BDNF Promotes EGF-Induced Proliferation and Migration of Human Fetal Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells via the PI3K/Akt Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Neurosphere Formation of Human NSPCs
2.2. BDNF Treatment Increased EGF-Induced Proliferation of Human NSPCs
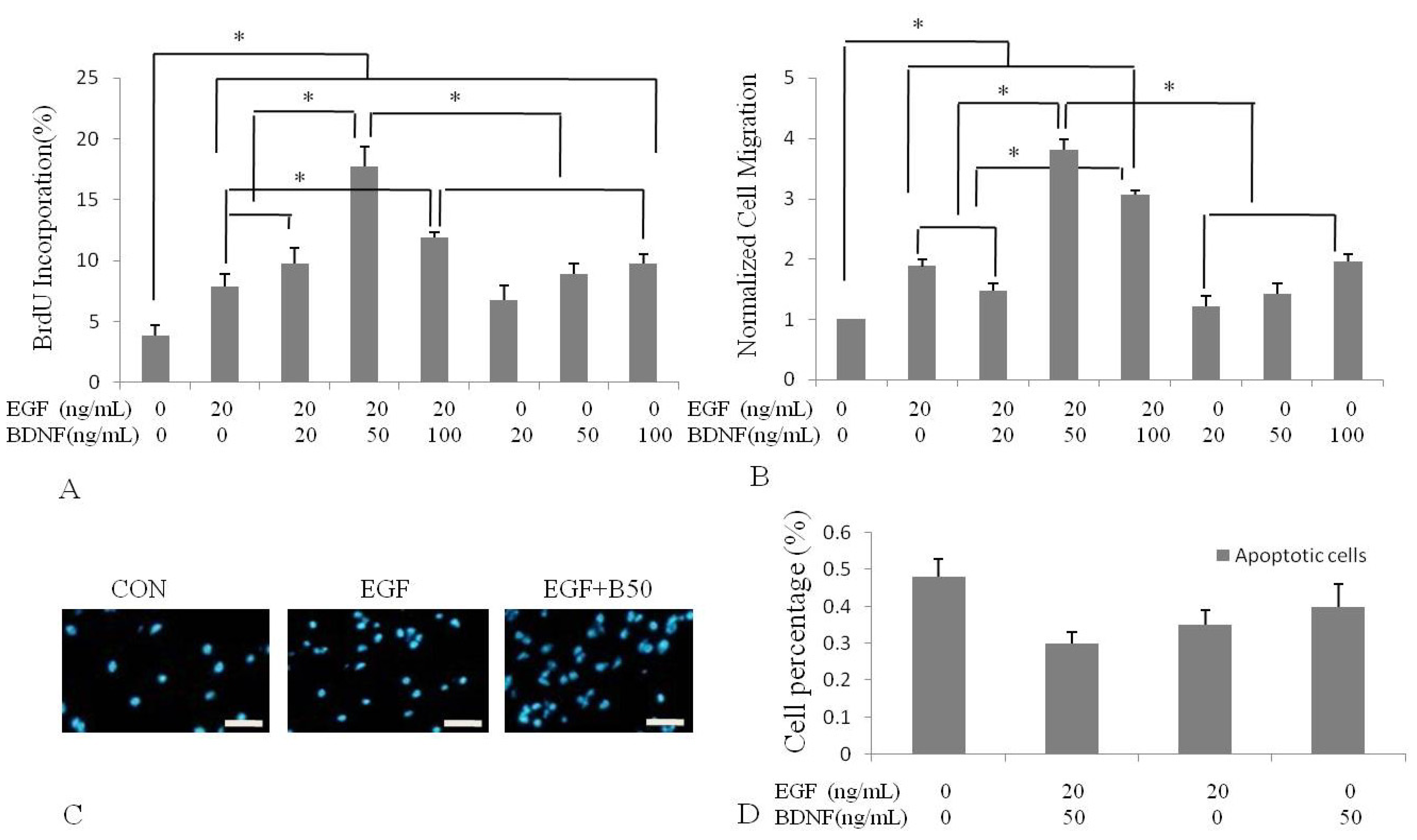
2.3. BDNF Treatment Increased EGF-Induced Human NSPC Migration
2.4. BDNF Promotes EGF-Induced NSPC Proliferation and Migration via the PI3K/Akt Kinase Pathway
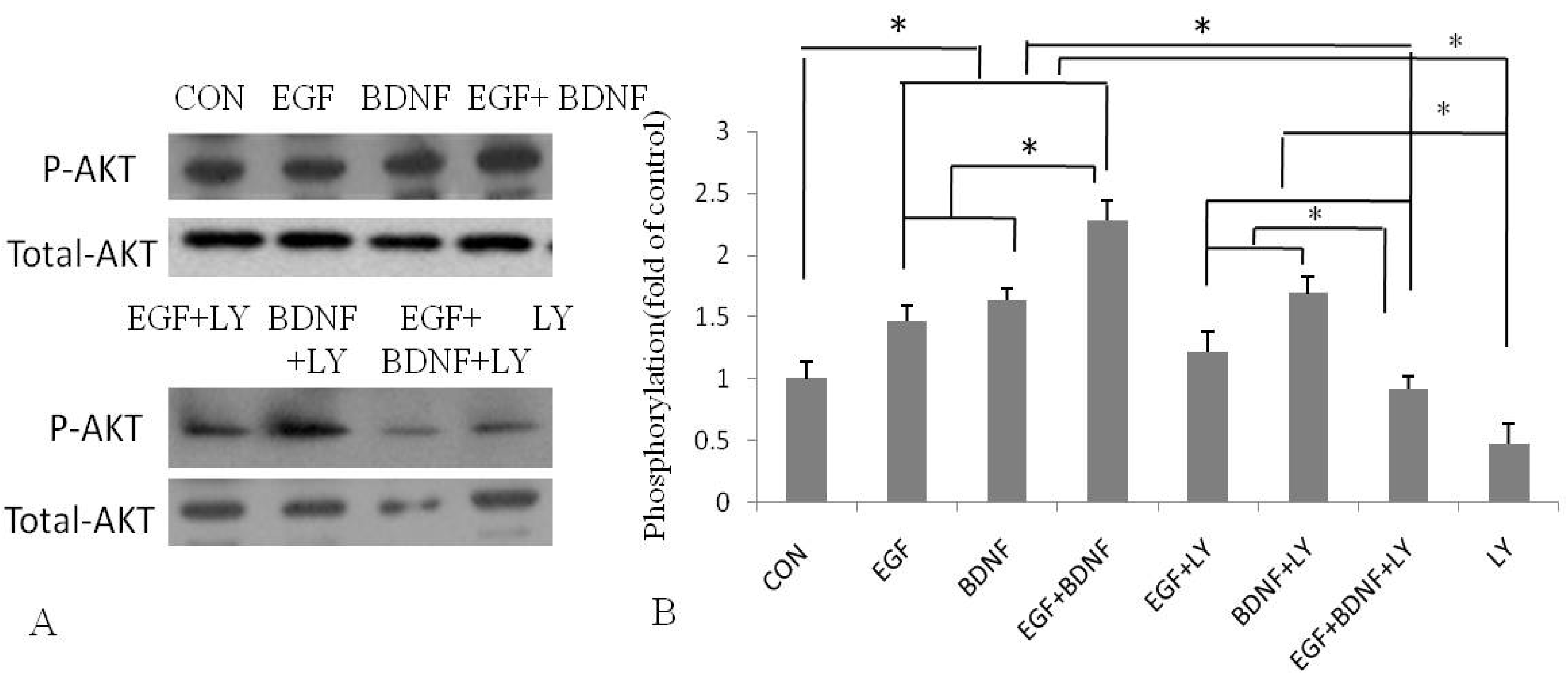
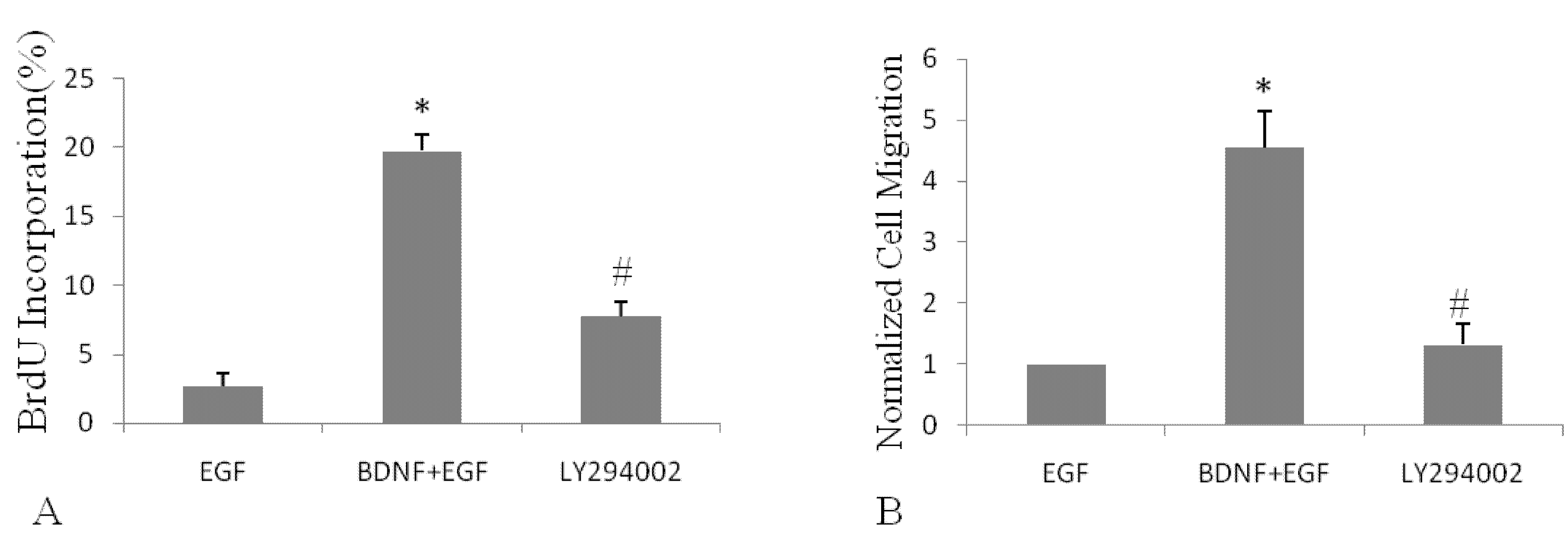
3. Discussion
4. Experimental
4.1. Primary Cell Culture Preparation
4.2. Proliferation Assay
4.3. Flow Cytometry Assay
4.4. Transwell Cell Migration Assay
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Wu, Y.; Peng, H.; Cui, M.; Whitney, N.P.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, J.C. CXCL12 increases human neural progenitor cell proliferation through Akt-1/FOXO3a signaling pathway. J. Neurochem. 2009, 109, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, X. MicroRNAs in adult and embryonic neurogenesis. Neuromol. Med. 2009, 11, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leker, R.R.; Lasri, V.; Chernoguz, D.J. Neural Transm Growth factors improve neurogenesis and outcome after focal cerebral ischemia. J. Neural Transm. 2009, 116, 1397–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türeyen, K.; Vemuganti, R.; Bowen, K.K.; Sailor, K.A.; Dempsey, R.J. EGF and FGF-2 infusion increases post-ischemic neural progenitor cell proliferation in the adult rat brain. Neurosurgery 2005, 57, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar]
- IM, S.H.; Yu, J.H.; Park, E.S.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, H.O.; Park, K.I.; Kim, G.W.; Park, C.I.; Cho, S.R. Induction of striatal neurogenesisenhances functional recovery in an adult animal model of neonatal hypoxic-ischemicbrain injury. Neuroscience 2010, 169, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.W.; Guillaud, L. The role of epidermal growth factor and its receptors in mammalian CNS. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004, 15, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Perez, O.; Quiñones-Hinojosa, A. Dose-dependent effect of EGF on migration and differentiation of adult subventricular zone astrocytes. Glia 2010, 58, 975–983. [Google Scholar]
