Kinetic, Equilibrium and Thermodynamic Studies of Cadmium (II) Adsorption by Modified Agricultural Wastes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Properties of Native and Maleic Acid-Treated Tamrix articulata Wastes
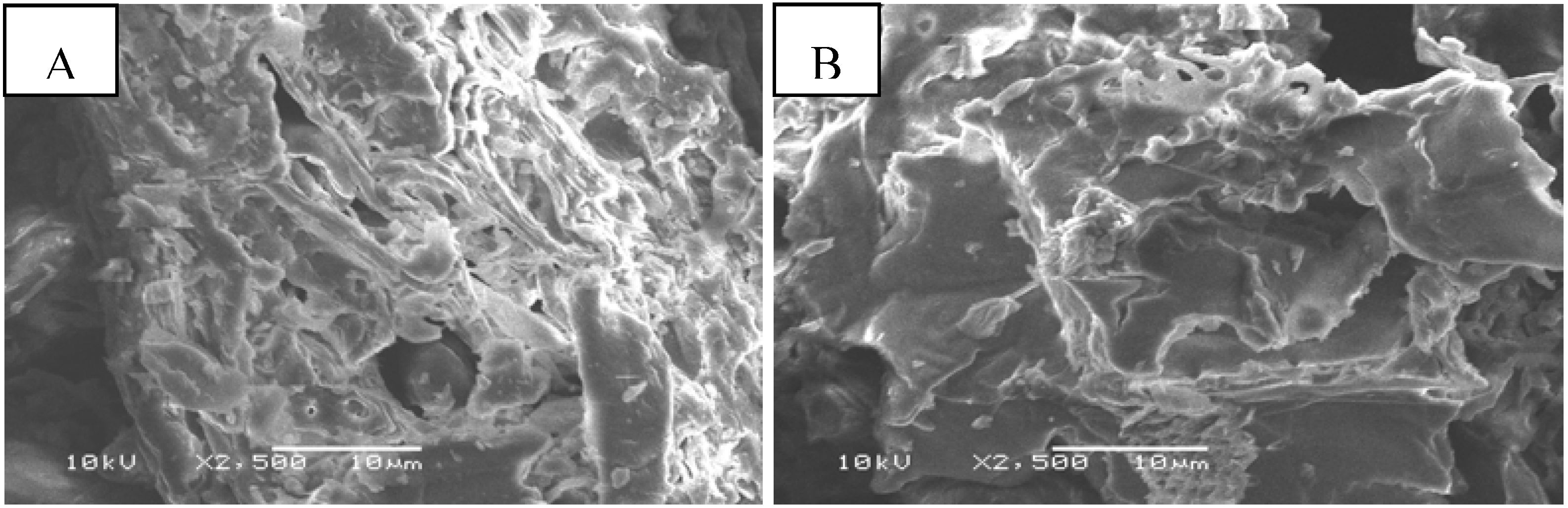
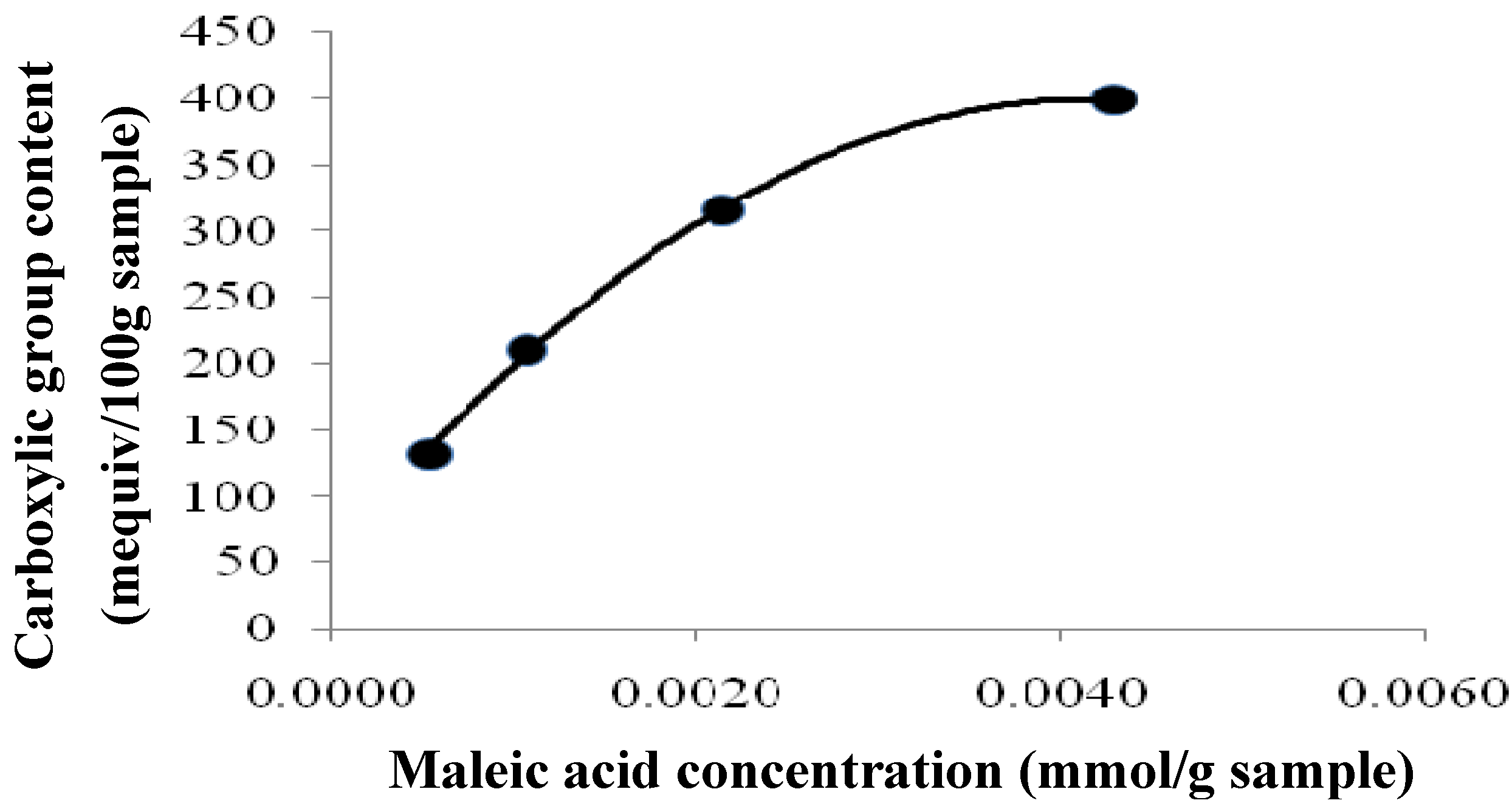
2.2. Effect of Carboxyl Group Content of Treated Tamrix articulata Wastes on Cd (II) Adsorption
| Maleic Acid (mmol/g waste) | Esterification (Carboxylic group content) (mequiv/100 g Sample) | Adsorption Capacity (qe) (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0043 | 399 | 195.5 |
| 0.0022 | 315 | 137.70 |
| 0.0011 | 210 | 88.84 |
| 0.0005 | 131.2 | 53.3 |
2.3. Adsorption Studies
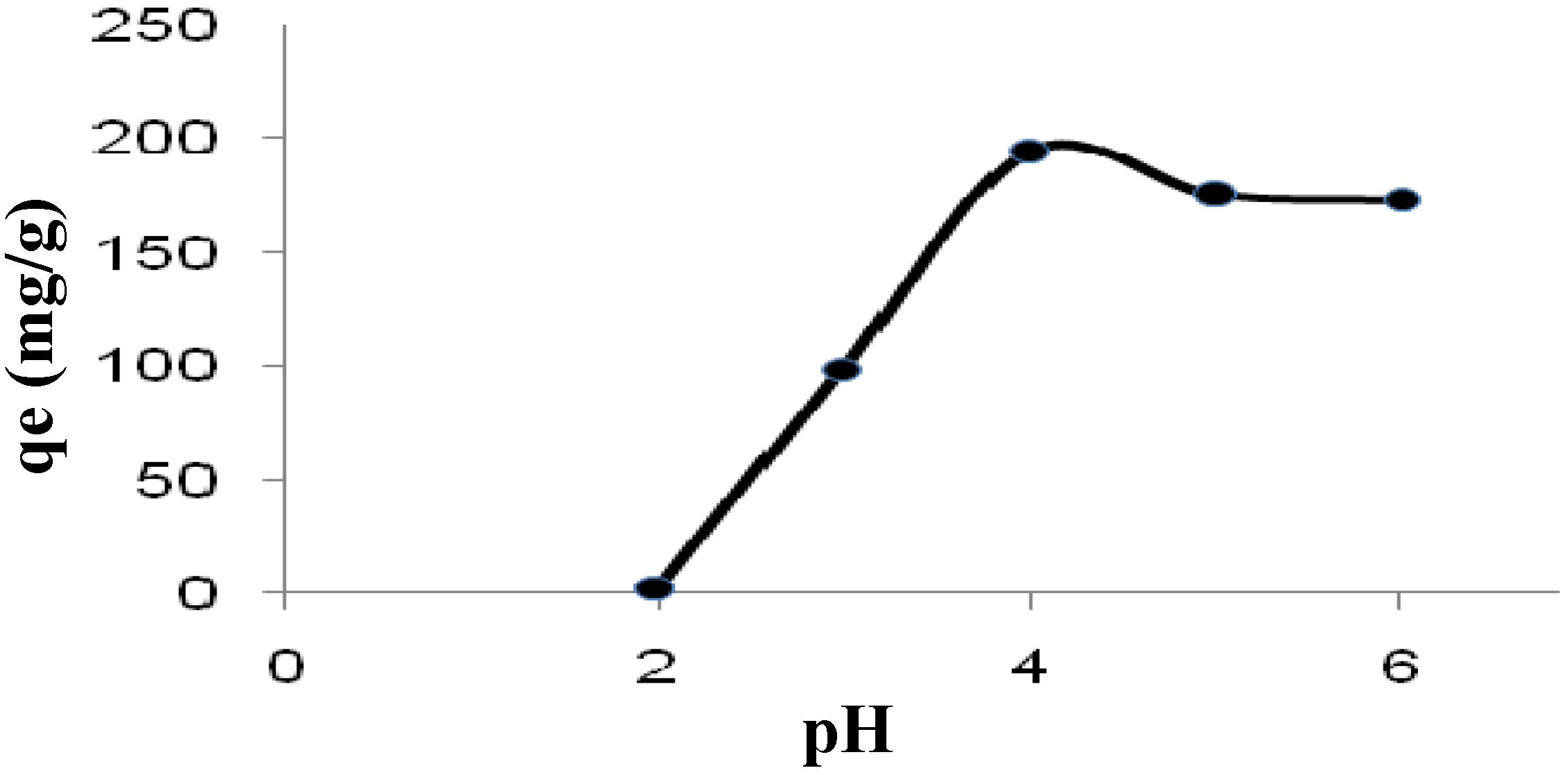
2.3.1. Effect of pH
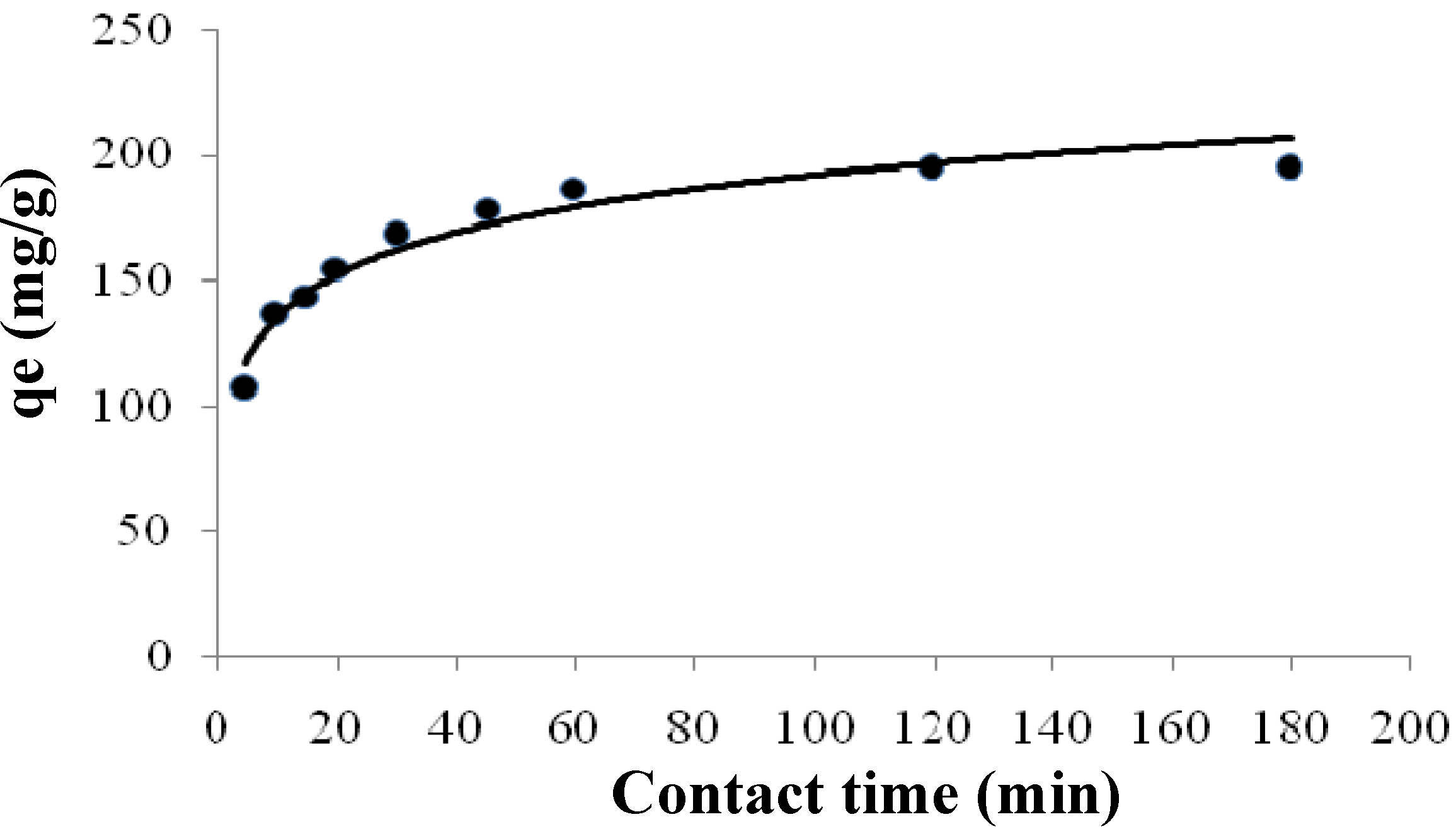
2.3.2. Kinetics of Adsorption
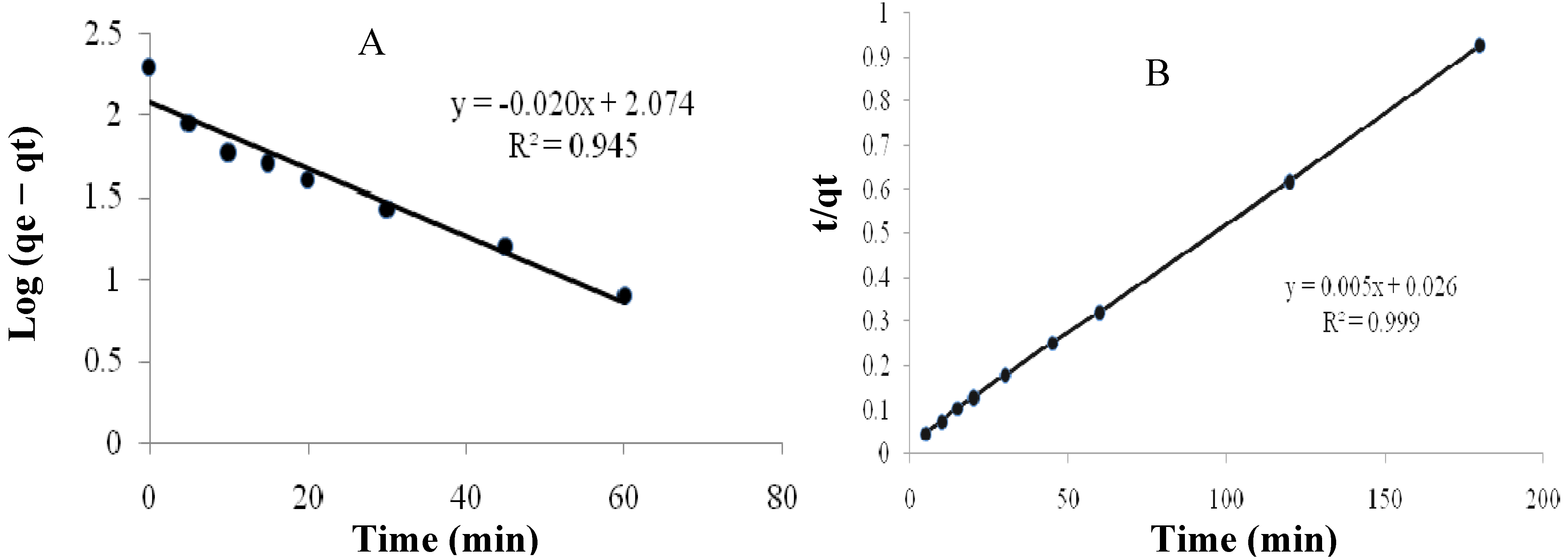
| The pseudo-first-order | The pseudo-second-order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rate Constant (K1) | qe (mg/g) | (R12) | Rate Constant (K2) | qe (mg/g) | (R22) |
| 0.046 | 118.5 | 0.945 | 0.00096 | 200 | 0.999 |
2.3.3. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
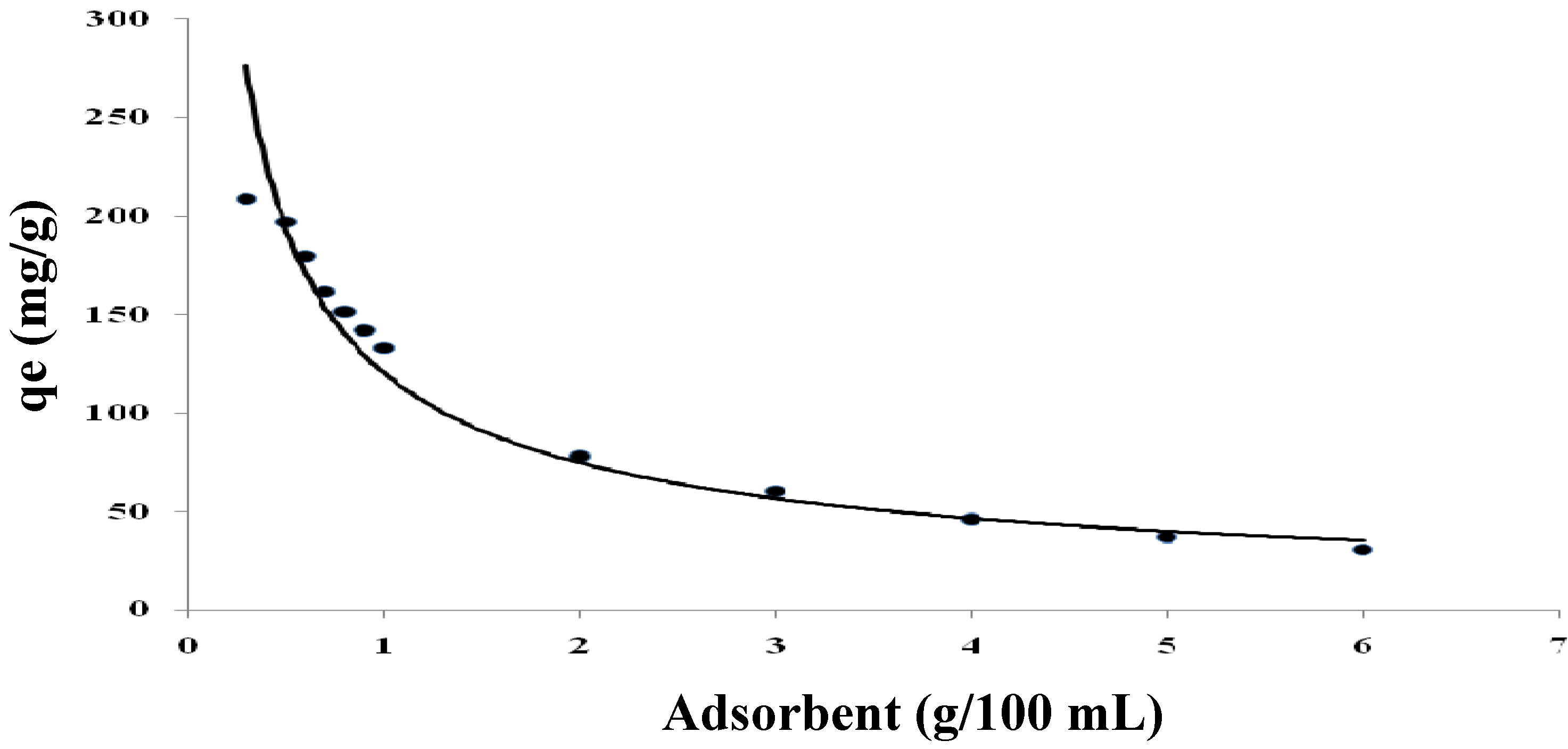
2.3.4. Adsorption Isotherms
2.3.4.1. Langmuir Isotherm
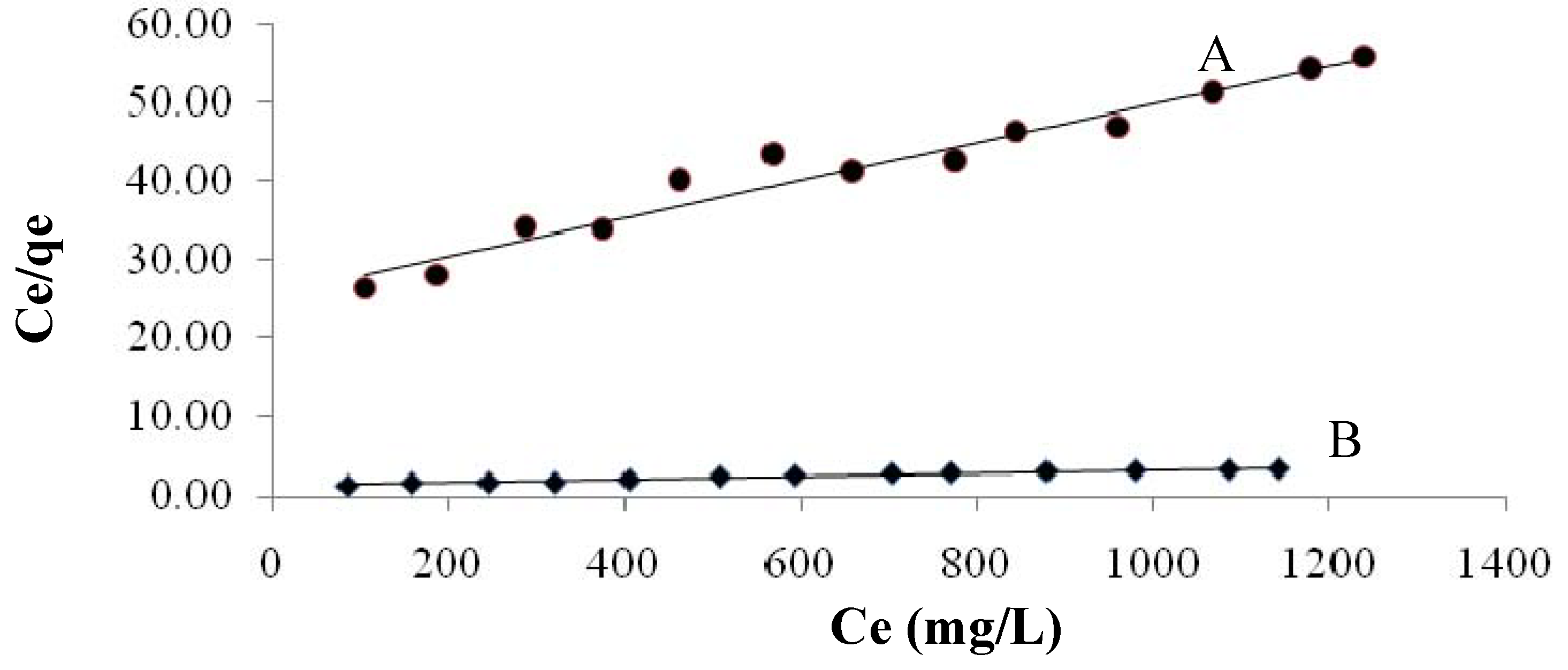
2.3.4.2. Freundlich Isotherm
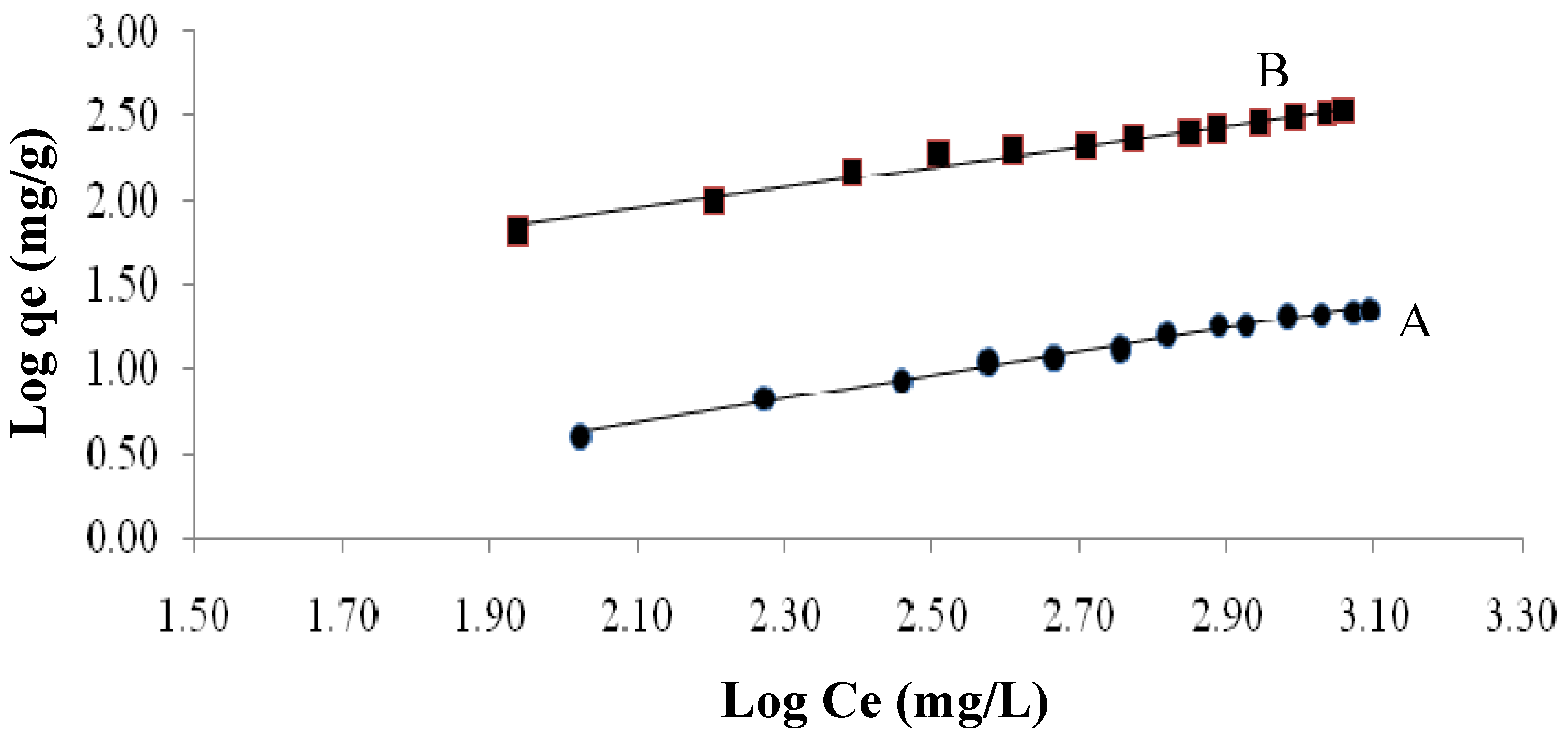
| Constant | Native | Maleic acid-treated plant | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir constants | KL | 0.024 | 0.8 |
| b | 0.00057 | 0.0016 | |
| Q max. | 41.6 | 500 | |
| R2 | 0.957 | 0.966 | |
| Freundlich constants | KF | 0.168 | 4.93 |
| n | 1.44 | 1.66 | |
| R2 | 0.991 | 0.973 |
2.3.5. Thermodynamic Studies
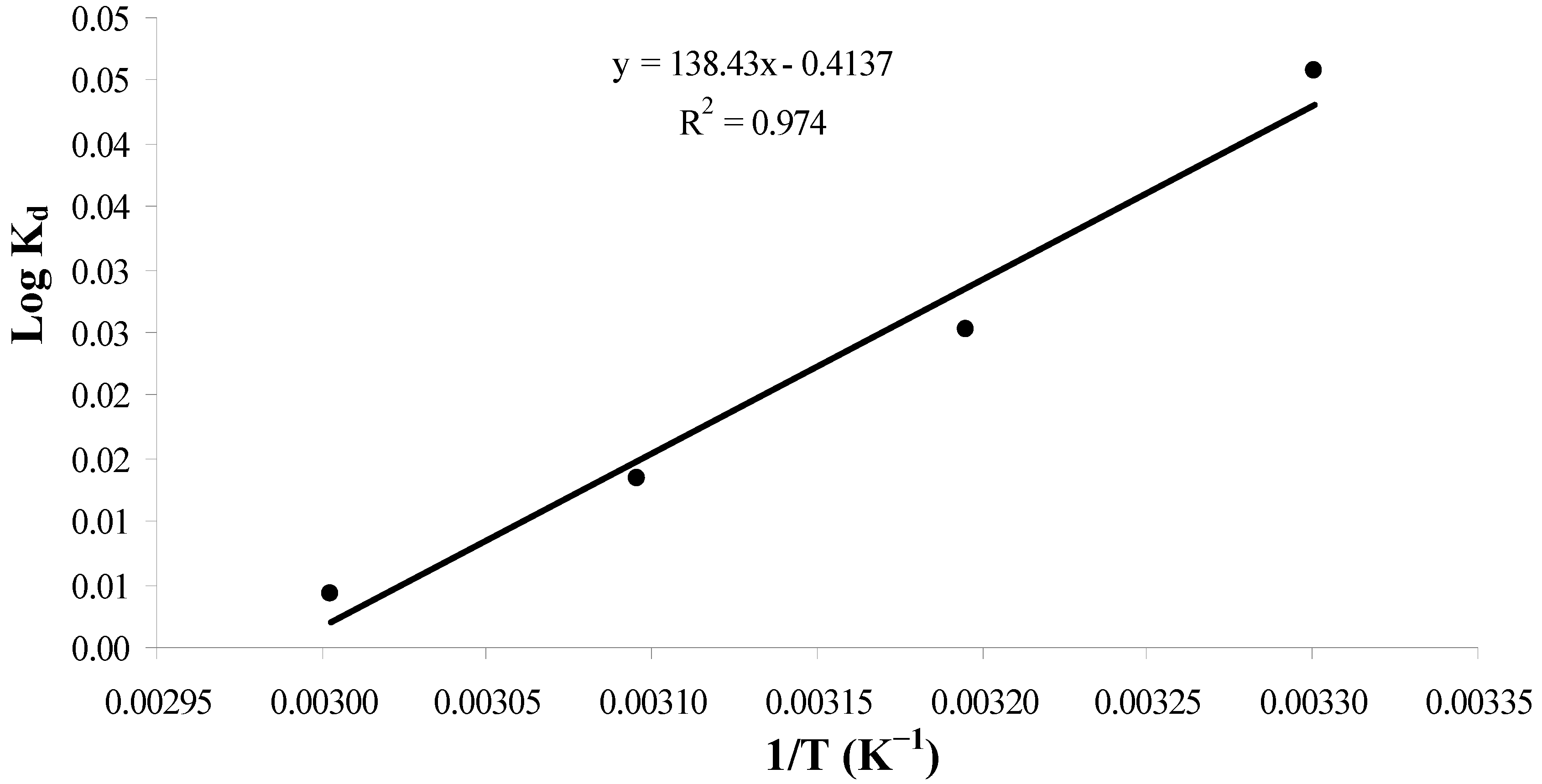
