Abstract
The rapid development of network communication technology has led to an increased focus on the security of image storage and transmission in multimedia information. This paper proposes an enhanced image security communication scheme based on Fibonacci interleaved diffusion and non-degenerate chaotic system to address the inadequacy of current image encryption technology. The scheme utilizes a hash function to extract the hash characteristic values of the plaintext image, generating initial perturbation keys to drive the chaotic system to generate initial pseudo-random sequences. Subsequently, the input image is subjected to a light scrambling process at the bit level. The Q matrix generated by the Fibonacci sequence is then employed to diffuse the obtained intermediate cipher image. The final ciphertext image is then generated by random direction confusion. Throughout the encryption process, plaintext correlation mechanisms are employed. Consequently, due to the feedback loop of the plaintext, this algorithm is capable of resisting known-plaintext attacks and chosen-plaintext attacks. Theoretical analysis and empirical results demonstrate that the algorithm fulfils the cryptographic requirements of confusion, diffusion, and avalanche effects, while also exhibiting a robust password space and excellent numerical statistical properties. Consequently, the security enhancement mechanism based on Fibonacci interleaved diffusion and non-degenerate chaotic system proposed in this paper effectively enhances the algorithm’s resistance to cryptographic attacks.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the exponential growth of computer communication technology and network technology has led to a significant increase in the frequency, extent, and speed of data and information transmission via networks [1,2,3,4]. This has led to the emergence of new requirements for a secure transmission environment. Among the various types of data exchanged for information exchange, images present a particularly sensitive case, as they contain a significant amount of valuable information [5,6,7]. Consequently, the utilisation of image encryption technology [8,9,10] can effectively prevent the leakage of crucial data during the transmission process. A plethora of encryption methodologies have been proposed, including image steganography [11,12,13], biometric encoding [14,15], semi-tensor product [16,17,18], bit-level encryption [9,19,20], chaos theory [9,21,22,23] and others [24,25,26,27]. Among these, the unpredictability, pseudo-randomness, and high sensitivity to chaotic initial values make it the most effective and widely used method for image encryption algorithms [28,29,30,31,32].
From an international perspective, numerous scholars have achieved a series of significant theoretical and applied results in the utilization of chaotic systems for image encryption [33,34,35,36]. In existing research on chaotic image encryption, the performance of chaotic systems and algorithms has a significant impact on the security and efficiency of cryptographic systems [19,37,38]. On the other hand, image encryption methods based on Fibonacci have also gradually gained attention. In 2021, Ref. [39] proposed a novel image encryption scheme based on Quasigroup and Fibonacci transform. This scheme employs a novel image encryption structure that can encrypt images of any size. Experimental results have demonstrated the superiority of this scheme. In 2023, Ref. [40] presented a secure image encryption method using Fibonacci and Tribonacci transforms. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed image encryption algorithm can securely resist various illegal attacks. In 2024, Ref. [41] introduced a reversible fragile watermark model. This model first generates a watermark from the image using DCT transform and then encrypts the watermark using Fibonacci Q matrix technology to enhance the security of the model. Despite some progress in digital image encryption research in this area, the algorithms designed still have certain limitations due to inherent flaws in encryption systems [21,42]. From a security perspective, existing pixel-level chaotic image encryption algorithms still require further improvement to combat various illegal attacks. Continued research in this field is of great significance for protecting user data privacy [43,44,45], ensuring data integrity, and defending against various forms of attacks [46,47,48]. It is expected to provide more innovative solutions for the development of information security [49,50,51] and secure digital image transmission.
This paper presents a novel image privacy protection scheme based on Fibonacci interleaved diffusion and non-degenerate discrete chaos. Experimental results show that the algorithm exhibits excellent encryption effectiveness and good efficiency. The proposed image encryption algorithm is able to effectively resist various illegal attacks. The main contributions and innovations of the paper are as follows:
- This encryption algorithm introduces a novel diffusion mechanism. By leveraging the principles of Fibonacci-related mathematics, a Fibonacci sequence interleaved diffusion method is devised, which effectively resists statistical analysis and enhances the security of encryption.
