Gene-Regulatory Activity of α-Tocopherol
Abstract
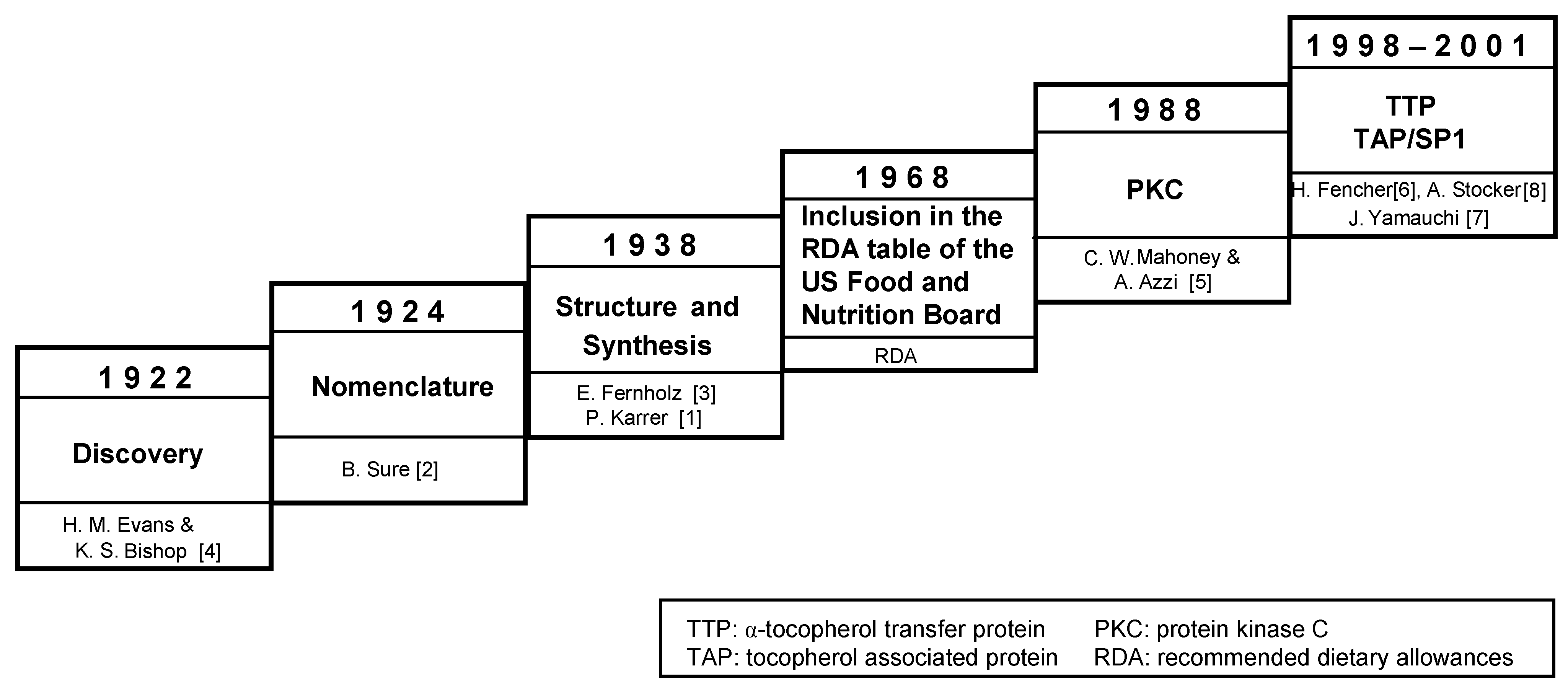
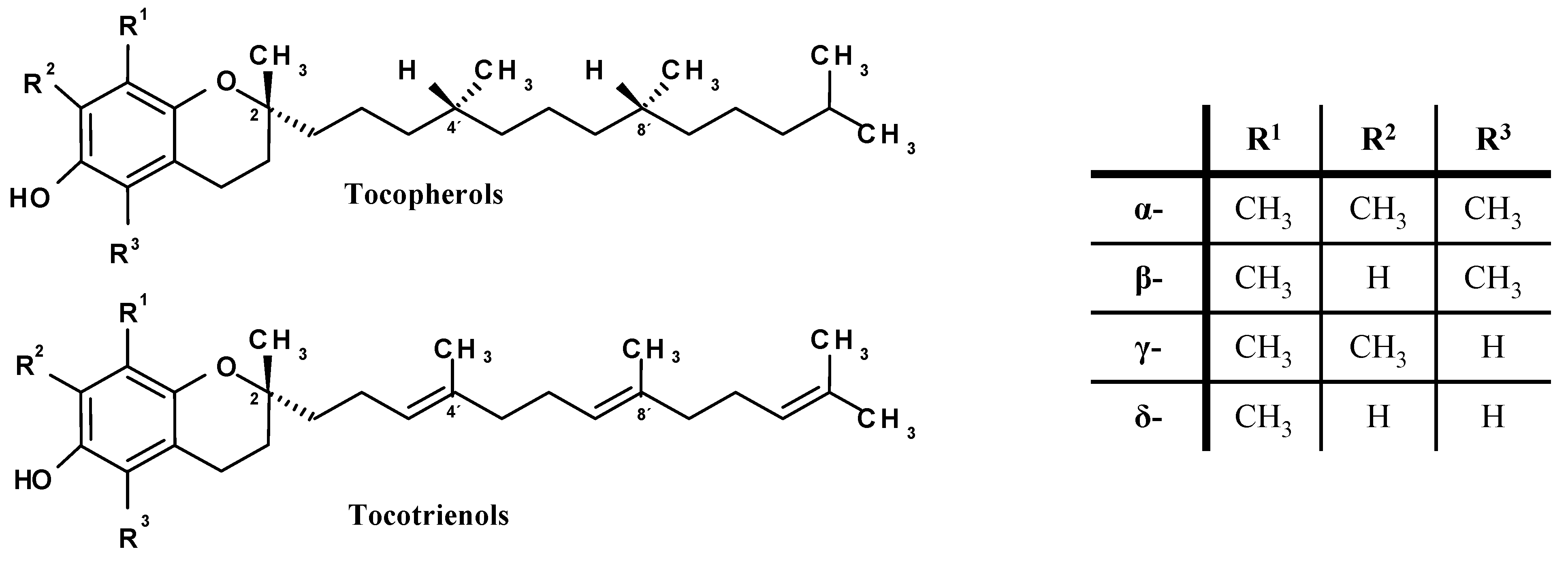
