Natural Alkaloid Compounds as Inhibitors for Alpha-Synuclein Seeded Fibril Formation and Toxicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
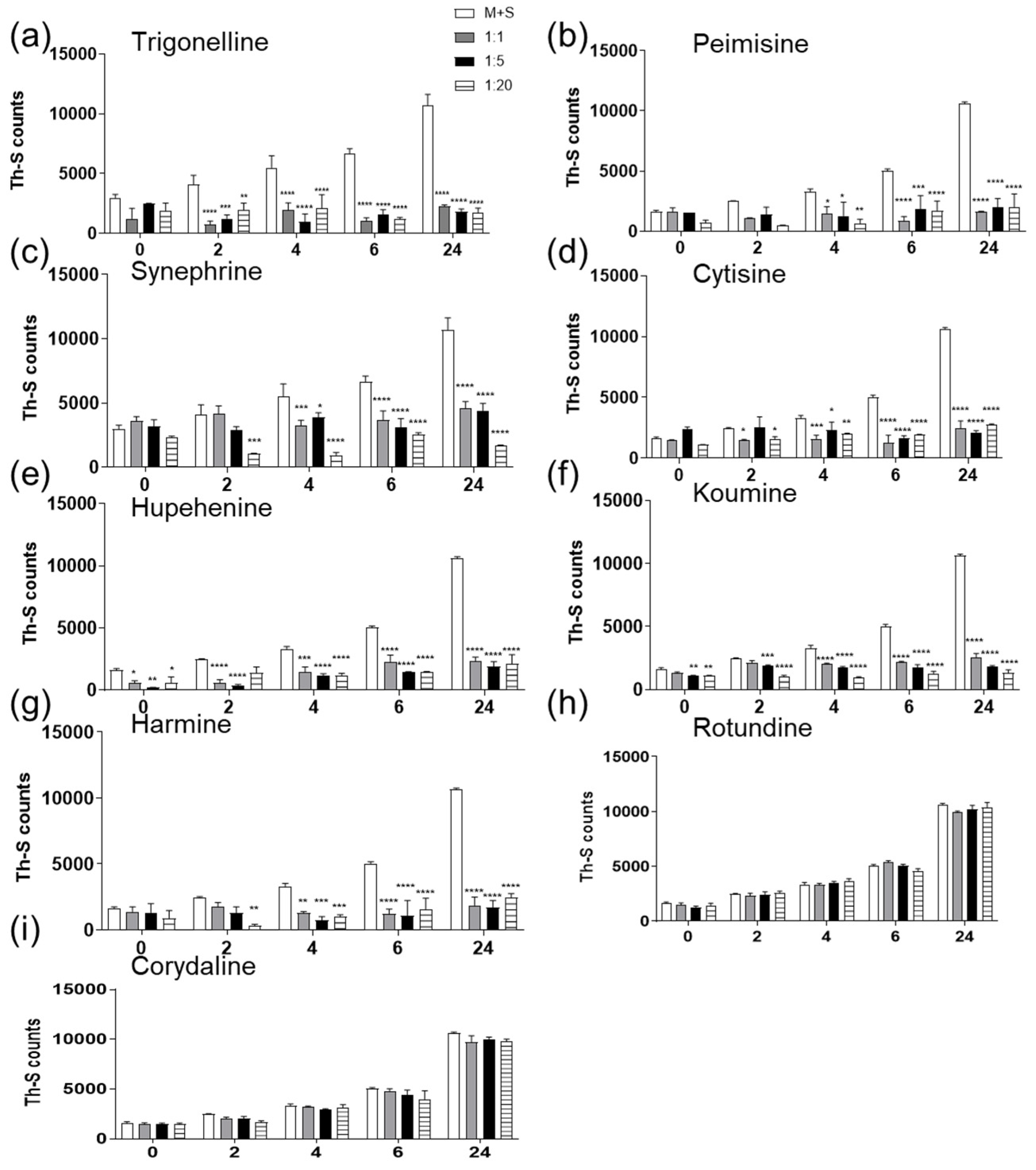
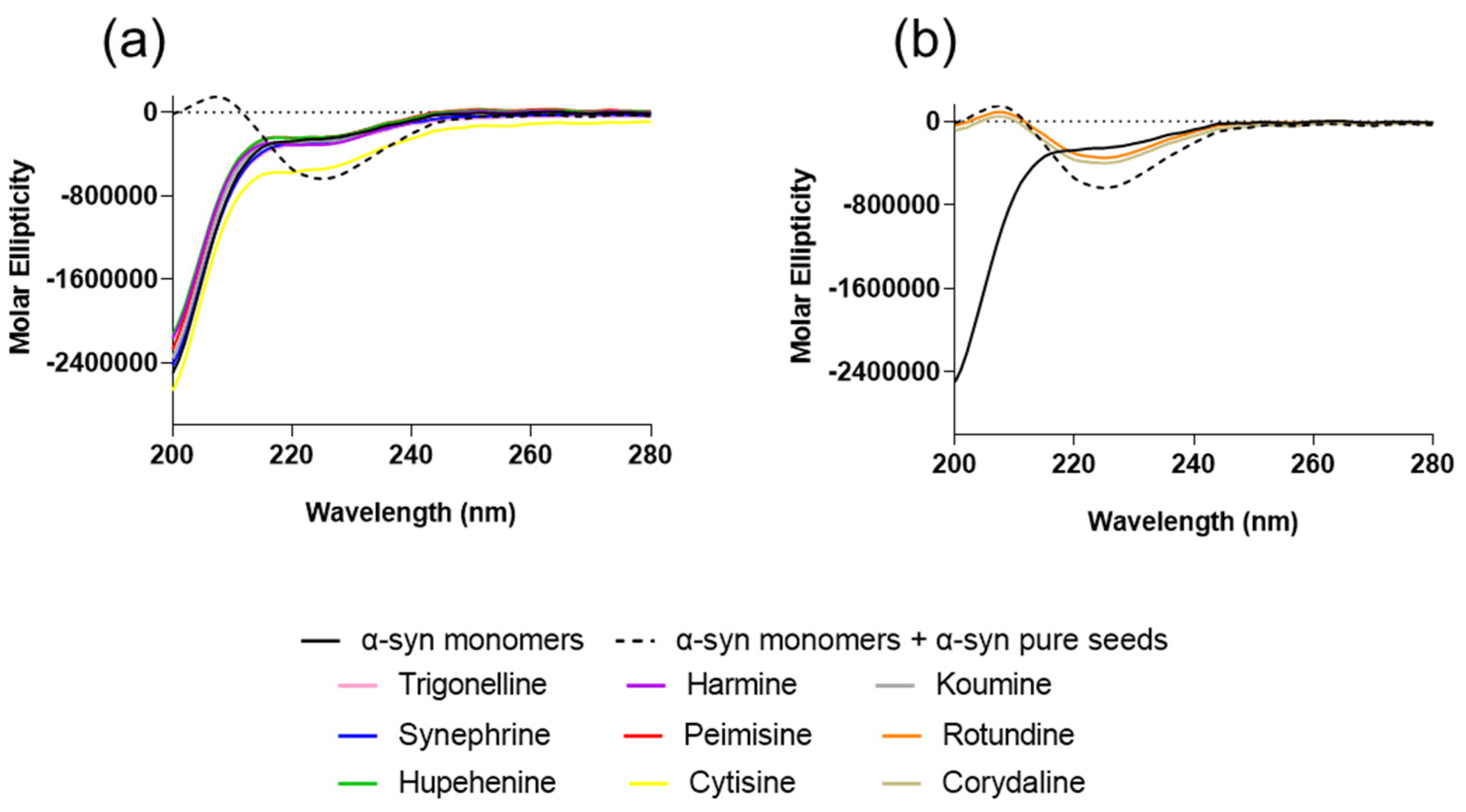
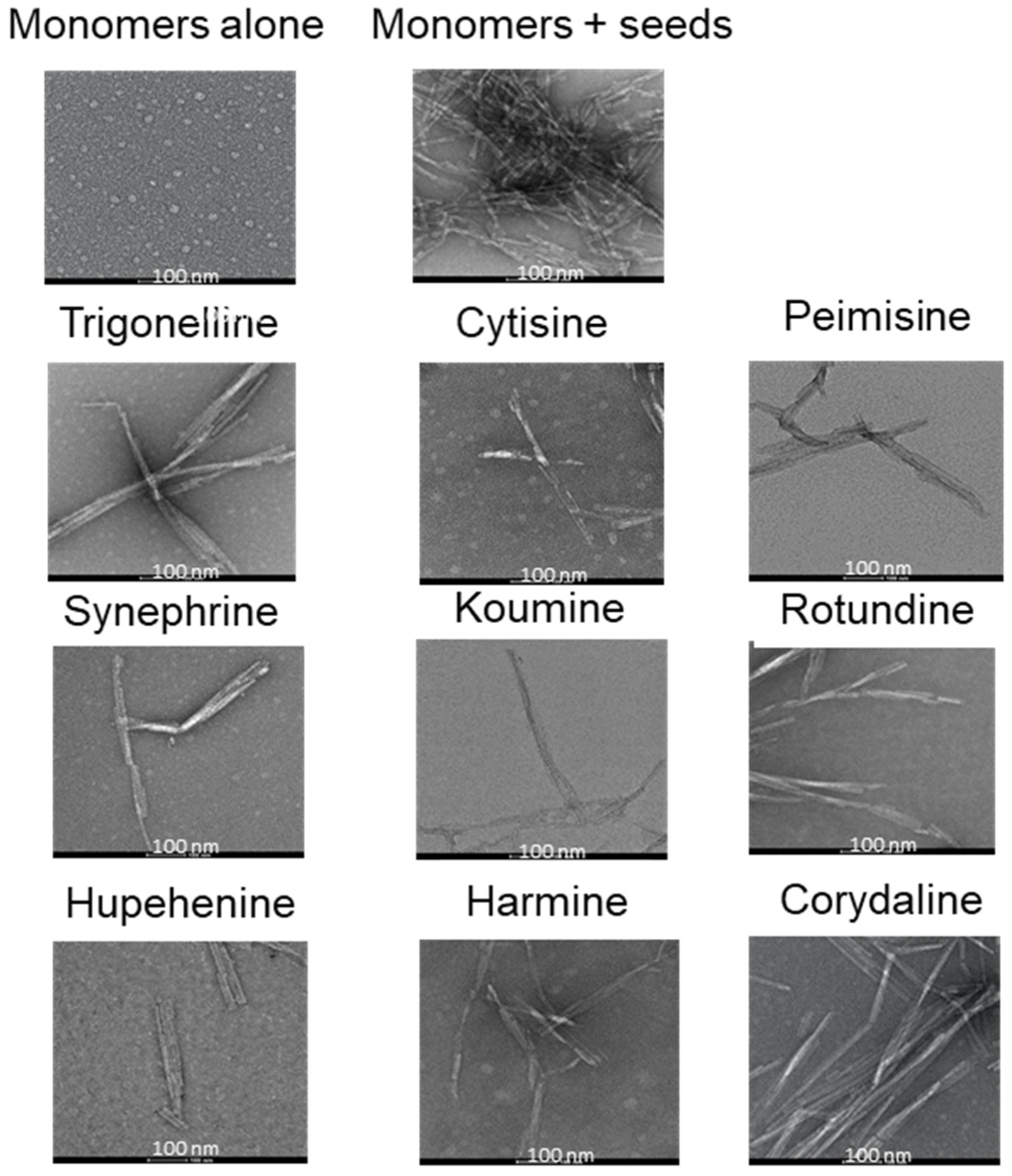
2.1. The Effect of Alkaloid Compounds on In Vitro Induced α-Syn Seeded Fibril Formation
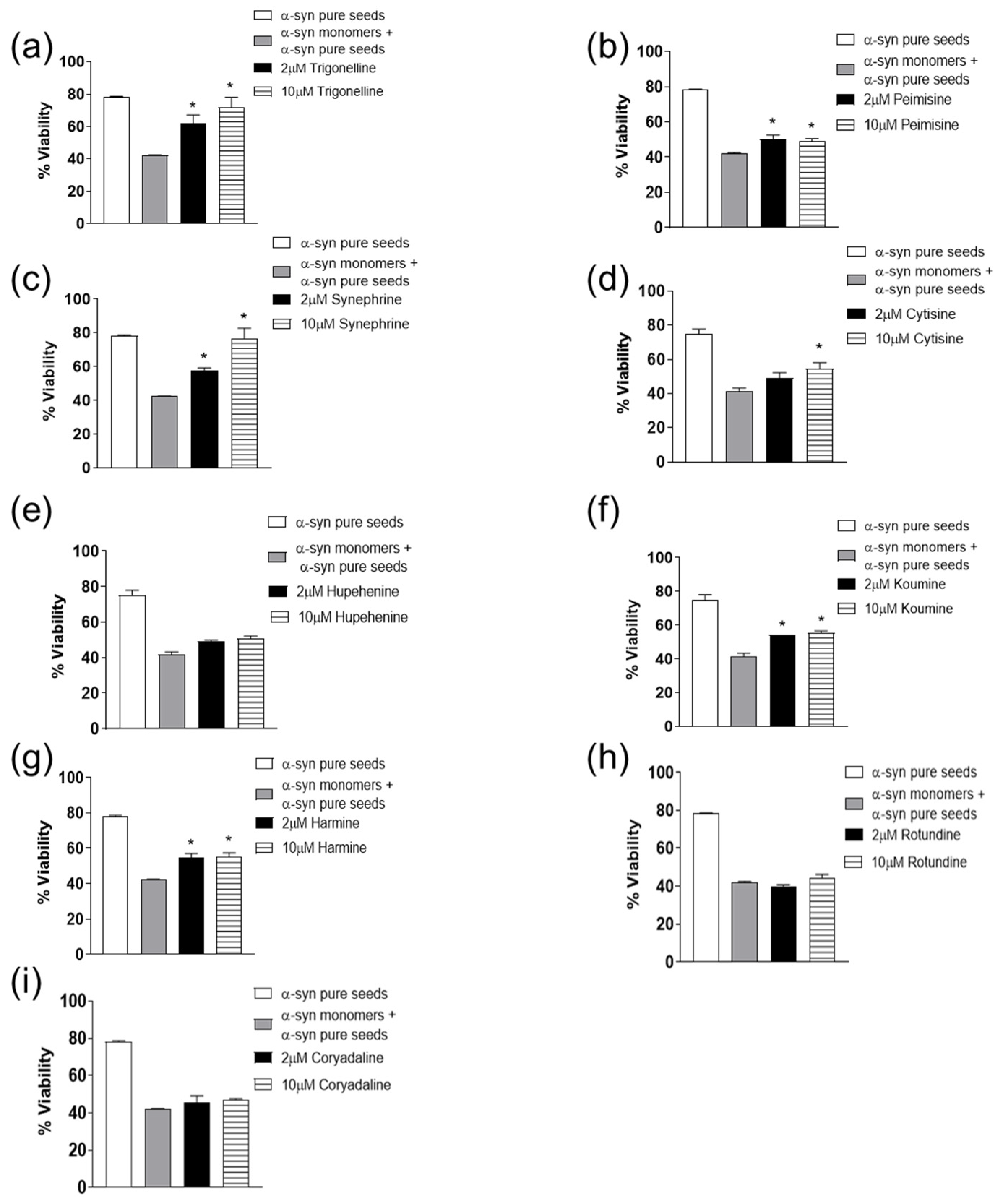
2.2. The Effect of Alkaloid Compounds on α-Syn Seeded Induced Toxicity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Recombinant α-Syn Protein
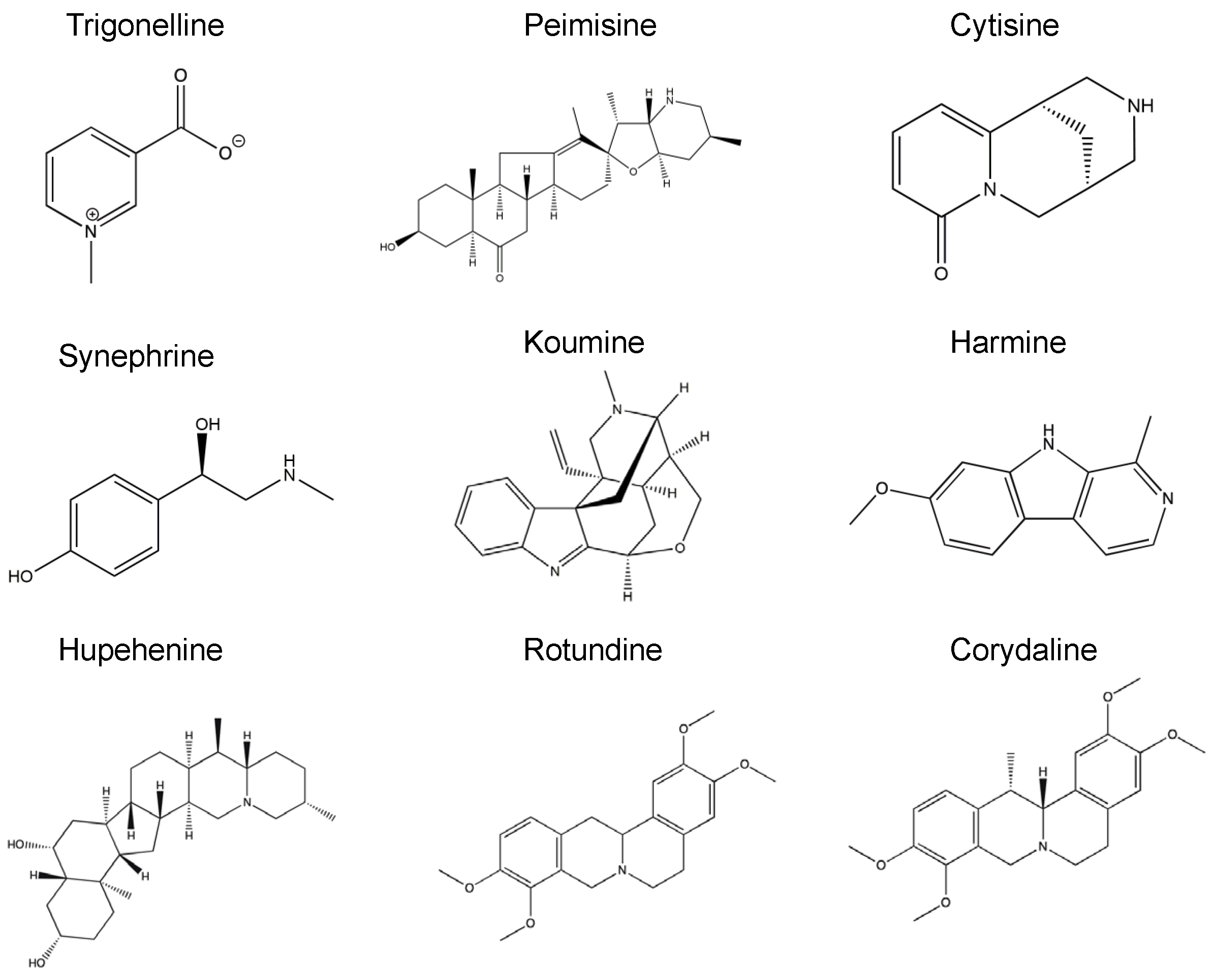
4.2. Alkaloid Compounds
4.3. Thioflavin-S (Th-S) Assay
4.4. Congo Red (CR) Binding Assay
4.5. Circular Dichroism (CD)
4.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.7. Tissue Culture of WT SH-SY5Y
4.8. Measurement of Cell Viability
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. α-Synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, K.; Kehm, V.; Carroll, J.; Zhang, B.; O’Brien, P.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M.-Y. Pathological -Synuclein Transmission Initiates Parkinson-like Neurodegeneration in Nontransgenic Mice. Science 2012, 338, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, P.; Park, H.; Baumann, M.; Dunlop, J.; Frydman, J.; Kopito, R.; McCampbell, A.; Leblanc, G.; Venkateswaran, A.; Nurmi, A.; et al. Protein misfolding in neurodegenerative diseases: Implications and strategies. Transl. Neurodegener. 2017, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strecker, K.; Schwarz, J. Parkinson’s disease: Emerging pharmacotherapy. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2008, 13, 573–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeso, J.A.; Rodríguez-Oroz, M.C.; Temiño, B.B.; Blesa, J.; Guridi, J.; Marin, C.; Rodriguez, M. Functional organization of the basal ganglia: Therapeutic implications for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, S548–S559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, J.E.; Lee, V.M.; Schmidt, M.L.; Tu, P.H.; Iwatsubo, T.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Pathobiology of the Lewy body. Adv. Neurol. 1999, 80, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Crowther, R.A.; Jakes, R.; Hasegawa, M.; Goedert, M. Alpha-Synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson’s disease and dementia with lewy bodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6469–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, M.; Spillantini, M.G.; Del Tredici, K.; Braak, H. 100 years of Lewy pathology. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinreb, P.H.; Zhen, W.; Poon, A.W.; Conway, K.A.; Lansbury, P.T., Jr. NACP, A Protein Implicated in Alzheimer’s Disease and Learning, Is Natively Unfolded. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 13709–13715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N.; Lee, H.-J.; Li, J.; Fink, A.L.; Lee, S.-J. Stabilization of Partially Folded Conformation during α-Synuclein Oligomerization in Both Purified and Cytosolic Preparations. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 43495–43498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Agnaf, O.M.; Jakes, R.; Curran, M.D.; Middleton, D.; Ingenito, R.; Bianchi, E.; Pessi, A.; Neill, D.; Wallace, A. Aggregates from mutant and wild-type alpha-synuclein proteins and NAC peptide induce apoptotic cell death in human neuroblastoma cells by formation of beta-sheet and amyloid-like filaments. FEBS Lett. 1998, 440, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.J.; Wypych, J.; Steavenson, S.; Louis, J.C.; Citron, M.; Biere, A.L. α-Synuclein Fibrillogenesis Is Nucleation-dependent. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 19509–19512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremades, N.; Cohen, S.I.; Deas, E.; Abramov, A.; Chen, A.Y.; Orte, A.; Sandal, M.; Clarke, R.; Dunne, P.; Aprile, F.A.; et al. Direct Observation of the Interconversion of Normal and Toxic Forms of α-Synuclein. Cell 2012, 149, 1048–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuda, T.; Qureshi, M.M.; Ardah, M.T.; Varghese, S.; Shehab, S.A.S.; Kasai, T.; Ishigami, N.; Tamaoka, A.; Nakagawa, M.; El-Agnaf, O.M.A. Detection of elevated levels of -synuclein oligomers in CSF from patients with Parkinson disease. Neurology 2010, 75, 1766–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Agnaf, O.M.A.; Salem, S.A.; Paleologou, K.E.; Curran, M.D.; Gibson, M.J.; Court, J.A.; Schlossmacher, M.; Allsop, D. Detection of oligomeric forms of α-synuclein protein in human plasma as a potential biomarker for Parkinson’s disease. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Agnaf, O.M.A.; Walsh, M.M.; Allsop, D. Soluble oligomers for the diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases. Lancet Neurol. 2003, 2, 461–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paleologou, K.E.; Kragh, C.L.; Mann, D.M.A.; Salem, S.A.; Al-Shami, R.; Allsop, D.; Hassan, A.H.; Jensen, P.H.; El-Agnaf, O.M.A. Detection of elevated levels of soluble -synuclein oligomers in post-mortem brain extracts from patients with dementia with Lewy bodies. Brain 2009, 132, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beitz, J.M. Parkinson s disease: A review. Front Biosci. (Schol. Ed.) 2014, S6, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, C.R.; Bengoa-Vergniory, N.; Wade-Martins, R. Targeting Alpha-Synuclein as a Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehay, B.; Bourdenx, M.; Gorry, P.; Przedborski, S.; Vila, M.; Hunot, S.; Singleton, A.; Olanow, C.W.; Merchant, K.M.; Bezard, E.; et al. Targeting α-synuclein for treatment of Parkinson’s disease: Mechanistic and therapeutic considerations. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanis, L.; Emmanouilidou, E.; Pantazopoulou, M.; Kirik, D.; Vekrellis, K.; Tofaris, G.K. How is alpha-synuclein cleared from the cell? J. Neurochem. 2019, 150, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaikath, N.N.; Hmila, I.; Gupta, V.; Erskine, D.; Ingelsson, M.; El-Agnaf, O.M.A. Antibodies against alpha-synuclein: Tools and therapies. J. Neurochem. 2019, 150, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.J. Mechanism of Anti-α-Synuclein Immunotherapy. J. Mov. Disord. 2016, 9, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheruvara, H.; Allen-Baume, V.L.; Kad, N.M.; Mason, J.M. Intracellular Screening of a Peptide Library to Derive a Potent Peptide Inhibitor of α-Synuclein Aggregation. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 7426–7435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huggins, K.N.; Bisaglia, M.; Bubacco, L.; Tatarek-Nossol, M.; Kapurniotu, A.; Andersen, N.H. Designed Hairpin Peptides Interfere with Amyloidogenesis Pathways: Fibril Formation and Cytotoxicity Inhibition, Interception of the Preamyloid State. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 8202–8212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, J.M.; Fairlie, D.P. Toward peptide-based inhibitors as therapies for Parkinson’s disease. Futur. Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 2103–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torpey, J.H.; Meade, R.M.; Mistry, R.; Mason, J.M.; Madine, J. Insights Into Peptide Inhibition of Alpha-Synuclein Aggregation. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 561462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amer, D.A.; Irvine, G.B.; El-Agnaf, O.M.A. Inhibitors of α-synuclein oligomerization and toxicity: A future therapeutic strategy for Parkinson’s disease and related disorders. Exp. Brain Res. 2006, 173, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Agnaf, O.M.A.; Paleologou, K.E.; Greer, B.; Abogrein, A.M.; King, J.E.; Salem, S.A.; Fullwood, N.J.; Benson, F.E.; Hewitt, R.; Ford, K.J.; et al. A strategy for designing inhibitors of α -synuclein aggregation and toxicity as a novel treatment for Parkinson’s disease and related disorders. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1315–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangwan, S.; Sahay, S.; Murray, K.A.; Morgan, S.; Guenther, E.L.; Jiang, L.; Williams, C.K.; Vinters, H.V.; Goedert, M.; Eisenberg, D.S. Inhibition of synucleinopathic seeding by rationally designed inhibitors. eLife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Gong, K.