| Temperature T(K) | Thermodynamic parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ΔGo (kJ/mol) | ΔSo (J/mol/K) | ΔHo (kJ/mol) | |
| 303 | −0.265 | −7.9 | −2.6 |
| 313 | −0.151 | ||
| 323 | −0.082 | ||
| 333 | −0.027 | ||
| Adsorbent | q max (mg/g) | References |
|---|---|---|
| Techtona grandis L.f | 23.20 | [39] |
| Wheat bran | 15.71 | [40] |
| Corncorb | 55.2 | [41] |
| Juniper fibre | 29.54 | [42] |
| Sawdust(Cedrus deodar wood) | 73.62 | [43] |
| Spent grain | 17.3 | [44] |
| Wheat bran | 101 | [45] |
| Algae, marine, dead Biomass | 80 | [46] |
| Algae, Nile water | 37.43 | [47] |
| Tamrix articulata | 195.5 | This study |
3. Experimental
3.1. Raw Material and Chemicals
3.2. Preparation and Characterization of Adsorbent
3.3. Carboxyl Content
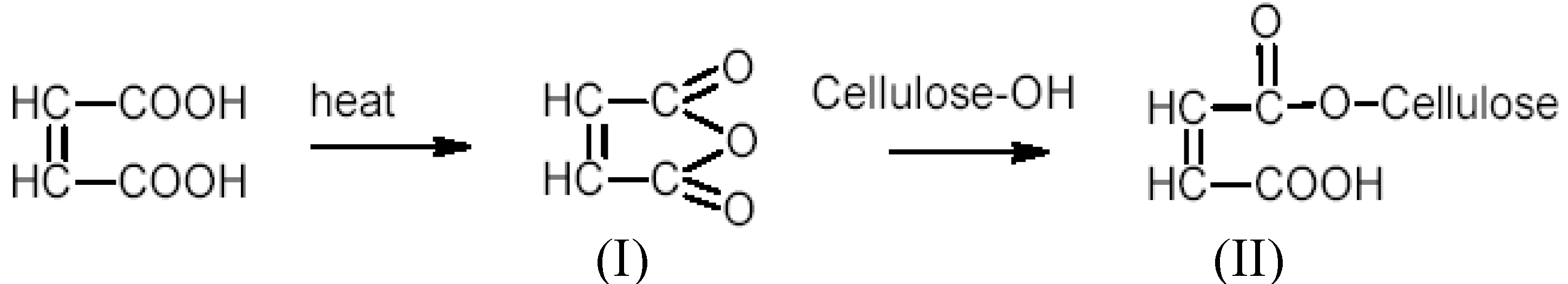
3.4. Adsorption Studies
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References and Notes
- Waalkes, M.P. Cadmium carcinogenesis in review. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2000, 79, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadirvelu, K.; Namasivayam, C. Agricultural by-products as metal adsorbents: Sorption of lead (II) from aqueous solutions onto coirpith carbon. Environ. Technol. 2000, 21, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, H.T.; Hassan, M.A.H.; Abo-Melha, A.; Talaat, I.R. Cadmium and zinc concentrations in the potable water of the eastern provinces of Saudi Arabia. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1988, 40, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y.C. Thermodynamics of removal of cadmium by adsorption on indigenous clay. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 145, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, C.P.C. Removal of Cd (II) from Wastewaters. In Cadmium in the Environment; Mislin, H., Raverva, O., Eds.; Birkhauser: Basel, Switzerland, 1986; pp. 6–55. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, G.Q.; Xiao, D. Adsorption of cadmium ion from aqueous solution by ground wheat stems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1359–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarı, A.; Tuzen, M. Biosorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solution using green alga (Ulva lactuca) biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anayurt, R.A.; Sari, A.; Tuzen, M. Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies on biosorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solution by macrofungus (Lactarius scrobiculatus) biomass. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 151, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarı, A.; Tuzen, M. Kinetic and equilibrium studies of biosorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solution by macrofungus (Amanita rubescens) biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarı, A.; Tuzen, M. Removal of mercury(II) from aqueous solution using moss (Drepanocladus revolvens) biomass: Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzen, M.; Sari, A.; Mendil, D.; Soylak, M. Biosorptive removal of mercury(II) from aqueous solution using lichen (Xanthoparmelia conspersa) biomass: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benguella, B.; Benaissa, H. Cadmium removal from aqueous solutions by chitin: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2463–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.T.; Zheng, Y.M.; Zhang, L.M.; He, J.Z. Biogenic Mn oxides for effective adsorption of Cd from aquatic environment. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 2577–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, R.D.C.; Jafari, A.J.; Khorramabadi, Gh.S. Investigation of cadmium (II) ions biosorption onto pretreated dried activated sludge. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 5, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- An, H.K.; Park, B.Y.; Kim, D.S. Crab shell for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3551–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes-Martinez, R.; Martinez-Miranda, V.; Solache-Rios, M.; Garcia-Sosa, I. Evaluation of natural and surfactant-modified zeolites in the removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2004, 39, 2711–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, U.; Kaur, M.P.; Jawa, G.K.; Sud, D.; Garg, V.K. Removal of cadmium (II) from aqueous solutions by adsorption on agricultural waste biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semerjian, L. Equilibrium and kinetics of cadmium adsorption from aqueous solutions using untreated Pinus halepensis sawdust. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Z.; Katsumi, T.; Imaizumi, S.; Tang, X.W.; Inui, T. Cd(II) adsorption on various adsorbents obtained from charred biomaterials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.Y.; Wang, H.; Ma, J.W. Adsorption of cadmium (II) ions from aqueous solution by a new low-cost adsorbent-Bamboo charcoal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashauoei, H.R.; Attar, H.M.; Amin, M.M.; Kamali, M.; Nikaeen, M.; Dastjerdi, M.V. Removal of cadmium and humic acid from aqueous solutions using surface modi.ed nanozeoliteA. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 7, 497–508. [Google Scholar]
