Abstract
A facile synthesis of potential acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors, the tacrine analogues 3a-p, has been accomplished by direct cyclocondensation of 1-aryl-4-cyano-5-aminopyrazole with β-ketoesters using tin(IV) chloride as catalyst. The structures of all the compounds have been confirmed by IR, 1H- and 13C-NMR.
1. Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the most common form of dementia among the elderly, is a progressive, degenerative disorder of the brain with a loss of memory and cognition [1]. Tacrine is a reversible inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) that was launched in 1993 as the first drug for the treatment of AD [2]. The evaluation of the clinical effects of tacrine has shown efficacy in delaying the deterioration of the symptoms of AD, but the poor selectivity of this drug for AChE has resulted in a number of side effects, specially hepatotoxicity [3], and current research is focused on developing new AChE inhibitors with improved activity and reduced adverse side effects, therefore novel tacrine analogues have been reported [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18].
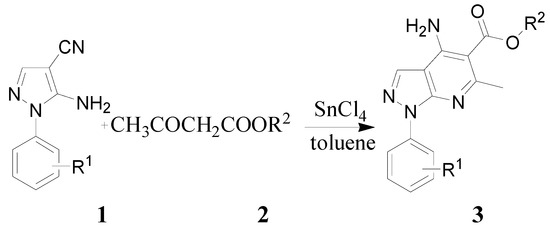
Friedlander annulation is one of the simplest and most straightforward protocols for the preparation of quinoline derivatives [19,20]. Although it has been known for more than a century, it is still a hotspot of research. Herein, we report that the Friedlander annulation of 1-aryl-4-cyano-5-aminopyrazole with β-ketoesters using SnCl4 as catalyst afforded the novel tacrine analogues 3a-p in good yields.
2. Results and Discussion
The main synthetic approach to tacrine analogues is the cyclocondensation of o-aminonitrile derivatives with ketones using anhydrous AlCl3 as catalyst, but that method gives low to moderate yields [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. Cabrera and co-workers [21] have reported that the synthesis of 4-aminoquinolines from 2-aminobenzonitrile and β-dicarbonyl compounds could be accomplished using Lewis acids as catalysts. They found that SnCl4 was a very effective catalyst for the preparation of the target compounds compared with other Lewis acids.
For the investigation of reaction conditions for cyclocondensation of 1-aryl-4-cyano-5-amino-pyrazole with β-ketoesters, we chose the reaction of 1-phenyl-4-cyano-5-aminopyrazole (1a) with methyl acetoacetate as a model reaction. Because the choice of the catalyst played a crucial role, we initially studied the effect of several catalysts on the yields and found the use of anhydrous AlCl3, ZnCl2 and TiCl4 to be much less effective and tacrine analogue 3a was obtained in less than 43% yield. Moreover, none of the product desired 3a was obtained when we used CuCl and CuCl2 as catalysts. However, when a mixture of 1-phenyl-4-cyano-5-aminopyrazole (1a) and methyl acetoacetate in toluene was stirred under reflux in the presence of SnCl4, the reaction was complete within 3 h and after work up, the product 3a was obtained in 78% yield (Table 1).

Table 1.
Effect of the catalyst on the yields. a
A profound solvent effect on the reaction was observed. We initially studied the effect on the reaction of non-polar solvents, such as DCM, DCE, THF and toluene, in which SnCl4 is easily dissolved. Then we went on to study the polar solvent DMF. The results are summarized in Table 2. These results suggest that the solvent had a dramatic effect on the yields. Toluene was found to be the best solvent.

Table 2.
Effect of the solvent on the yields. a
Under the optimized reaction conditions (SnCl4 as catalyst and anhydrous toluene as solvent, reflux for 3 h), a series of reactions between 1-aryl-4-cyano-5-aminopyrazoles and β-ketoesters were tested and a series of tacrine analogues 3 was thus prepared in good yields, regardless of the position of the group R1 on the aromatic ring. The results were summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Cyclocondensation of substituted o-aminobenzonitrile and β-ketoesters. a
The mechanism of formation of tacrine analogue 3 can be explained by Scheme 2. The attack of the amino group of 1 onto the carbonyl carbon atom of 2 gave intermediate I, from which product 3 was obtained through the Friedlander reaction.
