Optimum Criteria on the Performance of an Irreversible Braysson Heat Engine Based on the new Thermoeconomic Approach
Abstract
:Introduction
An Irreversible Braysson Cycle

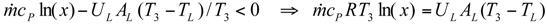
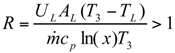
The Expressions of Several Parameters
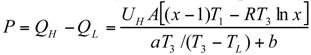
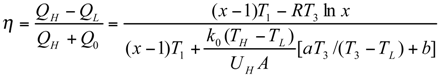
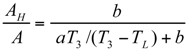
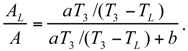
The Thermoeconomic Objective Function
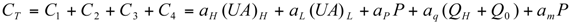
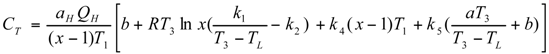
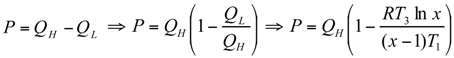
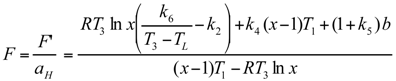
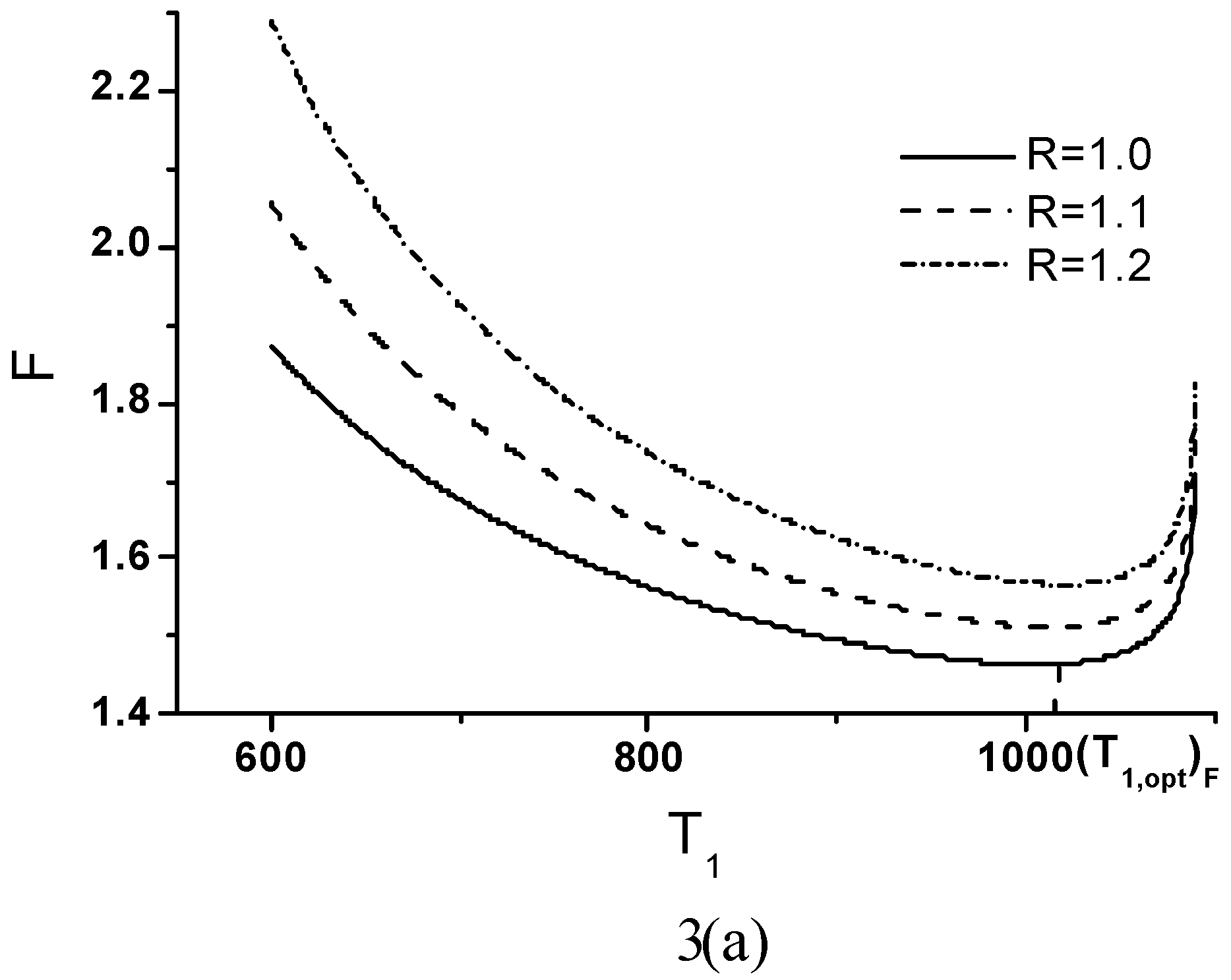
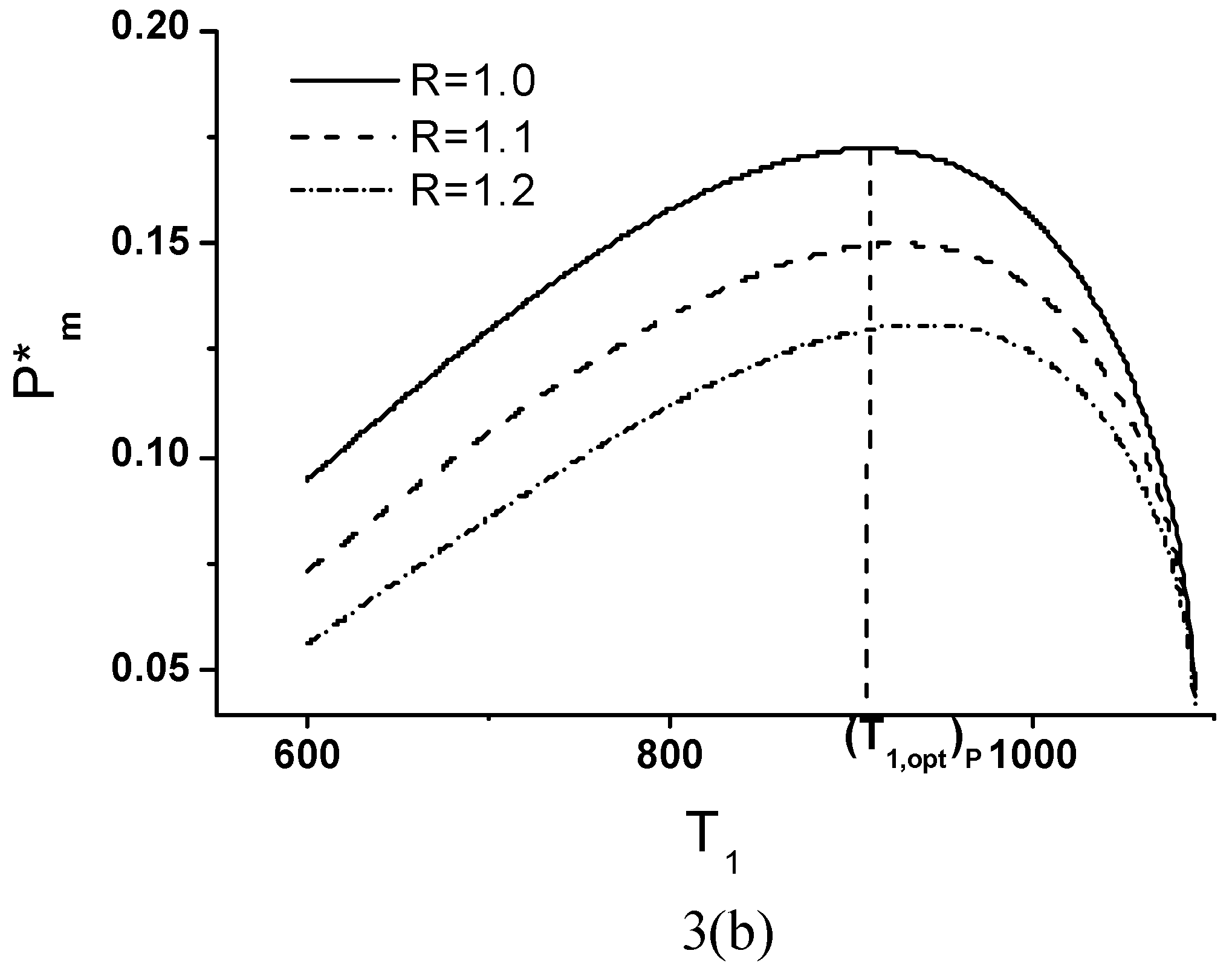
Optimal Performance Characteristics
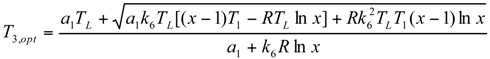
Minimum Value of Objective Function
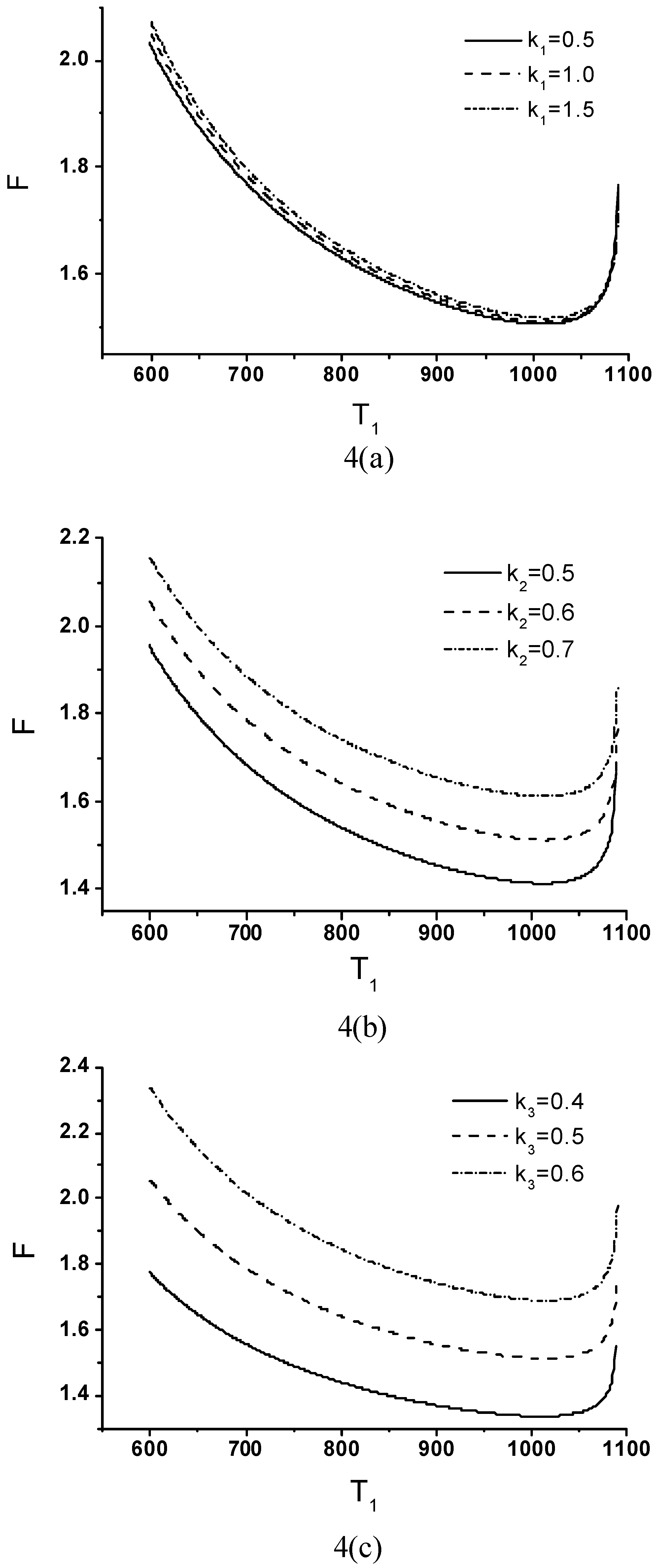
Effects of Economic Parameters
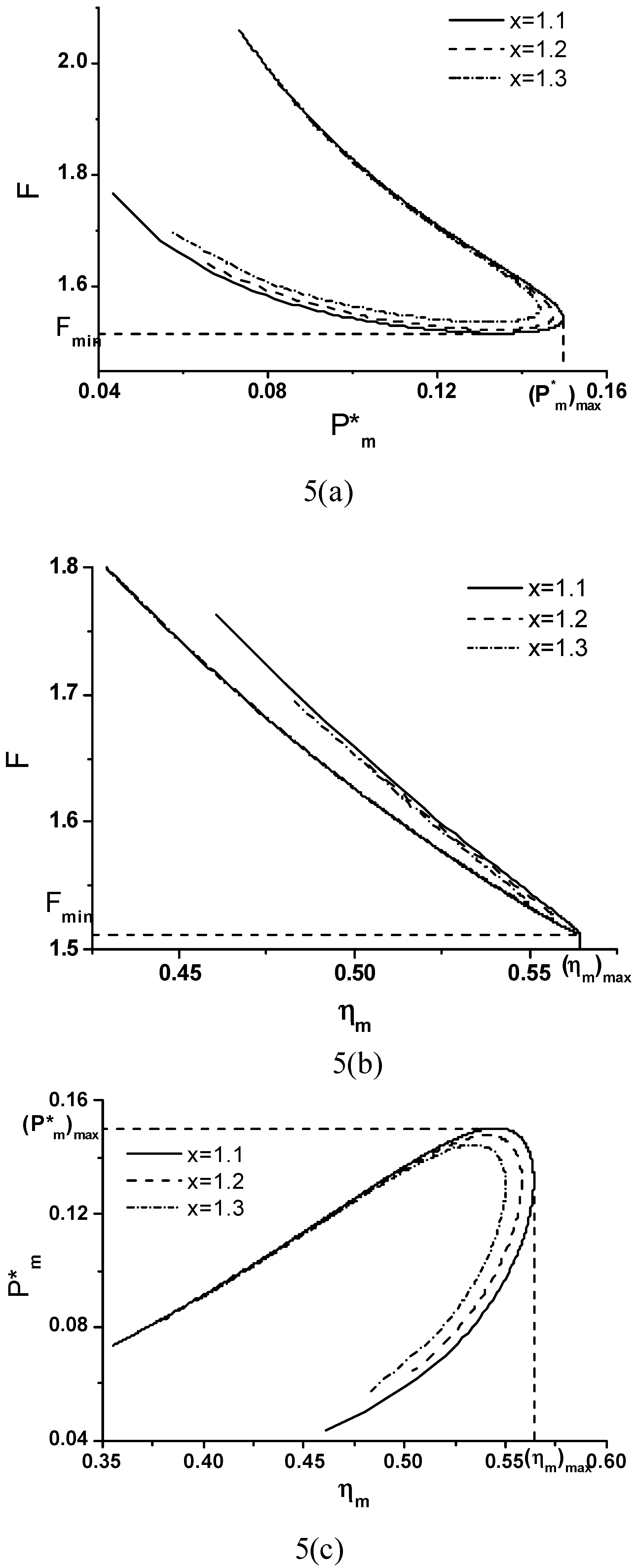
Objective Function, Corresponding Power Output and Thermal Efficiency
A Special Case
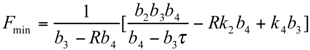
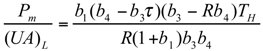
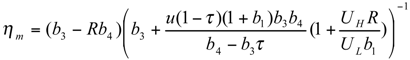
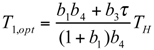
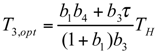
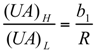
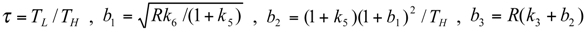 and
and 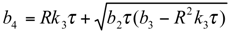
Conclusions
Acknowledgement
Nomenclature
| NCU = National Currency Unit | |
| A = Area (m2) | P = Power output (kW) |
| a’s = Cost parameters | P* =Dimensionless power output |
| cp = Specific heat (kJ/kg-K) | Q = Heat transfer rates (kW) |
| C’s = Cost parameters | R = Internal irreversibility parameter |
| CT = Total cost (defined in Eq.10) | S = Entropy (kJ/K) |
