Abstract
Botulinum neurotoxins (BoNTs) are the most potent of known toxins and are listed as category A biothreat agents by the U.S. CDC. The BoNT-mediated proteolysis of SNARE proteins inhibits the exocytosis of acetylcholine into neuromuscular junctions, leading to life-threatening flaccid paralysis. Currently, the only therapy for BoNT intoxication (which results in the disease state botulism) includes experimental preventative antibodies and long-term supportive care. Therefore, there is an urgent need to identify and develop inhibitors that will serve as both prophylactic agents and post-exposure ‘rescue’ therapeutics. This review focuses on recent progress to discover and develop small molecule inhibitors as therapeutic countermeasures for BoNT intoxication.
1. Introduction
Botulinum neurotoxins (BoNTs), secreted by the anaerobic spore-forming bacterial Clostridia species botulinum, baratii, and butyricum, are the most poisonous of known biological toxins [1,2], and as a result are listed as category A biothreat agents by the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). BoNTs can be easily produced and may be delivered by either aerosol route, [2,3,4] or through contamination of the food supply. Consequently, these toxins represent a serious threat to both military personnel and civilians [5,6,7]. Moreover, since both BoNT/A (Botox™) and BoNT/B (Myobloc™) are available commercially, and are now used for cholinergic nerve and muscle dysfunction therapy, as well as cosmetic treatments [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16], it is likely that overdose, misuse and/or adverse side effects [17] may result in systemic toxin exposure. The currently available BoNT toxoid vaccine, as well as experimental preventative antibodies, cannot counter these toxins in the neuronal cytosol. This is an important point, as it is likely that individuals will seek medical attention only after clinical symptoms of intoxication manifest (i.e., life-threatening paralysis). Currently, critical care mechanical ventilation is the only treatment option once neurons have been intoxicated and diaphragm muscles cease to function. However, long-term mechanical ventilation would be impractical for the treatment of a large population of intoxicated individuals. Therefore, there is an urgent need to identify and develop low molecular weight, non-peptidic inhibitors that will serve as both prophylactic agents and post-exposure ‘rescue’ therapeutics.
There are seven botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) serotypes (A-G), which possess different tertiary structures and significant sequence divergence. Of the seven BoNT serotypes, A, B, and E are known to cause human botulism [18,19], with BoNT/A and BoNT/B exhibiting the longest durations of activity in the neuronal cytosol (i.e., from several weeks to months, depending on the severity of the poisoning [20,21,22]). Hence, the vast majority of research to develop inhibitors to counter BoNT intoxication post-neuronal internalization has focused on the BoNT/A and BoNT/B light chains (LCs). Once inhaled into the lungs or ingested into the gastrointestinal tract, BoNTs are transcytosed across the respiratory epithelium or mucosa into the blood stream, where they can enter the intracellular space prior to accessing peripheral cholinergic nerve endings. Structurally, BoNTs are synthesized as single polypeptide chains that undergo bacterial or host-mediated cleavage resulting in a 100 kDa heavy chain (HC) component and a 50 kDa light chain (LC) component. These two components, which compose the biologically active holotoxin, are connected by a disulfide bridge until reaching the reducing cytosolic environment of the neuronal target cells [23,24]. The LC is a zinc-dependent endopeptidase. The intoxication of cells involves a stepwise sequence of cell surface binding, receptor-mediated endocytosis, pH-induced translocation, and cytosolic metalloendoprotease activity [24]. The HC serves as a delivery system for the proteolytic LC by binding to neurons and transporting the LC into the cytosol via endosomes. Each BoNT LC cleaves a component of the soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) proteins [25,26], which are responsible for transporting acetylcholine into neuromuscular junctions. BoNT serotypes A and E cleave SNAP-25 (synaptosomal-associated protein (25 kDa)) [27], serotypes B, D, F, and G cleave VAMP-2 (vesicle-associated membrane protein, also referred to as synaptobrevin) [28,29,30,31,32], and serotype C cleaves both SNAP-25 and syntaxin 1 [33]. BoNT-mediated cleavage of any one of the three SNARE proteins terminates the function of autonomic nerves via the inhibition of acetylcholine release, which produces flaccid paralysis. Once diaphragm muscles are affected, suffocation results.
2. Crystal Structures of Botulinum Neurotoxins
The structures of BoNT proteins have been fairly well characterized. The crystal structures of the BoNT/A, B, and E holotoxins have been reported [23,34,35], and a handful of LC crystal structures and receptor binding domains of BoNT HCs are also available [36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43]. The BoNT proteins contain three functional domains: the binding domain, the translocation domain, and the catalytic domain. The LC folds into the catalytic domain and functions as a Zn-dependent endopeptidase that cleaves SNARE proteins in the neuronal cytosol. The C-terminus of the HC forms the binding domain, which targets the cell surface, while the N-terminus of the HC is involved in the translocation of the toxin across the neuronal membrane [44,45,46] (Figure 1). Based on sequence and functional similarity, it was originally believed that the three-dimensional structures of BoNTs would also be similar. Indeed, the structures of the individual functional domains in serotypes BoNT/A, B and E are similar; however, the overall domain arrangements are different [35]. In the BoNT/A and BoNT/B holotoxins, the three domains are arranged in a linear fashion, with the translocation domain in the center (Figure 1, left panel). However, in the BoNT/E holotoxin, both the binding domain and the catalytic domain are on the same side of the translocation domain, and all three domains mutually interact with one another (Figure 1, right panel). This unique association may result in the faster rate of internalization and translocation observed for the BoNT/E, and thus explains the faster intoxication rate of BoNT/E with respect to other BoNT serotypes.
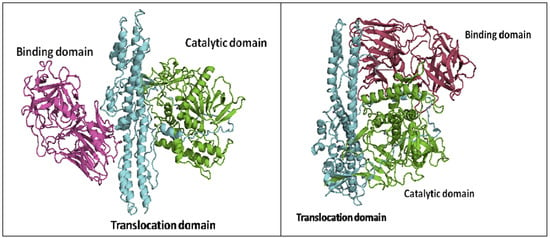
Figure 1.
Cartoon representations of two types of three-domain organizations of BoNTholotoxins, (a) BoNT/A, left panel, and (b) BoNT/E, right panel. The two structures were obtained from the Protein Data Bank (PDB codes: 3BTA for BoNT/A and 3FFZ for BoNT/E).
Figure 1.
Cartoon representations of two types of three-domain organizations of BoNTholotoxins, (a) BoNT/A, left panel, and (b) BoNT/E, right panel. The two structures were obtained from the Protein Data Bank (PDB codes: 3BTA for BoNT/A and 3FFZ for BoNT/E).
Comparison of the x-ray structures of the BoNT/A holotoxin and the BoNT/B holotoxin indicate that the enzymes’ translocation domain protective belts, which wrap around the LCs of both holotoxins, possess different orientations. Specifically, in the BoNT/A, the protective belt completely obstructs the active site and inhibits substrate binding. Thus, the BoNT/A LC is catalytically active only after translocation into the neuronal cytosol and dissociation from the HC. Experimental evidence indicates that the BoNT/A LC, after separation from the rest of the holotoxin, is the actual active component [47]. In contrast, the orientation of the BoNT/B protective belt allows for active site access relative to the BoNT/A holotoxin [39], making the BoNT/B LC catalytically active prior to reduction of the disulfide bond.
The active sites of BoNT LCs contain a common HEXXH (X is any amino acid) zinc-binding motif with two His residues and one Glu residue ligating the zinc [30,31,32], the catalytic water molecule provides the fourth zinc ligand (the structure of active site of the BoNT/A LC is shown in Figure 2). All seven BoNT serotype LCs contain one zinc atom, with the exception of the BoNT/C LC, which possesses two zinc atoms [48]. Superimposition of the x-ray structures of the catalytic clefts of the BoNT/A, B and E LCs indicates that their compositions and geometries are essentially identical [38]. Interestingly, BoNT LC sequence identities range from 31-59%, while sequence similarities range from 52-75% [49]. However, even though the active sites of BoNT LCs are highly homologous, serotype-specific inhibitors, which preferentially target different LC active sites, have been identified [50,51,52,53,54].
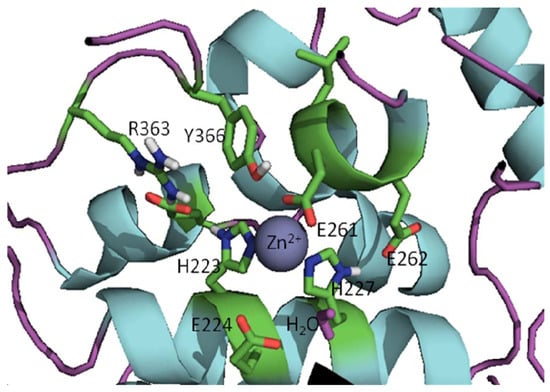
Figure 2.
