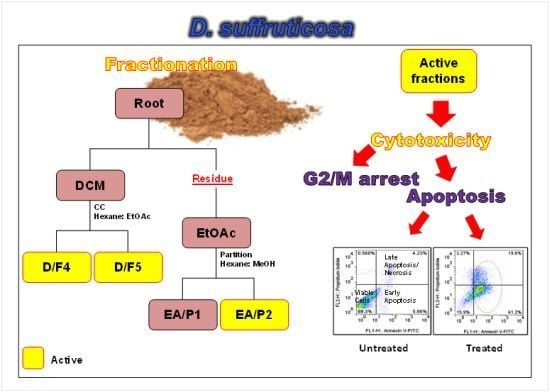
Dillenia Suffruticosa Extract Inhibits Proliferation of Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231) via Induction of G2/M Arrest and Apoptosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Cytotoxicity of DCM and EtOAc Fractions of D. Suffruticosa towards Selected Cancer Cell Lines
| Fraction | TLC Mobile Phase | TLC Rf Values | Weight (mg) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D/F1 | Hexane-EA, 9:1 v/v | 0.90, 0.98 | 17.90 | 0.90 |
| D/F2 | Hexane-EA, 9:1 v/v | 0.85, 0.90, 0.94, 0.98 | 89.40 | 4.47 |
| D/F3 | Hexane-EA, 9:1 v/v | 0.15, 0.26, 0.48, 0.52, 0.66, 0.74, 0.80, 0.89 | 139.30 | 6.97 |
| D/F4 | Hexane-EA, 4:1 v/v | 0.54, 0.68, 0.77, 0.92, 0.95 * | 606.70 | 30.34 |
| D/F5 | Hexane-EA, 3:2 v/v | 0.25, 0.48, 0.60, 0.72 * | 571.00 | 28.55 |
| D/F6 | Hexane-EA, 1:1 v/v | 0.43, 0.49, 0.59, 0.67, 0.78, 0.85 | 141.80 | 7.09 |
| D/F7 | Hexane-EA, 1:1 v/v | 0.23, 0.39, 0.48, 0.61, 0.94, 0.97 | 41.20 | 2.06 |
| D/F8 | Hexane-EA, 2:3 v/v | 0.31, 0.62, 0.74, 0.92 | 9.30 | 0.47 |
| D/F9 | Hexane-EA, 2:3 v/v | 0.24, 0.35, 0.95 | 30.20 | 1.51 |
| D/F10 | EA, 100% | 0.48, 0.93 | 8.80 | 0.44 |
| D/F11 | EA, 100% | 0.34, 0.41, 0.62, 0.77, 0.91 | 12.10 | 0.61 |
