Abstract
Oral administration remains the most convenient way of delivering drugs. Recent advances in biotechnology have produced highly potent new molecules such as peptides, proteins and nucleic acids. Due to their sensitivity to chemical and enzymatic hydrolysis as well as a poor cellular uptake, their oral bioavailability remains very low. Despite sophisticated new delivery systems, the development of a satisfactory oral formulation remains a challenge. Among the possible strategies to improve the absorption of drugs, micro- and nanoparticles represent an exciting approach to enhance the uptake and transport of orally administered molecules. Increasing attention has been paid to their potential use as carriers for peptide drugs for oral administration.
This article reviews the most common manufacturing methods for polymeric particles and the physiology of particle absorption from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. In a second part, the use of polymeric particulate systems to improve the oral absorption of insulin is discussed.
Keywords:
Nanoparticle; microparticle; oral route; peptide; mechanisms of absorption; protein; insulin; calcitonin. Introduction
Advances in the field of biotechnology have brought a lot of new and potent active compounds. However, the development of these molecules as medicines is largely impaired by the fact that they are not administrable by the oral route. Indeed, the oral one is the most convenient route of administration for both patients and medical staff. However, administering peptide and protein drugs orally is a formidable challenge due to their very short life in the gastric and intestinal fluids [1]. In addition, they suffer from a poor absorption rate through the intestinal barrier. Among the different approaches developed, polymeric micro- and nanoparticles represent an interesting strategy. Indeed, they shield the encapsulated drug from the external harsh conditions; they also may favour the uptake by intestinal cells.
Given orally, peptides and proteins are degraded by the enzymes from the gastric and intestinal juices rich in proteases such as trypsin or chymotrypsin. Therefore, they do not reach intact the site of absorption, namely the enterocytes. Furthermore, the brush border and the cytosol of the absorptive cells are full of peptidases that will degrade small peptides resulting from the hydrolysis of the proteins into amino acids that are readily resorbed in the blood. Thus, the first goal to develop an oral formulation for peptide and protein drugs is to reduce or even better to avoid enzyme degradation. Polymeric particles will isolate the encapsulated drug from the external medium therefore protecting the peptide from the peptidases, allowing, then, their uptake by enterocytes. After absorption, polymeric particles will slowly degrade according to a kinetic profile depending on the nature of the polymer, thus providing a sustained and controlled release of the drug [2].
Polymeric particles have been shown to cross the intestinal wall, although only in minute quantities. The size of the particles as well as the nature of the polymer are critical parameters involved in particle uptake by the GI tract. Therefore, this review will first introduce a brief overview of particle preparation methods and the physiology of particle absorption. Then, the studies using polymeric particles to improve oral insulin delivery will be reviewed.
Polymeric Particulates: Definitions and Manufacturing
Polymeric particles used for drug delivery are defined as colloidal systems made of solid polymers that may be classified according to their size and preparation processes (Figure 1). The term microparticle designates systems larger than 1 μm whereas nanoparticles are submicronic particles. Micro- and nanocapsules are composed of a polymeric wall containing a liquid inner core where the drug is entrapped while micro- and nanospheres are made of a solid polymeric matrix in which the drug can be dispersed. Active substances may be either adsorbed at the surface of the polymer or encapsulated within the particle. Particles may be produced by polymerization of synthetic monomers, or dispersion of synthetic polymers or natural macromolecules. The preparation methods have been extensively reviewed in the literature [3,4,5,6] and will only be briefly described here.
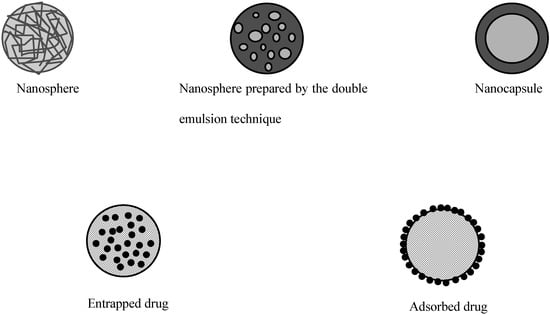
Figure 1.
Different types of polymeric particles
Figure 1.
Different types of polymeric particles
The physico-chemical properties of particles play a critical role in the rate of absorption by the intestinal tract. Since those properties are greatly influenced by the preparation method, it is useful to have a brief presentation of these techniques. As summarized in Table 1, the polymers used to make particles for oral administration are rather diverse. The choice of a preparation method depends greatly on both the nature of the drug and the polymer.

Table 1.
Nature of the polymers and preparation methods for polymeric particles intended for oral administration.
| Polymer | Method | Nature of the particles | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | Emulsion-evaporation | Spheres | [62] |
| PLGA | Emulsion-evaporation | Spheres | [62] |
| PACA | Interfacial polymerization | Capsules | [67] [24] |
| Chitosan | Emulsion-diffusion | Spheres | [70] |
| Eudragit® | Emulsion-diffusion | Spheres | [71] |
| P(MMA-g-EG) | Suspension polymerization | Spheres | [72] |
| HPMC-AS | Emulsion-evaporation | Spheres | [73] |
| Poly FA:SA | Phase inversion | Spheres | [74] |
| Insulin | Dessolvation-crosslinking | Spheres | [19] |
| LHRH-n-butylcyanoacrylate | Copolymerization | Spheres | [20] |
| Cyclosporin A | Emulsion-precipitation | Spheres | [22] |
| Derivatized amino acids | Self-aggregation | Spheres | [75, 76] |
| Soybean protein hydrolysates | Self-aggregation | Spheres | [77] |
- Key to abbreviations :
- PLA : poly(lactic acid)
- PLGA : poly(lactic-co-glycolide)
- PACA : poly(alkylcyanoacrylate)
- Eudragit® : poly(methylacrylic acid-co-methylmethacrylate)
- P(MAA-g-EG) : poly(methacrylic-g-ethylene glycol)
- FA:SA : fumaric acid:sebacic acid
- HPMC-AS : hydroxypropylmethylcellulose acetate succinate
- LHRH : luteinizing hormone releasing hormone
Particle formation by polymerization reactions (emulsion-polymerization) has been primarily developed for polymers such as poly(methylmethacrylate) (PMMA), poly(alkylcyanoacrylate) (PACA), and poly(methylidenemalonate) (PMM) [7,8,9]. Briefly, the water insoluble monomer is dispersed in an aqueous phase and the polymerization is induced and controlled by addition of a chemical initiator or by variations in physical parameters such as pH or γ-radiation in the presence or the absence of surfactants to stabilize the emulsion. Drugs are entrapped in the polymeric wall when added to the polymerization medium or adsorbed on preformed particles afterwards.
