Synthesis and Thermotropic Phase Behavior of Four Glycoglycerolipids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of the Glycoglycerolipids
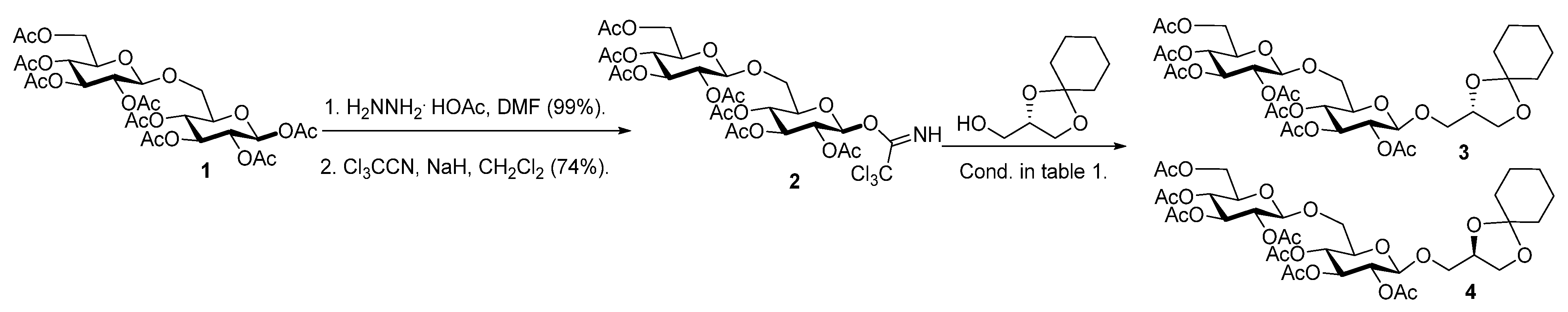
| T (°C) | Promotor | Yield (%) a | α-x (%) b | Epimer (%) c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | TMSOTf | 63 | 5 | 25 |
| −40→0 | TMSOTf | 75 | 5 | 10 |
| −60→0 | TMSOTf | 84 | 5–10 | 10–15 |
| −60→0 | BF3.OEt2 | 84 | 5–10 | 5 |
| −20→−10 | BF3.OEt2 | 76 | 5 | 10 |
| −35→0 | BF3.OEt2 | 70 d | 0 | 0 |

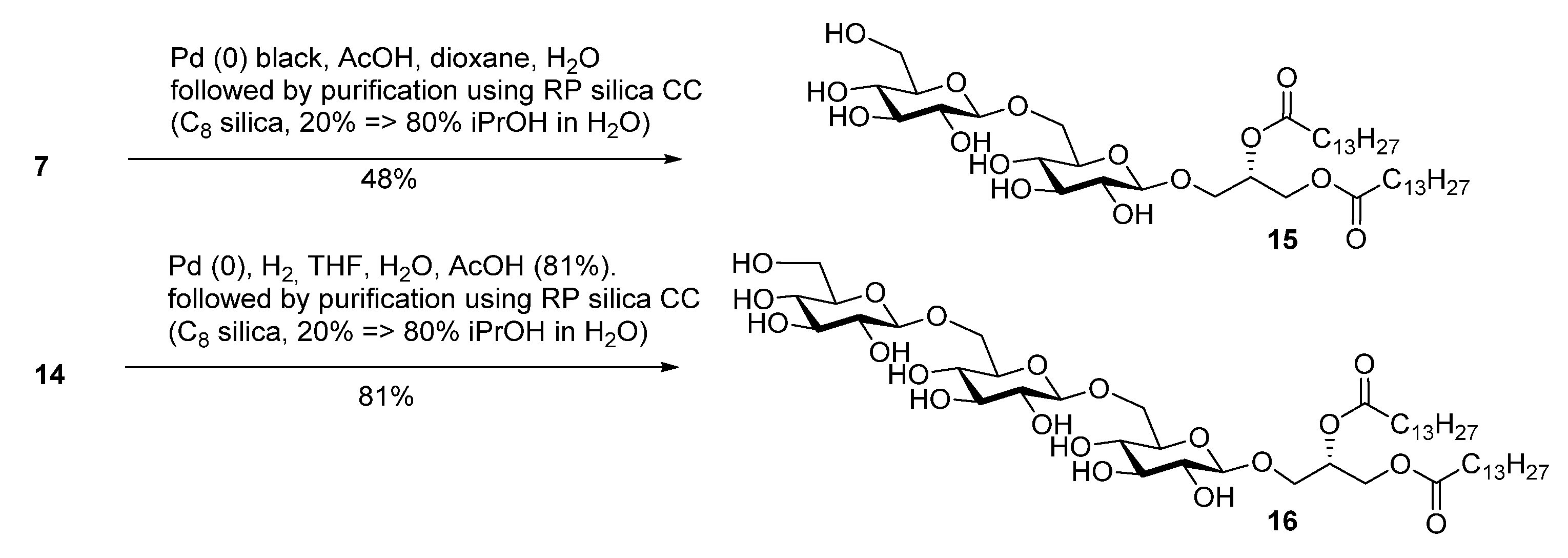

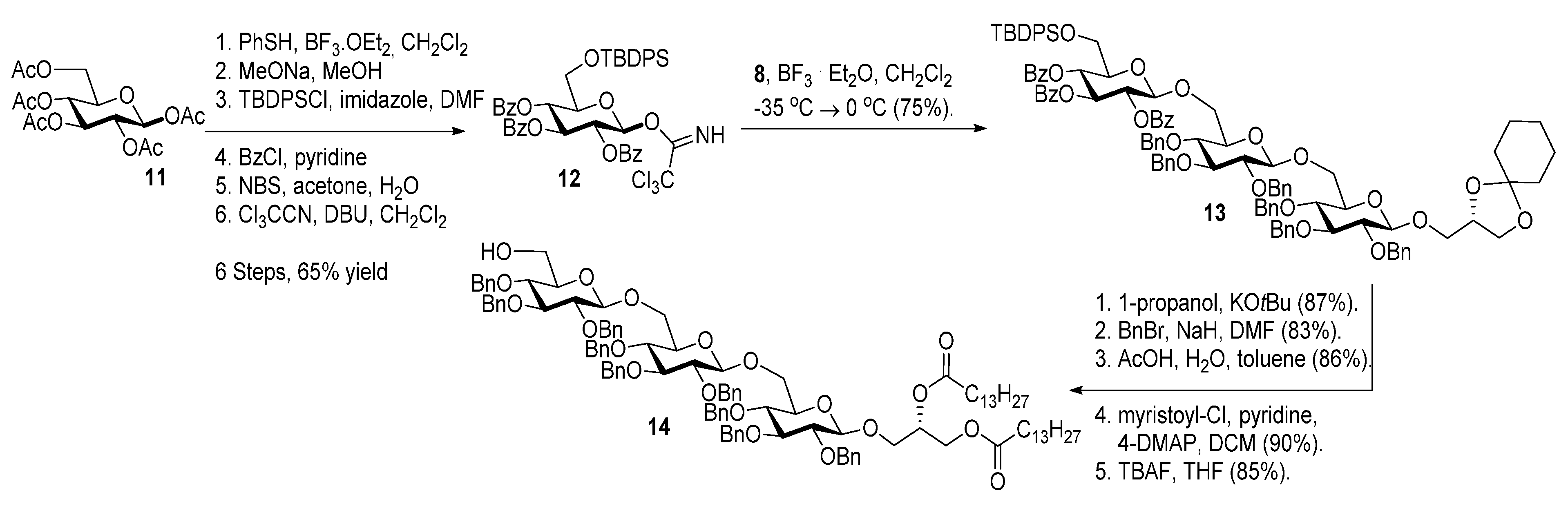
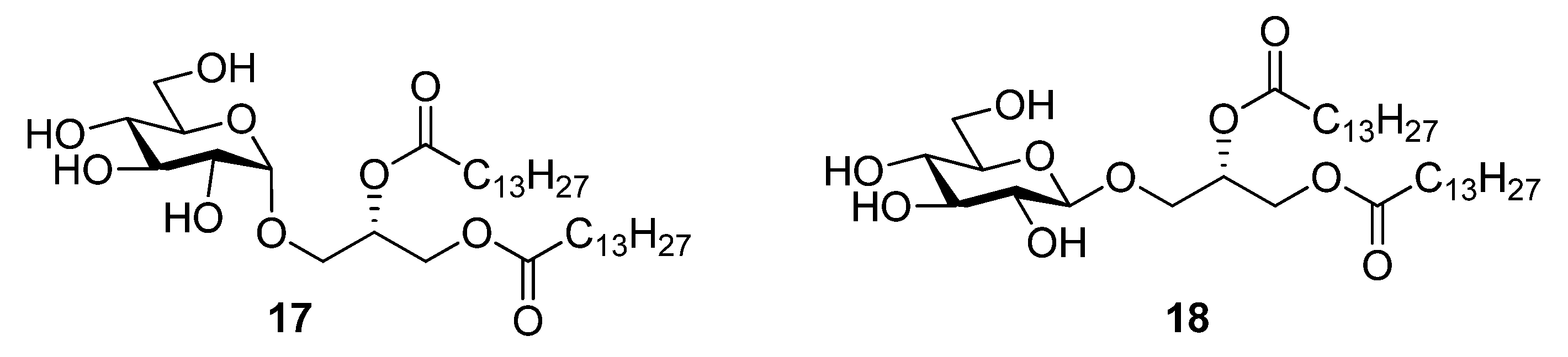
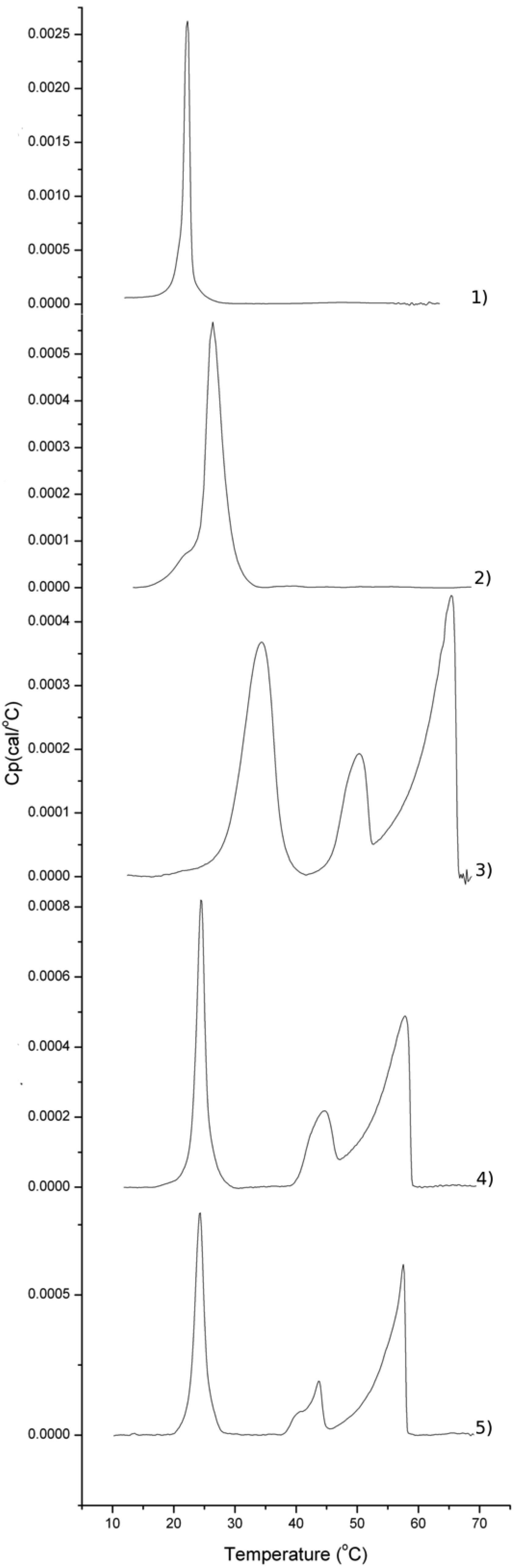
2.2. Thermotropic Behavior of Glycoglycerolipid and Glycerophospholipids
| Sample/mol% | DMPC | DMPS | Glycoglycerolipid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glycerophospholipids | 92 | 8 | 0 |
| 18 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 18 | 79 | 8 | 13 |
| 17 | 79 | 8 | 13 |
| 15 | 79 | 8 | 13 |
| 16 | 79 | 8 | 13 |

3. Experimental
3.1. Synthesis
 ) were performed on a Perkin Elmer 341 polarimeter (Sodium D-line, λ = 589 nm) with a concentration of 10 mg/ml (c = 1), unless stated otherwise. 1H- and 13C-NMR spectra were recorded with a Bruker 500 MHz spectrometer (500 and 125 MHz respectively). Chemical shifts (δ) are reported in ppm relative to the residual solvent signal of either CDCl3 (δ = 7.26 for 1H-NMR and 77.0 for 13C-NMR) or CD3OD (δ = 3.31 for 1H-NMR and 49.0 for 13C-NMR). NMR assignments were based on COSY and HSQC NMR experiments. High-resolution mass spectral (HRMS) data were obtained on an electrospray (ESI) mass spectrometer analyzing time-of-flight (Q-TOF instrument from Micromass).