| F = Objective function (defined in Eq.12) | T = Temperature (K) |
| U = Overall heat transfer coefficient (kW/m2-KL) = Sink/cold -side | |
| x = Isobaric temperature ratio | m=Related to the minimum objective |
| 1, 2, 3, 4 = State points | function/maintenance |
| Greeks | max = Maximum |
| η = Efficiency | min = Minimum |
| Subscripts | opt = Optimum |
| a = Ambient | p = Related to power production cost |
| c = Compressor | q = Related to input energy rate cost |
| H = Heat source/hot -side | |
References
- Frost, T. H.; Anderson, A.; Agnew, B. A hybrid gas turbine cycle (Brayton/Ericsson): an alternative to conventional combined gas and steam turbine power plant. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A 1997, 211, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Chen, L.; Sun, F.; Wu, C. Power, power density and efficiency optimization of an endoreversible Brays son cycle. Exergy 2002, 2, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Chen, L.; Sun, F.; Wu, C. Powers and efficiency performance of an endoreversible Braysson cycle. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2002, 41, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Kiang, R. S. Work and power optimization of a finite time Brayton cycle. Int. J. Ambient Energy 1990, 11, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Kiang, R. S. Power performance of a nonisentropic Brayton cycle, J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 1991, 113, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leff, H. S. Thermal efficiency at maximum power output: New results for old engines. Am. J. Phys. 1987, 55, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, O. M.; Klein, S. A.; Mitchell, J. W. Optimum heat power cycles for specified boundary conditions. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 1991, 113, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C. Specific power bounds of real heat engines. Energy Convers. Mgmt. 1991, 31, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C. Power optimization of an endoreversible Brayton gas heat engine. Energy Convers. Mgmt. 1991, 31, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, L.; Sun, F. Performance of a regenerative Brayton heat engine. Energy 1996, 21, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.Y.; Chen, C.K. Power optimization of an endoreversible regenerative Brayton cycle. Energy 1996, 21, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, F.; Wu, C.; Kiang, R. L. Theoretical analysis of the performance of a regenerative closed Brayton cycle with internal irreversibilities. Energy Convers. Mgmt. 1997, 38, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radcenco, V.; Vargas, J. V. C.; Bejan, A. Thermodynamic optimization of a gas turbine power plant with pressure drop irreversibilities. J. Energy Res. Tech. 1998, 129, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, D. A. Analysis of a combined law power optimized open Joule -Brayton heat engine cycle with a finite interactive heat source. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 1999, 32, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, B.; Kodal, A.; Kaya, S. S. A comparative performance analysis of irreversible regenerative reheating Joule-Brayton heat engine under maximum power density and maximum power conditions. J. Phys D: Appl. Phys. 1998, 31, 2125–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roco, J. M. M.; Velasco, S.; Medina, A.; Hernandez, A. C. Optimum performance of a regenerative Brayton thermal cycle. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 82, 2735–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feidt, M. Optimization of Brayton cycle engine in contract with fluid thermal capacities. Rev. Gen. Them. 1996, 35, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ni, N.; Cheng, G.; Sun, F.; Wu, C. Performance of a real closed regenerated Brayton cycle via method of finite time thermodynamics. Int. J. Ambient Energy 1999, 20, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C. Y.; Chen, C. K. Power optimization of an irreversible Brayton heat engine. Energy Sources 1997, 19, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, D. A.; Wu, C. A combined power optimized Joule -Brayton heat engine cycle with fixed thermal reservoir. Int. J. Power and Energy 2000, 20, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, T. H.; Agnew, B.; Anderson, A. Optimizations for Brayton-Joule gas turbine cycles. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A: J. Power and Energy 1992, 206, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horlock, J. H.; Woods, W. A. Determination of the optimum performance of gas turbine. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C: J. Mech. Sci. 2000, 214, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, S. C.; Tyagi, S. K. Finite time thermodynamic analysis of an irreversible regenerative closed Brayton cycle heat engine. Int. J. Solar Energy 2002, 22, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, D. A.; Wu, C. Power limit of an endoreversible Ericsson cycle with regeneration. Energy Convers. Mgmt. 1996, 37, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, D. A.; Wu, C. Finite