Effect of Some Biopolymers on the Rheological Behavior of Surimi Gel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Surimi-Starch Mixture
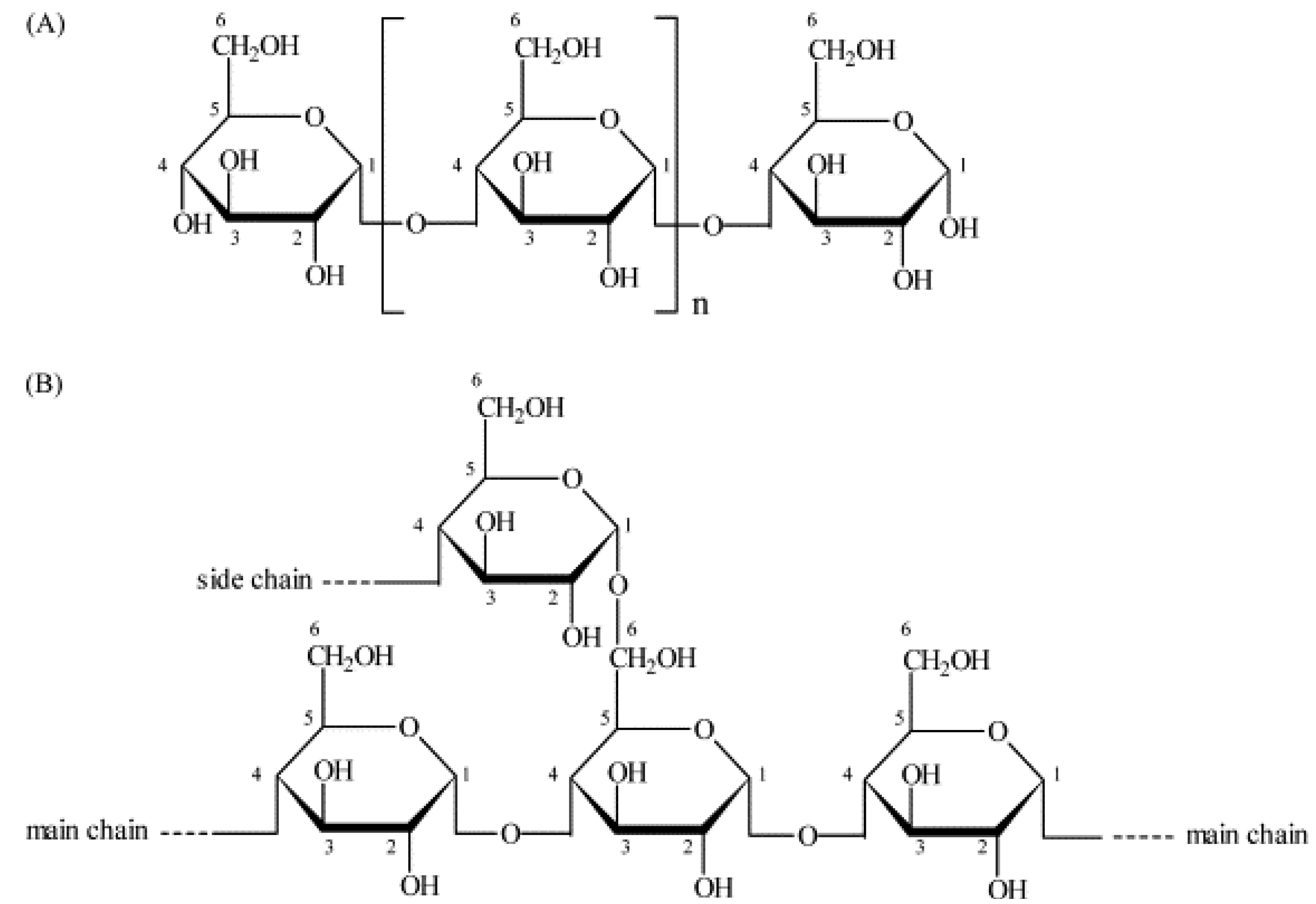
3. Surimi-Cryoprotectant Mixtures