) were performed on a Perkin Elmer 341 polarimeter (Sodium D-line, λ = 589 nm) with a concentration of 10 mg/ml (c = 1), unless stated otherwise. 1H- and 13C-NMR spectra were recorded with a Bruker 500 MHz spectrometer (500 and 125 MHz respectively). Chemical shifts (δ) are reported in ppm relative to the residual solvent signal of either CDCl3 (δ = 7.26 for 1H-NMR and 77.0 for 13C-NMR) or CD3OD (δ = 3.31 for 1H-NMR and 49.0 for 13C-NMR). NMR assignments were based on COSY and HSQC NMR experiments. High-resolution mass spectral (HRMS) data were obtained on an electrospray (ESI) mass spectrometer analyzing time-of-flight (Q-TOF instrument from Micromass).
 (CHCl3): −15.8; 1H-NMR: δ = 1.33–1.43 (m, 2H, CH2 cyclohexylidene), 1.53–1.63 (m, 8H, 4 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 1.98–2.10 (7 × s, 21H, 7 × CH3 acetyl), 3.59–3.71 (m, 4H, H-5, H-5', 2 × H-6), 3.78 (dd, 1H, J = 5.9 Hz, 8.3 Hz, CHH glycerol), 3.83–3.88 (m, 2H, CH2 glycerol), 3.99 (dd, 1H, J = 6.4 Hz, 8.2 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.12 (dd, 1H, J = 2.3 Hz, 12.3 Hz, H-6'), 4.21–4.24 (m, 1H, CH glycerol), 4.27 (dd, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, 12.4 Hz, H-6'), 4.57–4.61 (2 × d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, J = 8.0 Hz, H-1, H-1'), 4.87–5.01 (m, 3H, H-2, H-2', H-4), 5.07 (t, 1H, J = 9.7 Hz, H-4'), 5.15–5.21 (m, 2H, H-3, H-3'); 13C-NMR: δ = 20.6–20.7 (7 × CH3 acetyl), 23.8, 24.0, 25.1, 34.6, 36.2 (5 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 61.8 (C-6'), 65.8 (CH2 glycerol), 68.1 (CH2 glycerol), 68.3 (C-4'), 68.9 (C-6), 69.1 (C-4), 71.1, 71.2 (C-2, C-2'), 72.0 (C-5'), 72.8 (C-3, C-3'), 73.3 (C-5), 73.9 (CH glycerol), 100.7, 100.8 (C-1, C-1'), 109.9 (Cq cyclohexylidene), 169.2, 169.3, 169.4, 169.6, 170.2, 170.2, 170.6 (7 × Cq acetyl); HRMS: C35H50O20 + Na+ requires 813.2788, found 813.2785.
(CHCl3): −15.8; 1H-NMR: δ = 1.33–1.43 (m, 2H, CH2 cyclohexylidene), 1.53–1.63 (m, 8H, 4 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 1.98–2.10 (7 × s, 21H, 7 × CH3 acetyl), 3.59–3.71 (m, 4H, H-5, H-5', 2 × H-6), 3.78 (dd, 1H, J = 5.9 Hz, 8.3 Hz, CHH glycerol), 3.83–3.88 (m, 2H, CH2 glycerol), 3.99 (dd, 1H, J = 6.4 Hz, 8.2 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.12 (dd, 1H, J = 2.3 Hz, 12.3 Hz, H-6'), 4.21–4.24 (m, 1H, CH glycerol), 4.27 (dd, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, 12.4 Hz, H-6'), 4.57–4.61 (2 × d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, J = 8.0 Hz, H-1, H-1'), 4.87–5.01 (m, 3H, H-2, H-2', H-4), 5.07 (t, 1H, J = 9.7 Hz, H-4'), 5.15–5.21 (m, 2H, H-3, H-3'); 13C-NMR: δ = 20.6–20.7 (7 × CH3 acetyl), 23.8, 24.0, 25.1, 34.6, 36.2 (5 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 61.8 (C-6'), 65.8 (CH2 glycerol), 68.1 (CH2 glycerol), 68.3 (C-4'), 68.9 (C-6), 69.1 (C-4), 71.1, 71.2 (C-2, C-2'), 72.0 (C-5'), 72.8 (C-3, C-3'), 73.3 (C-5), 73.9 (CH glycerol), 100.7, 100.8 (C-1, C-1'), 109.9 (Cq cyclohexylidene), 169.2, 169.3, 169.4, 169.6, 170.2, 170.2, 170.6 (7 × Cq acetyl); HRMS: C35H50O20 + Na+ requires 813.2788, found 813.2785.
 (MeOH): −24.1; 1H-NMR (CD3OD): δ = 1.37–1.46 (m, 2H, CH2 cyclohexylidene), 1.56–1.68 (m, 8H, 4 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 3.18–3.25 (m, 2H, H-2, H-2'), 3.28–3.39 (m, 5H, H-3, H-3', H-4, H-4', H-5'), 3.45–3.49 (m, 1H, H-5), 3.62 (dd, 1H, J = 6.0 Hz, 10.6 Hz, CHH glycerol), 3.68 (dd, 1H, J = 5.3 Hz, 11.9 Hz, H-6'), 3.77–3.84 (m, 2H, H-6, CHH glycerol), 3.86–3.94 (m, 2H, H-6', CHH glycerol), 4.08 (dd, 1H, J = 6.4 Hz, 8.4 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.16 (dd, 1H, J = 2.0 Hz, 11.5 Hz, H-6), 4.32 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1), 4.33–4.37 (m, 1H, CH glycerol), 4.38 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1'); 13C-NMR (CD3OD): δ = 24.8, 25.0, 26.2, 35.9, 37.5 (5 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 62.7 (C-6'), 67.4 (CH2 glycerol), 69.9 (C-6), 71.4, 71.6 (C-4, C-4'), 71.6 (CH2 glycerol), 75.0, 75.1 (C-2, C-2'), 75.5 (CH glycerol), 77.0 (C-5'), 77.8 (C-5), 78.0 (C-3. C-3'), 104.7, 104.9 (C-1, C-1'), 111.1 (Cq cyclohexylidene); HRMS: C21H36O13 + Na+ requires 519.2048, found 519.2053.
(MeOH): −24.1; 1H-NMR (CD3OD): δ = 1.37–1.46 (m, 2H, CH2 cyclohexylidene), 1.56–1.68 (m, 8H, 4 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 3.18–3.25 (m, 2H, H-2, H-2'), 3.28–3.39 (m, 5H, H-3, H-3', H-4, H-4', H-5'), 3.45–3.49 (m, 1H, H-5), 3.62 (dd, 1H, J = 6.0 Hz, 10.6 Hz, CHH glycerol), 3.68 (dd, 1H, J = 5.3 Hz, 11.9 Hz, H-6'), 3.77–3.84 (m, 2H, H-6, CHH glycerol), 3.86–3.94 (m, 2H, H-6', CHH glycerol), 4.08 (dd, 1H, J = 6.4 Hz, 8.4 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.16 (dd, 1H, J = 2.0 Hz, 11.5 Hz, H-6), 4.32 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1), 4.33–4.37 (m, 1H, CH glycerol), 4.38 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1'); 13C-NMR (CD3OD): δ = 24.8, 25.0, 26.2, 35.9, 37.5 (5 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 62.7 (C-6'), 67.4 (CH2 glycerol), 69.9 (C-6), 71.4, 71.6 (C-4, C-4'), 71.6 (CH2 glycerol), 75.0, 75.1 (C-2, C-2'), 75.5 (CH glycerol), 77.0 (C-5'), 77.8 (C-5), 78.0 (C-3. C-3'), 104.7, 104.9 (C-1, C-1'), 111.1 (Cq cyclohexylidene); HRMS: C21H36O13 + Na+ requires 519.2048, found 519.2053.
 (MeOH): −21.9; 1H-NMR (CD3OD): δ = 1.06 (s, 9H, tBu), 1.37–1.43 (m, 2H, CH2 cyclohexylidene), 1.55–1.62 (m, 8H, 4 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 3.22–3.28 (m, 2H, H-2, H-2'), 3.35–3.45 (m, 5H, H-3, H-3', H-4, H-4', H-5'), 3.47–3.51 (m, 1H, H-5), 3.61 (dd, 1H, J = 6.0 Hz, 10.5 Hz, CHH glycerol), 3.76–3.82 (m, 2H, H-6, CHH glycerol), 3.89 (dd, 1H, J = 5.1 Hz, 11.1 Hz, H-6'), 3.93 (dd, 1H, J = 5.5 Hz, 10.5 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.01–4.07 (m, 2H, H-6', CHH glycerol), 4.21 (dd, 1H, J = 2.0 Hz, 11.4 Hz, H-6), 4.30–4.35 (m, 2H, H-1, CH glycerol), 4.41 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1'), 7.39–7.44 (m, 6H, Harom), 7.74–7.77 (m, 4H, Harom); 13C-NMR (CD3OD): δ = 20.2 (Cq tBu), 24.8, 25.0, 26.2 (3 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 27.4 (3 × CH3 tBu), 35.9, 37.5 (2 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 64.7 (C-6'), 67.4 (CH2 glycerol), 69.4 (C-6), 71.2, 71.4 (C-4, C-4'), 71.7 (CH2 glycerol), 75.0, 75.1 (C-2, C-2'), 75.5 (CH glycerol), 77.0 (C-5), 77.8 (C-5'), 78.2, 78.2 (C-3. C-3'), 104.7, 104.7 (C-1, C-1'), 111.0 (Cq cyclohexylidene), 128.8, 130.7, 130.8 (CHarom), 134.7, 134.9 (2 × Cq Ph), 136.7, 136.8, 136.9 (CHarom); HRMS: C37H54O13Si + Na+ requires 757.3226, found 757.3224.