The preparation of particles from preformed polymers is based on polymer precipitation (Figure 2). Basically, an organic solution of the polymer is emulsified in an aqueous solution with or without a surfactant. In a second step, the organic solvent is removed by different methods such as evaporation, diffusion or salting out under stirring to allow particle formation. With these techniques, the drug has to be at least partially soluble in an organic solvent to be encapsulated. This is a major limitation to the encapsulation of hydrophilic compounds such as peptides, proteins or nucleic acids. Therefore, alternative methods have been developed to increase the encapsulation rate of hydrophilic molecules. It is possible, for example, to derivatize a hydrophilic compound to form a hydrophobic complex [10,11]. A more common way is to use a double emulsion technique in which an aqueous solution of the hydrophilic compound is first emulsified in an organic solution of the polymer (Figure 2). The primary emulsion is then poured into a large volume of water with or without surfactant. Freeze fracture micrographs of these particles show the alveolar structure specific to this process [12,13]. The double emulsion technique has a fairly good encapsulation efficiency for hydrophilic compounds, however, particle size is usually larger than with single emulsion technique [14].
Another way of preparing particles from a preformed polymer is the spray-drying method where the drug is solubilized or dispersed in an organic solution of the polymer to be nebulized in a hot air flow. The solvent is almost instantly evaporated and dried microparticles are readily recovered. This technique, easily applicable at the industrial scale, is used for hydrophilic [15,16], as well as lipophilic [17,18] molecules. However, particle size remains rather large, rarely smaller than 5 µm. Therefore, this method is seldom used in the context of oral administration.
Some authors have used an interesting approach in which the drug itself was polymerized. Oppenheim et al. obtained 200 nm insulin nanospheres by dessolvation of the protein and crosslinking with glutaraldehyde [19]. Particle formation, however, was accompanied by a substantial degradation of the protein since an almost 80% loss in activity was observed. Hillery et al. developed a new technique of co-polymerization of a peptide (LHRH) and n-butylcyanoacrylate radicals followed by the precipitation of the co-polymer to form nanoparticles with an average diameter of 100 nm [20,21]. With this method, the peptide integrity and biological activity were preserved. More recently, Ford et al. reported the formation of approximately 300 and 800 nm nanoparticles made of the hydrophobic cyclosporin A [22].
Nano- and microcapsule technology offers several advantages for improving the entrapment efficiency of lipophilic compounds, or for providing a controlled release system. It has also been used with hydrophilic drugs especially with oily suspensions of insulin [23,24]. Micro- and nanocapsules may be prepared by interfacial polymerization from alkylcyanoacrylate monomers [25]. The drug and the monomer are then dissolved or dispersed in a mixture of ethanol and oil under magnetic stirring into an aqueous phase. Capsules may also be obtained from preformed polymer, based on a dessolvation process [26,27]. Recently, a new method based on the emulsification-diffusion process has been described [28]. Vranckx et al. reported an interesting preparation method for capsules with a hydrophilic core that may be particularly attractive for peptides and proteins [29]. Lambert et al. also used this technique to encapsulate oligonucleotides where the nanocapsules were suspended in an aqueous medium more suitable for intravenous administration [30].
Regardless of the preparation process, the ultimate physico-chemical properties of the particles are greatly influenced by the experimental conditions of manufacturing. For example, stirring mode and speed greatly influence the particle size and, similarly, the solvent elimination process will affect the hardening process and the final morphology of the particles. For more details, refer to the following reviews: Magenheim and Benita [31], Allémann et al. [3] and Alonso [4].
Once the particles are formed, spheres or capsules, a purification step is needed to remove the potentially toxic additives necessary for the manufacturing or to separate unincorporated drug. It is used as well as a concentration technique. This may be achieved by centrifugation or ultra-centrifugation depending on the size of the particles, by filtration (centrifugal filtration or cross flow filtration), gel permeation or dialysis.
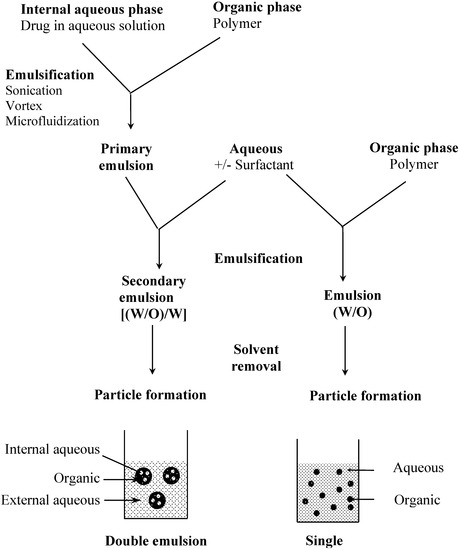
Figure 2.
Particle preparation methods by polymer precipitation, examples of single and double emulsion techniques
Figure 2.
Particle preparation methods by polymer precipitation, examples of single and double emulsion techniques
Final concentration and drying are usually achieved by lyophilisation. This step is crucial for preservation of formulation quality to ensure both drug and polymer stability. However, lyophilization may affect the particles themselves causing morphological changes or even wall rupture, especially in the case of capsules. Furthermore, particle aggregation may occur, generating resuspension problems. Optimizing the settings of the freeze-drying parameters and addition of lyoprotecting agents may correct this side effect [32,33].