Active site of the BoNT/A LC (prepared from PDB code 2IMC) [55].
Figure 2.
Active site of the BoNT/A LC (prepared from PDB code 2IMC) [55].
The seven BoNT LC serotypes exhibit unique substrate selectivity and cleavage site specificity. Hence, the virtually identical structures of the active sites of the neurotoxins suggest that substrate recognition is not dictated by the enzymes’ catalytic clefts [38]. Rather, and as evidenced by the crystal structure of the BoNT/A LC:SNAP-25 complex which comprises 4,840 Å2 of the enzyme-substrate interface area, the substrate recognition locations of BoNT LCs are discontinuous and distal to the catalytic site. Further evidence supporting this hypothesis is the large size of the substrate recognition requirement for the BoNT/A LC (i.e., a minimum of 17 substrate amino acids are required for SNAP-25 cleavage) [56], which is unusual for metalloproteases. Based on the BoNT/A LC:SNAP-25 complex, two exosites, termed the a-exosite and the b-exosite, are required for substrate recognition [38]. In addition, a Cys165 site (we have termed it as the ¡-exosite), which is adjacent to the active site, has also been proposed for small molecule ligand binding [57]. The putative exosites of the BoNT/F LC, which were identified based on the crystal structure and molecular modeling, are different from that of the BoNT/A LC and the BoNT/B LC [41]. In general, the substrate selectivity and cleavage site specificities of the BoNT proteases have provided the bases for the discovery and development of serotype specific BoNT inhibitors.
3. Approaches to BoNT Inhibition
To counter the BoNT threat, several different approaches are currently being explored. While vaccines will likely play a role in biodefense [58,59], the development of therapeutic approaches that are effective both pre- and post-exposure are essential. In particular, vaccines are useless for the post-exposure protection of previously unvaccinated individuals, and the identification and inoculation of all members of large, at-risk populations prior to exposure is problematic. Therapeutic approaches under development include the following: (a) anti-BoNT antibodies, with the most effective strategy involving the simultaneous administration of three monoclonal antibodies. The antibodies bind the BoNT/A with non-overlapping reactivity, and provide potent protection against toxin challenge in mice [60]; (b) soluble versions of the BoNT/B and the BoNT/G receptors (“receptor decoys”),which function as anti-toxins in cell culture and in mice [61,62] (however, in the case of the BoNT/B, the anti-toxin effect requires the co-administration of gangliosides); and (c) small molecule approaches to BoNT inhibition. This final category is the focus of this review.
4. Broad-Spectrum Small Molecule BoNT Inhibitors
Numerous attempts to develop broad spectrum antagonists of BoNTs have met with limited success. One approach is to inhibit toxin-cell interactions by targeting carbohydrates in general, and sialic acid in particular, on cellular receptors. This approach is based on the premise that the cellular receptors for the toxins may not be identical, but may possess certain elements of commonality. Lectins, which are large glycoproteins that are highly specific for their sugar moieties, and which exert their effects by preventing the binding of the BoNT HC to the membrane receptor [63], were found to antagonize several serotypes. Finally, no small molecules that inhibit toxin-cell receptor interactions have been identified.
BoNT-induced muscle paralysis involves holotoxin translocation and subsequent release from an acidic endosome. In the early 1980s, the triterpenoid toosendanin (1, Figure 3), was reported to protect monkeys against BoNT/A, BoNT/B and BoNT/E-induced death in a dose-dependent fashion [64,65,66,67]. In a spinal cord cell-based assay, toosendanin completely inhibits SNAP-25 cleavage at concentrations above 200 nM, and partial inhibition can be observed with concentrations as low as 8 nM for BoNT/A and 40 nM for BoNT/E. Single molecule channel experiments have demonstrated that toosendanin exhibits an unprecedented dual mode of action within the protein-conducting channel, acting both as a cargo-dependent inhibitor of translocation and as a cargo-free channel activator [68]. To elucidate the mechanistic nature of its anti-BoNT properties, several toosendanin analogs have been prepared by semisynthetic approaches (Figure 3) [69,70]. Only the THF-toosendanin analog 2 exhibited similar activity, indicating that the furan ring of toosendanin can be modified. However, the epoxide moiety on the five-membered-ring still seems to be important for anti-BoNT activity, as replacement of the epoxide moiety with a thermodynamically more stable ketone resulted in inactive compound 3. Ketone 4 and deacetylated compound 5 also lack activity against BoNTs.
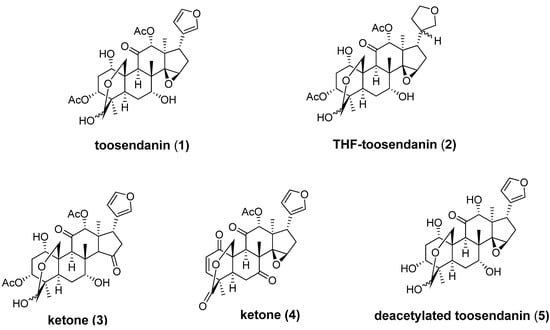
Figure 3.
Chemical structures of toosendanin (1) and its analogs.
Figure 3.
Chemical structures of toosendanin (1) and its analogs.
The total synthesis of toosendanin (1) and its analogs would allow for a more thorough assessment of the structure-activity relationships (SARs) associated with this chemotype; however, due to the complexity of the toosendanin structure, and the unlikely possibility that a total synthesis will be developed, an alternative Function-Oriented Synthesis (FOS) [71] strategy has been applied to determine the structural features important for the anti-BoNT activity of this compound. The principle of FOS is that the function of a biologically active lead structure can be emulated, tuned, or possibly improved by replacement with simpler scaffolds designed to encompass the key activity-determining structural features of the natural product. To this end, a CD-ring fragment with an epoxide moiety on the five-member-ring [69] and two epimers of an AB-ring fragment [70] (Figure 4) have been synthesized and tested.
In a rat spinal cord cellular assay (RSC), addition of two epimers of the AB-ring fragment at 1 mM concentrations did not prevent BoNT/A induced SNAP-25 cleavage in primary neuronal cells, while 200 µM toosendanin (1) resulted in complete inhibition of BoNT/A activity. In a mouse lethality assay (MLA), intravenous administration of the synthesized CD-ring fragment compound did not protect or prolong the mean time to death, while at the same concentration toosendanin extended time to death 7.1 h. No in vitro assay data was reported for the CD-ring fragment.
The endosome acidification process is required for BoNT-induced muscle paralysis. This is evidenced by the fact that ammonium chloride and methylamine hydrochloride exhibit concentration- and time-dependent antagonism of the onset of neuromuscular blockade by BoNT/A, /B, /C, and tetanus toxin [72,73]. However, these amines act solely by antagonizing the internalization of the toxins by inhibiting endosome acidification, since they neither inactivate the toxins, nor irreversibly change tissue function at concentrations that antagonize the onset of BoNT-induced paralysis.
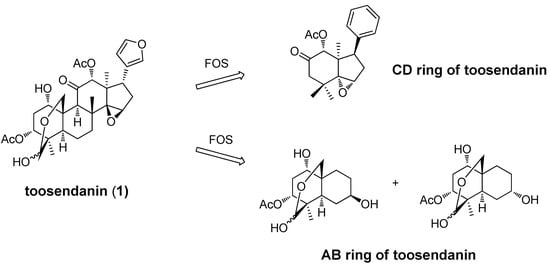
Figure 4.
AB-ring and CD-ring fragments generated from a function-oriented synthesis (FOS) strategy.
Figure 4.
AB-ring and CD-ring fragments generated from a function-oriented synthesis (FOS) strategy.
Following the same logic, cellular ATPase is required for the acidification of endocytotic vesicles. Thus, the inhibition of a vesicle H+-ATPase could result in the antagonism of a broad-spectrum of BoNTs. To this end, bafilomycin A (Figure 5, compound 6), an ATPase inhibitor, has been shown to be a universal antagonist of BoNTs A-G, as well as tetanus toxin [74].
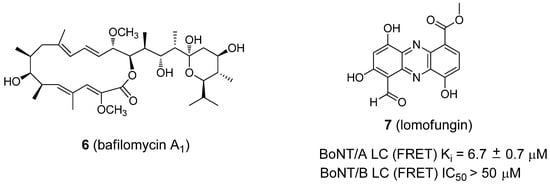
Figure 5.
Structures of BoNT inhibitors 6 (bafilomycin A1) and 7 (lomofungin).
Figure 5.
Structures of BoNT inhibitors 6 (bafilomycin A1) and 7 (lomofungin).