- The majority of existing encryption algorithms are susceptible to potential risks. This image privacy protection scheme employs plaintext correlation to generate dynamic chaotic keys, significantly enhancing the ability to resist cryptographic attacks.
- A significant number of the encryption algorithms currently in use are considered to be unreasonable. In the absence of relevant plaintext or ciphertext feedback, they become highly vulnerable to known-plaintext or chosen-plaintext attacks. In order to address this issue, the proposed secure image encryption scheme employs a dynamic feedback mechanism to continuously update encryption keys based on encrypted data. Building upon our current foundation of cryptanalysis research [52,53,54], it enhances security and strengthens the ability to withstand attacks like chosen-plaintext and chosen-ciphertext attacks.
The following section outlines the structure of the remainder of this paper. Section 2 provides an introduction to robust discrete hyper-chaotic systems and the rules of Fibonacci. Section 3 introduces the encryption algorithm designed in this paper. Section 4 presents the experimental and simulation results. The final section presents the conclusion of the paper.
2. Related Theory
2.1. Non-Degenerate Chaotic System
The non-degenerate discrete-time chaotic system [55] was selected for this study due to its simplicity, ease of implementation, and demonstrated chaotic properties. The chaotic system was derived step-by-step from the following formula.
In order to obtain the matrix , which is the result of a transformation of the matrix T, an asymptotically stable nominal system matrix T is required initially. This is achieved by applying a similar transformation to the matrix T using the non-singular matrix N.
Consequently, the iterative equation of the system is expressed as follows:
The poles of the nominal system are defined by the unit matrix and the uniform bounded inverse controller. The results of the designed discrete-time chaotic system are presented in Equation (3).
The final mathematical formulation of the chaotic system employed in this study is presented below:
2.2. Fibonacci Q Matrix
The Fibonacci Sequence is a sequence that the mathematician Fibonacci studied using the study of rabbit reproduction as an example, hence its designation as the “Rabbit Sequence”, also known as the Golden Section Sequence. It attracted considerable interest from society as soon as it was proposed. Following research, it was discovered that this sequence, which is characterized by a seemingly magical quality, plays an immeasurably important role. In particular, the sequence begins with 0 and 1, with each subsequent item being the sum of the previous two items. This can be expressed mathematically as follows:
This sequence has a wide range of applications in the fields of mathematics and computing, demonstrating some special mathematical properties and patterns. In this paper, the Fibonacci sequence is combined with image encryption to explore a diffusion method based on this mathematical approach. The specific steps are as follows:
The elements of the Fibonacci sequence are denoted as .
The initial term of the Fibonacci matrix is as follows:
The n-th power of the Fibonacci matrix is as follows:
The inverse matrix of the n-th power of the Fibonacci matrix is as follows:
3. The Proposed Encryption Algorithm
In contrast to traditional algorithms, this paper utilizes a discrete hyper-chaotic system and a hash function to generate the chaotic key required for encryption. This enhances the security of the algorithm and increases the difficulty of code breaking. The flowchart depicting the algorithm design is presented in Figure 1.
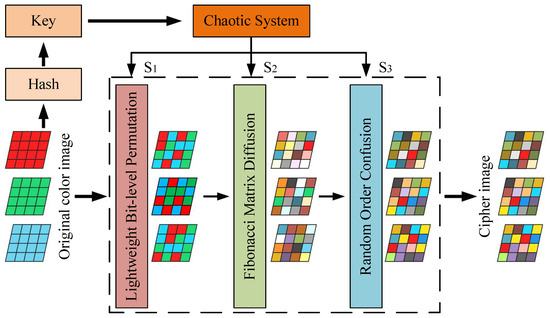
Figure 1.
The proposed algorithm flowchart.
Take the matrix as an example to encrypt a single channel, and the specific encryption process is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2.
