Computational Insights on Sulfonamide Imprinted Polymers
Abstract
:Introduction
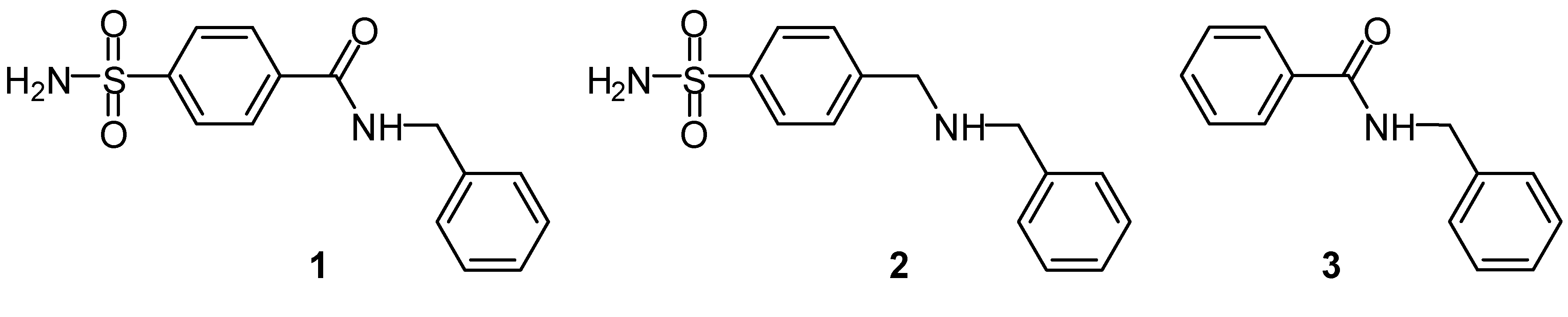
Results and Discussion
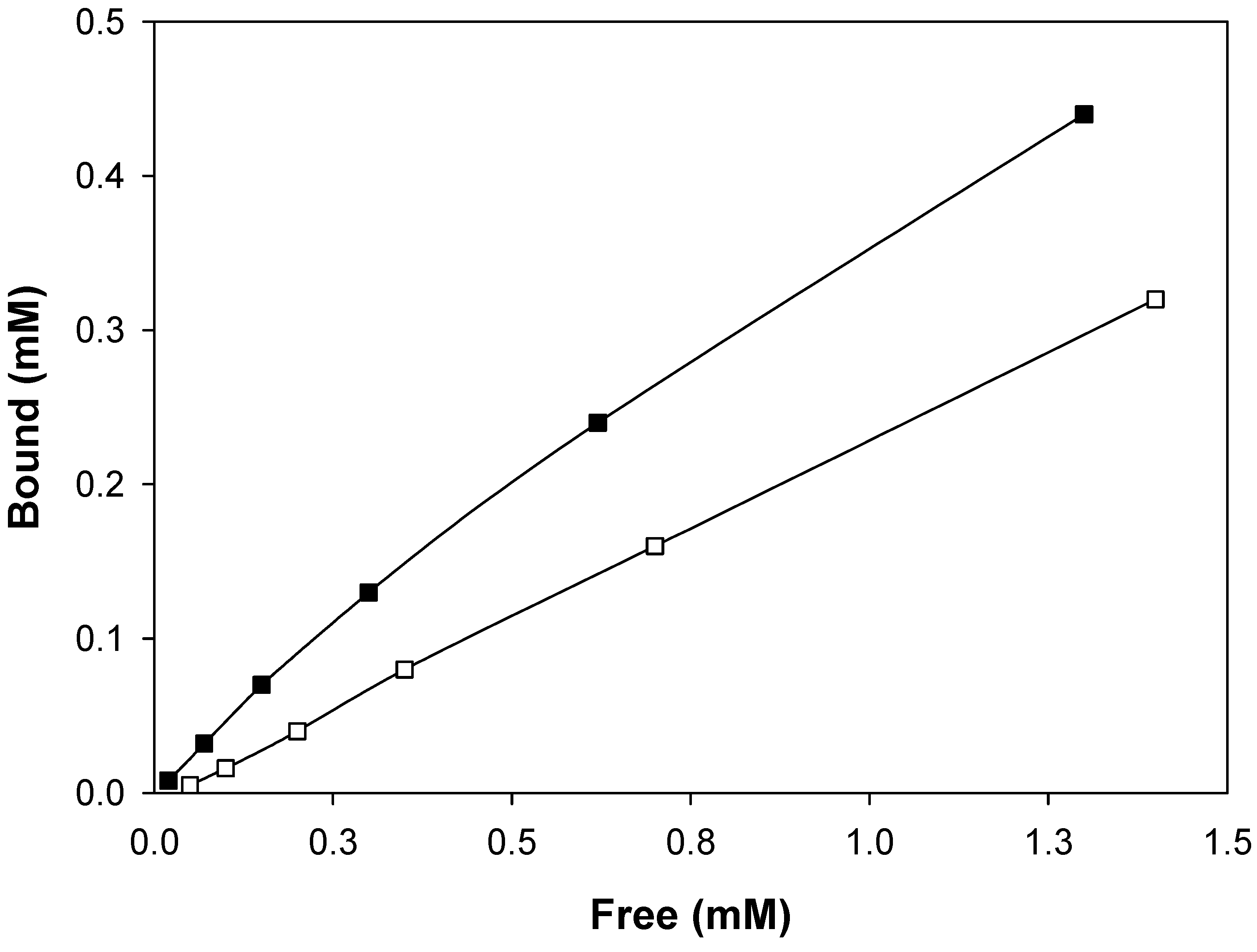
Molecular imprinting using MAA as functional monomer
Molecular imprinting using VIM as functional monomer
| Polymer | 1 (mmol) | Functional monomer (mmol) | TRIM (mmol) | Selectivity index (SI)a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAA | VIM | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| MIP 1a | 0.6 | 2.4 | ― | 24 | 2.7 | n.d. b | n.d. b |
| NIP 1a | ― | 2.4 | ― | 24 | ― | ― | ― |
| MIP 1b | 4.8 | ― | 19.2 | 19.2 | 1.8 | 1.1 | 1.0 |
| NIP 1b | ― | ― | 19.2 | 19.2 | ― | ― | ― |
Computer simulation
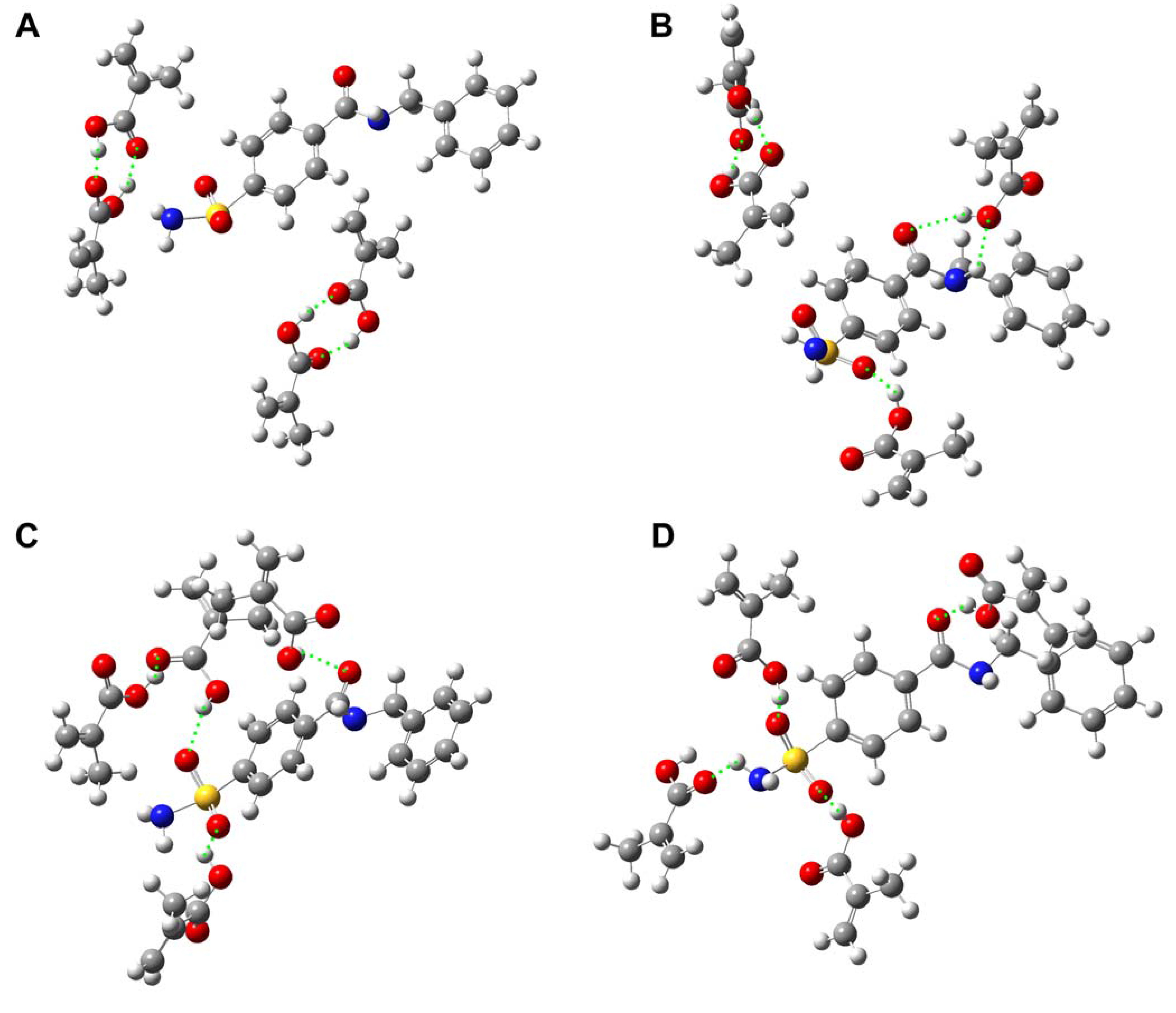
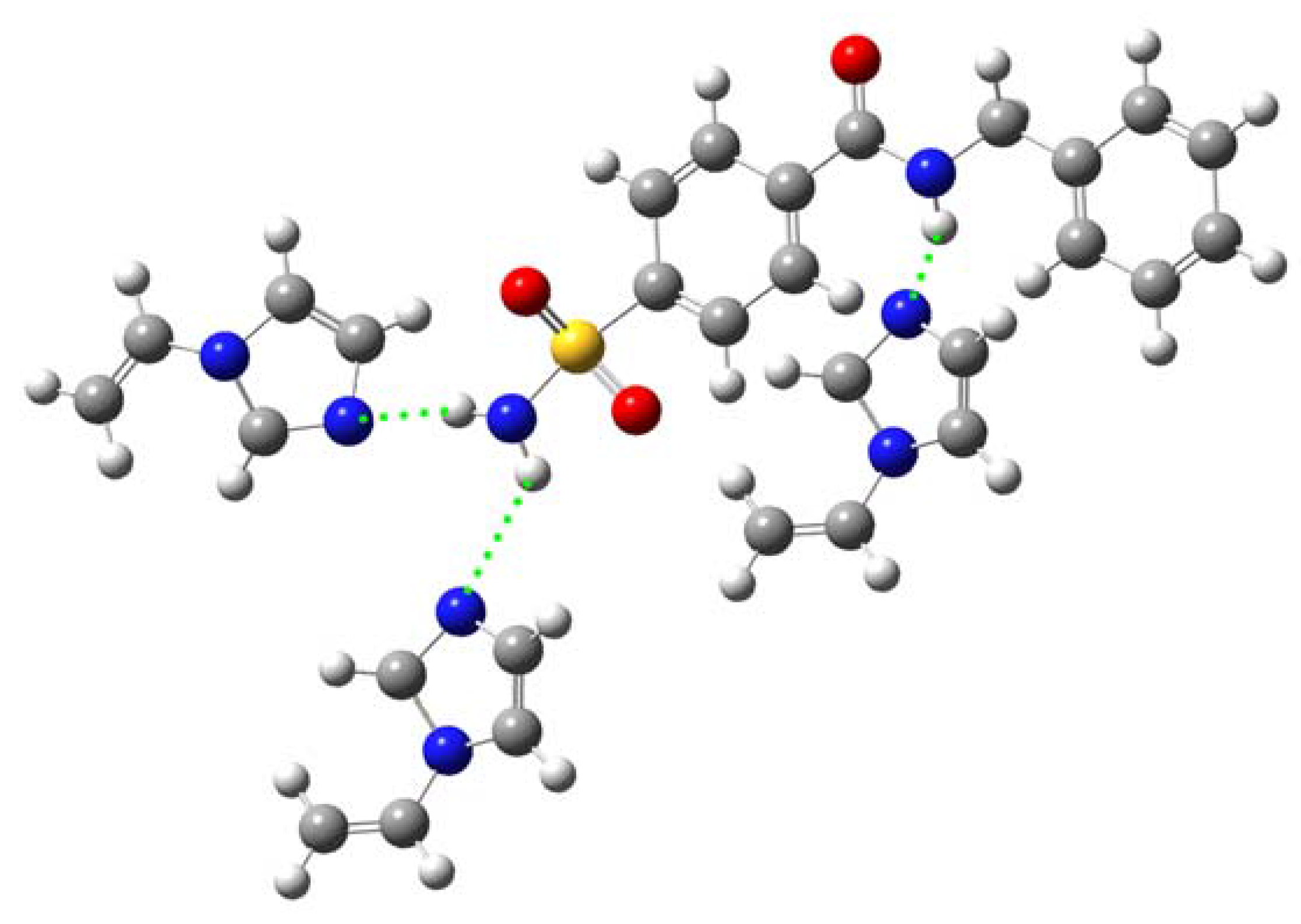
| E (a.u.) | ΔE (a.u.)a | ΔE (kJ/mol)b | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | –1,275.2206 | ||
| MAA | –306.4671 | ||
| VIM | –303.6062 | ||
| THF | –232.4475 | ||
| 1-MAA 1c | –1,581.7052 | –0.0175 | –45.8398 |
| 1-MAA 2d | –1,581.7227 | –0.0350 | –91.9364 |
| 1-MAA 3e | –1,581.7112 | –0.0235 | –61.7582 |
| 1-MAA 4f | –1,581.7038 | –0.0160 | –42.1389 |
| 1-MAA 5g | –1,581.7035 | –0.0158 | –41.4375 |
| 1-VIM 1h | –1,578.8458 | –0.0190 | –49.9639 |
| 1-VIM 2i | –1,578.8427 | –0.0158 | –41.5927 |
| MAA-MAA | –612.9857 | –0.0514 | –135.0195 |
| THF-MAA | –538.9426 | –0.0279 | –73.2438 |
| THF-VIM | –536.0615 | –0.0077 | –20.1504 |



Conclusions
Experimental
General
NMR titration
Molecularly imprinted polymers using 1 as template
Binding analysis
HPLC analysis
Computer simulation
Acknowledgements
References
- Batra, D.; Shea, K.J. Combinatorial methods in molecular imprinting. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2003, 7, 434–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, G. Enzyme-like catalysis by molecularly imprinted polymers. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Mosbach, K. The Technique of Molecular Imprinting - Principle, State of the Art, and Future Aspects. J. Incl. Phenom. Macro. 2001, 41, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turiel, E.; Martin-Esteban, A. Molecularly imprinted polymers: towards highly selective stationary phases in liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 1876–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Haupt, K. Molecularly imprinted polymers as antibody and receptor mimics for assays, sensors and drug discovery. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 1887–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, M.; Allender, C.; Brain, K.; Heard, C. Drug Development Assay Approaches, including Molecular Imprinting and Biomarkers; Reid, E., Hill, H., Wilson, I., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 1998; Vol. 25, pp. 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Ramström, O.; Ye, L.; Mosbach, K. Screening of a combinatorial steroid library using molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Commun. 1998, 35, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallano, P.T.; Remcho, V.T. Affinity screening by packed capillary high-performance liquid chromatography using molecular imprinted sorbents. I. Demonstration of feasibility. J. Chromatogr. A. 2000, 888, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosbach, K.; Yu, Y.; Andersch, J.; Ye, L. Generation of new enzyme inhibitors using imprinted binding sites: the anti-idiotypic approach, a step toward the next generation of molecular imprinting. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 12420–12421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitcombe, M.J.; Alexander, C.; Vulfson, E.N. Imprinted Polymers: Versatile New Tools in Synthesis. Synlett 2000, 6, 911–923. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Mosbach, K. Molecular Imprinting Utilizing an Amide Functional Group for Hydrogen Bonding Leading to Highly Efficient Polymers. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 4057–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Fu, Q.; Li, Y.-Z.; Chang, W.-B.; Wang, Z.-M.; Li, T.-J. Chromatographic characterization of sulfonamide imprinted polymers. Microchem. J. 2001, 69, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Li, Y.Z.; Wen, M.J. Sulfamethoxazole-imprinted polymer for selective determination of sulfamethoxazole in tablets. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1033, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, N.; Li, Y.-Z.; Chang, W.-B.; Wang, Z.-M.; Li, T.-J. Sulfonamide imprinted polymers using co-functional monomers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 452, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, R.; Shangguan, D.; Liu, G. Preparation and evaluation of uniform-sized molecularly imprinted polymer beads used for the separation of sulfamethazine. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2005, 19, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puoci, F.; Iemma, F.; Muzzalupo, R.; Spizzirri, U.G.; Trombino, S.; Cassano, R.; Picci, N. Spherical Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (SMIPs) via a Novel Precipitation Polymerization in the Controlled Delivery of Sulfasalazine. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, T.; Dobashi, A.; Kimura, K. Molecular Imprinting of Biotin Derivatives and Its Application to Competitive Binding Assay Using Nonisotopic Labeled Ligands. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 2418–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Hatate, Y.; Uezu, K.; Goto, M.; Furusaki, S. Chiral-recognition polymer prepared by surface molecular imprinting technique. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2000, 169, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianella, I.; Karim, K.; Piletska, E.V.; Preston, C.; Piletsky, S.A. Computational design and synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymers with high binding capacity for pharmaceutical applications-model case: Adsorbent for abacavir. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 559, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianella, I.; Lotierzo, M.; Piletsky, S.A.; Tothill, I.E.; Chen, B.; Karim, K.; Turner, A.P.F. Rational Design of a Polymer Specific for Microcystin-LR Using a Computational Approach. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 1288–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chianella, I.; Piletsky, S.A.; Tothill, I.E.; Chen, B.; Turner, A.P. MIP-based solid phase extraction cartridges combined with MIP-based sensors for the detection of microcystin-LR. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 18, 119–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piletska, E.; Piletsky, S.; Karim, K.; Terpetschnig, E.; Turner, A. Biotin-specific synthetic receptors prepared using molecular imprinting. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 504, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piletska, E.V.; Romero-Guerra, M.; Chianella, I.; Karim, K.; Turner, A.P.F.; Piletsky, S.A. Towards the development of multisensor for drugs of abuse based on molecular imprinted polymers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 542, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piletska, E.V.; Romero-Guerra, M.; Guerreiro, A.R.; Karim, K.; Turner, A.P.F.; Piletsky, S.A. Adaptation of the molecular imprinted polymers towards polar environment. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 542, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piletska, E.V.; Turner, N.W.; Turner, A.P.; Piletsky, S.A. Controlled release of the herbicide simazine from computationally designed molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Control. Release 2005, 108, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piletsky, S.; Piletska, E.; Karim, K.; Foster, G.; Legge, C.; Turner, A. Custom synthesis of molecular imprinted polymers for biotechnological application: Preparation of a polymer selective for tylosin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 504, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piletsky, S.A.; Karim, K.; Piletska, E.V.; Turner, A.P.F.; Day, C.J.; Freebairn, K.W.; Legge, C. Recognition of ephedrine enantiomers by molecularly imprinted polymers designed using a computational approach. Analyst 2001, 126, 1826–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.W.; Piletska, E.V.; Karim, K.; Whitcombe, M.; Malecha, M.; Magan, N.; Baggiani, C.; Piletsky, S.A. Effect of the solvent on recognition properties of molecularly imprinted polymer specific for ochratoxin A. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 20, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nantasenamat, C.; Naenna, T.; Isarankura Na Ayudhya, C.; Prachayasittikul, V. Quantitative prediction of imprinting factor of molecularly imprinted polymers by artificial neural network. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2005, 19, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nantasenamat, C.; Isarankura-Na-Ayudhya, C.; Naenna, T.; Prachayasittikul, V. Quantitative structure-imprinting factor relationship of molecularly imprinted polymers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 3309–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Yu, Y.; Mosbach, K. Towards the development of molecularly imprinted artificial receptors for the screening of estrogenic chemicals. Analyst 2001, 126, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Surugiu, I.; Haupt, K. Scintillation proximity assay using molecularly imprinted microspheres. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirion, B.; Schillinger, E.; Sellergren, B. Molecularly Imprinted Materials (Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings); Kofinas, P., Sellergren, B., Roberts, M., Eds.; Materials Research Society: Warrendale, USA, 2004; Vol. 787, p. 53. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, B.R.; Rush, D.J.; Shea, K.J. Discrimination between Enantiomers of Structurally Related Molecules: Separation of Benzodiazepines by Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitz, L.; Andersson, L.I.; Nilsson, S. Capillary Electrochromatography with Predetermined Selectivity Obtained through Molecular Imprinting. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 1179–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nantasenamat, C.; Isarankura-Na-Ayudhya, C.; Bülow, L.; Ye, L.; Prachayasittikul, V. In silico design for synthesis of molecularly imprinted microspheres specific towards bisphenol A by precipitation polymerization. EXCLI J. 2006, 5, 103–117. [Google Scholar]
- Diñeiro, Y.; Menendez, M.I.; Blanco-Lopez, M.C.; Lobo-Castanon, M.J.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Tunon-Blanco, P. Computational approach to the rational design of molecularly imprinted polymers for voltammetric sensing of homovanillic acid. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 6741–6746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diñeiro, Y.; Menendez, M.I.; Blanco-Lopez, M.C.; Lobo-Castanon, M.J.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Tunon-Blanco, P. Computational predictions and experimental affinity distributions for a homovanillic acid molecularly imprinted polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, K.; Breton, F.; Rouillon, R.; Piletska, E.V.; Guerreiro, A.; Chianella, I.; Piletsky, S.A. How to find effective functional monomers for effective molecularly imprinted polymers? Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1795–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Huang, S.G.; Whitesides, G.M. Lack of Effect of the Length of Oligoglycine- and Oligo(ethylene glycol)-Derived para-Substituents on the Affinity of Benzenesulfonamides for Carbonic Anhydrase II in Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 5057–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huc, I.; Lehn, J.M. Virtual combinatorial libraries: dynamic generation of molecular and supramolecular diversity by self-assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 2106–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennington II, R.; Keith, T.; Millam, J.; Eppinnett, K.; Hovell, W.L.; Gilliland, R. GaussView, Version 3.09, Semichem Inc.: Shawnee Mission, 2003.
