Bioactivity-Guided Isolation of Ethyl-p-methoxycinnamate, an Anti-inflammatory Constituent, from Kaempferia galanga L. Extracts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Results
2.1.1. Acute Toxicity Study
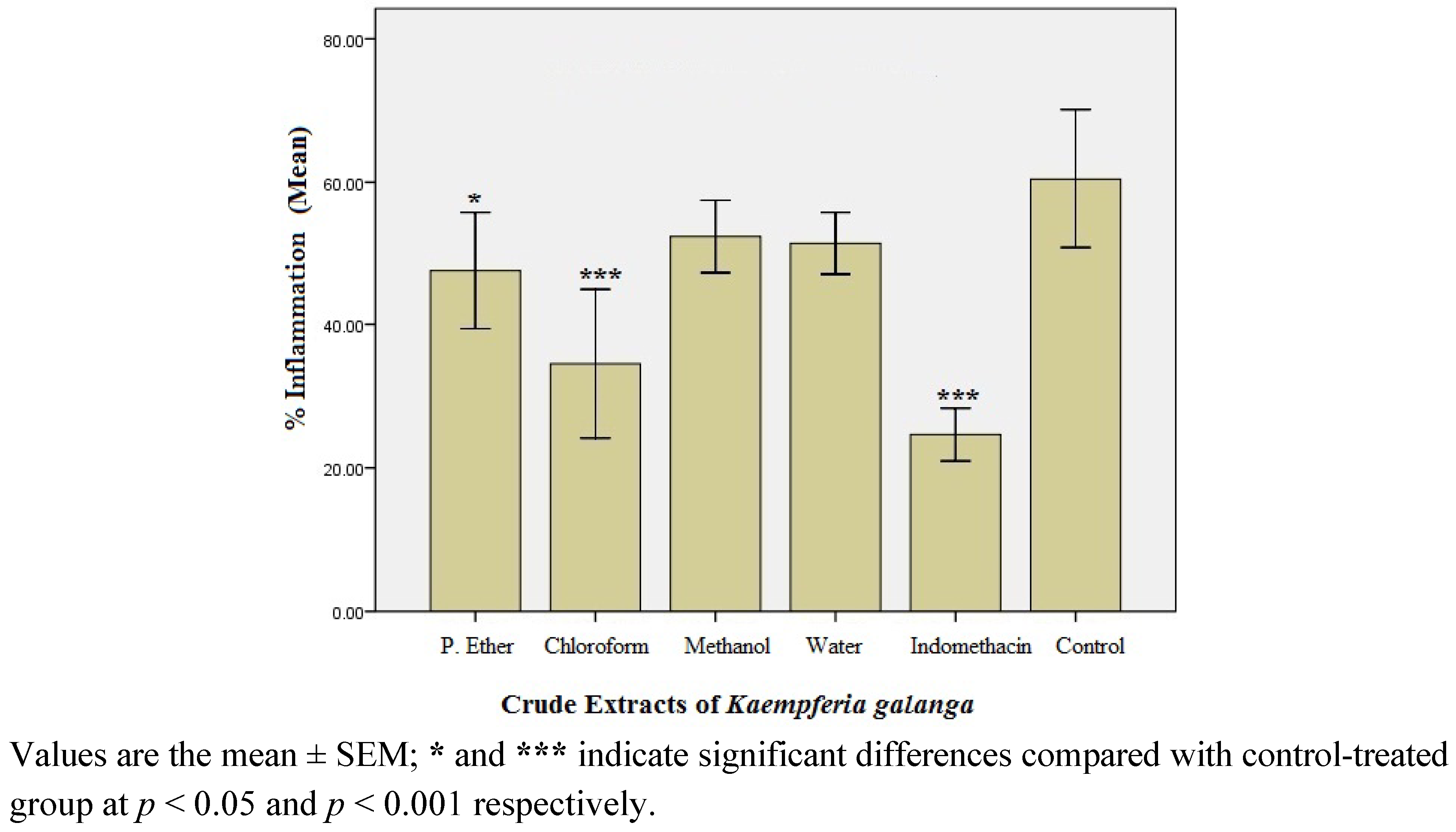
2.1.2. Preliminary Anti-inflammatory Effect of Crude Extracts of K. Galanga
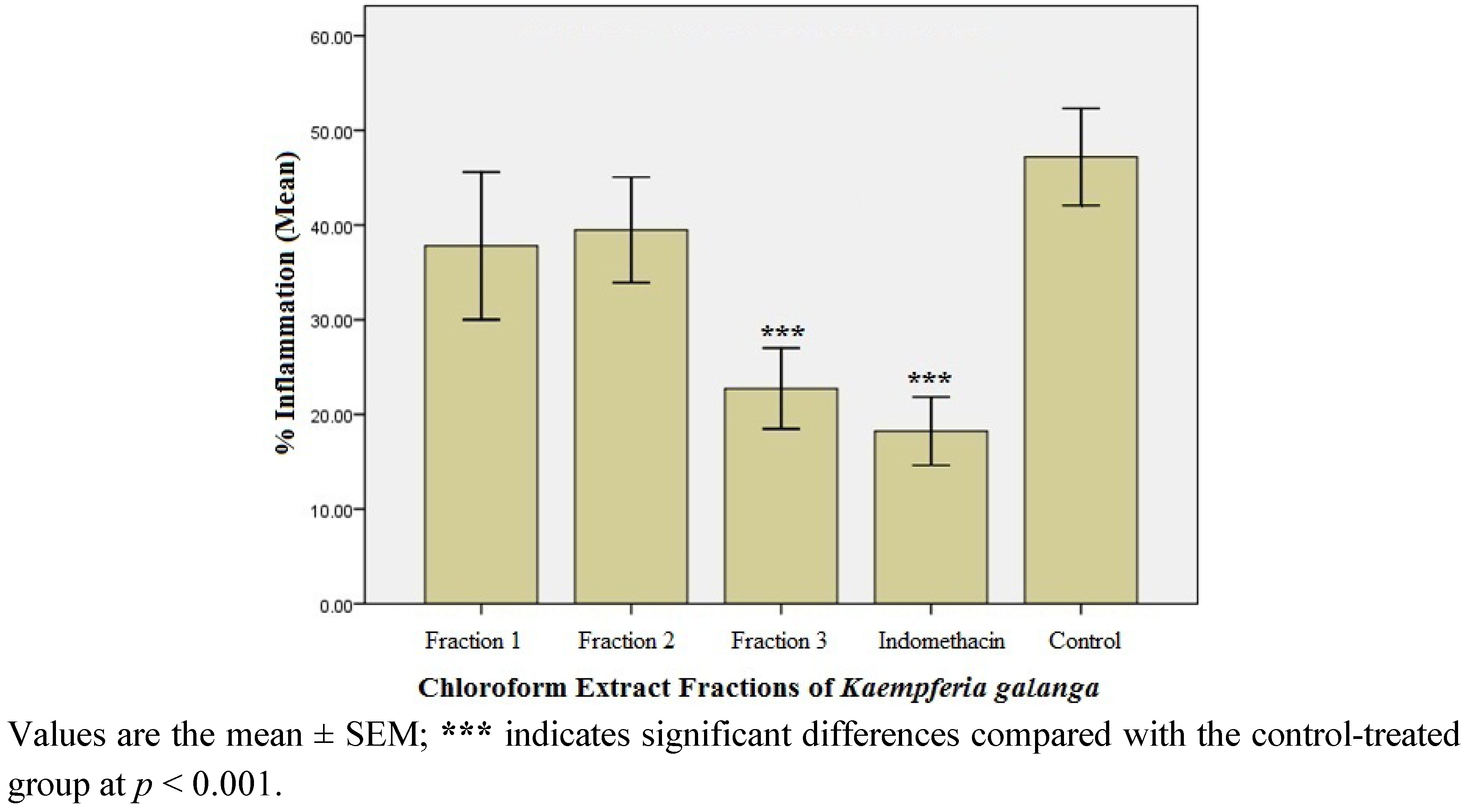
2.1.3. Anti-inflammatory Effect of the Fractions of the Active Chloroform Extract
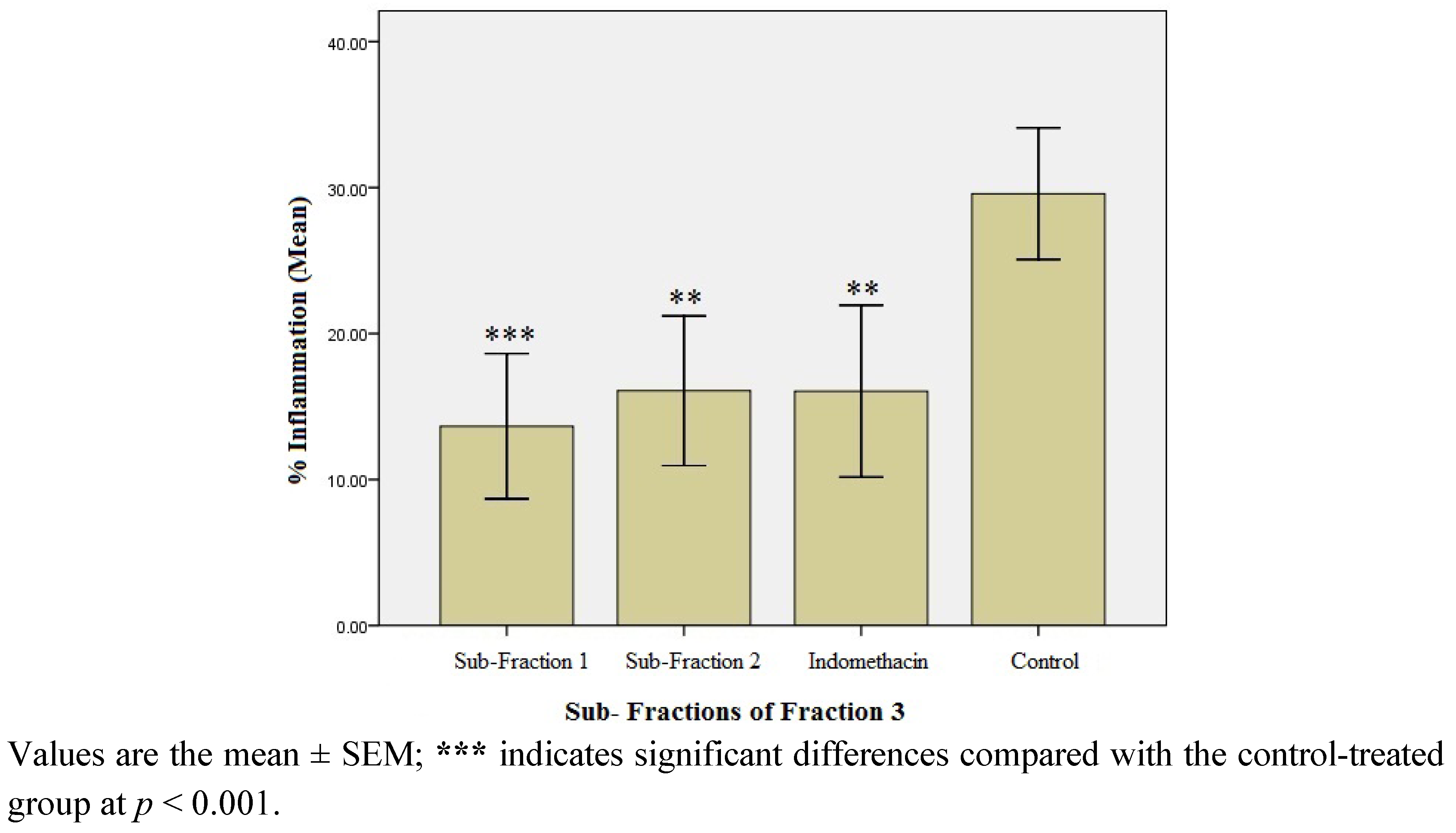
2.1.4. Anti-inflammatory Effect of the Sub-fractions of Fraction 3
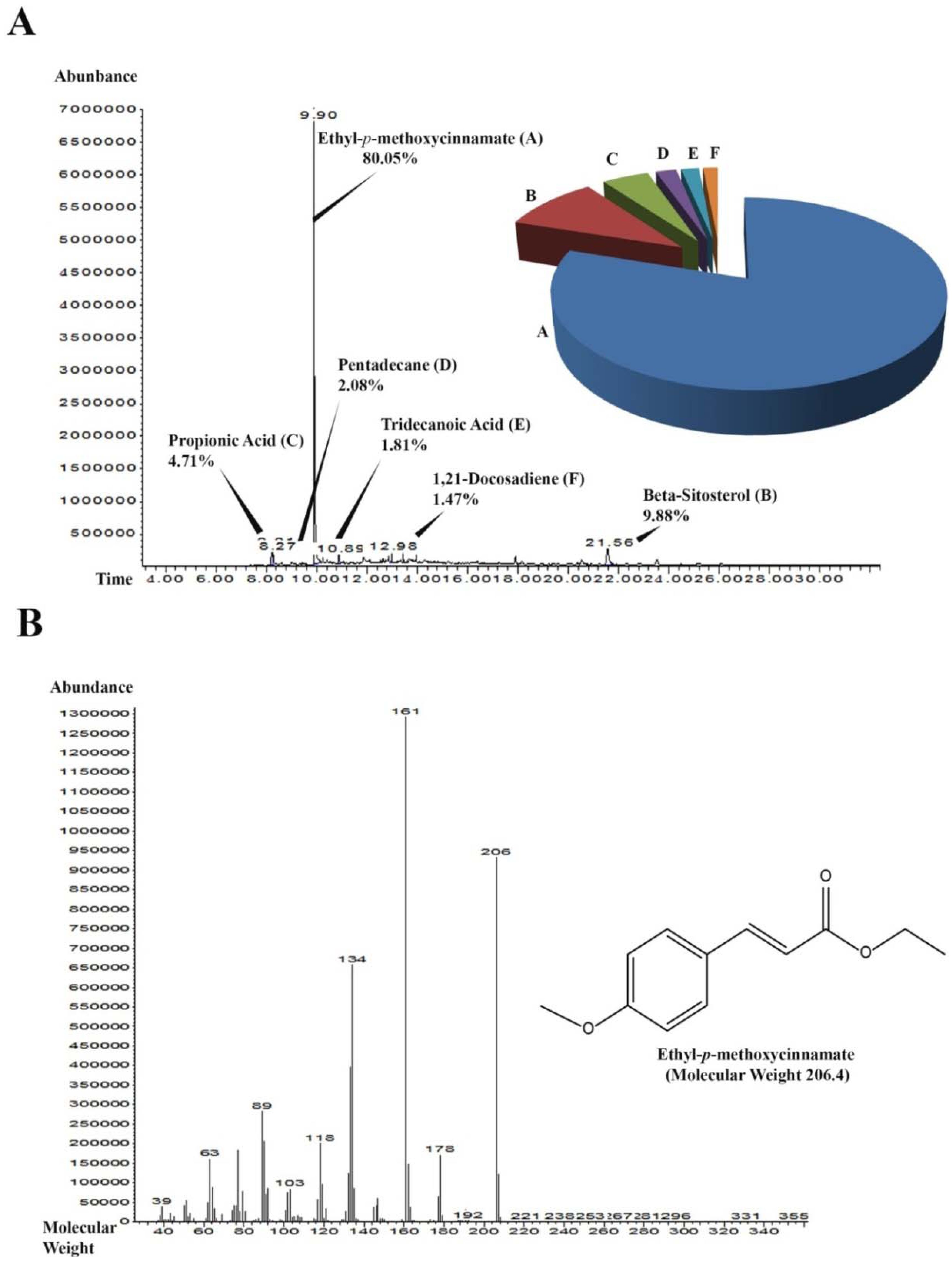
2.1.5. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) Analysis of SF-1
2.1.6. Isolation of Ethyl-p-methoxycinnamate (EPMC) Crystals
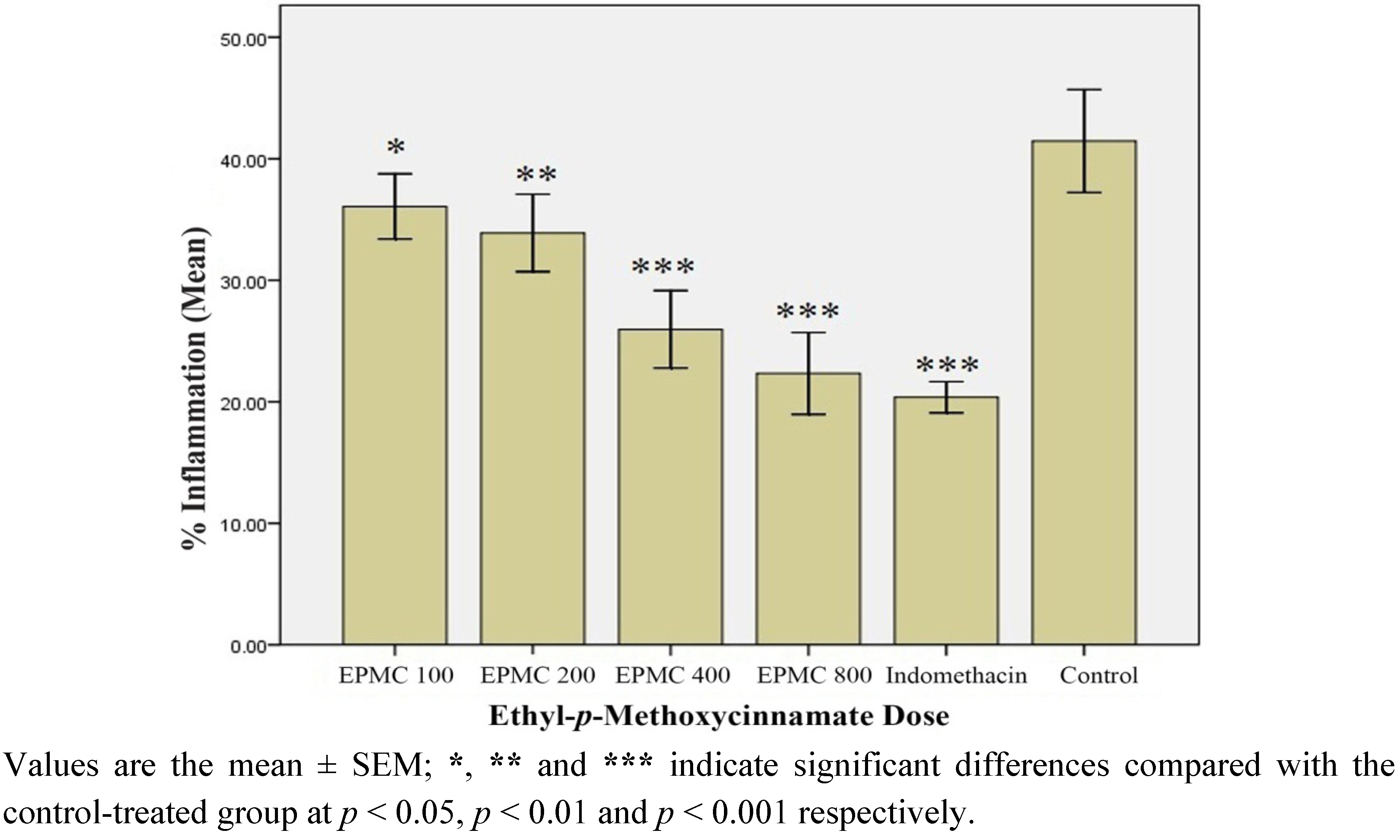
2.1.7. In Vivo Anti-inflammatory Effect of Ethyl-p-methoxycinnamate (EPMC)
2.1.8. In Vitro Anti-inflammatory Effect of Ethyl-p-methoxycinnamate (EPMC)
2.2. Discussion
3. Experimental
3.1. Chemicals and Equipment
3.2. Plant Material
3.2.1. Extraction of Plant Material for Preliminary Activity Assessment
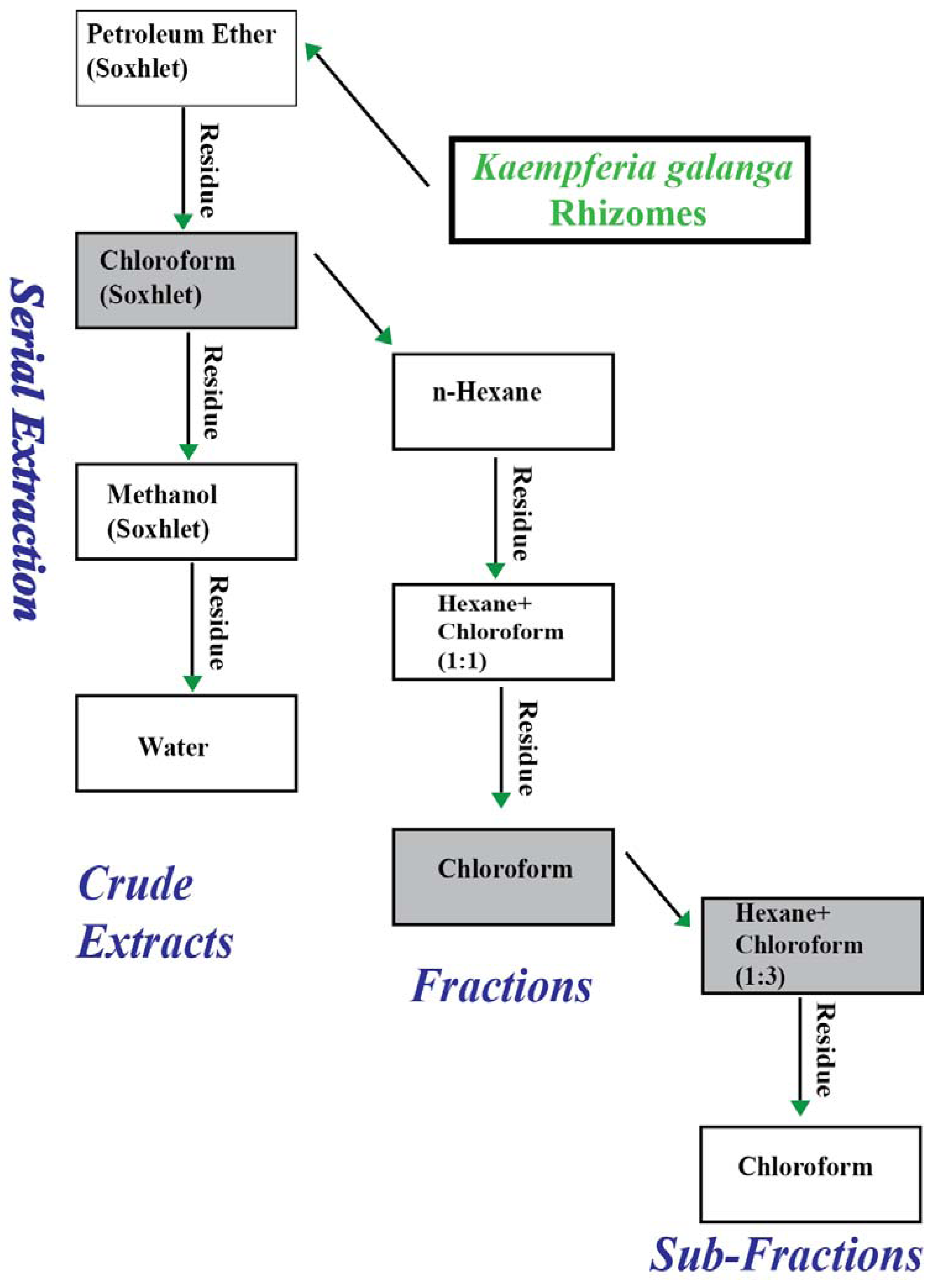
3.2.2. Liquid-Liquid Fractionation of Chloroform Extract
3.2.3. Liquid-liquid Fractionation of Fraction 3
3.3. Chemical Analysis of the Most Effective Sub-Fraction (SF-1)
3.4. Pharmacological Procedures
3.4.1. Animals
3.4.2. Acute Toxicity Study in Rat
3.4.3. Preparation of Test Samples and Dose Selection for Bioassays
3.4.4. In Vivo Anti-inflammatory Assay
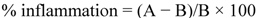