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tang, P.; Zhang, X.; Gong, Y. Huperzine A promotes hippocampal neurogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Brain Res. 2013, 1506, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, L.; Zhou, S. Trigonelline: A Plant Alkaloid with Therapeutic Potential for Diabetes and Central Nervous System Disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 3523–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohda, C.; Kuboyama, T.; Komatsu, K. Search for Natural Products Related to Regeneration of the Neuronal Network. Neurosignals 2005, 14, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferger, B.; Spratt, C.; Teismann, P.; Seitz, G.; Kuschinsky, K. Effects of cytisine on hydroxyl radicals in vitro and MPTP-induced dopamine depletion in vivo. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 360, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sha, R.; Wang, K.; Li, H.; Yan, B.; Zhou, N. Protective effects of tetrahydropalmatine against ketamine-induced learning and memory injury via antioxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic mechanisms in mice. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 6873–6880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.-Z.; Zhou, H.-F.; Yuan, N.-N.; Wu, M.-Y.; Lee, S.M.-Y.; Ren, J.-Y.; Su, H.; Lu, J.-J.; Chen, X.-P.; Li, M.; et al. Natural alkaloid harmine promotes degradation of alpha-synuclein via PKA-mediated ubiquitin-proteasome system activation. Phytomedicine 2019, 61, 152842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Liang, Z.; Yi, J.; Chen, X.; Li, R.; Wu, J.; Sun, Z. Koumine Promotes ROS Production to Suppress Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Proliferation Via NF-κB and ERK/p38 MAPK Signaling. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, B.-J.; Xu, Y.; Jin, G.L.; Liu, M.; Yang, J.; Yu, C.X. Analgesic effects and pharmacologic mechanisms of the Gelsemium alkaloid koumine on a rat model of postoperative pain. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, G.; Rasul, A.; Anwar, H.; Aziz, N.; Razzaq, A.; Wei, W.; Ali, M.; Li, J.; Li, X. Role of Plant Derived Alkaloids and Their Mechanism in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushnie, T.T.; Cushnie, B.; Lamb, A.J. Alkaloids: An overview of their antibacterial, antibiotic-enhancing and antivirulence activities. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2014, 44, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Y.P.; Or, T.C.; Ip, N.Y. Plant alkaloids as drug leads for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. Int. 2015, 89, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, A.K.; Dandapat, J.; Dash, U.C.; Kanhar, S. Features and outcomes of drugs for combination therapy as multi-targets strategy to combat Alzheimer’s disease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 215, 