Biosorption Potential of Bacillus salmalaya Strain 139SI for Removal of Cr(VI) from Aqueous Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
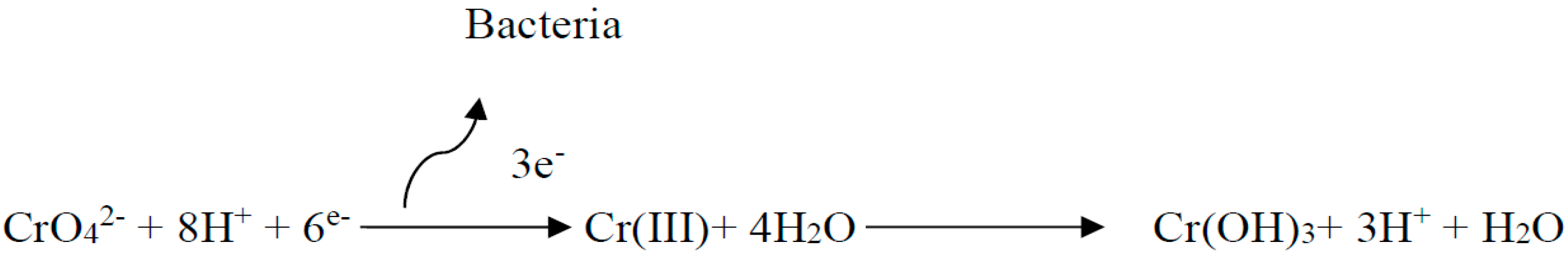
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganism and Growth Conditions
2.2. Identification of Bacteria Using 16S rRNA
2.3. Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations and Antibiotic Resistance of Strain 139SI
2.4. Preparation of Live and Dead Cells
2.5. Batch Biosorption Experiments
2.6. Desorption Efficiency
2.7. Biosorption Equilibrium
- Qe = amount adsorbed metal per unit weight biomass at equilibrium (mg/g)
- Qmax = maximum adsorption capacity (mg/g)
- β = equilibrium constant for adsorption (L/mg)
- Ce = residual metal concentration in solution (mg/l)
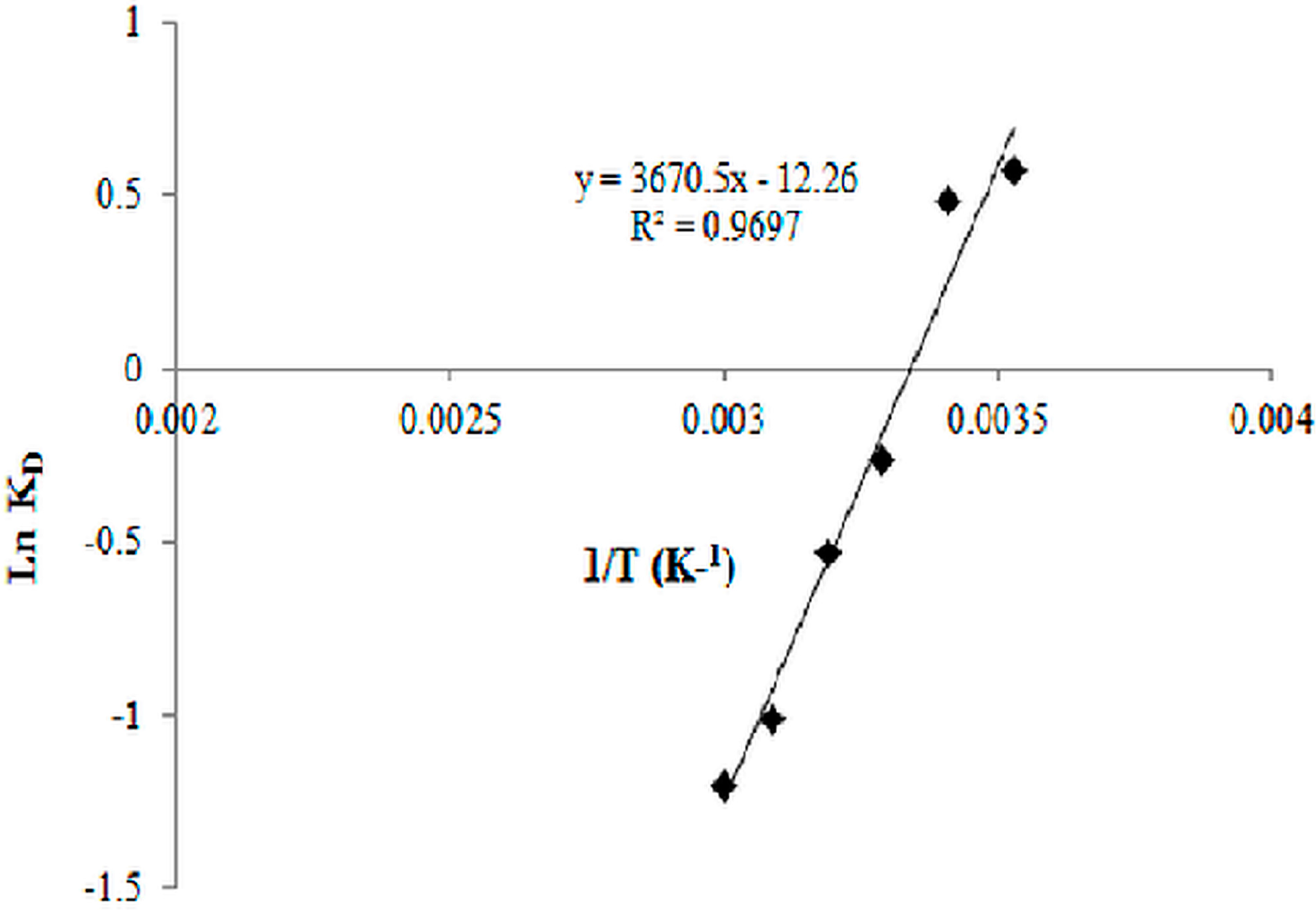
2.8. Biosorption Thermodynamics
∆G0 = −RT lnK,
ln K = (∆S0/R)−(∆H0/RT)
K = Qe/ Ce
2.9. Kinetic Studies
- K1 (L/min) and K2 (g/mg min) = rate constants of the respective kinetic models
- Q = sorption capacities at equilibrium (mg/g)
- Qe = sorption capacities at time t (mg/g)
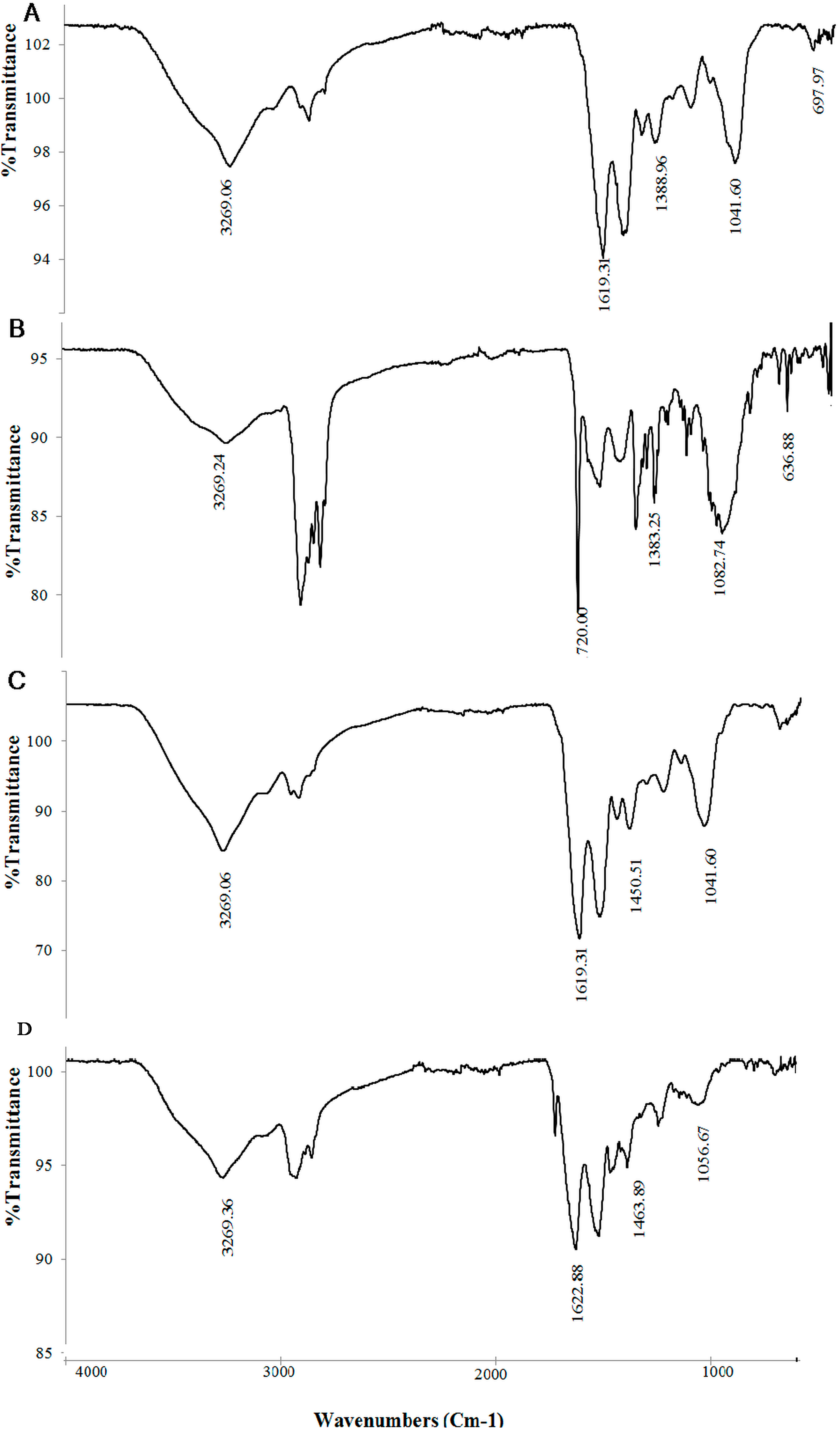
2.10. FT-IR, EDS, and SEM Analysis
2.11. Bioaccumulation of Chromium in B. salmalaya 139SI
2.12. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Molecular Identification of Bacterial Isolate Using 16S rRNA
| Description | Max Score | Total Score | Query Cover | E Value | Ident | Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillus salmalaya strain 139SI 16S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence | 2719 | 2719 | 100% | 0.0 | 100% | KM051837.1 |
| Uncultured bacterium clone 11 St 10 16S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence | 2713 | 2713 | 100% | 0.0 | 99% | KM464089.1 |
| Uncultured bacterium clone EGSB 200 5-5 16S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence | 2713 | 2713 | 100% | 0.0 | 99% | KJ881337.1 |
| Bacillus anthracis str A16, complete genome | 2713 | 29732 | 100% | 0.0 | 99% | CP001970.1 |
| Bacillus sp. C20 16S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence | 2713 | 2713 | 100% | 0.0 | 99% | KF479614.1 |
| Bacillus sp. B10 16S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence | 2713 | 2713 | 100% | 0.0 | 99% | KF479574.1 |
