Isolation and Structure Elucidation of a Novel Yellow Pigment from the Marine Bacterium Pseudoalteromonas tunicata
Abstract
:Introduction
Experimental
General
Bacterial culture conditions and isolation of the yellow pigment
Results and Discussion
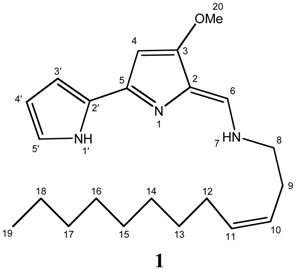
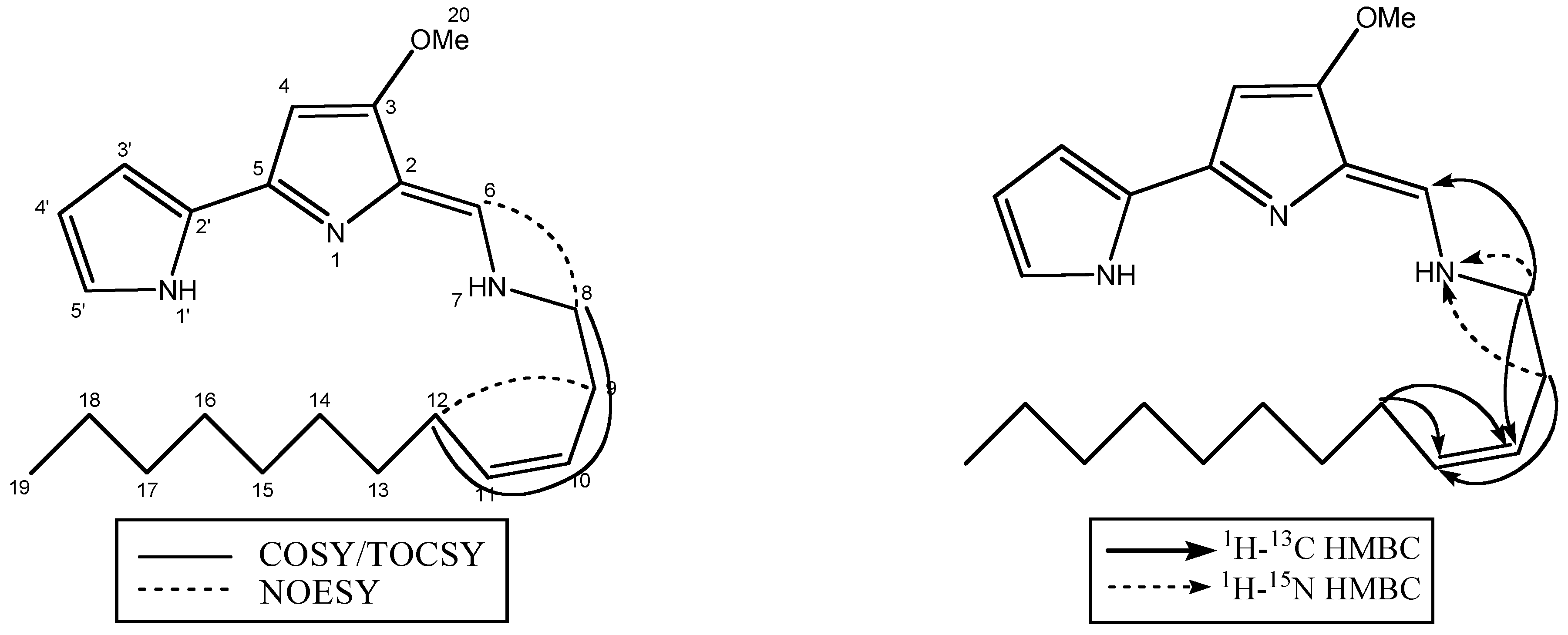
| Yellow Pigment | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Position | 13C | 1H | 15N |
| 1 | 142 | ||
| 2 | 111.3 | ||
| 3 | 163.9 | ||
| 4 | 91.6 | 5.95, s | |
| 5 | 143.4 | ||
| 6 | 141.1 | 7.29, d | |
| 7 | 132 | ||
| 8 | 51.2 | 3.46, m | |
| 9 | 28.8 | 2.46, m | |
| 10 | 124.1 | 5.35, dt | |
| 11 | 134.5 | 5.55, dt | |
| 12 | 27.8 | 2.01, m | |
| 13 – 18 | 26.5-27.7 | 1.21-1.70 | |
| 19 | 14.5 | 0.86, t | |
| 20 | 58.8 | 3.90, s | |
| 1’ | 155 | ||
| 2’ | 123.5 | ||
| 3’ | 113.0 | 6.70, m | |
| 4’ | 110.5 | 6.25, m | |
| 5’ | 124.1 | 7.06, m | |
Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Holmström, C.; Kjelleberg, S. Marine Pseudoalteromonas species are associated with higher organisms and produce active extracellular agents. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1999, 30, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkholder, P. R.; Pfister, R. M.; Leitz, F. H. Production of a pyrrole antibiotic by a marine bacterium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1966, 14, 649–653. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, S. A.; Johnson, R. M.; Kakimoto, D. Characterization of an antibiotic produced by Alteromonas luteoviolacea Gauthier 1982, 85 isolated from Kinko Bay, Japan. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1994, 77, 426–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, M. J. Alteromonas citrea, a new gram-negative yellow-pigmented species from seawater. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1977, 27, 349–354. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, R. W.; Chapman, P. J. Formation of indigo and related compounds from indolecarboxylic acids by aromatic acid-degrading bacteria: chromogenic reactions for cloning genes encoding dioxygenases that act on aromatic acids. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 6983–6988. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holmström, C.; Egan, S.; Franks, A.; McCloy, S.; Kjelleberg, S. Antifouling activities expressed by marine surface associated Pseudoalteromonas species. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2002, 41, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, S.; Holmström, C.; Kjelleberg, S. Pseudoalteromonas ulvae sp. nov., a bacterium with antifouling activities isolated from the surface of a marine alga. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, S.; James, S.; Holmström, C.; Kjelleberg, S. Correlation between pigmentation and antifouling compounds produced by Pseudoalteromonas tunicata. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 4, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackman, A. J.; Li, C. New tambjamine alkaloids from the marine bryozoan Bulgula dentata. Aust. J. Chem. 1994, 47, 1625–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R. A.; Carroll, A. R.; Quinn, R. J. The synthesis of a combinatorial library using a tambjamine natural product template. Aust. J. Chem. 2001, 54, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojiri, K.; Nakajima, S.; Suzuki, H. A new antitumour substance, BE-18591, produced by Streptomycete II. Structure determination. J. Antibiotics. 1993, 46, 1894–1896. [Google Scholar]
