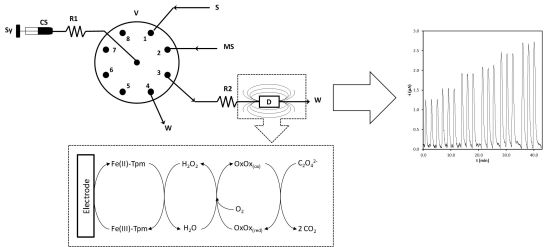
Amperometric Biosensor for Oxalate Determination in Urine Using Sequential Injection Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
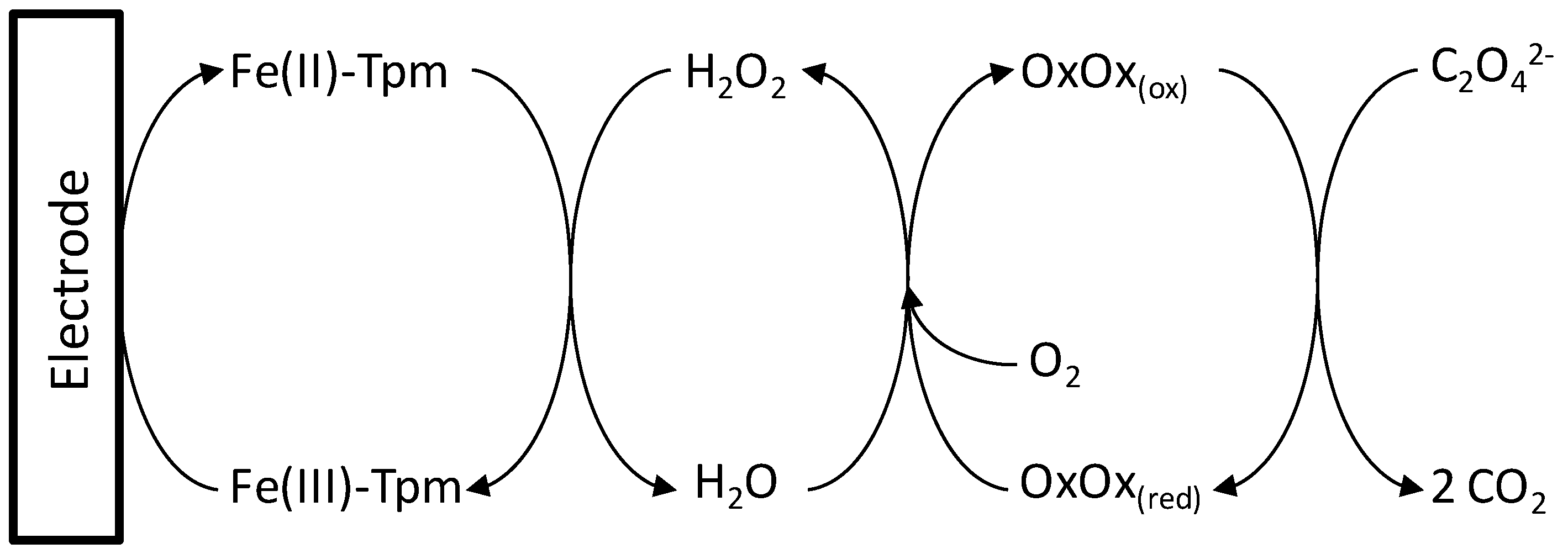
2.1. Electrocatalytic Properties of Fe-Tmp Modified Electrode for H2O2 Detection
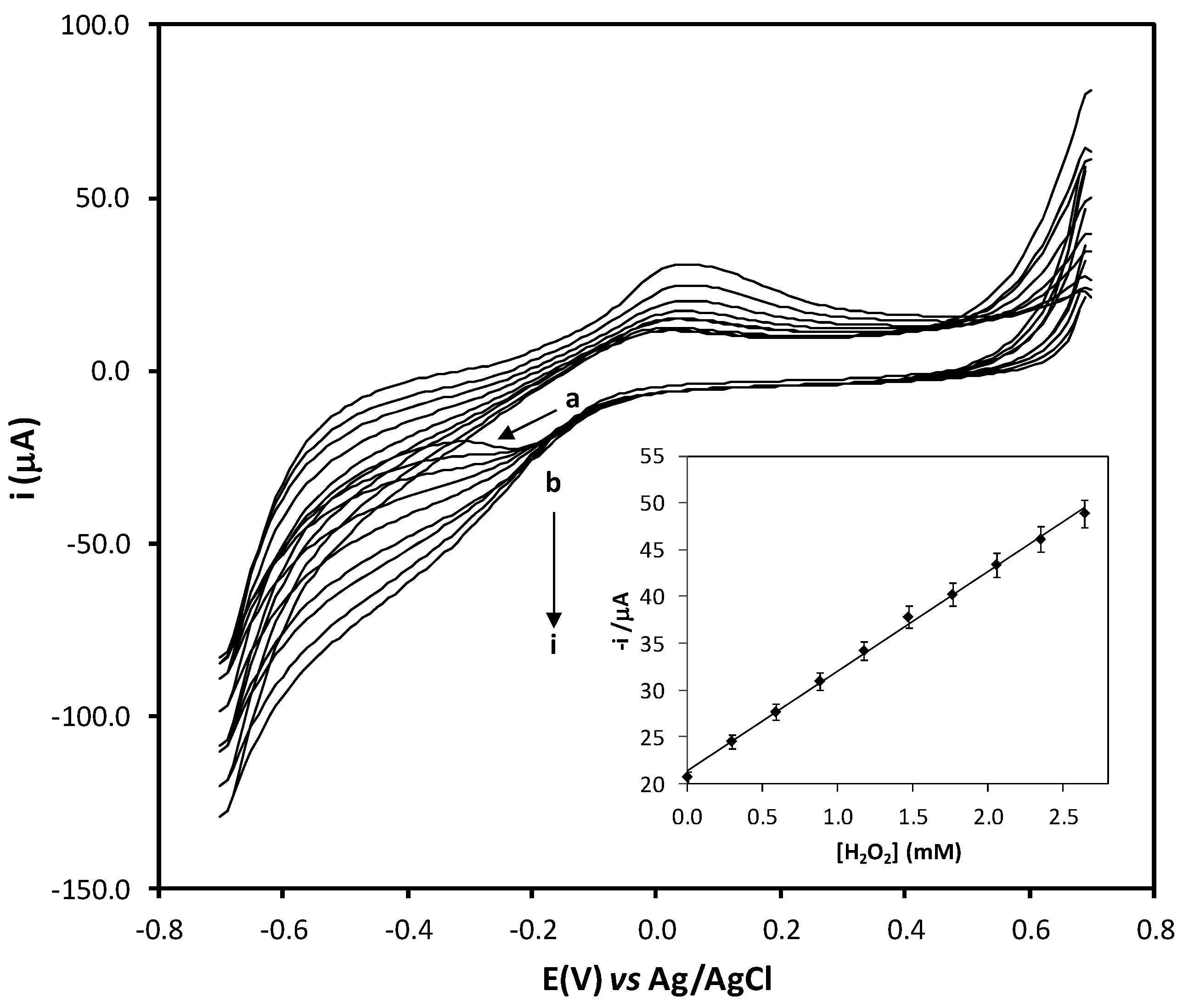
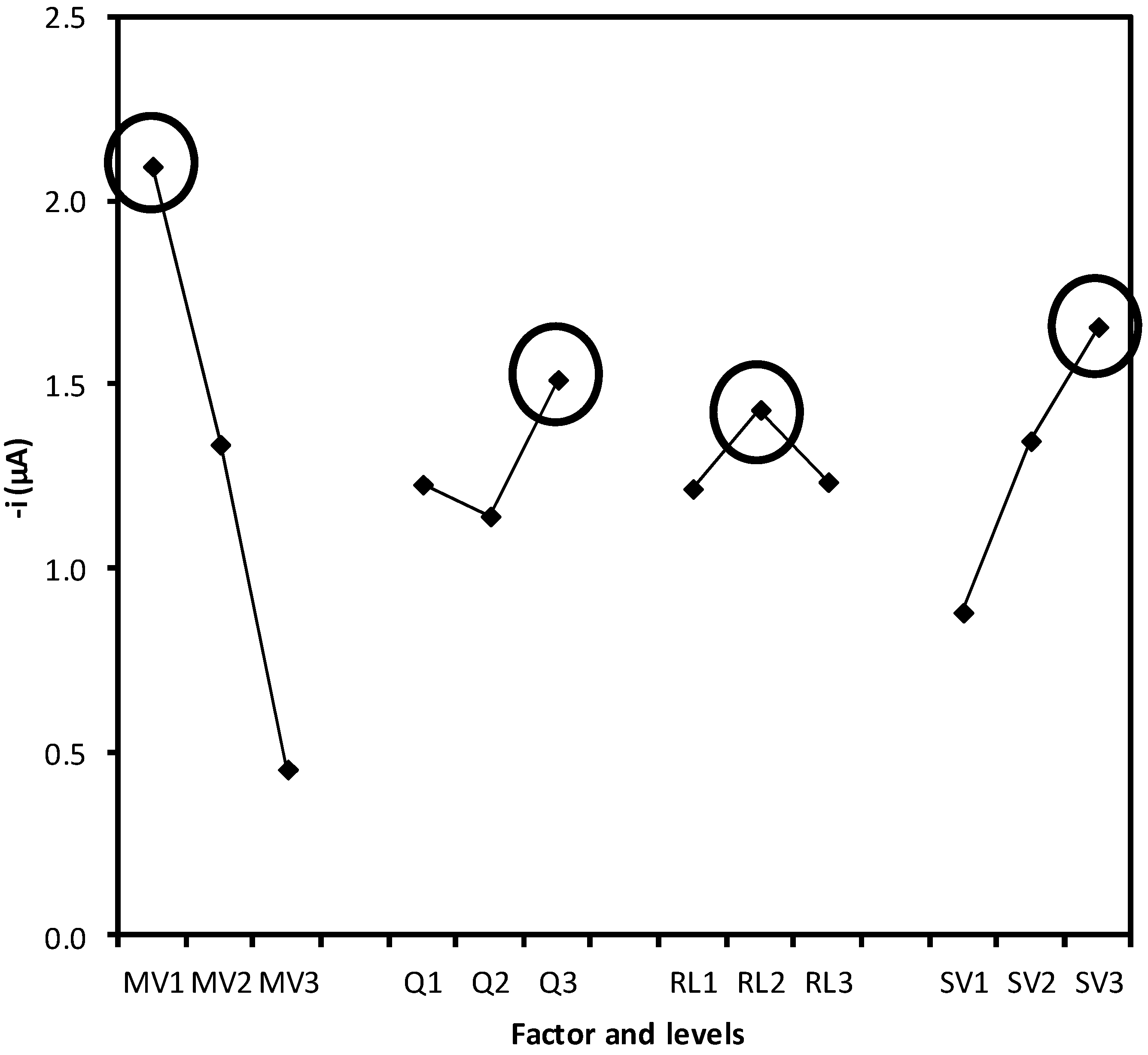
2.2. Optimization of the System Variables
| MV (µL) a | Q (mL·min−1) | RL (cm) | SV (µL) | Peak height, µA (%RSD, n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.50 | 30 | 100 | 1.54 (0.23) |
| 10 | 0.75 | 50 | 150 | 2.13 (0.05) |
| 10 | 1.00 | 70 | 200 | 2.62 (0.10) |
| 20 | 0.50 | 50 | 200 | 1.77 (0.08) |
| 20 | 0.75 | 70 | 100 | 0.71 (0.28) |
| 20 | 1.00 | 30 | 150 | 1.53 (0.26) |
| 30 | 0.50 | 70 | 150 | 0.38 (0.37) |
| 30 | 0.75 | 30 | 200 | 0.59 (0.09) |
| 30 | 1.00 | 50 | 100 | 0.40 (0.13) |
| Variance source | Variance | Variance ratio ( F) a | Influence (%) b |
|---|---|---|---|
| MV | 6.300 | 11340 | 77.34 |
| Q | 0.345 | 621 | 4.24 |
| RL | 0.130 | 234 | 1.60 |
| VI | 1.370 | 2466 | 16.82 |
| Residual | 0.001 | 0.01 |
2.3. Analytical Properties of the Procedure
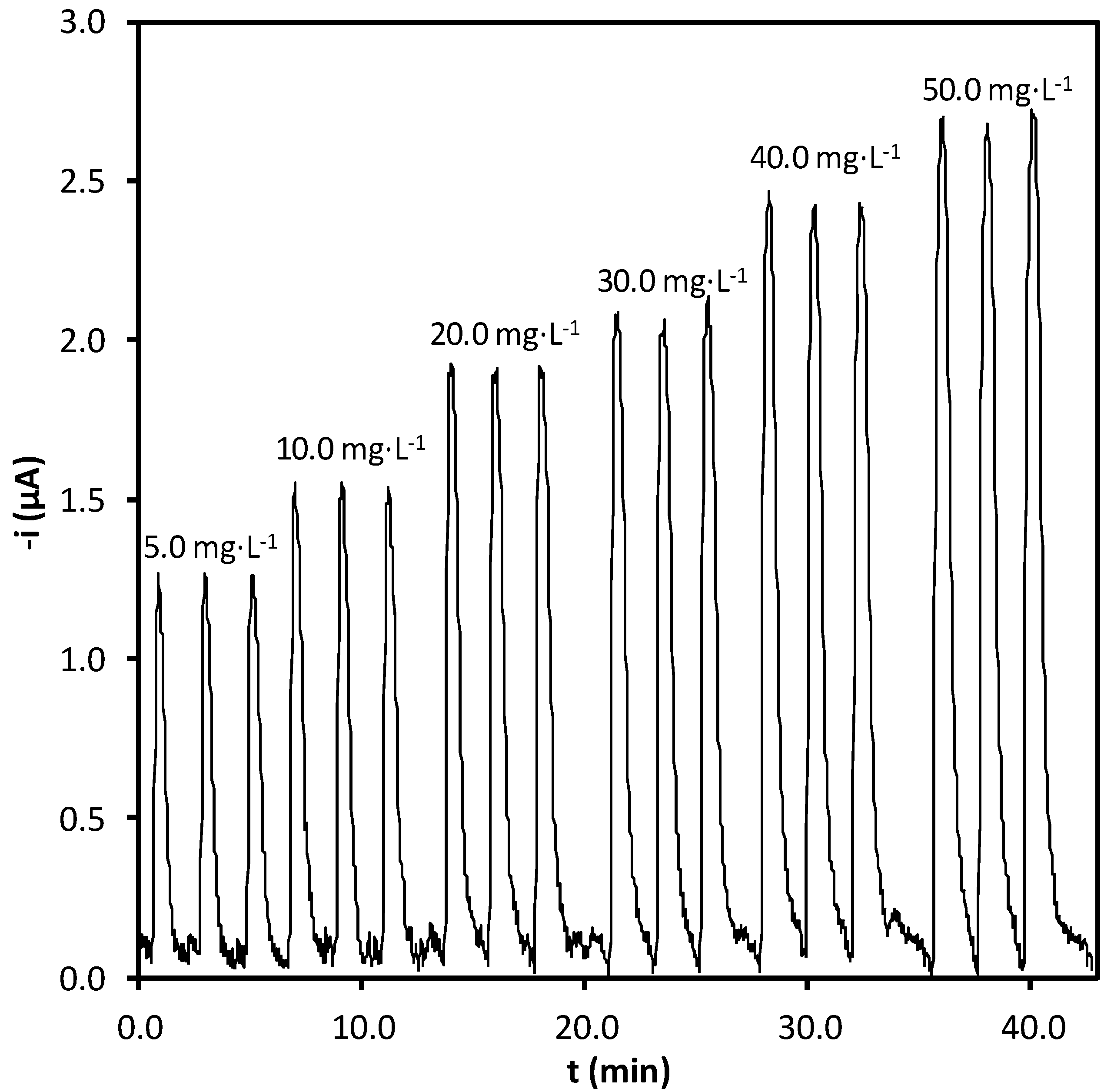
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Square root of residual variance, Se | 0.009 |
| Determination coefficient, r2 | 0.999 |
| Intercept confidence interval, b0 ± ts (b0) | 0.017 ± 0.019 |