3.4.5. In Vitro Anti-inflammatory Assay of EPMC
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Valentin, F.; Javier, S. Vascular inflammation. J. Am. Soc. Hyperten. 2007, 1, 68–81. [Google Scholar]
- Julia, K.; Moshe, S.F.; Michal, B. New insights into chronic inflammation-induced immunosuppression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2012, 22, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joydeb, K.K.; Young, J.S. Inflammation: Gearing the journey to cancer. Mutat. Res. 2008, 659, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joydeb, K.K.; Young, J.S. Emerging avenues linking inflammation and cancer. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 2013–2037. [Google Scholar]
- Thiefin, G.; Beaugerie, L. Toxic effects of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs on the small bowel, colon, and rectum. Joint Bone Spine 2005, 72, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, H.L. Guide to Medicinal Plants: An Illustrated Scientific and Medicinal Approach; World Scientific: Toh Tak, Singapore, 2009; pp. 85–86. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, R.; Orbell, J.; Muralitharan, M.S. Agriculture-Medicinal Plants of Malaysia. Asia Pacific Biotech News 2007, 11, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Peter, K.V. Handbook of Herbs and Spices; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2004; pp. 53–54. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, I.H.; Park, J.Y.; Shin, S.C.; Park, I.K. Nematicidal activity of medicinal plant extracts and two cinnamates isolated from Kaempferia galanga L. (Proh Hom) against the pine wood nematode, bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Nematol 2006, 8, 359–365. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, T.K.; Lee, J.K.; Heo, J.W.; Kim, S.I.; Choi, D.R.; Ahn, Y.J. Toxicity of Kaempferia galanga rhizome-derived extract and steam distillate to Meloidogyne incognita juveniles and eggs, and their effects on Lycopersicon esculentum germination and growth. Nematol 2010, 12, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.K.; Kim, S.I.; Heo, J.W.; Lee, J.K.; Choi, D.R.; Ahn, Y.J. Toxicity of Kaempferia galanga rhizome constituents to Meloidogyne incognita juveniles and eggs. Nematol 2011, 13, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choochote, W.; Kanjanapothi, D.; Panthong, A.; Taesotikul, T.; Jitpakdi, A.; Chaithong, U.; Pitasawat, B. Larvicidal, adulticidal and repellent effects of Kaempferia galanga. Southeast Asian J. Trop.Med. Publ. Health 1999, 30, 470–476. [Google Scholar]
- Choochote, W.; Chaithong, U.; Kamsuk, K.; Jitpakdi, A.; Tippawangkosol, P.; Tuetun, B.; Champakaew, D.; Pitasawat, B. Repellent activity of selected essential oils against Aedes aegypti. Fitoterapia 2007, 78, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutthanont, N.; Choochote, W.; Tuetun, B.; Junkum, A.; Jitpakdi, A.; Chaithong, U.; Riyong, D.; Pitasawat, B. Chemical composition and larvicidal activity of edible plant-derived essential oils against the pyrethroid-susceptible and -resistant strains