| D/F12 | EA-MeOH, 98:2 v/v | 0.06, 0.69, 0.89 | 32.20 | 1.61 |
| D/F13 | EA-MeOH, 97:3 v/v | 0.70, 0.80, 0.90 | 41.40 | 2.07 |
| D/F14 | EA-MeOH, 95:5 v/v | 0.74, 0.79, 0.93 | 13.00 | 0.65 |
| D/F15 | EA-MeOH, 9:1 v/v | 0.68, 0.77, 0.80, 0.90 | 18.50 | 0.93 |
| D/F16 | EA-MeOH, 9:1 v/v | 0.12, 0.69, 0.77, 0.83, 0.89 | 64.30 | 3.22 |
| D/F17 | EA-MeOH, 9:1 v/v | 0.11, 0.82, 0.89 | 10.20 | 0.51 |
| Cell Line/Fraction | IC50 (µg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|
| EA/P1 | EA/P2 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | >150 | 70.00 ± 1.00 |
| MCF-7 | >150 | 34.33 ± 1.53 |
| CaOV3 | >150 | 53.67 ± 0.58 |
| HeLa | >150 | 140.67 ± 2.08 |
| A549 | >150 | >150 |
| 3T3 | >150 | 94.67 ± 2.31 |
| Fraction/Cell line | IC50 (µg/mL) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDA-MB-231 | MCF-7 | HeLa | CaOV3 | A549 | 3T3 | |
| D/F1 | >150 | >150 | >150 | >150 | >150 | NA |
| D/F2 | >150 | >150 | >150 | >150 | >150 | NA |
| D/F3 | 37.33 ± 6.43 | 58.33 ± 0.58 | 50.67 ± 0.58 | 63.33 ± 0.58 | 91.00 ± 1.73 | NA |
| D/F4 | 11.67 ± 0.58 | 9.50 ± 0.50 | 21.00 ± 0.57 | 20.33 ± 1.53 | 23.00 ± 2.65 | 18.00 ± 1.15 |
| D/F5 | 17.67 ± 0.58 | 18.33 ± 0.58 | 19.00 ± 1.00 | 22.00 ± 0.58 | 21.00 ± 0.58 | 18.00 ± 0.57 |