A natural product, lomofungin (7, Figure 5) [75], was identified as an inhibitor of the BoNT/A LC (Ki value of 6.7 ± 0.7 µM) from the high-throughput screening (HTS) of a drug library. The screening was conducted by The Scripps Research Institute. Lomofungin displayed classical noncompetitive inhibition kinetics and was not mutually exclusive when examined in tandem with an active site inhibitor (2,4-dichlorocinnamic hydroxamate) [76] and a noncompetitive inhibitor, D-chicoric acid. These data suggest that lomofungin binds to a different ligand binding site on the BoNT/A LC. In the same report, lomofungin was reported to display weak BoNT/B LC inhibition (IC50 ≥ 50 µM) in a FRET-based assay.
5. Small Molecule BoNT/A LC Inhibitors
BoNT LCs induce neuronal paralysis via the specific proteolysis of SNARE proteins. Therefore, inhibiting BoNT LC activity has been the major focus of research efforts to discover and develop selective therapeutic agents. Several ligand binding sites have been identified within the BoNT/A LC substrate binding domain, including the active site, a- and b-exosites, and the Cys165 site (¡-exosite). Active site inhibitors usually exhibit competitive kinetics vs the SNAP-25 substrate. Co-crystal structures of 2,4-dichlorocinamic hydroxamate (Figure 6, compound 8) and L-arginine hydroxamate (Figure 6, compound 9) in complex with the BoNT/A LC have shown that the hydroxamates bind in the enzyme’s active site, with the cinnamyl side chain oriented toward the 370 loop, and the catalytic water molecule (which ligates the zinc ion), displaced by the hydroxamate moiety (Figure 7).
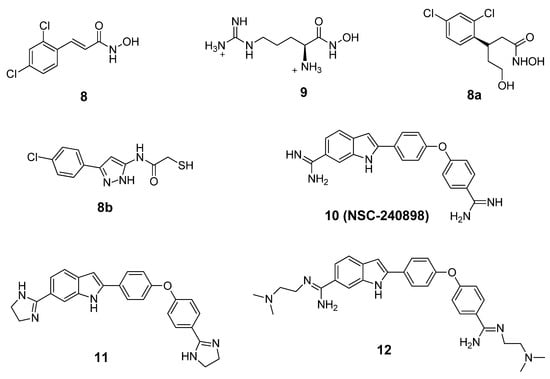
Figure 6.
Structures of BoNT/A LC inhibitors.
Figure 6.
Structures of BoNT/A LC inhibitors.
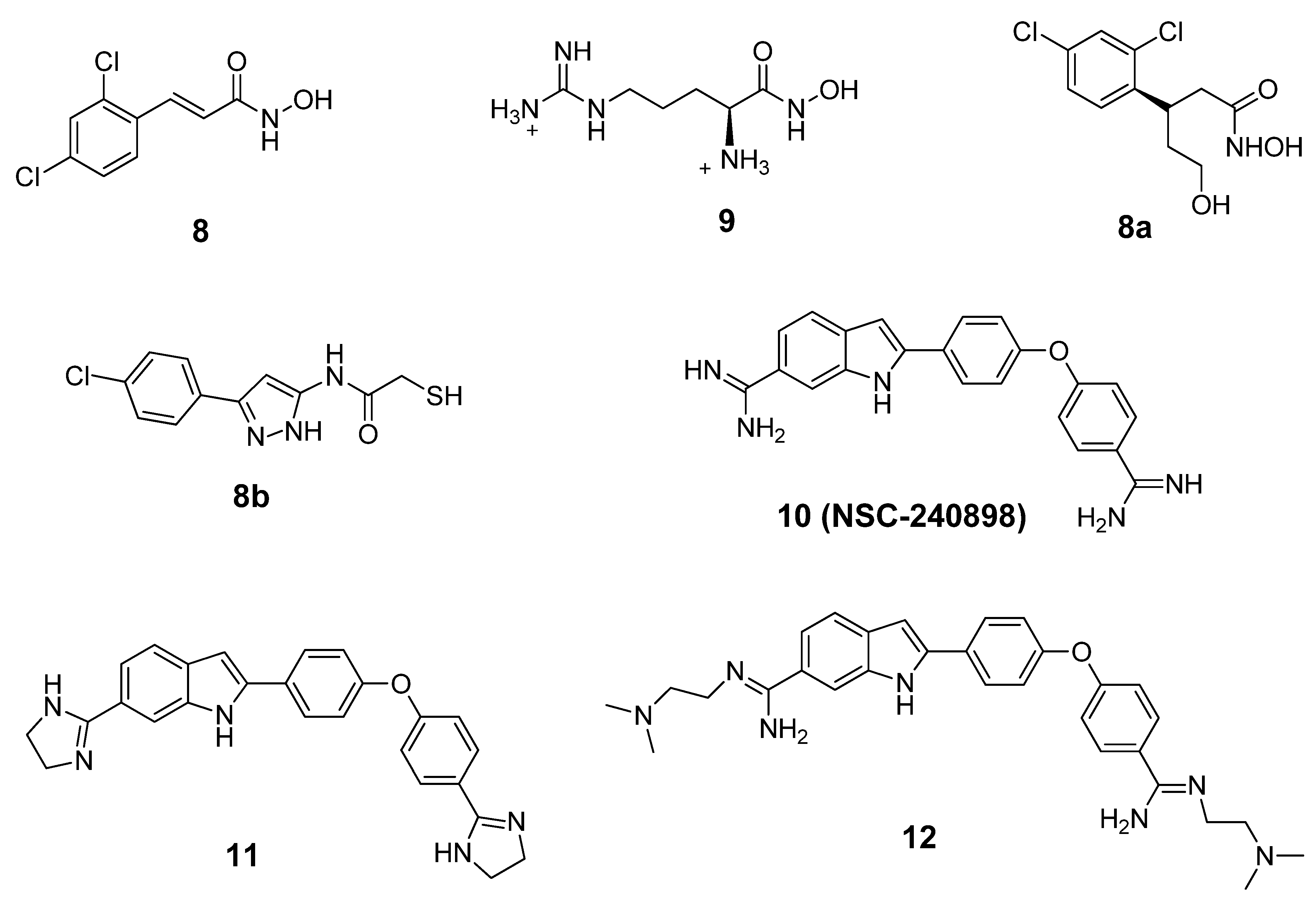
The hydroxyl oxygen of the hydroxamate moiety coordinates the catalytic zinc ion. However, a dramatic conformational change is observed for the 370 loop in comparing the two complexes. In the complex LC:9, the side chain of Phe369 is withdrawn from the catalytic cleft and the side chain of Asp370 is exposed, thereby allowing it to form a salt bridge with the guanidinium functionality of compound 9. Rational design based on this co-crystal data resulted in the identification of chiral compound 8a, which possesses an R-configuration at the b-carbon. Compound 8a displayed a Ki value of 0.16 mM ± 0.002 µM [77]. Moe et al. [78] have reported a series of mercaptoacetamides, for example compound 8b, which provide low μM anti-BoNT/A LC activity. The SAR of the mercaptoacetamides is very similar to that of the cinnamic hydroxamates, suggesting that these inhibitors also bind in the BoNT/A LC catalytic cleft.
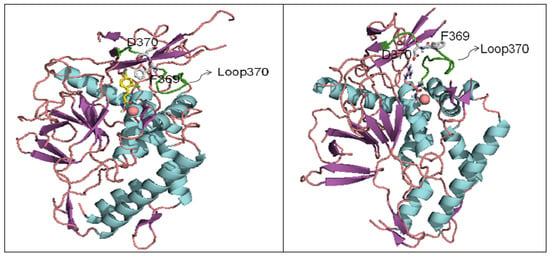
Figure 7.
(a) Co-crystal structure of BONT/A LC:8 (PDB code: 2IMA). (b) Co-crystal structure of BONT/A LC:9 (PDB code: 2IMB).
Figure 7.
(a) Co-crystal structure of BONT/A LC:8 (PDB code: 2IMA). (b) Co-crystal structure of BONT/A LC:9 (PDB code: 2IMB).
NSC-240898 (Figure 6, compound 10), a bisamidine compound, has been identified as a BoNT/A LC inhibitor from screening a diversity set of small molecules from the National Cancer Institute’s Open Repository (using a high throughput FRET-based enzyme assay) [79,80]. Chemical optimization studies of this lead structure have been conducted at both the University of Pittsburgh [81] and Microbiotix, Inc. [54].