From this brief overview, it is clear that various materials and numerous methods are available to prepare drug loaded polymeric particles. The choice is usually dictated by criteria such as biodegradability and biocompatibility, expected release profiles and compatibility with drugs.
Absorption of Polymeric Particulates from the Gastrointestinal Tract
Oral absorption of particulates has been described as early as 1844 (as cited in [34,35]). Several studies conducted either after chronic or single administration defined the parameters and the mechanisms involved in intestinal absorption of particles. A better knowledge of the mechanisms implicated in particle absorption is needed to design new polymers and better-targeted systems for the oral route.
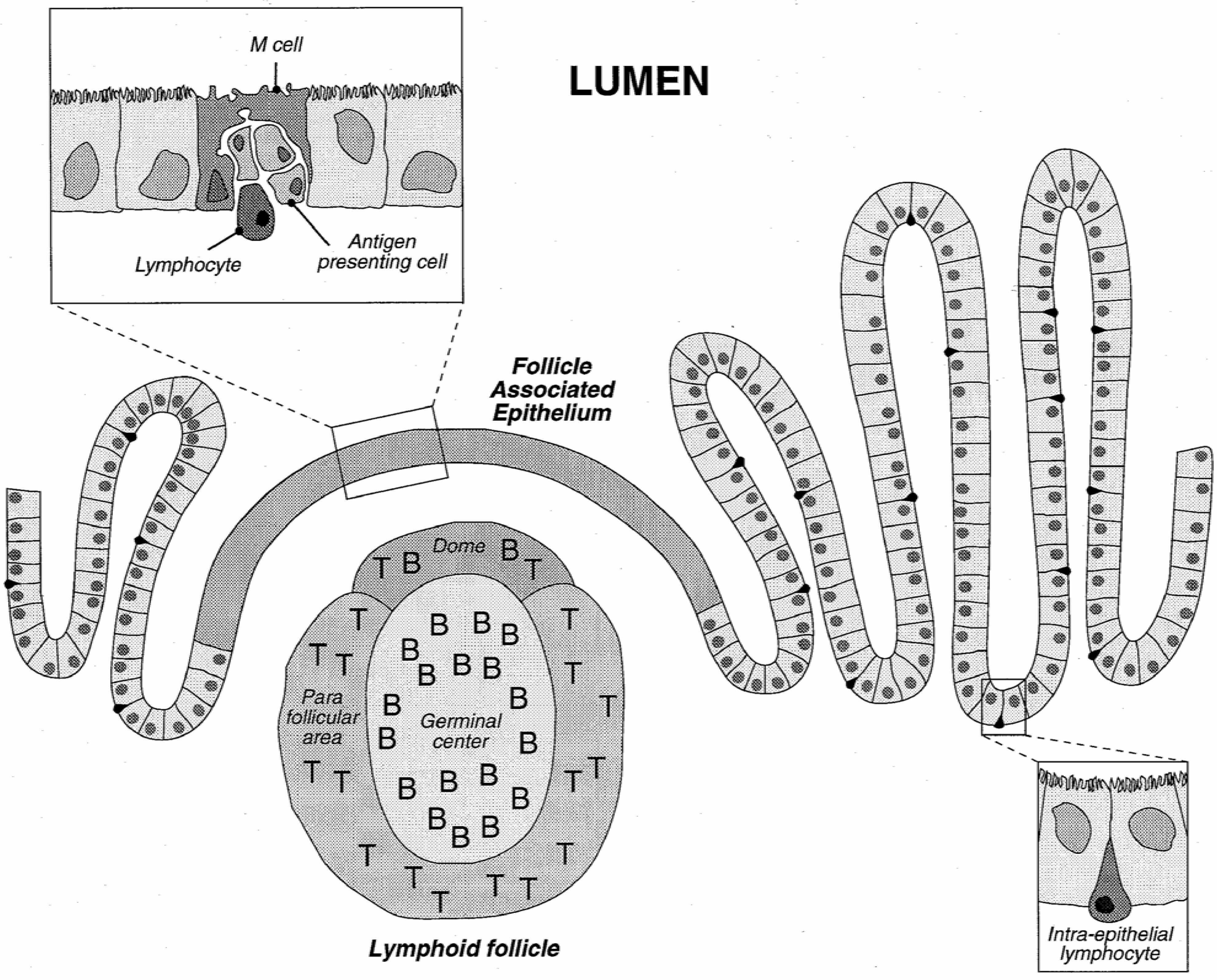
Physiologically, gastrointestinal functions are to digest and to absorb nutrients, water and vitamins from food. On the other hand, it is also designed as a barrier to restrain the entry of pathogens, toxins and undigested macromolecules. The histological architecture of the enteric wall is schematically depicted in Figure 3.
The GI tract is lined with an epithelium made of a mosaic of cells, among which absorptive cells (enterocytes) and goblet cells (secreting the mucus) may be distinguished. These cells are tightly held together and form a strong barrier covered by a layer of mucus. Lymphoid follicles, part of the gut associated lymphoid system (GALT), involved in the development of the mucosal immune response, are interspersed in the enterocyte layer. Lymphoid follicles may be diffusely distributed or clustered in so-called Peyer's patches. The number and location of Peyer's patches vary widely between species and individuals and are also age dependent [36]. These follicles are overlaid by the follicle-associated epithelium (FAE) which comprises enterocytes, M cells differentiated from the enterocytes, and a few goblet cells. It is the site where antigens are first encountered. FAE and the M cells have been described as a privileged place for particle uptake.
Physicochemical properties of particles influence greatly their rate of uptake by the intestinal tract. The two main factors are the size and the nature of the polymer used to make the particles. Early studies on “persorbabiliy” of solid undissolved food particles showed that the uptake was determined by their size and hardness [37,38,39]. Those particles were later observed either in the blood or the lymph. Absorption of particles as big as 150 µm was reported and the influence of xenobiotics such as atropine, barbiturics or neostigmine was reported as well [35,40].
