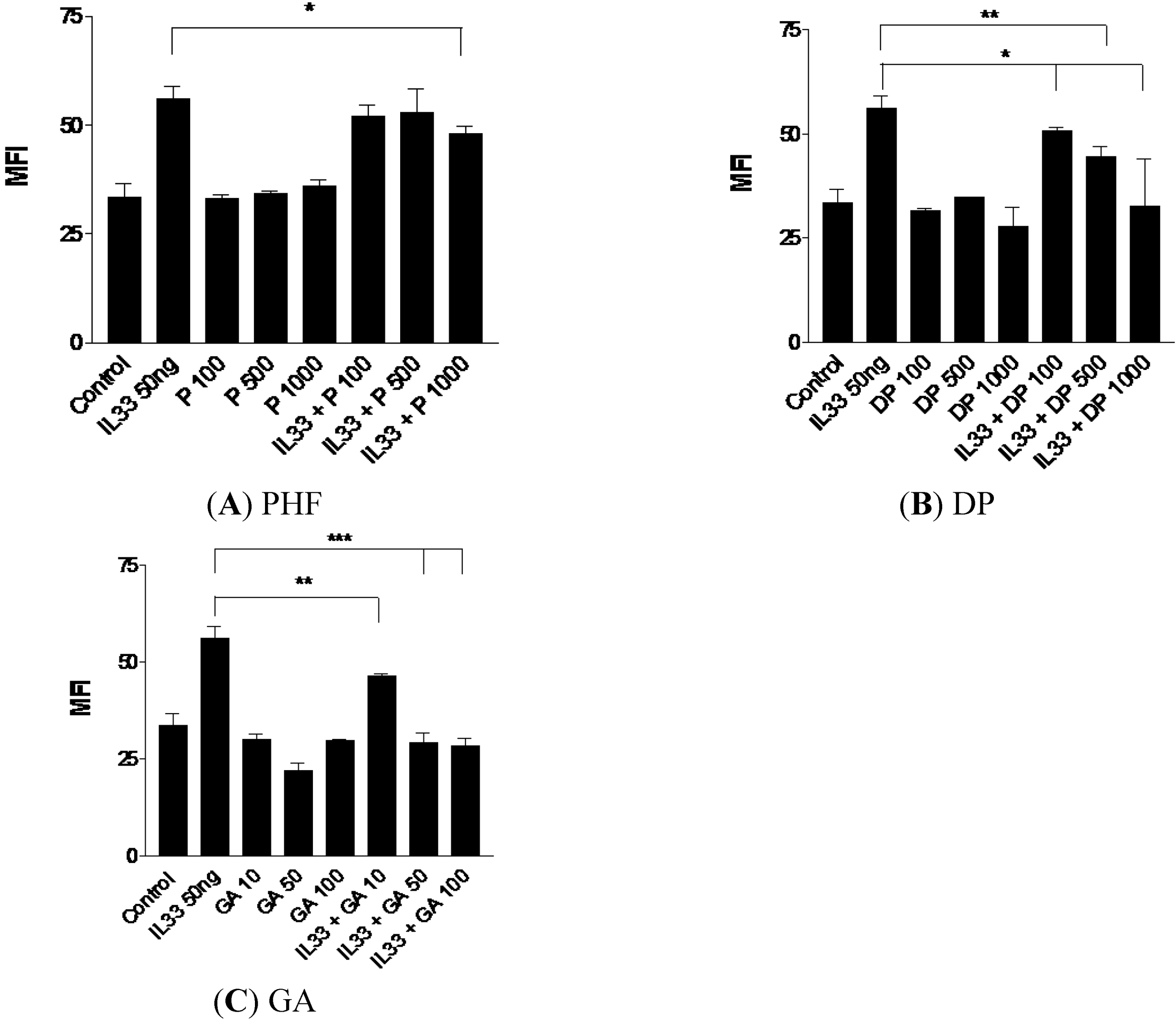

2.3. Effect of PHF, DP and GA on Inflammatory Cytokine IL-6 Production from IL-33-Activated KU812 Cells

2.4. Effect of GA on the Phosphorylation of Intracellular Signaling Molecules p38 Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK), Inhibitory-κBα (IκBα) and c-Jun Amino-terminal Kinase (JNK) on IL-33 Activated KU812 Cells
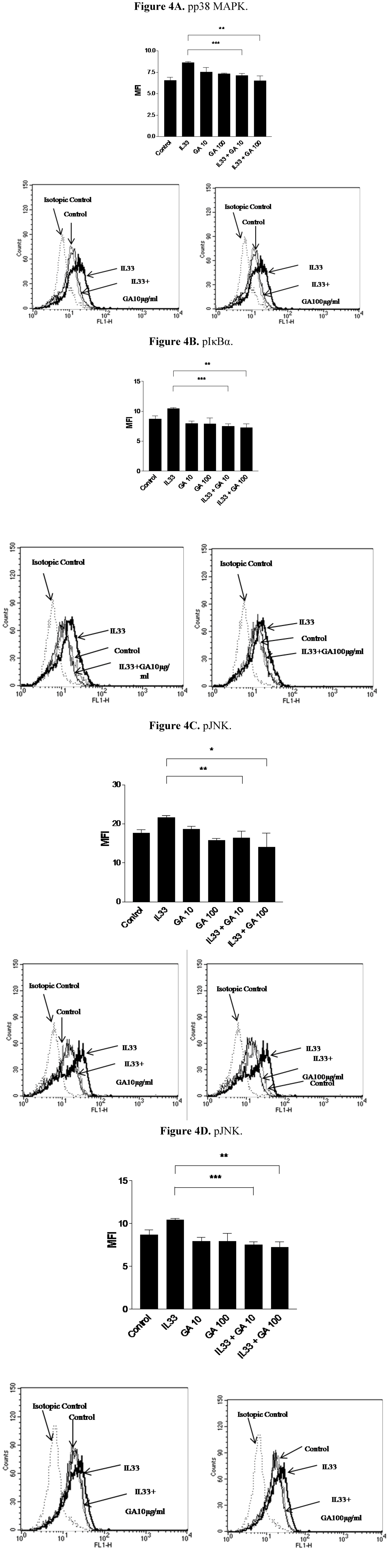
2.5. Enhanced Suppressive Effect on ICAM-1, CCL5 and IL-6 Expression of IL-33-Activated KU812 Cells with the Combined Treatment of Dexamethasone and GA

3. Experimental
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Preparation of Plant Extracts
3.3. HPLC Analyses of GA and Danpi Aqueous Extract
3.4. Cell Culture and Treatment
3.5. Immunofluorescence Staining and Flow Cytometry for the Analysis of ICAM-1, Cytokines and Intracellular Signaling Molecules
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Sicherer, S.H.; Leung, D.Y. Advances in allergic skin disease, anaphylaxis, and hypersensitivity reactions to foods, drugs, and insects in 2011. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bever, H.P.; Samuel, S.T.; Lee, B.W. Halting the allergic march. World Allergy Organ J. 2008, 1, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawankar, R.; Bunnag, C.; Khaltaev, N.; Bousquet, J. Allergic Rhinitis and Its Impact on Asthma in Asia Pacific and the ARIA Update 2008. World Allergy Organ J. 2012, 5, S212–S217. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, H.C. Clinical practice. Atopic dermatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 2314–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spergel, J.M. Epidemiology of atopic dermatitis and atopic march in children. Immunol. Allergy Clin. North Am. 2010, 30, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, D.; Sjöberg, O.; Foucard, T. Development of allergies and asthma in infants and young children with atopic dermatitis—a prospective follow-up to 7 years of age. Allergy 2000, 55, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, M.I.; Montefort, S.; Björkstén, B.; Lai, C.K.; Strachan, D.P.; Weiland, S.K.; Williams, H. ISAAC Phase Three Study Group. Worldwide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC Phases One and Three repeat multicountry cross-sectional surveys. Lancet 2006, 368, 733–743. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.I.; Kim, J.; Han, Y.; Ahn, K. A proposal: Atopic Dermatitis Organizer (ADO) guideline for children. Asia Pac. Allergy 2011, 1, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, K.L.; Leung, T.F.; Ng, P.C.; Lam, M.C.; Kam, W.Y., Wong; Lee, K.C.; Sung, Y.T.; Cheng, K.F.; Fok, T.F.; et al. Efficacy and tolerability of a Chinese herbal medicine concoction for treatment of atopic dermatitis: A randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 157, 357–363. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, W.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, P.; Tang, X.P. One-year evaluation of radiographic progress in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated by Qingre Huoxue decoction. Zhongguo Gu Shang 2011, 24, 992–996. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Hu, C.; Cheng, Y. Effects of Salviae Mitiorrhizae and Cortex Moutan extract on the rat heart after myocardial infarction: a proteomic study. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 415–424. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.P.; Wong, C.K.; Leung, P.C.; Fung, K.P.; Lau, C.B.; Lau, C.P.; Li, E.K.; Tam, L.S.; Lam, C.W. Anti-inflammatory activities of Chinese herbal medicine sinomenine and Liang Miao San on tumor necrosis factor-α-activated human fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, B.C.; Hon, K.L.; Leung, P.C.; Sam, S.W.; Fung, K.P.; Lee, M.Y.; Lau, H.Y. Traditional Chinese medicine for atopic eczema: PentaHerbs formula suppresses inflammatory mediators release from mast cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 120, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ow, Y.Y.; Stupans, I. Gallic acid and gallic acid derivatives: Effects on drug metabolizing enzymes. Curr. Drug MeTable 2003, 4, 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Faried, A.; Kurnia, D.; Faried, L.S.; Usman, N.; Miyazaki, T.; Kato, H.; Kuwano, H. Anticancer effects of gallic acid isolated from Indonesian herbal medicine, Phaleria macrocarpa (Scheff.) Boerl, on human cancer cell lines. Int. J. Oncol. 2007, 30, 605–613. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, M.; Velmurugan, B.; Rajamanickam, S.; Agarwal, R.; Agarwal, C. Gallic acid, an active constituent of grape seed extract, exhibits anti-proliferative, pro-apoptotic and anti-tumorigenic effects against prostate carcinoma xenograft growth in nude mice. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 2133–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrina, C.D.; Padovani, G.; Mainente, F.; Zoccatelli, G.; Bissoli, G.; Mosconi, S.; Veneri, G.; Peruffo, A.; Andrighetto, G.; Rizzi, C.; et al. Anti-tumour potential of a gallic acid-containing phenolic fraction from Oenothera biennis. Cancer Lett. 2005, 226, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroes, B.H.; van den Berg, A.J.; Quarles van Ufford, H.C.; van Dijk, H.; Labadie, R.P. Anti-inflammatory activity of gallic acid. Planta Med. 1992, 58, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Fang, Y. Anti-inflammatory gallic acid and wedelolactone are G protein-coupled receptor-35 agonists. Pharmacology 2012, 89, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.K.; Leung, K.M.; Qiu, H.N.; Chow, J.Y.; Choi, A.O.; Lam, C.W. Activation of eosinophils interacting with dermal fibroblasts by pruritogenic cytokine IL-31 and alarmin IL-33: implications in atopic dermatitis. PLoS One 2012, 7, e29815. [Google Scholar]
- Smithgall, M.D.; Comeau, M.R.; Yoon, B.R.; Kaufman, D.; Armitage, R.; Smith, D.E. IL-33 amplifies both Th1- and Th2-type responses through its activity on human basophils, Allergen-reactive Th2 cells, iNKT and NK cells. Int. Immunol. 2008, 20, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzukawa, M.; Iikura, M.; Koketsu, R.; Nagase, H.; Tamura, C.; Komiya, A.; Nakae, S.; Matsushima, K.; Ohta, K.; Yamamoto, K.; et al. An IL-1 cytokine member, IL-33, induces human basophil activation via its ST2 receptor. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 5981–5989. [Google Scholar]