- Visa, M.; Bogatu, C.; Duta, A. Simultaneous adsorption of dyes and heavy metals from multicomponent solutions using fly ash. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 5486–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.E.; Olin, T.J.; Bricka, R.M.; Adrian, D. A review of potentially low cost sorbents for heavy metal. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2469–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.P.; Blankenship, B.W. The removal of mercury(II) from dilute aqueous Solution by activated carbon. Water Res. 1989, 18, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; Chiang, T.H.; Hsueh, Y.M. Removal of basic dye from aqueous solution using tree fern as a biosorbent. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, S.; Aggarwal, V.K.; Kumar, P. Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from the Wastewater by Adsorption. Indian J. Environ. Health 1994, 36, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, K.; Balasubramaniam, N.; Ramakrishna, T.V. Studies on Chromium Removal by Rice Husk Carbon. Indian J. Environ. Health 1998, 30, 376–387. [Google Scholar]
- Ajmal, M.; Rao, R.A.K.; Siddiqui, B.A. Studies on Removal and Recovery of Cr (VI) from Electroplating Wastes. Water Res. 1996, 30, 1478–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.T.; Ooi, S.T.; Lee, C.K. Removal of Chromium (VI) from Solution by Coconut Husk and palm Pressed Fibre. Environ. Technol. 1993, 14, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Shaaban, M.G.; Hassan, M.H.A. Removal of heavy metal using an inexpensive adsorbent. In Proceedings of UM Research SeminarUniversity of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 11th–12th March 2003; University of Malaya: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2003; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ayub, S.; Ali, S.I.; Khan, N.A. Efficiency evaluation of neem (Azadirachta indica) bark in treatment of industrial wastewater. Environ. Pollut. Control J. 2001, 4, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, R.; Ding, Y.D.; Liu, H.