Particles are described as crossing either at the level of Peyer’s patches or through the enterocyte layer. Peyer’s patches were for a long time thought as the only site of absorption for particles. This feature raised the rationale of using particulate formulations for the development of mucosal vaccination. The major interest of mucosal is that the resulting immunity will be expressed at the level of all the mucosae independently of where it has been induced [41,42]. Therefore, numerous studies were published where a protein was encapsulated into nanoparticles for oral vaccination. Encapsulation of proteins not being under the scope of this paper, this aspect will not be developed; the readers are driven to the following review articles [43,44]. It is clearly stated now that particle uptake may occur in Peyer’s patches, however, it is not the exclusive site of absorption and uptake at the level of non Peyer’s patch area is fully documented [45,46].
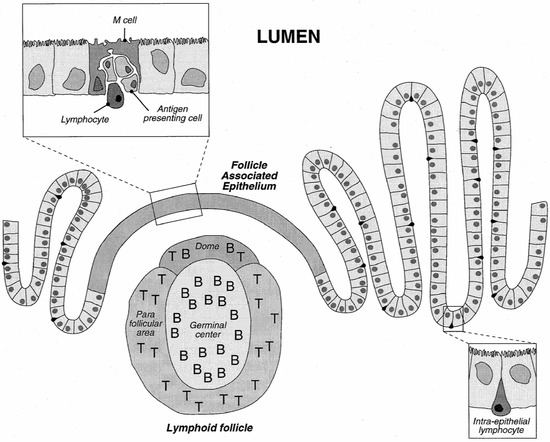
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of the intestinal epithelium with a view of a Peyer's patch and detail of the follicle associated epithelium.
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of the intestinal epithelium with a view of a Peyer's patch and detail of the follicle associated epithelium.
The uptake is preceded by the interaction between the particles and the cell surface. Therefore, the nature of the polymer; mainly, the hydrophobic/hydrophilic balance and the charge; used to make the particles as well as the possible presence of the drug at the particle surface will affect the rate of uptake.
Once internalized, the particles are phagocytosed by macrophages and distributed in the whole body [43,47,48]. Particles are then preferentially encountered in the liver, the spleen and the lungs [49,50].
Despite some rules of thumb showing the influence of certain factors on particle absorption, there are still numerous discrepancies and the identification of the best carrier is still not defined. This is mainly due to the use of different in vivo models, with different administration regimen making difficult to compare the various reports [51].
Size and hydrophilicity of the particles have been clearly described as important factors influencing intestinal absorption [51]. However, there are still numerous discrepancies in the studies reporting the internalization of particles with the same characteristics, therefore, the identification of the best carrier is still not defined. This is mainly due to the use of different in vivo models, with different administration regimen making difficult to compare the various reports [51].
Therefore, the use of an in vitro model would be greatly profitable to the development of new particulate drug carriers for the oral route. Such a model would allow the screening in a systematic manner of the effect of the physicochemical properties of the particles. Caco-2 cells derived from a colonic cancer cells has been tested for different types of particles and seems to be an interesting tool. [52,53,54]. However, all the parameters for this model have not been fully characterized.
In summary, many studies have been conducted on particle absorption from the GI tract, and some discrepancies exist, especially regarding the uptake mechanisms, the location of the absorption site as well as the quantity of particle taken up, however, several conclusions can be drawn. The absorption takes place primarily, but not exclusively, in the Peyer's patches at the level of the M cells. Uptake is very fast and seems to be the result of a transcellular mechanism but a paracellular pathway, although very unlikely, cannot be excluded. The particulate/cell membranes interface appears to play an important role and all the parameters involved in the binding of particles at the cell surface have not been yet identified. The modification of particle surface properties due to the nature of the polymer or due to the binding of specific proteins or lectins can modulate the absorption rate.
Polymeric Particles for the Oral Administration of Peptides
Combinatorial chemistry and the growing knowledge of the biochemistry of the body have lead to an ever-increasing number of therapeutic peptides and proteins for the treatment of diseases. However, these molecules often lack the stability that more traditional small molecular weight drug possesses. Encapsulation of the protein or peptide within polymeric carrier can physically protect the bioactive from proteolytic enzymes. Further, as stated before, these carriers have been shown to translocate across the intestinal mucosa and hence can facilitate the absorption of peptides and proteins from the gut lumen [51].
The main body of literature about the use of particulates for oral drug delivery is devoted to insulin. In this review we will evaluate and discuss the major in vivo studies that have been conducted with polymeric particles (particularly using biodegradable poly(alkylcyanoacrylates) and polylactic polymers) loaded with insulin and administered by the oral route.
The first attempt to seek hypoglycemic effects after oral administration of insulin-loaded nanoparticles to diabetic rats was reported by Couvreur et al. [55]. Insulin was adsorbed on the surface of 200 nm poly(alkylcyanoacrylate) nanoparticles. No decrease in glucose level was observed after oral administration to diabetic rats. Insulin, however, remained active after subcutaneous administration. This result suggests that the peptide was not protected from the proteolytic degradation in the gastrointestinal tract.
Subsequently, 200 nm particles were directly prepared from cross-linked insulin [19]. Nanoparticles were administered to rats and mice intragastrically by gastric tube. The glucose blood level in some animals was reduced to about 15 to 20% of the initial level 3 hours after administration. However, the hypoglycemic effect was quite erratic and some animals responded poorly to the treatment whereas others developed hypoglycemic shocks. The authors speculated that these particles were partially absorbed from the GI tract of mice and of normal and diabetic rats. The nanoparticles appeared to exert a slower but more pronounced response than a similarly administered commercially available Actrapid® formulation, although no dose response relationship was established. Moreover, the high doses of nanoparticles needed would preclude the development of a commercially viable product.