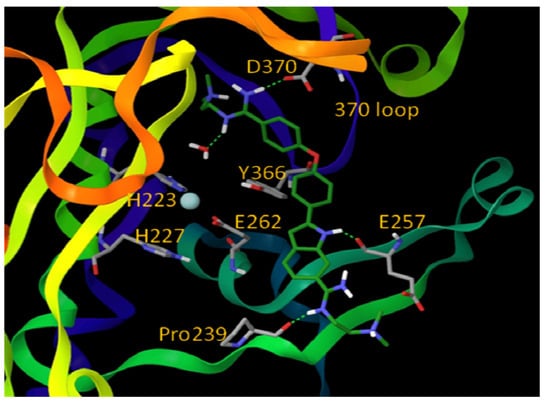
Figure 8.
Proposed binding mode for inhibitor 12 (shown in green stick model). Oxygen atoms are red, nitrogen atoms are blue, hydrogen atoms are white, and Zn is cyan. The BoNT/A LC is rendered ribbon. (Reproduced from Li, B. et al. J. Med. Chem.; published by American Chemical Society [54].)
Figure 8.
Proposed binding mode for inhibitor 12 (shown in green stick model). Oxygen atoms are red, nitrogen atoms are blue, hydrogen atoms are white, and Zn is cyan. The BoNT/A LC is rendered ribbon. (Reproduced from Li, B. et al. J. Med. Chem.; published by American Chemical Society [54].)
One of the most potent analogs of this chemotype is compound 12 (Figure 6), which possesses an IC50 value of 2.5 µM in a FRET-based enzyme assay. Hence, 12 is 4.4-fold more potent than the lead structure (IC50 = 11 µM), 3-fold more potent than cinnamic acid hydroxamate 8 (IC50 = 8.9 µM), and 11.2-fold more selective for the BoNT/A LC than anthrax lethal factor (also a metalloprotease). Compound 11, another analog of NSC-240898, possesses IC50 values of 12.5 µM and 9.4 µM in a FRET-based and an HPLC-based assay, respectively, and has shown protection against BoNT/A-induced cleavage of SNAP-25 in both rat and chicken neuronal cell-based assays [82]. Bisamidine 10 and its analogs are competitive BoNT/A LC inhibitors, and molecular modeling studies suggest that they bind in the active site of the BoNT/A LC and do not directly interact with the catalytic zinc ion (Figure 8).
Recently, an in silico screening campaign, coupled with biochemical assays, has been used to identify BoNT/A LC inhibitors. From this study, quinolinol derivative CB7969312 (Figure 9), has been reported as a potent inhibitor that protects against neuromuscular block in an ex vivo mouse phrenic nerve hemidiaphram assay (EC50 = 0.5 µM).
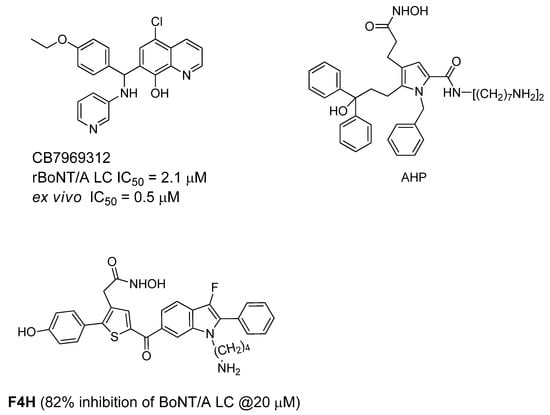
Figure 9.
Active site BoNT/A LC inhibitors.
Figure 9.
Active site BoNT/A LC inhibitors.
This compound also significantly neutralizes the BoNT/A holotoxin in N2a cells [83]. Biochemical analysis of the inhibition and binding of this quinolinol compound with the BoNT/A LC suggest that it exhibits atypical noncompetitive kinetics [84]. A molecular docking study suggests that the quinolinol compound binds within a large hydrophobic pocket in the BoNT/A LC active site, and that the hydroxyquinoline moiety purportedly binds the catalytic zinc. Pang et al. [85] reported a series of competitive, active site inhibitors based on pyrrole and thiophene structures using synthesis-based computer-aided molecular design. The most potent compound (AHP) displayed BoNT/A inhibition with a Ki value of 0.76 ± 0.17 µM and an IC50 value of <1 µM, and a thiophene-based compound (F4H) demonstrated 100% and 70% protection of mice against BoNT/A at 5ED50 within periods of two and four half-lives, respectively, of the inhibitors [86]. In the study, a single dose of inhibitor was administered IP (concentration = 2 mg/kg) pre-BoNT challenge.
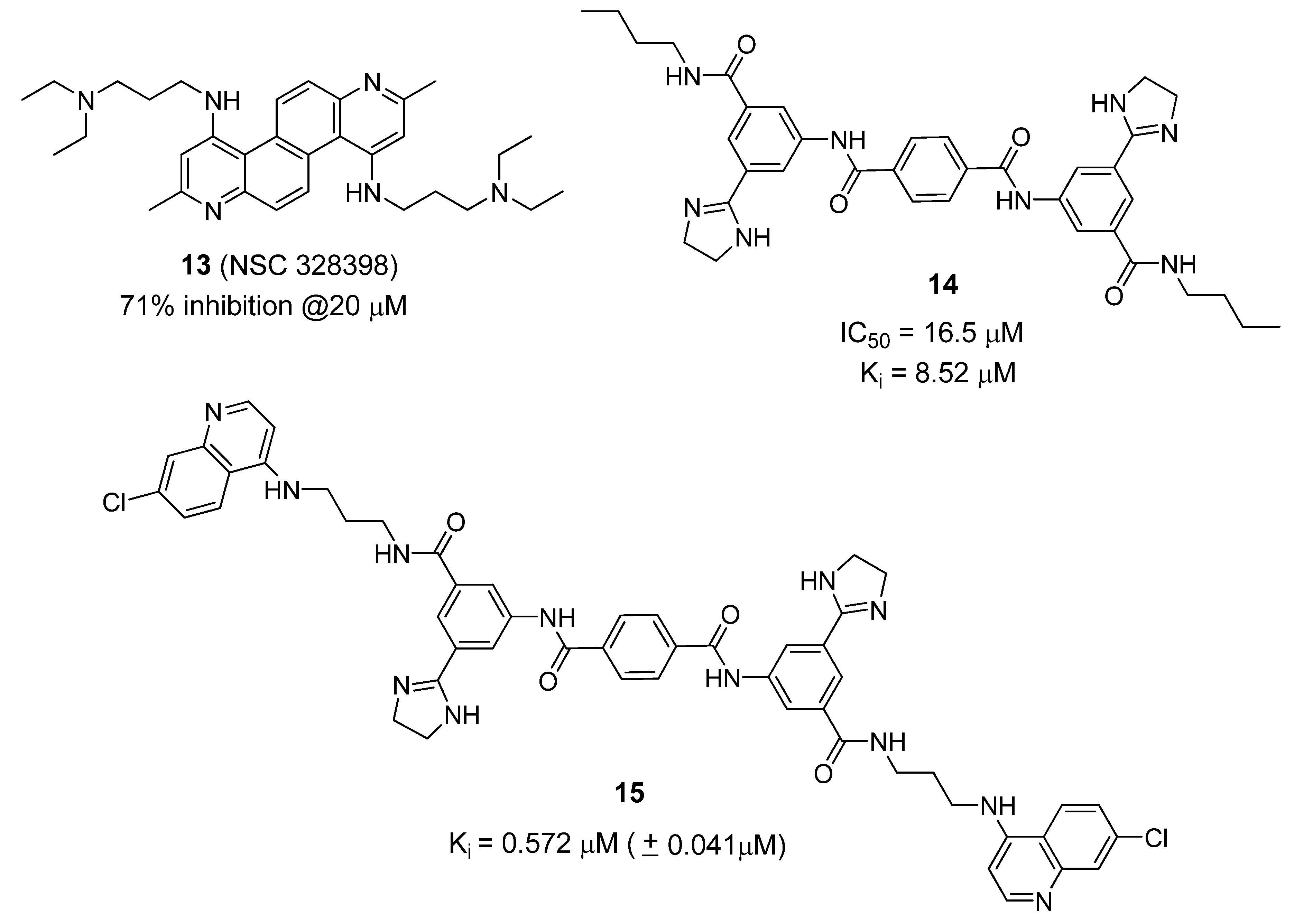
Several non-Zn-chelating small molecule (non-peptidic) BoNT/A LC inhibitors (SMNPIs) have been described based on pharmacophore-based design [80,87,88,89]. SMNPIs are continually integrated into the pharmacophore to both develop three-dimensional (3D) search queries to discover novel SMNPI chemotypes and guide the rational design of more potent SMNPI derivatives. Employing this iterative approach, new chemotypes including diazachrysene (Figure 10, compound 13) and phenylterephthalamide (Figure 10, compound 14), have been identified. The pharmacophore model has guided design and synthesis of compound 15 (Figure 10), which possesses a Ki value of 0.572 µM (± 0.041 µM) vs. the BoNT/A LC.