(MeOH): −21.9; 1H-NMR (CD3OD): δ = 1.06 (s, 9H, tBu), 1.37–1.43 (m, 2H, CH2 cyclohexylidene), 1.55–1.62 (m, 8H, 4 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 3.22–3.28 (m, 2H, H-2, H-2'), 3.35–3.45 (m, 5H, H-3, H-3', H-4, H-4', H-5'), 3.47–3.51 (m, 1H, H-5), 3.61 (dd, 1H, J = 6.0 Hz, 10.5 Hz, CHH glycerol), 3.76–3.82 (m, 2H, H-6, CHH glycerol), 3.89 (dd, 1H, J = 5.1 Hz, 11.1 Hz, H-6'), 3.93 (dd, 1H, J = 5.5 Hz, 10.5 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.01–4.07 (m, 2H, H-6', CHH glycerol), 4.21 (dd, 1H, J = 2.0 Hz, 11.4 Hz, H-6), 4.30–4.35 (m, 2H, H-1, CH glycerol), 4.41 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1'), 7.39–7.44 (m, 6H, Harom), 7.74–7.77 (m, 4H, Harom); 13C-NMR (CD3OD): δ = 20.2 (Cq tBu), 24.8, 25.0, 26.2 (3 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 27.4 (3 × CH3 tBu), 35.9, 37.5 (2 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 64.7 (C-6'), 67.4 (CH2 glycerol), 69.4 (C-6), 71.2, 71.4 (C-4, C-4'), 71.7 (CH2 glycerol), 75.0, 75.1 (C-2, C-2'), 75.5 (CH glycerol), 77.0 (C-5), 77.8 (C-5'), 78.2, 78.2 (C-3. C-3'), 104.7, 104.7 (C-1, C-1'), 111.0 (Cq cyclohexylidene), 128.8, 130.7, 130.8 (CHarom), 134.7, 134.9 (2 × Cq Ph), 136.7, 136.8, 136.9 (CHarom); HRMS: C37H54O13Si + Na+ requires 757.3226, found 757.3224.
 (CHCl3): +10.4; 1H-NMR: δ = 1.05 (s, 9H, t-Bu), 1.33–1.40 (m, 2H, CH2 cyclohexylidene), 1.51–1.58 (m, 8H, 4 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 3.31 (dt, J = 2.8 Hz, 9.7 Hz, H-5'), 3.41–3.52 (m, 4H, H-2, H-2', H-4, CHH glycerol), 3.56–3.60 (m, 1H, H-5), 3.61-3.71 (m, 4H, H-3, H-3', H-6, CHH glycerol), 3.76 (t, 1H, J = 9.4 Hz, H-4'), 3.89–3.95 (m, 4H, 2 × H-6', 2 × CHH glycerol), 4.15–4.19 (m, 1H, CH glycerol), 4.23 (dd, 1H, J = 1.8 Hz, 11.4 Hz, H-6), 4.39 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1), 4.47 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1'), 4.54 (d, 1H, J = 11.2 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.68–4.83 (m, 6H, 3 × CH2 Bn), 4.88–4.95 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 Bn), 5.01 (d, 1H, J = 11.2 Hz, CHH Bn), 7.16–7.42 (m, 36H, Harom), 7.69–7.72 (m, 2H, Harom), 7.76–7.78 (m, 2H, Harom); 13C-NMR: δ = 19.3 (Cq tBu), 23.8, 24.0, 25.1 (3 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 26.8 (3 × CH3 tBu), 34.8, 36.4 (2 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 62.7 (C-6'), 66.3 (CH2 glycerol), 68.2 (C-6), 70.3 (CH2 glycerol), 73.9 (CH glycerol), 74.8, 74.8, 74.9, 75.1 (4 × CH2 Bn), 75.2 (C-5), 75.6 (CH2 Bn), 75.7 (C-5’), 75.9 (CH2 Bn), 77.6 (C-4'), 78.1 (C-4), 82.1 (C-2), 82.4 (C-2'), 84.6, 84.9 (C-3, C-3'), 103.7 (C-1), 104.0 (C-1'), 109.9 (Cq cyclohexylidene), 127.4–128.4 (CHarom), 129.6, 129.6 (CHarom), 133.1, 133.6 (2 × Cq Ph), 135.6, 135.9 (CHarom), 138.1, 138.3, 138.4, 138.5, 138.6, 138.6 (6 × Cq Bn); HRMS: C79H90O13Si + Na+ requires 1297.6043, found 1297.6042.
(CHCl3): +10.4; 1H-NMR: δ = 1.05 (s, 9H, t-Bu), 1.33–1.40 (m, 2H, CH2 cyclohexylidene), 1.51–1.58 (m, 8H, 4 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 3.31 (dt, J = 2.8 Hz, 9.7 Hz, H-5'), 3.41–3.52 (m, 4H, H-2, H-2', H-4, CHH glycerol), 3.56–3.60 (m, 1H, H-5), 3.61-3.71 (m, 4H, H-3, H-3', H-6, CHH glycerol), 3.76 (t, 1H, J = 9.4 Hz, H-4'), 3.89–3.95 (m, 4H, 2 × H-6', 2 × CHH glycerol), 4.15–4.19 (m, 1H, CH glycerol), 4.23 (dd, 1H, J = 1.8 Hz, 11.4 Hz, H-6), 4.39 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1), 4.47 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1'), 4.54 (d, 1H, J = 11.2 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.68–4.83 (m, 6H, 3 × CH2 Bn), 4.88–4.95 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 Bn), 5.01 (d, 1H, J = 11.2 Hz, CHH Bn), 7.16–7.42 (m, 36H, Harom), 7.69–7.72 (m, 2H, Harom), 7.76–7.78 (m, 2H, Harom); 13C-NMR: δ = 19.3 (Cq tBu), 23.8, 24.0, 25.1 (3 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 26.8 (3 × CH3 tBu), 34.8, 36.4 (2 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 62.7 (C-6'), 66.3 (CH2 glycerol), 68.2 (C-6), 70.3 (CH2 glycerol), 73.9 (CH glycerol), 74.8, 74.8, 74.9, 75.1 (4 × CH2 Bn), 75.2 (C-5), 75.6 (CH2 Bn), 75.7 (C-5’), 75.9 (CH2 Bn), 77.6 (C-4'), 78.1 (C-4), 82.1 (C-2), 82.4 (C-2'), 84.6, 84.9 (C-3, C-3'), 103.7 (C-1), 104.0 (C-1'), 109.9 (Cq cyclohexylidene), 127.4–128.4 (CHarom), 129.6, 129.6 (CHarom), 133.1, 133.6 (2 × Cq Ph), 135.6, 135.9 (CHarom), 138.1, 138.3, 138.4, 138.5, 138.6, 138.6 (6 × Cq Bn); HRMS: C79H90O13Si + Na+ requires 1297.6043, found 1297.6042.
 (CHCl3): +10.3; 1H-NMR: δ = 1.05 (s, 9H, t-Bu), 3.33 (dt, J = 2.7 Hz, 9.6 Hz, H-5’), 3.39–3.44 (m, 3H, H-2, H-4, CHH glycerol), 3.48–3.52 (m, 1H, H-2'), 3.55 (dd, 1H, J = 4.0 Hz, 11.4 Hz, CHH glycerol), 3.59–3.77 (m, 8H, H-3, H-3', H-4', H-5, H-6, CH glycerol, 2 × CHH glycerol), 3.91–3.94 (m, 2H, 2 × H-6'), 4.19–4.22 (m, 1H, H-6), 4.38 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1), 4.47 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1'), 4.53 (d, 1H, J = 11.2 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.67 (d, 1H, J = 10.8 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.71–4.93 (m, 9H, 4 × CH2 Bn, CHH Bn), 4.97 (d, 1H, J = 11.0 Hz, CHH Bn) 7.16–7.40 (m, 36H, Harom), 7.68–7.70 (m, 2H, Harom), 7.73–7.76 (m, 2H, Harom); 13C-NMR): δ = 19.3 (Cq tBu), 26.8 (3 × CH3 tBu), 62.7 (C-6'), 63.5 (CH2 glycerol), 68.3 (C-6), 70.6 (CH glycerol), 73.2 (CH2 glycerol), 74.9, 74.9, 75.1, 75.1 (4 × CH2 Bn), 75.2 (C-5), 75.7 (CH2 Bn), 75.7 (C-5'), 75.8 (CH2 Bn), 77.7 (C-4'), 78.2 (C-4), 82.1 (C-2), 82.5 (C-2'), 84.6, 84.7 (C-3, C-3'), 103.9, 103.9 (C-1, C-1'), 127.6–128.1 (CHarom), 128.3–128.4 (CHarom), 129.6, 129.6 (CHarom), 133.1, 133.6 (2 × Cq Ph), 135.5, 135.9 (CHarom), 137.9, 138.2, 138.2, 138.4, 138.4, 138.5 (6 × Cq Bn); HRMS: C73H82O13Si + Na+ requires 1217.5417, found 1217.5424.
(CHCl3): +10.3; 1H-NMR: δ = 1.05 (s, 9H, t-Bu), 3.33 (dt, J = 2.7 Hz, 9.6 Hz, H-5’), 3.39–3.44 (m, 3H, H-2, H-4, CHH glycerol), 3.48–3.52 (m, 1H, H-2'), 3.55 (dd, 1H, J = 4.0 Hz, 11.4 Hz, CHH glycerol), 3.59–3.77 (m, 8H, H-3, H-3', H-4', H-5, H-6, CH glycerol, 2 × CHH glycerol), 3.91–3.94 (m, 2H, 2 × H-6'), 4.19–4.22 (m, 1H, H-6), 4.38 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1), 4.47 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1'), 4.53 (d, 1H, J = 11.2 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.67 (d, 1H, J = 10.8 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.71–4.93 (m, 9H, 4 × CH2 Bn, CHH Bn), 4.97 (d, 1H, J = 11.0 Hz, CHH Bn) 7.16–7.40 (m, 36H, Harom), 7.68–7.70 (m, 2H, Harom), 7.73–7.76 (m, 2H, Harom); 13C-NMR): δ = 19.3 (Cq tBu), 26.8 (3 × CH3 tBu), 62.7 (C-6'), 63.5 (CH2 glycerol), 68.3 (C-6), 70.6 (CH glycerol), 73.2 (CH2 glycerol), 74.9, 74.9, 75.1, 75.1 (4 × CH2 Bn), 75.2 (C-5), 75.7 (CH2 Bn), 75.7 (C-5'), 75.8 (CH2 Bn), 77.7 (C-4'), 78.2 (C-4), 82.1 (C-2), 82.5 (C-2'), 84.6, 84.7 (C-3, C-3'), 103.9, 103.9 (C-1, C-1'), 127.6–128.1 (CHarom), 128.3–128.4 (CHarom), 129.6, 129.6 (CHarom), 133.1, 133.6 (2 × Cq Ph), 135.5, 135.9 (CHarom), 137.9, 138.2, 138.2, 138.4, 138.4, 138.5 (6 × Cq Bn); HRMS: C73H82O13Si + Na+ requires 1217.5417, found 1217.5424.
 (CHCl3): +12.3; 1H-NMR): δ = 0.91 (t, 6H, J = 6.8 Hz, 2 × CH3 myristoyl), 1.08 (s, 9H, t-Bu), 1.21–1.37 (m, 40H, 20 × CH2 myristoyl), 1.53–1.61 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 myristoyl), 2.20–2.29 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 myristoyl), 3.32–3.36 (m, 1H, H-5'), 3.43–3.46 (m, 1H, H-2), 3.47–3.62 (m, 4H, H-2', H-4, H-5, CHH glycerol), 3.63–3.73 (m, 3H, H-3, H-3', H-6), 3.80 (t, 1H, J = 9.4 Hz, H-4'), 3.93–3.97 (m, 2H, 2 × H-6'), 4.00 (dd, 1H, J = 4.6 Hz, 10.8 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.16 (dd, 1H, J = 7.1 Hz, 11.9 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.23–4.28 (m, 2H, H-6, CHH glycerol), 4.37 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1), 4.46 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1'), 4.57 (d, 1H, J = 11.2 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.69–4.87 (m, 6H, 3 × CH2 Bn), 4.91–4.98 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 Bn), 5.04 (d, 1H, J = 11.2 Hz, CHH Bn), 5.15–5.19 (m, 1H, CH glycerol), 7.17–7.44 (m, 36H, Harom), 7.71–7.74 (m, 2H, Harom), 7.77–7.81 (m, 2H, Harom); 13C-NMR): δ = 14.1 (2 × CH3 myristoyl), 19.3 (Cq tBu), 22.7 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 24.8, 24.9 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 26.8 (3 × CH3 tBu), 29.1–29.7 (16 × CH2 myristoyl), 31.9 (2 × CH2 myristoyl, 34.0, 34.2 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 62.7, 62.7 (C-6', CH2 glycerol), 68.1 (CH2 glycerol), 68.3 (C-6), 69.8 (CH glycerol), 74.7, 74.8, 74.8 (3 × CH2 Bn), 75.0 (C-5), 75.1, 75.6 (2 × CH2 Bn), 75.7 (C-5'), 75.9 (CH2 Bn), 77.6 (C-4'), 78.0 (C-4), 81.9 (C-2), 82.3 (C-2'), 84.5, 84.8 (C-3, C-3'), 103.8, 104.0 (C-1, C-1'), 127.5–128.4 (CHarom), 129.5, 129.6 (CHarom), 133.1, 133.6 (2 × Cq Ph), 135.5, 135.9 (CHarom), 138.1, 138.3, 138.3, 138.5, 138.5, 138.6 (6 × Cq Bn), 172.9, 173.2 (2 × Cq myristoyl).
