Synthesis and Biological Activity of Novel Amino Acid-(N'-Benzoyl) Hydrazide and Amino Acid-(N'-Nicotinoyl) Hydrazide Derivatives
Abstract
:Introduction:
Results and Discussion
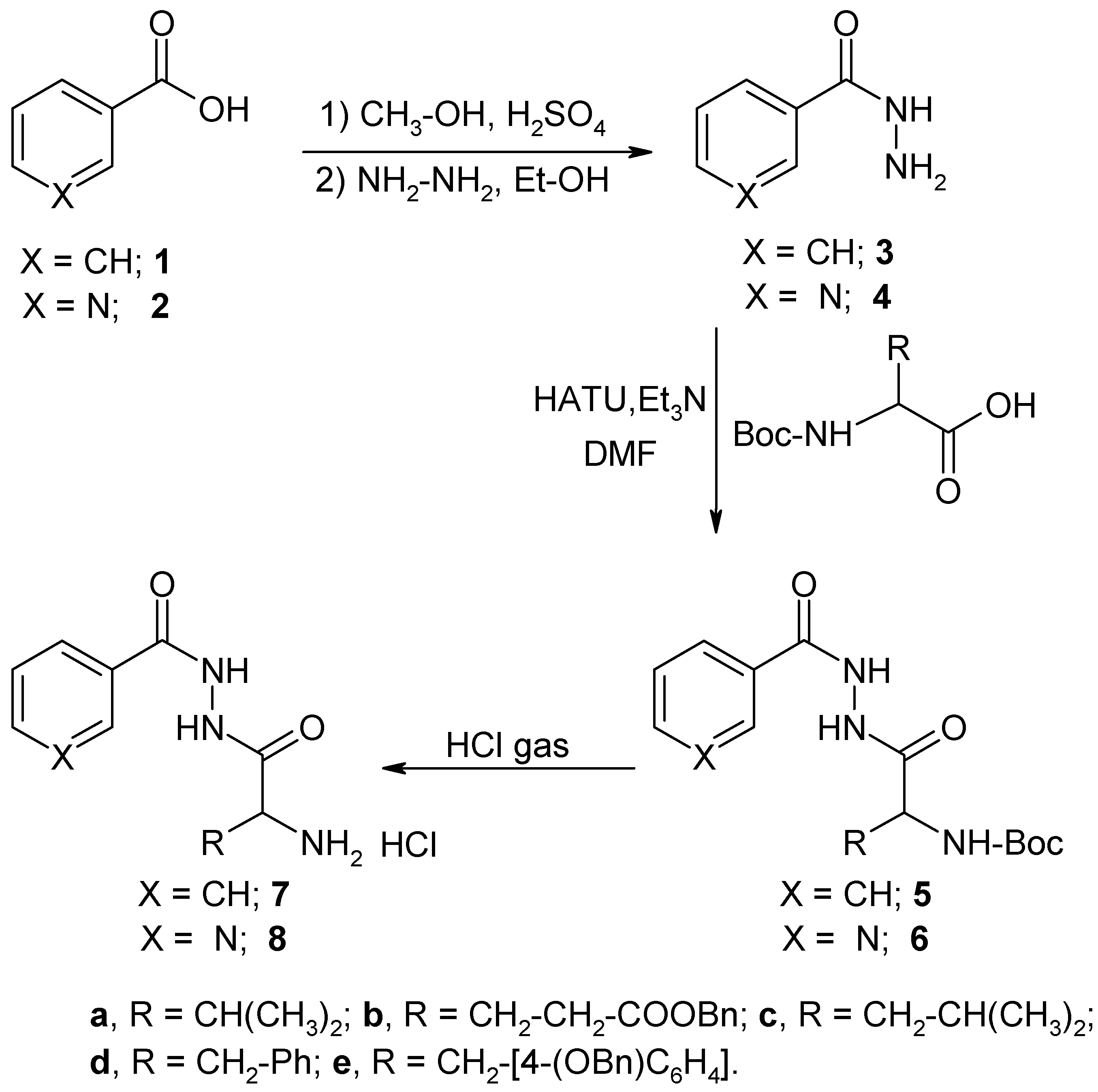
Chemistry
| Cmpd | Yield (%) | Color | mp (°C) | Elemental Analysis (Found) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7a | 75 | White | 244 | 53.04(52.89) | 6.68 (6.83) | 15.46(15.62) |
| 7b | 84 | White | 155 | 58.24(58.39) | 5.66 (5.89) | 10.72(10.96) |
| 7c | 93 | White | 190 | 54.64(54.91) | 7.05 (7.32) | 14.70(14.95) |
| 7d | 83 | White | 238 | 60.09(59.84) | 5.67 (5.92) | 13.14(13.32) |
| 7e | 89 | White | 233 | 64.86(64.58) | 5.68 (5.89) | 9.87 (9.59) |
| 8a* | 77 | White | 290 | --------------- | --------------- | --------------- |
| 8b* | 81 | White | 267 | --------------- | --------------- | --------------- |
| 8c* | 78 | White | 253 | --------------- | --------------- | --------------- |
| 8d* | 89 | White | 215 | --------------- | --------------- | --------------- |
| 8e* | 96 | White | 197 | --------------- | --------------- | --------------- |
| Compound | 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6): (δ) ppm |
|---|---|
| 7a | 0.89, 0.97 (2d, 6H, 2 CH3), 1.92 (m, 1H, CH), 4.89 (d, 1H, CH), 7.40-7.88 (m, 5H, aromatic), 8.38 (br.s, 2H, 2 NH), 10.64 (br.s, 2H, 2 NH). |
| 7b | 1.99 (m, 2H, CH2), 2.63, 2.75 (2m, 2H, CH2-CO), 4.55 (m, 1H, CH), 5.14 m, 2H, CH2-O), 7.21-7.90 (m, 10H, aromatic), 8.36 (br.s, 2H, 2 NH), 10.66 (br.s, 2H, 2 NH). |
| 7c | 0.91 (dd, 6H, 2 CH3), 1.63 (m, 2H, CH2), 1.81 (m, 1H, CH), 3.83 (m, 1H, CH), 7.46-7.87 (m, 5H, aromatic), 8.42 (br.s, 2H, 2 NH), 10.61 (br.s, 2H, 2 NH). |
| 7d | 3.07 (2m, 2H, CH2), 4.16 (m, 1H, CH), 7.22-7.89 (m, 10H, aromatic), 8.34 (br.s, 2H, 2 NH), 10.65 (br.s, 2H, 2 NH). |
| 7e | 3.08 (m, 2H, CH2), 4.29 (m, 1H, CH), 5.11 (br.s, 2H, CH2), 7.24-7.96 (m, 14H, aromatic), 8.45 (br.s, 2H, 2 NH), 10.59 (br.s, 2H, 2 NH). |
| 8a | δ 0.87, 0.96 (2d, 6H, 2 CH3), 1.96 (m, 1H, CH), 4.01 (m, 1H, CH), 7.79 (d, 2H, aromatic), 8.40 (br.s, 2H, 2 NH), 8.78 (d, 2H, aromatic), 10.62 (br.s, 2H, 2 NH). |
| 8b | 2.03 (m, 2H, CH2), 2.35 (m, 2H, CH2-CO), 4.09 (m, 1H, CH), 5.14 m, 2H, CH2-O), 7.33-7.82 (m, 7H, aromatic), 8.44 (br.s, 2H, 2 NH), 8.77 (d, 2H, aromatic), 10.66 ( br.s, 2H, 2 NH). |
| 8c | δ 0.92 (d, 6H, 2 CH3), 1.59 (m, 2H, CH2), 1.79 (m, 1H, CH), 4.07 (m, 1H, CH), 7.79 (d, 2H, aromatic), 8.39 (br.s, 2H, 2 NH), 8.75 (d, 2H, aromatic), 10.71 (br.s, 2H, 2 NH). |
| 8d | 3.09 (m, 2H, CH2), 4.33 (m, 1H, CH), 7.25-7.39 (m, 5H, aromatic), 7.85 (d, 2H, aromatic), 8.43 (br.s, 2H, 2 NH), 8.79 (d, 2H, aromatic), 10.79 (br.s, 2H, 2 NH). |
| 8e | 3.04 (m, 2H, CH2), 4.27 (m, 1H, CH), 5.14 (br.s, 2H, CH2), 7.24-7.47 (m, 9H, aromatic), 7.82 (d, 2H, aromatic), 8.45 (br.s, 2H, 2 NH), 8.79 (d, 2H, aromatic), 10.62 (m, 2H, 2 NH); |
Biological Test Results
| Test compound | E. coli | S. aureus | C. albicans | Test compound | E. coli | S. aureus | C. albicans |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ampicillin | 25 | 12.5 | --------- | (Cu:L),(1:1) of 6e | 100 | 12.5 | 200 |