| Bacillus sp. A52 16S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence | 2713 | 2713 | 100% | 0.0 | 99% | KF479557.1 |
| Bacillus cereus strain XX2010 16S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence | 2713 | 2713 | 100% | 0.0 | 99% | JX993816.1 |
| Bacillus cereus F837/76, complete genome | 2713 | 32440 | 100% | 0.0 | 99% | CP003187.1 |
| Bacillus cereus strain 7D, 16S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence | 2713 | 2713 | 100% | 0.0 | 99% | JF714217.1 |
| Bacillus sp, LM24(2011)16S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence | 2713 | 2713 | 100% | 0.0 | 99% | HQ891939.1 |
| Bacillus thuringiensis serovar finitimus YBT-020, complete genome | 2713 | 37883 | 100% | 0.0 | 99% | CP002508.1 |
| Bacillus cereus strain PPB13 16S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence | 2713 | 2713 | 100% | 0.0 | 99% | HM771668.1 |
| Bacillus cereus strain SBD1-8 16S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence | 2713 | 2713 | 100% | 0.0 | 99% | HQ236038.1 |
| Bacillus cereus strain DZ-h 16S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence | 2713 | 2713 | 100% | 0.0 | 99% | HM345997.1 |
| Bacillus thuringiensis strain, IWF24 16S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence | 2713 | 2713 | 100% | 0.0 | 99% | GU120652.1 |
| Bacillus cereus 03BB102, complete genome | 2713 | 37938 | 100% | 0.0 | 99% | CP001407.1 |
| Bacillus cereus AH820, complete genome | 2713 | 32444 | 100% | 0.0 | 99% | CP001283.1 |
| Bacillus sp. NS-4 16S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence | 2713 | 2713 | 100% | 0.0 | 99% | EU622630.1 |
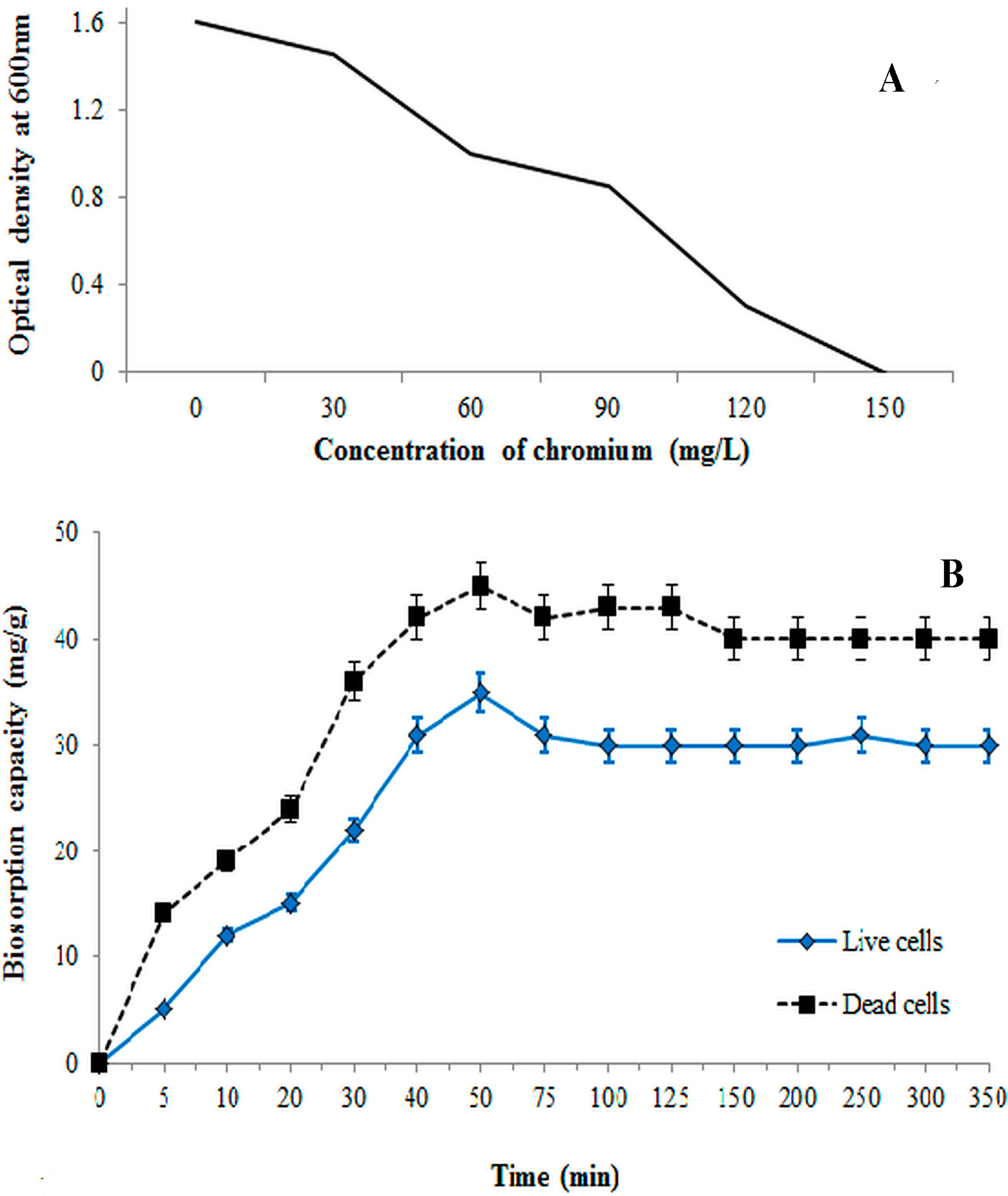
3.2. Effect of Time on Biosorption Process
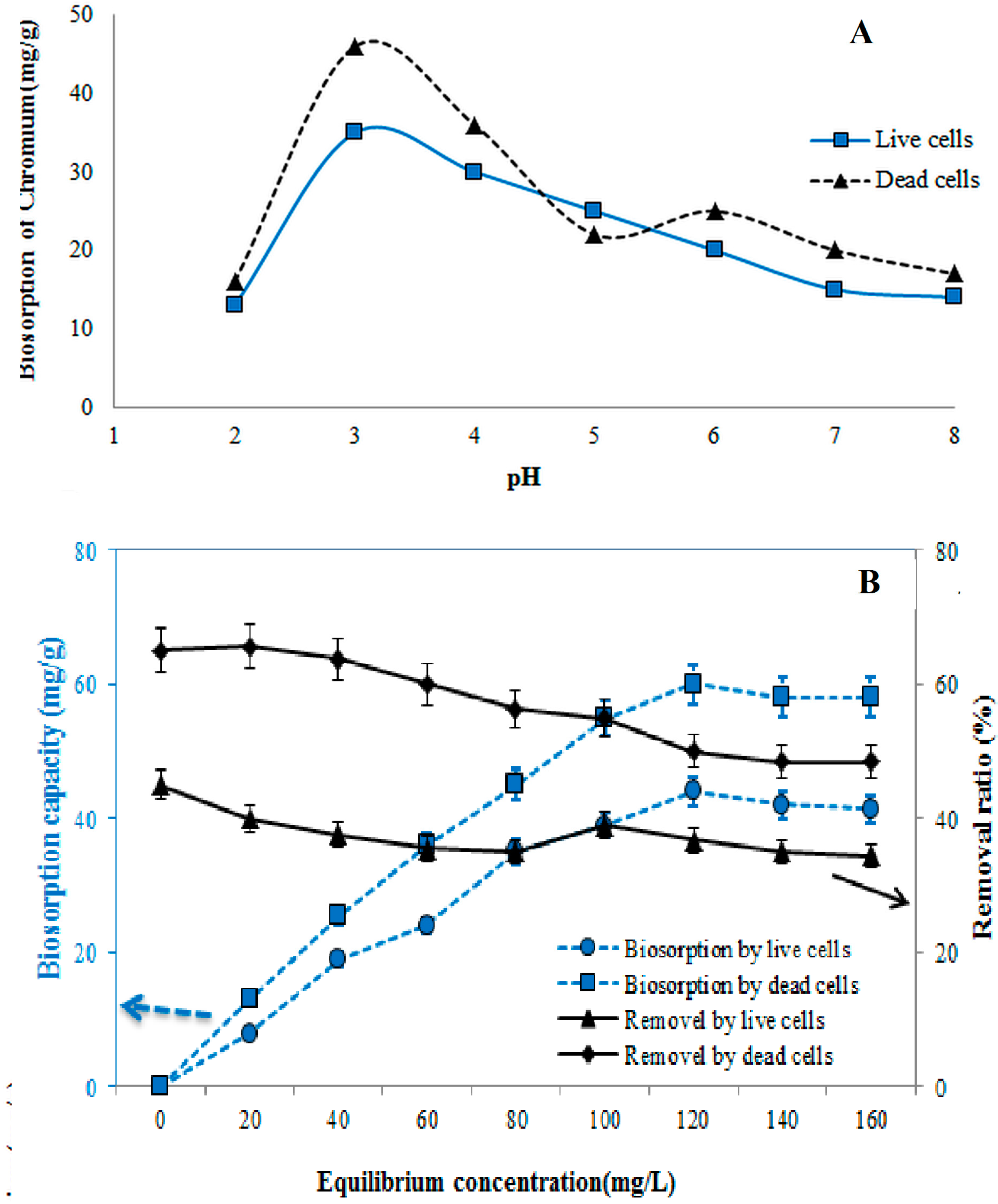
3.3. Effect of pH on Biosorption Process
3.4. Effect of Initial Cr(VI) Concentration on Biosorption Process
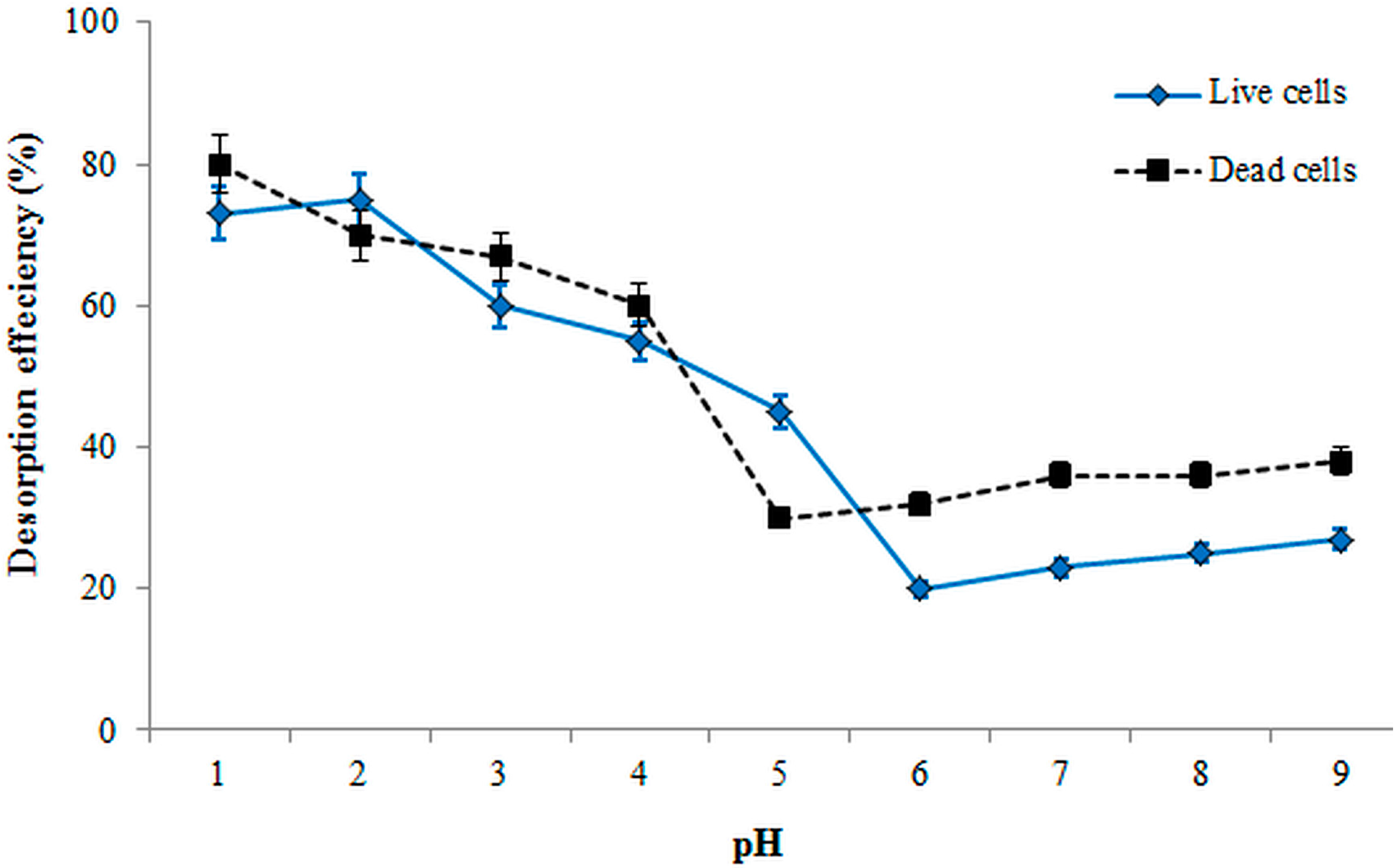
3.5. Desorption Efficiency
3.6. Biosorption Equilibrium
| Cells | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax(mg/g) | β | RL | R2 | n | Kf (L/g) | R2 | |
| Live | 12.94 | 0.032 | 0.257 | 0.971 | 1.12 | 1.369 | 0.813 |
| Dead | 20.35 | 0.728 | 0.015 | 0.966 | 2.541 | 4.165 | 0.933 |
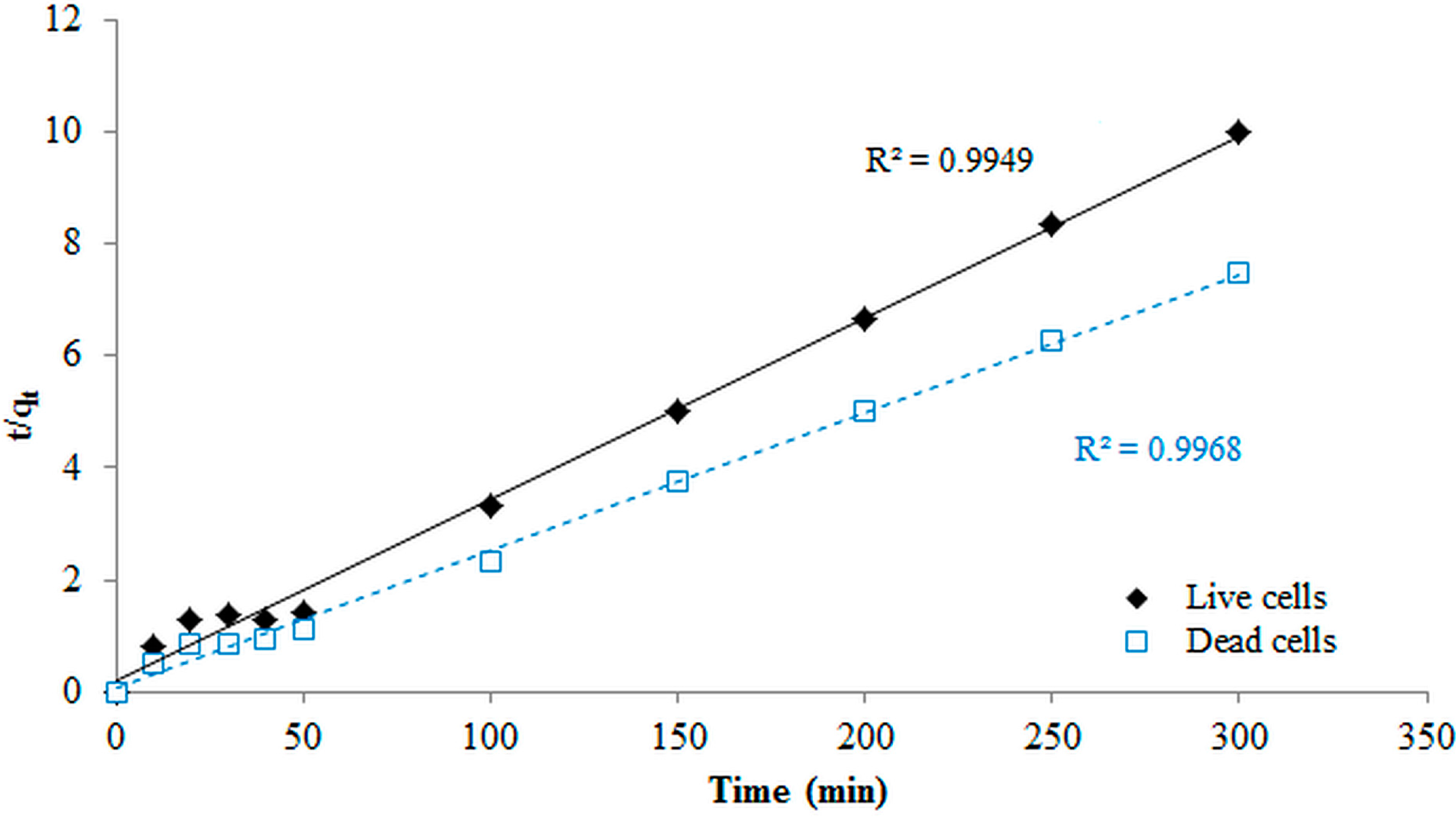
3.7. Kinetic Modeling Studies