42–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.; Giunta, B.; Bickford, P.C.; Fountain, M.; Tan, J.; Shytle, R.D. Nanolipidic particles improve the bioavailability and α-secretase inducing ability of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 389, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, R.; Singh, D.; Prakash, A.; Mishra, N. Development, characterization and nasal delivery of rosmarinic acid-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for the effective management of Huntington’s disease. Drug Deliv. 2013, 22, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Prado-Audelo, M.L.; Caballero-Florán, I.H.; Meza-Toledo, J.A.; Mendoza-Muñoz, N.; González-Torres, M.; Florán, B.; Cortés, H.; Leyva-Gómez, G. Formulations of Curcumin Nanoparticles for Brain Diseases. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Lankatillake, C.; Dias, D.A.; Docea, A.O.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Lobine, D.; Chazot, P.L.; Kurt, B.; Tumer, T.B.; Moreira, A.C.; et al. Impact of Natural Compounds on Neurodegenerative Disorders: From Preclinical to Pharmacotherapeutics. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, C.; Angot, E.; Bergström, A.-L.; Steiner, J.A.; Pieri, L.; Paul, G.; Outeiro, T.F.; Melki, R.; Kallunki, P.; Fog, K.; et al. α-Synuclein propagates from mouse brain to grafted dopaminergic neurons and seeds aggregation in cultured human cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.R.; Tay, K.C.; Su, Y.X.; Wong, C.K.; Tan, W.N.; Khaw, K.Y. Potential of Naturally Derived Alkaloids as Multi-Targeted Therapeutic Agents for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules 2021, 26, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasco, D.; Vicidomini, C.; Krupa, P.; Cioffi, F.; Huy, P.D.Q.; Li, M.S.; Florio, D.; Broersen, K.; De Pandis, M.F.; Roviello, G.N. Plant isoquinoline alkaloids as potential neurodrugs: A comparative study of the effects of benzo[c]phenanthridine and berberine-based compounds on β-amyloid aggregation. Chem. Interact. 2021, 334, 109300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrett, J.T.; Lansbury, P.T., Jr. Seeding “one-dimensional crystallization” of amyloid: A pathogenic mechanism in Alzheimer’s disease and scrapie? Cell 1993, 73, 1055–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, J.D.; Lansbury, P.T., Jr. Models of Amyloid Seeding in Alzheimer’s Disease and Scrapie: Mechanistic Truths and Physiological Consequences of the Time-Dependent Solubility of Amyloid Proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1997, 66, 385–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpicelli-Daley, L.A.; Luk, K.; Patel, T.P.; Tanik, S.A.; Riddle, D.M.; Stieber, A.; Meaney, D.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M.