:1. Introduction, Chemistry and Antioxidant Properties of Vitamin E
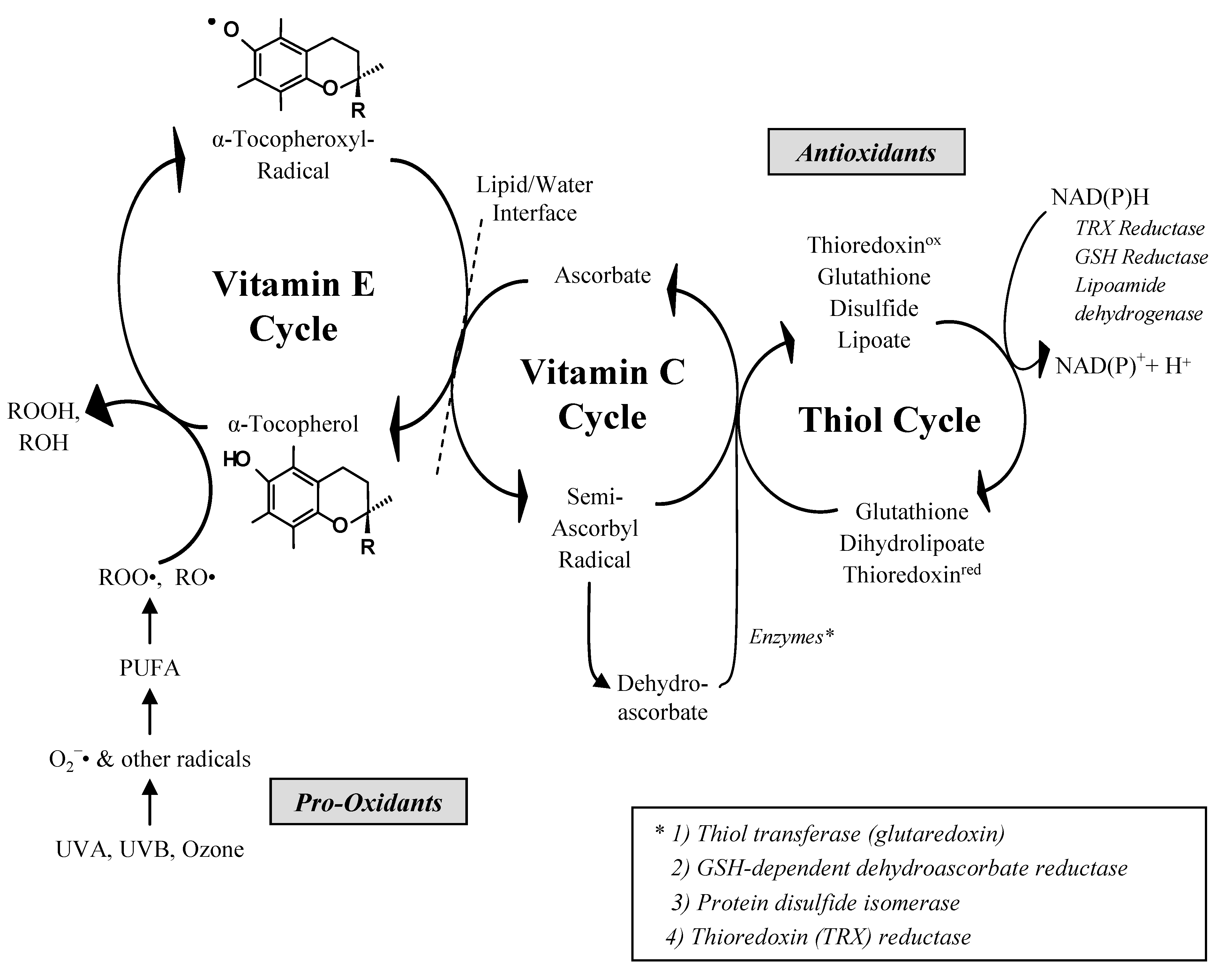
- (1)
- -LH + ROS → L
- (2)
- (-L. + O2 → -LOO.