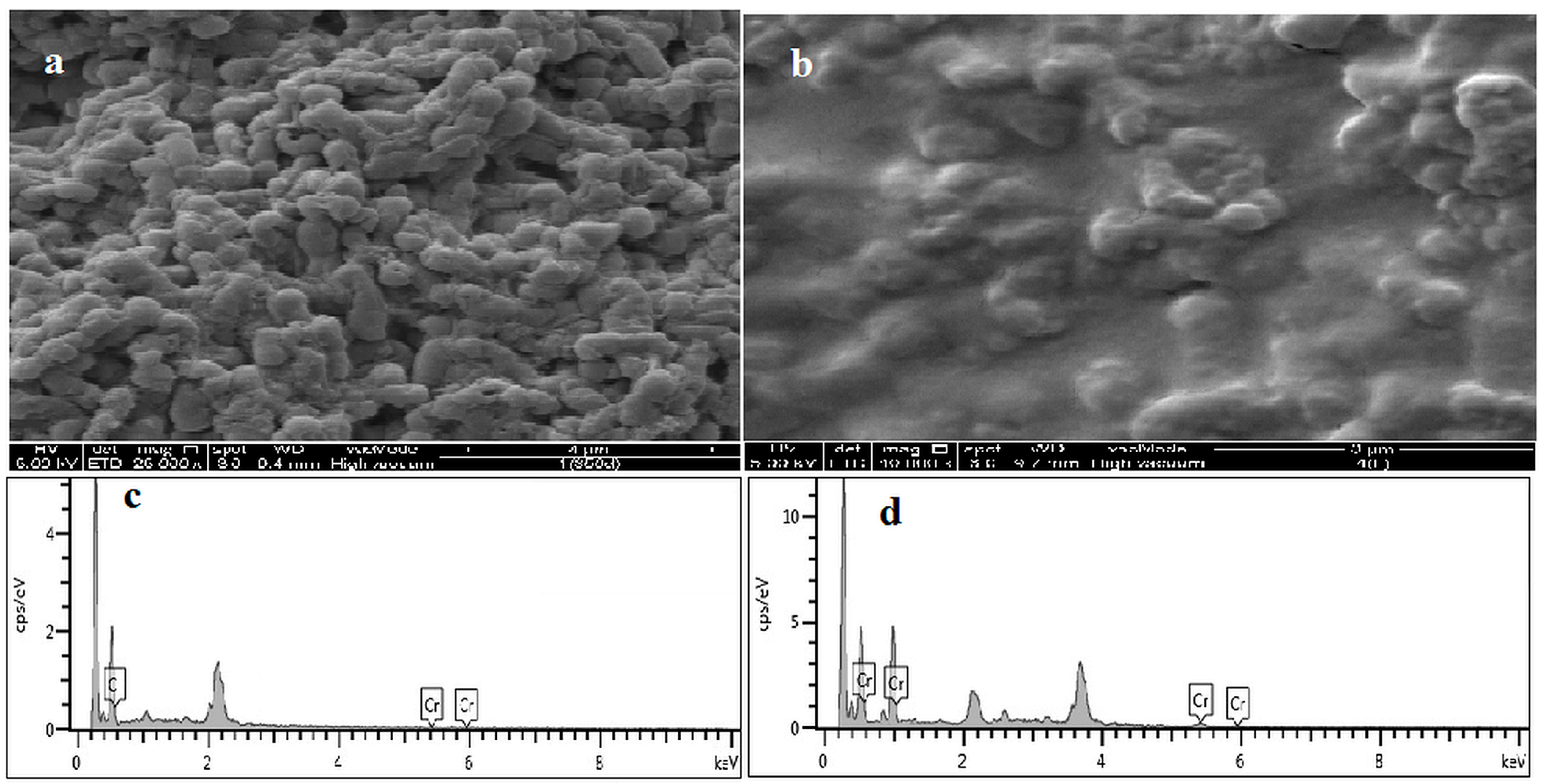
3.8. Mechanism Discussion
3.9. Bioaccumulation of Chromium by Strain 139SI
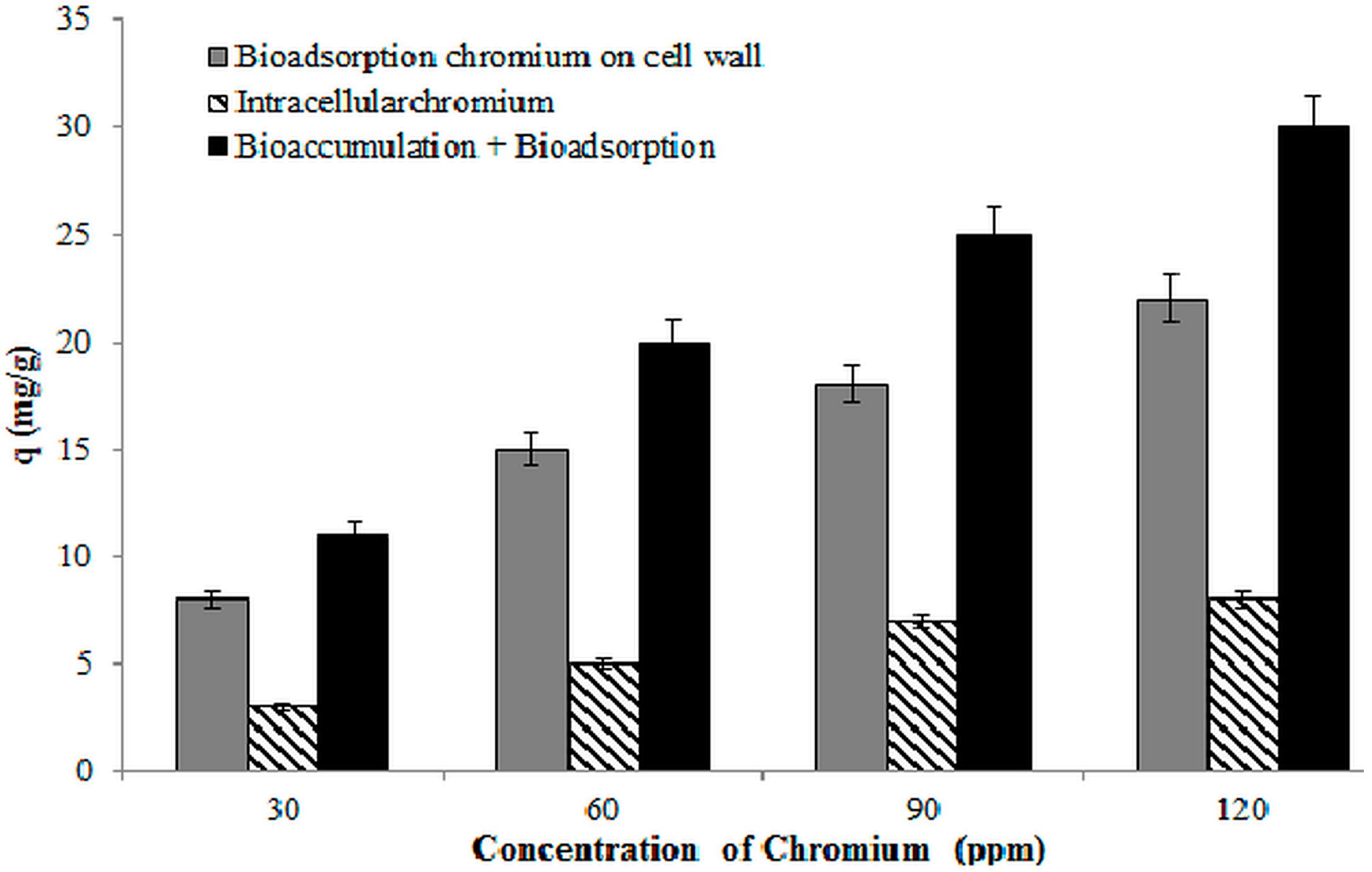
3.10. Biosorption Thermodynamics
3.11. Comparison Of Dead and Live Biosorbents
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, M.; Xu, P.; Zeng, G.; Yang, C.; Huang, D.; Zhang, J. Bioremediation of soils contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, petroleum, pesticides, chlorophenols and heavy metals by composting: Applications, microbes and future research needs. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, M.A. New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arabian J. Chem. 2011, 4, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, N.; Husain Khan, A.; Pathak, V.; Agnihotri, N.; Rehman, M. Removal of hexavalent chromium from synthetic waste water using synthetic nano zero valent iron (NZVI) as adsorbent. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2013, 2, 6140–6149. [Google Scholar]
- Madhavi, V.; Reddy, A.V.B.; Reddy, K.G.; Madhavi, G.; Prasad, T. An overview on research trends in remediation of chromium. Res. J. Recent Sci. 2013, 2, 71–83. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, K.H.; Gu, J.-D. Mechanism of hexavalent chromium detoxification by microorganisms and bioremediation application potential: A review. Int. Biodeterior Biodegradation. 2007, 59, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rita Evelyne, J.; Ravisankar, V. Bioremediation of chromium contamination—A review. Int. J. Res. Earth Environ. Sci. 2014, 1, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Aroua, M.K.; Zuki, F.M.; Sulaiman, N.M. Removal of chromium ions from aqueous solutions by polymer-enhanced ultrafiltration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, G.; Bhattacharya, P.K. Hexavalent chromium ion removal through micellar enhanced ultrafiltration. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 119, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, T.C.; Lansarin, M.A.; Matte, N. Reduction of hexavalent chromium: Photocatalysis and photochemistry and their application in wastewater remediation. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoa, L.N.; prabhakara, D.G. Removal of heavy metals by absorption—An overall review. J. Eng. Res. Stud. 2013, 2, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Joutey, N.T.; Bahafid, W.; Sayel, H.; Abed, S.E.; Ghachtouli, N.E. Remediation of hexavalent chromium by consortia of indigenous bacteria from tannery waste-contaminated biotopes in Fez, Morocco. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2011, 68, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Bahari, Z.; Ali Hamood Altowayti, W.; Ibrahim, Z.; Jaafar, J.; Shahir, S. Biosorption of As(III) by non-living biomass of an arsenic-hypertolerant Bacillaceae cereus strain SZ2 isolated from a gold mining environment: Equilibrium and kinetic study. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 171, 2247–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Dang, Z.; Guo, C.-L.; Lu, G.-N.; Gu, R.R.; Liu, H.-J.; Zhang, H. Biosorption of Cd(II) by live and dead cells of bacillus cereus RC-1 isolated from cadmium-contaminated soil. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 107, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durve, A.; Naphade, S.; Bhot, A.; Varghese, J.; Chandra, N. Quantitative evaluation of heavy metal bioaccumulation by microbes. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Res. 2013, 3, 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, M.; Chirwa, N.; Molokwane, P.E. Biological Cr(VI) reduction: Microbial diversity, kkinetics and biotechnological solutions to pollution. In Biodiversity; Sofo, D.A., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 75–100. [Google Scholar]
- Benazir, J.F.; Suganthi, R.; Rajvel, D.; Pooja, P.M.; Mathithumilan, B. Bioremediation of chromium in tannery effluent by microbial consortia. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 3140–3143. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, L.; Huang, S.; Yang, Z.; Peng, B.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y. Cr (VI) remediation by indigenous bacteria in soils contaminated by chromium-containing slag. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elangovan, R.; Philip, L. Performance evaluation of various bioreactors for the removal of Cr(VI) and organic matter from industrial effluent. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 44, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Xiao, H.; Xiao, B.; Xu, W.; Gao, L.; Lin, G. Bioremediation of heavy metal contaminated aqueous solution by using red algae Porphyra leucosticta. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawale, A.M. Bioremediation of waste water from an industrial effluent system in Nigeria using pseudomonas aeruginosa: Effectiveness tested on albino rats. J. Pet. Environ. Biotechnol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadrasnia, A.; Ismail, S. Biosurfactant production by Bacillus salmalaya for lubricating oil solubilization and biodegradation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 9848–9863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadrasnia, A.; Salmah, I. Bio-enrichment of waste crude oil polluted soil: Amended with bacillus 139si and organic waste. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2014, 4, 241–245. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, S.; Dadrasnia, A. Biotechnological potential of Bacillus salmalaya 139SI: A novel strain for remediating water polluted with crude oil waste. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmah, I.; Teoh, T.C.; Ung, C.Y.; Alasil, S.M.; Omar, R. Paenibacillus hemolyticus, the first hemolytic paenibacillus with growth-promoting activities discovered. Biologia 2012, 67, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Rajesh, V.; Kumar, A.S.K.; Rajesh, N. Biosorption of cadmium using a novel bacterium isolated from an electronic industry effluent. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 235, 176–185. [Google Scholar]
- Aleem, A.; Isar, J.; Malik, A. Impact of long-term application of industrial wastewater on the emergence of resistance traits in azotobacter chroococcum isolated from rhizospheric soil. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 86, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lin, Y.; Guan, W.; Chang, J.; Xu, L.; Guo, J.; Wei, G. Biosorption of Zn(II) by live and dead cells of streptomyces ciscaucasicus strain ccnwhx 72-14. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, A.A.; Khedr, S.A.; Elkholy, S.A. Adsorption of chromium ion (VI) by acid activated carbon. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 27, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmorsi, T.M.; Mohamed, Z.H.; Shopak, W.; Ismaiel, A.M. Kinetic and equilibrium isotherms studies of adsorption of Pb(II) from water onto natural adsorbent. J. Environ. Prot. 2014, 5, 1667–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febrianto, J.; Kosasih, A.N.; Sunarso, J.; Ju, Y.-H.; Indraswati, N.; Ismadji, S. Equilibrium and kinetic studies in adsorption of heavy metals using biosorbent: A summary of recent studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 616–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Ghani, N.T.; El-Chaghab, G.A. Biosorption for metal ions removal from aqueous solutions: A review of recent studies. Int. J. Latest Res. Sci. Technol. 2014, 3, 24–42. [Google Scholar]
- Rivas, B.L.; Villegas, S.; Ruf, B.; Peric, I. Removal of metal ions with impact on the environment by water-insoluble functional copolymers: Synthesis and metal ion uptake properties. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2007, 52, 1164–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, M.M.; El-Desoky, H.S.; El-Moselhy, K.M.; Amer, A.; Abou El-Naga, E.H.; Mohamedein, L.I.; Al-Prol, A.E. Removal of cadmium from aqueous solution using marine green algae, Ulva lactuca. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2014, 40, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomina, M.; Gadd, G.M. Biosorption: Current perspectives on concept, definition and application. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, S.; Hashim, M.A.; Gupta, B.S. Adsorption of Ni(SO4) on malaysian rubber-wood ash. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 72, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Pal, A.; Singh, J.; Garg, S.; Bala, M.; Vyas, A.; Khasa, Y.P.; Pachour, U.C. Removal of chromium from water effluent by adsorption onto vetiveria zizanioides and anabaena species. Nat. Sci. 2013, 5, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- WIierzba, S. Biosorption of copper(II)by live and dead cells of yarrowia lipolytica. Ecol. Chem. Eng. A 2013, 20, 875–883. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.S.; Kirthinka, K. Equilibrium and kinetic study of adsorption of nickel from aqueous solution onto bael tree leaf powder. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2009, 4, 351–363. [Google Scholar]