-Y. Exogenous α-Synuclein Fibrils Induce Lewy Body Pathology Leading to Synaptic Dysfunction and Neuron Death. Neuron 2011, 72, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahul-Mellier, A.L.; Vercruysse, F.; Maco, B.; Ait-Bouziad, N.; De Roo, M.; Muller, D.; Lashuel, H.A. Fibril growth and seeding capacity play key roles in α-synuclein-mediated apoptotic cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 2107–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.C.; Krainc, D. α-synuclein toxicity in neurodegeneration: Mechanism and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Salim, S.; Hmila, I.; Vaikath, N.N.; Sudhakaran, I.P.; Ghanem, S.S.; Majbour, N.K.; Abdulla, S.A.; Emara, M.M.; Abdesselem, H.B.; et al. Fibrillar form of α-synuclein-specific scFv antibody inhibits α-synuclein seeds induced aggregation and toxicity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorsey, E.R.; Constantinescu, R.; Thompson, J.P.; Biglan, K.M.; Holloway, R.G.; Kieburtz, K.; Marshall, F.J.; Ravina, B.M.; Schifitto, G.; Siderowf, A.; et al. Projected number of people with Parkinson disease in the most populous nations, 2005 through. Neurololgy 2006, 68, 384–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, M. Aggregation of alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies of sporadic Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 152, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Irvine, G.B.; El-Agnaf, O.M.; Shankar, G.M.; Walsh, D.M. Protein Aggregation in the Brain: The Molecular Basis for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases. Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldman, B.A.; Wijn, A.M.; Knoers, N.; Praamstra, P.; Horstink, M.W. Genetic and environmental risk factors in Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 1998, 100, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidler, A.; Hellenbrand, W.; Robra, B.-P.; Vieregge, P.; Nischan, P.; Joerg, J.; Oertel, W.H.; Ulm, G.; Schneider, E. Possible environmental, occupational, and other etiologic factors for Parkinson’s disease: A case-control study in Germany. Neurology 1996, 46, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardah, M.T.; Paleologou, K.E.; Lv, G.; Menon, S.A.; Khair, S.B.A.; Lu, J.; Safieh-Garabedian, B.; Al-Hayani, A.A.; Eliezer, D.; Li, M.; et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibits fibrillation and toxicity of alpha-synuclein and disaggregates preformed fibrils. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 74, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Ardah, M.T.; Durairajan, S.S.K.; Liu, L.-F.; Xie, L.-X.; Fong, W.D.; Hasan, M.Y.; Huang, J.