4. Surimi-Mannans Mixtures

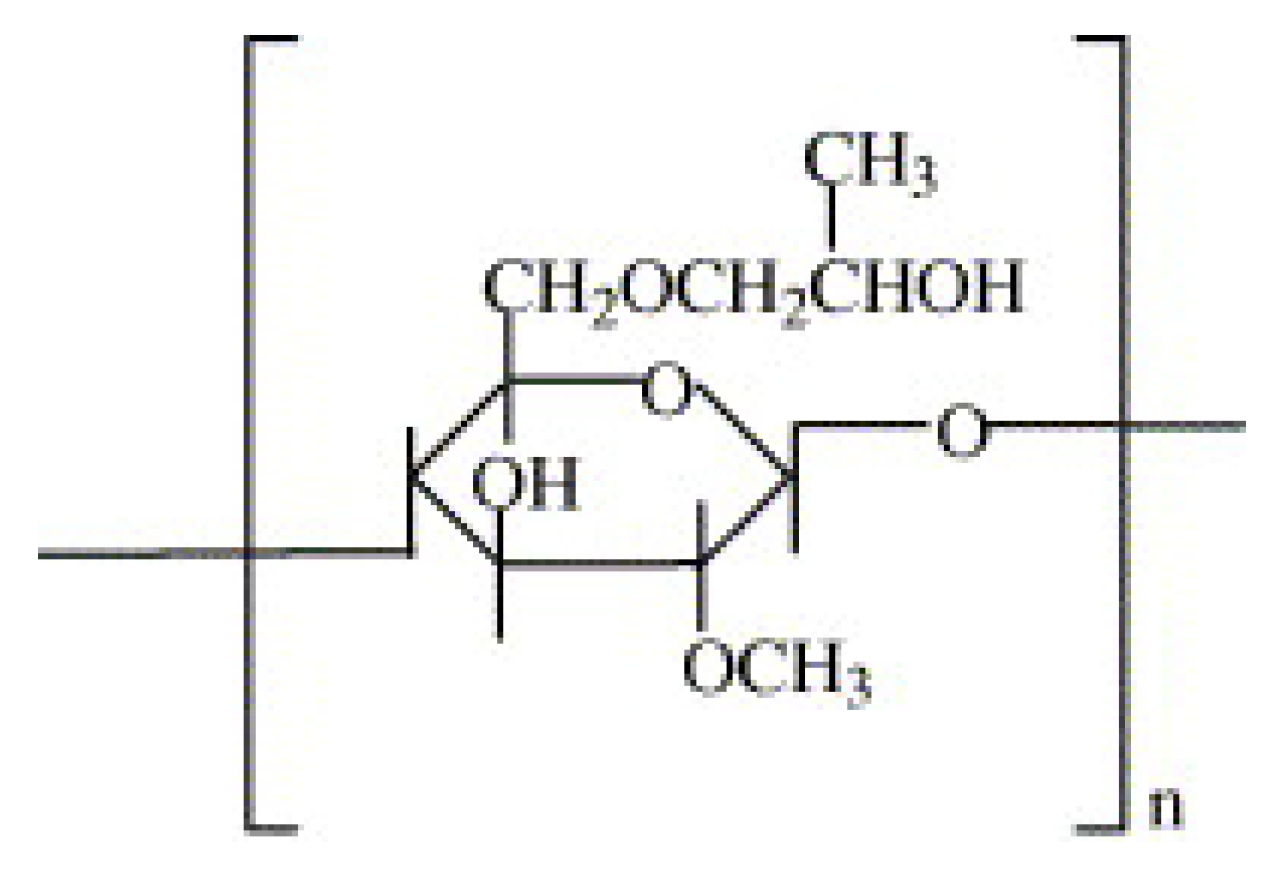
5. Surimi-Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC) Mixtures
6. Conclusions
- Samples Availability: Not available.