Surprising results were obtained by Damgé et al. [23] with the encapsulation of insulin inside oil-filled poly(isobutylcyanoacrylate) (PIBCA). In diabetic rats, nanocapsules given by a single intragastric dose, reduced glycemia by 50-60%. This effect appears 2 days after administration and was maintained for up 20 days depending on the insulin dose, although the amplitude of the pharmacological effect (minimum level of blood glucose) did not depend on the insulin dose. Free insulin did not affect glycemia when administered orally under the same experimental conditions [23]. Damgé et al., suggested that nanocapsules could protect the peptide from proteolytic degradation in the intestinal fluids as observed in the presence of different proteolytic enzymes in vitro [56]. Furthermore, the capacity of insulin nanocapsules to reduce glycemia can also be explained by their translocation through the intestinal barrier [56]. In recent studies the use of Texas Red®-labeled insulin allowed to visualize this translocation more readily [57]. Although this passage is certainly an important factor, it does not explain the duration of the hypoglycemia. The authors suggested that the prolonged action could be due to the retention of a proportion of the colloidal system in the gastrointestinal tract. In another study, a prolonged hypoglycemic effect was also observed with insulin entrapped in poly(alkylcyanoacrylate) nanospheres dispersed in an oily phase containing surfactant, suggesting that some components of the nanocapsules can act as absorption promoters [58]. Recently, insulin has also been encapsulated in water-containing nanocapsules. These nanocapsules, dispersed in a biocompatible microemulsion, could facilitate the intestinal absorption of the encapsulated insulin after oral administration, as suggested by the reduced glucose level observed in diabetic rats [59].
Carino et al. encapsulated zinc insulin in various polyester (polylactic acid; PLA, poly(lactide-co-glycolide); PLGA) and polyanhydride (poly-fumaric anhydride-co-sebacic anhydride; P(FA:SA) and fumaric acid and sebacic acid oligomers; FAO and SAO respectively) nanosphere formulations using phase inversion nanoencapsulation [60]. A specific formulation, 1.6% zinc insulin in PLGA with FAO and iron oxide additives was active orally when administered to normal fasted rats. This formulation was shown to have 11,4% of the efficacy of intraperitoneally delivered insulin and was able to control plasma glucose levels when faced with a simultaneously administered glucose challenge. The authors hypothesized that each components of the formulation contributes to the overall efficacy; the polyanhydride and iron oxide seems to be necessary, possibly to increase the bioadhesive properties of the spheres, allowing for greater interaction between the nanospheres and the gastrointestinal epithelium and possibly uptake of the nanospheres.
Ma et al. developed PLA microcapsules loaded with insulin [61]. The particles were prepared by a water-in-oil-in-water emulsion/solvent extraction. 2.5 mg of insulin encapsulated in PLA microcapsules (2-5 μm) were administered orally to alloxan induced diabetic rats. The blood glucose lowering effect was quite erratic. Although in 68% of diabetic rats peripheral blood glucose level decreased by 68.5%, in 21% the blood glucose decreased by 39.7%, and in 12% of the diabetic rats no effect was found (the number of animals used in the study was sixty-six). The authors speculated that these differences might be the results of variability in absorption of insulin in the gastrointestinal tract.
Conclusions
Although very scarce, particle absorption is still sufficient to enhance the oral bioavailability of some drugs such as insulin. Efforts need to be conducted, however, in developing new polymers and new surface characteristics to increase the particle affinity to the epithelium surface. On the other hand, one has to bear in mind that particle resorption is not a prerequisite. Indeed, the presence of a polymeric wall provides a protection from the gastrointestinal environment and may favor a prolonged contact with the epithelium that may be sufficient to increase the bioavailability of certain drugs.
Although the oral route is one of the preferred modes for drug administration, owing to its non-invasive nature, adequate peptide or protein drug delivery has not yet been attained via this route. This is, in part, a consequence of the low bioavailability presented by most oral protein delivery systems. This low bioavailability implies a large variation in absorption and high manufacturing costs, which are both unacceptable for the development of most peptide and protein drugs. As a result, millions of diabetics worldwide have to give themselves insulin shots daily, resulting in a high rate of side effects and non compliance in this treatment. The possibility of using biodegradable nano- or microparticles for oral administration of insulin has been a controversial issue. Even if a dosage form is developed to produce a reasonable bioavailability, reproducibility is another potential problem. For drugs such as insulin that have a relatively narrow therapeutic window, the effects of age, genomics factors, pathophysiological conditions and other individual variations on GI absorption must be carefully investigated. Finally, insulin requires chronic administration and hence the effects of long-term oral administration of absorption carriers on both the GI and systemic physiology must also be seriously evaluated.