-D.; El-Agnaf, O.M.A.; Li, M. Baicalein Inhibits Formation of α-Synuclein Oligomers within Living Cells and Prevents Aβ Peptide Fibrillation and Oligomerisation. ChemBioChem 2011, 12, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Findeis, M.A. Approaches to discovery and characterization of inhibitors of amyloid beta-peptide polymerization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1502, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardah, M.T.; Ghanem, S.S.; Abdulla, S.A.; Lv, G.; Emara, M.M.; Paleologou, K.E.; Vaikath, N.N.; Lu, J.-H.; Li, M.; Vekrellis, K.; et al. Inhibition of alpha-synuclein seeded fibril formation and toxicity by herbal medicinal extracts. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, P.J.; Howes, M.-J. Natural Products and Derivatives Affecting Neurotransmission Relevant to Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease. Neurosignals 2005, 14, 6–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.-Q.; Lu, X.-Z.; Liang, X.-B.; Zhou, H.-F.; Xue, B.; Liu, X.-Y.; Niu, D.-B.; Han, J.-S.; Wang, X.-M. Triptolide, a Chinese herbal extract, protects dopaminergic neurons from inflammation-mediated damage through inhibition of microglial activation. J. Neuroimmunol. 2004, 148, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohda, C.; Nakamura, N.; Komatsu, K.; Hattori, M. Trigonelline-Induced Neurite Outgrowth in Human Neuroblastoma SK-N-SH Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 22, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahanik-Babaei, J.; Baluchnejadmojarad, T.; Nikbakht, F.; Roghani, M. Trigonelline protects hippocampus against intracerebral Aβ(1–40) as a model of Alzheimer’s disease in the rat: Insights into underlying mechanisms. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 34, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, V.; Bodhankar, S.L.; Mohan, V.; Thakurdesai, P.A. Neurobehavioral assessment of hydroalcoholic extract of Trigonella foenum-graecumseeds in rodent models of Parkinson’s disease. Pharm. Biol. 2013, 51, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reavill, C.; Walther, B.; Stolerman, I.; Testa, B. Behavioural and pharmacokinetic studies on nicotine, cytisine and lobeline. Neuropharmacology 1990, 29, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Meng, L.; Zou, N.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Huang, L.; Cheng, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Wang, C. Mechanism-based pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamics studies of harmine and harmaline on neurotransmitters regulatory effects in healthy rats: Challenge on monoamine oxidase and acetylcholinesterase inhibition. Phytomedicine 2019, 62, 152967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Wu, H.; Wei, Y.; Liu, W.; Huang, F.; Shi, H.; Zhang, B.; Wu, X.; Wang, C. Effects of harmine, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, on spatial learning and memory of APP/PS1 transgenic mice and scopolamine-induced