of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Vector Ecol. 2010, 35, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Park, I.K.; Kim, E.H.; Lee, H.S.; Ahn, Y.J. Larvicidal activity of medicinal plant extracts against Aedes aegypti, Ochlerotatus togoi, and Culex pipiens pallens (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Asia-Pacific Entomol. 2004, 7, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yagura, T.; Chen, S. Sedative activity of hexane extract of Keampferia galanga L. and its active compounds. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 120, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjanapothi, D.; Panthong, A.; Lertprasertsuke, N.; Taesotikul, T.; Rujjanawate, C.; Kaewpinit, D.; Sudthayakorn, R.; Choochote, W.; Chaithong, U.; Jitpakdi, A.; Pitasawat, B. Toxicity of crude rhizome extract of Kaempferia galanga L. (Proh Hom). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 90, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, D.; Werngren, J.; Jose, L.; Suja, K.P.; Nair, M.S.; Varma, R.L.; Mundayoor, S.; Hoffner, S.; Kumar, R.A. Ethyl p-methoxycinnamate isolated from a traditional anti-tuberculosis medicinal herb inhibits drug resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in vitro. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 757–761. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, R.; Ibrahim, H.; Mohd, M.A.; Mustafa, M.R.; Awang, K. Bioassay-Guided isolation of a vasorelaxant active compound from Kaempferia galanga L. Phytomedicine 2006, 13, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, R.; Ibrahim, H.; Mohd, M.A.; Awang, K.; Gilani, A.