References
- Lee, V. H. L.; Robinson, J. R. Enzymatic Barriers to Peptide and Protein Absorption. CRC Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst. 1988, 5, 69–97. [Google Scholar]
- Allémann, E.; Leroux, J. C.; Gurny, R. Polymeric Nano- and Microparticles for the Oral Delivery of Peptides and Peptidomimetics. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 1998, 34, 171–189. [Google Scholar]
- Allémann, E.; Gurny, R.; Doelker, E. Drug Loaded Nanoparticles - Preparation Methods and Drug Targeting Issues. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1993, 39, 173–191. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, M. J. Nanoparticulate Drug Carrier Technology. Drugs Pharm. Sci. 1996, 77, 203–242. [Google Scholar]
- Couvreur, P.; Dubernet, C.; Puisieux, F. Controlled Drug Delivery With Nanoparticles: Current Possibilities and Future Trends. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1995, 41, 2–13. [Google Scholar]
- Soppimath, K. S.; Aminabhavi, T. M.; Kulkarni, A. R.; Rudzinski, W. E. Biodegradable Polymeric Nanoparticles As Drug Delivery Devices. J. Control. Release 2001, 70, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Couvreur, P.; Kante, B.; Roland, M.; Guiot, P.; Bauduin, P.; Speiser, P. Polycyanoacrylate Nanocapsules As Potential Lysosomotropic Carriers: Preparation, Morphological and Sorptive Properties. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1979, 31, 331–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuter, J.; Speiser, P. P. In Vitro Studies of Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Adjuvants. J. Pharm. Sci. 1976, 11, 1624–1626. [Google Scholar]
- Lescure, F.; Seguin, C.; Breton, P.; Bourrinet, P.; Roy, D.; Couvreur, P. Preparation and Characterization of Novel Poly(Methylidene Malonate 2.1.2.)-Made Nanoparticles. Pharm. Res 1994, 11, 1270–1277. [Google Scholar]
- Berton, M.; Benimetskaya, L.; Allémann, E.; Stein, C. A.; Gurny, R. Uptake of Oligonucleotide-Loaded Nanoparticles in Prostatic Cancer Cells and Their Intracellular Localization. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1999, 47, 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer, A. Antisense Oligonucleotide Delivery With Polyhexylcyanoacrylate Nanoparticles As Carriers. Methods 1999, 18, 286–295. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco-Prieto, M. J.; Delie, F.; Fattal, E.; Tartar, A.; Puisieux, F.; Gulik, A.; Couvreur, P. Characterization of V3BRU Peptide Loaded Small PLGA Microspheres Prepared by (W1/O)W2 Emulsion Solvent Evaporation. Int. J. Pharm. 1994, 111, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafati, H.; Coombes, A. G. A.; Adler, J.; Holland, J.; Davis, S. S. Protein-Loaded Poly(DL-Lactide-Co-Glycolide) Microparticles for Oral Administration: Formulation, Structural and Release Characteristics. J. Contr. Rel. 1997, 43, 89–102. [Google Scholar]
- Delie, F.; Berton, M.; Allémann, E.; Gurny, R. Comparison of Two Methods of Encapsulation of an Oligonucleotide into Poly(D,L-Lactic Acid) Particles. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 214, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Bruhn, B. W.; Müller, B. W. Preparation and Characterization of Spray-Dried Poly(Dl-Lactide) Microspheres. Proceed. Int. Symp. Contr. Rel. Bioact. Mater. 1991, 18, 668–669. [Google Scholar]
- Kissel, T.; Brich, Z.; Bantle, S.; Lankranjan, J.; Nimmerfall, F.; Vit, P. Parenteral Depot-Systems on the Basis of Biodegradable Polyesters. J. Contr. Rel. 1991, 16, 27–42. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco-Príeto, M. J.; Orsolini, P.; Heimgartner, F.; Besseghir, K.; Merkle, H. P.; Gander., B. Importance of the Test Medium for the Release Kinetics of a Somatostatin Analogue From Poly(D,L-Lactide-Co-Glycolide) Micropheres. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 184, 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P. K.; Johnson, H.; Alexon, C. In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation of Clarithromycin/Poly(Lactic Acid) Microspheres for Intramuscular Drug Delivery. J. Contr. Rel. 1993, 26, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim, R. C.; Stewert, N. F.; Gordon, L.; Patel, H. M. The Production and Evaluation of Orally Administred Insulin Nanoparticles. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1982, 8, 531–546. [Google Scholar]
- Hillery, A. M.; Toth, I.; Florence, A. T. Co-Polymerised Peptide Particles (CPP) II: Oral Uptake of a Novel Co-Polymeric Nanoparticulate Delivery System for Peptides. J. Control. Rel. 1996, 42, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Hillery, A. M.; Toth, I.; Shaw, A. J.; Florence, A. T. Co-Polymerised Peptide Particles (CPP) I: Synthesis, Charaterisation and in Vitro Studies on a Novel Oral Nanoparticulate Delivery System. J. Control. Rel. 1996, 41, 271–281. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, J.; Woolfe, J.; Florence, A. T. Nanospheres of Cyclosporin A: Poor Oral Absorption in Dogs. Int J Pharm 1999, 183, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Damgé, C.; Michel, C.; Aprahamian, M.; Couvreur, P. New Approach for Oral Administration of Insulin With Polyalkylcyanoacrylate Nanocapsules As Drug Carrier. Diabetes 1988, 37, 246–251. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, C.; Aprahamian, M.; Defontaine, L.; Couvreur, P.; Damgé, C. The Effect of Site of Administration in Gastrointestinal Tract on the Absorption of Insulin From Nanocapsules in Diabetic Rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1991, 43, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Khouri Fallouh, N.; Roblot-Treupel, L.; Fessi, H.; Devissaguet, J. P.; Puisieux, F. Development of a New Process for the Manufacture of Polyisobutylcyanoacrylate Nanocapsules. Int. J. Pharm 1986, 28, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Ammoury, N.; Fessi, H.; Devissaguet, J. P.; Dubrasquet, M.; Benita, S. Jejunal Absorption, Pharmacological Activity, and Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Indomethacin-Loaded Poly(DL-Lactide) and Poly(Isobutyl-Cyanoacrylate) Nanocapsules in Rats. Pharm. Res. 1991, 8, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Fessi, H.; Devissaguet, J. P.; Puisieux, F.; Thies, C. Procédé De Préparation De Systèmes Colloïdaux Dispersibles D'Une Substance, Sous Forme De Nanoparticules. Brevet français 1986, 2, 608–998. [Google Scholar]