memory impairment mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 768, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieri, L.; Madiona, K.; Bousset, L.; Melki, R. Fibrillar α-Synuclein and Huntingtin Exon 1 Assemblies Are Toxic to the Cells. Biophys. J. 2012, 102, 2894–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, N.; Soragni, A.; Rabe, M.; Verdes, D.; Liverani, E.; Handschin, S.; Riek, R.; Seeger, S. Mechanism of Membrane Interaction and Disruption by α-Synuclein. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 19366–19375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, N.; Mishra, S.; Jain, M.K.; Surolia, A.; Gupta, S. Curcumin Pyrazole and its derivative (N-(3-Nitrophenylpyrazole) Curcumin inhibit aggregation, disrupt fibrils and modulate toxicity of Wild type and Mutant α-Synuclein. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perni, M.; Galvagnion, C.; Maltsev, A.; Meisl, G.; Mueller, M.B.D.; Challa, P.K.; Kirkegaard, J.B.; Flagmeier, P.; Cohen, S.I.A.; Cascella, R.; et al. A natural product inhibits the initiation of α-synuclein aggregation and suppresses its toxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E1009–E1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaikath, N.N.; Erskine, D.; Morris, C.M.; Majbour, N.K.; Vekrellis, K.; Li, J.; El-Agnaf, O.M.A. Heterogeneity in α-synuclein subtypes and their expression in cortical brain tissue lysates from Lewy body diseases and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2018, 45, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghanem, S.S.; Fayed, H.S.; Zhu, Q.; Lu, J.-H.; Vaikath, N.N.; Ponraj, J.; Mansour, S.; El-Agnaf, O.M.A. Natural Alkaloid Compounds as Inhibitors for Alpha-Synuclein Seeded Fibril Formation and Toxicity. Molecules 2021, 26, 3736. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123736
Ghanem SS, Fayed HS, Zhu Q, Lu J-H, Vaikath NN, Ponraj J, Mansour S, El-Agnaf OMA. Natural Alkaloid Compounds as Inhibitors for Alpha-Synuclein Seeded Fibril Formation and Toxicity. Molecules. 2021; 26(12):3736. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123736
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhanem, Simona S., Hend S. Fayed, Qi Zhu, Jia-Hong Lu, Nishant N. Vaikath, Janarthanan Ponraj, Said Mansour, and Omar M. A. El-Agnaf. 2021. "Natural Alkaloid Compounds as Inhibitors for Alpha-Synuclein Seeded Fibril Formation and Toxicity" Molecules 26, no. 12: 3736. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123736
APA StyleGhanem, S. S., Fayed, H. S., Zhu, Q., Lu, J.-H., Vaikath, N. N., Ponraj, J., Mansour, S., & El-Agnaf, O. M. A. (2021). Natural Alkaloid Compounds as Inhibitors for Alpha-Synuclein Seeded Fibril Formation and Toxicity. Molecules, 26(12), 3736. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123736