| clotrimazole | ------- | -------- | 12.5 | (Cd:L),(1:1) of 5a | 100 | >200 | >200 |
| 5a | >200 | >200 | >200 | (Cd:L),(1:1) of 5b | >200 | 25 | >200 |
| 5b | >200 | >200 | >200 | (Cd:L),(1:1) of 5c | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| 5c | 100 | 100 | >200 | (Cd:L),(1:1) of 5d | >200 | 25 | >200 |
| 5d | 50 | >200 | >200 | (Cd:L),(1:1) of 5e | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| 5e | >200 | >200 | >200 | (Cd:L),(1:1) of 6a | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| 6a | >200 | >200 | >200 | (Cd:L),(1:1) of 6b | >200 | 100 | >200 |
| 6b | 100 | >200 | >200 | (Cd:L),(1:1) of 6c | 100 | >200 | >200 |
| 6c | 50 | >200 | >200 | (Cd:L),(1:1) of 6d | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| 6d | 100 | >200 | >200 | (Cd:L),(1:1) of 6e | 100 | >200 | >200 |
| 6e | 50 | >200 | >200 | (Cu:L),(1:1) of 7a | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| 7a | 100 | 100 | >200 | (Cu:L),(1:1) of 7b | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| 7b | 25 | >200 | >200 | (Cu:L),(1:1) of 7c | >200 | 100 | >200 |
| 7c | 100 | 50 | >200 | (Cu:L),(1:1) of 7d | >200 | 50 | >200 |
| 7d | 100 | >200 | >200 | (Cu:L),(1:1) of 7e | >200 | 50 | >200 |
| 7e | 200 | 50 | >200 | (Cu:L),(1:1) of 8a | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| 8a | 25 | >200 | >200 | (Cu:L),(1:1) of 8b | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| 8b | 100 | 100 | >200 | (Cu:L),(1:1) of 8c | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| 8c | 50 | >200 | >200 | (Cu:L),(1:1) of 8d | 100 | >200 | >200 |
| 8d | 100 | 100 | >200 | (Cu:L),(1:1) of 8e | >200 | 100 | >200 |
| 8e | 50 | 100 | >200 | (Cd:L),(1:1) of 7a | 100 | >200 | >200 |
| (Cu:L),(1:1) of 5a | 200 | 100 | >200 | (Cd:L),(1:1) of 7b | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| (Cu:L),(1:1) of 5b | >200 | >200 | 100 | (Cd:L),(1:1) of 7c | 100 | 12.5 | >200 |
| (Cu:L),(1:1) of 5c | 100 | 50 | >200 | (Cd:L),(1:1) of 7d | 50 | >200 | >200 |
| (Cu:L),(1:1) of 5d | >200 | 50 | >200 | (Cd:L),(1:1) of 7e | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| (Cu:L),(1:1) of 5e | 200 | 25 | >200 | (Cd:L),(1:1) of 8a | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| (Cu:L),(1:1) of 6a | >200 | 100 | >200 | (Cd:L),(1:1) of 8b | 100 | >200 | >200 |
| (Cu:L),(1:1) of 6b | >200 | >200 | >200 | (Cd:L),(1:1) of 8c | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| (Cu:L),(1:1) of 6c | >200 | >200 | >200 | (Cd:L),(1:1) of 8d | 100 | >200 | >200 |
| (Cu:L),(1:1) of 6d | 200 | 100 | >200 | (Cd:L),(1:1) of 8e | >200 | >200 | >200 |
Conclusions
Experimental
General
Chemistry
General Procedure for the Reaction of N-Boc-L-Amino Acids with Benzoic Acid Hydrazide.
General Procedure for the Reaction of N-Boc-L-Amino Acids with Nicotinic Acid Hydrazide.
General Procedure for the Preparation of the Hydrochloride Salts 7 and 8.
General Procedure for the Preparation of the Cu Complexes.
General Procedure for the Preparation of the Cd Complexes
In vitro antimicrobial activity
Acknowledgements
References