- Boger, D. L.; Patel, M. Total synthesis of prodigiosin, prodigiosene, and desmethoxyprodigiosin: Diels-Alder reactions of heterocyclic azadienes and development of an effective palladium(II)- promoted 2,2’-bipyrrole coupling procedure. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, S.; Kojiri, K.; Suda, H. A new antitumour substance, BE-18591, produced by Streptomycete I. Fermentation, isolation, physico-chemical and biological properties. J. Antibiotics. 1993, 46, 1799–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S. B.; Kim, H. M.; Kim, Y. H.; Lee, C. W.; Jang, E. S.; Son, K. H.; Kim, S. U.; Kim, Y. K. T- cell specific immunosuppression by prodigiosin isolated from Serratia marcescens. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 1998, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanigaki, K.; Sato, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Ochi, T.; Nishikawa, A.; Nagai, K.; Kawashima, H.; Ohkuma, S. BE-18591 as a new H+/Cl- symport ionophore that inhibits immunoproliferation and gastritis. FEBS Lett. 2002, 524, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmström, C.; James, S.; Neilan, B.; White, D.; Kjelleberg, S. Pseudoalteromonas tunicata sp. nov., a bacterium that produces antifouling agents. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1998, 48, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marden, P.; Tunlid, A.; Malmcronafriberg, K.; Odham, G.; Kjelleberg, S. Physiological and morphological changes during short-term starvation of marine bacterial isolates. Arch. Microbiol. 1985, 142, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carté, B.; Faulkner, D. J. Defensive metabolites from three nembrothid nudibranchs. J. Org. Chem. 1983, 48, 2314–2318. [Google Scholar]
- Sample availability: Contact the authors.
© 2005 by MDPI (http:www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
Share and Cite
Franks, A.; Haywood, P.; Holmström, C.; Egan, S.; Kjelleberg, S.; Kumar, N. Isolation and Structure Elucidation of a Novel Yellow Pigment from the Marine Bacterium Pseudoalteromonas tunicata. Molecules 2005, 10, 1286-1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/10101286
Franks A, Haywood P, Holmström C, Egan S, Kjelleberg S, Kumar N. Isolation and Structure Elucidation of a Novel Yellow Pigment from the Marine Bacterium Pseudoalteromonas tunicata. Molecules. 2005; 10(10):1286-1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/10101286
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranks, A., P. Haywood, C. Holmström, S. Egan, S. Kjelleberg, and N. Kumar. 2005. "Isolation and Structure Elucidation of a Novel Yellow Pigment from the Marine Bacterium Pseudoalteromonas tunicata" Molecules 10, no. 10: 1286-1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/10101286
APA StyleFranks, A., Haywood, P., Holmström, C., Egan, S., Kjelleberg, S., & Kumar, N. (2005). Isolation and Structure Elucidation of a Novel Yellow Pigment from the Marine Bacterium Pseudoalteromonas tunicata. Molecules, 10(10), 1286-1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/10101286