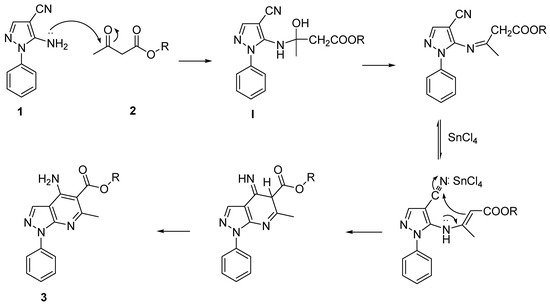
Scheme 2.
Proposed mechanism.
3. Experimental
3.1. General
All melting points were determined on an XT-4A apparatus. TLC was performed using precoated silica gel GF254 (0.25 mm), column chromatography was performed using silica gel (200–300 mesh). The 1H- and 13C-NMR spectra were measured at 300 and 75 MHz, respectively, on a Bruker Advance 300 spectrometer at 25 °C, using TMS as internal standard. J-values are given in Hz. The IR spectra were taken on a Bruker Vector 55 spectrometer. 1-Aryl-4-cyano-5-aminopyrazoles 1 were prepared according to a reported procedure [22].
3.2. Typical procedure
1-Aryl-4-cyano-5-aminopyrazole 1 (10 mmol) and SnCl4 (2.3 mL, 20 mmol) were added to a stirred solution of β-ketoester (10 mmol) in dry toluene (20 mL). The reaction mixture was stirred under nitrogen at room temperature for 30 min and then heated under reflux for 3 h. The reaction mixture was cooled and dispersed into water and titrated to pH 12–13 with a saturated aqueous solution of Na2CO3. After filtration, the filtrate was extracted three times with ethyl acetate, the organic layers were dried and evaporated at reduced pressure to give the solid product. The product was purified by silica gel column chromatography to give 3a-p.
Methyl 4-amino-6-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate (3a). Colorless solid. m.p. 125–126 °C. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 8.24 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 2H, Ar-H), 8.04 (s, 1H, pyrazole H), 7.41–7.48 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.23–7.28 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 6.74 (br, 2H, -NH2), 3.90 (s, 3H, -OCH3), 2.80 (s, 3H, -CH3). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 169.9, 163.1, 151.8, 150.0, 138.7, 131.6, 128.8, 126.3, 121.6, 105.3, 101.2, 51.6, 28.1. MS-ESI (m/z, relative intensity, %): 285 (M++3) (3), 284 (M++2) (18), 283 (M++1) (100). IR (KBr, cm−1) ν: 3,451, 3,330 (NH2), 3,111 (ArH), 2,976, 2,926 (CH3), 1,665 (C=O), 1,590, 1,495, 1,460 (C=N and aromatic ring skeleton vibration), 1,260 (O-CH3).
Methyl 4-amino-6-methyl-1-p-tolyl-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate (3b). Colorless solid. m.p. 167–168 °C. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 8.08 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, Ar-H), 8.05 (s, 1H, pyrazole H), 7.25–7.29 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 6.74 (br, 2H, -NH2), 3.91 (s, 3H, -OCH3), 2.80 (s, 3H, pyridine-CH3), 2.38 (s, 3H, benzene-CH3). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 169.2, 162.1, 151.9, 149.5, 136.3, 135.4, 130.6, 128.9, 121.0, 104.7, 100.5, 51.5, 27.9, 20.8. MS-ESI (m/z, relative intensity, %): 299 (M++3) (3), 298 (M++2) (20), 297 (M++1) (100). IR (KBr, cm−1) ν: 3,452, 3,333 (NH2), 3,110 (ArH), 2,976, 2,925 (CH3), 1,660 (C=O), 1,590, 1,495, 1,460 (C=N and aromatic ring skeleton vibration), 1,246 (O-CH3).