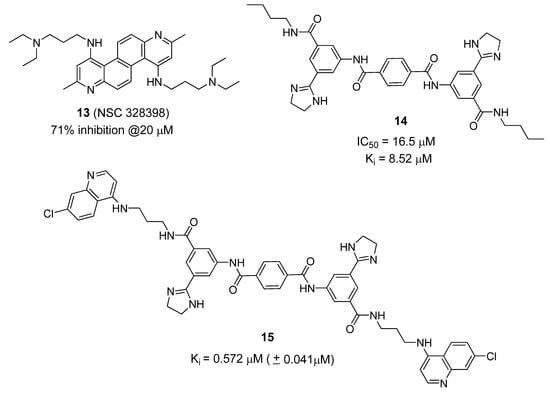
Figure 10.
Small molecule BoNT/A LC inhibitors identified using phamacophore-based design.
Figure 10.
Small molecule BoNT/A LC inhibitors identified using phamacophore-based design.
A series of benzylidene cyclopentenedione-based inhibitors has been reported to inhibit the BoNT/A LC metalloprotease by putatively forming a covalent bond with the enzyme [90]. Among these inhibitors, compound 16 (Figure 11) displayed a kinact/KI value of 520 M-1s-1 and SNAP-25 cleavage was significantly decreased at concentrations of 600 µM in a primary rat spinal cord neuron assay. Unfortunately, compound 16 is highly bound to serum and is reactive with glutathione. Such a poor pharmacokinetic profile prevents further development of this type of inhibitor. Researchers at Microbiotix have identified benzimidazole compound 17 (Figure 11) from high throughput, FRET-based screening of compound libraries against the BoNT/A LC. Compound 17 inhibited the BoNT/A LC with an IC50 value of 7.2 µM in the FRET-based assay (and 10 µM in an HPLC-based assay); however, no cell-based activity was observed.
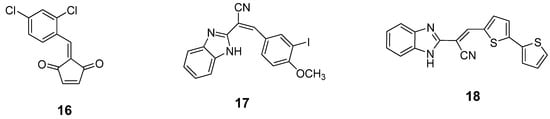
Figure 11.
Covalent inhibitors of BoNT/A LC.
Figure 11.
Covalent inhibitors of BoNT/A LC.
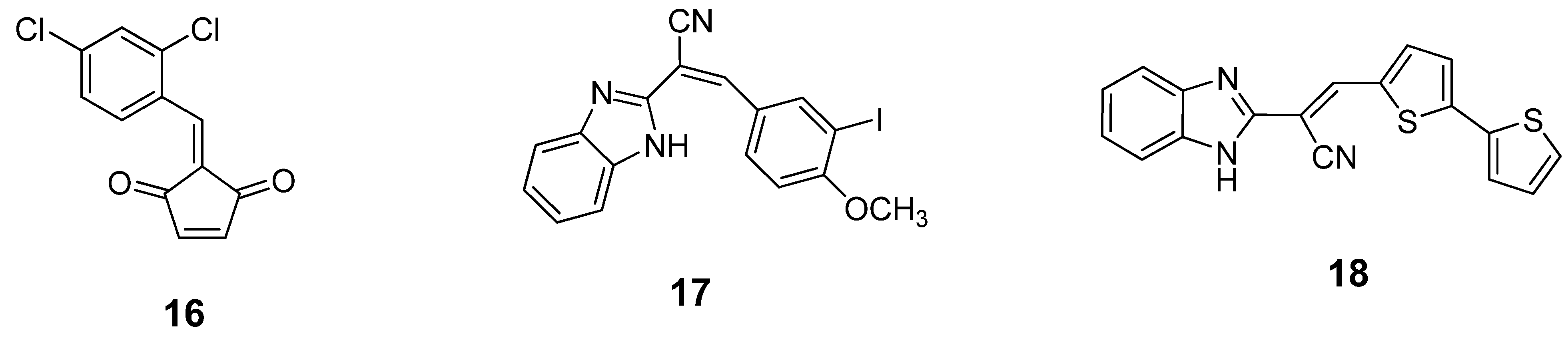
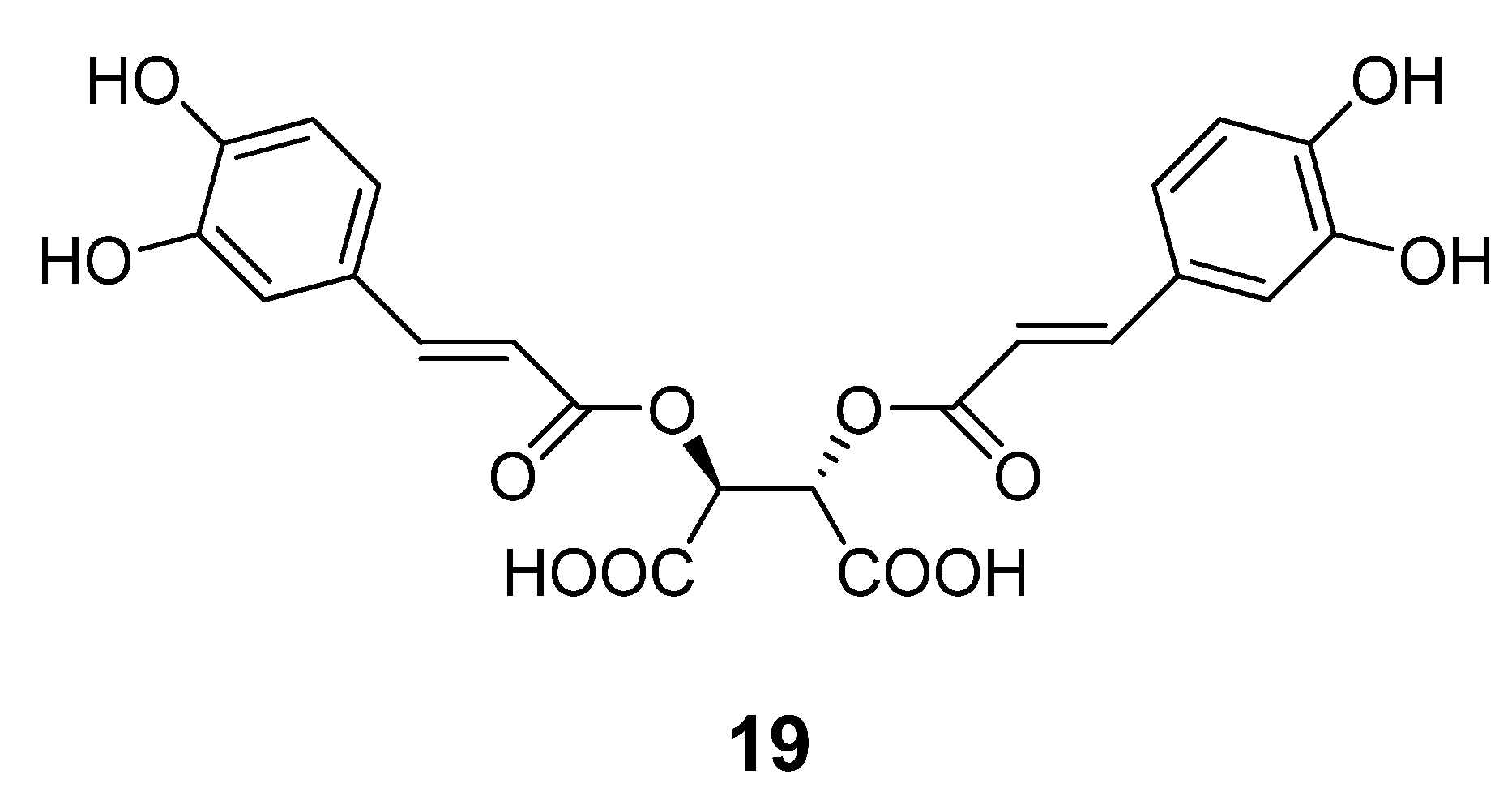
Chemical optimization of the benzimidazole acrylonitrile series of BoNT/A LC inhibitors yielded compound 18, which possesses an IC50 value of 26 µM. Moreover, compound 18 displays 58% protection of SNAP-25 cleavage at an inhibitor concentration of 30 µM [57]. Silhar et al. reported that a natural product isolated from Echinacea, D-chicoric acid (19) (Figure 12), inhibits BoNT/A LC activity by binding to an exosite, and displays noncompetitive partial inhibition of the LC with a submicromolar inhibition constant [76]. In a combination study, D-chicoric acid was synergistic with competitive BoNT/A LC inhibitor 2,4-dichlorocinnamic hydroxamic acid (8).