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Z. Lead biosorption by intact and pretreated Spirulina maxima biomass. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. About The Theory of So-Called Adsorption of Soluble Substances. Kungliga Svenska Ventenskapsakademiens Handlingar 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, E. The kinetics of sorption of basic dyes from aqueous solution by Sphagnum moss pea. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1998, 76, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, K.G.; Sharma, A. Adsorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solution by Azadirachta indica (Neem) leaf powder. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, B113, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Geundi, M.S. Homogeneous surface diffusion model for the adsorption of basic dyestuffs onto natural clay in batch absorbers. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 1991, 8, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsfall, M.; Spiff, A.I.; Abia, A.A. Studies on the influence of mercaptoacetic acid (MAA) modification of cassava (Manihot sculenta cranz) waste Biomass on the adsorption of Cu2+ and Cd2+ from aqueous solution. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2004, 25, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.S.; Anand, S.; Venkateswarlu, P. Adsorption of cadmium (II) ions from aqueous solutions by Tectona Grandis L.F. (Teak leaves powder). BioResources 2010, 5, 438–454. [Google Scholar]
- Nouri, L.; Ghodbane, I.; Hamdaoui, O.; Chiha, M. Batch sorption dynamics and equilibrium for removal of cadmium ions from aqueous phase using wheat bran. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, R.L; Jacome, L.A.B.; Rodriguez, I.A. Adsorption of cadmium(II) from aqueous solution on natural and oxidized corncob. Separ. Purif. Technol. 2005, 4, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Min, S.H.; Han, J.S.; Shin, E.W.; Park, J.K. Improvement of cadmium ion removal by base treatment of juniper fiber. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, S.Q.; Memon, N.; Shaw, S.W.; Khuhawar, M.Y.; Bhanger, M.I. Saw dust-A green economical sorbent for the removal of cadmium(II) ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, B139, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Low, K.S.; Lee, C.K.; Liew, S.C. Adsorption of cadmium and lead from aqueous solutions by spent grain. Process Biochem. 2000, 36, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, A.; Pirincci, H.B. The adsorption of Cd(II) ions on sulphuric acid-treated wheat bran. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, B137, 849–855. [Google Scholar]
- Herrero, R.; Cordero, B.; Lodeiro, P.; Rey-Castro, C.; Sastre de Vicente, M.E. Interactions of cadmium(II) and protons with dead biomass of marine algae Fucus sp. Mar. Chem. 2006, 99, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, Y.E.; Ashmawy, A.; Badr, S. Biosorption of cadmium and nickel by Nilewater algae. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2008, 4, 391–396. [Google Scholar]