- Valent, P. Interleukin-33: A regulator of basophils. Blood 2009, 113, 1396–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, W.A. Mechanisms of Transendothelial Migration of Leukocytes. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.K.; Lam, C.W.; Wu, A.K.; Ip, W.K.; Lee, N.L.; Chan, I.H.; Lit, L.C.; Hui, D.S.; Chan, M.H.; Chung, S.S.; et al. Plasma inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in severe acute respiratory syndrome. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2004, 136, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.A.; Luster, A.D. T cell homing to epithelial barriers in allergic disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.K.; Cao, J.; Yin, Y.B.; Lam, C.W. Interleukin-17A activation on bronchial epithelium and basophils: A novel inflammatory mechanism. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 35, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Satoh, T.; Takayama, K.; Miyagishi, C.; Walls, A.F.; Yokozeki, H. Basophil recruitment and activation in inflammatory skin diseases. Allergy 2011, 66, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, A.J.; Kon, O.M.; Smith, S.J.; Zeibecoglou, K.; Khan, L.N.; Barata, L.T.; McEuen, A.R.; Buckley, M.G.; Walls, A.F.; Meng, Q.; et al. Basophils, eosinophils, and mast cells in atopic and nonatopic asthma and in late-phase allergic reactions in the lung and skin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 105, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Sniadecki, N.J.; Chen, C.S. Mechanical forces in endothelial cells during firm adhesion and early transmigration of human monocytes. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2010, 3, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochner, B.S.; Luscinskas, F.W.; Gimbrone, M.A.; Newman, W.; Sterbinsky, S.A.; Derse-Anthony, C.P.; Klunk, D.; Schleimer, R.P. Adhesion of human basophils, eosinophils and neutrophils to interleukin 1-activated human vascular endothelial cells: Contribution of endothelial cell adhesion molecules. J. Exp. Med. 1991, 173, 1553–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Fazal, F. Hug tightly and say goodbye:role of endothelial ICAM-1 in leukocyte transmigration. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 823–839. [Google Scholar]
- Homey, B.; Steinhoff, M.; Ruzicka, T.; Leung, D.Y. Cytokines and chemokines orchestra atopic skin inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Zlotnik, A. The biology of chemokines and their receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 18, 217–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.K.; Lam, C.W. Clinical applications of cytokine assays. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2003, 37, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takizawa, H. Bronchial epithelial cells in allergic reactions. Curr. Drug Targets Inflamm. Allergy 2005, 4, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechet, B.; Meseri-Delwail, A.; Arock, M.; Wijdenes, J.; Lecron, J.C.; Sarrouilhe, D. Immunoglobulin D enhances Interleukin-6 release from the KU812 human prebasophil cell line. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2003, 22, 255–263. [Google Scholar]
