Sea Surface Wind Speed Retrieval from Marine Radar Image Sequences Based on GLCM-Derived Texture Features
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Retrieving Wind Speed Using the Empirical Function Model
- ①
- Parameter inaccuracy: The wind field imaging mechanism is complex and influenced by many factors (e.g., atmospheric refraction, scattering characteristics, the geometry between the radar and the wind field). Relying only on mean echo intensity cannot fully reflect the effects of these factors, which may lead to model parameters deviating from actual wind field conditions and failing to capture the spatiotemporal variations and fine details of the wind field.
- ②
- Poor model adaptability: Different wind field environments (such as typhoon winds or localized strong convective winds) have unique characteristics. Without considering the wind field imaging mechanism, the chosen model parameters may only apply to radar images under specific conditions. For other types of wind fields or environments, the model’s adaptability and generalization are very poor, making accurate wind field retrieval difficult.
- ③
- Large retrieval error: Because the model parameters may be inaccurate and not universally applicable, using this model for wind field retrieval can produce large errors. It might not accurately capture key information such as wind speed and direction, and assessments of wind field intensity, extent, and trends can be biased. This impairs scientific understanding of the wind field and its practical applications.
- ④
- Neglect of important information: The wind field imaging mechanism contains important information related to wind characteristics (e.g., Doppler shift, polarization). Focusing only on mean echo intensity ignores this additional information, leading to an incomplete understanding of the wind field. This prevents deeper exploration of the wind field’s underlying physical processes and patterns, limiting more accurate analysis and research.
3. The GLCM-Derived Texture Features Wind Speed Estimation Model
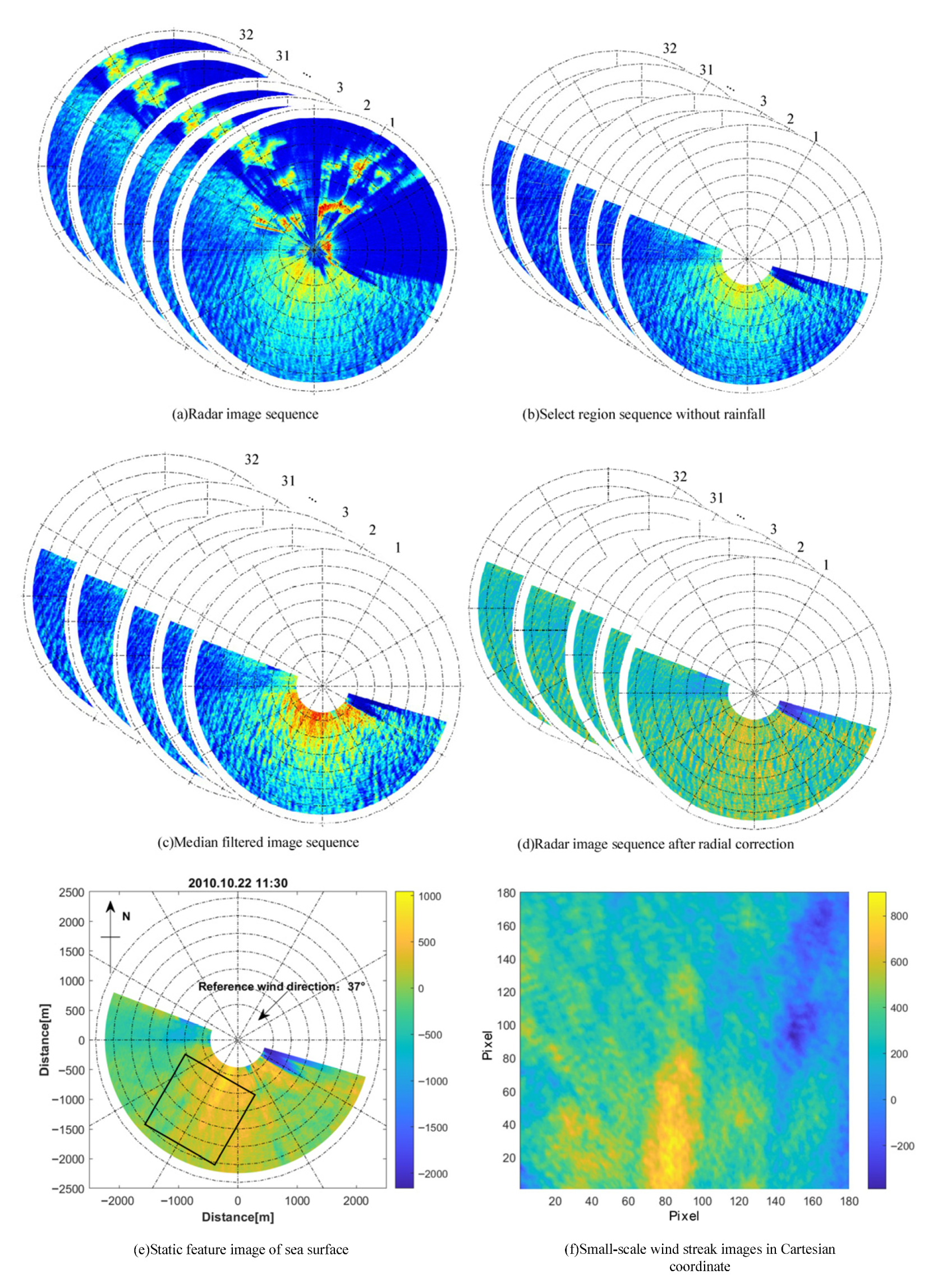
3.1. Small-Scale Wind Streaks Extraction
3.2. Streak Characteristics of Different Wind Speeds
3.3. Calculating the Features of Small-Scale Wind Streaks Based on GLCM
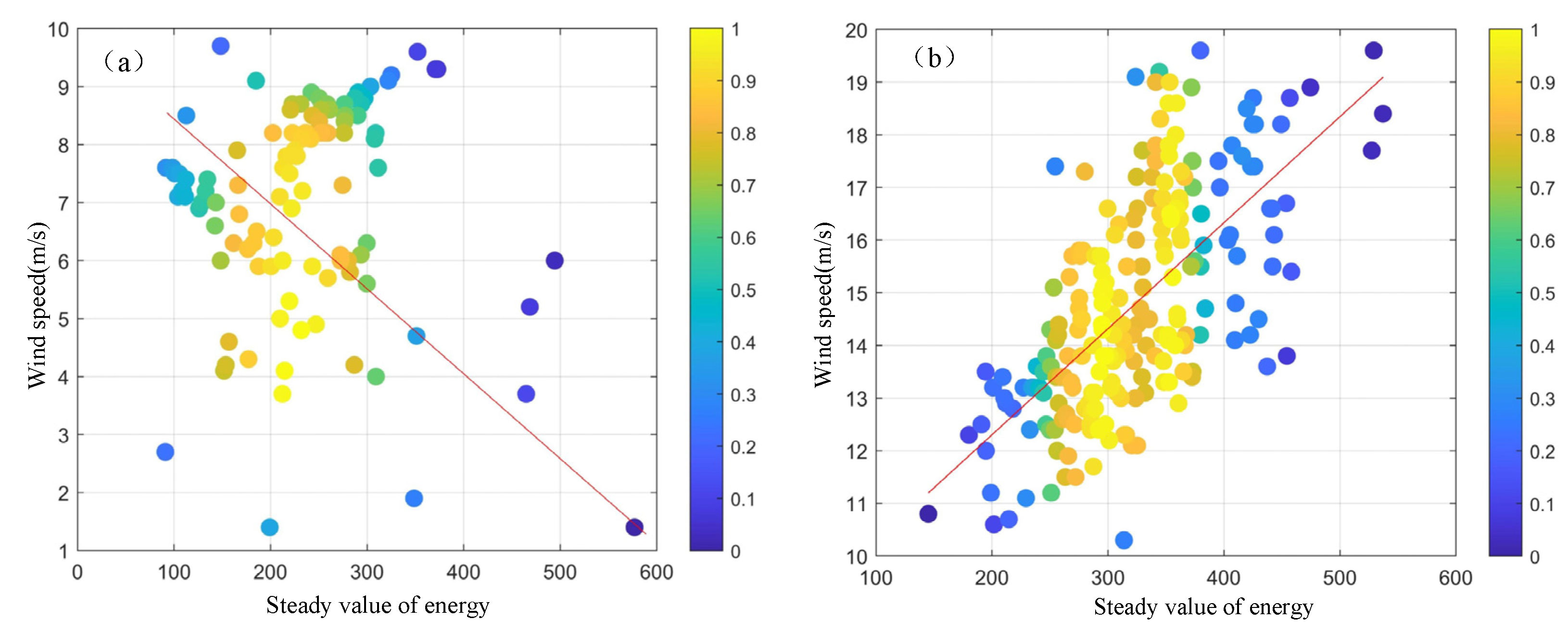
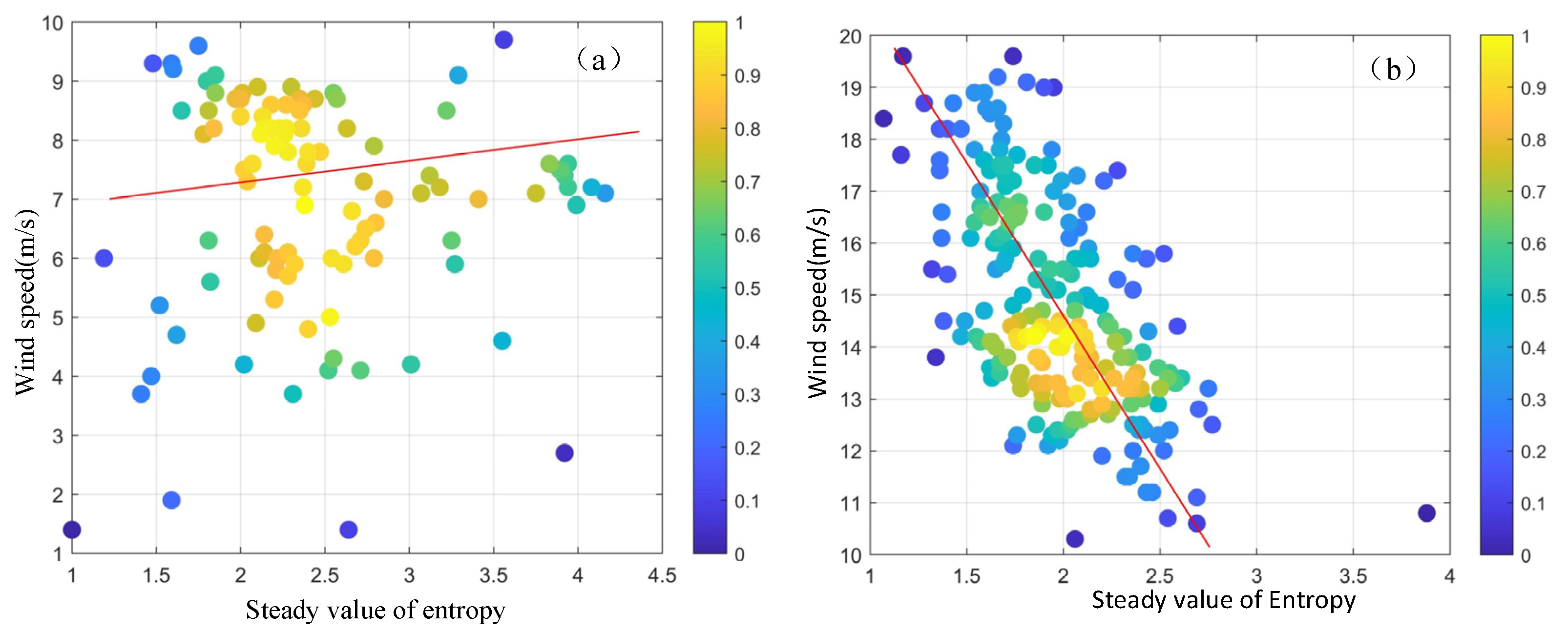
3.4. Analysis of the Relationship Between GLCM-Derived Features and Wind Speed
3.5. Wind Speed Estimation Model
4. Validation and Testing
4.1. Data Overview
4.2. Results Validation
4.3. Model Applicability Verification