| D/F6 | 56.00 ± 2.00 | 69.00 ± 1.73 | 59.00 ± 1.00 | 43.00 ± 1.00 | 41.33 ± 1.15 | NA |
| D/F7 | 75.67 ± 1.53 | 122.67 ± 3.06 | 93.33 ± 2.08 | 91.22 ± 1.15 | 90 ± 2 | NA |
| D/F8 | >150 | >150 | 118.33 ± 1.53 | >150 | >150 | NA |
| D/F9 | >150 | >150 | >150 | >150 | >150 | NA |
| D/F10 | >150 | >150 | >150 | >150 | >150 | NA |
| D/F11 | >150 | 42.33 ± 3.21 | 133.33 ± 1.53 | 141.67 ± 1.53 | >150 | NA |
| D/F12 | >150 | 88.67 ± 1.15 | 117.33 ± 1.53 | 125.67 ± 3.06 | 114.76 ± 2.31 | NA |
| D/F13 | 105.00 ± 2.65 | 111.00 ± 1.00 | 93.67 ± 0.58 | 95.67 ± 0.58 | 88.33 ± 2.52 | NA |
| D/F14 | 146.67 ± 1.53 | 147.33 ± 2.08 | >150 | >150 | 146.00 ± 0.58 | NA |
| D/F15 | >150 | >150 | >150 | >150 | >150 | NA |
| D/F16 | >150 | >150 | >150 | >150 | >150 | NA |
| D/F17 | 114.67 ± 3.51 | >150 | >150 | >150 | >150 | NA |
2.2. Morphological Changes of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 Cells Treated with Active Fractions of D. Suffruticosa
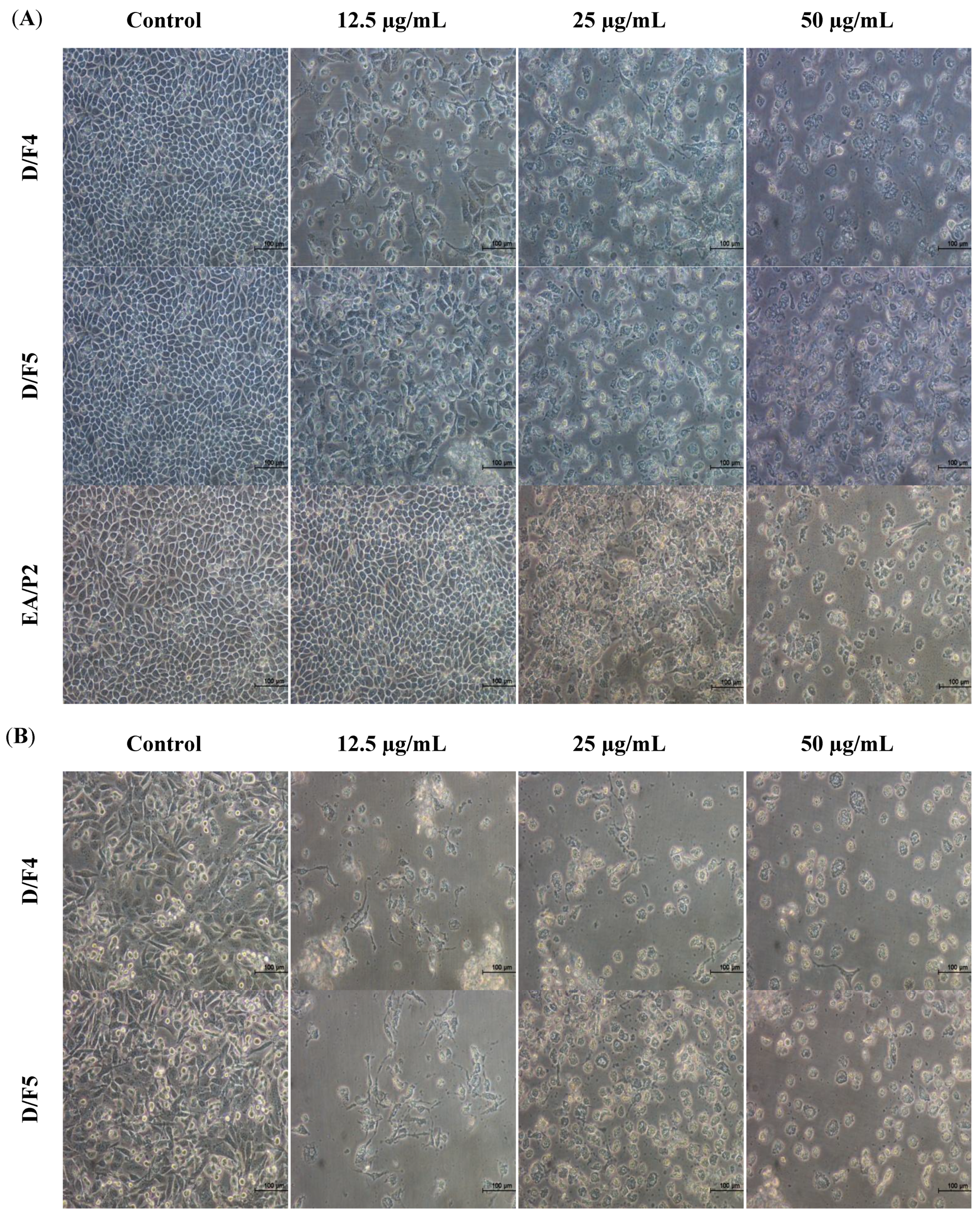
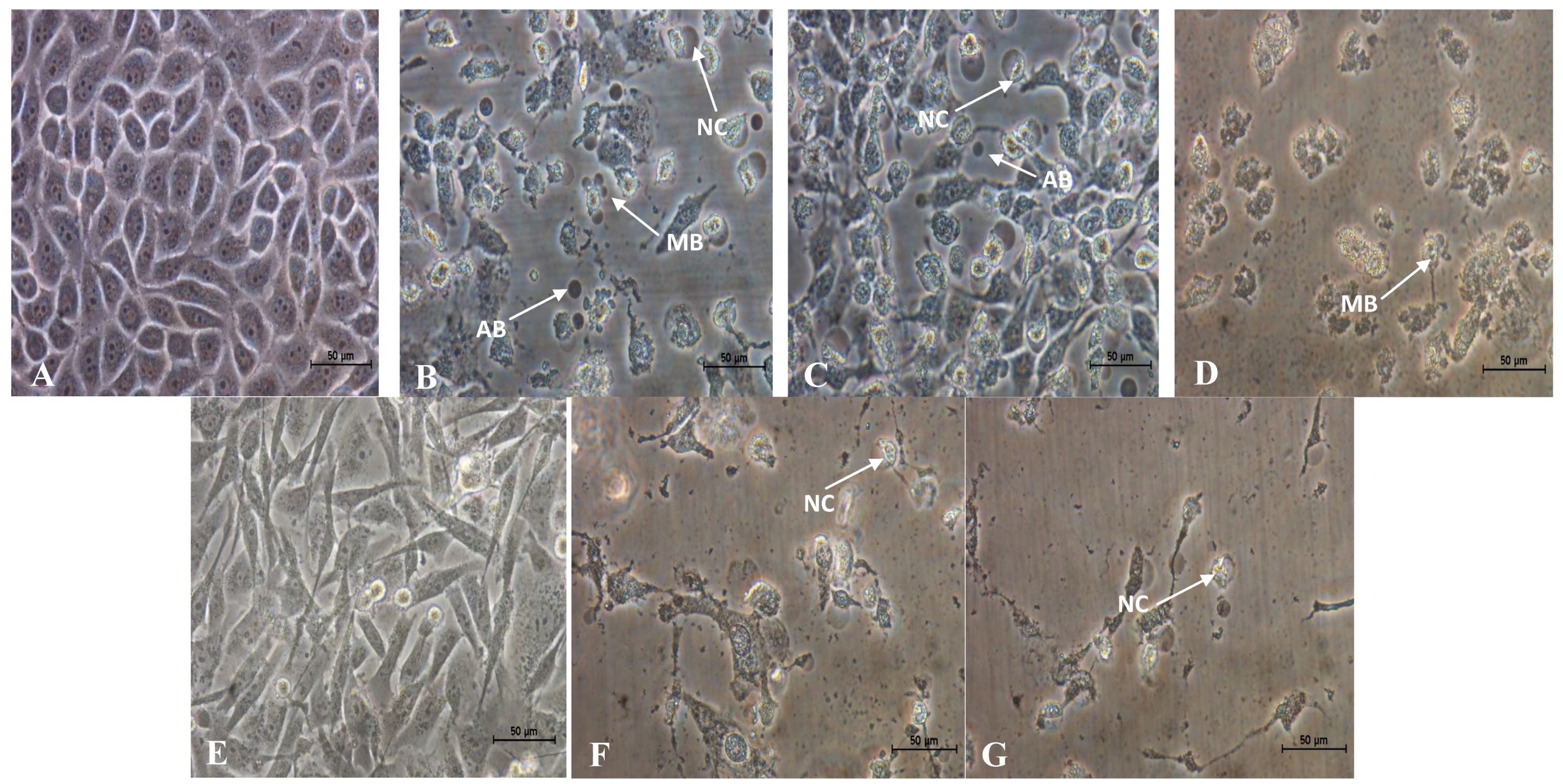
2.3. Treatment with D/F4 and D/F5 of D. Suffruticosa Induced Apoptosis in Cancer Cell Lines
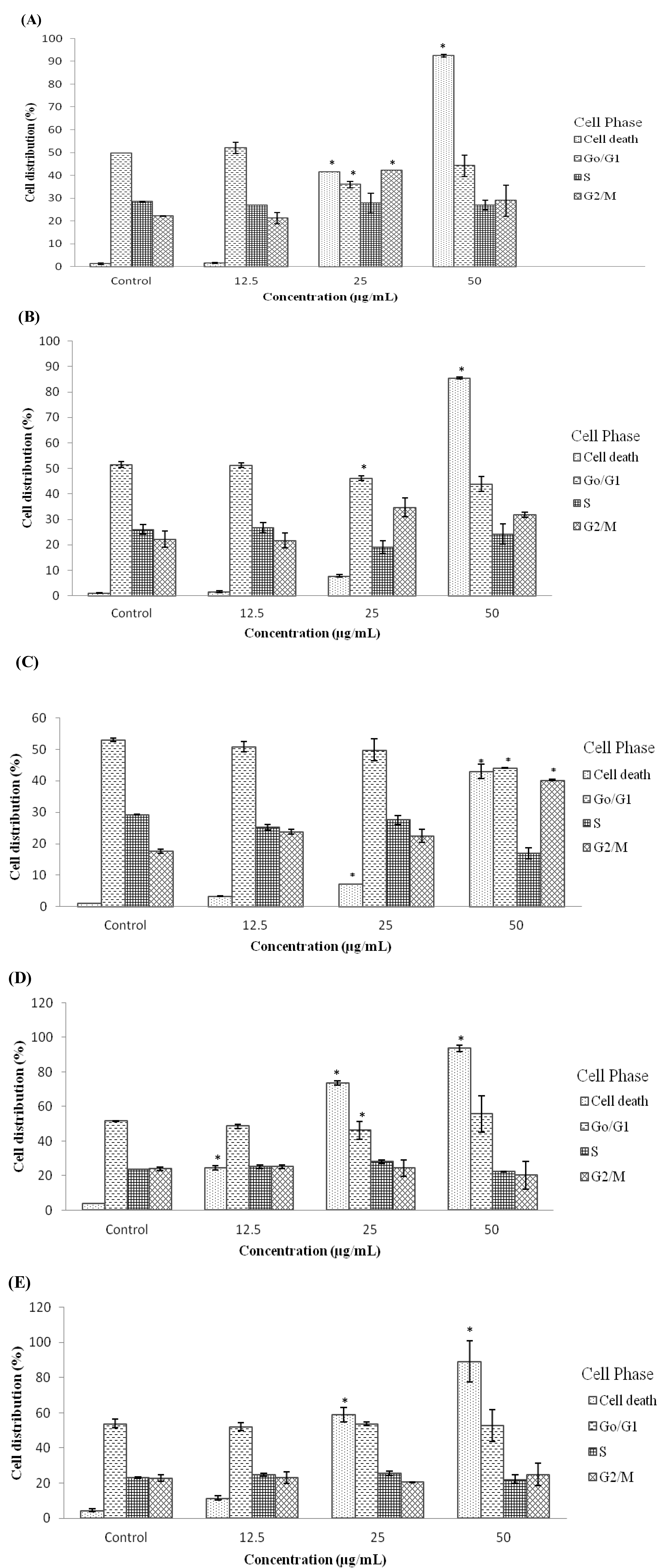
2.4. Treatment with D/F4 and EA/P2 of D. Suffruticosa Induced G2/M Phase Cell Cycle Arrest in Cancer Cell Lines

3. Experimental