(CHCl3): +12.3; 1H-NMR): δ = 0.91 (t, 6H, J = 6.8 Hz, 2 × CH3 myristoyl), 1.08 (s, 9H, t-Bu), 1.21–1.37 (m, 40H, 20 × CH2 myristoyl), 1.53–1.61 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 myristoyl), 2.20–2.29 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 myristoyl), 3.32–3.36 (m, 1H, H-5'), 3.43–3.46 (m, 1H, H-2), 3.47–3.62 (m, 4H, H-2', H-4, H-5, CHH glycerol), 3.63–3.73 (m, 3H, H-3, H-3', H-6), 3.80 (t, 1H, J = 9.4 Hz, H-4'), 3.93–3.97 (m, 2H, 2 × H-6'), 4.00 (dd, 1H, J = 4.6 Hz, 10.8 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.16 (dd, 1H, J = 7.1 Hz, 11.9 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.23–4.28 (m, 2H, H-6, CHH glycerol), 4.37 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1), 4.46 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1'), 4.57 (d, 1H, J = 11.2 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.69–4.87 (m, 6H, 3 × CH2 Bn), 4.91–4.98 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 Bn), 5.04 (d, 1H, J = 11.2 Hz, CHH Bn), 5.15–5.19 (m, 1H, CH glycerol), 7.17–7.44 (m, 36H, Harom), 7.71–7.74 (m, 2H, Harom), 7.77–7.81 (m, 2H, Harom); 13C-NMR): δ = 14.1 (2 × CH3 myristoyl), 19.3 (Cq tBu), 22.7 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 24.8, 24.9 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 26.8 (3 × CH3 tBu), 29.1–29.7 (16 × CH2 myristoyl), 31.9 (2 × CH2 myristoyl, 34.0, 34.2 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 62.7, 62.7 (C-6', CH2 glycerol), 68.1 (CH2 glycerol), 68.3 (C-6), 69.8 (CH glycerol), 74.7, 74.8, 74.8 (3 × CH2 Bn), 75.0 (C-5), 75.1, 75.6 (2 × CH2 Bn), 75.7 (C-5'), 75.9 (CH2 Bn), 77.6 (C-4'), 78.0 (C-4), 81.9 (C-2), 82.3 (C-2'), 84.5, 84.8 (C-3, C-3'), 103.8, 104.0 (C-1, C-1'), 127.5–128.4 (CHarom), 129.5, 129.6 (CHarom), 133.1, 133.6 (2 × Cq Ph), 135.5, 135.9 (CHarom), 138.1, 138.3, 138.3, 138.5, 138.5, 138.6 (6 × Cq Bn), 172.9, 173.2 (2 × Cq myristoyl).
 (CHCl3): +14.0; 1H-NMR: δ = 0.89 (t, 6H, J = 7.0 Hz, 2 × CH3 myristoyl), 1.23–1.33 (m, 40H, 20 × CH2 myristoyl), 1.53–1.61 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 myristoyl), 2.10 (t, 1H, J = 6.4 Hz, 6'-OH), 2.20–2.29 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 myristoyl), 3.35 (ddd, 1H, J = 2.7 Hz, 4.8 Hz, 9.6 Hz, H-5'), 3.39–3.58(m, 6H, H-2, H-2', H-4, H-4', H-5, CHH glycerol), 3.63–3.73 (m, 4H, H-3, H-3', H-6, H-6'), 3.83–3.88 (m, 1H, H-6'), 3.94 (dd, 1H, J = 4.6 Hz, 10.9 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.10 (dd, 1H, J = 1.4 Hz, 11.3 Hz, H-6), 4.16 (dd, 1H, J = 7.0 Hz, 12.0 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.27 (dd, 1H, J = 3.5 Hz, 12.0 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.33 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1), 4.47 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1'), 4.55 (d, 1H, J = 11.1 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.65 (d, 1H, J = 11.0 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.69 (d, 1H, J = 11.1 Hz, CHH Bn) , 4.75–4.80 (m, 3H, CH2 Bn, CHH Bn), 4.82 (d, 1H, J = 10.9 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.87 (d, 1H, J = 11.0 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.91–4.96 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 Bn), 5.15–5.19 (m, 1H, CH glycerol), 7.21–7.37 (m, 30H, Harom); 13C-NMR: δ = 14.1 (2 × CH3 myristoyl), 22.7 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 24.9, 24.9 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 29.1–29.7 (16 × CH2 myristoyl), 31.9 (2 × CH2 myristoyl, 34.1, 34.2 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 62.0 (C-6'), 62.7 (CH2 glycerol), 68.0 (CH2 glycerol), 68.8 (C-6), 69.9 (CH glycerol), 74.7, 74.8, 74.9 (3 × CH2 Bn), 74.9 (C-5), 75.0 (CH2 Bn), 75.1 (C-5'), 75.7 (2 × CH2 Bn), 77.6 (C-4'), 77.8 (C-4), 81.9 (C-2), 82.1 (C-2'), 84.5, 84.6 (C-3, C-3'), 103.8 (C-1), 103.9 (C-1'), 127.6–128.4 (CHarom), 137.9, 138.0, 138.3, 138.3, 138.4, 138.5 (6 × Cq Bn), 173.0, 173.3 (2 × Cq myristoyl); HRMS: C85H116O15 + Na+ requires 1399.8206, found 1399.8209.
(CHCl3): +14.0; 1H-NMR: δ = 0.89 (t, 6H, J = 7.0 Hz, 2 × CH3 myristoyl), 1.23–1.33 (m, 40H, 20 × CH2 myristoyl), 1.53–1.61 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 myristoyl), 2.10 (t, 1H, J = 6.4 Hz, 6'-OH), 2.20–2.29 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 myristoyl), 3.35 (ddd, 1H, J = 2.7 Hz, 4.8 Hz, 9.6 Hz, H-5'), 3.39–3.58(m, 6H, H-2, H-2', H-4, H-4', H-5, CHH glycerol), 3.63–3.73 (m, 4H, H-3, H-3', H-6, H-6'), 3.83–3.88 (m, 1H, H-6'), 3.94 (dd, 1H, J = 4.6 Hz, 10.9 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.10 (dd, 1H, J = 1.4 Hz, 11.3 Hz, H-6), 4.16 (dd, 1H, J = 7.0 Hz, 12.0 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.27 (dd, 1H, J = 3.5 Hz, 12.0 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.33 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1), 4.47 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1'), 4.55 (d, 1H, J = 11.1 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.65 (d, 1H, J = 11.0 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.69 (d, 1H, J = 11.1 Hz, CHH Bn) , 4.75–4.80 (m, 3H, CH2 Bn, CHH Bn), 4.82 (d, 1H, J = 10.9 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.87 (d, 1H, J = 11.0 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.91–4.96 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 Bn), 5.15–5.19 (m, 1H, CH glycerol), 7.21–7.37 (m, 30H, Harom); 13C-NMR: δ = 14.1 (2 × CH3 myristoyl), 22.7 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 24.9, 24.9 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 29.1–29.7 (16 × CH2 myristoyl), 31.9 (2 × CH2 myristoyl, 34.1, 34.2 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 62.0 (C-6'), 62.7 (CH2 glycerol), 68.0 (CH2 glycerol), 68.8 (C-6), 69.9 (CH glycerol), 74.7, 74.8, 74.9 (3 × CH2 Bn), 74.9 (C-5), 75.0 (CH2 Bn), 75.1 (C-5'), 75.7 (2 × CH2 Bn), 77.6 (C-4'), 77.8 (C-4), 81.9 (C-2), 82.1 (C-2'), 84.5, 84.6 (C-3, C-3'), 103.8 (C-1), 103.9 (C-1'), 127.6–128.4 (CHarom), 137.9, 138.0, 138.3, 138.3, 138.4, 138.5 (6 × Cq Bn), 173.0, 173.3 (2 × Cq myristoyl); HRMS: C85H116O15 + Na+ requires 1399.8206, found 1399.8209.
 (CHCl3): +13.9; 1H-NMR: δ = 1.28–1.43 (m, 2H, CH2 cyclohexylidene), 1.50–1.60 (m, 8H, 4 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 2.13 (bs, 1H, 6'-OH), 3.33 (ddd, J = 2.6 Hz, 4.7 Hz, 9.5 Hz, H-5'), 3.40–3.48 (m, 4H, H-2, H-2', H-4, CHH glycerol), 3.50–3.56 (m, 2H, H-4', H-5), 3.60–3.75 (m, 5H, H-3, H-3', H-6, H-6', CHH glycerol), 3.81–3.86 (m, 1H, H-6'), 3.89 (dd, 1H, J = 4.9 Hz, 10.4 Hz, CHH glycerol), 3.93 (dd, 1H, J = 6.3 Hz, 8.2 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.04–4.07 (m, 1H, H-6), 4.17–4.22 (m, 1H, CH glycerol), 4.35 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1), 4.48 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1'), 4.53 (d, 1H, J = 11.1 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.63 (d, 1H, J = 11.0 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.68 (d, 1H, J = 11.1 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.72–4.85 (m, 6H, 2 × CH2 Bn, CHH Bn), 4.89–4.94 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 Bn), 7.18–7.39 (m, 30H, Harom); 13C-NMR: δ = 23.7, 23.9, 25.1 (3 × CH2 cyclo-hexylidene), 34.8, 36.4 (2 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 62.0 (C-6’), 66.4 (CH2 glycerol), 68.9 (C-6), 70.3 (CH2 glycerol), 73.8 (CH glycerol), 74.7, 74.8, 74.9, 75.0 (4 × CH2 Bn), 75.0 (C-5), 75.1 (C-5'), 75.6, 75.6 (2 × CH2 Bn), 77.5 (C-4'), 77.9 (C-4), 82.0 (C-2), 82.1 (C-2'), 84.6, 84.6 (C-3, C-3'), 103.6 (C-1), 104.0 (C-1'), 109.9 (Cq cyclohexylidene), 127.6–128.4 (CHarom), 137.9, 138.0, 138.3, 138.3, 138.4, 138.5 (6 × Cq Bn); HRMS: C63H72O13 + Na+ requires 1059.4865, found 1059.4878.