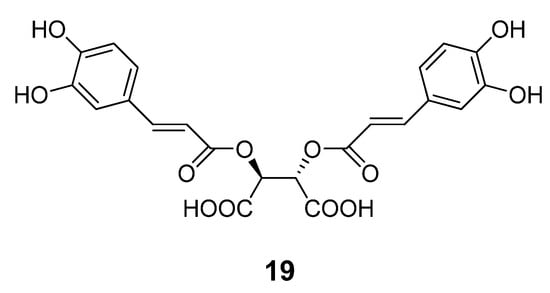
Figure 12.
Chemical structure of D-chicoric acid (19).
Figure 12.
Chemical structure of D-chicoric acid (19).
6. Small Molecule BoNT/B LC Inhibitors
Known zinc chelators, such as bis(5-amidino-2-benzimidazolyl)methane (BABIM, Figure 13, compound 20), have been shown to be weak BoNT/B LC inhibitors (IC50 = 5-10 µM) [91]. X-ray co-crystal structures of BABIM in complex with the BoNT/B LC have been reported [39,91]. As shown in the latter published BABIM:BoNT/B structure, two inhibitor molecules are bound to the holotoxin. One molecule of BABIM enters through a cleft formed between the translocation domain and the catalytic domain. Another molecule of BABIM sits in the cleft formed between the translocation domain and the binding domain, suggesting that there are two pathways for the inhibitor to enter the toxin. The two inhibitor molecules do not bind to the enzyme’s catalytic zinc, as was observed in a previously reported BoNT/B LC:BABIM structure [39]. The co-crystal structures suggest that, in the presence of inhibitor, the environment of the active site rearranges, and the catalytic zinc is gradually removed from the active site and transported to a different site of the protein. ICD 1578 (22, Figure 12), a human leukocyte elastase inhibitor, was reported to inhibit the BoNT/B LC with an IC50 value of 27.6 µM in a FRET-based assay using a 50-mer synaptobrevin peptide as substrate [92]. However, no enzyme selectivity data has been presented for compound 22. To date, BoNT/B LC specific small molecule inhibitors suitable for clinical use have not been reported.
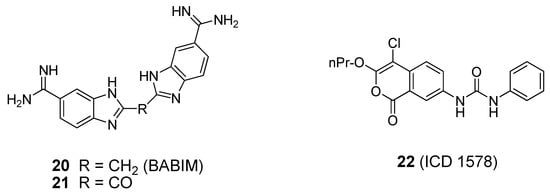
Figure 13.
Small molecule BoNT/B LC inhibitors.
Figure 13.
Small molecule BoNT/B LC inhibitors.
7. Summary
As described above, large molecule biologics such as monoclonal antibodies and receptor decoys may be effective in mouse models or cellular systems if they are administered simultaneously with BoNT; however, they have not been tested for, and are unlikely to be useful for, post-exposure therapy (i.e., after BoNT penetration into the neuronal cytosol). Peptide-based inhibitors suffer from a similar limitation because their large molecular size and metabolic instability limit their ability to reach the BoNT endopeptidase within neurons. Therefore, small molecule, non-peptidic inhibitors offer the best opportunity for the development of post-exposure therapeutics. However, none of the reported agents demonstrate adequate therapeutic utility and none have shown protection in mice due to limited efficacy, poor cell membrane permeability, cytotoxicity, or poor pharmacokinetic properties, although some of them may have prolonged the mean time to death. Thus, more drug-like small molecule botulinum inhibitors, which are potent, effective, safe, and possess suitable absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADMET) profiles are urgently needed. The key would be to further refine the design strategy to develop analogs of the lead molecules with improved solubility or ADMET properties. Viable biological assays to target different phases of BoNT intoxication are also needed to identify inhibitors with novel mechanisms of action. The development of high-throughput screening enzymatic and cell-based assays, as well as structure-based drug design approaches, are valuable for the identification of inhibitor ‘leads’ for further optimization. Finally, the validation of in vivo models of BoNT intoxication will be important for the determination of compounds that will be of clinical use.
References
- Arnon, S.S.; Schechter, R.; Inglesby, T.V.; Henderson, D.A.; Bartlett, J.G.; Ascher, M.S.; Eitzen, E.; Fine, A.D.; Hauer, J.; Layton, M.; Lillibridge, S.; Osterholm, M.T.; O'Toole, T.; Parker, G.; Perl, T.M.; Russell, P.K.; Swerdlow, D.L.; Tonat, K. Botulinum toxin as a biological weapon: Medical and public health management. JAMA 2001, 285, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Paddle, B.M. Therapy and prophylaxis of inhaled biological toxins. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2003, 23, 139–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, J.C.; Henchal, E.A.; Schmaljohn, A.L.; Bavari, S. The evolving field of biodefense: Therapeutic developments and diagnostics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 281–297. [Google Scholar]
- Burnett, J.C.; Schmidt, J.J.; McGrath, C.F.; Nguyen, T.L.; Hermone, A.R.; Panchal, R.G.; Vennerstrom, J.L.; Kodukula, K.; Zaharevitz, D.W.; Gussio, R.; Bavari, S. Conformational sampling of the botulinum neurotoxin serotype A light chain: Implications for inhibitor binding. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 333–341. [Google Scholar]
- Josko, D. Botulin toxin: A weapon in terrorism. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2004, 17, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, S.C. Bacteria as potential tools in bioterrorism, with an emphasis on bacterial toxins. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2005, 62, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Hicks, R.P.; Hartell, M.G.; Nichols, D.A.; Bhattacharjee, A.K.; van Hamont, J.E. Skillman, D.R. The medicinal chemistry of botulinum, ricin and anthrax toxins. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 667–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, J.C.; Henchal, E.A.; Schmaljohn, A.L.; Bavari, S. The evolving field of biodefense: Therapeutic developments and diagnostics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 281–297. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, H.D.; Sharma, S.K. Clostridium botulinum: A bug with beauty and weapon. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 31, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comella, C.L.; Pullman, S.L. Botulinum toxins in neurological disease. Muscle Nerve 2004, 29, 628–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glogau, R.G. Review of the use of botulinum toxin for hyperhidrosis and cosmetic purposes. Clin. J. Pain 2002, 18 (6 Suppl.), S191–S197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, J.D. Medical aspects of biologic toxins. Anesthesiol. Clin. N. Amer. 2004, 22, 509–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montecucco, C.; Molgo, J. Botulinal neurotoxins: Revival of an old killer. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2005, 5, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhidayasiri, R.; Truong, D.D. Expanding use of botulinum toxin. J. Neurol. Sci. 2005, 235, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigalke, H.; Rummel, A. Medical aspects of toxin weapons. Toxicology 2005, 214, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, K.A. A new wrinkle on pain relief: Re-engineering clostridial neurotoxins for analgesics. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, T.R.; Mohan, A.K.; Polder, J.A.; Walton, M.K.; Braun, M.M. Botulinum toxin type A injections: Adverse events reported to the US Food and Drug Administration in therapeutic and cosmetic cases. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2005, 53, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnon, S.S.; Schechter, R.; Inglesby, T.V.; Henderson, D.A.; Bartlett, J.G.; Ascher, M.S.; Eitzen, E.; Fine, A.D.; Hauer, J.; Layton, M.; Lillibridge, S.; Osterholm, M.T.; O'Toole, T.; Parker, G.; Perl, T.M.; Russell, P.K.; Swerdlow, D.L.; Tonat, K. Botulinum toxin as a biological weapon: Medical and public health management. JAMA 2001, 285, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Foran, P.G.; Mohammed, N.; Lisk, G.O.; Nagwaney, S.; Lawrence, G.W.; Johnson, E.; Smith, L.; Aoki, K.R.; Dolly, J.O. Evaluation of the therapeutic usefulness of botulinum neurotoxins B, C1, E, and F compared with the long lasting type A. Basis for distinct durations of inhibition of exocytosis in central neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield, R.A.; Brown, B.R.; Hutchins, J.B.; Iandolo, J.J.; Jackson, R.; Slater, L.N.; Bronze, M.S. Microbiological, biological, and chemical weapons of warfare and terrorism. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2002, 323, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbloom, M.; Leikin, J.B.; Vogel, S.N.; Chaudry, Z.A. Biological and chemical agents: A brief synopsis. Am. J. Ther. 2002, 9, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, F.A.; Lisk, G.; Sesardic, D.; Dolly, J.O. Dynamics of motor nerve terminal remodeling unveiled using SNARE-cleaving botulinum toxins: the extent and duration are dictated by the sites of SNAP-25 truncation. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2003, 22, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, D.B.; Tepp, W.; Cohen, A.C.; DasGupta, B.R.; Stevens, R.C. Crystal structure of botulinum neurotoxin type A and implications for toxicity. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998, 5, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, L.L. Identification of the major steps in botulinum toxin action. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2004, 44, 167–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.R. Intimate details of the most poisonous poison. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 617–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turton, K.; Chaddock, J.A.; Acharya, K.R. Botulinum and tetanus neurotoxins: Structure, function and therapeutic utility. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binz, T.; Blasi, J.; Yamasaki, S.; Baumeister, A.; Link, E.; Sudhof, T.C.; Jahn, R.; Niemann, H. Proteolysis of SNAP-25 by types E and A botulinal neurotoxins. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 1617–1620. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, J.J.; Stafford, R.G. Fluorogenic substrates for the protease activities of botulinum neurotoxins, serotypes A, B, and F. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, G.; Malizio, C.; Trimble, W.S.; Polverino de Laureto, P.; Milan, G.; Sugiyama, H.; Johnson, E.A.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum G neurotoxin cleaves VAMP/synaptobrevin at a single Ala-Ala peptide bond. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 20213–20216. [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo, G.; Benfenati, F.; Poulain, B.; Rossetto, O.; de Polverino, L.P.; DasGupta, B.R.; Montecucco, C. Tetanus and botulinum-B neurotoxins block neurotransmitter release by proteolytic cleavage of synaptobrevin. Nature 1992, 359, 832–835. [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo, G.; Rossetto, O.; Catsicas, S.; de Polverino, L.P.; DasGupta, B.R.; Benfenati, F.; Montecucco, C. Identification of the nerve terminal targets of botulinum neurotoxin serotypes A, D, and E. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 23784–23787. [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo, G.; Shone, C.C.; Rossetto, O.; Alexander, F.C.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum neurotoxin serotype F is a zinc endopeptidase specific for VAMP/synaptobrevin. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 11516–11519. [Google Scholar]
- Blasi, J.; Chapman, E.R.; Yamasaki, S.; Binz, T.; Niemann, H.; Jahn, R. Botulinum neurotoxin C1 blocks neurotransmitter release by means of cleaving HPC-1/syntaxin. EMBO.J. 1993, 12, 4821–4828. [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan, S.; Eswaramoorthy, S. Structural analysis of the catalytic and binding sites of Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin B. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaran, D.; Eswaramoorthy, S.; Furey, W.; Navaza, J.; Sax, M.; Swaminathan, S. Domain organization in Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin type E is unique: Its implication in faster translocation. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 386, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuniga, J.E.; Schmidt, J.J.; Fenn, T.; Burnett, J.C.; Arac, D.; Gussio, R.; Stafford, R.G.; Badie, S.S.; Bavari, S.; Brunger, A.T. A potent peptidomimetic inhibitor of botulinum neurotoxin serotype A has a very different conformation than the SNAP-25 substrate. Structure 2008, 16, 1588–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvaggi, N.R.; Wilson, D.; Tzipori, S.; Allen, K.N. Catalytic features of the botulinum neurotoxin A light chain revealed by high resolution structure of an inhibitory peptide complex. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 5736–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breidenbach, M.A.; Brunger, A.T. Substrate recognition strategy for botulinum neurotoxin serotype A. Nature 2004, 432, 925–929. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, M.A.; Stevens, R.C. Co-crystal structure of synaptobrevin-II bound to botulinum neurotoxin type B at 2.0 Å resolution. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Eswaramoorthy, S.; Kumaran, D.; Binz, T.; Swaminathan, S. Structural analysis of botulinum neurotoxin type E catalytic domain and its mutant Glu212-->Gln reveals the pivotal role of the Glu212 carboxylate in the catalytic pathway. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 6637–6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Binz, T.; Swaminathan, S. Structural analysis of botulinum neurotoxin serotype F light chain: implications on substrate binding and inhibitor design. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 11758–11765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, J.W.; Yu, W.; Bi, F.; Stevens, R.C. Crystal structure of botulinum neurotoxin type G light chain: Serotype divergence in substrate recognition. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 9574–9580. [Google Scholar]
- Arndt, J.W.; Chai, Q.; Christian, T.; Stevens, R.C. Structure of botulinum neurotoxin type D light chain at 1.65 Å resolution: repercussions for VAMP-2 substrate specificity. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 3255–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montecucco, C.; Schiavo, G. Structure and function of tetanus and botulinum neurotoxins. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1995, 28, 423–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieglstein, K.G.; DasGupta, B.R.; Henschen, A.H. Covalent structure of botulinum neurotoxin type A: Location of sulfhydryl groups, and disulfide bridges and identification of C-termini of light and heavy chains. J. Protein. Chem. 1994, 13, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagane, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Kouguchi, H.; Sunagawa, H.; Inoue, K.; Fujinaga, Y.; Oguma, K.; Ohyama, T. Dichain structure of botulinum neurotoxin: Identification of cleavage sites in types C, D, and F neurotoxin molecules. J. Protein. Chem. 1999, 18, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, N.; Smith, L.A.; Ahmed, S.A. Light chain separated from the rest of the type a botulinum neurotoxin molecule is the most catalytically active form. PLoS One 2010, 5, e12872. [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo, G.; Shone, C.C.; Bennett, M.K.; Scheller, R.H.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum neurotoxin type C cleaves a single Lys-Ala bond within the carboxyl-terminal region of syntaxins. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 10566–10570. [Google Scholar]
- Lebeda, F.J.; Cer, R.Z.; Mudunuri, U.; Stephens, R.; Singh, B.R.; Alder, M. The zinc-dependent protease activity of the botulinum neurotoxins. Toxins 2010, 2, 978–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, R.P.; Hartell, M.G.; Nichols, D.A.; Bhattacharjee, A.K.; van Hamont, J.E.; Skillman, D.R. The medicinal chemistry of botulinum, ricin and anthrax toxins. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 667–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, B.; Eubanks, L.M.; Dickerson, T.J.; Janda, K.D. The strange case of the botulinum neurotoxin: Using chemistry and biology to modulate the most deadly poison. Angew.Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8360–8379. [Google Scholar]
- Burnett, J.C.; Schmidt, J.J.; Stafford, R.G.; Panchal, R.G.; Nguyen, T.L.; Hermone, A.R.; Vennerstrom, J.L.; McGrath, C.F.; Lane, D.J.; Sausville, E.A.; Zaharevitz, D.W.; Gussio, R.; Bavari, S. Novel small molecule inhibitors of botulinum neurotoxin A metalloprotease activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 310, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, J.C.; Opsenica, D.; Sriraghavan, K.; Panchal, R.G.; Ruthel, G.; Hermone, A.R.; Nguyen, T.L.; Kenny, T.A.; Lane, D.J.; McGrath, C.F.; Schmidt, J.J.; Vennerstrom, J.L.; Gussio, R.; Solaja, B.A.; Bavari, S. A refined pharmacophore identifies potent 4-amino-7-chloroquinoline-based inhibitors of the botulinum neurotoxin serotype A metalloprotease. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 2127–2136. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Pai, R.; Cardinale, S.C.; Butler, M.M.; Peet, N.P.; Moir, D.T.; Bavari, S.; Bowlin, T.L. Synthesis and biological evaluation of botulinum neurotoxin A protease inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2264–2276. [Google Scholar]
- Silvaggi, N.R.; Boldt, G.E.; Hixon, M.S.; Kennedy, J.P.; Tzipori, S.; Janda, K.D.; Allen, K.N. Structures of clostridium botulinum neurotoxin serotype A light chain complexed with small-molecule inhibitors highlight active-site flexibility. Chem. Biol. 2007, 14, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.J.; Bostian, K.A. Proteolysis of synthetic peptides by type Abotulinum neurotoxin. J. Protein Chem. 1995, 14, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, S.C.; Butler, M.M.; Ruthel, G.; Nuss, J.E.; Wanner, L.M.; Li, B.; Pai, R.; Peet, N.P.; Bavari, S.; Bowlin, T.L. Novel benzimidazole inhibitors of botulinum neurotoxin/A display enzyme and cell based potency. The Botulinum J. 2010, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.B.; Simpson, L.L. Progress toward development of an inhalation vaccine against botulinum toxin. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2004, 3, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M.P.; Smith, L.A. Development of vaccines for prevention of botulism. Biochimie 2000, 82, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, A.; Wang, C.; Powers, D.B.; Amersdorfer, P.; Smith, T.J.; Montgomery, V.A.; Sheridan, R.; Blake, R.; Smith, L.A.; Marks, J.D. Potent neutralization of botulinum neurotoxin by recombinant oligoclonal antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11346–11350. [Google Scholar]
