Material Removal Rate Enhancement Induced by Electrochemical Discharge Machining for Refractory High-Entropy Alloys Compared with EDM
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of RHEAs
2.2. Electrochemical Measurements
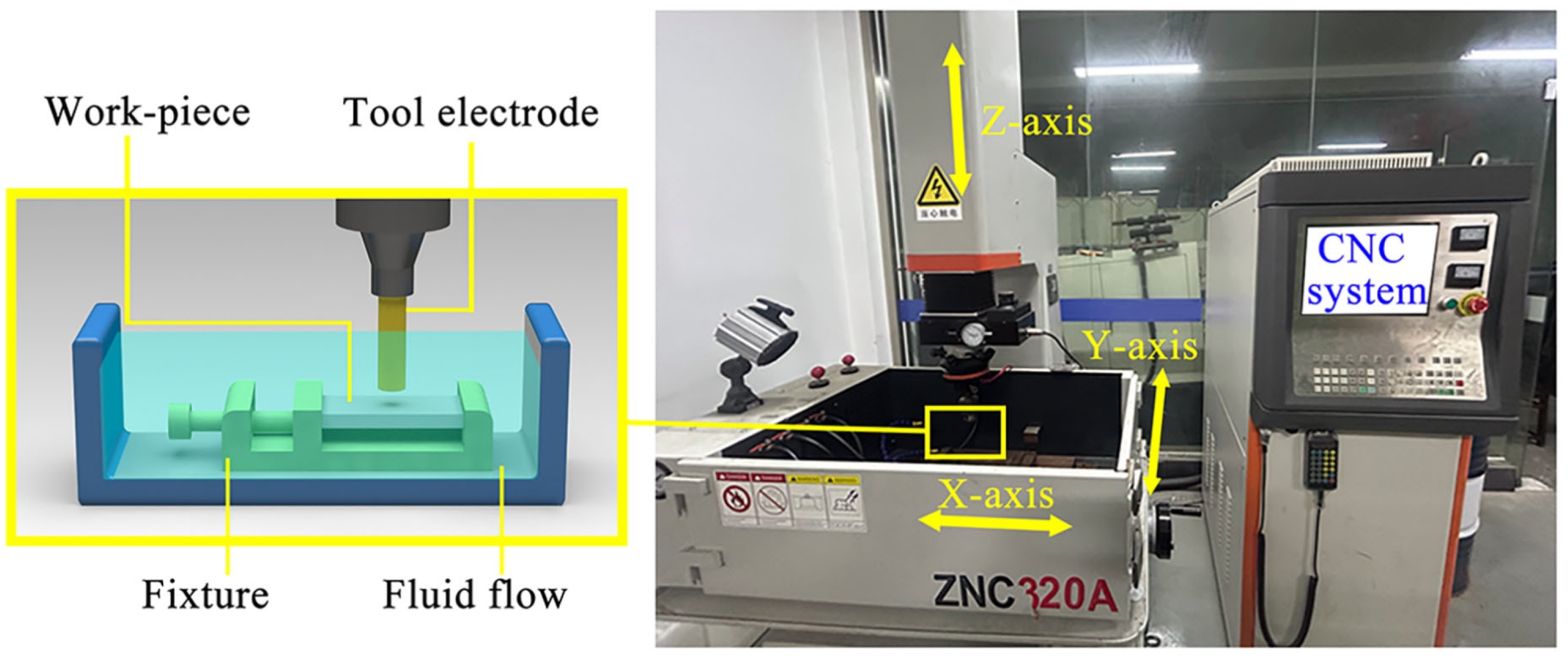
2.3. ECDM and EDM Setup
2.4. Microstructure and Element Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Materials Properties of W20N0.5 and W5
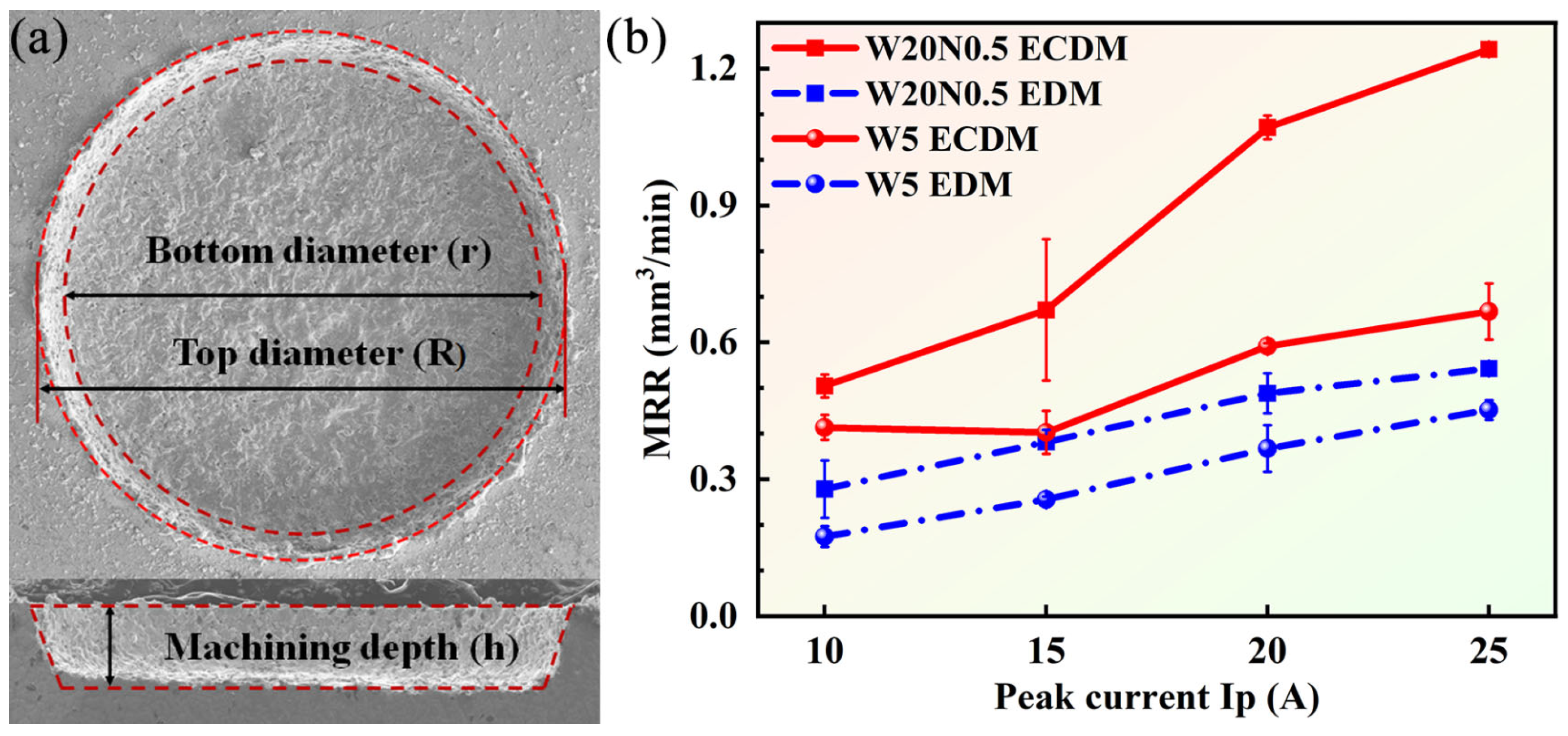
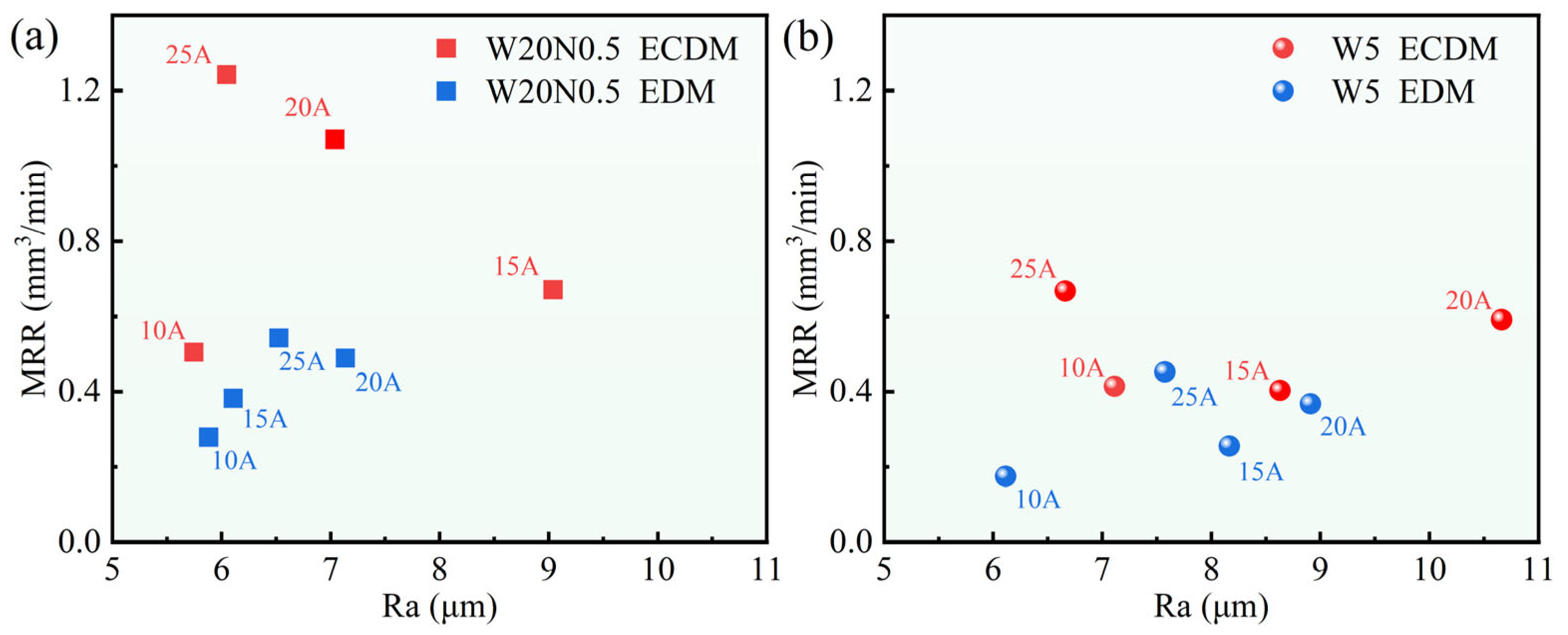
3.2. Machining Efficiency of W20N0.5 and W5
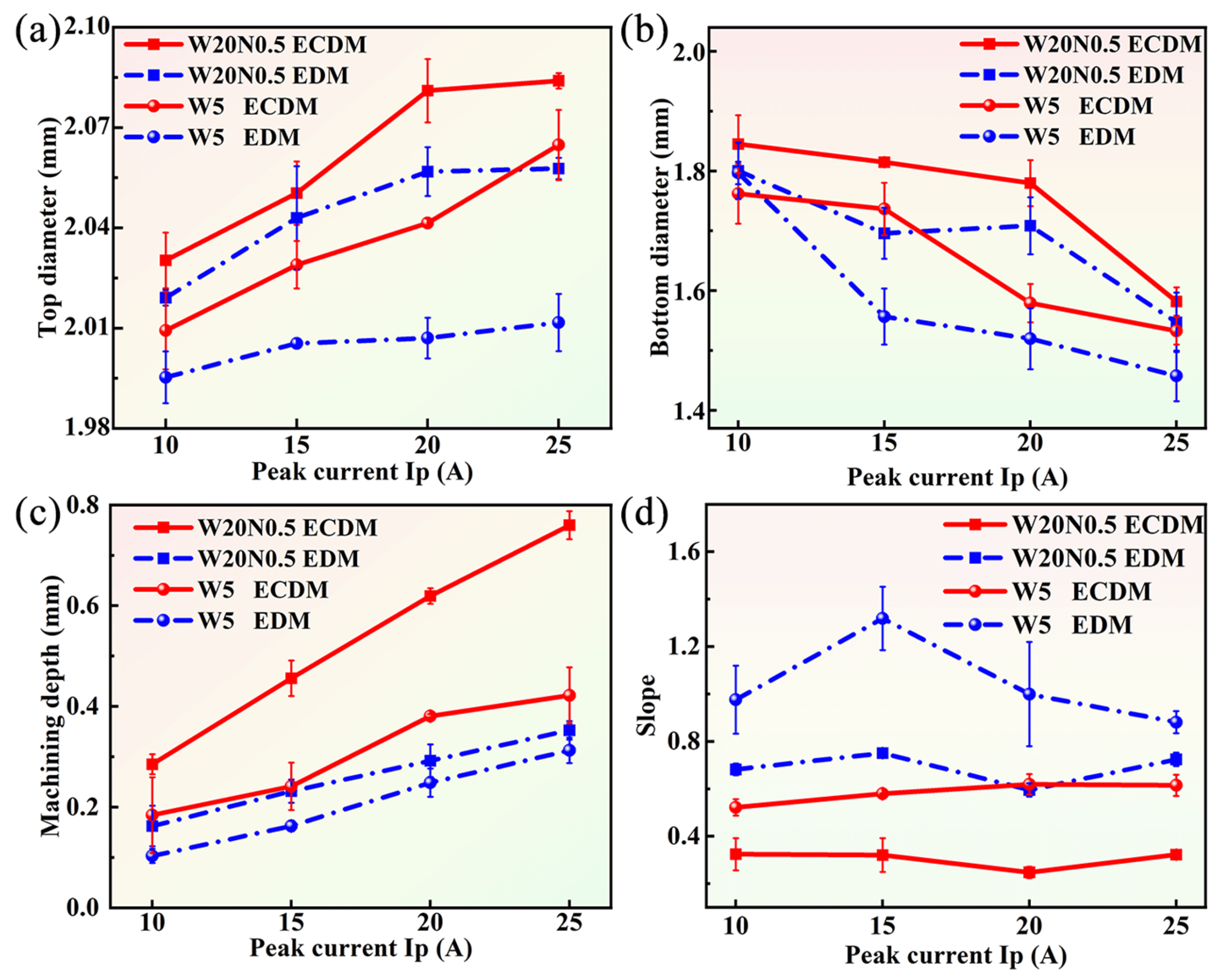
3.3. Effects of Peak Current on the Hole Shape
3.4. Morphology of Holes at Lower Peak Current
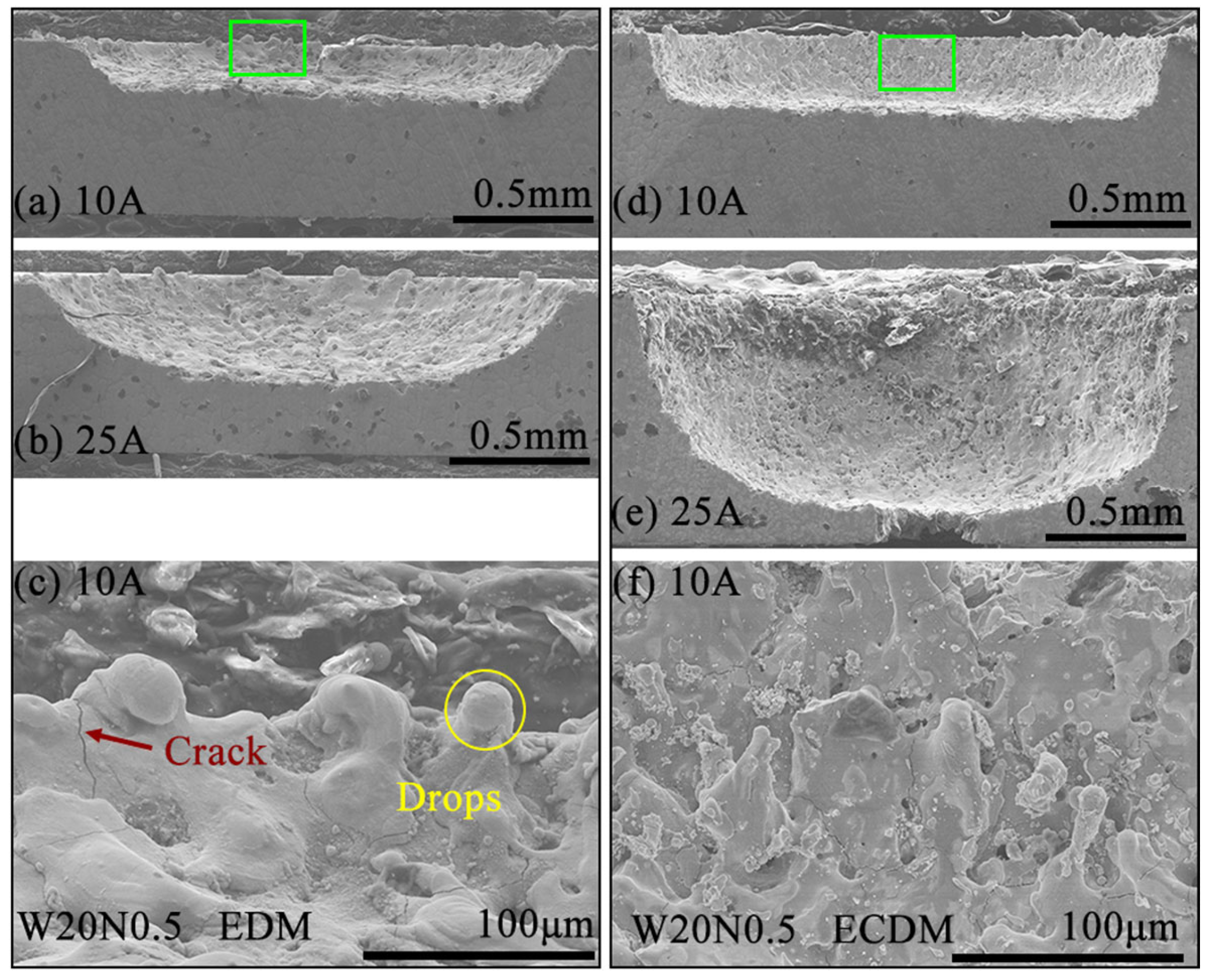
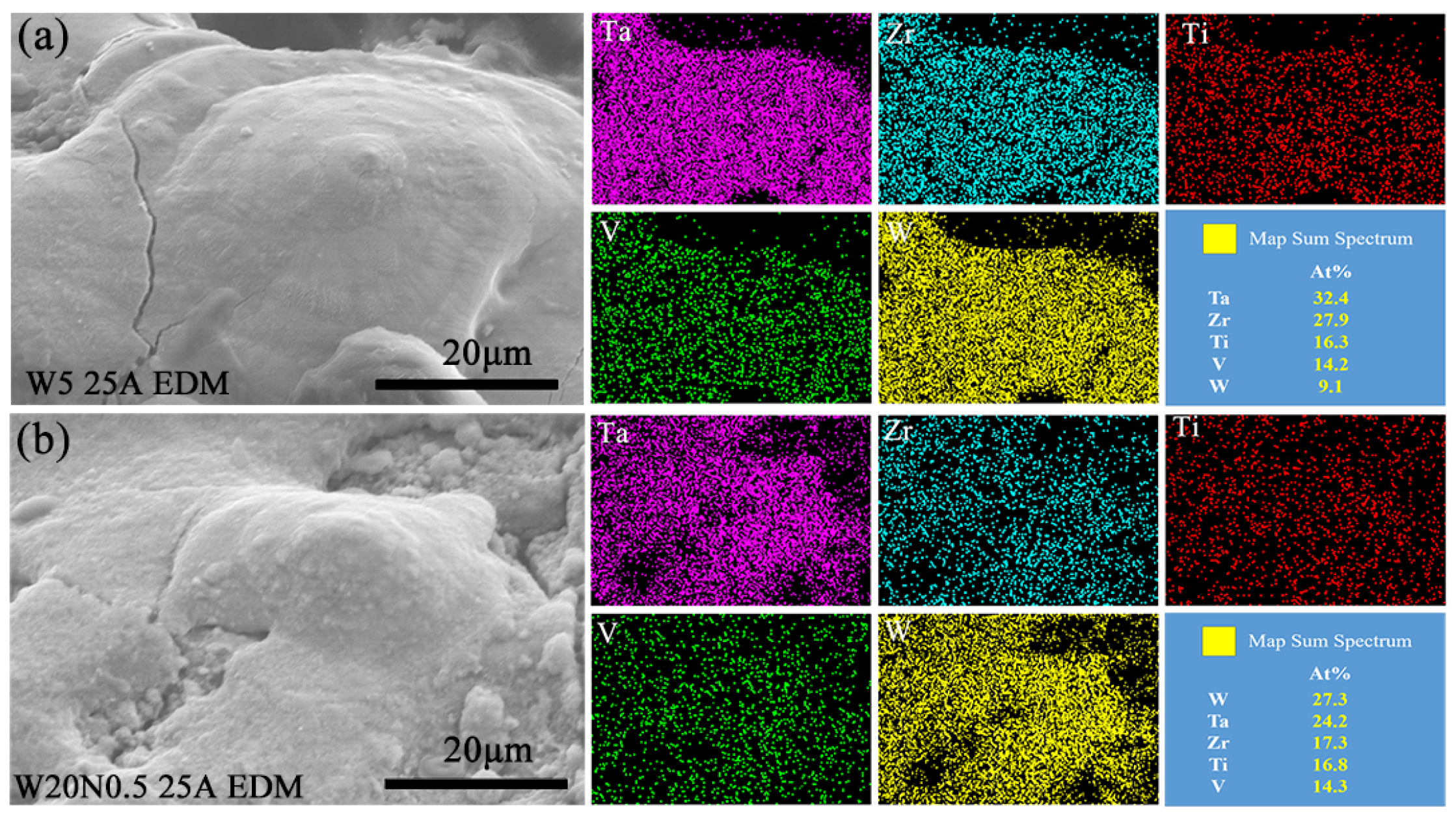
3.5. Sidewall Surface Characteristics of Machined Blind Holes by ECDM and EDM
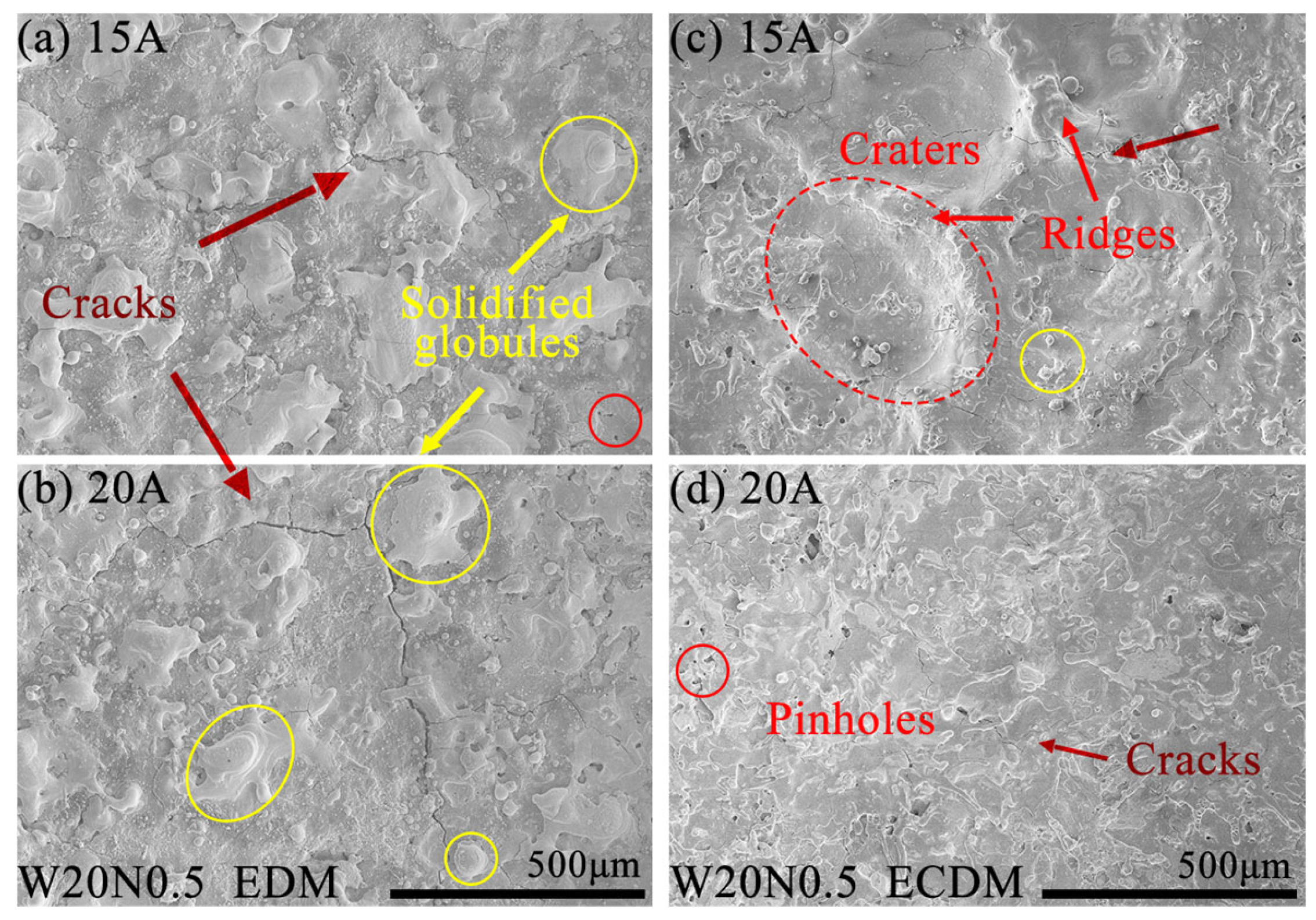
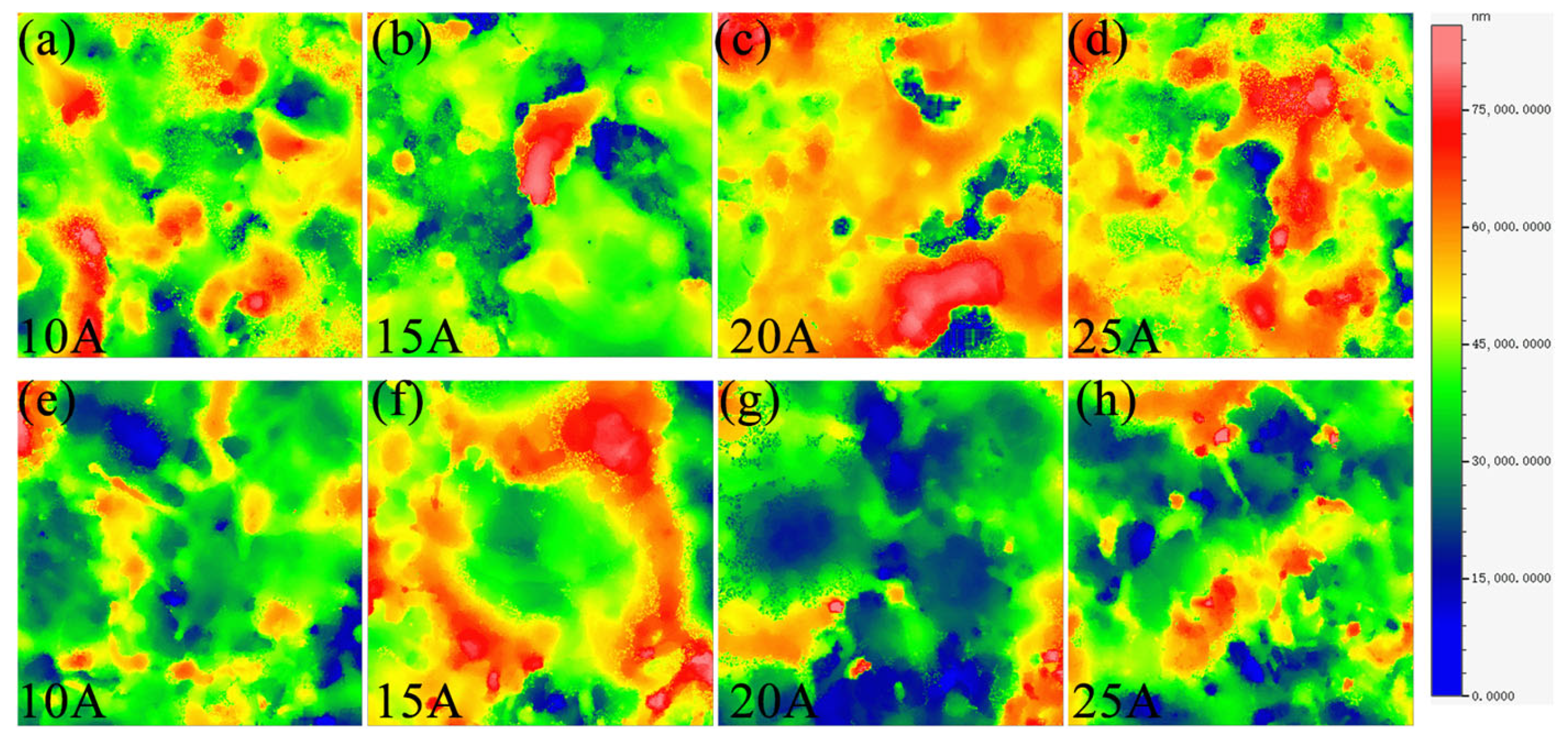
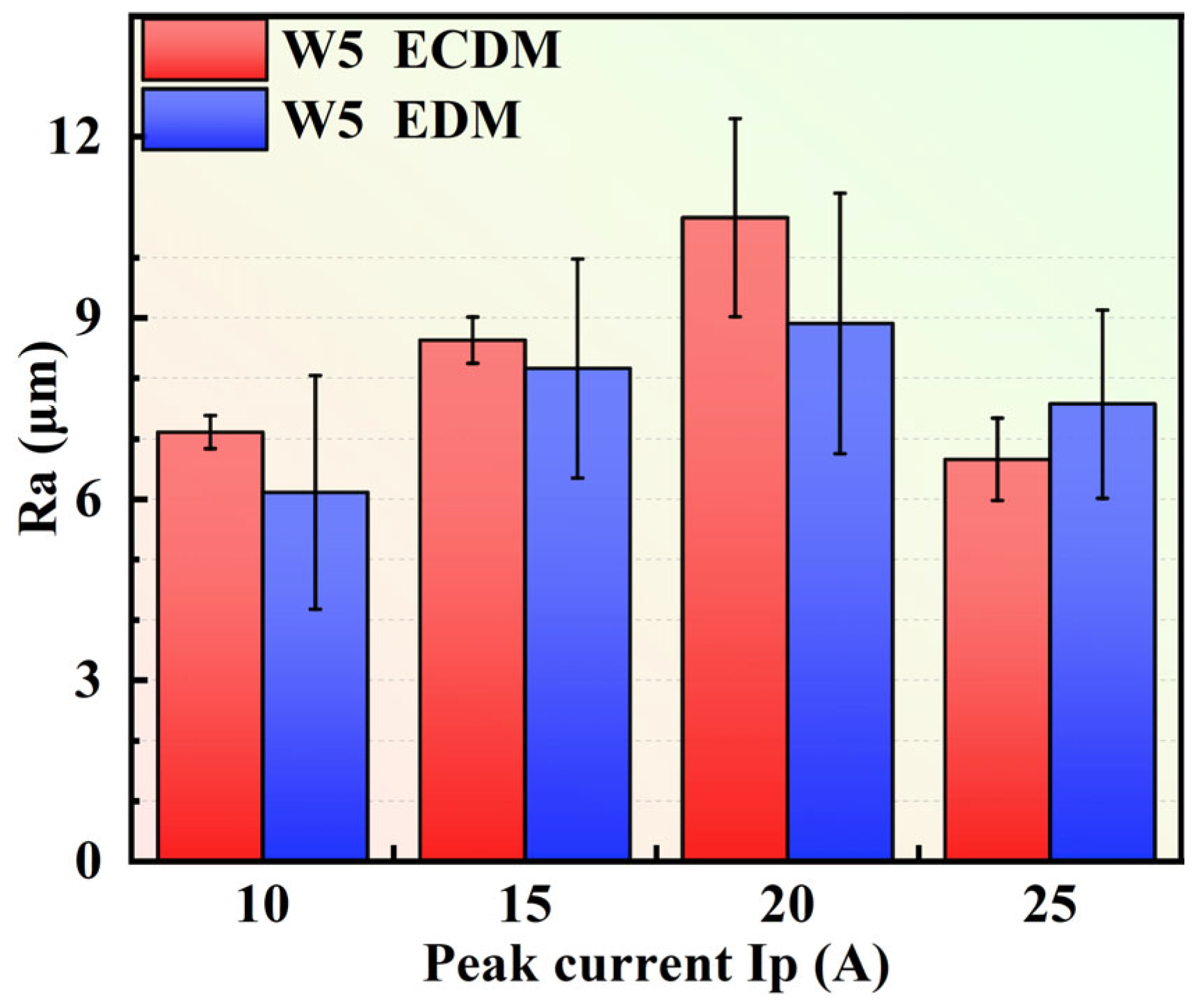
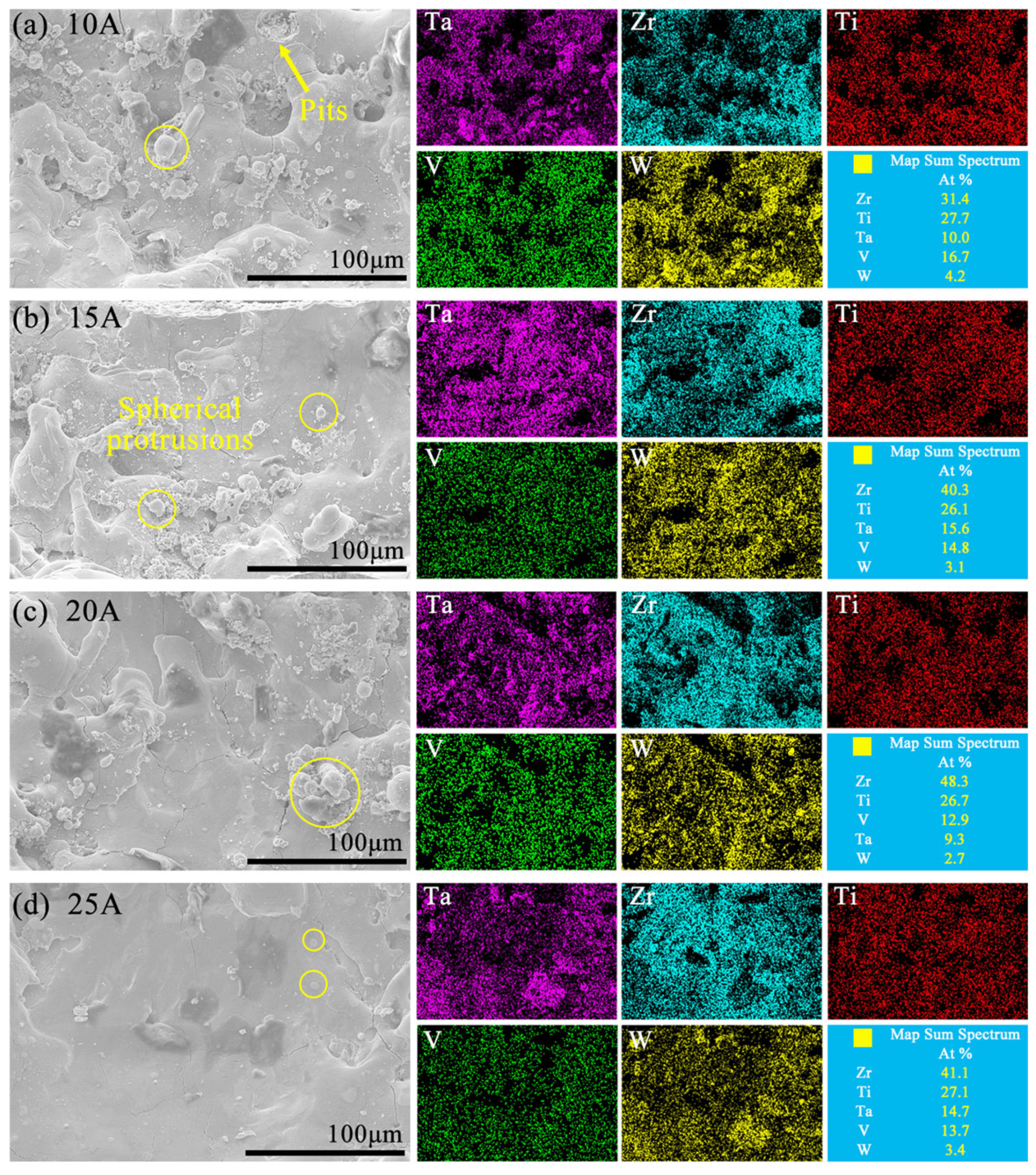
3.6. Machined Bottom Surfaces and Surface Roughness of RHEAs
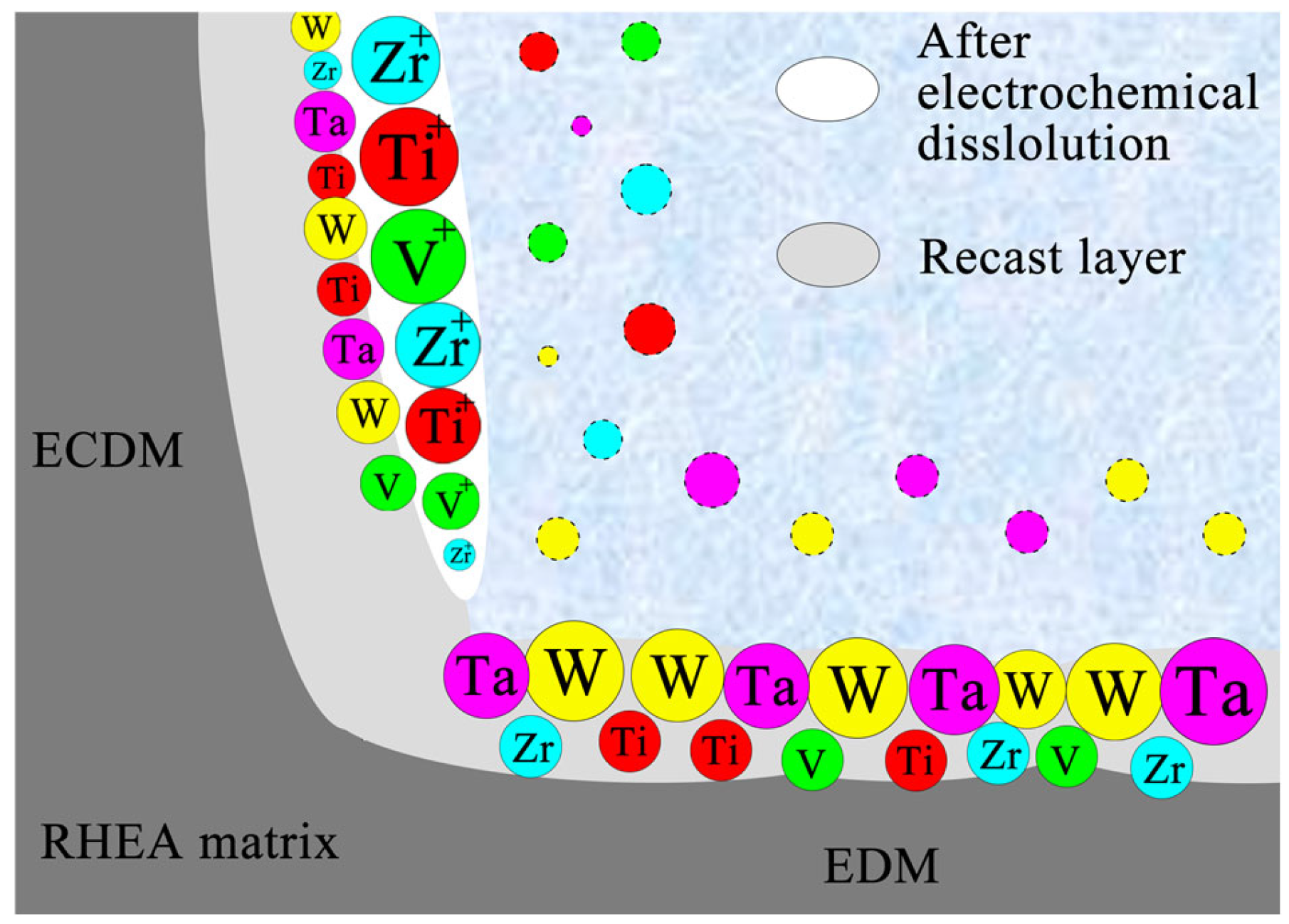
3.7. Material Removal Process and Mechanism
4. Conclusions
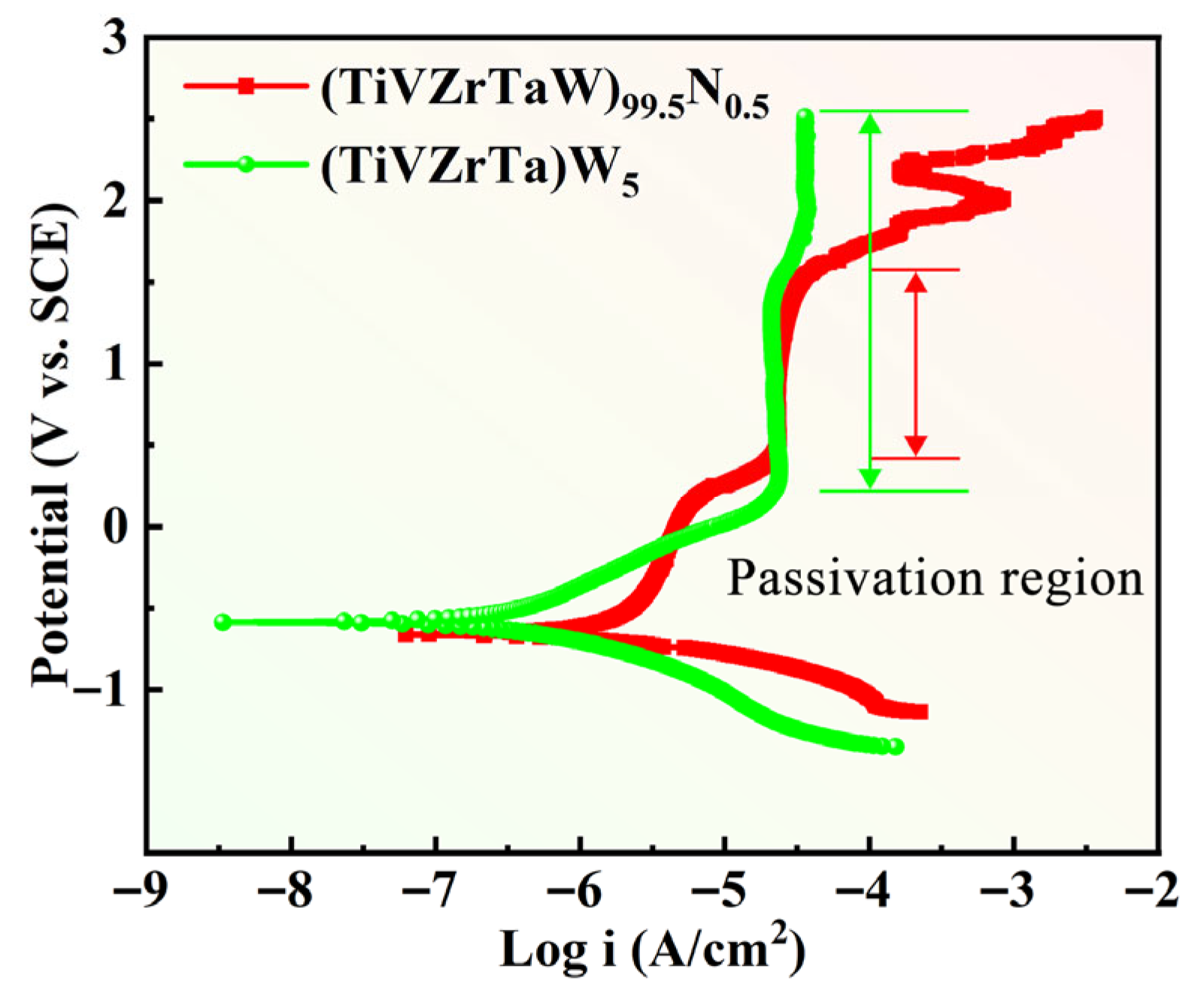
- The W5 alloy exhibited better corrosion resistance than W20N0.5, as indicated by an Icorr 1.133 × 10−7 A/cm2, a wider passive zone, and a transpassive potential above 2.5 VSCE. However, the W20N0.5 alloy showed superior mechanical properties, including higher hardness and strength. These differences in corrosion resistance resulted in different MRR performance during ECDM.