References and Notes
- Park, J.W.; Morrissey, M.T. Manufacturing of surimi from light muscle fish. In Surimi and Surimi Seafood; Park, J.W., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 23–58. [Google Scholar]
- Lanier, T.C. Surimi gelation chemistry. In Surimi and Surimi Seafood; Park, J.W., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 237–265. [Google Scholar]
- Benjakul, S.; Chantarasuwan, C.; Visessanguan, W. Effect of medium temperature setting on gelling characteristics of surimi from some tropical fish. Food Chem. 2003, 82, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, W.B.; Gunasekaran, S.; Park, J.W. Characterization of thermorheological behavior of Alaska Pollock and Pacific Whiting surimi. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, 338–343. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.W. Effects of salt, surimi and/or starch content on fracture properties of gels at various test temperatures. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 1995, 4, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Lee, C.M. Effect of starch on textural properties of surimi gel. J. Food Sci. 1987, 52, 722–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Park, J.W. Effects of starch properties and thermal-processing conditions on surimi-starch gels. Lebensm.Wiss. Technol. 1998, 31, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.S.; Ogawa, H.; Iso, N. Compression properties of fish-meat gel as affected by gelatinization of added starch. J. Food Sci. 1999, 64, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabilo-Munizaga, G.; Barbosa-Cánovas, V. Colour and textural parameters of pressurizedand heat-treatedsurimi gelsas affected by potato starch and egg white. Food Res. Int. 2004, 37, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo-Deaño, L.; Tovar, C.A. Influence of the starch content in the viscoelastic properties of surimi gels. J. Food Eng. 2008, 84, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo-Deaño, L.; Tovar, C.A.; Pombo, M.J.; Solas, M.T.; Borderías, A.J. Rheological study of giant squid surimi(Dosidicus gigas) made by two methods with different cryoprotectants added. J. Food Eng. 2009, 94, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Cheng, W.; Ye, L.; Du, X.; Zhou, M.; Lin, R.; Geng, S.; Chen, M.; Corke, H.; Cai, Y.Z. Effects of konjac glucomannan on physicochemical properties of myofibrillar protein and surimigels from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Food Chem. 2009, 116, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.H.; Huang, Y.C. Rheological properties of HPMC enhanced surimi analyzed by small–and large– strain tests–II: effect of water content and ingredients. Food Hydrocolloid. 2008, 22, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Benjakul, S.; Pan, K.; Gong, J.; Liu, X. Cryoprotective effects of trehalose and sodium lactate on tilapia (Sarotherodon nilotica)surimi during frozen storage. Food Chem. 2006, 96, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.S.; Lee, C.M. Cryoprotectant effects insurimi and surimi/mince–based extruded products. J. Food Sci. 1990, 55, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, P.A.; MacDonald, G.A.; Lanier, T.C. Cryostabilization mechanism of fish muscle proteins by maltodextrins. Cryobiology 1999, 38, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somjit, K.; Ruttanapornwareesakul, Y.; Hara, K.; Nozaki, Y. The cryoprotectant effect of shrimp chitin and shrimp chitin hydrolysate on denaturation and unfrozen water of lizardfish surimi during frozen storage. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkuma, C.; Kawai, K.; Viriyarattanasak, C.; Mahawanich, T.; Tantratian, S.; Takai, R.; Suzuki, T. Glass transition properties of frozen and freeze-dried surimi products: Effects of sugar and moisture on the glass transition temperature. Food Hydrocolloid. 2008, 22, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hizukuri, S.; Takeda, Y.; Yasuda, M.; Suzuki, A. Multi-branched nature of amylose and the action of debranching enzymes. Carbohydr. Res. 1981, 94, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Hizukuri, S.; Juliano, B.O. Purification and structure of amylose from rice starch. Carbohydr. Res. 1986, 148, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hizukuri, S. Polymodal distribution of the chain lengths of amylopectins, and its significance. Carbohydr. Res. 1986, 147, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manners, D.J. Recent developments in our understanding of amylopectin structure. Carbohydr. Polym. 1989, 11, 87–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colonna, P.; Mercier, C. Macromolecular structure of wrinkled- and smooth-pea starch components. Carbohydr. Res. 1984, 126, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.S.; Capitani, T.; Trzasko, P.; Jeffcoat, R. Molecular stucture of a low–amylopectin starch and other high–amylose maize starches. J. Cereal Sci. 1998, 27, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matveev, V.I.; van Soest, J.J.G.; Nieman, C.; Wasserman, L.A.; Protserov, V.A.; Ezernitskaja, M.; Yuryev, V.P. The relationship between thermodynamic and structural properties of low and high amylose maize starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2001, 44, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidley, M.J.; Bulpin, P.V. Aggregation of amylose in aqueous systems—The effect of chain length on phase-behavior and aggregation kinetics. Macromolecules 2004, 22, 341–346. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, V.J. Starch gelation and retrogradation. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 1990, 1, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Martínez, J.M.; Schoenmakers, P.J.; Kok, W.T. Determination of the amylose-amylopectin ratio of starches by iodine-affinity capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1053, 227–234. [Google Scholar]