4.4. Verification of Different Sea Conditions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Jafari, Z.; Bobby, P.; Karami, E.; Taylor, R. A Novel Method for the Estimation of Sea Surface Wind Speed from SAR Imagery. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liu, X.; Gill, E.W. Ocean wind and wave measurements using X-band marine radar: A comprehensive review. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qiu, H.; Zhi, P.; Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Akhtar, R.; Raja, M.A.Z. Study of Algorithms for Wind Direction Retrieval from X-Band Marine Radar Images. Electronics 2019, 8, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Yan, Q.; Fan, C.; Meng, J.; Zhang, J.; Song, T.; Sun, W. Optimized Estimation of Azimuth Cutoff for Retrieval of Significant Wave Height and Wind Speed From Polarimetric Gaofen-3 SAR Wave Mode Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 10938–10955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Grieco, G.; Lin, J.; Portabella, M.; Wang, X. On the Use of Azimuth Cutoff for Sea Surface Wind Speed Retrieval From SAR. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 10367–10379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstmann, J.; Bödewadt, J.; Cysewski, M.; Seemann, J.; Streβer, M. A coherent on receive X-band marine radar for ocean observations. Sensors 2021, 21, 7828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Huang, W. Spatial–temporal convolutional gated recurrent unit network for significant wave height estimation from shipborne marine radar data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 4201711. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lu, Z. A Method for retrieving wave parameters from synthetic X-band marine radar images. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 204880–204890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Carrasco, R.; Shen, C.; Gill, E.W.; Horstmann, J. Surface current measurements using X-band marine radar with vertical polarization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 2988–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Huang, W.; Zhao, C.; Tian, Y. Rain detection from X-band marine radar images: A support vector machine-based approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 2115–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Huang, W.; Haller, M.C.; Pittman, R. Rain-contaminated region segmentation of X-band marine radar images with an ensemble of SegNets. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Tian, C.; Wei, Y.; Liu, F. A Method for Estimating Ship Surface Wind Parameters by Combining Anemometer and X-Band Marine Radar Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Lu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Wang, H. Multi-anemometer optimal layout and weighted fusion method for estimation of ship surface steady-state wind parameters. Ocean Eng. 2022, 266, 112793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankert, H.; Horstmann, J.; Rosenthal, W. Wind-and wave-field measurements using marine X-band radar-image sequences. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2005, 30, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fan, D.; Qiu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhi, P.; Zhu, W. An Improved RBF Neural Network based on Clustering Algorithm for Estimating Wind Speed from X-band Marine Radar Images. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th IEEE International Conference on Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems (ICPS), Victoria, BC, Canada, 10–13 May 2021; pp. 775–779. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Huang, W.; Yao, G. Wind speed estimation from X-band marine radar images using support vector regression method. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 1312–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Huang, W. A CNN-based Hybrid Dehazing and Regression Model for Sea Surface Wind Speed Retrieval from Rain-contaminated Marine Radar Data. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2024-Singapore, Singapore, 14–18 April 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Huang, W. WSTCNN: A Wavelet Scattering Transform-CNN Model for Wind Speed Estimation From Radar Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5105813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatten, H.; Ziemer, F.; Seemann, J.; Nieto-Borge, J. Correlation between the Spectral Background Noise of a Nautical Radar and the Wind Vector. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering (OMAE), Lisbon, Portugal, 5–9 July 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Izquierdo, P.; Soares, C.G. Analysis of sea waves and wind from X-band radar. Ocean Eng. 2005, 32, 1404–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, B.; Graber, H.C.; Romeiser, R. Wind retrieval from shipborne nautical X-band radar data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3800–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicen-Bueno, R.; Horstmann, J.; Terril, E.; de Paolo, T.; Dannenberg, J. Real-time ocean wind vector retrieval from marine radar image sequences acquired at grazing angle. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, W.; Gill, E.W.; Peters, D.K.; Vicen-Bueno, R. Comparison of algorithms for wind parameters extraction from shipborne X-band marine radar images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 896–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; He, Y.; Zhang, B.; Qiu, Z. Determination of nearshore sea surface wind vector from marine X-band radar images. Ocean Eng. 2015, 96, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Yang, J.; Huang, Y. Sea wind direction extraction algorithm by X-band radar in moving platform. Syst. Eng. Electron 2016, 38, 799–803. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Huang, W.; Gill, E.W. Wind direction estimation from rain-contaminated marine radar data using the ensemble empirical mode decomposition method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 55, 1833–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, R. Using texture analysis for medical diagnosis. IEEE Multimed. 2012, 19, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, K.R.; Radhakrishnan, S. Focal and diffused liver disease classification from ultrasound images based on isocontour segmentation. IET Image Process. 2015, 9, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Li, X.; Zhou, L.; Yang, J.; Ren, L.; Chen, P.; Zhang, H.; Lou, X. Development of a gray-level co-occurrence matrix-based texture orientation estimation method and its application in sea surface wind direction retrieval from SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 5244–5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zheng, G.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, H.; Chen, P.; Wang, Y. Sea surface wind speed retrieval from textures in synthetic aperture radar imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstmann, J.; Dankert, H. Estimation of friction velocity using tower based marine radars. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Denver, CO, USA, 31 July–4 August 2006; Volume 7, pp. 1323–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Qiu, H.; Lu, Z.; Wang, L.; Akhtar, R.; Wei, Y. An energy spectrum algorithm for wind direction retrieval from X-band marine radar image sequences. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 4074–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, W. An algorithm for wind direction retrieval from X-band marine radar images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankert, H.; Horstmann, J.; Magnusson, A.K.; Rosenthal, W. Ocean Winds Retrieved from X-band Radar-Image Sequences. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; Volume 108, p. 3352. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Li, S.; Qiu, H.; Lu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Ge, H. Development of a fast convergence gray-level co-occurrence matrix for sea surface wind direction extraction from marine radar images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiko, D.; Horstmann, J. A marine radar wind sensor. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2007, 24, 1629–1642. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Barlow, J.F.; Chan, P.W.; Fung, J.C.H.; Li, Y.; Ren, C.; Mak, H.W.L.; Ng, E. A review of progress and applications of pulsed Doppler wind LiDARs. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatten, H.; Seemann, J.; Horstmann, J.; Ziemer, F. Azimuthal dependence of the radar cross section and the spectral background noise of a nautical radar at grazing incidence. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Seattle, WA, USA, 6–10 July 1998; Volume 5, pp. 2490–2492. [Google Scholar]