- Based on single-factor experiments, the difference in MRR between EDM and ECDM increased with the increment of Ip. The MRR of the W5 alloy was lower than that of the W20N0.5 alloy due to the excellent corrosion resistance of W5. Nevertheless, the findings confirm that, compared with conventional EDM, significantly higher MRR can be achieved in RHEAs by using ECDM.
- The EDS results showed that elements with high melting points (Ta and W) enriched at the bottom of the machined surface after EDM. In contrast, elements with low melting points (Zr and Ti) enriched at the machined surface after ECDM.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Senkov, O.N.; Wilks, G.B.; Scott, J.M.; Miracle, D.B. Mechanical Properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and V20Nb20Mo20Ta20W20 Refractory High Entropy Alloys. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Guo, A.X.Y.; Zhan, S.; Liu, C.-T.; Cao, S.C. Refractory High-Entropy Alloys: A Focused Review of Preparation Methods and Properties. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 142, 196–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.S.; Chen, S.H.; Yue, X.K.; Zhang, J.S.; Wu, Y.C. Synergistic Deformation Induced Excellent Mechanical Properties of Low-Activation W-Ta-Ti-V-C Refractory High Entropy Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 927, 148028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, A.O.; Salgado, A.S.; Niño, E.B. Thermodynamic analysis of high entropy alloys and their mechanical behavior in high and low-temperature conditions with a microstructural approach—A Review. Intermetallics 2020, 124, 106850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, E.P.; Curtin, W.A.; Tasan, C.C. High entropy alloys: A focused review of mechanical properties and deformation mechanisms. Acta Mater. 