- Wing, R.E.; Peoria, I.L. Corn fiber citrate: Preparation and ion-exchange properties. Ind. Crops Prod. 1996, 5, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daul, G.C.; Reinhardt, R.M.; Reid, J.D. The carboxymethylation of cotton. Text. Res. J. 1953, 23, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, A.; Abdel-Halim, E.S.; El-Tahlawy, Kh.F.; Hebeish, A. Enhancement of the Adsorption of Co(II) and Ni(II) Ions onto Peanut Hulls through Esterification Using Citric Acid. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2005, 23, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, B.A.K.; Blanchard, E.J.; Einhardt, R.M. Fabric Whiteness Press Finishing with Citric Acid. Text. Chem. Color. 1993, 25, 52–54. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds (Tamrix articulata wastes and maleic acid-treated Tamrix articulata wastes) are available from the authors.
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Othman, Z.A.; Hashem, A.; Habila, M.A. Kinetic, Equilibrium and Thermodynamic Studies of Cadmium (II) Adsorption by Modified Agricultural Wastes. Molecules 2011, 16, 10443-10456. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules161210443
Al Othman ZA, Hashem A, Habila MA. Kinetic, Equilibrium and Thermodynamic Studies of Cadmium (II) Adsorption by Modified Agricultural Wastes. Molecules. 2011; 16(12):10443-10456. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules161210443
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Othman, Zeid A., Ali Hashem, and Mohamed A. Habila. 2011. "Kinetic, Equilibrium and Thermodynamic Studies of Cadmium (II) Adsorption by Modified Agricultural Wastes" Molecules 16, no. 12: 10443-10456. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules161210443
APA StyleAl Othman, Z. A., Hashem, A., & Habila, M. A. (2011). Kinetic, Equilibrium and Thermodynamic Studies of Cadmium (II) Adsorption by Modified Agricultural Wastes. Molecules, 16(12), 10443-10456. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules161210443