- Whistler, R.L.; Daniel, J.R. Carbohydrate. In Food Chemistry; Fennema, O.R., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 69–137. [Google Scholar]
- Srichuwong, S.; Sunarti, T.C.; Mishima, T.; Isono, N.; Hisamatsu, M. Starches from different botanical sources I: Contribution of amylopectin fine structure to thermal properties and enzyme digestibility. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 60, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srichuwong, S.; Sunarti, T.C.; Mishima, T.; Isono, N.; Hisamatsu, M. Starches from different botanical sources II: Contribution of starch structure to swelling and pasting properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 62, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Yasui, T.; Matsuki, J. Effect of amylose content on gelatinisation, retrogradation, and pasting properties from waxy and nonwaxy wheat and their F1 seeds. Cereal Chem. 2000, 77, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandeputtea, G.E.; Vermeylena, R.; Geeromsb, J.; Delcoura, J.A. Rice starches. I. Structural aspects provide insight into crystallinity characteristics and gelatinisation behaviour of granular starch. J. Cereal Sci. 2003, 38, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidul, I.S.M.; Yamauchi, H.; Takigawa, S.; Matsuura-Endo, C.; Suzuki, T.; Noda, T. Correlation between the compositional and pasting properties of various potato starches. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.C.; Seib, P.A. Fine structure of maize starches from four wx-containing genotypes of the W64A inbred line in relation to gelatinization and retrogradation. Carbohydr. Polym. 1995, 26, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, T.; Takahata, Y.; Sato, T.; Suda, I.; Morishita, T.; Ishiguro, K.; Yamakawa, O. Relationship between chain length distribution of amylopectin and gelatinization properties within the same origin for sweet potato and buckwheat. Carbohydr. Polym. 1998, 37, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemoto, T.; Yano, M.; Satoh, H.; Shomura, A.; Nakamura, Y. Mapping of a gene responsible for the difference in amylopectin structure between japonica-type and indica-type rice varieties. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 104, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohyama, K.; Matsuki, J.; Yasui, T.; Sasaki, T. A differential thermal analysis of the gelatinization and retrogradation of wheat starches with different amylopectin chain lengths. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 58, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, T.; Isono, N.; Krivandin, A.V.; Shatalova, O.V.; Błaszczak, W.; Yuryev, V.P. Origin of defects in assembled supramolecular structures of sweet potato starches with different amylopectin chain-length distribution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 76, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.; Ring, S.G. Aspects of the physical chemistry of starch. J. Cereal Sci. 2001, 34, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde-Petit, B. The structure and texture of starch–based foods. In Texture in Food Semi-Solid Foods; McKenna, B.M., Ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 1, pp. 86–108. [Google Scholar]
- Closs, C.B.; Conde-Petit, B.; Roberts, I.D.; Tolstoguzov, V.B.; Escher, F. Phase separation and rheology of aqueous starch/galactomannan systems. Carbohydr. Polym. 1999, 39, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde-Petit, B.; Closs, C.; Escher, F. Processing–structure–rheology relationships of microphase separated starch/non–starch polysaccharide mixtures. In Starch Advances in Structure and Function; Barsby, T.L., Donald, A.M., Frazier, P.J., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2001; pp. 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.M.; Wu, M.C.; Okada, M. Ingredient and formulation technology for surimi–based products. In Surimi Technology; Lanier, T.C., Lee, C.M., Eds.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 273–302. [Google Scholar]
- Verrez-Bagnis, V.; Bouchet, B.; Gallant, D.J. Relationship between the starch granule structure and the textural properties of heat–induced surimi gel. Food Struct. 1993, 12, 309–320. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, K.H.; Lee, C.M. Water binding and ingredient dispersion pattern effect on surimi gel texture. J. Food Sci. 1991, 56, 1263–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuankriangkrai, S.; Benjakul, S. Effect of modified tapioca starch on the stability of fish mince gels subjected to multiple freeze-thawing. J. Muscle Foods 2010, 21, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.C.; Hamann, D.D.; Lanier, T.C. Rheological changes in starch-fish protein systems during thermal processing. In Proceeding of IX International Congress on Rheology, Acapulco, Mexico, 8–13 October 1984; pp. 169–187.