- Fricker-Gates, R.A.; Winkler, C.; Kirik, D.; Rosenblad, C.; Carpenter, M.K.; Björklund, A. EGF infusion stimulates the proliferation and migration of embryonic progenitor cells transplanted in the adult rat striatum. Exp. Neurol. 2000, 165, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigova, T.; Pencea, V.; Wiegand, S.J.; Luskin, M.B. Intraventricular administration of BDNF increases the number of newly generated neurons in the adult olfactory bulb. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 1998, 11, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, A.K.; Turner, D.A. In Vitro Survival and Differentiation of Neurons Derived from EpidermalGrowth Factor-Responsive Postnatal Hippocampal Stem Cells: Inducing Effects of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor. J. Neurobiol. 1998, 35, 395–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvao, R.P.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling does not stimulate subventricular zone neurogenesis in adult mice and rats. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 13368–13383. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.; Zhou, C.; Sun, Y.; Di, W.; Scheffler, E.; Healey, S.; Kouttab, N.; Chu, W.; Wan, Y. Crosstalk between EGFR and TrkB enhances ovarian cancer cell migration and proliferation. Int. J. Oncol. 2006, 29, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Gschwind, A.; Fischer, O.M.; Ullrich, A. The discovery of receptor tyrosine kinases: Targets for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shioda, N.; Han, F.; Fukunaga, K. Role of Akt and ERK signaling in the neurogenesis following brain ischemia. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2009, 85, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, P.J.; Gage, F.H. Regenerating the damaged central nervous system. Nature 2000, 407, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiltrout, C.; Lang, B.; Yan, Y.; Dempsey, R.J.; Vemuganti, R. Repairing brain after stroke: A review on post-ischemic neurogenesis. Neurochem. Int. 2007, 50, 1028–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagg, T. Molecular regulation of adult CNS neurogenesis: An integrated view. Trends Neurosci. 2005, 28, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; You, Y.; Levison, S.W. Neonatal hypoxic/ischemic brain injury induces production of calretinin-expressing interneurons in the striatum. J. Comp. Neurol. 2008, 511, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grote, H.E.; Hannan, A.J. Regulators of adult neurogenesis in the healthy and diseased brain. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2007, 34, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Perez, O.; Romero-Rodriguez, R.; Soriano-Navarro, M.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Epidermal growth factor induces the progeny of subventricular zone type B cells to migrate and differentiate into oligodendrocytes. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 2032–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, A.; Rubio, M.E.; Gallo, V. Notch and EGFRpathwayinteractionregulatesneuralstemcellnumber and self-renewal. Nature 2010, 467, 323–327. [Google Scholar]
- Aguirre, A.; Rizvi, T.A.; Ratner, N.; Gallo, V. Overexpression of the epidermal growth factor receptor confers migratory properties to nonmigratory postnatal neural progenitors. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 11092–11106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Perez, O.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Oligodendrogenesis in the subventricular zone and the role of epidermal growth factor. Brain Res. Rev. 2011, 67, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwindt, T.T.; Motta, F.L.; Gabriela, F.B.; Cristina, G.M.; Guimarães, A.O.; Calcagnotto, M.E.; Pesquero, J.B.; Mello, L.E. Effects of FGF-2 and EGF removal on the differentiation of mouse neural precursor cells. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2009, 81, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Bullock, M.R.; Altememi, N.; Zhou, Z.; Hagood, S.; Rolfe, A.; McGinn, M.J.; Hamm, R.; Colello, R.J. The Effect of Epidermal Growth Factor in the Injured Brain after Trauma in Rats. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 923–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcez, R.C.; Teixeira, B.L.; dos Santos Schmitt, S.; Alvarez-Silva, M.; Trentin, A.G. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) promotes the in vitro differentiation of neural crest cells to neurons and melanocytes. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2009, 29, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johanson, C.; Stopa, E.; Baird, A.; Sharma, H. Traumatic brain injury and recovery mechanisms: Peptide modulation of periventricular neurogenic regions by the choroid plexus-CSF nexus. J. Neural Transm. 2011, 118, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzumaki, N.; Ikegami, D.; Tamura, R.; Hareyama, N.; Imai, S.; Narita, M.; Torigoe, K.; Niikura, K.; Takeshima, H.; Ando, T.; et al. Hippocampal Epigenetic Modification at the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Gene Induced by an Enriched Environment. Hippocampus 2011, 21, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, H.Y.; Chen, J.Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, P.Y.; Wang, P.; Chen, L.P.; Cheng, G.X.; Zhu, J.H. Fates of donor and recipient mitochondrial DNA during generation of interspecies SCNT-derived human ES-like cells. Cloning Stem Cells 2009, 11, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svendsen, C.N.; TerBorg, M.G.; Armstrong, R.J.; Rosser, A.E.; Chandran, S.; Ostenfeld, T.; Caldwell, M.A. A new method for the rapid and long term growth of human neural precursor cells. J. Neurosci. Methods 1998, 85, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, H.L.; Brummer, T.; Jeanes, A.; Yap, A.S.; Daly, R.J. Gab2 and Src co-operate in human mammary epithelial cells to promote growth factor independence and disruption of acinar morphogenesis. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2693–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornberg, L.J.; Grant, M.B. Adenoviruses increase endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation: Partial reversal by the focal adhesion kinase inhibitor, FRNK. Microvasc. Res. 2007, 73, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Liu, G.; Wu, Y.; Sha, H.; Zhang, P.; Jia, J. BDNF Promotes EGF-Induced Proliferation and Migration of Human Fetal Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells via the PI3K/Akt Pathway. Molecules 2011, 16, 10146-10156. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules161210146
Zhang Q, Liu G, Wu Y, Sha H, Zhang P, Jia J. BDNF Promotes EGF-Induced Proliferation and Migration of Human Fetal Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells via the PI3K/Akt Pathway. Molecules. 2011; 16(12):10146-10156. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules161210146
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qi, Gang Liu, Yi Wu, Hongying Sha, Pengyue Zhang, and Jie Jia. 2011. "BDNF Promotes EGF-Induced Proliferation and Migration of Human Fetal Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells via the PI3K/Akt Pathway" Molecules 16, no. 12: 10146-10156. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules161210146
APA StyleZhang, Q., Liu, G., Wu, Y., Sha, H., Zhang, P., & Jia, J. (2011). BDNF Promotes EGF-Induced Proliferation and Migration of Human Fetal Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells via the PI3K/Akt Pathway. Molecules, 16(12), 10146-10156. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules161210146