(CHCl3): +13.9; 1H-NMR: δ = 1.28–1.43 (m, 2H, CH2 cyclohexylidene), 1.50–1.60 (m, 8H, 4 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 2.13 (bs, 1H, 6'-OH), 3.33 (ddd, J = 2.6 Hz, 4.7 Hz, 9.5 Hz, H-5'), 3.40–3.48 (m, 4H, H-2, H-2', H-4, CHH glycerol), 3.50–3.56 (m, 2H, H-4', H-5), 3.60–3.75 (m, 5H, H-3, H-3', H-6, H-6', CHH glycerol), 3.81–3.86 (m, 1H, H-6'), 3.89 (dd, 1H, J = 4.9 Hz, 10.4 Hz, CHH glycerol), 3.93 (dd, 1H, J = 6.3 Hz, 8.2 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.04–4.07 (m, 1H, H-6), 4.17–4.22 (m, 1H, CH glycerol), 4.35 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1), 4.48 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1'), 4.53 (d, 1H, J = 11.1 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.63 (d, 1H, J = 11.0 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.68 (d, 1H, J = 11.1 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.72–4.85 (m, 6H, 2 × CH2 Bn, CHH Bn), 4.89–4.94 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 Bn), 7.18–7.39 (m, 30H, Harom); 13C-NMR: δ = 23.7, 23.9, 25.1 (3 × CH2 cyclo-hexylidene), 34.8, 36.4 (2 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 62.0 (C-6’), 66.4 (CH2 glycerol), 68.9 (C-6), 70.3 (CH2 glycerol), 73.8 (CH glycerol), 74.7, 74.8, 74.9, 75.0 (4 × CH2 Bn), 75.0 (C-5), 75.1 (C-5'), 75.6, 75.6 (2 × CH2 Bn), 77.5 (C-4'), 77.9 (C-4), 82.0 (C-2), 82.1 (C-2'), 84.6, 84.6 (C-3, C-3'), 103.6 (C-1), 104.0 (C-1'), 109.9 (Cq cyclohexylidene), 127.6–128.4 (CHarom), 137.9, 138.0, 138.3, 138.3, 138.4, 138.5 (6 × Cq Bn); HRMS: C63H72O13 + Na+ requires 1059.4865, found 1059.4878.
 (CHCl3): +3.9; 1H-NMR: δ = 1.03 (s, 9H, t-Bu), 1.23–1.40 (m, 2H, CH2 cyclohexylidene), 1.50–1.61 (m, 8H, 4 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 3.35 (dd, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, 9.1 Hz, H-2'), 3.38–3.44 (m, 6H, H-2, H-4, H-4', H-5, H-5', CHH glycerol), 3.52–3.56 (m, 1H, H-3'), 3.59–3.63 (m, 2H, H-3, H-6'), 3.70 (dd, 1H, J = 6.2 Hz, 8.2 Hz, CHH glycerol), 3.72–3.80 (m, 2H, H-5″, H-6), 3.85–3.87 (m, 2H, 2 × H-6″), 3.91–3.95 (m, 2H, 2 × CHH glycerol), 4.06–4.10 (m, 1H, H-6'), 4.17–4.25 (m, 2H, H-6, CH glycerol), 4.31 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1), 4.39–4.43 (m, 2H, H-1', CHH Bn), 4.48 (d, 1H, J = 11.1 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.57 (d, 1H, J = 11.2 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.66–4.73 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 Bn), 4.76 (d, 1H, J = 11.0 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.84 (d, 1H, J = 7.9 Hz, H-1″), 4.87 (d, 1H, J = 11.0 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.90–4.94 (m, 3H, CH2 Bn, CHH Bn), 5.57 (dd, 1H, J = 7.9 Hz, 9.7 Hz, H-2″), 5.62 (t, 1H, J = 9.7 Hz, H-4″), 5.81 (t, 1H, J = 9.7 Hz, H-3″), 7.10–7.13 (m, 2H, Harom), 7.16–7.41 (m, 42H, Harom), 7.51–7.54 (m, 1H, Harom), 7.57–7.59 (m, 2H, Harom), 7.70–7.72 (m, 2H, Harom), 7.81–7.87 (m, 4H, Harom), 7.89–7.92 (m, 2H, Harom); 13C-NMR: δ = 19.1 (Cq tBu), 23.8, 24.0, 25.1 (3 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 26.6 (3 × CH3 tBu), 34.8, 36.4 (2 × CH2 cyclo-hexylidene), 62.8 (C-6″), 66.3 (CH2 glycerol), 68.0, 68.0 (C-6, C-6'), 69.2 (C-4″), 70.2 (CH2 glycerol), 72.1 (C-2″), 73.3 (C-3″), 73.9 (CH glycerol), 74.3 (C-5'), 74.5, 74.7, 74.8, 74.9 (4 × CH2 Bn), 75.2, 75.3 (C-5, C-5″), 75.5, 75.5 (2 × CH2 Bn), 77.4 (C-4'), 78.0 (C-4), 82.0 (C-2'), 82.0 (C-2), 84.6 (C-3), 84.7 (C-3'), 101.3 (C-1″), 103.5 (C-1), 103.9 (C-1'), 109.9 (Cq cyclohexylidene), 127.5–128.4 (CHarom), 128.9, 129.2, 129.4 (3 × Cq Bz), 129.6–129.8 (CHarom), 133.0 (Cq Ph), 133.0 (CHarom), 133.0 (Cq Ph), 133.1, 133.2 (CHarom), 135.5, 135.6 (CHarom), 138.1, 138.1, 138.4, 138.5, 138.5, 138.6 (6 × Cq Bn), 164.9, 164.9, 165.9 (3 × Cq Bz); HRMS: C106H112O21Si + Na+ requires 1771.7358, found 1771.7367.
(CHCl3): +3.9; 1H-NMR: δ = 1.03 (s, 9H, t-Bu), 1.23–1.40 (m, 2H, CH2 cyclohexylidene), 1.50–1.61 (m, 8H, 4 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 3.35 (dd, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, 9.1 Hz, H-2'), 3.38–3.44 (m, 6H, H-2, H-4, H-4', H-5, H-5', CHH glycerol), 3.52–3.56 (m, 1H, H-3'), 3.59–3.63 (m, 2H, H-3, H-6'), 3.70 (dd, 1H, J = 6.2 Hz, 8.2 Hz, CHH glycerol), 3.72–3.80 (m, 2H, H-5″, H-6), 3.85–3.87 (m, 2H, 2 × H-6″), 3.91–3.95 (m, 2H, 2 × CHH glycerol), 4.06–4.10 (m, 1H, H-6'), 4.17–4.25 (m, 2H, H-6, CH glycerol), 4.31 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1), 4.39–4.43 (m, 2H, H-1', CHH Bn), 4.48 (d, 1H, J = 11.1 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.57 (d, 1H, J = 11.2 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.66–4.73 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 Bn), 4.76 (d, 1H, J = 11.0 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.84 (d, 1H, J = 7.9 Hz, H-1″), 4.87 (d, 1H, J = 11.0 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.90–4.94 (m, 3H, CH2 Bn, CHH Bn), 5.57 (dd, 1H, J = 7.9 Hz, 9.7 Hz, H-2″), 5.62 (t, 1H, J = 9.7 Hz, H-4″), 5.81 (t, 1H, J = 9.7 Hz, H-3″), 7.10–7.13 (m, 2H, Harom), 7.16–7.41 (m, 42H, Harom), 7.51–7.54 (m, 1H, Harom), 7.57–7.59 (m, 2H, Harom), 7.70–7.72 (m, 2H, Harom), 7.81–7.87 (m, 4H, Harom), 7.89–7.92 (m, 2H, Harom); 13C-NMR: δ = 19.1 (Cq tBu), 23.8, 24.0, 25.1 (3 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 26.6 (3 × CH3 tBu), 34.8, 36.4 (2 × CH2 cyclo-hexylidene), 62.8 (C-6″), 66.3 (CH2 glycerol), 68.0, 68.0 (C-6, C-6'), 69.2 (C-4″), 70.2 (CH2 glycerol), 72.1 (C-2″), 73.3 (C-3″), 73.9 (CH glycerol), 74.3 (C-5'), 74.5, 74.7, 74.8, 74.9 (4 × CH2 Bn), 75.2, 75.3 (C-5, C-5″), 75.5, 75.5 (2 × CH2 Bn), 77.4 (C-4'), 78.0 (C-4), 82.0 (C-2'), 82.0 (C-2), 84.6 (C-3), 84.7 (C-3'), 101.3 (C-1″), 103.5 (C-1), 103.9 (C-1'), 109.9 (Cq cyclohexylidene), 127.5–128.4 (CHarom), 128.9, 129.2, 129.4 (3 × Cq Bz), 129.6–129.8 (CHarom), 133.0 (Cq Ph), 133.0 (CHarom), 133.0 (Cq Ph), 133.1, 133.2 (CHarom), 135.5, 135.6 (CHarom), 138.1, 138.1, 138.4, 138.5, 138.5, 138.6 (6 × Cq Bn), 164.9, 164.9, 165.9 (3 × Cq Bz); HRMS: C106H112O21Si + Na+ requires 1771.7358, found 1771.7367.
 (CHCl3): +3.2; 1H-NMR: δ = 1.06 (s, 9H, t-Bu), 1.28–1.42 (m, 2H, CH2 cyclohexylidene), 1.50–1.61 (m, 8H, 4 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 3.30 (dd, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, 9.2 Hz, H-2″), 3.37–3.51 (m, 8H, H-2, H-2', H-3″, H-4, H-4', H-5', H-5″, CHH glycerol), 3.54–3.66 (m, 5H, H-3, H-3', H-4″, H-5, H-6'), 3.72–3.78 (m, 2H, H-6, CHH glycerol), 3.87–3.93 (m, 2H, 2 × H-6″), 3.93–4.00 (m, 2H, 2 × CHH glycerol), 4.04–4.09 (m, 2H, H-6, H-6'), 4.26–4.30 (m, 2H, H-1″, CH glycerol), 4.39 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1), 4.47 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1'), 4.52 (d, 1H, J = 11.1 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.59 (d, 1H, J = 11.1 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.68 (d, 1H, J = 11.1 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.73–4.79 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 Bn), 4.84 (d, 1H, J = 11.0 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.89–4.94 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 Bn), 7.18–7.43 (m, 36H, Harom), 7.69–7.72 (m, 4H, Harom); 13C-NMR: δ = 19.2 (Cq tBu), 23.8, 24.0, 25.1 (3 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 26.8 (3 × CH3 tBu), 34.8, 36.5 (2 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 64.7 (C-6″), 66.5 (CH2 glycerol), 66.9 (C-6'), 68.9 (C-6), 70.4 (CH2 glycerol), 71.9 (C-4″), 72.4 (C-2″), 73.8 (CH glycerol), 74.2 (C-5’), 74.8 (CH2 Bn), 74.8 (C-5″), 74.8 (CH2 Bn), 74.9 (C-5), 75.0, 75.0, 75.7, 75.7 (4 × CH2 Bn), 76.1 (C-3″), 77.9 (C-4'), 78.0 (C-4), 82.0 (C-2'), 82.1 (C-2), 84.6, 84.6 (C-3, C-3'), 102.9 (C-1″), 103.6 (C-1), 103.9 (C-1'), 110.0 (Cq cyclohexylidene), 127.6–128.4 (CHarom), 129.8, 129.8 (CHarom), 132.8 (Cq Ph), 132.9 (Cq Ph), 135.6, 135.6 (CHarom), 137.9, 137.9, 138.2, 138.3, 138.4, 138.5 (6 × Cq Bn); HRMS: C85H100O18Si + Na+ requires 1459.6571, found 1459.6587.