3.1. Plant Material
3.2. Chemicals
3.3. Extraction of Plant Material
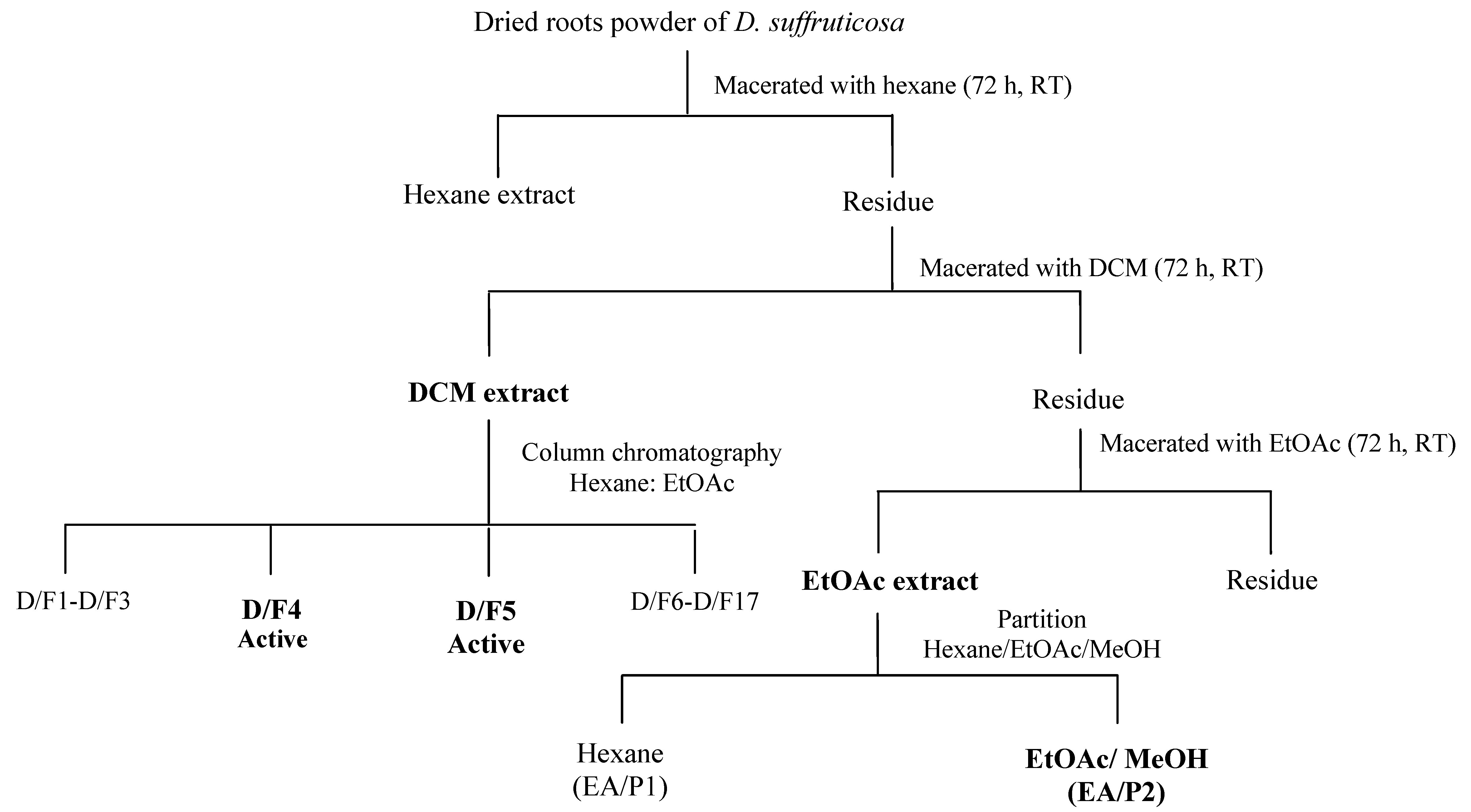
3.4. Fractionation of DCM and EtOAc Extract of D. Suffruticosa
3.5. Cell Culture
3.6. Test Sample Preparation
3.7. Determination of Cytotoxic Properties
3.8. Morphological Changes of Cells Treated with Active Fractions of D. Suffruticosa
3.9. Determination of Mode of Cell Death by Annexin V-Propidium Iodide (AnnV-PI)
3.10. Determination of Cell Cycle Arrest by Flow Cytometer
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusion
Conflicts of Interest
Acknowledgments
References
- Fahad Ullah, M.; Aatif, M. The footprints of cancer development: Cancer biomarkers. Cancer Treatment Rev. 2009, 35, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Felay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA-Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, J.; Lukas, C.; Bartek, J. Mammalian cell cycle checkpoints: Signaling pathways and their organization in space and time. DNA Repair 2004, 3, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, I. Cancer: A cell cycle defect. Radiography 2008, 14, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.W. Recycling the cell cycle: Cyclins revisited. Cell 2004, 116, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buolamwini, J.K. Cell cycle molecular targets in novel anticancer drug discovery. Curr. Pharm. Design 2000, 6, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Ganapathy, S.; Hingorani, S.R.; Srivastava, R.K. EGCG inhibits growth, Invasion, Angiogenesis and metastasis of pancreatic cancer. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.N.; Shankar, S.; Srivastava, R.K. Green tea catechin, Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): Mechanisms, Perspectives and clinical applications. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 1807–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majno, G.; Joris, I. Apoptosis, Oncosis, and necrosis. An overview of cell death. Am. J. Pathol. 1995, 146, 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- He, G.; Kuang, J.; Khokhar, A.R.; Siddik, Z.H. The impact of S and G2 checkpoint response on the fidelity of G1-arrest by cisplatin and its comparison to a non-cross-resistant platinum (IV) analog. Gynecol. Oncol. 2011, 122, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khalaf, H.H.; Lach, B.; Allam, A.; Hassounah, M.; Al-Khani, A.; Elkum, N.; Alrokayan, S.A.; Aboussekhra, A. Expression of survivin and p16INK4a/Cdk6/pRB proteins and induction of apoptosis in response to radiation and cisplatin in meningioma cells. Brain Res. 2008, 1188, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Han, P.; Kang, J.H.; Li, H.L.; Hu, S.X.; Lian, H.H.; Qiu, P.P.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.G.; Chen, Q.X. Antiproliferation and apoptosis induced by tamoxifen in human bile duct carcinoma QBC939 cells via upregulated p53 expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 385, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupertz, R.; Watjen, W.; Kahl, R.; Chovolou, Y. Dose and time-dependent effects of doxorubicin on cytotoxicity, Cell cycle and apoptotic cell death in human colon cancer cells. Toxicology 2010, 271, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corners, E.J.H. Wayside Trees of Malaya, 4th ed.; Malayan Nature Society: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hanum, F.; Hamzah, N. The use of medicinal plant species by the Temuan Tribe of Ayer Hitam Forest, Selangor, Peninsular Malaysia. Pertanika J. Trop. Agric. Sci. 1999, 22, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Tumbuhan Ubatan Malaysia; Mat Salleh, K.; Latiff, A. (Eds.) Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia: Bangi, Malaysia, 2002.