Methyl 4-amino-6-methyl-1-m-tolyl-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate (3c). Colorless solid. m.p. 151–153 °C. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 8.07 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H, Ar-H), 8.04 (s, 1H, pyrazole H), 7.33–7.39 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 7.11–7.16 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 6.72 (br, 2H, -NH2), 3.91 (s, 3H, -OCH3), 2.82 (s, 3H, pyridine-CH3), 2.40 (s, 3H, benzene-CH3). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 169.0, 162.1, 151.0, 149.5, 138.6, 131.4, 128.1, 126.2, 125.1, 121.5, 118.7, 104.9, 101.0, 51.8, 28.1, 21.0. MS-ESI (m/z, relative intensity, %): 299 (M++3) (2), 298 (M++2) (22), 297 (M++1) (100). IR (KBr, cm−1) ν: 3,453, 3,332 (NH2), 3,112 (ArH), 2,978, 2,923 (CH3), 1,672 (C=O), 1,596, 1,497, 1,465 (C=N and aromatic ring skeleton vibration), 1,260 (O-CH3).
Methyl 4-amino-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate (3d). Colorless solid. m.p. 160–162 °C. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 8.26 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, Ar-H), 8.04 (s, 1H, pyrazole H), 7.40–7.48 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 6.72 (br, 2H, -NH2), 3.91 (s, 3H, -OCH3), 2.81 (s, 3H, -CH3). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 168.8, 161.7, 151.2, 135.0, 131.7, 130.6, 127.9, 121.0, 118.2, 104.9, 100.4, 51.7, 28.0. MS-ESI (m/z, relative intensity, %): 320 (9), 319 (32), 317 (M++1) (100). IR (KBr, cm−1) ν: 3,451, 3,330 (NH2), 3,111 (ArH), 2,976, 2,926 (CH3), 1,665 (C=O), 1,592, 1,494, 1,458 (C=N and aromatic ring skeleton vibration), 1,260 (O-CH3).
Methyl 4-amino-1-(3-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate (3e). Colorless solid. m.p. 127–128 °C. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 8.36–8.40 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 8.27–8.31 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 8.05 (s, 1H, pyrazole H), 7.40–7.43 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 7.24–7.26 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 6.74 (br, 2H, -NH2), 3.90 (s, 3H), 2.82 (s, 3H, -CH3). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 168.9, 161.7, 151.1, 132.7, 131.5, 130.6, 130.1, 129.6, 128.4, 125.6, 121.7, 120.8, 118.4, 51.7, 28.0. MS-ESI (m/z, relative intensity, %): 319 (7), 318 (33), 317 (M++1) (100). IR (KBr) ν: 3,453, 3,333 (NH2), 3,110 (ArH), 2,976, 2,924 (CH3), 1,668 (C=O), 1,592, 1,496, 1,461 (C=N and aromatic ring skeleton vibration), 1,258 (O-CH3).
Methyl 4-amino-1-(2-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate (3f). Color-less solid. m.p. 154–155 °C. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 8.12 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 8.05 (s, 1H, pyrazole H), 7.55–7.58 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 7.39–7.42 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 6.74 (br, 2H, -NH2), 3.90 (s, 3H, -OCH3), 2.80 (s, 3H, -CH3). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 169.2, 162.8, 151.4, 151.3, 135.9, 131.7, 132.1, 130.5, 129.4, 129.1, 126.4, 103.1, 100.9, 51.6, 27.9. MS-ESI (m/z, relative intensity, %): 319 (8), 318 (33), 317 (M++1) (100). IR (KBr, cm−1) ν: 3,451, 3,330 (NH2), 3,112 (ArH), 2,975, 2,923 (CH3), 1,665 (C=O), 1,591, 1,495, 1,458 (C=N and aromatic ring skeleton vibration), 1,262 (O-CH3).