(CHCl3): +3.2; 1H-NMR: δ = 1.06 (s, 9H, t-Bu), 1.28–1.42 (m, 2H, CH2 cyclohexylidene), 1.50–1.61 (m, 8H, 4 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 3.30 (dd, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, 9.2 Hz, H-2″), 3.37–3.51 (m, 8H, H-2, H-2', H-3″, H-4, H-4', H-5', H-5″, CHH glycerol), 3.54–3.66 (m, 5H, H-3, H-3', H-4″, H-5, H-6'), 3.72–3.78 (m, 2H, H-6, CHH glycerol), 3.87–3.93 (m, 2H, 2 × H-6″), 3.93–4.00 (m, 2H, 2 × CHH glycerol), 4.04–4.09 (m, 2H, H-6, H-6'), 4.26–4.30 (m, 2H, H-1″, CH glycerol), 4.39 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1), 4.47 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1'), 4.52 (d, 1H, J = 11.1 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.59 (d, 1H, J = 11.1 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.68 (d, 1H, J = 11.1 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.73–4.79 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 Bn), 4.84 (d, 1H, J = 11.0 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.89–4.94 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 Bn), 7.18–7.43 (m, 36H, Harom), 7.69–7.72 (m, 4H, Harom); 13C-NMR: δ = 19.2 (Cq tBu), 23.8, 24.0, 25.1 (3 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 26.8 (3 × CH3 tBu), 34.8, 36.5 (2 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 64.7 (C-6″), 66.5 (CH2 glycerol), 66.9 (C-6'), 68.9 (C-6), 70.4 (CH2 glycerol), 71.9 (C-4″), 72.4 (C-2″), 73.8 (CH glycerol), 74.2 (C-5’), 74.8 (CH2 Bn), 74.8 (C-5″), 74.8 (CH2 Bn), 74.9 (C-5), 75.0, 75.0, 75.7, 75.7 (4 × CH2 Bn), 76.1 (C-3″), 77.9 (C-4'), 78.0 (C-4), 82.0 (C-2'), 82.1 (C-2), 84.6, 84.6 (C-3, C-3'), 102.9 (C-1″), 103.6 (C-1), 103.9 (C-1'), 110.0 (Cq cyclohexylidene), 127.6–128.4 (CHarom), 129.8, 129.8 (CHarom), 132.8 (Cq Ph), 132.9 (Cq Ph), 135.6, 135.6 (CHarom), 137.9, 137.9, 138.2, 138.3, 138.4, 138.5 (6 × Cq Bn); HRMS: C85H100O18Si + Na+ requires 1459.6571, found 1459.6587.
 (CHCl3): +9.6; 1H-NMR: δ = 1.06 (s, 9H, t-Bu), 1.28–1.41 (m, 2H, CH2 cyclohexylidene), 1.50–1.61 (m, 8H, 4 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 3.27–3.31 (m, 2H, H-4, H-5″), 3.36–3.41 (m, 2H, H-2', CHH glycerol), 3.45–3.49 (m, 2H, H-2″, H-5), 3.52–3.73 (m, 9H, H-2, H-3, H-3', H-3″, H-4, H-5', H-6, H-6', CHH glycerol), 3.78 (t, 1H, J = 9.3 Hz, H-4″), 3.89–3.94 (m, 4H, 2 × H-6″, 2 × CHH glycerol), 4.14–4.20 (m, 2H, H-6, CH glycerol), 4.25–4.29 (m, 1H, H-6'), 4.28 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1'), 4.36 (d, 1H, J = 10.9 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.41 (d, 1H, J = 7.7 Hz, H-1), 4.56 (d, 1H, J = 11.4 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.59 (d, 1H, J = 7.9 Hz, H-1″), 4.63–4.81 (m, 9H, 4 × CH2 Bn, CHH Bn), 4.87–4.97 (m, 6H, 3 × CH2 Bn), 5.06 (d, 1H, J = 11.2 Hz, CHH Bn), 7.12-7.42 (m, 51H, Harom), 7.69–7.73 (m, 2H, Harom), 7.75–7.80 (m, 2H, Harom); 13C-NMR: δ = 19.3 (Cq tBu), 23.8, 24.0, 25.1 (3 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 26.8 (3 × CH3 tBu), 34.9, 36.4 (2 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 62.6 (C-6″), 66.3 (CH2 glycerol), 68.4, 68.4 (C-6, C-6'), 70.2 (CH2 glycerol), 73.9 (CH glycerol), 74.6 (C-5'), 74.6, 74.7, 74.8, 74.8, 74.9, 75.1 (6 × CH2 Bn), 75.4 (C-5″), 75.5, 75.7 (2 × CH2 Bn), 75.7 (C-5), 75.8 (CH2 Bn), 77.6 (C-4″), 78.0 (C-4), 78.2 (C-4'), 82.0 (C-2'), 82.2 (C-2″), 82.3 (C-2), 84.5, 84.8, 84.9 (C-3, C-3', C-3″), 103.5 (C-1'), 104.1 (C-1, C-1″), 109.9 (Cq cyclohexylidene), 127.5–128.4 (CHarom), 129.6, 129.6 (CHarom), 133.1 (Cq Ph), 133.7 (Cq Ph), 135.5, 135.9 (CHarom), 137.9–138.6 (9 × Cq Bn); HRMS: C106H118O18Si + Na+ requires 1729.7980, found 1729.7984.
(CHCl3): +9.6; 1H-NMR: δ = 1.06 (s, 9H, t-Bu), 1.28–1.41 (m, 2H, CH2 cyclohexylidene), 1.50–1.61 (m, 8H, 4 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 3.27–3.31 (m, 2H, H-4, H-5″), 3.36–3.41 (m, 2H, H-2', CHH glycerol), 3.45–3.49 (m, 2H, H-2″, H-5), 3.52–3.73 (m, 9H, H-2, H-3, H-3', H-3″, H-4, H-5', H-6, H-6', CHH glycerol), 3.78 (t, 1H, J = 9.3 Hz, H-4″), 3.89–3.94 (m, 4H, 2 × H-6″, 2 × CHH glycerol), 4.14–4.20 (m, 2H, H-6, CH glycerol), 4.25–4.29 (m, 1H, H-6'), 4.28 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1'), 4.36 (d, 1H, J = 10.9 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.41 (d, 1H, J = 7.7 Hz, H-1), 4.56 (d, 1H, J = 11.4 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.59 (d, 1H, J = 7.9 Hz, H-1″), 4.63–4.81 (m, 9H, 4 × CH2 Bn, CHH Bn), 4.87–4.97 (m, 6H, 3 × CH2 Bn), 5.06 (d, 1H, J = 11.2 Hz, CHH Bn), 7.12-7.42 (m, 51H, Harom), 7.69–7.73 (m, 2H, Harom), 7.75–7.80 (m, 2H, Harom); 13C-NMR: δ = 19.3 (Cq tBu), 23.8, 24.0, 25.1 (3 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 26.8 (3 × CH3 tBu), 34.9, 36.4 (2 × CH2 cyclohexylidene), 62.6 (C-6″), 66.3 (CH2 glycerol), 68.4, 68.4 (C-6, C-6'), 70.2 (CH2 glycerol), 73.9 (CH glycerol), 74.6 (C-5'), 74.6, 74.7, 74.8, 74.8, 74.9, 75.1 (6 × CH2 Bn), 75.4 (C-5″), 75.5, 75.7 (2 × CH2 Bn), 75.7 (C-5), 75.8 (CH2 Bn), 77.6 (C-4″), 78.0 (C-4), 78.2 (C-4'), 82.0 (C-2'), 82.2 (C-2″), 82.3 (C-2), 84.5, 84.8, 84.9 (C-3, C-3', C-3″), 103.5 (C-1'), 104.1 (C-1, C-1″), 109.9 (Cq cyclohexylidene), 127.5–128.4 (CHarom), 129.6, 129.6 (CHarom), 133.1 (Cq Ph), 133.7 (Cq Ph), 135.5, 135.9 (CHarom), 137.9–138.6 (9 × Cq Bn); HRMS: C106H118O18Si + Na+ requires 1729.7980, found 1729.7984.
 (CHCl3): +8.1; 1H-NMR: δ = 1.06 (s, 9H, t-Bu), 3.31–3.79 (m, 19H, H-2, H-2', H-2″, H-3, H-3', H-3″, H-4, H-4', H-4″, H-5, H-5', H-5″, H-6, H-6', 2 × CH2 glycerol, CH glycerol), 3.92–3.94 (m, 2H, 2 × H-6″), 4.16 (dd, 1H, J = 1.6 Hz, 11.6 Hz, H-6), 4.24–4.27 (m, 1H, H-6'), 4.29 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1'), 4.36 (d, 1H, J = 10.9 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.47–4.51 (m, 2H, H-1, H-1″), 4.55 (d, 1H, J = 11.3 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.61 (d, 1H, J = 10.9 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.68–4.95 (m, 14H, 7 × CH2 Bn), 5.04 (d, 1H, J = 11.2 Hz, CHH Bn), 7.09–7.41 (m, 51H, Harom), 7.69–7.72 (m, 2H, Harom), 7.75–7.79 (m, 2H, Harom); 13C-NMR: δ = 19.3 (Cq tBu), 26.8 (3 × CH3 tBu), 62.7 (C-6″), 63.4 (CH2 glycerol), 68.2, 68.3 (C-6, C-6'), 70.7 (CH glycerol), 72.8 (CH2 glycerol), 74.8, 74.9, 74.9 (3 × CH2 Bn), 74.9, 75.0 (C-5, C-5'), 75.0, 75.0, 75.2 (3 × CH2 Bn), 75.5 (C-5″), 75.6, 75.6, 75.8 (3 × CH2 Bn), 77.7, 78.0, 78.3 (C-4, C-4', C-4″), 81.9, 82.1, 82.5 (C-2, C-2', C-2″), 84.5, 84.6, 84.7 (C-3, C-3', C-3″), 103.7, 104.0, 104.0 (C-1, C-1', C-1″), 127.5–128.4 (CHarom), 129.6, 129.6 (CHarom), 133.1 (Cq Ph), 133.6 (Cq Ph), 135.5, 135.9 (CHarom), 137.9–138.6 (9 × Cq Bn); HRMS: C100H110O18Si + Na+ requires 1649.7354, found 1649.7360.
(CHCl3): +8.1; 1H-NMR: δ = 1.06 (s, 9H, t-Bu), 3.31–3.79 (m, 19H, H-2, H-2', H-2″, H-3, H-3', H-3″, H-4, H-4', H-4″, H-5, H-5', H-5″, H-6, H-6', 2 × CH2 glycerol, CH glycerol), 3.92–3.94 (m, 2H, 2 × H-6″), 4.16 (dd, 1H, J = 1.6 Hz, 11.6 Hz, H-6), 4.24–4.27 (m, 1H, H-6'), 4.29 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1'), 4.36 (d, 1H, J = 10.9 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.47–4.51 (m, 2H, H-1, H-1″), 4.55 (d, 1H, J = 11.3 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.61 (d, 1H, J = 10.9 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.68–4.95 (m, 14H, 7 × CH2 Bn), 5.04 (d, 1H, J = 11.2 Hz, CHH Bn), 7.09–7.41 (m, 51H, Harom), 7.69–7.72 (m, 2H, Harom), 7.75–7.79 (m, 2H, Harom); 13C-NMR: δ = 19.3 (Cq tBu), 26.8 (3 × CH3 tBu), 62.7 (C-6″), 63.4 (CH2 glycerol), 68.2, 68.3 (C-6, C-6'), 70.7 (CH glycerol), 72.8 (CH2 glycerol), 74.8, 74.9, 74.9 (3 × CH2 Bn), 74.9, 75.0 (C-5, C-5'), 75.0, 75.0, 75.2 (3 × CH2 Bn), 75.5 (C-5″), 75.6, 75.6, 75.8 (3 × CH2 Bn), 77.7, 78.0, 78.3 (C-4, C-4', C-4″), 81.9, 82.1, 82.5 (C-2, C-2', C-2″), 84.5, 84.6, 84.7 (C-3, C-3', C-3″), 103.7, 104.0, 104.0 (C-1, C-1', C-1″), 127.5–128.4 (CHarom), 129.6, 129.6 (CHarom), 133.1 (Cq Ph), 133.6 (Cq Ph), 135.5, 135.9 (CHarom), 137.9–138.6 (9 × Cq Bn); HRMS: C100H110O18Si + Na+ requires 1649.7354, found 1649.7360.