| Slope confidence interval, b1 ± ts(b1) (µA L·mg−1) | 0.031 ± 0.001 |
| Linear range (mg·L−1) | 3.0–50.0 |
| Limit of detection (mg·L−1) | 1.0 |
| Repeatability (%RSD, n = 3, 30 mg·L−1) | 0.7 |
| Intermediate precision (%RSD, n = 3, 30 mg·L−1) | 2.2 |
| Sampling rate (samples·h−1) | 30 |
| Age group (years) | Sex | [Oxalate] (mg·L−1) | texperimental | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIA | FIA-Vis | |||
| Children (1−20) | Male | 10.5 ± 4.0 | 10.8 ± 4.3 | 0.15 |
| Female | 17.2 ± 3.8 | 17.4 ± 1.9 | 0.19 | |
| Adult (21−45) | Male | 21.0 ± 6.3 | 20.5 ± 2.2 | 1.35 |
| Female | 20.3 ± 1.2 | 21.1 ± 2.3 | 1.23 | |
| Old (>45) | Male | 23.5 ± 2.3 | 23.6 ± 2.4 | 0.08 |
| Female | 37.4 ± 4.1 | 36.8 ± 3.5 | 0.15 | |
3. Experimental
3.1. Synthesis of Enzyme Magnetic Solid
3.2. Characterization of the Magnetic Solid

3.3. Synthesis of Fe (III)-Tpm
3.4. Apparatus
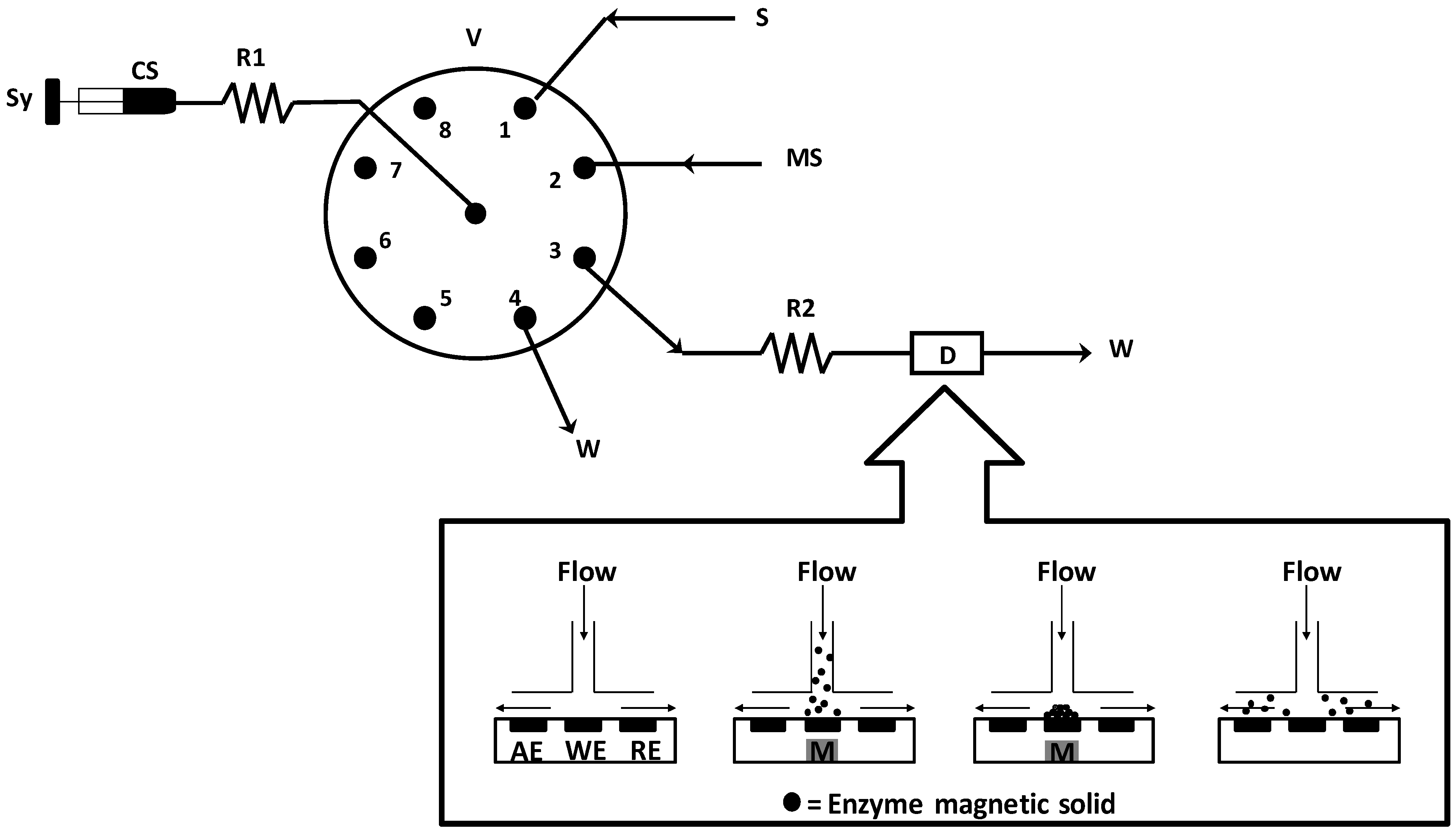
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Verhulst, A.; de Broe, M.E. Oxalate. In Clinical Nephrotoxins: Renal Injury from Drugs and Chemicals, 3rd; de Broe, M.E., Porter, G.A., Bennett, W.M., Deray, G., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 749–756. [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa, Y.; Miyazato, T.; Hatano, T. Oxalate and urinary stones. World J. Surg. 2000, 24, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perello, J.; Sanchis, P.; Grases, F. Determination