- Suresh, A.; Shunmuganathan, K.L. Image texture classification using gray level co-occurrence matrix based statistical features. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2012, 75, 591–597. [Google Scholar]













| Model | Correlation Coefficient | Average error (m/s) | Root Mean Square Error (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Empirical function model | 0.83 | 1.50 | 1.03 |
| Energy stable value model | 0.96 | 0.76 | 0.53 |
| Entropy stable value model | 0.84 | 1.25 | 0.99 |
| Wind Speed | Performance | ESM | SSM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low wind speed | correlation coefficient | 0.76 | 0.77 |
| average deviation (m/s) | 0.88 | 0.64 | |
| RMSE (m/s) | 1.83 | 1.5 | |
| Moderate wind speed | correlation coefficient | 0.88 | 0.81 |
| average deviation (m/s) | −0.39 | −0.94 | |
| RMSE (m/s) | 1.21 | 2.54 | |
| High wind speed | correlation coefficient | 0.92 | 0.83 |
| average deviation (m/s) | 0.29 | 0.56 | |
| RMSE (m/s) | 1.08 | 1.41 |
| Sea Conditions | Wind Speed Model | Correlation Coefficient | Mean Deviation (m/s) | RMSE (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low sea state | Energy stable value model | 0.81 | 0.64 | 1.16 |
| Entropy stable value model | 0.89 | 0.30 | 0.81 | |
| High sea state | Energy stable value model | 0.94 | 0.16 | 0.73 |
| Entropy stable value model | 0.82 | 0.17 | 1.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Qiu, H.; Wang, L.; Huang, J.; Ruan, X. Sea Surface Wind Speed Retrieval from Marine Radar Image Sequences Based on GLCM-Derived Texture Features. Entropy 2025, 27, 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27080877
Wang H, Qiu H, Wang L, Huang J, Ruan X. Sea Surface Wind Speed Retrieval from Marine Radar Image Sequences Based on GLCM-Derived Texture Features. Entropy. 2025; 27(8):877. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27080877
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hui, Haiyang Qiu, Lei Wang, Jingxi Huang, and Xingbo Ruan. 2025. "Sea Surface Wind Speed Retrieval from Marine Radar Image Sequences Based on GLCM-Derived Texture Features" Entropy 27, no. 8: 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27080877
APA StyleWang, H., Qiu, H., Wang, L., Huang, J., & Ruan, X. (2025). Sea Surface Wind Speed Retrieval from Marine Radar Image Sequences Based on GLCM-Derived Texture Features. Entropy, 27(8), 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27080877