- (3)
- -LOO. + VEH → LOOH + VE.
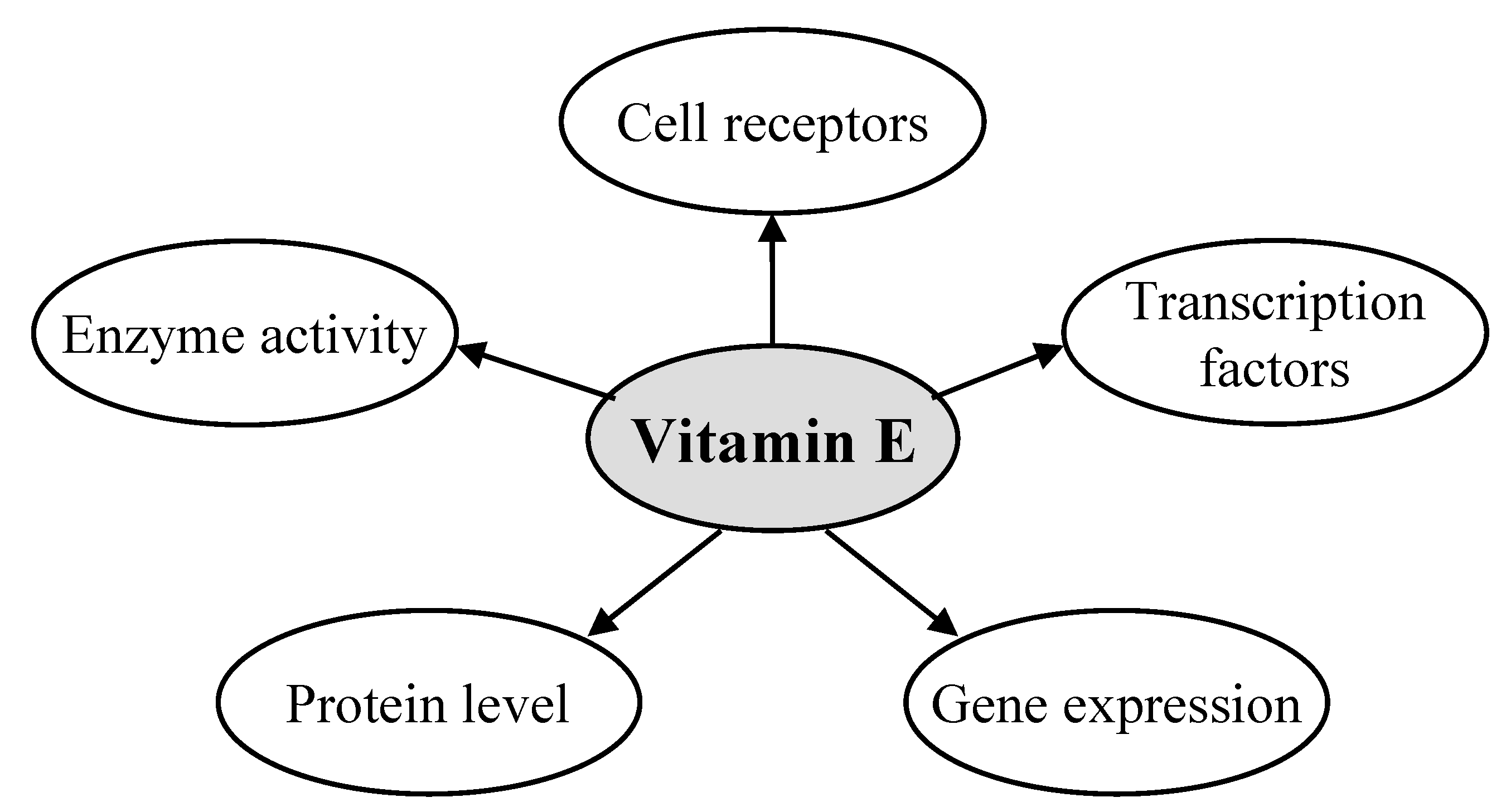
2. Gene Regulatory Activity of Vitamin E
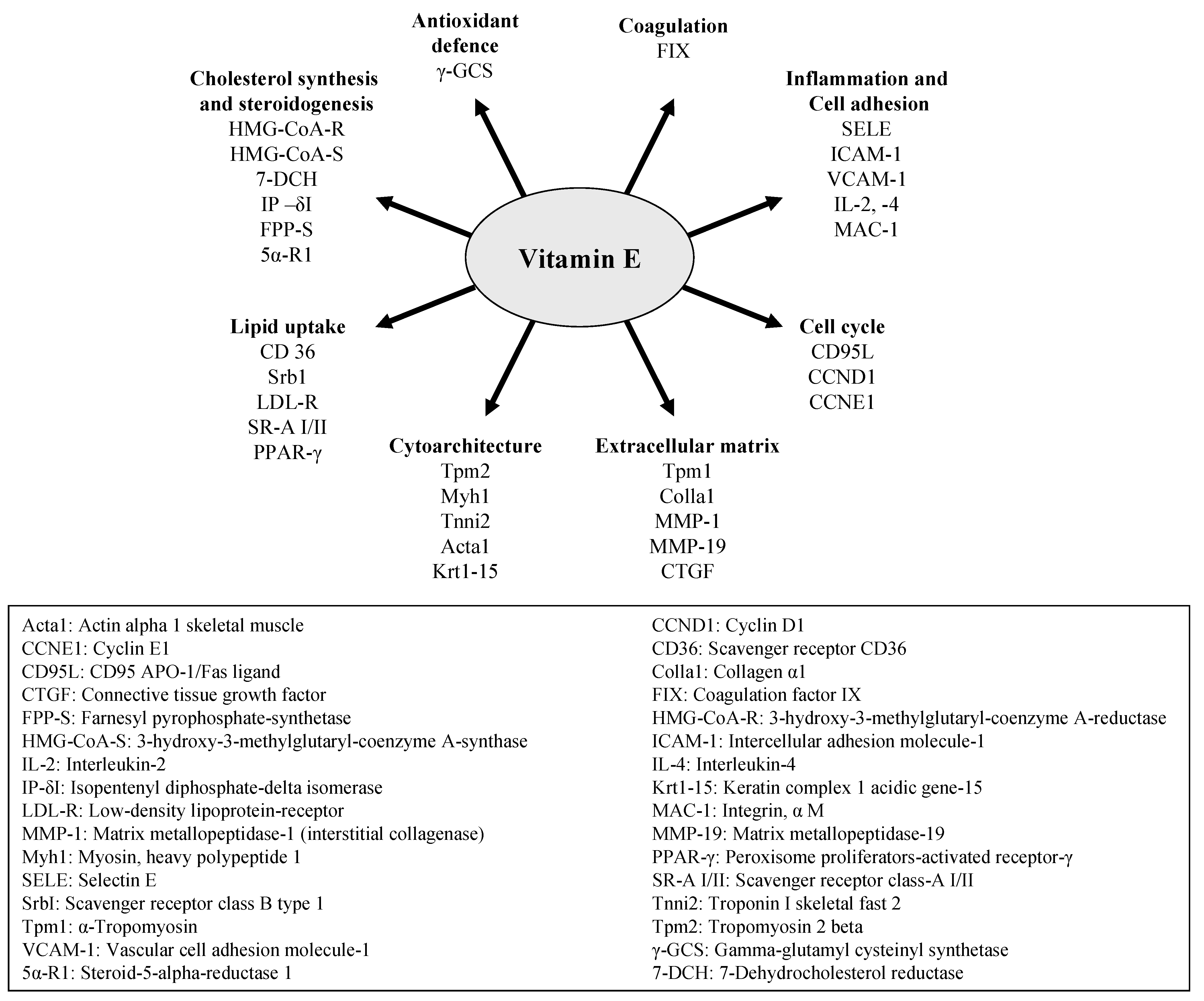
3. Comparative Quantification of Pharmacodynamic Parameters of RRR- vs. all-rac-α Tocopherol by Global Gene Expression Profiling
4. Vitamin E Regulated miRNAs
5. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Genes Important in Vitamin E Homeostasis
6. ApoE—Vitamin E Interactions

- Sample Availability: Please contact the authors.