2020, 188, 435–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, W.P.; Fu, Z.Q.; Chu, C.L.; Tian, Z.; Jiang, Z.F.; Wen, H.M. Lightweight Ti-Zr-Nb-Al-V Refractory High-Entropy Alloys with Superior Strength-Ductility Synergy and Corrosion Resistance. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2023, 116, 106331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.J.; Chen, Q.J.; Cui, X.; Peng, X.Y.; Huang, G.S. Evaluation of Corrosion Resistance of the Single-Phase Light Refractory High Entropy Alloy TiCrVNb0.5Al0.5 in Chloride Environment. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 857, 158278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, W.; Fu, Y.Z. High-Entropy Alloys: Emerging Materials for Advanced Functional Applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 663–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, N.; Meena, A.; Mali, H.S. Flat-End Mill Machining Analysis of Processed CrMnFeCoNi High-Entropy Alloys. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2023, 38, 755–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibria, G.; Sarkar, B.R.; Pradhan, B.B.; Bhattacharyya, B. Comparative Study of Different Dielectrics for Micro-EDM Performance during Microhole Machining of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 48, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Z.; Liu, Z.D.; Xue, R.Y.; Tian, Z.J.; Huang, Y.H. Research on the Influence of Dielectric Characteristics on the EDM of Titanium Alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 72, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakar, K.; Kumar, R.; Katheria, A.; Nagdeve, L.; Kumar, H. Effect of Various Dielectric Fluids on Electric Discharge Machining (EDM): A Review. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2022, 44, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaumik, M.; Maity, K. Effect of Different Tool Materials during EDM Performance of Titanium Grade 6 Alloy. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2018, 21, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beranoagirre, A.; Urbikain, G.; Calleja, A.; López De Lacalle, L.N. Hole Making by Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) of γ-TiAl Intermetallic Alloys. Metals 2018, 8, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, M.P.; Alavi, F. A Study on the Surface Composition and Migration of Materials and Their Effect on Surface Microhardness during Micro-EDM of Ti-6Al-4V. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2019, 28, 3517–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Lian, M.Q.; Chen, S.G.; Lei, J.G.; Wu, X.Y.; Guo, C.; Peng, T.J.; Yang, J.; Luo, F.; Zhao, H. Combining PMEDM with the Tool Electrode Sloshing to Reduce Recast Layer of Titanium Alloy Generated from EDM. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 117, 1535–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Tong, H.; Ding, S.L.; Kong, Q.C.; Zhao, L.; Ding, J. Effects of Dielectric Fluids on Surface Integrity for the Recast Layer in High Speed EDM Drilling of Nickel Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 783, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y.F.; Feng, Y.R.; Du, Y.L. Investigation on Surface Morphology and Phase Transition Characteristics in EDM for 8YSZ TBC on Inconel 718 Superalloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 124, 3615–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, S.; Prakash, K.S.; Gopal, P.M.; Jothi, S. Influence of Materials and Machining Parameters on WEDM of Al/AlCoCrFeNiMo0.5 MMC. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2019, 34, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.H.; Tan, P.C.; Aligiri, E.; Tor, S.B.; Loh, N.H. Processing of Zirconium-Based Bulk Metallic Glass (BMG) Using Micro Electrical Discharge Machining (Micro-EDM). Mater. Manuf. Process. 2009, 24, 1242–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Gu, H.W.; Wang, J.Y.; Chang, W.J.; Chan, K.C. Processing of Monolithic Bulk Metallic Glass Using Sinking Electrical Discharge Machining. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 126, 5057–5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yan, J.W. On the Surface Characteristics of a Zr-Based Bulk Metallic Glass Processed by Microelectrical Discharge Machining. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 355, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Xu, K.; Chang, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.C. On the WEDM of WNbMoTaZrx (x = 0.5, 1) Refractory High Entropy Alloys. Entropy 2022, 24, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günen, A.; Ceritbinmez, F.; Patel, K.; Akhtar, M.A.; Mukherjee, S.; Kanca, E.; Karakas, M.S. WEDM Machining of MoNbTaTiZr Refractory High Entropy Alloy. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2022, 38, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceritbinmez, F. Wire Electric Discharge Machining and Its Effect on the Surface Finish of HfNbTaTiZr Refractory High-Entropy Alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 125, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.S.; Yue, X.K.; Zhang, J.S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.H. Effect of Constituent Phase and Processing Parameter on the WEDM Performance of Refractory High Entropy Alloys. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 130, 1509–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, S.H.; Yue, X.K.; Tang, H.H.; Guan, S.; Wu, Y.C. Controllable Sinking Electrical Discharge Machining Performance of Dendritic-Structured W-Containing Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. Tungsten 2024, 7, 564–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashedul, I.M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, K.; Wang, G.; Xi, T.; Ji, L. Influence of Different Tool Electrode Materials on Electrochemical Discharge Machining Performances. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Dvivedi, A. Developments in Electrochemical Discharge Machining: A Review on Electrochemical Discharge Machining, Process Variants and Their Hybrid Methods. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2016, 105, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, T.Y.; Xu, Z.Y.; Ning, J.; Liu, L. Investigation of External Capacitance Effects on Electrochemical Discharge Drilling. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2023, 38, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, N.; Kumar, N.; Das, A.K. Powder Mixed Electrochemical Discharge Process for Micro Machining of C103 Niobium Alloy. Def. Technol. 