Optimization of an Efficient Semi-Solid Culture Protocol for Sterilization and Plant Regeneration of Centella asiatica (L.) as a Medicinal Herb
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Sterilization Protocol
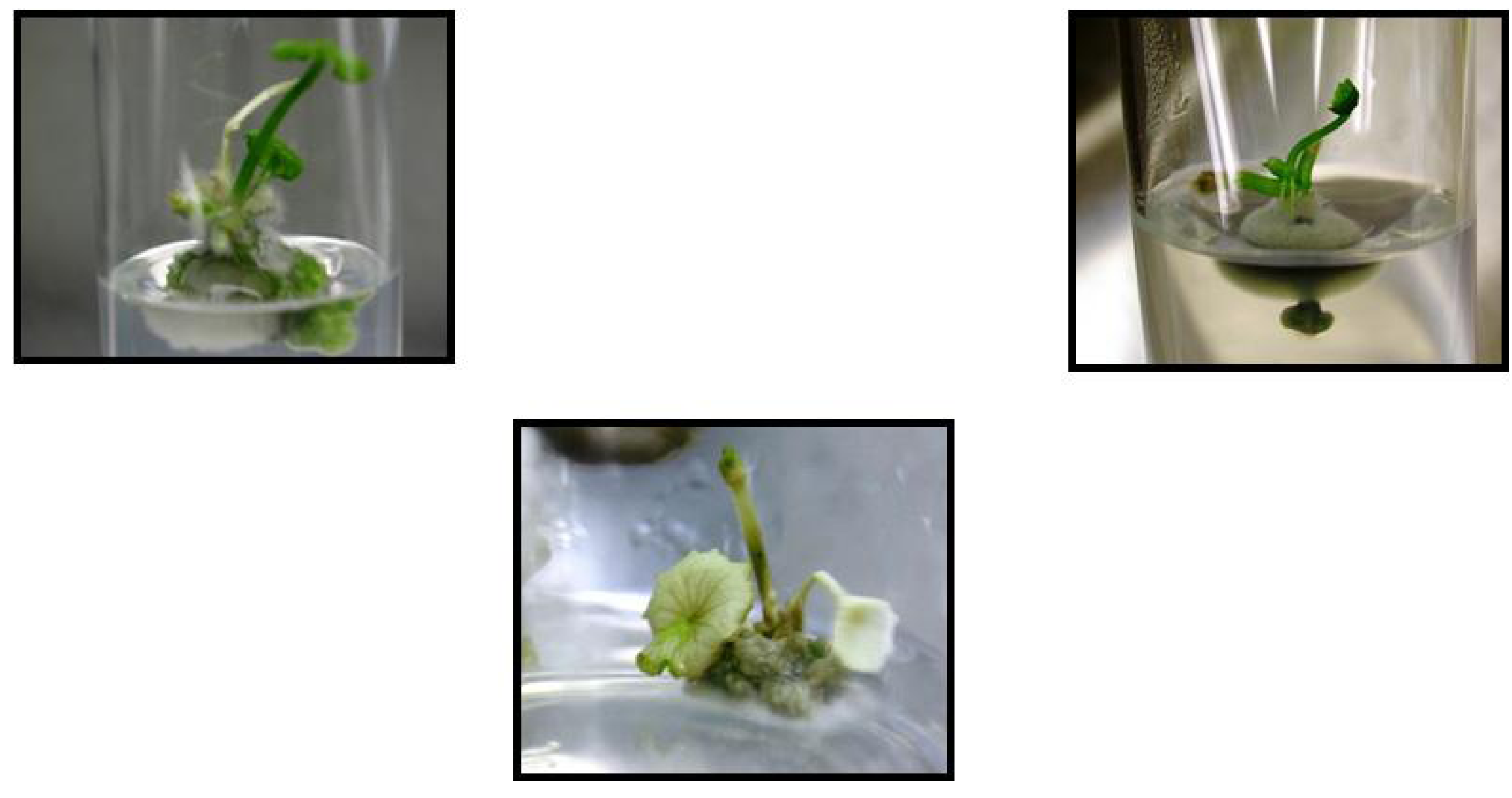

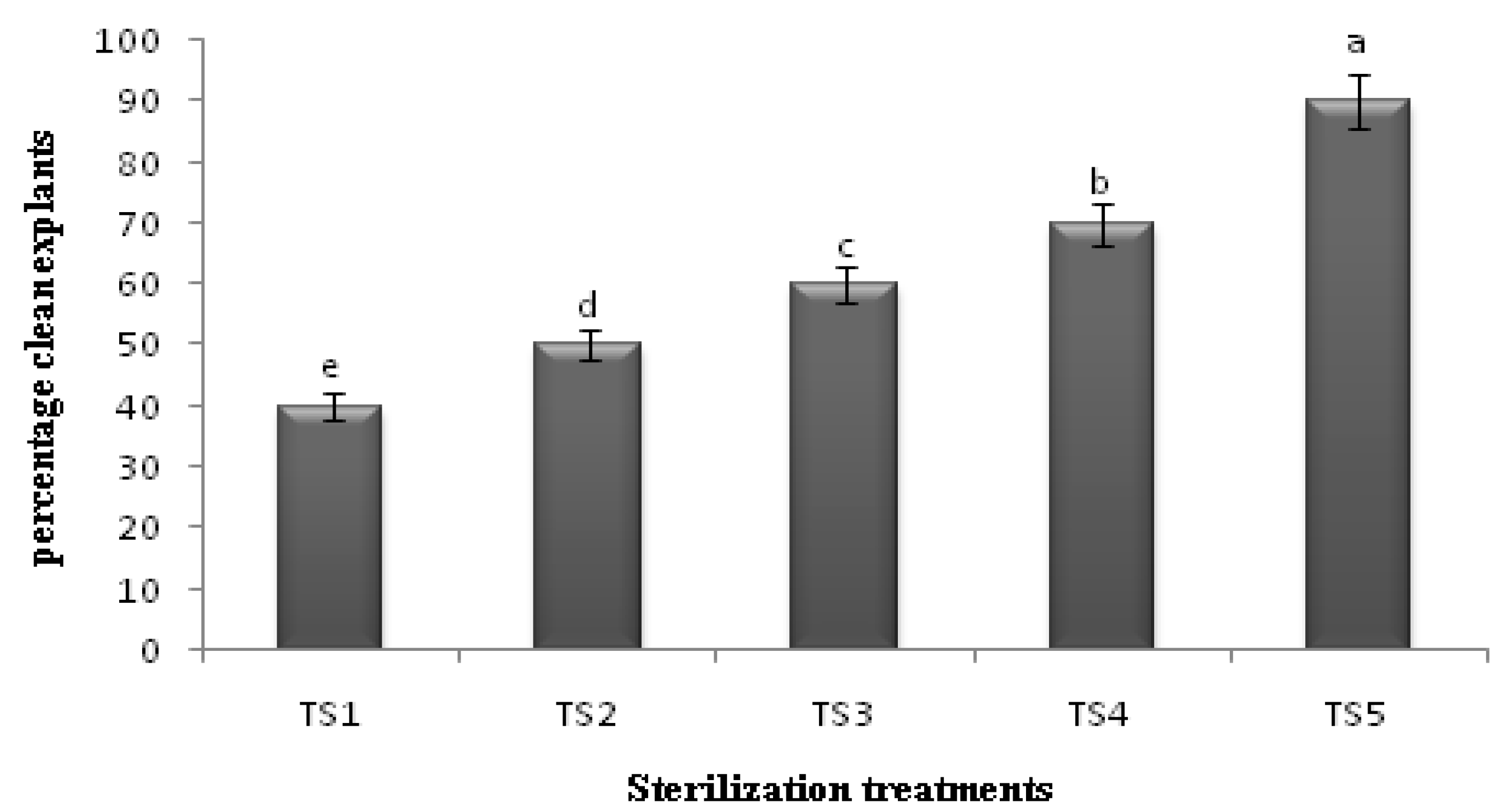
2.2. Aseptic Culture Establishment
2.2.1. Semi-Solid Culture Method
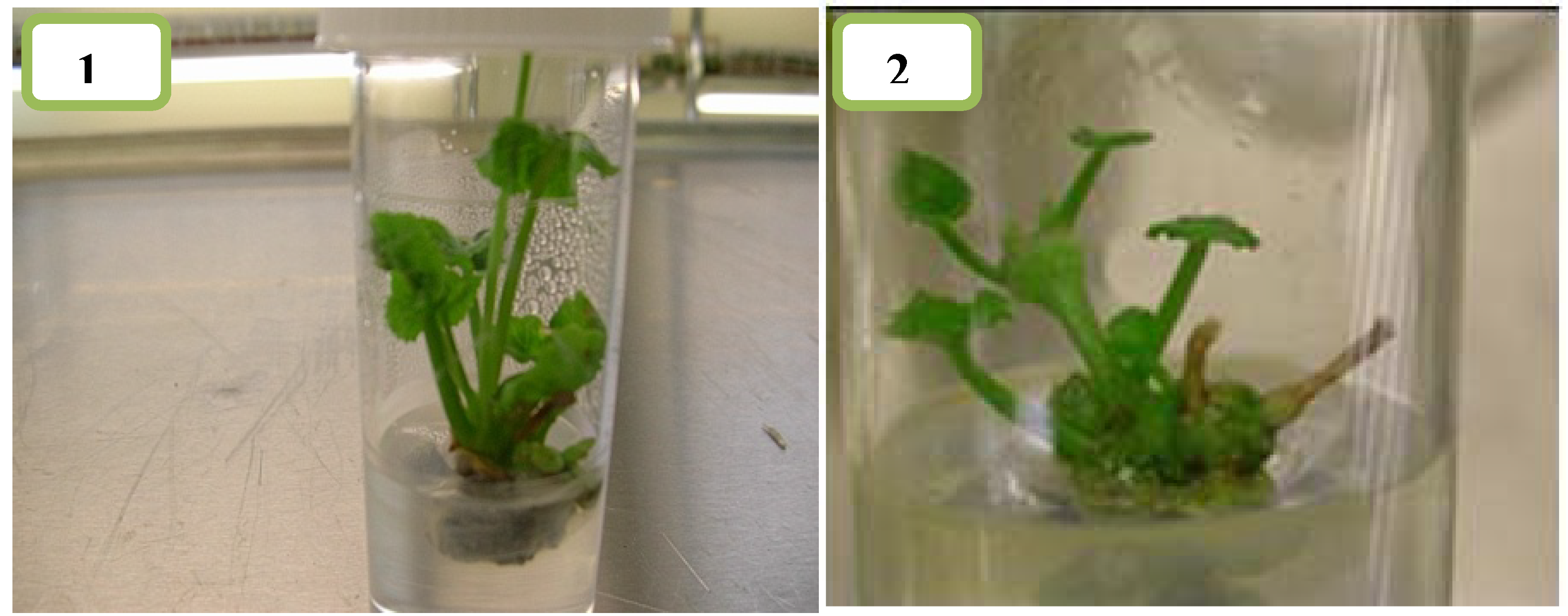

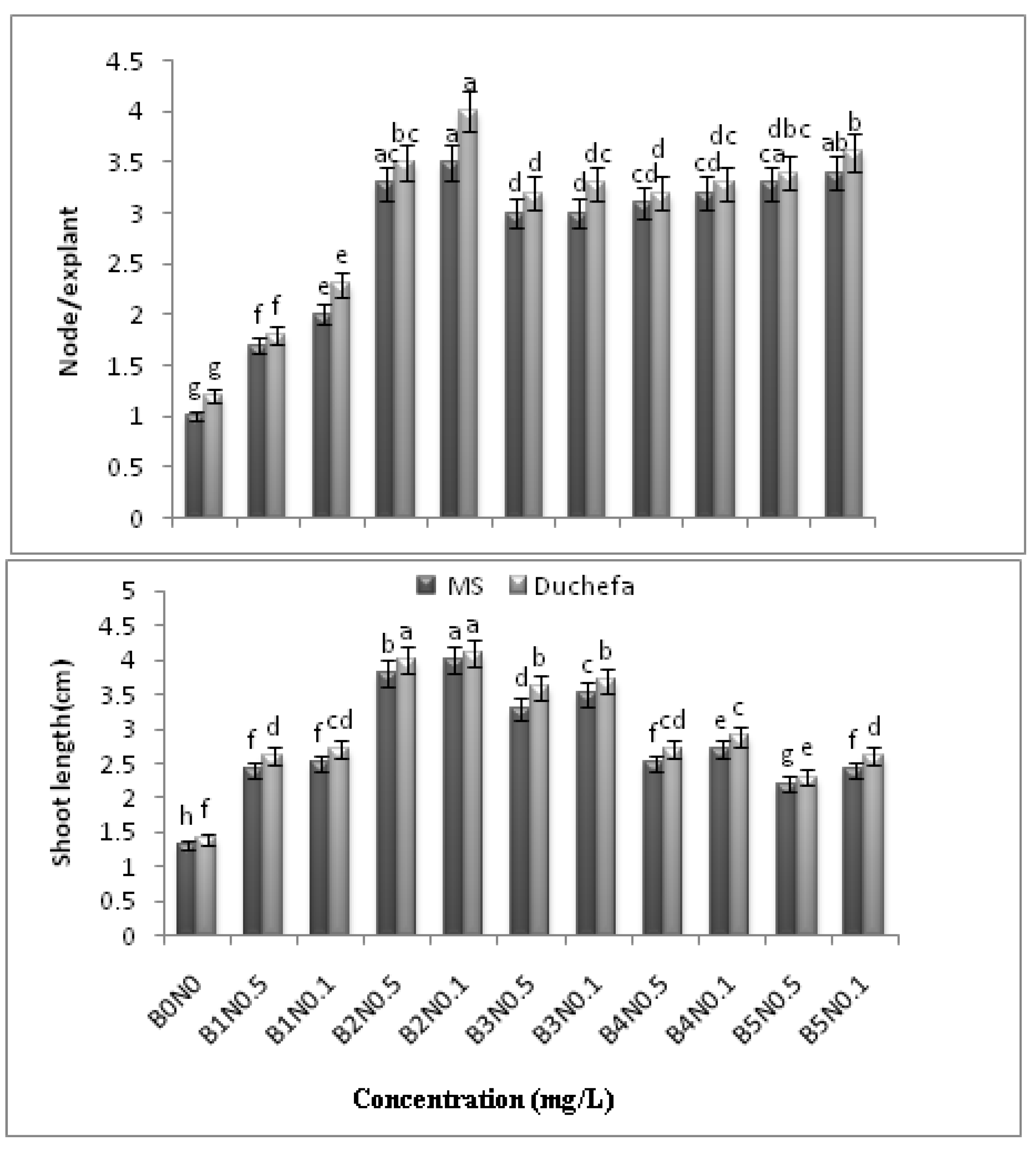

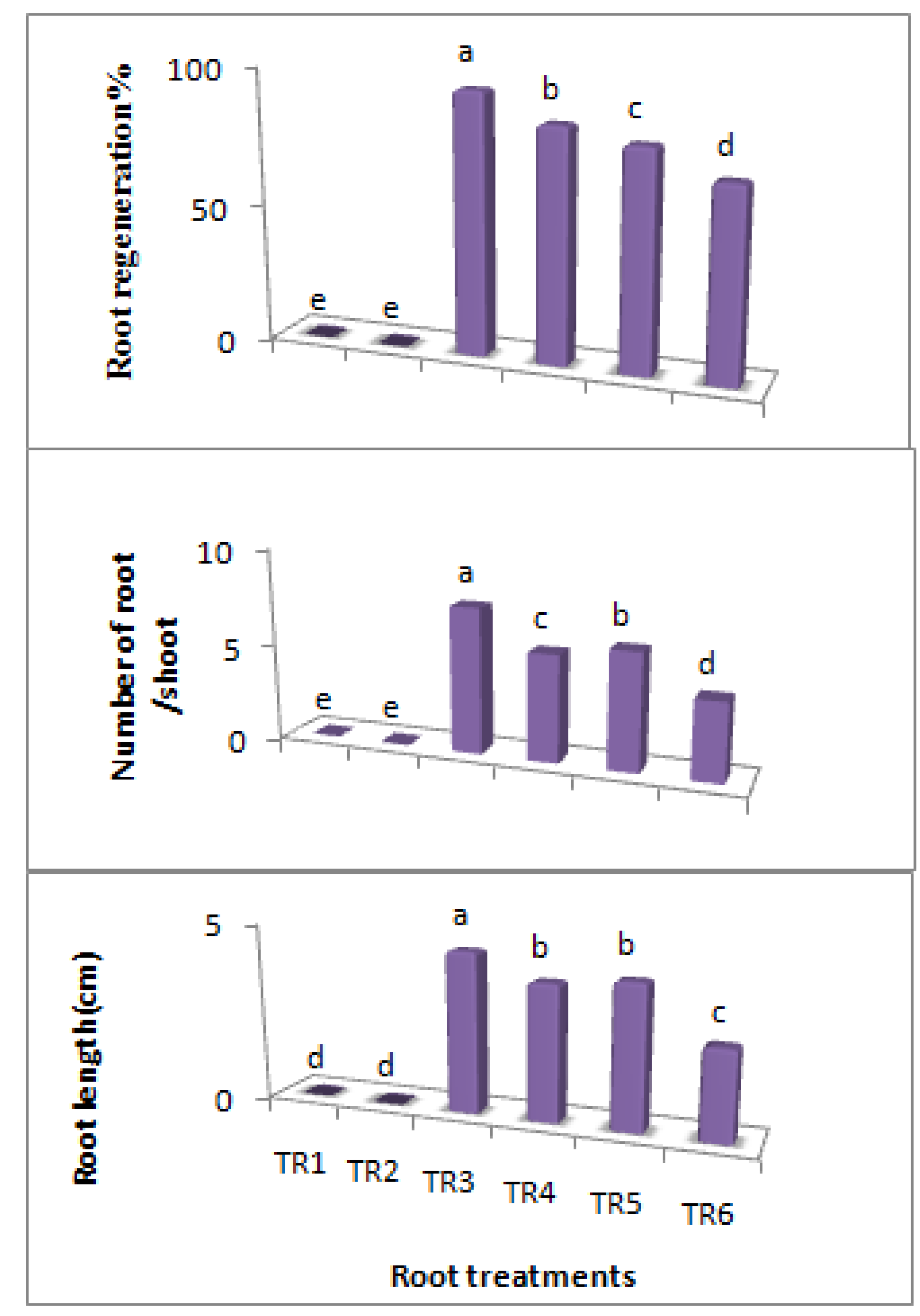
2.3. Rooting
2.4. Establihment of Plants in Soil
3. Experimental
3.1. Evaluation of Different Sterilization Protocols
| Sterilization Treatments |
|---|
| TS1= Decon + benomyl (20 min) + Clorox 15% and 10% (15 and 10 min respectively) |
| TS2= TS1 + benomyl 100 mg/L in medium |
| TS3= Decon + benomyl + Clorox 15%, 12 min + PPM in medium 2mL/L |
| TS4= TS3 + soak in PPM 2% for 1 hour |
| TS5= Decon + cetrimide 1% + bavistin 150 mg/L + trimethoprim 50 mg/L + HgCl2 0.1% + PPM 2% soak and 2 mL/L in medium |