References and Notes
- Karrer, P.; Fritsche, H.; Ringier, B.H.; Salomon, H. Synthesis of alpha-tocopherol. Helv. Chim. Acta 1938, 21, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sure, B. Dietary requirements for reproduction: II. The existence of a specific vitamin for reproduction. J. Biol. Chem. 1924, 58, 693–709. [Google Scholar]
- Fernholz, E. On the constitution of alpha-tocopherol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, H.M.; Bishop, K.S. On the existence of a hitherto unrecognized dietary factor essential for reproduction. Science 1922, 56, 650–651. [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney, C.W.; Azzi, A. Vitamin E inhibits protein kinase C activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1988, 154, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fechner, H.; Schlame, M.; Guthmann, F.; Stevens, P.A.; Rustow, B. Alpha- and delta-tocopherol induce expression of hepatic alpha-tocopherol-transfer-protein mRNA. Biochem. J. 1998, 331, 577–581. [Google Scholar]
- Stocker, A.; Zimmer, S.; Spycher, S.E.; Azzi, A. Identification of a novel cytosolic tocopherol-binding protein: Structure, specificity, and tissue distribution. IUBMB Life 1999, 48, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi, J.; Iwamoto, T.; Kida, S.; Masushige, S.; Yamada, K.; Esashi, T. Tocopherol-associated protein is a ligand-dependent transcriptional activator. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 285, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, L.; Weber, S.U.; Rimbach, G. Molecular aspects of alpha-tocotrienol antioxidant action and cell signalling. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 369S–373S. [Google Scholar]
- Rimbach, G.; Minihane, A.M.; Majewicz, J.; Fischer, A.; Pallauf, J.; Virgli, F.; Weinberg, P.D. Regulation of cell signalling by vitamin E. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2002, 61, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, S.; Kadoma, Y. Kinetic study of the radical-scavenging activity of vitamin E and ubiquinone. In Vivo 2005, 19, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Stocker, P.; Lesgards, J.F.; Vidal, N.; Chalier, F.; Prost, M. ESR study of a biological assay on whole blood: Antioxidant efficiency of various vitamins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1621, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, G. gamma-Tocopherol: An efficient protector of lipids against nitric oxide-initiated peroxidative damage. Nutr. Rev. 1997, 55, 376–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottstein, T.; Grosch, W. Model study of different antioxidant properties of α- and γ-tocopherol in fats. Fat Sci. Technol. 1990, 92, 201–206. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, M.Y.; Min, D.B. Effects of oxidized α-, γ- and δ−tocopherol on the oxidative stability of purified soybean oil. J. Food Sci. 1990, 55, 1464–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, S.; Woodall, A.A.; Shigenaga, M.K.; Southwell-Keely, P.T.; Duncan, M.W.; Ames, B.N. Gamma-tocopherol traps mutagenic electrophiles such as NO(X) and complements alpha-tocopherol: Physiological implications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 3217–3222. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, A.; Liebner, F.; Netscher, T.; Mereiter, K.; Rosenau, T. Vitamin E chemistry. Nitration of non-alpha-tocopherols: Products and mechanistic considerations. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 6504–6512. [Google Scholar]
- Traber, M.G.; Atkinson, J. Vitamin E, antioxidant and nothing more. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, J. Beyond vitamin E supplementation: An alternative strategy to improve vitamin E status. J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 162, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, K.; Blank, R.; Boesch-Saadatmandi, C.; Frank, J.; Wolffram, S.; Rimbach, G. Dietary green tea polyphenols do not affect vitamin E status, antioxidant capacity and meat quality of growing pigs. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2008, 92, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, H.; Boesch-Saadatmandi, C.; Wein, S.; Wolffram, S.; Frank, J.; Rimbach, G. Dietary flavonoids do not affect vitamin E status in growing rats. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, J.; George, T.W.; Lodge, J.K.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A.M.; Spencer, J.P.; Minihane, A.M.; Rimbach, G. Daily consumption of an aqueous green tea extract supplement does not impair liver function or alter cardiovascular disease risk biomarkers in healthy men. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Azzi, A.; Gysin, R.; Kempna, P.; Munteanu, A.; Negis, Y.; Villacorta, L.; Visarius, T.; Zingg, J.M. Vitamin E mediates cell signaling and regulation of gene expression. Ann.NY Acad Sci. 2004, 1031, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscoboinik, D.; Szewczyk, A.; Azzi, A. Alpha-tocopherol (vitamin E) regulates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and protein kinase C activity. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1991, 286, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscoboinik, D.; Szewczyk, A.; Hensey, C.; Azzi, A. Inhibition of cell proliferation by alpha-tocopherol. Role of protein kinase C. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 6188–6194. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, A.; Pallauf, J.; Gohil, K.; Weber, S.U.; Packer, L.; Rimbach, G. Effect of selenium and vitamin E deficiency on differential gene expression in rat liver. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 285, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barella, L.; Muller, P.Y.; Schlachter, M.; Hunziker, W.; Stocklin, E.; Spitzer, V.; Meier, N.; de Pascual-Teresa, S.; Minihane, A.M.; Rimbach, G. Identification of hepatic molecular mechanisms of action of alpha-tocopherol using global gene expression profile analysis in rats. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1689, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimbach, G.; Fischer, A.; Stoecklin, E.; Barella, L. Modulation of hepatic gene expression by alpha-tocopherol in cultured cells and in vivo. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2004, 1031, 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Hundhausen, C.; Frank, J.; Rimbach, G.; Stoecklin, E.; Muller, P.Y.; Barella, Y. Effect of vitamin E on cytochrome P450 mRNA levels in cultured hepatocytes (HepG2) and in rat liver. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 2006, 3, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, M. In vitro and in vivo studies of the effect of vitamin E on microsomal cytochrome P450 in rat liver. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1991, 42, 2107–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustacich, D.J.; Gohil, K.; Bruno, R.S.; Yan, M.; Leonard, S.W.; Ho, E.; Cross, C.E.; Traber, M.G. Alpha-tocopherol modulates genes involved in hepatic xenobiotic pathways in mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2009, 20, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nier, B.; Weinberg, P.D.; Rimbach, G.; Stocklin, E.; Barella, L. Differential gene expression in skeletal muscle of rats with vitamin E deficiency. IUBMB Life 2006, 58, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rota, C.; Rimbach, G.; Minihane, A.M.; Stoecklin, E.; Barella, L. Dietary vitamin E modulates differential gene expression in the rat hippocampus: Potential implications for its neuroprotective properties. Nutr. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barella, L.; Rota, C.; Stocklin, E.; Rimbach, G. Alpha-tocopherol affects androgen metabolism in male rat. Ann. N. Y. Acad Sci. 2004, 1031, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodge, J.K. Vitamin E bioavailability in humans. J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 162, 79–96. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, P.Y.; Netscher, T.; Frank, J.; Stoecklin, E.; Rimbach, G.; Barella, L. Comparative quantification of pharmacodynamic parameters of chiral compounds (RRR- vs. all-rac-alpha tocopherol) by global gene expression profiling. J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 162, 811–817, Copyright Elsevier (reproduced with permission). [Google Scholar]
- Acuff, R.V.; Thedford, S.S.; Hidiroglou, N.N.; Papas, A.M.; Odom, T.A., Jr. Relative bioavailability of RRR- and all-rac-alpha-tocopheryl acetate in humans: Studies using deuterated compounds. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1994, 60, 397–402. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, G.W.; Traber, M.G.; Acuff, R.V.; Walters, D.N.; Kayden, H.; Hughes, L.; Ingold, K.U. Human plasma and tissue alpha-tocopherol concentrations in response to supplementation with deuterated natural and synthetic vitamin E. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 67, 669–684. [Google Scholar]
- Traber, M.G.; Winklhofer-Roob, B.M.; Roob, J.M.; Khoschsorur, G.; Aigner, R.; Cross, C.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Brigelius-Flohe, R. Vitamin E kinetics in smokers and nonsmokers. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2001, 31, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proteggente, A.R.; Turner, R.; Majewicz, J.; Rimbach, G.; Minihane, A.M.; Kramer, K.; Lodge, J.K. Noncompetitive plasma biokinetics of deuterium-labeled natural and synthetic alpha-tocopherol in healthy men with an apoE4 genotype. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Weiser, H.; Vecchi, M. Stereoisomers of alpha-tocopheryl acetate. II. Biopotencies of all eight stereoisomers, individually or in mixtures, as determined by rat resorption-gestation tests. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 1982, 52, 351–370. [Google Scholar]