Methyl 4-amino-6-methyl-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate (3g). Yellowish solid. m.p. 190–192 °C. 1H-NMR (DMSO) δ: 8.62–8.74 (m, 3H, Ar-H and pyrazole H), 8.37–8.40 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.84 (br, 2H, -NH2), 3.92 (s, 3H, -OCH3), 2.79 (s, 3H, -CH3). 13C-NMR (DMSO) δ: 168.0, 161.4, 151.3, 150.9, 144.6, 136.6, 125.1, 119.8, 118.5, 105.0, 102.4, 51.8, 29.0. MS-ESI (m/z, relative intensity, %): 330 (M++3) (3), 329 (M++2) (18), 328 (M++1) (100). IR (KBr, cm−1) ν: 3,451, 3,330 (NH2), 3,111 (ArH), 2,976, 2,926 (CH3), 1,680 (C=O), 1,610, 1,543, 1,508 (C=N and aromatic ring skeleton vibration), 1,272 (O-CH3).
Methyl 4-amino-1-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)-6-methyl-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate (3h). Yellowish solid. m.p. 202–204 °C. 1H-NMR (DMSO) δ: 8.86 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 8.69-8.73 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 8.52 (s, 1H, pyrazole H), 8.41–8.45 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 7.76 (br, 2H, -NH2), 3.91 (s, 3H, -OCH3), 2.80 (s, 3H, -CH3). 13C-NMR (DMSO) δ: 167.8, 162.2, 151.4, 150.7, 137.4, 134.9, 128.6, 128.4, 126.3, 126.1, 126.0, 121.7, 119.5, 51.8, 28.2. MS-ESI (m/z, relative intensity, %): 375 (M++3) (5), 374 (M++2) (21), 373 (M++1) (100). IR (KBr, cm−1) ν: 3,453, 3,332 (NH2), 3,112 (ArH), 2,979, 2,933 (CH3), 1,679 (C=O), 1,612, 1,550, 1,515 (C=N and aromatic ring skeleton vibration), 1,277 (O-CH3).
Ethyl 4-amino-6-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate (3i). Colorless solid. m.p. 130–131 °C. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 8.25 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H, Ar-H), 8.04 (s, 1H, pyrazole H), 7.46–7.50 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.25–7.31 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 6.76 (br, 2H), 4.39 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, -CH2CH3), 2.81 (s, 3H, -CH3), 1.42 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H, -CH2CH3). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 169.2, 162.5, 151.4, 150.2, 139.4, 131.7, 128.9, 126.1, 121.4, 105.1, 101.5, 60.7, 28.4, 14.3. MS-ESI (m/z, relative intensity, %): 299 (M++3) (3), 298 (M++2) (19), 297 (M++1) (100). IR (KBr, cm−1) ν: 3,453, 3,333 (NH2), 3,110 (ArH), 2,976, 2,926 (CH2 and CH3), 1,665 (C=O), 1,592, 1,494, 1,460 (C=N and aromatic ring skeleton vibration), 1,260 (O-CH3).
Ethyl 4-amino-6-methyl-1-p-tolyl-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate (3j). Colorless solid. m.p. 173–174 °C. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 8.09 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 2H, Ar-H), 8.04 (s, 1H, pyrazole H), 7.25–7.29 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 6.72 (br, 2H, -NH2), 4.40 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, -CH2CH3), 2.81 (s, 3H, pyridine-CH3), 2.39 (s, 3H, benzene-CH3), 1.43 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H, -CH2CH3). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 168.9, 162.0, 151.0, 149.7, 136.5, 135.5, 130.9, 129.1, 121.1, 104.5, 100.9, 60.3, 28.0, 20.6, 13.9. MS-ESI (m/z, relative intensity, %): 313 (M++3) (2.5), 312 (M++2) (22), 311 (M++1) (100). IR (KBr, cm−1) ν: 3,453, 3,335 (NH2), 3,112 (ArH), 2,977, 2,930 (CH2 and CH3), 1,658 (C=O), 1,590, 1,492, 1,460 (C=N and aromatic ring skeleton vibration), 1,260 (O-CH3).
