Biodegradability and Biocompatibility Study of Poly(Chitosan-g-lactic Acid) Scaffolds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
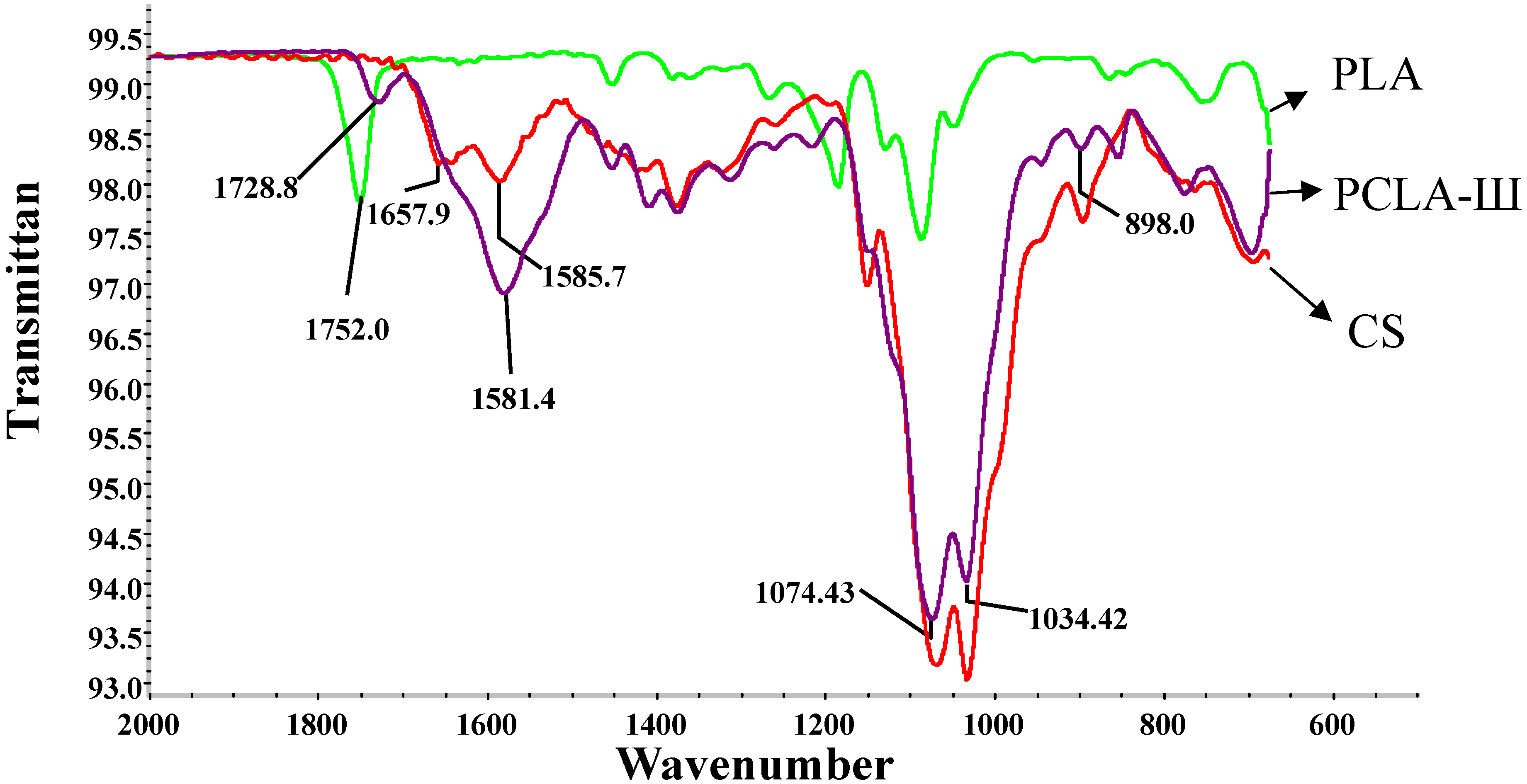
2.1. FTIR Analysis
2.2. SEM and Porosity
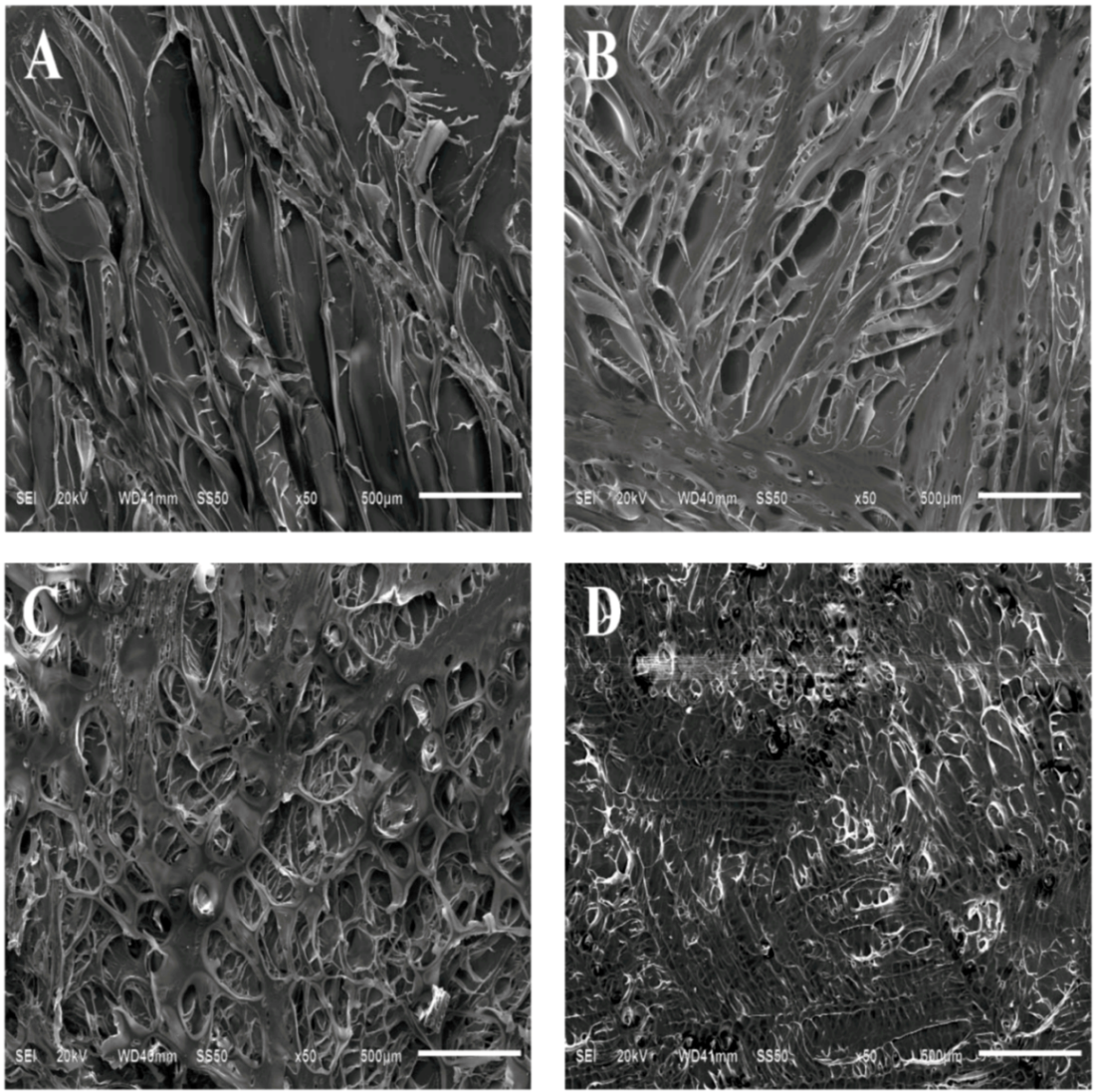
| Copolymer Samples | CS | PCLA-Ι | PCLA-ΙΙ | PCLA-ΙΙΙ | PLA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LA/CS (wt/wt) | - | 2 | 3 | 4 | - |
| [COOH]/[NH2] (mole ratio) | - | 3.27 | 4.91 | 6.54 | - |
| Porosity | 62.03 ± 0.07 | 46.97 ± 0.06 # | 41.30 ± 0.05 * | 34.37 ± 0.06 * | 0 |
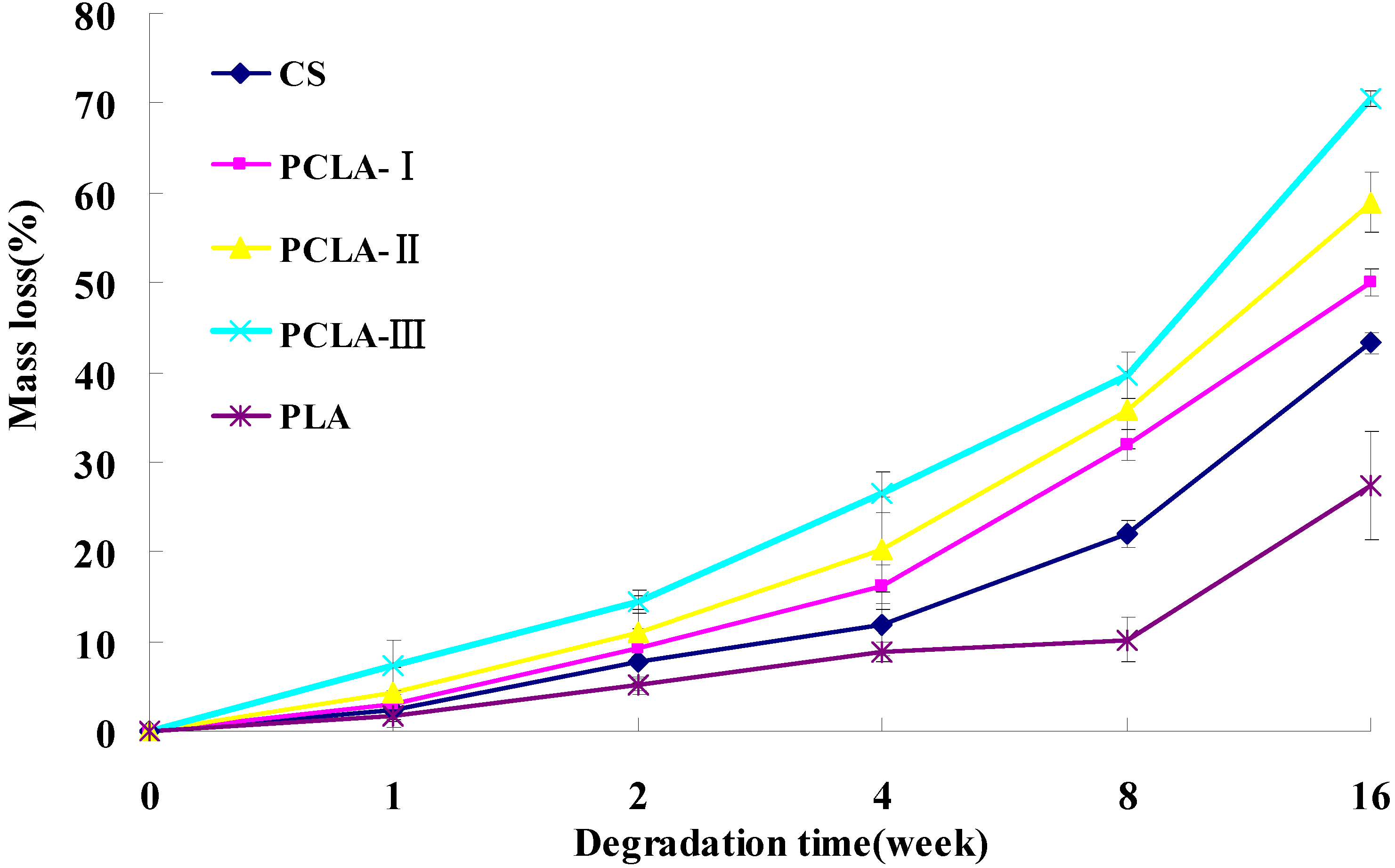
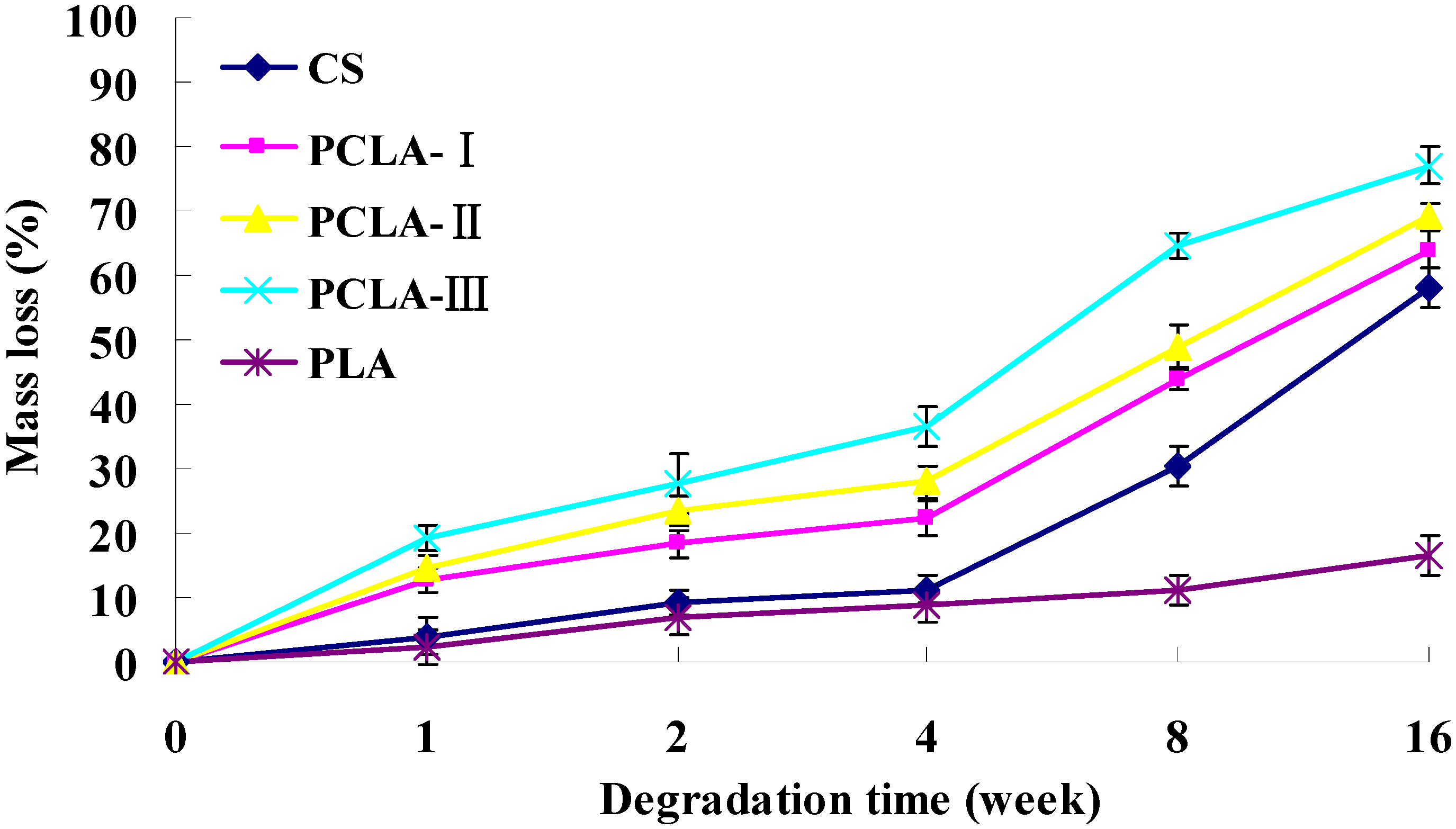
2.3. Mass Loss in Vitro
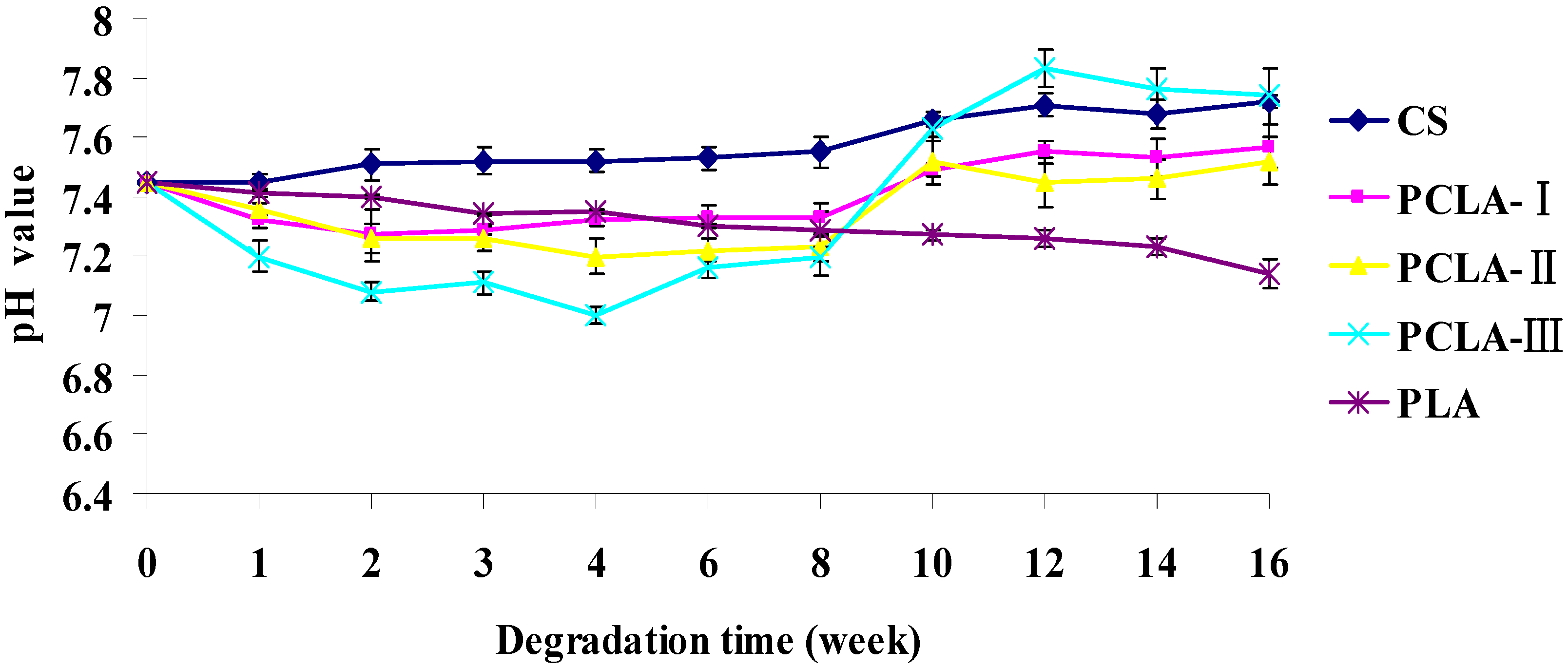
2.4. pH Fluctuation
2.5. Mass Loss in Vivo
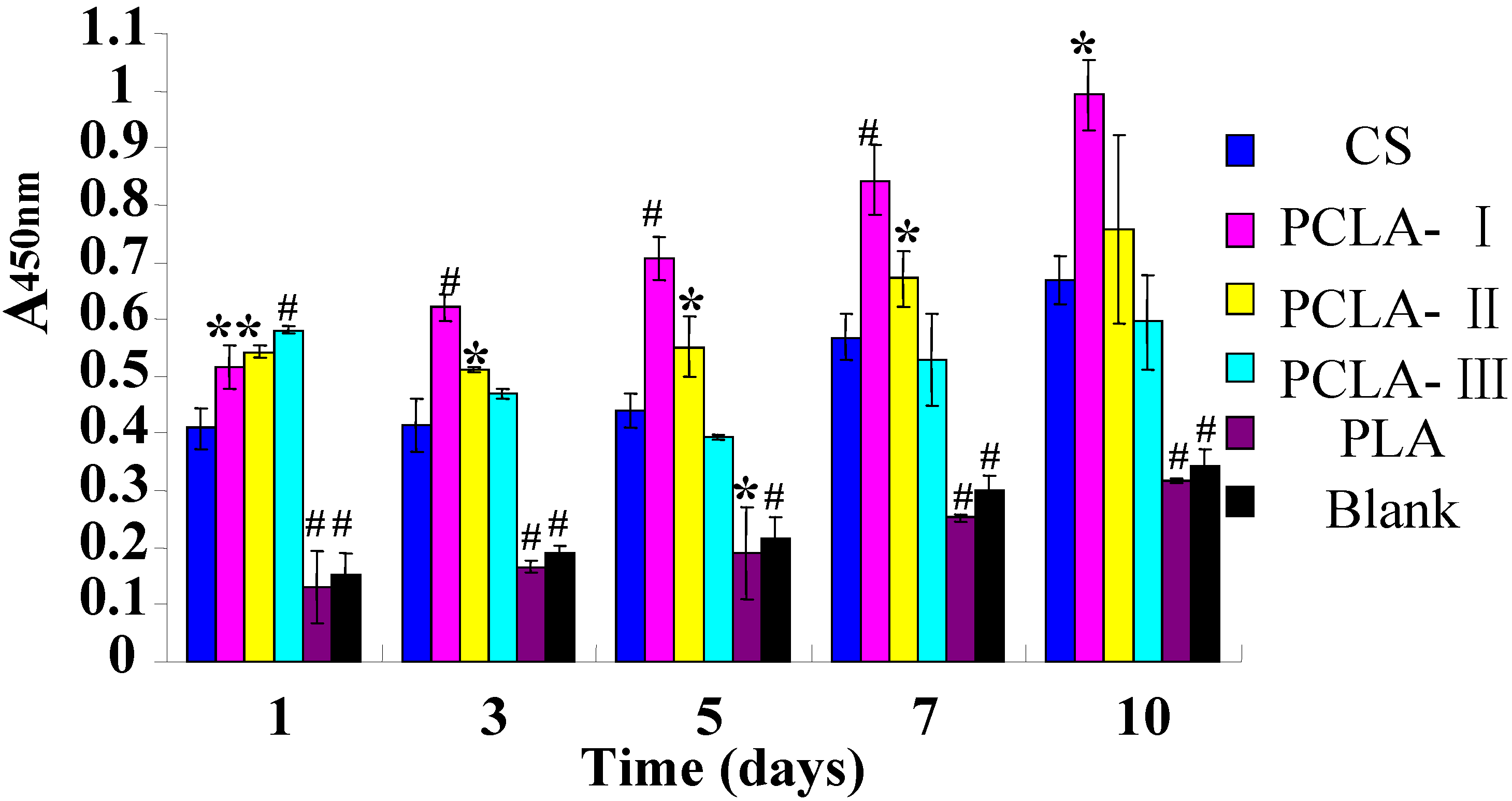
2.6. Cytocompatible Evaluation
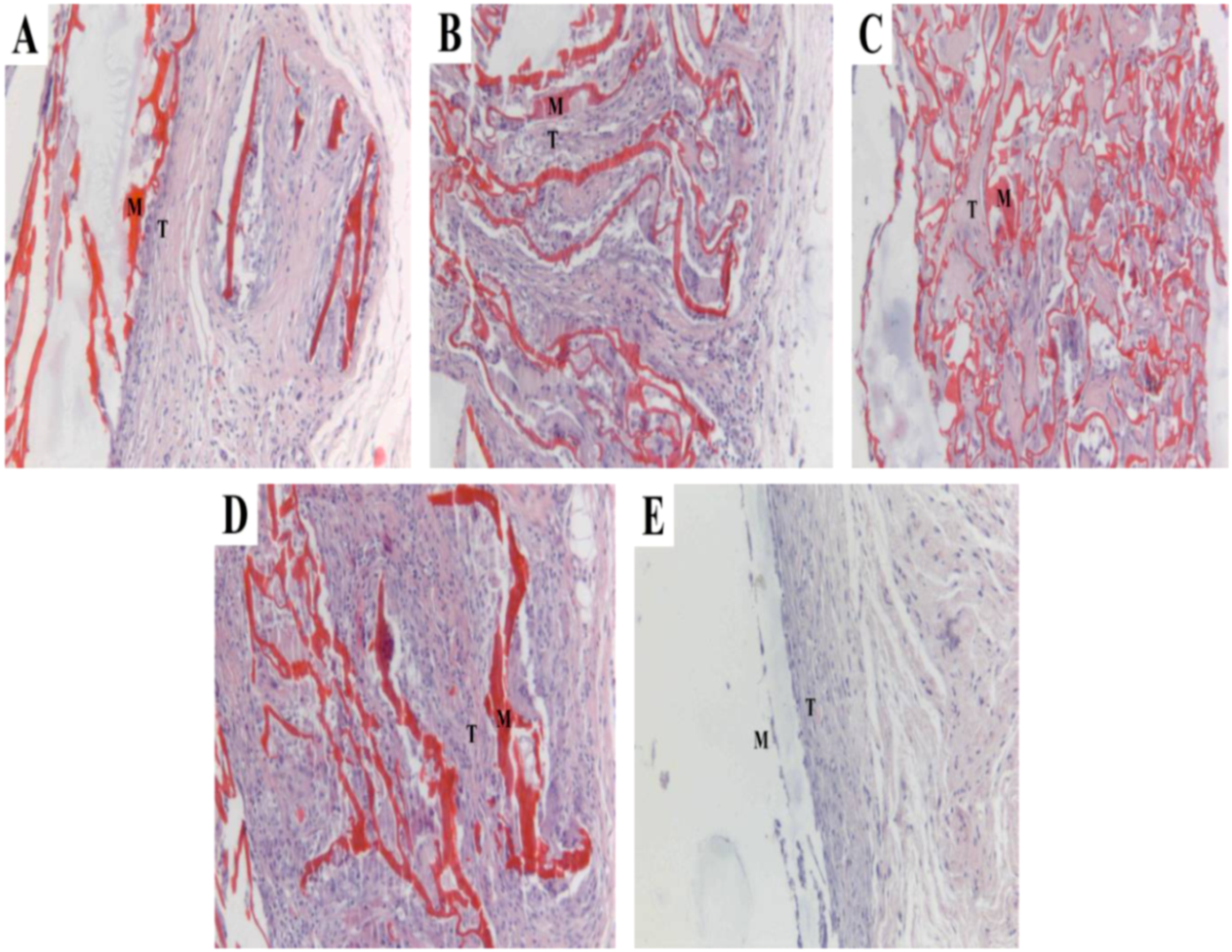
2.7. Histocompatibility
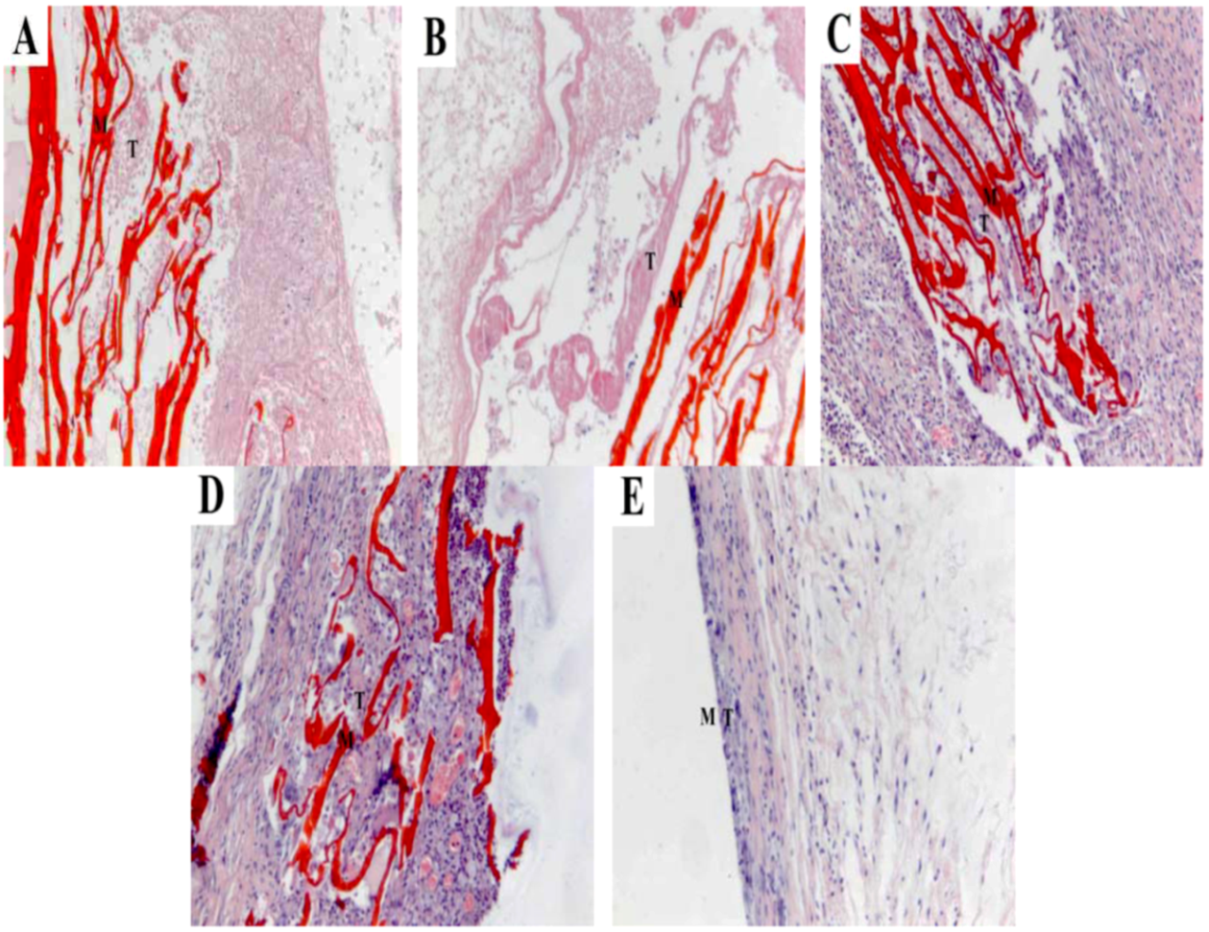
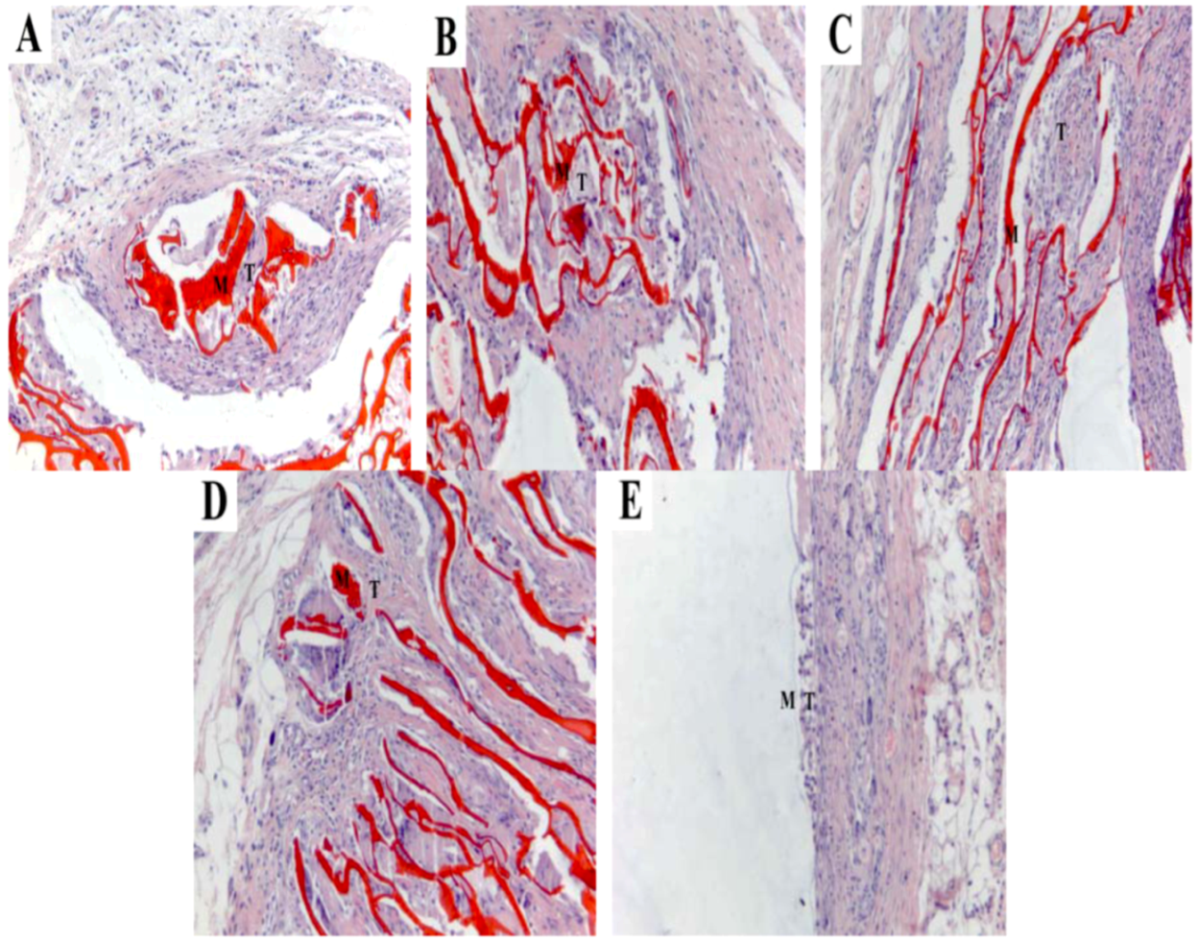
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of PCLA
3.3. Characterization of Scaffolds
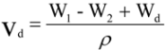
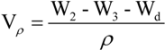
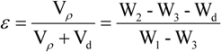
3.4. Mass Loss in Vitro
3.5. pH Change
3.6. Mass Loss in Vitro
3.7. Cytocompatibility Evaluation
3.8. Histocompatibility
3.8.1. Rat in Vitro Protocol
3.8.2. Histological Staining
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