- Rummel, A.; Karnath, T.; Henke, T.; Bigalke, H.; Binz, T. Synaptotagmins I and II act as nerve cell receptors for botulinum neurotoxin G. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 30865–30870. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, M.; Richards, D.A.; Goodnough, M.C.; Tepp, W.H.; Johnson, E.A.; Chapman, E.R. Synaptotagmins I and II mediate entry of botulinum neurotoxin B into cells. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 162, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakry, N.; Kamata, Y.; Simpson, L.L. Lectins from Triticumvulgaris and Limaxflavus are universal antagonists of botulinum neurotoxin and tetanus toxin. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1991, 258, 830–836. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.-Z.; Zhou, J.; Miao, W.-Y.; Ding, F.-H.; Meng, J.-Y.; Jia, G.-R.; Li, J.-F.; Ye, H.-J.; He, X.-Y.; Chen, M.-Y.; Huang, Z.-M. Therapeutic effect of toosendanin on animal botulism. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 1982, 13, 28–30. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.-L.; Li, M.-F. Biological effects of toosendanin, a triterpenoid extracted from Chinese traditional medicine. Prog. Neurobiol. 2007, 82, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.-L.; Wang, Z.-F. Cure of experimental botulism and antibotulismic effect of toosendanin. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2004, 25, 839–848. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.; Miao, W.-Y.; Ding, F.-H.; Meng, J.-Y.; Ye, H.-J.; Jia, G.-R.; He, X.-Y.; Sun, G.-Z.; Li, P.-Z. The effect of toosendanin on monkey botulism. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 1985, 5, 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, A.; Nakai, Y.; Eubanks, L.M.; Clancy, C.M.; Tepp, W.H.; Pellett, S.; Dickerson, T.J.; Johnson, E.A.; Janda, K.D.; Montal, M. Bimodal modulation of the botulinum neurotoxin protein-conducting channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Nakai, Y.; Tepp, W.H.; Dickerson, T.J.; Johnson, E.A.; Janda, K.D. Function-oriented synthesis applied to the anti-botulinum natural product toosendanin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 1152–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Nakai, Y.; Pellett, S.; Tepp, W.H.; Johnson, E.A.; Janda, K.D. Toosendanin: Synthesis of the AB-ring and investigations of its anti-botulinum properties (Part II). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wender, P.A.; Verma, V.A.; Paxton, T.J.; Pillow, T.H. Function-oriented synthesis, step economy, and drug design. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, L.L. The interaction between aminoquinolines and presynaptically acting neurotoxins. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1982, 222, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, L.L. Ammonium chloride and methylamine hydrochloride antagonize clostridial neurotoxins. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1983, 225, 546–552. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, L.L.; Coffield, J.A.; Bakry, N. Inhibition of vacuolar adenosine triphosphatase antagonizes the effects of clostridial neurotoxins but not phospholipase A2 neurotoxins. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1994, 269, 256–262. [Google Scholar]
- Eubanks, L.M.; Silhar, P.; Salzameda, N.T.; Zakhari, J.S.; Xiaochuan, F.; Barbieri, J.T.; Shoemaker, C.B.; Hixon, M.S.; Janda, K.D. Identification of a natural product antagonist against the botulinum neurotoxin light chain protease. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silhar, P.; Capkova, K.; Salzameda, N.T.; Barbieri, J.T.; Hixon, M.S.; Janda, K.D. Botulinum neurotoxin A protease: Discovery of natural product exosite inhibitors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 2868–2869. [Google Scholar]
- Stowe, G.N.; Silhar, P.; Hixon, M.S.; Silvaggi, N.R.; Allen, K.N.; Moe, S.T.; Jacobson, A.R.; Barbieri, J.T.; Janda, K.D. Chirality holds the key for potent inhibition of the botulinum neurotoxin serotype a protease. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 756–759. [Google Scholar]
- Moe, S.T.; Thompson, A.B.; Smith, G.M.; Fredenburg, R.A.; Stein, R.L.; Jacobson, A.R. Botulinum neurotoxin serotype A inhibitors: Small molecule mercaptoacetamide analogs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 3072–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, J.C.; Ruthel, G.; Stegmann, C.M.; Panchal, R.G.; Nguyen, T.L.; Hermone, A.R.; Stafford, R.G.; Lane, D.J.; Kenny, T.A.; McGrath, C.F.; Wipf, P.; Stahl, A.M.; Schmidt, J.J.; Gussio, R.; Brunger, A.T.; Bavari, S. Inhibition of metalloproteasebotulinum serotype A from a pseudo-peptide binding mode to a small molecule that is active in primary neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 5004–5014. [Google Scholar]
- Burnett, J.C.; Wang, C.; Nuss, J.E.; Nguyen, T.L.; Hermone, A.R.; Schmidt, J.J.; Gussio, R.; Wipf, P.; Bavari, S. Pharmacophore-guided lead optimization: The rational design of a non-zinc coordinating, sub-micromolar inhibitor of the botulinum neurotoxin serotype A metalloprotease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 5811–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Widom, J.; Petronijevic, F.; Burnett, J.C.; Nuss, J.E.; Bavari, S.; Gussio, R.; Wipf, P. Synthesis and biological evaluation of inhibitors of botulinum neurotoxin metalloprotease. Heterocycles 2009, 79, 487–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M. M.; Cardinale, S. C.; Li, B.; Pai, R.; Ruthel, G.; Nuss, J. E.; Wanner, L. M.; Park, J.-B.; Rich, C.; Basu, A.; Mills, D.; Williams, J.D.; Peet, N.P.; Moir, D.; Bavari, S.; Bowlin, T.L. Unpublished results.
- Roxas-Duncan, V.; Enyedy, I.; Montgomery, V.A.; Eccard, V.S.; Carrington, M.A.; Lai, H.; Gul, N.; Yang, D.C.H.; Smith, L.A. Identification and biochemical characterization of small molecule inhibitors of clostridium botulinum neurotoxin seroptype A. Antimicro. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 3478–3486. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, H.; Feng, M.; Roxas-Duncan, V.; Dakshanamurthy, S.; Smith, L. A.; Yang, D.C.H. Quinolinol and peptide inhibitors of zinc protease in botulinum neurotoxin A: Effects of zinc ion and peptides on inhibition. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 491, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.-P.; Vummenthala, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Park, J.G.; Wang, S.; Davis, J.; Millard, C.B.; Schmidt, J.J. Potent new small molecule inhibitor of botulinum neurotoxin serotype A endopeptidase developed by synthesis-based computer-aided molecular design. PLos One 2009, 4, e7730. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Y.-P.; Davis, J.; Wang, S.; Park, J.G.; Nambiar, M.P.; Schmidt, J.J.; Millard, C.B. Small molecules showing significant protection of mice against botulinum neurotoxin serotype A. PLoS One 2010, 5, e10129. [Google Scholar]
- Hermone, A.R.; Burnett, J.C.; Nuss, J.E.; Tressler, L.E.; Nguyen, T.L.; Solaja, B.A.; Vennerstrom, J.L.; Schmidt, J.J.; Wipf, P.; Bavari, S.; Gussio, R. Three-dimensional database mining identifies a unique chemotype that unites structurally diverse botulinum neurotoxin serotype A inhibitors in a three-zone pharmacophore. ChemMedChem 2008, 3, 1905–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuss, J.E.; Dong, Y.; Wanner, L.M.; Ruthel, G.; Wipf, P.; Gussio, R.; Vennerstrom, J.L.; Bavari, S.; Burnett, J.C. Pharmacophore refinement guides the rational design of nanomolar-range inhibitors of the botulinum neurotoxin serotype A metalloprotease. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaja, B.A.; Opsenica, D.; Smith, K.S.; Milhous, W.K.; Terzic, N.; Opsenica, I.; Burnett, J.C.; Nuss, J.; Gussio, R.; Bavari, S. Novel 4-aminoquinolines active against chloroquine-resistant and sensitive P. falciparum strains that also inhibit botulinum serotype A. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 4388–4391. [Google Scholar]
- Capkova, K.; Hixon, M.S.; Pellett, S.; Barbieri, J.T.; Johnson, E.A.; Janda, K.D. Benzylidene cyclopentenediones: First irreversible inhibitors against botulinum neurotoxin A's zinc endopeptidase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 20, 206–208. [Google Scholar]
- Eswaramoorthy, S.; Kumaran, D.; Swaminathan, S. A novel mechanism for clostridium botulinum neurotoxin inhibition. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 9795–9802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, M.; Nicholson, J.D.; Cornille, F.; Hackley, B.E., Jr. Efficacy of a novel metalloprotease inhibitor on botulinum neurotoxin B activity. FEBS Lett. 1998, 429, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