time power limit for solar-radiant Ericsson engines in space applications. Appl. Therm. Eng. 1998, 18, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Schouten, J. A. The comprehensive influence of several major irreversibilities on the performance of an Ericsson heat engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 1999, 19, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S. K. Application of finite time thermodynamics and second law evaluation of thermal energy conversion systems. Ph. D. Thesis, CCS. University, Meerut, India, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik, S. C.; Kumar, S. Finite time thermodynamic evaluation of irreversible Ericsson and Stirling heat engines. Energy Convers. Mgmt. 2001, 42, 295–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curzon, F. L.; Ahlborn, B. Efficiency of Carnot engine at maximum power output. Am. J. Phys. 1975, 19, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejan, A. Theory of heat transfer irreversible power plants. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 1988, 31, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Kiang, R. L. Finite time thermodynamic analysis of a finite time Carnot heat engine with internal irreversibility. Energy 1992, 17, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. The maximum power output and maximum efficiency of an irreversible Carnot heat engine. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 1994, 27, 1144–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Thermodynamic and thermoeconomic analyses of an irreversible combined Carnot heat engine system. Int. J. Energy Res. 2001, 25, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodal, A.; Sahin, B.; Yilmaz, T. Effects of internal irreversibility and heat leakage on the finite time thermoeconomic performance of refrigerators and heat pumps. Energy Convers. Mgmt. 2000, 41, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, B.; Kodal, A. Performance analysis of an endoreversible heat engine based on a new thermoeconomic optimization criterion. Energy Convers. Mgmt. 2001, 42, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antar, M. A.; Zubair, S. M. Thermoeconomic considerations in the optimum allocation of heat exchanger inventory for a power plant. Energy Convers. Mgmt. 2001, 42, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2004 by MDPI (http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction for noncommercial purposes permitted.
Share and Cite
Tyagi, S.K.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J. Optimum Criteria on the Performance of an Irreversible Braysson Heat Engine Based on the new Thermoeconomic Approach. Entropy 2004, 6, 244-256. https://doi.org/10.3390/e6020244
Tyagi SK, Zhou Y, Chen J. Optimum Criteria on the Performance of an Irreversible Braysson Heat Engine Based on the new Thermoeconomic Approach. Entropy. 2004; 6(2):244-256. https://doi.org/10.3390/e6020244
Chicago/Turabian StyleTyagi, Sudhir Kumar, Yinghui Zhou, and Jincan Chen. 2004. "Optimum Criteria on the Performance of an Irreversible Braysson Heat Engine Based on the new Thermoeconomic Approach" Entropy 6, no. 2: 244-256. https://doi.org/10.3390/e6020244
APA StyleTyagi, S. K., Zhou, Y., & Chen, J. (2004). Optimum Criteria on the Performance of an Irreversible Braysson Heat Engine Based on the new Thermoeconomic Approach. Entropy, 6(2), 244-256. https://doi.org/10.3390/e6020244