3.2. Culture Medium
| PGR Treatments (MS or Duchefa shoot media) mg/L |
|---|
| T1 = B0N0 |
| T2 = B1N0.5 |
| T3 = B1N0.1 |
| T4 = B2N0.5 |
| T5 = B2N0.1 |
| T6 = B3N0.5 |
| T7 = B3N0.1 |
| T8 = B4N0.5 |
| T9 = B4N0.1 |
| T10 = B5N0.5 |
| T11 = B5N0.1 |
| Treatments mg/L |
|---|
| TR1 = MS without IBA |
| TR2 = ½ MS |
| TR3 = MS + IBA 0.5 mg/L |
| TR4 = ½ MS + IBA 0.5 mg/L |
| TR5 =MS + IBA 0.75 mg/L |
| TR6 = ½ MS + IBA 0.75 mg/L |
3.3. Culture Conditions
4. Conclusions
References and Notes
- Mohd-Zainol, M.; Abdul-Hamid, A.; Abu-Bakar, F.; Pak-Dek, S. Effect of different drying methods on the degradation of selected flavonoids in Centella asiatica. Int. Food Res. J. 2009, 16, 531–537. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, S.; Zehra, M.; Kumar, S. In vitro multiplication of Centella asiatica, a medicinal herb from leaf explants. Curr. Sci. (Bangalore) 1999, 76, 147–148. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, K. Plant regeneration through somatic embryogenesis in medicinally important Centella asiatica L. In Vitro Cell. Dev.Biol. Plant 2004, 40, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, K.; Chandran, C.; Kulothungan, S. Rapid clonal multiplication through in vitro axillary shoot proliferation of Centella asiatica L. Indian J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 232–235. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, K.N.; Sharma, N.C.; Tiwari, V.; Singh, B.D. Micropropagation of Centella asiatica (L.), a valuable medicinal herb. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2000, 63, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, A.; Rai, B.; Rout, G.; Das, P. Successful plant regeneration from callus cultures of Centella asiatica (linn.) urban. Plant Growth Regul. 1998, 24, 13–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshee, N.; Biswas, B.K.; Yadav, A.K. Somatic embryogenesis and plant development in C.asiatica L., a highly prized medicinal plant of the tropics. HortScience 2007, 42, 633–637. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S. Micropropagation studies on Centella asiatica linn—An important medicinal plant. Master Dissertation, Thapar Institute of Engineering and Technology, Patiala, India, , 2004; p. 31. [Google Scholar]
- Mineo, L. Plant tissue culture techniques. In Tested Studies for Laboratory Teaching; Proceedings of the Eleventh Workshop/Conference of the Association for Biology Laboratory Education (ABLE), 195 pages, Easton, PA, USA, 1990; Goldman, C.A., Ed.; Association for Biology Laboratory Education (ABLE); 11, pp. 151–174.
- Sivakumar, G.; Alagumanian, S.; Rao, M. High frequency in vitro multiplication of Centella asiatica: An important industrial medicinal herb. Eng. Life Sci. 2006, 6, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.C.; Murashige, T. Murashige & Skoog Shoot Multiplication Medium B, Plant tissue culture media major constituents, their preparartion and some applications. TCA Manual 1976, 3, 539–548. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, C.D.; Johnson, K.; Torpy, F. Liquid culture for efficient micropropagation of wasabia japonica (miq.) matsumura. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2006, 42, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, K.A.; Gomez, A.A. Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research, 2nd ed; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1984; p. 704. [Google Scholar]
- Samples Availability: Contact the authors.
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Moghaddam, S.S.; Jaafar, H.B.; Aziz, M.A.; Ibrahim, R.; Rahmat, A.B.; Philip, E. Optimization of an Efficient Semi-Solid Culture Protocol for Sterilization and Plant Regeneration of Centella asiatica (L.) as a Medicinal Herb. Molecules 2011, 16, 8981-8991. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16118981
Moghaddam SS, Jaafar HB, Aziz MA, Ibrahim R, Rahmat AB, Philip E. Optimization of an Efficient Semi-Solid Culture Protocol for Sterilization and Plant Regeneration of Centella asiatica (L.) as a Medicinal Herb. Molecules. 2011; 16(11):8981-8991. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16118981
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoghaddam, Sina Siavash, Hawa Binti Jaafar, Maheran Abdul Aziz, Rusli Ibrahim, Asmah Bt Rahmat, and Elizabeth Philip. 2011. "Optimization of an Efficient Semi-Solid Culture Protocol for Sterilization and Plant Regeneration of Centella asiatica (L.) as a Medicinal Herb" Molecules 16, no. 11: 8981-8991. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16118981
APA StyleMoghaddam, S. S., Jaafar, H. B., Aziz, M. A., Ibrahim, R., Rahmat, A. B., & Philip, E. (2011). Optimization of an Efficient Semi-Solid Culture Protocol for Sterilization and Plant Regeneration of Centella asiatica (L.) as a Medicinal Herb. Molecules, 16(11), 8981-8991. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16118981