Ethyl 4-amino-6-methyl-1-m-tolyl-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate (3k). Colorless solid. m.p. 148–149 °C. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 8.08 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H, Ar-H), 8.01 (s, 1H, pyrazole H), 7.38 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.11 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 6.72 (br, 2H, -NH2), 4.40 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, -CH2CH3), 2.82 (s, 3H, pyridine-CH3), 2.45 (s, 3H, benzene-CH3), 1.43 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H, -CH2CH3). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 168.8, 162.1, 150.9, 149.6, 138.5, 131.1, 128.3, 126.6, 125.6, 121.7, 118.3, 104.6, 101.1, 60.4, 28.0, 21.2, 13.9. MS-ESI (m/z, relative intensity, %): 313 (M++3) (2), 312 (M++2) (20), 311 (M++1) (100). IR (KBr, cm−1) ν: 3,453, 3,336 (NH2), 3,111 (ArH), 2,976, 2,926 (CH2 and CH3), 1,662 (C=O), 1,590, 1,494, 1,462 (C=N and aromatic ring skeleton vibration), 1,262 (O-CH3).
Ethyl 4-amino-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate (3l). Colorless solid. m.p. 143–144 °C. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 8.27 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 2H, Ar-H), 8.04 (s, 1H, pyrazole H), 7.43–7.49 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 6.74 (br, 2H, -NH2), 4.40 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, -CH2CH3), 2.81 (s, 3H, -CH3), 1.43 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H, -CH2CH3). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 168.9, 162.0, 151.0, 135.3, 131.6, 130.9, 128.1, 121.1, 118.5, 104.5, 100.9, 60.3, 28.0, 13.9. MS-ESI (m/z, relative intensity, %): 334 (8), 333 (33), 331 (M++1) (100). IR (KBr, cm−1) ν: 3,453, 3,338 (NH2), 3,113 (ArH), 2,973, 2,925 (CH2 and CH3), 1,660 (C=O), 1,593, 1,457 (C=N and aromatic ring skeleton vibration), 1,260 (O-CH3).
Ethyl 4-amino-1-(3-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate (3m). Colorless solid. m.p. 105–106 °C. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 8.37–8.42 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 8.28–8.33 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 8.04 (s, 1H, pyrazole H), 7.41–7.46 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 7.23–7.27 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 6.73 (br, 2H, -NH2), 4.41 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, -CH2CH3), 2.83 (s, 3H, -CH3), 1.44 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H, -CH2CH3). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 168.7, 161.9, 150.9, 132.9, 131.6, 130.6, 130.2, 129.5, 128.6, 125.4, 121.8, 120.6, 118.5, 60.4, 27.9, 13.8. MS-ESI (m/z, relative intensity, %): 334 (6), 333 (31), 331 (M++1) (100). IR (KBr, cm−1) ν: 3,453, 3,337 (NH2), 3,111 (ArH), 2,974, 2,928 (CH2 and CH3), 1,661 (C=O), 1,592, 1,490, 1,458 (C=N and aromatic ring skeleton vibration), 1,258 (O-CH3).
Ethyl 4-amino-1-(2-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate (3n). Colorless solid. m.p. 164–165 °C. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 8.11 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 8.04 (s, 1H, pyrazole H), 7.51–7.57 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 7.38–7.42 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 6.83 (br, 2H, -NH2), 4.40 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, -CH2CH3), 2.72 (s, 3H), 1.41 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H, -CH2CH3). 13C-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 168.8, 162.5, 151.1, 150.9, 135.4, 131.9, 131.8, 130.2, 129.6, 129.4, 126.9, 103.4, 101.2, 60.3, 27.7, 13.9. MS-ESI (m/z, relative intensity, %): 334 (5), 333 (32), 331 (M++1) (100). IR (KBr, cm−1) ν: 3,453, 3,338 (NH2), 3,112 (ArH), 2,973, 2,930 (CH2 and CH3), 1,660 (C=O), 1,590, 1,493, 1,457 (C=N and aromatic ring skeleton vibration), 1,263 (O-CH3).