-U.H.; Mustafa, M.R. Vasorelaxant effects of ethyl cinnamate isolated from Kaempferia galanga on smooth muscles of the rat aorta. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 655–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, M.; Mustafa, A.M. Traditional Malay Medicinal Plants; Fajar Bakti: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1994; p. 129. [Google Scholar]
- Kirana, C.; Record, I.R.; McIntosh, G.H.; Jones, G.P. Screening for antitumor activity of 11 species of indonesian zingiberaceae using human MCF-7 and HT-29 cancer cells. Pharm. Biol. 2003, 41, 271–276. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Liu, F.; Chen, C.; Gao, H. Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of ethyl p-methoxycinnamate from Kaempferia galanga L. rhizome and its apoptotic induction in human HepG2 cells. Nat. Prod. Res. 2010, 24, 1927–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimala, S.; Norhanom, A.W.; Yadav, M. Anti-Tumour promoter activity in Malaysian ginger rhizobia used in traditional medicine. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 80, 110–116. [Google Scholar]
- Tewtrakul, S.; Subhadhirasakul, S. Anti-Allergic activity of some selected plants in the Zingiberaceae family. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 109, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.W.C.; Lim, Y.Y.; Wong, L.F.; Lianto, F.S.; Wong, S.K.; Lim, K.K.; Joe, C.E.; Lim, T.Y. Antioxidant and tyrosinase inhibition properties of leaves and rhizomes of ginger species. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 477–483. [Google Scholar]