2023, 26, 84–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargav, K.V.J.; Pyla, K.R.; Balaji, P.S.; Sahu, R.K. Micromachining of Al7075 Alloy Using an in-Situ Ultrasonicated µ-ECDM System. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2023, 38, 1663–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, K.M.; Kirk, D.W.; Singh, C.V.; Thorpe, S.J. Optimizing Electrochemical Micromachining Parameters for Zr-Based Bulk Metallic Glass. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 25, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Speidel, A.; Murray, J.W.; Ahmed, N.; Cuttell, M.; Clare, A.T. Electrolytic-Dielectrics: A Route to Zero Recast Electrical Discharge Machining. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2022, 181, 103941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Bharti, P.S. Multi-Objective Parametric Optimization during Micro-EDM Drilling of Ti-6Al-4V Using Teaching Learning Based Optimization Algorithm. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.S.; Yue, X.K.; Chen, S.H. Study on the Material Erosion Mechanisms in WEDM of Refractory High Entropy Alloys via Selective Corrosion. J. Mech. Eng. 2025, 61, 440–448. [Google Scholar]



| Parameters | Machining Methods | |
|---|---|---|
| ECDM | EDM | |
| Work fluids | NaCl solution | EDM oil |
| Electrical conductivity | 58.35 μS/cm | 0.064 μS/cm |
| Tool electrode | Copper electrode | |
| Gap voltage Vg | 30 V | |
| Pulse duration Ton | 30 μs | |
| Pulse interval Toff | 80 μs | |
| Machining time T | 100 s | |
| Peak current Ip | 10, 15, 20, 25 A | |
| RHEAs | Properties | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tm (K) | Hardness (HV) | σy (MPa) | Icorr (A/cm2) | Ecorr (VSCE) | ΔE (V) | Et (V) | |