of uric acid in urine, saliva and calcium oxalate renal calculi by high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 824, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.; Goyal, L.; Pundir, C.S. Discrete analysis of plasma oxalate with alkylamine glass bound sorghum oxalate oxidase and horseradish peroxidase. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2000, 44, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chai, X.S.; DeMartini, N.; Zhan, H.; Fu, S. Determination of oxalate in black liquor by headspace gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1192, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Fang, Y.L.; Meng, J.F.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.X.; Zhang, Z.W. Analysis of low molecular weight organic acids in several complex liquid biological systems via HPLC with switching detection wavelength. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2011, 24, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, J.A.; Lopez-Mesas, M. Development and validation of a simple determination of urine metabolites (oxalate, citrate, uric acid and creatinine) by capillary zone electrophoresis. Talanta 2010, 81, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladwing, P.M.; Liedtke, R.R.; Larson, T.S.; Lieske, J.C. Sensitive spectrophotometric assay for plasma oxalate. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 2377–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pundir, C.S.; Sharma, M. Oxalate biosensor: A review. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2010, 69, 489–494. [Google Scholar]
- Chaubey, A.; Malhotra, B.D. Mediated biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2002, 17, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, G.; Hamilton, A.; Mitchell, B.; Owen, G.R. A new family of flexible scorpionate ligants based on 2-mercaptopyridine. Dalton Trans. 2009, 6120–6126. [Google Scholar]
- Trofimenko, S. Recent advances in poly (pyrazolyl) borate (scorpionate) chemistry. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 943–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriz, D.; Johansson, A. A preliminary study of a biosensor based on flow injection of recognition element. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1996, 11, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F; Milvebrant, N.; Jonsson, L.J. Rapid and convenient determination of oxalic acid employing a novel oxalate biosensor based on oxalate oxidase and SIRE technology. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 18, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M.; Ruzicka, J. Flow injection based renewable electrochemical sensor system. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 3808–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzicka, J.; Marshall, G.D. Sequential injection: A concept for chemical sensors, process analysis and laboratory assays. Anal. Chim. Acta 1990, 237, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Arteaga, K.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Barrado, E. Magnetic solids in analytical chemistry: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 674, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrero, M.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarron, J.M. Magnetic beads-based electrochemical sensors applied to the detection and quantification of bioterrorism/biohazard agents. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrado, E.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Castrillejo, Y. Renewable stationary phase liquid magnetochromatography: Determining aspartame and its hydrolysis products in diet soft drinks. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, C.I.C.; Pinto, P.C.A.G.; Segundo, M.A.; Saraiva, M.L.M.F.S.; Lima, J.L.F.C. Enzyme based assays in a sequential injection format: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 689, 160–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarley, C.R.T.; Silveira, G.; Santos, W.N.L.; Mantos, G.D.; Silva, E.G.P.; Bezerra, M.A.; Miro, M.; Ferreira, S.L.C. Chemometric tools in electroanalytical chemistry: Methods for optimization based on factorial design and response surface methodology. Microchem. J. 2009, 92, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, L.A. Nomenclature in evaluation of analytical methods including detection and quantification capabilities. Pure Appl. Chem. 1995, 67, 1699–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Yadav, H.; Pundir, C.S. An amperometric oxalate biosensor based on sorghum leaf oxalate oxidase immobilized on carbon paste electrode. Anal. Lett. 2010, 43, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, R.; Pundir, C.S. An electrochemical oxalate biosensor based on CA membrane bound sorghum oxalate oxidase. Sens. Trans. 2010, 113, 127–139. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, J.A.; Espinosa, J.; Aguilar-Arteaga, K.; Ibarra, I.S.; Miranda, J.M. Determination of tetracyclines in milk by magnetic solid phase extraction flow injection analysis. Michrochim. Acta 2010, 171, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, P.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Salazar, V.; Alvarez-Romero, G.A.; Gonzalez-Montiel, S.; Castrillejo, Y. Determination of glucose by flow injection analysis with amperometric detection at Fe (III)-(tris-(3,5-dimethyl-1-pyrazolyl)borate)2 modified electrodes. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2011, 55, 120–125. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Ruiz, T.; Martinez-Lozano, C.; Tomas, V.; Sanz, A. Flow injection with spectrophotometric determination of oxalate, citrate and tartrate based on photochemical reactions. Anal. Lett. 1988, 31, 1413–1427. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the enzyme magnetic solid, Fe(III)-Tpm and urine samples are available from the authors.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodriguez, J.A.; Hernandez, P.; Salazar, V.; Castrillejo, Y.; Barrado, E. Amperometric Biosensor for Oxalate Determination in Urine Using Sequential Injection Analysis. Molecules 2012, 17, 8859-8871. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17088859
Rodriguez JA, Hernandez P, Salazar V, Castrillejo Y, Barrado E. Amperometric Biosensor for Oxalate Determination in Urine Using Sequential Injection Analysis. Molecules. 2012; 17(8):8859-8871. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17088859
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodriguez, Jose A., Prisciliano Hernandez, Veronica Salazar, Yolanda Castrillejo, and Enrique Barrado. 2012. "Amperometric Biosensor for Oxalate Determination in Urine Using Sequential Injection Analysis" Molecules 17, no. 8: 8859-8871. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17088859
APA StyleRodriguez, J. A., Hernandez, P., Salazar, V., Castrillejo, Y., & Barrado, E. (2012). Amperometric Biosensor for Oxalate Determination in Urine Using Sequential Injection Analysis. Molecules, 17(8), 8859-8871. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17088859