- Wu, M.C.; Hamann, D.D.; Lanier, T.C. Thermal transitions of admixed starch/fish protein systems during heating. J. Food Sci. 1985, 50, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, M.; Moresi, M. Viscoelastic properties of Bologna sausages by dynamic methods. J. Food Eng. 2004, 63, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresi, M.; Bruno, M.; Parente, E. Viscoelastic properties of microbial alginate gels by oscillatory dynamic tests. J. Food Eng. 2004, 64, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.K.; Lanier, T.C. Combined effects of phosphates and sugar or polyols on protein stabilization of fish myofibris. J. Food Sci. 1987, 52, 1509–1513. [Google Scholar]
- Sych, J.; Lacroix, C.; Carrier, M. Determination of optimal level of lactitol for surimi. J. Food Sci. 1991, 56, 285–290. [Google Scholar]
- Campo-Deaño, L.; Tovar, C.A.; Borderías, J. Effect of several cryoprotectants on the physicochemical and rheological properties of suwari gels from frozen squid surimi made by two methods. J. Food Eng. 2010, 97, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dea, I.C.M.; Morrison, A. Chemistry and interactions of seed galactomannans. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 1975, 31, 214–312. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, M.; Shibahara, H.; Sugiyama, N. Detailed examination of the branched structure of Konjac glucomannan. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1980, 44, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, M.C.; Gil, A.M. A solid state NMR study of locust bean gum galactomannan and Konjac glucomannan gels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 60, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Hydrocolloids at interfaces and the influence on the properties of dispersed systems. Food Hydrocolloid. 2003, 17, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.A.K.; Foster, T.J.; Martin, D.R.; Norton, I.T.; Yoshimura, M.; Nishinari, K. A molecular description of the gelation mechanism of konjac mannan. Macromolecules 2000, 1, 440–450. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, A.M.; Zeng, Q.X.; Liu, X.; Huang, W.H.; Chen, Y.Q. Study on the improvement of gel properties of Aristichthy nobilis surimi. J. South China Agric. Univ. 2004, 25, 104–107. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Dong, W.; Xu, Y. Synthesis and characterization of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and ethyl acrylate graft copolymers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 68, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.H. Effects of polysaccharides on the thermo-gelation of surimi and cooking-tolerance of kamaboko prepared from horse mackerel. Food Sci. Agric. Chem. (Taiwan) 2000, 2, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.H.; Ferng, L.H.; Chen, S.D.; Sun, W.C.; Lee, Y.C. Combination model for the spatial partition of surimi protein and hydroxylpropylmethylcellulose. Food Hydrocolloid. 2005, 19, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.H. Rheological properties of HPMC enhanced Surimi analyzed by small– and large–strain tests: I. The effect of concentration and temperature on HPMC flow properties. Food Hydrocolloid. 2007, 21, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarker, M.Z.I.; Elgadir, M.A.; Ferdosh, S.; Akanda, M.J.H.; Manap, M.Y.A.; Noda, T. Effect of Some Biopolymers on the Rheological Behavior of Surimi Gel. Molecules 2012, 17, 5733-5744. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17055733
Sarker MZI, Elgadir MA, Ferdosh S, Akanda MJH, Manap MYA, Noda T. Effect of Some Biopolymers on the Rheological Behavior of Surimi Gel. Molecules. 2012; 17(5):5733-5744. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17055733
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarker, Md. Zaidul Islam, M. Abd Elgadir, Sahena Ferdosh, Md. Jahurul Haque Akanda, Mohd Yazid Abdul Manap, and Takahiro Noda. 2012. "Effect of Some Biopolymers on the Rheological Behavior of Surimi Gel" Molecules 17, no. 5: 5733-5744. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17055733
APA StyleSarker, M. Z. I., Elgadir, M. A., Ferdosh, S., Akanda, M. J. H., Manap, M. Y. A., & Noda, T. (2012). Effect of Some Biopolymers on the Rheological Behavior of Surimi Gel. Molecules, 17(5), 5733-5744. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17055733