Ethyl 4-amino-6-methyl-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate (3o). Yellowish solid. m.p. 197–199 °C. 1H-NMR (DMSO) δ: 8.62–8.74 (m, 3H, Ar-H and pyrazole H), 8.36–8.41 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.84 (br, 2H, -NH2), 4.32 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, -CH2CH3), 2.67 (s, 3H, -CH3), 1.33 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H, -CH2CH3). 13C-NMR (DMSO) δ: 167.8, 161.2, 151.0, 150.5, 144.4, 136.3, 124.9, 119.6, 118.9, 105.4, 102.6, 60.6, 29.3, 14.2. MS-ESI (m/z, relative intensity, %): 344 (M++3) (2.5), 343 (M++2) (18), 342 (M++1) (100). IR (KBr, cm−1) ν: 3,453, 3,333 (NH2), 3,112 (ArH), 2,978, 2,930 (CH2 and CH3), 1,678 (C=O), 1,616, 1,545, 1,512 (C=N and aromatic ring skeleton vibration), 1,275 (O-CH3).
Ethyl 4-amino-1-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)-6-methyl-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-carboxylate (3p). Yellowish solid. m.p. 205–206 °C. 1H-NMR (DMSO) δ: 8.86 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 8.69–8.73 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 8.52 (s, 1H, pyrazole H), 8.43 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.74 (br, 2H, -NH2), 4.39 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, -CH2CH3), 2.66 (s, 3H, -CH3), 1.39 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H, -CH2CH3). 13C-NMR (DMSO) δ: 167.8, 162.2, 151.4, 150.7, 137.4, 134.9, 128.6, 128.4, 126.3, 126.1, 126.0, 121.7, 119.5, 60.2, 27.9, 14.0. MS-ESI (m/z, relative intensity, %): 389 (M++3) (4), 388 (M++2) (19), 387 (M++1) (100). IR (KBr, cm−1) ν: 3,453, 3,331 (NH2), 3,113 (ArH), 2,979, 2,932 (CH2 and CH3), 1,680 (C=O), 1,617, 1,545, 1,512 (C=N and aromatic ring skeleton vibration), 1,272 (O-CH3).
4. Conclusions
We have developed an efficient catalyst system using SnCl4 in anhydrous toluene for the reaction between o-aminonitriles containing pyrazole moieties with β-ketoesters. A series of novel tacrine analogues 3a-p has been thus synthesized and their spectroscopic characterization and structural features have been presented.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for financial support from Taizhou University (Project No. 2010PY21), and the Undergraduate Scientific and Technological Innovation Project of Zhejiang Province, and the Nature Science Foundation of China (Project No. 20905057).
References and Notes
- Bartus, R.T.; Dean, R.L.; Beer, B.; Lippa, A.S. The Cholinergic Hypothesis of Geriatric Memory Dysfunction. Science 1982, 217, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, K.L.; Powchik, P. Tacrine. Lancet 1995, 345, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracon, S.I.; Berghoff, W.G. Pharmacological Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecular and Neurobiological Foundations; Brioni, J.D., Decker, M.W., Eds.; Wiley-Liss Inc: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 389–408. [Google Scholar]
- Carlier, P.R.; Han, Y.F.; Chow, E.S.H.; Li, C.P.L.; Wang, H.; Lieu, Y.P.; Wong, H.S.; Pang, Y.P. Evaluation of Short-tether Bis-THA AChE Inhibitors. A Further Test of the Dual Binding Site Hypothesis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1999, 7, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps, P.; Achab, R.E.; Morral, J.; Torrero, D.M.; Badia, A.; Banos, J.E.; Vivas, N.M.; Barril, X.; Orozco, M.; Luque, F.J. New Tacrine-huperzine A Hybrids (Huprines): Highly Potent Tight-binding Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors of Interest for the Treatment Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 4657–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, M.; Proctor, G.R.; Young, L.C.; Harvey, A.L. Novel Tacrine Analogues for Potential Use against Alzheimer’s Disease: Potent and Selective Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors and 5-HT Uptake Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 1997, 40, 3516–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savini, L.; Campiani, G.; Gaeta, A.; Pellerano, C.; Fattorusso, C.; Chiasserini, L.; Fedorko, J.M.; Saxena, A. Novel and Potent Tacrine-related Hetero- and Homobivalent Ligands for Acetylcholinesterase and Butyrylcholinesterase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 1779–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, J.L.; Rios, C.; Carreiras, M.C.; Banos, J.E.; Badia, A.; Vivas, N.M. Synthesis and Acetylcholinesterase/butyrylcholinesterase Inhibition Activity of New Tacrine-like Analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2001, 9, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabarrini, O.; Cecchetti, V.; Temperini, A.; Filipponi, E.; Lamperti, M.G.; Fravoloni, A. Velnacrine Thiaanalogues as Potential Agents for Treating Alzheimer’s Disease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2001, 9, 2921–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, C.; Marco, J.L.; Carreiras, M.D.C.; Chinchon, P.M.; Garcia, A.G.; Villarroya, M. Novel Tacrine Derivatives that Block Neuronal Calcium Channels. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2002, 10, 2077–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, W.G.; Green, L.G.; Grynszpan, F.; Radic, Z.; Carlier, P.R.; Taylor, P.; Finn, M.G.; Sharpless, K.B. Click Chemistry in Situ: Acetylcholinesterase as a Reaction Vessel for the Selective Assembly of a Femtomolar Inhibitor from an Array of Building Blocks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 1053–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, J.L.; Rios, C.; Garcia, A.G.; Villarroya, M.; Carreiras, M.C.; Martins, C.; Eleuterio, A.; Morreale, A.; Orozco, M.; Luque, F.J. Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Molecular Modelling of Diversely Functionalized Heterocyclic Derivatives as Inhibitors of Acetyl-cholinesterase/butyrylcholinesterase and Modulators of Ca2+ Channels and Nicotinic Receptors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 2199–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, R.; Marco-Contelles, J.; Garcia, A.G.; Villarroya, M. Synthesis, Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition and Neuroprotective Activity of New Tacrine Analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Kraus, B.; Lehmann, J.; Heilmann, J.; Zhang, Y.; Deckera, M. Design and Synthesis of Tacrine–ferulic Acid Hybrids as Multi-potent Anti-Alzheimer Drug Candidates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 2905–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marco-Contelles, J.; Leon, R.; de los Rios, C.; Guglietta, A.; Terencio, J.; Lopez, M.G.; Garcia, A.G.; Villarroya, M. Novel Multipotent Tacrine-Dihydropyridine Hybrids with Improved Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory and Neuroprotective Activities as Potential Drugs for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 7607–7610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Appenroth, D.; Decker, M.; Kiehntopf, M.; Roegler, C.; Deufel, T.; Fleck, C.; Peng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lehmann, J. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of NO-Donor-Tacrine Hybrids as Hepatoprotective Anti-Alzheimer Drug Candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 713–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsinghorst, P.W.; Gonzalez Tanarro, C.M.; Gutschow, M. Novel Heterobivalent Tacrine Derivatives as Cholinesterase Inhibitors with Notable Selectivity toward Butyrylcholinesterase. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 7540–7544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.N.; Zhang, A.J.; Ding, L.S. Facile Synthesis of Novel Tacrine Analogues. J. Chem. Res. 2009, 562–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, M.P.; Sheets, K.R.; McVety, K.; Spada, A.P.; Zilberstein, A. A New Series of PDGF Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: 3-Substituted Quinoline Derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 2129–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, J.S.; Rao, P.P.; Sreenu, D.; Rao, R.S.; Kumar, V.N.; Nagaiah, K.; Prasad, A.R. Sulfamic Acid: an Efficient, Cost-effective and Recyclable Solid Acid Catalyst for the Friedlander Quinoline Synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 7249–7253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, G.; Márquez, C. Lewis Acids Mediated Synthesis of 4-Aminoquinolines. Acta Científica Venezolana 1999, 50, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holla, B.S.; Mahalinga, M.; Karthikeyan, M.S.; Akberali, P.M.; Shetty, N.S. Synthesis of Some Novel Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine Derivatives as Potential Antimicrobial Agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 2040–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of compounds 3a-p are available from the authors. |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).