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Montgomery Jr., J.A.; Vreven, T.; Kudin, K.N.; Burant, J.C.; Millam, J.M.; Iyengar, S.S.; Tomasi, J.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Cossi, M.; Scalmani, G.; Rega, N.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; Hada, M.; Ehara, M.; Toyota, K.; Fukuda, R.; Hasegawa, J.; Ishida, M.; Nakajima, T.; Honda, Y.; Kitao, O.; Nakai, H.; Klene, M.; Li, X.; Knox, J.E.; Hratchian, H.P.; Cross, J.B.; Bakken, V.; Adamo, C.; Jaramillo, J.; Gomperts, R.; Stratmann, R.E.; Yazyev, O.; Austin, A.J.; Cammi, R.; Pomelli, C.; Ochterski, J.W.; Ayala, P.Y.; Morokuma, K.; Voth, G.A.; Salvador, P.; Dannenberg, J.J.; Zakrzewski, V.G.; Dapprich, S.; Daniels, A.D.; Strain, M.C.; Farkas, O.; Malick, D.K.; Rabuck, A.D.; Raghavachari, K.; Foresman, J.B.; Ortiz, J.V.; Cui, Q.; Baboul, A.G.; Clifford, S.; Cioslowski, J.; Stefanov, B.B.; Liu, G.; Liashenko, A.; Piskorz, P.; Komaromi, I.; Martin, R.L.; Fox, D.J.; Keith, T.; Al-Laham, M.A.; Peng, C.Y.; Nanayakkara, A.; Challacombe, M.; Gill, P.M.W.; Johnson, B.; Chen, W.; Wong, M.W.; Gonzalez, C.; Pople, J.A. Gaussian 03W, Revision C.02, Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, 2004.
- Sample Availability: Contact the authors.
© 2008 by the authors. Licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Isarankura-Na-Ayudhya, C.; Nantasenamat, C.; Buraparuangsang, P.; Piacham, T.; Ye, L.; Bülow, L.; Prachayasittikul, V. Computational Insights on Sulfonamide Imprinted Polymers. Molecules 2008, 13, 3077-3091. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules13123077
Isarankura-Na-Ayudhya C, Nantasenamat C, Buraparuangsang P, Piacham T, Ye L, Bülow L, Prachayasittikul V. Computational Insights on Sulfonamide Imprinted Polymers. Molecules. 2008; 13(12):3077-3091. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules13123077
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsarankura-Na-Ayudhya, Chartchalerm, Chanin Nantasenamat, Prasit Buraparuangsang, Theeraphon Piacham, Lei Ye, Leif Bülow, and Virapong Prachayasittikul. 2008. "Computational Insights on Sulfonamide Imprinted Polymers" Molecules 13, no. 12: 3077-3091. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules13123077
APA StyleIsarankura-Na-Ayudhya, C., Nantasenamat, C., Buraparuangsang, P., Piacham, T., Ye, L., Bülow, L., & Prachayasittikul, V. (2008). Computational Insights on Sulfonamide Imprinted Polymers. Molecules, 13(12), 3077-3091. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules13123077