- Weiser, H.; Vecchi, M.; Schlachter, M. Stereoisomers of alpha-tocopheryl acetate. III. Simultaneous determination of resorption-gestation and myopathy in rats as a means of evaluating biopotency ratios of all-rac- and RRR-alpha-tocopheryl acetate. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 1985, 55, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Cohn, W. Evaluation of vitamin E potency. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 156–158. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, S.D. Everything you wanted to know about small RNA but were afraid to ask. Lab. Invest. 2008, 88, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, B.P.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 2005, 120, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esau, C.; Davis, S.; Murray, S.F.; Yu, X.X.; Pandey, S.K.; Pear, M.; Watts, L.; Booten, S.L.; Graham, M.; McKay, R.; Subramaniam, A.; Propp, S.; Lollo, B.A.; Freier, S.; Bennett, C.F.; Bhanot, S.; Monia, B.P. miR-122 regulation of lipid metabolism revealed by in vivo antisense targeting. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutay, H.; Bai, S.; Datta, J.; Motiwala, T.; Pogribny, I.; Frankel, W.; Jacob, S.T.; Ghoshal, K. Downregulation of miR-122 in the rodent and human hepatocellular carcinomas. J. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 99, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozen, M.; Creighton, C.J.; Ozdemir, M.; Ittmann, M. Widespread deregulation of microRNA expression in human prostate cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 1788–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porkka, K.P.; Pfeiffer, M.J.; Waltering, K.K.; Vessella, R.L.; Tammela, T.L.; Visakorpi, T. MicroRNA expression profiling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6130–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkoly, E.; Wei, T.; Janson, P.C.; Saaf, A.; Lundeberg, L.; Tengvall-Linder, M.; Norstedt, G.; Alenius, H.; Homey, B.; Scheynius, A.; Stahle, M.; Pivarcsi, A. MicroRNAs: Novel regulators involved in the pathogenesis of Psoriasis? PloS One 2007, 2, e610. [Google Scholar]
- Nagayama, K.; Kohno, T.; Sato, M.; Arai, Y.; Minna, J.D.; Yokota, J. Homozygous deletion scanning of the lung cancer genome at a 100-kb resolution. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2007, 46, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, M.V.; Ferracin, M.; Liu, C.G.; Veronese, A.; Spizzo, R.; Sabbioni, S.; Magri, E.; Pedriali, M.; Fabbri, M.; Campiglio, M.; Menard, S.; Palazzo, J.P.; Rosenberg, A.; Musiani, P.; Volinia, S.; Nenci, I.; Calin, G.A.; Querzoli, P.; Negrini, M.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7065–7070. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, T.S.; Liu, X.B.; Wong, B.Y.; Ng, R.W.; Yuen, A.P.; Wei, W.I. Mature miR-184 as Potential Oncogenic microRNA of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Tongue. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 2588–2592. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.B.; Xue, L.; Yang, J.; Ma, A.H.; Zhao, J.; Xu, M.; Tepper, C.G.; Evans, C.P.; Kung, H.J.; deVere White, R.W. An androgen-regulated miRNA suppresses Bak1 expression and induces androgen-independent growth of prostate cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19983–19988. [Google Scholar]
- Tili, E.; Michaille, J.J.; Cimino, A.; Costinean, S.; Dumitru, C.D.; Adair, B.; Fabbri, M.; Alder, H.; Liu, C.G.; Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. Modulation of miR-155 and miR-125b levels following lipopolysaccharide/TNF-alpha stimulation and their possible roles in regulating the response to endotoxin shock. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 5082–5089. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, Y.; Vasu, V.T.; Valacchi, G.; Leonard, S.; Aung, H.H.; Schock, B.C.; Kenyon, N.J.; Li, C.S.; Traber, M.G.; Cross, C.E. Severe vitamin E deficiency modulates airway allergic inflammatory responses in the murine asthma model. Free Radical Res. 2008, 42, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaoka, S.; Kim, H.S.; Ogihara, T.; Oue, S.; Takitani, K.; Yoshida, Y.; Tamai, H. Severe Vitamin E deficiency exacerbates acute hyperoxic lung injury associated with increased oxidative stress and inflammation. Free Radical Res. 2008, 42, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaedicke, S.; Zhang, X.; Schmelzer, C.; Lou, Y.; Doering, F.; Frank, J.; Rimbach, G. Vitamin E dependent microRNA regulation in rat liver. FEBS lett. 2008, 582, 354–546. [Google Scholar]
- Brigelius-Flohe, R. Vitamin E: The shrew waiting to be tamed. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodge, J.K.; Hall, W.L.; Jeanes, Y.M.; Proteggente, A.R. Physiological factors influencing vitamin E biokinetics. Ann.NY Acad. Sci. 2004, 1031, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doring, F.; Rimbach, G.; Lodge, J.K. In silico search for single nucleotide polymorphisms in genes important in vitamin E homeostasis. IUBMB Life 2004, 56, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebbe, P.; Jofre-Monseny, L.; Boesch-Saadatmandi, C.; Minihane, A.M.; Rimbach, G. Effect of apoE genotype and vitamin E on biomarkers of oxidative stress in cultured neuronal cells and the brain of targeted replacement mice. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2007, 58, 683–698. [Google Scholar]