| W20N0.5 | 2632.29 | 585 | 1949.72 | 4.920 × 10−7 | −0.660 | 1.166 | 1.615 |
| W5 | 2448.36 | 458 | 1435.45 | 1.133 × 10−7 | −0.586 | 1.262 | >2.5 |
| Anodic Chemical Reaction | Standard Electrode Potential (V) |
|---|---|
| Ti(s) → Ti2+ + 2e | −1.63 |
| Zr(s) → Zr4+ + 4e | −1.45 |
| V(s) → V2+ + 2e | −1.175 |
| Ta(s) → Ta3+ + 3e | −0.6 |
| W(s) → W3+ + 3e | 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, B.; Yao, Z.; Qi, C.; Yue, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, S. Material Removal Rate Enhancement Induced by Electrochemical Discharge Machining for Refractory High-Entropy Alloys Compared with EDM. Entropy 2025, 27, 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090912
Dong B, Yao Z, Qi C, Yue X, Zhang Z, Chen S. Material Removal Rate Enhancement Induced by Electrochemical Discharge Machining for Refractory High-Entropy Alloys Compared with EDM. Entropy. 2025; 27(9):912. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090912
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Bolin, Zirui Yao, Chen Qi, Xiaokang Yue, Zufang Zhang, and Shunhua Chen. 2025. "Material Removal Rate Enhancement Induced by Electrochemical Discharge Machining for Refractory High-Entropy Alloys Compared with EDM" Entropy 27, no. 9: 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090912
APA StyleDong, B., Yao, Z., Qi, C., Yue, X., Zhang, Z., & Chen, S. (2025). Material Removal Rate Enhancement Induced by Electrochemical Discharge Machining for Refractory High-Entropy Alloys Compared with EDM. Entropy, 27(9), 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090912