- Quintanar-Guerrero, D.; Allémann, E.; Doelker, E.; Fessi, H. Preparation and Characterization of Nanocapsules From Preformed Polymers by a New Process Based on Emulsification-Diffusion Technique. Pharm.Res. 1998, 15, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar]
- Vranckx, H.; Demoustier, M.; Deleers, M. A New Nanocapsule Formulation With Hydrophilic Core: Application to the Oral Administration of Salmon Calcitonin in Rats. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1996, 42, 345–347. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, G.; Fattal, E.; Pinto-Alphandary, H.; Gulik, A.; Couvreur, P. Polyisobutylcyanoacrylate Nanocapsules Containing an Aqueous Core As a Novel Colloidal Carrier for the Delivery of Oligonucleotides. Pharm.Res. 2000, 17, 707–714. [Google Scholar]
- Magenheim, B.; Benita, S. Nanoparticle Characterization: a Comprehensive Physicochemical Approach. S.T.P.Pharma 1991, 1, 221–241. [Google Scholar]
- de Chasteigner, S.; Fessi, H.; Cavé, G.; Devissaguet, J. P.; Puisieux, F. Gastro-Intestinal Tolerance Study of a Freeze-Dried Oral Dosage Form of Indomethacin-Loaded Nanocapsules. S. T. P. Pharma Sciences 1995, 5, 242–246. [Google Scholar]
- De Jaeghere, F.; Allémann, E.; Leroux, J. C.; Stevels, W.; Feijen, J.; Doelker, E.; Gurny, R. Formulation and Lyoprotection of Poly(Lactic Acid-Co-Ethylene Oxide) Nanoparticles: Influence on Physical Stability and in Vitro Cell Uptake. Pharm. Res. 1999, 16, 859–866. [Google Scholar]
- Kreuter, J. Peroral Administration of Nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 1991, 7, 71–86. [Google Scholar]
- Volkheimer, G. Persorption of Particles: Physiology and Pharmacology. Adv. Pharmaco. Chemother. 1977, 14, 163–187. [Google Scholar]
- Cornes, J. S. Number, Size, and Distribution of Peyer's Patches in the Human Small Intestine. Gut 1965, 6, 225–233. [Google Scholar]
- Volkheimer, G.; Schulz, F. H.; Aurich, I.; Strauch, S.; Beuthin, K.; Wendlandt, H. Persorption of Particles. Digestion 1968, 1, 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Volkheimer, G.; Schultz, F. H. The Phenomenon of Persorption. Digestion 1968, 1, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Volkheimer, G. Hematogenous Dissemination of Ingested Polyvinyl Chloride Particles. Proceed. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1975, 246, 164–171. [Google Scholar]
- Volkheimer, G.; Schulz, F. H.; Hofmann, I.; Pieser, J.; Rack, O.; Rotenbaecher, W.; Schurig, B.; Teicher, G.; Weiss, B. The Effect of Drugs on the Rate of Persorption. Pharmacology 1968, 1, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Simecka, J. W. Mucosal Immunity of the Gastrointestinal Tract and Oral Tolerance. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 1998, 34, 235–259. [Google Scholar]
- McGhee, J. R.; Mestecky, J.; Dertzbaugh, M. T.; Eldridge, J. H.; Hirasawa, M.; Kiyono, H. The Mucosal Immune System: From Fundamental Concepts to Vaccine Development. Vaccine 1997, 10, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge, J. H.; Gilley, R. M.; Staas, J. K.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Tice, T. R. Biodegradable Microspheres: Vaccine Delivery System for Oral Immunization. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 1989, 146, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- O'Hagan, D. T. Microparticles and Polymers for the Mucosal Delivery of Vaccines. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 1998, 34, 305–320. [Google Scholar]
- Jepson, M. A.; Simmons, N. L.; O'Hagan, D. T.; Hirst, B. H. Comparison of Poly(DL-Lactide-Co-Glycolide) and Polystyrene Microsphere Targeting to Intestinal M Cells. J. Drug Targ. 1993, 1, 245–249. [Google Scholar]
- McClean, S.; Prosser, E.; Meehan, E.; O'Malley, D.; Clarke, N.; Ramtoola, Z.; Brayden, D. Binding and Uptake of Biodegradable Poly-DL-Lactide Micro- and Nanoparticles in Intestinal Epithelia. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 6, 153–163. [Google Scholar]
- Jeurissen, S. H. M.; Kraal, G.; Sminia, T. The Role of Peyer's Patches in Intestinal Humoral Immune Responses Is Limited to Memory Formation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1987, 216A, 257–265. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, C. L.; Maddaus, M. A.; Erlandsen, S. L.; Simmons, R. L. Evidence for the Phagocytic Transfer of Intestinal Particles in Dogs and Rats. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 278–282. [Google Scholar]
- Jani, P. U.; Haklbert, G. W.; Langridge, J.; Florence, A. T. Nanoparticles Uptake by the Rat Gastrointestinal Mucosa: Quantitation and Particle Size Dependency. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1990, 42, 821–826. [Google Scholar]
- LeFevre, M. E.; Hancock, D. C.; Joel, D. D. Intestinal Barrier to Large Particulates in Mice. J. Toxicol. Env. Health. 1980, 6, 691–704. [Google Scholar]
- Delie, F. Evaluation of Nano- and Microparticle Uptake by the Gastrointestinal Tract. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 1998, 34, 221–233. [Google Scholar]
- Delie, F.; Rubas, W. Caco-2 Monolayers As a Tool to Examine Intestinal Uptake of Particulates. Proceed. Intern. Symp. Control. Rel. Bioact. Mater. 1996, 23, 149–150. [Google Scholar]
- Desai, M. P.; Labhasetva, V.; Walter, E.; Levy, R. L.; Amidon, G. L. The Mechanism of Uptake of Biodegradable Microparticles in Caco-2 Cells Is Size Dependent. Pharm. Res. 1997, 14, 1568–1573. [Google Scholar]
- Le Visage, C.; Couvreur, P.; Mysiakine, E.; Breton, P.; Bru, N.; Fattal, E. In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation of Poly(Methylidene Malonate 2.1.2) Microparticles Behavior for Oral Administration. J. Drug Target. 2001, 9, 141–153. [Google Scholar]