 (CHCl3): +10.7; 1H-NMR: δ = 0.88 (t, 6H, J = 6.9 Hz, 2 × CH3 myristoyl), 1.04 (s, 9H, t-Bu), 1.19–1.29 (m, 40H, 20 × CH2 myristoyl), 1.51–1.58 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 myristoyl), 2.18–2.26 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 myristoyl), 3.25–3.68 (m, 11H, H-2, H-2', H-2″, H-3, H-3', H-4, H-4', H-5, H-5', H-5″, CHH glycerol), 3.63–3.68 (m, 3H, H-3″, H-6, H-6'), 3.76 (t, 1H, J = 9.3 Hz, H-4″), 3.90–3.93 (m, 3H, CHH glycerol, 2 × H-6″), 4.11 (dd, 1H, J = 7.3 Hz, 11.9 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.16 (m, 1H, H-6), 4.20–4.27 (m, 3H, H-1', H-6', CHH glycerol), 4.36 (d, 1H, J = 11.0 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.39 (d, 1H, J = 7.7 Hz, H-1), 4.51 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1″), 4.54 (d, 1H, J = 11.4 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.60–4.79 (m, 9H, 4 × CH2 Bn, CHH Bn), 4.85–4.96 (m, 6H, 3 × CH2 Bn), 5.04 (d, 1H, J = 11.2 Hz, CHH Bn), 5.12-5.15 (m, 1H, CH glycerol), 7.11–7.41 (m, 51H, Harom), 7.69–7.71 (m, 2H, Harom), 7.74–7.77 (m, 2H, Harom); 13C-NMR: δ = 14.1 (2 × CH3 myristoyl), 19.3 (Cq tBu), 22.7 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 24.9, 24.9 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 26.8 (3 × CH3 tBu), 29.1–29.7 (16 × CH2 myristoyl), 31.9 (2 × CH2 myristoyl, 34.1, 34.3 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 62.6 (C-6″), 62.8 (CH2 glycerol), 68.0 (CH2 glycerol) 68.4, 68.5 (C-6, C-6'), 69.8 (CH glycerol), 74.6 (CH2 Bn), 74.6 (C-5'), 74.7, 74.8, 74.9, 74.9, 75.1 (5 × CH2 Bn), 75.2 (C-5), 75.5, 75.6 (2 × CH2 Bn), 75.7 (C-5″), 75.8 (CH2 Bn), 77.6 (C-4″), 78.0, 78.1 (C-4, C-4'), 81.8, 82.1, 82.3 (C-2, C-2', C-2″), 84.4, 84.8, 84.8 (C-3, C-3', C-3″), 103.6, 104.1, 104.2 (C-1, C-1', C-1″), 127.5–128.4 (CHarom), 129.6, 129.6 (CHarom), 133.1 (Cq Ph), 133.6 (Cq Ph), 135.5, 135.9 (CHarom), 138.0–138.6 (9 × Cq Bn), 172.9, 173.3 (2 × Cq myristoyl); HRMS: C128H162O20Si + Na+ requires 2071.1354, found 2071.1370.
(CHCl3): +10.7; 1H-NMR: δ = 0.88 (t, 6H, J = 6.9 Hz, 2 × CH3 myristoyl), 1.04 (s, 9H, t-Bu), 1.19–1.29 (m, 40H, 20 × CH2 myristoyl), 1.51–1.58 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 myristoyl), 2.18–2.26 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 myristoyl), 3.25–3.68 (m, 11H, H-2, H-2', H-2″, H-3, H-3', H-4, H-4', H-5, H-5', H-5″, CHH glycerol), 3.63–3.68 (m, 3H, H-3″, H-6, H-6'), 3.76 (t, 1H, J = 9.3 Hz, H-4″), 3.90–3.93 (m, 3H, CHH glycerol, 2 × H-6″), 4.11 (dd, 1H, J = 7.3 Hz, 11.9 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.16 (m, 1H, H-6), 4.20–4.27 (m, 3H, H-1', H-6', CHH glycerol), 4.36 (d, 1H, J = 11.0 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.39 (d, 1H, J = 7.7 Hz, H-1), 4.51 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1″), 4.54 (d, 1H, J = 11.4 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.60–4.79 (m, 9H, 4 × CH2 Bn, CHH Bn), 4.85–4.96 (m, 6H, 3 × CH2 Bn), 5.04 (d, 1H, J = 11.2 Hz, CHH Bn), 5.12-5.15 (m, 1H, CH glycerol), 7.11–7.41 (m, 51H, Harom), 7.69–7.71 (m, 2H, Harom), 7.74–7.77 (m, 2H, Harom); 13C-NMR: δ = 14.1 (2 × CH3 myristoyl), 19.3 (Cq tBu), 22.7 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 24.9, 24.9 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 26.8 (3 × CH3 tBu), 29.1–29.7 (16 × CH2 myristoyl), 31.9 (2 × CH2 myristoyl, 34.1, 34.3 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 62.6 (C-6″), 62.8 (CH2 glycerol), 68.0 (CH2 glycerol) 68.4, 68.5 (C-6, C-6'), 69.8 (CH glycerol), 74.6 (CH2 Bn), 74.6 (C-5'), 74.7, 74.8, 74.9, 74.9, 75.1 (5 × CH2 Bn), 75.2 (C-5), 75.5, 75.6 (2 × CH2 Bn), 75.7 (C-5″), 75.8 (CH2 Bn), 77.6 (C-4″), 78.0, 78.1 (C-4, C-4'), 81.8, 82.1, 82.3 (C-2, C-2', C-2″), 84.4, 84.8, 84.8 (C-3, C-3', C-3″), 103.6, 104.1, 104.2 (C-1, C-1', C-1″), 127.5–128.4 (CHarom), 129.6, 129.6 (CHarom), 133.1 (Cq Ph), 133.6 (Cq Ph), 135.5, 135.9 (CHarom), 138.0–138.6 (9 × Cq Bn), 172.9, 173.3 (2 × Cq myristoyl); HRMS: C128H162O20Si + Na+ requires 2071.1354, found 2071.1370.
 (CHCl3): +12.5; 1H-NMR: δ = 0.89 (t, 6H, J = 7.0 Hz, 2 × CH3 myristoyl), 1.19–1.34 (m, 40H, 20 × CH2 myristoyl), 1.51–1.59 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 myristoyl), 2.17–2.25 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 myristoyl), 3.26–3.69 (m, 15H, H-2, H-2', H-2″, H-3, H-3', H-3″, H-4, H-4', H-4″, H-5, H-5', H-5″, H-6, H-6″, CHH glycerol), 3.74 (dd, 1H J = 5.2 Hz, 11.1 Hz, H-6'), 3.83 (dd, 1H, J = 2.6 Hz, 11.9 Hz, H-6″), 3.92 (dd, 1H, J = 4.6 Hz, 10.9 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.06–4.15 (m, 3H, H-6, H-6', CHH glycerol), 4.23–4.27 (m, 2H, H-1, CHH glycerol), 4.39–4.44 (m, 2H, H-1', CHH Bn), 4.46 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1″), 4.55 (d, 1H, J = 11.2 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.62–4.68 (m, 3H, CH2 Bn, CHH Bn), 4.71–4.79 (m, 6H, 3 × CH2 Bn), 4.84 (d, 1H, J = 11.0 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.87–4.96 (m, 6H, 3 × CH2 Bn), 5.13–5.17 (m, 1H, CH glycerol), 7.16–7.36 (m, 45H, Harom); 13C-NMR: δ = 14.1 (2 × CH3 myristoyl), 22.7 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 24.9, 24.9 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 29.1–29.7 (16 × CH2 myristoyl), 31.9 (2 × CH2 myristoyl, 34.1, 34.3 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 62.0 (C-6″), 62.8 CH2 glycerol), 68.0 (CH2 glycerol), 68.7 (C-6), 69.3 (C-6'), 69.8 (CH glycerol), 74.6 (C-5'), 74.6, 74.8, 74.8, 74.9, 74.9 (5 × CH2 Bn), 75.0 (C-5), 75.0 (CH2 Bn), 75.2 (C-5″), 75.6, 75.6, 75.7 (3 × CH2 Bn), 77.6, 78.0, 78.0 (C-4, C-4', C-4″), 81.8, 82.1, 82.1 (C-2, C-2', C-2″), 84.5, 84.5, 84.8 (C-3, C-3', C-3″), 103.5, 104.0, 104.2 (C-1, C-1', C-1″), 127.5–128.4 (CHarom), 137.9–138.5 (9 × Cq Bn), 172.9, 173.3 (2 × Cq myristoyl); HRMS: C112H144O20 + Na+ requires 1832.0143, found 1832.0149.
(CHCl3): +12.5; 1H-NMR: δ = 0.89 (t, 6H, J = 7.0 Hz, 2 × CH3 myristoyl), 1.19–1.34 (m, 40H, 20 × CH2 myristoyl), 1.51–1.59 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 myristoyl), 2.17–2.25 (m, 4H, 2 × CH2 myristoyl), 3.26–3.69 (m, 15H, H-2, H-2', H-2″, H-3, H-3', H-3″, H-4, H-4', H-4″, H-5, H-5', H-5″, H-6, H-6″, CHH glycerol), 3.74 (dd, 1H J = 5.2 Hz, 11.1 Hz, H-6'), 3.83 (dd, 1H, J = 2.6 Hz, 11.9 Hz, H-6″), 3.92 (dd, 1H, J = 4.6 Hz, 10.9 Hz, CHH glycerol), 4.06–4.15 (m, 3H, H-6, H-6', CHH glycerol), 4.23–4.27 (m, 2H, H-1, CHH glycerol), 4.39–4.44 (m, 2H, H-1', CHH Bn), 4.46 (d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1″), 4.55 (d, 1H, J = 11.2 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.62–4.68 (m, 3H, CH2 Bn, CHH Bn), 4.71–4.79 (m, 6H, 3 × CH2 Bn), 4.84 (d, 1H, J = 11.0 Hz, CHH Bn), 4.87–4.96 (m, 6H, 3 × CH2 Bn), 5.13–5.17 (m, 1H, CH glycerol), 7.16–7.36 (m, 45H, Harom); 13C-NMR: δ = 14.1 (2 × CH3 myristoyl), 22.7 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 24.9, 24.9 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 29.1–29.7 (16 × CH2 myristoyl), 31.9 (2 × CH2 myristoyl, 34.1, 34.3 (2 × CH2 myristoyl), 62.0 (C-6″), 62.8 CH2 glycerol), 68.0 (CH2 glycerol), 68.7 (C-6), 69.3 (C-6'), 69.8 (CH glycerol), 74.6 (C-5'), 74.6, 74.8, 74.8, 74.9, 74.9 (5 × CH2 Bn), 75.0 (C-5), 75.0 (CH2 Bn), 75.2 (C-5″), 75.6, 75.6, 75.7 (3 × CH2 Bn), 77.6, 78.0, 78.0 (C-4, C-4', C-4″), 81.8, 82.1, 82.1 (C-2, C-2', C-2″), 84.5, 84.5, 84.8 (C-3, C-3', C-3″), 103.5, 104.0, 104.2 (C-1, C-1', C-1″), 127.5–128.4 (CHarom), 137.9–138.5 (9 × Cq Bn), 172.9, 173.3 (2 × Cq myristoyl); HRMS: C112H144O20 + Na+ requires 1832.0143, found 1832.0149.