- Barrett, D.; Tanaka, A.; Harada, K.; Ohki, H.; Watabe, E.; Maki, K.; Ikeda, F. Synthesis and biological activity of novel macrocyclic antifungals: acylated conjugates of the ornithine moiety of the lipopeptidolactone FR901469. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalainen, J. T.; Christians, J. A. M.; Kotisaari, S.; Laitinen, J. T.; Mannisto, P.T. Synthesis and in vitro pharmacology of a series of new chiral histamine H3-receptor ligands:2-(R and S)-amino-3-(1H-imidazol-4(5)-yl)propyl ether derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 1999, 42, 1193–202. [Google Scholar]
- El-Faham, A.; El Massry, A. M.; Amer, A.; Gohar, Y. M. A versatile synthetic route to chiral quinoxaline derivatives from amino acids precursors. Lett. Pept. Sci. 2002, 9, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Polyak, F.; Lubell, W. D. Rigid dipeptide mimics: Synthesis of enantiopure 5- and 7-benzyl, and 5,7-dibenzyl indolizidinone amino acids via enolization and alkylation of δ-oxo α,ω-di-[N-(9-(9-phenylfluorenyl))amino]azelate esters. J. Org. Chem 1998, 63, 5937–5949. [Google Scholar] Roy, S.; Lombart, H.-G.; Lubell, W. D.; Hancock, R. E. W.; Farmer, S. W. Exploring relationships between mimic configuration, peptide conformation and biological activity in indolizidin-2-one amino acid analogs of gramicidin S. J. Peptide Res. 2002, 60, 198–214. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, Y.; Tsukatani, M.; Taguchi, H.; Yokoi, T.; Bryant, S. D.; Lazarus, L. H. Amino acids and peptides. Design and synthesis of opioidmimetics containing pyrazinone ring and examination of their opioid receptor binding activity. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1998, 46, 1374–82. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.; Uretsky, N. J.; Wallace, L. J.; Shams, G.; Weinstein, D. M.; Miller, D. D. Synthesis of chiral 1-(2`-amino-2`-carboxyethyl)-1,4-dihydro-6,7-quinoxaline-2,3-diones: α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionate receptor agonists and antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 4430–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsham, P. R.; Wardleworth, J. M.; Boyle, F. T.; Hennequin, L. F.; Kimbell, R.; Brown, M.; Jackman, A. L. Design and synthesis of potent nonpolyglutamatable quinozoline antifolate thymidylate synthase inhibitors. Med. Chem. 1999, 42, 3809–20. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Xia, P.; Bastow, K. F.; Nakanishi, Y.; Lee, K.-H. Antitumor agents. Part 202: Novel 2′-amino chalcones: design, synthesis and biological evaluation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2000, 10, 699–701. [Google Scholar]
- Kucukguzel, S. G.; Mazi, A.; Sahin, F.; Ozturk, S.; Stables, J. Synthesis and biological activities of diflunisal hydrazide-hydrazones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 38, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, H. M.; Shedid, S. A. M. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of some new Mannich bases, N-(2-hydroxy-1-naphthyl) amino acid, methyl ester and hydrazide derivatives. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 1998, 63, 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Dogan, H. N.; Rollas, S.; Erdeniz, H. Synthesis, structure elucidation and antimicrobial activity of some 3-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid hydrazide derivatives. Farmaco 1998, 53, 462–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesur, Z.; Büyüktimkin, S.; Büyüktimkin, N.; Derbentli, Ţ. Synthesis and antimicrobial evaluation of some arylhydrazones of 4-[(2-methylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-yl)azo]benzoic acid hydrazine. Arch. Pharm. (Weinheim) 1990, 323, 141–4. [Google Scholar]
- Cocco, M. T.; Congiu, C.; Onnis, V.; Pusceddu, M. C.; Schivo, M. L.; De Logu, A. Synthesis and antimycobacterial activity of some isonicotinoylhydrazones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 1999, 34, 1071–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uĝur, A.; Mercimek, B.; Özler, M. A.; Şahin, N. Antimicrobial effects of bis(Δ2-2-imidazolinyl)-5,5`-dioxime and its mono- and tri-nuclear complexes. Trans. Met. Chem. 2000, 25, 421–25. [Google Scholar]
- Chohan, Z. H.; Farooq, M. A.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C. T. Antibacterial Schiff bases of oxalyl-hydrazine/ diamide incorporating pyrrolyl and salicylyl moieties and their zinc(II) complexes. J. Enz. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2002, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Wang, G.; Fu, X.; Zhu, L. Synthesis, crystal structure, stacking effect and antimicrobial studies of novel quaternary copper(II) complex with quinolone. Molecules 2003, 8, 287–296. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson B. In Textbook of Immunopharmacology, 3rd ed; Dale, M. M.; Foreman, J. C.; Fan, T-P. D. (Eds.) Blackwell Scientific Publications: London, 1994; pp. 16, 193.
- Murray, P. R.; Baron, E. J.; Pfaller, M. A.; F. C., Tenover; Yolken, R. H. Manual of clinical microbiology. In Antimicrobial Agents and Susceptibility Testing; Woods, G. L., Washington, J. A., Eds.; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sample availability: Available from the author.
© 2005 by MDPI (http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
Share and Cite
Khattab, S.N. Synthesis and Biological Activity of Novel Amino Acid-(N'-Benzoyl) Hydrazide and Amino Acid-(N'-Nicotinoyl) Hydrazide Derivatives. Molecules 2005, 10, 1218-1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/10091218
Khattab SN. Synthesis and Biological Activity of Novel Amino Acid-(N'-Benzoyl) Hydrazide and Amino Acid-(N'-Nicotinoyl) Hydrazide Derivatives. Molecules. 2005; 10(9):1218-1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/10091218
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhattab, Sherine N. 2005. "Synthesis and Biological Activity of Novel Amino Acid-(N'-Benzoyl) Hydrazide and Amino Acid-(N'-Nicotinoyl) Hydrazide Derivatives" Molecules 10, no. 9: 1218-1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/10091218
APA StyleKhattab, S. N. (2005). Synthesis and Biological Activity of Novel Amino Acid-(N'-Benzoyl) Hydrazide and Amino Acid-(N'-Nicotinoyl) Hydrazide Derivatives. Molecules, 10(9), 1218-1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/10091218