- Delle Sitea, A. Factors affecting sorption of organic compounds in natural sorbentõ water systems and sorption coefficients for selected pollutants. A review. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 2001, 30, 188–439. [Google Scholar]
- Dmytryk, A.; Saeid, A.; Chojnacka, K. Biosorption of microelements by spirulina: Towards technology of mineral feed supplements. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, A.K.; Patel, R.K.; Mahapatra, S.S.; Mishra, P.C. Biosorption of arsenic(III) from aqueous solution by living cells of Bacillus cereus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 1281–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şahin, Y.; Öztürk, A. Biosorption of chromium(VI) ions from aqueous solution by the Bacillus thuringiensis thuringiensis. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 1895–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, M.W.; Miller, C.D.; Dimkpa, C.O.; Anderson, A.J.; McLean, J.E. Defining the surface adsorption and internalization of copper and cadmium in a soil bacterium, Pseudomonas putida. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Mohamad, O.; Wei, G. Bioaccumulation characterization of zinc and cadmium by streptomyces zinciresistens, a novel actinomycete. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 77, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allievi, M.C.; Sabbione, F.; Prado-Acosta, M.; Palomino, M.M.; Ruzal, S.M.; Sanchez-Rivas, C. Metal biosorption by surface-layer proteins from bacillus species. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 21, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussavi, G.; Barikbin, B. Biosorption of chromium(VI) from industrial wastewater onto pistachio hull waste biomass. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran Din, M.; Latif Mirza, M.; Ata, S.; Athar, M.; Ul Mohsin, I. Thermodynamics of biosorption for removal of Co(II) ions by an efficient and ecofriendly biosorbent (Saccharum bengalense): Kinetics and isotherm modeling. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, X.W.; Sethu, V.S.; Andresen, J.M.; Sivakumar, M. Copper(II) ion removal from aqueous solutions using biosorption technology: Thermodynamic and sem–edx studies. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2013, 15, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, L.; Dussan, J. Biosorption and bioaccumulation of heavy metals on dead and living biomass of Bacillus sphaericus. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 713–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Li, X.; Xu, W.; Fan, T. Kinetic and equilibrium studies of Cr(VI) biosorption by dead Bacillus licheniformis biomass. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 23, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedighi, M.; Ghasemi, M.; Hassan, S.A.; Daud, W.; Ismail, M.; Abdallah, E. Process optimization of batch biosorption of lead using Lactobacillius bulgaricus in an aqueous phase system using response surface methodology. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dadrasnia, A.; Chuan Wei, K.S.; Shahsavari, N.; Azirun, M.S.; Ismail, S. Biosorption Potential of Bacillus salmalaya Strain 139SI for Removal of Cr(VI) from Aqueous Solution. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 15321-15338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph121214985
Dadrasnia A, Chuan Wei KS, Shahsavari N, Azirun MS, Ismail S. Biosorption Potential of Bacillus salmalaya Strain 139SI for Removal of Cr(VI) from Aqueous Solution. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2015; 12(12):15321-15338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph121214985
Chicago/Turabian StyleDadrasnia, Arezoo, Kelvin Swee Chuan Wei, Nasser Shahsavari, Mohd Sofian Azirun, and Salmah Ismail. 2015. "Biosorption Potential of Bacillus salmalaya Strain 139SI for Removal of Cr(VI) from Aqueous Solution" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 12, no. 12: 15321-15338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph121214985
APA StyleDadrasnia, A., Chuan Wei, K. S., Shahsavari, N., Azirun, M. S., & Ismail, S. (2015). Biosorption Potential of Bacillus salmalaya Strain 139SI for Removal of Cr(VI) from Aqueous Solution. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 12(12), 15321-15338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph121214985