- Ahmad, F.B.; Holdsworth, D.K. Traditional medicinal plants of Sabah, Malaysia part III. The Rungus people of Kudat. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 33, 262–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armania, N.; Yazan, L.S.; Musa, S.N.; Ismail, I.S.; Foo, J.B.; Chan, K.W.; Noreen, H.; Hisyam, A.H.; Zulfahmi, S.; Ismail, M. Dillenia suffruticosa exhibited antioxidant and cytotoxic activity through induction of apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle arrest. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 146, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.J.; Cheon, J.H.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, T.; Kim, W.H. Guggulsterone induces apoptosis in colon cancer cells and inhibits tumor growth in murine colorectal cancer xenografts. Cancer Lett. 2009, 279, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.L.; Yazan, L.S.; Ismail, N.; Ismail, M. Apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of human colorectal cancer cell line HT-29 induced by vanillin. Cancer Epidemiol. 2009, 33, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangestel, C.; Peeters, M.; Oltenfreiter, R.; D’Asseler, Y.; Staelens, S.; Steenkiste, M.V.; Philippe, J.; Kusters, D.; Reutelingsperger, C.; Damme, N.V.; et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of [99mTc]-labeled tricarbonyl His-annexin A5 as an imaging agent for the detection of phosphatidylserine-expressing cells. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2010, 37, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekoj, T.; Lee, S.; Desai, S.; Trevino, J.; Babcock, T.A. G2/M cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis by n-3 fatty acids in a pancreatic cancer model. J. Surg. Res. 2007, 139, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.C.; Lieu, C.H. Cell cycle specific induction of apoptosis and necrosis by paclitaxel in the leukemic U937 cells. Life Sci. 2005, 76, 1623–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.; Ward, T.H.; Ranson, M.; Dive, C. Apoptosis pathway-targeted drugs from the bench to the clinic. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1705, 3–66. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Cheung, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chan, G.K.L.; Fong, W.F. Andrographolide induces cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase and cell death in HepG2 cells via alteration of reactive oxygen species. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 568, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Loughlin, C.; Heenan, M.; Coyle, S.; Clynes, M. Altered cell cycle response of drug-resistant lung carcinoma cells to doxorubicin. Eur. J. Cancer 2000, 36, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmink, O.H.; Hoebe, E.K.; Fukushima, M.; Peters, G.J. Irinotecan-induced cytotoxicity to colon cancer cells in vitro is stimulated by pre-incubation with trifluorothymidine. Eur. J. Cancer 2007, 43, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.C.; Li, C.H.; Ung, M.W.; Fuh, T.S.; Chen, W.L.; Fang, K. Etoposide (VP-16) elicits apoptosis following prolonged G2/M cell arrest in p53-mutated human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2005, 223, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, K.P.; Ngoubilly, N.; Neavyn, M.; Lanza-Jacoby, S. 3, 3'-Diindolylmethane and paclitaxel act synergistically to promote apoptosis in HER2/Neu human breast cancer cells. J. Surg. Res. 2006, 132, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.H.; Park, W.H. Growth inhibition in antimycin A treated-lung cancer Calu-6 cells via inducing a G1 phase arrest and apoptosis. Lung Cancer 2009, 65, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.K.; Yazan, L.S.; Ismail, M. Thymoquinone from Nigella sativa was more potent than cisplatin in eliminating of SiHa cells via apoptosis with down-regulation of Bcl-2 protein. Toxicol. Vitro 2011, 25, 1392–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, J.B.; Yazan, L.S.; Chan, K.W.; Tahir, P.M.; Ismail, M. Kenaf seed oil from supercritical carbon dioxide fluid extraction induced G1 phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in leukemia cells. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 5389–5397. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: The active fractions of D. suffruticosa are available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Armania, N.; Yazan, L.S.; Ismail, I.S.; Foo, J.B.; Tor, Y.S.; Ishak, N.; Ismail, N.; Ismail, M. Dillenia Suffruticosa Extract Inhibits Proliferation of Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231) via Induction of G2/M Arrest and Apoptosis. Molecules 2013, 18, 13320-13339. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181113320
Armania N, Yazan LS, Ismail IS, Foo JB, Tor YS, Ishak N, Ismail N, Ismail M. Dillenia Suffruticosa Extract Inhibits Proliferation of Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231) via Induction of G2/M Arrest and Apoptosis. Molecules. 2013; 18(11):13320-13339. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181113320
Chicago/Turabian StyleArmania, Nurdin, Latifah Saiful Yazan, Intan Safinar Ismail, Jhi Biau Foo, Yim Sim Tor, Nurshafini Ishak, Norsharina Ismail, and Maznah Ismail. 2013. "Dillenia Suffruticosa Extract Inhibits Proliferation of Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231) via Induction of G2/M Arrest and Apoptosis" Molecules 18, no. 11: 13320-13339. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181113320
APA StyleArmania, N., Yazan, L. S., Ismail, I. S., Foo, J. B., Tor, Y. S., Ishak, N., Ismail, N., & Ismail, M. (2013). Dillenia Suffruticosa Extract Inhibits Proliferation of Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231) via Induction of G2/M Arrest and Apoptosis. Molecules, 18(11), 13320-13339. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181113320