References and Notes
- Zheng, L.; Cui, H.F. Use of chitosan conduit combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for promoting peripheral nerve regeneration. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 1713–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Tian, F.; Yang, J.; He, C.N.; Xing, N.; Li, F. Chitosan and alginate polyelectrolyte complex membranes and their properties for wound dressing application. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Cao, Z.; Hu, Y.Y.; Song, Y.; Yu, L.; Yang, B.; Mu, J.H.; Huang, Z.S.; Han, Y.S. Effects of different cross-linking conditions on the properties of genipin-cross-linked chitosan/collagen scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Yeh, C.T. Alginate-crosslinked chitosan scaffolds as pentoxifylline delivery carriers. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 1611–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Jun, S.H.; Kim, H.E.; Kim, H.W.; Koh, Y.H.; Jang, J.H. Silica xerogel-chitosan nano-hybrids for use as drug eluting bone replacement. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Yao, J.; Lin, W.W.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.L.; Yang, Y.M.; Gu, X.S.; Wang, X.D. Bone marrow stromal cells-loaded chitosan conduits promote repair of complete transection injury in rat spinal cord. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 2347–2356. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.Y.; Shang, Y.; Yuan, Y.J.; Yang, J. Preparation and characterization of chitosan/galactosylated hyaluronic acid scaffolds for primary hepatocytes culture. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahul, M.R.; Amol, V.J.; Douglas, E.H. Poly(lactic acid) modifications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 338–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, K.; Maegawa, T.; Takahashi, T. Glass transition temperature of chitosan and miscibility of chitosan/poly(N-vinyl pyrrolidone) blends. Polymer 2000, 41, 7051–7056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ding, S.; Zhou, C. Preparation and degradation of PLA/chitosan composite materials. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 91, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugraha, E.; Copinet, A.; Tighzert, L.; Coma, V. Mechanical and barrier properties of biodegragable films made from chitosan and poly(lactic acid) blends. J. Polym. Environ. 2004, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peesan, M.; Supaphol, P.; Rujiravanit, R. Preparation and characterization of hexanoyl chitosan/ polylactide blend films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 60, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Dong, L.; Cheung, M.K. Preparation and characterization of biodegragable poly(L-lactide)/ chitosan blends. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Xiao, Y.C.; Sheng, M.Z.; Sheng, W.; Quan, W. Fibrous poly(chitosan-g-DL-lactic acid) scaffolds prepared via electro-wet-spinning. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 876–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.H.; Hua, Y.Y.; Pu, L.S. Chitosan-L-lactic acid scaffold for the regeneration of peripheral nerve and its NGF release properties. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. 2009, 24, 961–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.F.; Wei, C.; Hao, W.; Feng, L.H.; De, Y.K.; Sun, P.C.; Lin, H. A study on cytocompatible poly(chitosan-g-L-lactic acid). Polymer 2003, 44, 6435–6441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Ting, L.Y.; Hsiu, C.P.; Hao, H.C.; Wei, W.Y.; Hsin, C. Characterizing microporous PCL matrices for application of tissue engineering. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2009, 29, 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, X.H.; Zhi, Y.L.; Chen, X.; Jin, H.M.; Wang, L.L.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Yin, Z.; Ouyang, H.W. Mesenchymal stem cell seeded knitted silk sling for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4872–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhuber, B.; Swanger, S.A.; Howard, L.; Mackay, A.; Fischer, I. Effects of plating density and culture time on bone marrow stromal cell characteristics. Exp. Hematol. 2008, 36, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Ding, F.; Zhang, P.; Liu, J.; Gu, X. Biocompatibility evaluation of silk fibroin with peripheral nerve tissues cells in vitro. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.; Wu, H.; Yu, A.; Wen, D. Biodegradable polylactide/chitosan blend membranes. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1362–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Wirsen, A.; Albertsson, A.C. Synthesis and characterization of pH-sensitive hydrogels based on chitosan and DL-lactic acid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 3193–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varum, K.M.; Myhr, M.M.; Hjerde, R.J.; Smidsrod, O. In vitro degradation rates of partially N-acetylated chitosans in human serum. Carbohydr. Res. 1997, 299, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Peter, S.J.; Lyman, M.D.; Lai, H.-L.; Leite, S.M.; Tamada, J.A.; Shiro, U.; Joseph, P.V.; Robert, L.; Antonios, G.M. In vitro and in vivo degradation of porous poly (DL-lactic-co-glycolic acid) foams. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 1837–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellat, F.; Tabrizian, M.; Dumitriu, S.; Chornet, E.; Magny, P.; Rivard, C.H.; Yahia, L.H. In vitro and in vivo biocompatibility of chitosan-xanthan polyionic complex. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 51, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Yu, A.; Wu, H.; Wang, Z.; Wen, D. Porous-conductive chitosan scaffolds for tissue engineering II. In vitro and in vivo degradation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2005, 16, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, K.; Nishimura, S.; Seo, H.; Nishi, N.; Tokura, S.; Azuma, I. Macrophage activation with multi-porous beads prepared from partially deacetylated chitin. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1986, 20, 1359–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yomota, C.; Komuro, T.; Kimura, T. Studies on the degradation of chitosan films by lysozyme and release of loaded chemicals. Yakugazu-Zasshi 1990, 110, 442–448. [Google Scholar]
- Rozema, F.R.; Bruijn, W.C.; Bos, R.R.M.; Boering, G.; Pennings, A.J. Late tissue response to bone-plates and screws of poly (L-lactide) used for fracture fixation of the zygomatic bone plate. Adv. Biomater. 1992, 10, 349–355. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.M.; Miller, K.M. Biomaterial biocompatibility and the macrophage. Biomaterials 1984, 5, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutright, D.E.; Perez, B.; Beasley, J.D.; Larson, W.J.; Rosey, W.R. Degradationrates of polymers and copolymers of polylactic and polyglycolic acids. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1974, 37, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, A.M.; Gilding, D.K. Biodegradable polymers for use in surgery-polyglycolic/poly(lactic acid) homo-and copolymers: 2 In vitro degradation. Polymer 1981, 22, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilding, D.K.; Reed, A.M. Biodegradable polymers for use in surgery-polyglycolic/poly(lactic acid) homo-and copolymers: 1. Polymer 1979, 20, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, S.C. Physiological and biochemical evaluation of implanted polymers. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1968, 146, 225–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salthouse, T.N.; Matlage, B.F. Some Cellular Effects Related to Implant Shape and Surface. In Biomaterials in Reconstructive Surgery; Rubin, L.R., Ed.; Mosby: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1983; pp. 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Lu, G.Y.; Ao, Q.; Gong, Y.D.; Zhang, X.F. Preparation of cross-linked carboxymethyl chitosan for repairing sciatic nerve injury in rats. J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 32, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, J.; Peng, W.M.; Qiu, G.F. Biodegradability of conducting chitosan-g-polycaprolactone/polypyrrole conduits. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 1994–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBane, J.E.; Sharifpoor, S.; Cai, K.H.; Labowc, R.S.; Santerre, J.P. Biodegradation and in vivo biocompatibility of a degradable, polar/hydrophobic/ionic polyurethane for tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 6034–6044. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Jiang, H.; Chen, W. The biodegradability of electrospun dextran/PLGA scaffold in a fibroblast/macrophage co-culture. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Cui, H. Biodegradability and Biocompatibility Study of Poly(Chitosan-g-lactic Acid) Scaffolds. Molecules 2012, 17, 3243-3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17033243
Zhang Z, Cui H. Biodegradability and Biocompatibility Study of Poly(Chitosan-g-lactic Acid) Scaffolds. Molecules. 2012; 17(3):3243-3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17033243
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhe, and Huifei Cui. 2012. "Biodegradability and Biocompatibility Study of Poly(Chitosan-g-lactic Acid) Scaffolds" Molecules 17, no. 3: 3243-3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17033243
APA StyleZhang, Z., & Cui, H. (2012). Biodegradability and Biocompatibility Study of Poly(Chitosan-g-lactic Acid) Scaffolds. Molecules, 17(3), 3243-3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17033243