3.2. Physical Chemical Characterization
General
3.3. Methods
3.4. Fluorescence Microscopy Imaging
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Rilfors, L.; Lindblom, G. Regulation of lipid composition in biological membranes—Biophysical studies of lipids and lipid synthesizing enzymes. Colloid. Surface. B 2002, 26, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindblom, G.; Oräddd, G.; Rilfors, L.; Morein, S. Regulation of lipid composition in acholeplasmalaidlawii and escherichia coli membranes: NMR studies of lipid lateral diffusion at different growth temperatures. Biochemisty 2002, 41, 11512–11515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.S.; Thompson, M.N.; Fei, N.; Hütterman, M.; Greenberg, M.L. Cardiolipin and mitochondrial phosphatidylethanolamine have overlapping functions in mitochondrial fusion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 17589–17597. [Google Scholar]
- Rietveld, A.G.; Koorengevel, M.C.; De Kruijff, B. Non-bilayer lipids are required for efficient protein transport across the plasma membrane of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 5506–5513. [Google Scholar]
- Larsson, K.; Puang-Ngern, S. The aqueous system of monogalactosyl diglycerides and digalactosyl diglycerides—Significance to the structure of the thylakoid membrane. In Advances in the Biochemistry and Physiology of Plant Lipids; Appelqvist, L.Å., Liljenberg, C., Eds.; Elsevier/North Holland Biomedical Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1979; pp. 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Endo, T.; Inoue, K.; Nojima, S. Physical properties and barrier functions of synthetic glyceroglycolipids. J. Biochem. 1982, 92, 953–960. [Google Scholar]
- Mannock, D.A.; Lewis, R.N.A.H.; Sen, A.; McElhaney, R.N. The physical properties of glycosyldiacylglycerols. Calorimetric studies of a homologous series of 1,2-di-O-acyl-3-O-(beta-d-glucopyranosyl)-sn-glycerols. Biochemistry 1988, 27, 6852–6859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, R.; Mirzadeh, S.M.; Heidelberg, T.; Minamikawa, H.; Yoshiaki, T.; Sugimur, A. A reevaluation of the epimeric and anomeric relationship of glucosides and galactosides in thermotropic liquid crystal self-assemblies. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 2948–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meer, G. Dynamic Transbilayer Lipid Asymmetry. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, A004671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finean, J.B.; Michell, R.H. Membrane Structure; Elsevier/North Holland Biomedical Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Neurath, A.R.; Hartzell, R.W.; Rubin, B.A. Solubilization and some properties of the erythrocyte receptor for adenovirus type 7 haemagglutinin. Nature 1969, 221, 1069–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumoto, S.; Fukase, K.; Fujimoto, Y. Chemical synthesis of bacterial lipid A. In Microbial Glycobiology; Moran, A.P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 415–427. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, C.M.; Bols, M.; Qiao, Y. Total synthesis of biologically active lipoteichoic acids. ARKIVOC 2013, 2, 249–275. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, C.M.; Schmidt, R.R. Chemical synthesis of lipoteichoic acids and derivatives. In Microbial Glycobiology; Moran, A.P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 455–476. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, C.M.; Figueroa-Perez, I.; Lindner, B.; Ulmer, A.J.; Zähringer, U.; Schmidt, R.R. Total synthesis of lipoteichoic acid of streptococcus pneumonia. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 2585–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadelmaier, A.; Morath, S.; Hartung, T.; Schmidt, R.R. Synthesis of the first fully active lipoteichoic acid. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 916–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zähringer, U.; Pedersen, C.M.; Qiao, Y.; Schmidt, R.R. Chemical synthesis of bacterial lipoteichoic acids: An insight on its biological significance. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 2040–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cateni, F.; Bonivento, P.; Procida, G.; Zacchigna, M.; Favretto, L.G.; Scialino, G.; Banfi, E. Chemoenzymatic synthesis and antimicrobial activity evaluation of monoglucosyl diglycerides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannock, D.A.; Lewis, R.N.A.H.; McElhaney, R.N. An improved procedure for the preparation of 1,2-di-O-acyl-3-O-(β-d-glucopyranosyl)-sn-glycerols. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1987, 43, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, Y.; Shingu, Y.; Mengfei, Y.; Fukuda, K.; Dohi, H.; Matsuda, S.; Matsuda, K. An easy α-glycosylation methodology for the synthesis and stereochemistry of mycoplasma α-glycolipid antigens Beilsteins. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 629–639. [Google Scholar]
- Examples Of Glycerol Epimerization Under Glycosylation Conditions: Shvets, V.I.; Bashkatova, A.I.; Evstigneeva, R.P. Synthesis of glycosyl diglycerides. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1973, 10, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.M.; Danishefsky, S.J. Synthesis of a cyanobacterial sulfolipid: Confirmation of its structure, stereochemistry and anti-HIV-1 activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, H.; Oishi, T.; Kikuchi, T.; Hirama, M. Concise Synthesis of 3-O-(2-O-α-d-Glucopyranosyl-6-O-acyl-α-d-glucopyranosyl)-1,2-di-O-acyl-sn-glycerols. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 8451–8459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shingu, Y.; Nishida, Y.; Dohi, H.; Matsuda, K.; Kobayashi, K. Convenient access to halide ion-catalyzed a-glycosylation free from noxious fumes at the donor synthesis. J. Carbohyd. Chem. 2002, 21, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, E.; Ciavatta, M.L.; Pagano, D.; Fontana, A. An efficient and versatile chemical synthesis of bioactive glyco-glycerolipids. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 879–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blattner, R.; Furneaux, R.H.; Pakulski, Z. 1,3-Dideoxynojirimycin-3-yl glycosides of β-(1→3)- and β-(1→6)-linked gluco-oligosaccharides. Carbohydr. Res. 2006, 341, 2115–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-Perez, I. Synthesis of fragments and one analogue of S. Aureus LTA. Investigations toward the synthesis of S. Pneumoniae LTA. PhD Thesis, University of Konstanz, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Springfield, S.; Koh, J.T. Highly efficient synthesis of 1-thioglycosides in solution and solid phase using iminophosphorane bases. Carbohydr. Res. 2000, 325, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.R.; Behrendt, M.; Toepfer, A. Nitriles as solvents in glycosylation reactions: Highly selective β-glycoside synthesis. Synlett 1990, 11, 694–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Geng, Y.; Schmidt, R.R. Silicon fluorides for acid-base catalysis in glycosidations. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2012, 354, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield and coworkers have used 2-O-benzoyl protective groups in the synthesis of archaeal-derived glycolipid adjuvants. The optimized conditions gave high yields and -selectivity; see: Development of new glycosylation methodologies for the synthesis of archaeal-derived glycolipid adjuvants. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 214–229. [CrossRef]
- Uriel, C.; Gomez, A.M.; López, J.C.; Fraser-Reid, B. Some aspects of selectivity in the reaction of glycosyl donors. J. Carbohyd. Chem. 2005, 24, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, C.M.; Figueroa-Perez, I.; Boruwa, J.; Lindner, B.; Ulmer, A.J.; Zähringer, U.; Schmidt, R.R. Synthesis of the core structure of the lipoteichoic acid of streptococcus pneumonia. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 12627–12641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizuka, I.; Yamakawa, T. Glycoglycerolipids. In New Comprehensive Biochemistry–Glycolipids; Neuberger, A., Van Deenen, L.L.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1985; Volume 10, pp. 101–197. [Google Scholar]
- Kates, M. Glyco-, Phosphoglyco- and sulfoglycoglycerolipids of bacteria. In Handbook of Lipid Research–Glycolipids, Phosphoglycolipids, and Sulfoglycolipids; Kates, M., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; Volume 6, pp. 1–122. [Google Scholar]
- Harroun, T.A.; Koslowsky, M.; Nieh, M.-P.; DeLannoy, C.-F.; Raghunathan, V.A.; Katsaras, J. Comprehensive examination of mesophases formed by DMPC and DHPC mixtures. Langmuir 2005, 21, 5356–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, H.; Shipley, G. Interactions of divalent cations with phosphatidylserine bilayer membranes. Biochemistry 1984, 23, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trouard, T.P.; Mannock, D.A.; Lindblom, G.; Rilfors, L.; Akiyama, M.; Mcelhaney, R.N. Thermotropic phase properties of 1,2-di-O-tetradecyl-3-O-(3-O-methyl- beta-d-glucopyranosyl)-sn-glycerol. Biophys. J. 1994, 67, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, M.; Neumann, J.-M. Deuterium NMR study of head-group deuterated phosphatidylserine in pure and binary phospholipid bilayers. Interactions with monovalent cations Na+ and Li+. FEBS Lett. 1986, 199, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.; Hatzakis, N.S.; Stamou, D. Observation of inhomogeneity in the lipid composition of individual nanoscale liposomes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 10685–10687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- kesson, A.; Lundgaard, C.V.; Ehrlich, N.; Pomorski, T.G.; Stamou, D.; Cárdenas, M. Composition and structure of mixed phospholipid supported bilayers formed by POPC and DPPC. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 8972–8980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, F.; Akesson, A.; Chapuis, P.Y.; Nielsen, C.A.S.; Monopol, M.P.; Dawson, K.A.; Pomorski, T.G.; Cardenas, M. The dendrimer impact on vesicles can be tuned based on the lipid bilayer charge and the presence of albumin. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 8862–8870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, P.; Baird, B.; Holowka, D. Lipid rafts, Fluid/fluid phase separation, and their relevance to plasma membrane structure and function. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2007, 18, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, B.J.; Drummond, C.J.; Krodkiewska, I.; Grieser, F. How chain length, Headgroup polymerization, and anomeric configuration govern the thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystalline phase behavior and the air-water interfacial adsorption of glucose-based surfactants. Langmuir 2000, 16, 7359–7367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Feigenson, G.W. A microscopic interaction model of maximum solubility of cholesterol in lipid bilayers. Biophys. J. 1999, 76, 2142–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takuro, K.; Nobue, S.; Ikuo, G.; Yoshigoroa, K.; Makoto, O.; Gosuke, S.; Mitsuru, T. Incorporation and degradation of GM1 ganglioside and asialoGm1 ganglioside in cultured fibroblasts from normal individuals and patients with β-galactosidase deficiency. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1985, 31, 456–464. [Google Scholar]
- Veath, S.L.; Keller, S.L. Separation of liquid phases in giant vesicles of ternary mixtures of phospholipids and cholesterol. Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 3074–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahi, N.; Aulas, A.; Fantini, J. How Cholesterol Constrains Glycolipid Conformation for Optimal Recognition of Alzheimer's β Amyloid Peptide (Aβ1-40). PLoS One 2010, 5, e9079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.K. Nanobiotechnology of Biomimetic Membranes; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Harder, T.; Simons, K. Clusters of glycolipid and glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins in lymphoid cells: Accumulation of actin regulated by local tyrosine phosphorylation. Eur. J. Immunol. 1999, 29, 556–562. [Google Scholar]
- Varki, A. Glycobiology and medicine: An introduction. Glycolipids 1993, 3, 97–130. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hogendorf, W.F.J.; Jagalski, V.; Pomorski, T.G.; Bols, M.; Cárdenas, M.; Pedersen, C.M. Synthesis and Thermotropic Phase Behavior of Four Glycoglycerolipids. Molecules 2013, 18, 13546-13573. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181113546
Hogendorf WFJ, Jagalski V, Pomorski TG, Bols M, Cárdenas M, Pedersen CM. Synthesis and Thermotropic Phase Behavior of Four Glycoglycerolipids. Molecules. 2013; 18(11):13546-13573. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181113546
Chicago/Turabian StyleHogendorf, Wouter F. J., Vivien Jagalski, Thomas G. Pomorski, Mikael Bols, Marité Cárdenas, and Christian M. Pedersen. 2013. "Synthesis and Thermotropic Phase Behavior of Four Glycoglycerolipids" Molecules 18, no. 11: 13546-13573. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181113546
APA StyleHogendorf, W. F. J., Jagalski, V., Pomorski, T. G., Bols, M., Cárdenas, M., & Pedersen, C. M. (2013). Synthesis and Thermotropic Phase Behavior of Four Glycoglycerolipids. Molecules, 18(11), 13546-13573. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181113546