- Gabay, C. Interleukin-6 and chronic inflammation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besnard, A.G.; Togbe, D.; Couillin, I.; Tan, Z.; Zheng, S.G.; Erard, F.; Le Bert, M.; Quesniaux, V.; Ryffel, B. Inflammasome-IL-1-Th17 response in allergic lung inflammation. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 4, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.K.; Wang, C.B.; Ip, W.K.; Tian, Y.P.; Lam, C.W. Role of p38 MAPK and NF-κB for chemokine release in coculture of human eosinophils and bronchial epithelial cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2005, 139, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, P.P.; Blenis, J. ERK and p38 MAPK-activated protein kinases: A family of protein kinases with diverse biological functions. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 320–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lin, A. Role of JNK activation in apoptosis: A double-edged sword. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Verma, I.M. NF-κB regulation in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 2195–2224. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.P.; Wong, C.K.; Lam, C.W. Role of caspases in dexamethasone-induced apoptosis and activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in human eosinophils. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2000, 122, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Hirai, K.; Nakajima, K.; Ohtoshi, T.; Takaishi, T.; Ohta, K.; Morita, Y.; Ito, K. Dexamethasone inhibits basophil migration. Allergy 1994, 49, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, K.L.; Wang, S.S.; Pong, N.H.; Leung, T.F. Circulating Immunoglobulins, Leucocytes and Complements in Childhood-onset Atopic Eczema. Indian J. Pediatr. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, K.L.; Lee, V.W.; Leung, T.F.; Lee, K.K.; Chan, A.K.; Fok, T.F.; Leung, P.C. Corticosteroids are not present in a traditional Chinese medicine formulation for atopic dermatitis in children. Ann. Acad. Med. Singapore 2006, 35, 759–763. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the Pentaherb formula, Danpi and gallic acid are available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, K.Y.P.; Hu, S.; Chan, B.C.L.; Wat, E.C.L.; Lau, C.B.S.; Hon, K.L.; Fung, K.P.; Leung, P.C.; Hui, P.C.L.; Lam, C.W.K.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Allergic Activities of Pentaherb Formula, Moutan Cortex (Danpi) and Gallic Acid. Molecules 2013, 18, 2483-2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18032483
Liu KYP, Hu S, Chan BCL, Wat ECL, Lau CBS, Hon KL, Fung KP, Leung PC, Hui PCL, Lam CWK, et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Allergic Activities of Pentaherb Formula, Moutan Cortex (Danpi) and Gallic Acid. Molecules. 2013; 18(3):2483-2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18032483
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Kelly Y. P., Shuiqing Hu, Ben C. L. Chan, Elaine C. L. Wat, Clara B. S. Lau, Kam L. Hon, Kwok P. Fung, Ping C. Leung, Patrick C. L. Hui, Christopher W. K. Lam, and et al. 2013. "Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Allergic Activities of Pentaherb Formula, Moutan Cortex (Danpi) and Gallic Acid" Molecules 18, no. 3: 2483-2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18032483
APA StyleLiu, K. Y. P., Hu, S., Chan, B. C. L., Wat, E. C. L., Lau, C. B. S., Hon, K. L., Fung, K. P., Leung, P. C., Hui, P. C. L., Lam, C. W. K., & Wong, C. K. (2013). Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Allergic Activities of Pentaherb Formula, Moutan Cortex (Danpi) and Gallic Acid. Molecules, 18(3), 2483-2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18032483