- Couvreur, P.; Lenaerts, V.; Kante, B.; Roland, M.; Speiser, P. P. Oral and Parenteral Administration of Insulin Associated to Hydrolysable Nanoparticles. Acta Pharm. Technol. 1980, 26, 220–222. [Google Scholar]
- Damgé, C.; Michel, C.; Aprahamian, M.; Couvreur, P.; Devissaguet, J. P. Nanocapsules As Carriers for Oral Peptide Delivery. J. Contr. Rel. 1990, 13, 233–239. [Google Scholar]
- Aboubakar, M.; Couvreur, P.; Pinto-Alphandary, H.; Gouritin, B.; Lacour, B.; Farinotti, R.; Puisieux, F.; Vauthier, C. Insulin-Loaded Nanocapsules for Oral Administration: In Vitro and in Vivo Investigation. Drug Develop. Res. 2000, 49, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Damgé, C.; Vonderscher, J.; Marbach, P.; Pinget, M. Poly(Alkyl Cyanoacrylate) Nanocapsules As a Delivery System in the Rat for Octreotide, a Long-Acting Somatostatin Analogue. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1997, 49, 949–954. [Google Scholar]
- Watnasirichaikul, S.; Tucker, I. G.; Davies, N. M. Effect of Formulation Variables on Characteristics of Poly(Ethylcyanoacrylate) Nanocapsules Prepared From W/o Microemulsions. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 235, 237–246. [Google Scholar]
- Carino, G. P.; Jacob, J. S.; Mathiowitz, E. Nanospheres Based Oral Insulin Delivery. J. Contr. Rel. 2000, 65, 261–269. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X. Y.; Pan, G. M.; Lu, Z.; Hu, J. S.; Bei, J. Z.; Jia, J. H.; Wang, S. G. Preliminary Study of Oral Polylactide Microcapsulated Insulin in Vitro and in Vivo. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2000, 2, 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge, J. H.; Hammond, C. J.; Meulbroek, J. A.; Staas, J. K.; Gilley, R. M.; Tice, T. R. Controlled Vaccine Release in the Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissues. 1. Orally Administered Biodegradable Microspheres Target the Peyer's Patches. J. Contr. Rel. 1990, 11, 205–214. [Google Scholar]
- Leroux, J. C.; Cozens, R.; Roesel, J. L.; Galli, B.; Doelker, E.; Kubel, F.; Gurny, R. Pharmacokinetics of a Novel HIV-1 Protease Inhibitor Incorporated into Biodegradable or Enteric Nanoparticles Following Intravenous and Oral Administration to Mice. J. Pharm. Sci. 1995, 84, 1388–1391. [Google Scholar]
- Sordet, F.; Aumjaud, Y.; Fessi, H.; Derouin, F. Assessment of the Activity of Atovaquone-Loaded Nanocapsules in the Treatment of Acute and Chronic Murine Toxoplasmosis. Parasite 1998, 5, 223–229. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y. I.; Fluckiger, L.; Hoffman, M.; Lartaud-Idjouadiene, I.; Atkinson, J.; Maincent, P. The Antihypertensive Effect of Orally Administered Nifedipine-Loaded Nanoparticles in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 120, 399–404. [Google Scholar]
- Barichello, J. M.; Morishita, M.; Takayama, K.; Nagai, T. Encapsulation of Hydrophilic and Lipophilic Drugs in PLGA Nanoparticles by the Nanoprecipitation Method. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1999, 25, 471–476. [Google Scholar]
- Hubert, B.; Atkinson, J.; Guerret, M.; Hoffman, M.; Devissaguet, J. P.; Maincent, P. The Preparation and Acute Antihypertensive Effects of a Nanocapsular Form of Darodipine, a Dihydropyridine Calcium Entry Blocker. Pharm Res 1991, 8, 734–8. [Google Scholar]
- Löbenberg, R.; Maas, J.; Kreuter, J. Improved Body Distribution of 14C-Labelled AZT Bound to Nanoparticles in Rats Determined by Radioluminography. J. Drug Targ. 1997, 5, 171–179. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, P.; Kreuter, J.; Muller, W. E. G.; Schatton, W. Improved Peroral Delivery of Avarol With Polybutylcyanoacrylate Nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1994, 40, 134–137. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, U. V.; Udupa, N. Methotrexate Loaded Chitosan and Chitin Microspheres - in Vitro Characterization and Pharmacokinetics in Mice Bearing Ehrlich Ascite Carcinoma. J. Microencaps. 1998, 15, 581–594. [Google Scholar]
- Leroux, J. C.; Cozens, R. M.; Roesel, J. L.; Galli, B.; Doelker, E.; Gurny, R. pH-Sensitive Nanoparticles: an Effective Means to Improve the Oral Delivery of HIV-1 Protease Inhibitor in Dogs. Pharm. Res. 1996, 13, 485–487. [Google Scholar]
- Lowman, A. M.; Morishita, M.; Kajita, M.; Nagai, T.; Peppas, N. A. Oral Delivery of Insulin Using pH-Responsive Complexation Gels. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 88, 933–937. [Google Scholar]
- Nagareya, N.; Uchida, T.; Matsuyama, K. Preparation and Characterization of Enteric Microspheres Containing Bovine Insulin by a w/o/w Emulsion Solvent Evaporation Method. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1998, 46, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar]
- Mathiowitz, E.; Jacob, J. S.; Jong, Y. S.; Carino, G. P.; Chickering, D. E.; Chatuvedi, P.; Santos, C. A.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Montgomery, S.; Basset, M.; Morell, C. Biologically Erodable Microspheres As Potential Oral Drug Delivery Systems. Nature 1997, 386, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone-Bay, A.; Santiago, N.; Achan, D.; Chaudhary, K.; DeMorin, F.; Falzarano, L.; Haas, S.; Kalbag, S.; Kaplan, D.; Leipold, H.; Lercara, C.; O'Toole, D.; Rivera, T.; Rosado, C.; Sarubbi, D.; Vuocolo, E.; Wang, N.; Milstein, S.; Baughman, R. A. N-Acylated α-Amino Acids As Novel Oral Delivery Agents for Proteins. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 4263–4269. [Google Scholar]
- Leone-Bay, A.; McInnes, C.; Wang, N.; DeMorin, F.; Achan, D.; Lercara, C.; Sarubbi, D.; Haas, S.; Press, J.; Barantsevich, E.; O'Broin, B.; Milstein, S.; Paton, D. Microsphere Formation in a Series of Derivatized α-Amino Acids: Properties, Molecular Modeling, and Oral Delivery of Salmon Calcitonin. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 4257–4262. [Google Scholar]
- Milstein, S. J.; Barantsevich, E. N.; Grechanovski, V. A.; Sarubbi, D. J. PH-Dependent Microspheres From Modified Soybean Protein Hydrolysate. J. Microencaps. 1996, 13, 651–665. [Google Scholar]
© 2005 by MDPI (http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