- Jofre-Monseny, L.; de Pascual-Teresa, S.; Plonka, E.; Huebbe, P.; Boesch-Saadatmandi, C.; Minihane, A.M.; Rimbach, G. Differential effects of apolipoprotein E3 and E4 on markers of oxidative status in macrophages. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 97, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jofre-Monseny, L.; Loboda, A.; Wagner, A.E.; Huebbe, P.; Boesch-Saadatmandi, C.; Jozkowicz, A.; Minihane, A.M.; Dulak, J.; Rimbach, G. Effects of apoE genotype on macrophage inflammation and heme oxygenase-1 expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 357, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, M.; Hu, Y.; Block, G.; Olano, E.; Packer, L.; Morrow, J.D.; Hudes, M.; Abdukeyum, G.; Rimbach, G.; Minihane, A.M. Associations between apolipoprotein E genotype and circulating F2-isoprostane levels in humans. Lipids 2005, 40, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewicz, J.; Rimbach, G.; Proteggente, A.R.; Lodge, J.K.; Kraemer, K.; Minihane, A.M. Dietary vitamin C down-regulates inflammatory gene expression in apoE4 smokers. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 338, 951–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jofre-Monseny, L.; Minihane, A.M.; Rimbach, G. Impact of apoE genotype on oxidative stress, inflammation and disease risk. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 131–145, Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA (reproduced with permission). [Google Scholar]
- Huebbe, P.; Jofre-Monseny, L.; Rimbach, G. Alpha-tocopherol transport in the lung is affected by the apoE genotype--studies in transgenic apoE3 and apoE4 mice. IUBMB Life 2009, 61, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milman, U.; Blum, S.; Shapira, C.; Aronson, D.; Miller-Lotan, R.; Anbinder, Y.; Alshiek, J.; Bennett, L.; Kostenko, M.; Landau, M.; Keidar, S.; Levy, Y.; Khemlin, A.; Radan, A.; Levy, A.P. Vitamin E supplementation reduces cardiovascular events in a subgroup of middle-aged individuals with both type 2 diabetes mellitus and the haptoglobin 2-2 genotype: A prospective double-blinded clinical trial. Arterioscler. Throm. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 341–347. [Google Scholar]
- Lovegrove, J.A.; Gitau, R. Personalized nutrition for the prevention of cardiovascular disease: A future perspective. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2008, 21, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisel, S.H.; Freake, H.C.; Bauman, D.E.; Bier, D.M.; Burrin, D.G.; German, J.B.; Klein, S.; Marquis, G.S.; Milner, J.A.; Pelto, G.H.; Rasmussen, K.M. The nutritional phenotype in the age of metabolomics. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 1613–1616. [Google Scholar]
- German, J.B.; Bauman, D.E.; Burrin, D.G.; Failla, M.L.; Freake, H.C.; King, J.C.; Klein, S.; Milner, J.A.; Pelto, G.H.; Rasmussen, K.M.; Zeisel, S.H. Metabolomics in the opening decade of the 21st century: Building the roads to individualized health. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 2729–2732. [Google Scholar]
- Go, V.L.; Nguyen, C.T.; Harris, D.M.; Lee, W.N. Nutrient-gene interaction: Metabolic genotype-phenotype relationship. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 3016S–3020S. [Google Scholar]
- Lodge, K. Targeted and nontargeted approaches for metabolite profiling in nutritional research. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2010, 69, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodge, J.K. Mass spectrometry approaches for vitamin E research. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2008, 36, 1066–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, J.L.; Muller, D.; Woograsingh, R.; Jowatt, V.; Hindmarsh, A.; Nicholson, J.K.; Martin, J.E. Vitamin E deficiency and metabolic deficits in neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis described by bioinformatics. Physiol. Genomics 2002, 11, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.Y.; Kang, D.W.; Ma, X.; Ahn, S.H.; Krausz, K.W.; Luecke, H.; Idle, J.R.; Gonzalez, F.J. Metabolomics reveals a novel vitamin E metabolite and attenuated vitamin E metabolism upon PXR activation. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 924–937. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Rimbach, G.; Moehring, J.; Huebbe, P.; Lodge, J.K. Gene-Regulatory Activity of α-Tocopherol. Molecules 2010, 15, 1746-1761. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15031746
Rimbach G, Moehring J, Huebbe P, Lodge JK. Gene-Regulatory Activity of α-Tocopherol. Molecules. 2010; 15(3):1746-1761. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15031746
Chicago/Turabian StyleRimbach, Gerald, Jennifer Moehring, Patricia Huebbe, and John K. Lodge. 2010. "Gene-Regulatory Activity of α-Tocopherol" Molecules 15, no. 3: 1746-1761. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15031746
APA StyleRimbach, G., Moehring, J., Huebbe, P., & Lodge, J. K. (2010). Gene-Regulatory Activity of α-Tocopherol. Molecules, 15(3), 1746-1761. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15031746