- Mekseepralard, C.; Kamkaen, N.; Wilkinson, J.M. Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of traditional Thai herbal remedies for aphthous ulcers. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 1514–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridtitid, W.; Sae-Wong, C.; Reanmongkol, W.; Wongnawa, M. Antinociceptive activity of the methanolic extract of Kaempferia galanga Linn. in experimental animals. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 118, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tara Shanbhag, V.; Chandrakala, S.; Sachidananda, A.; Kurady, B.L.; Smita, S.; Ganesh, S. Wound healing activity of alcoholic extract of Kaempferia galanga in Wistar rats. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2006, 50, 384–390. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, N.J.; Byun, S.G.; Cho, J.E.; Chung, K.; Ahn, Y.J. Larvicidal activity of Kaempferia galanga rhizome phenylpropanoids towards three mosquito species. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 857–862. [Google Scholar]
- Sulaiman, M.R.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Daud, I.A.; Ng, F.N.; Ng, Y.C.; Hidayat, M.T. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of the aqueous extract of Kaempferia galanga leaves in animal models. J. Nat. Med. 2008, 62, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittalrao, A.M.; Shanbhag, T.; Kumari, M.; Bairy, K.L.; Shenoy, S. Evaluation of antiinflammatory and analgesic activities of alcoholic extract of Kaempferia galanga in rats. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2011, 55, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, C.A.; Risely, E.A.; Nussm, G.W. Carrageenan-induced edema in hind paws of the rat as an assay for anti-inflammatory drugs. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1962, 111, 544–547. [Google Scholar]
- Vinegar, R.; Schreiber, W.; Hugo, R. Biphasic development of carrageenan oedema in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1969, 166, 96–103. [Google Scholar]
- Riendeau, D.; Percival, M.D.; Boyce, S.; Brideau, C.; Charleson, S.; Cromlish, W.; Ethier, D.; Evans, J.; Falgueyret, J.P.; Ford-Hutchinson, A.W.; et al. Biochemical and pharmacological profile of a tetrasubstituted furanone as a highly selective COX-2 inhibitor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 121, 105–117. [Google Scholar]
- The Organization of Economic Co-Operation Development (OECD), The OECD guideline for testing of chemical. In 420 Acute Oral Toxicity; OECD: Paris, France, 2001; pp. 1–14.
- Bamidele, V.O.; Olubori, M.A.; Adeoye, A.F.; Ayodele, O.S. Anti-inflammatory activities of ethanolic extract of carica papaya leaves. Inflammopharmacology 2008, 16, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samud, A.M.; Asmawi, M.Z.; Sharma, J.N.; Yusof, A.P.M. Anti-Inflammatory activity of crinum asiaticum plant and its effect on bradykinin-induced contractions on isolated uterus. Immunopharmacology 1999, 43, 311–316. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of Ethyl-p-methoxycinnamateare available from the authors.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Umar, M.I.; Asmawi, M.Z.; Sadikun, A.; Atangwho, I.J.; Yam, M.F.; Altaf, R.; Ahmed, A. Bioactivity-Guided Isolation of Ethyl-p-methoxycinnamate, an Anti-inflammatory Constituent, from Kaempferia galanga L. Extracts. Molecules 2012, 17, 8720-8734. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17078720
Umar MI, Asmawi MZ, Sadikun A, Atangwho IJ, Yam MF, Altaf R, Ahmed A. Bioactivity-Guided Isolation of Ethyl-p-methoxycinnamate, an Anti-inflammatory Constituent, from Kaempferia galanga L. Extracts. Molecules. 2012; 17(7):8720-8734. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17078720
Chicago/Turabian StyleUmar, Muhammad Ihtisham, Mohd Zaini Asmawi, Amirin Sadikun, Item J. Atangwho, Mun Fei Yam, Rabia Altaf, and Ashfaq Ahmed. 2012. "Bioactivity-Guided Isolation of Ethyl-p-methoxycinnamate, an Anti-inflammatory Constituent, from Kaempferia galanga L. Extracts" Molecules 17, no. 7: 8720-8734. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17078720
APA StyleUmar, M. I., Asmawi, M. Z., Sadikun, A., Atangwho, I. J., Yam, M. F., Altaf, R., & Ahmed, A. (2012). Bioactivity-Guided Isolation of Ethyl-p-methoxycinnamate, an Anti-inflammatory Constituent, from Kaempferia galanga L. Extracts. Molecules, 17(7), 8720-8734. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17078720