Single-channel encryption example.
3.1. Chaos Key Generation and Sequence Preprocessing
After extracting features from the plaintext image P using a hash function, we obtain character-based fixed-length hexadecimal numbers. To simplify computation, each number is converted to a decimal number and represented by the variable . The image hash is then mathematically processed to obtain the initial key parameters, which are substituted into the chaotic system to obtain the chaotic sequences , and .
3.2. Lightweight Bit-Level Permutation
Image scrambling is a commonly employed encryption technique that aligns with the principles of confusion and diffusion as outlined in Shannon’s cryptography theory. This approach can enhance the security performance of encryption algorithms. There are two principal methods for scrambling images: pixel-level scrambling and bit-level scrambling. In pixel-level scrambling, only the pixel positions of the image are altered, while the statistical histogram of the scrambled image remains unchanged. This makes it susceptible to statistical analysis attacks. Bit-level scrambling not only changes the pixel positions of the image but also alters the pixel grayscale values, thereby providing stronger security performance. However, compared to pixel-level scrambling, efficiency is relatively lower for bit-level scrambling. Some researchers have highlighted that only scrambling image encryption schemes are insecure as they are vulnerable to chosen-plaintext or known-plaintext attacks, requiring a considerable amount of plaintext to decipher at least half of the equivalent passwords. The complexity of attacking encryption algorithms that only involve scrambling operations is proportional to the square of the required plaintext quantity. Based on this, a lightweight bit-level image scrambling method is proposed in this article, and Algorithm 1 introduces the specific operational process.
| Algorithm 1 Lightweight Bit-level Permutation |
| Require: Chaotic sequence ; plaintext image P of size Ensure: Intermediate ciphertext image
|
Step 1: Expand the RGB components of the color plaintext image P with dimensions bit by bit, each with a length of , represented as , and . Combine the RGB components in top-to-bottom order to form a binary matrix of dimensions , denoted as .
Step 2: Process the chaotic sequence to generate index sequences and . These are used for row and column scrambling of the bit image. By swapping the rows and columns of the image bit matrix, the scrambled bit matrix is obtained.
Step 3: Resize the scrambled bit matrix for subsequent diffusion operations. The size should be changed from the original back to , resulting in the scrambled image denoted as .
3.3. Fibonacci Matrix Diffusion
The RGB layering of the permuted image is performed, after which a selection of different Fibonacci number sequence matrices from the chaotic sequence is made, with the intention of diffusing each layer of . This results in the diffused image . The Fibonacci diffusion algorithm is shown in Algorithm 2, with specific operational steps as follows:
| Algorithm 2 Fibonacci Matrix Diffusion |
| Require: Chaotic matrix ; intermediate image of size Ensure: Diffused ciphertext image
|
Step 1: Reconstruct into a chaotic matrix of the same size as , and then preprocess it into integers within the range of [3:21] as follows:
where M and N represent the width and height of the image respectively.
Step 2: Substitute the obtained chaotic matrix into the Fibonacci Q matrix constructed by Formula (8) to obtain the matrix .
where ; .
Step 3: Substitute the intermediate ciphertext image into the Fibonacci Q matrix constructed by Formula (8) to obtain the matrix :
Step 4: Diffuse the two matrices and obtained block by block.
Step 5: The diffused matrix is the ciphertext matrix C.
Step 6: Place the values of the ciphertext matrix C in the appropriate range, where is the diffused ciphertext image.
3.4. Random Direction Confusion
Convert the chaotic sequence to a chaotic index matrix I of the same size as the intermediate ciphertext , then perform power operations on the index matrix I to obtain the operation matrix S. The specific operations are shown in Algorithm 3, and the calculation formula is as follows:
| Algorithm 3 Random Direction Confusion |
| Require: Computing matrix S; index matrix I; intermediate ciphertext of size Ensure: Final ciphertext
|
The encryption process is hereby completed, and is the final ciphertext image. The single-channel decryption flow is shown in Figure 3.
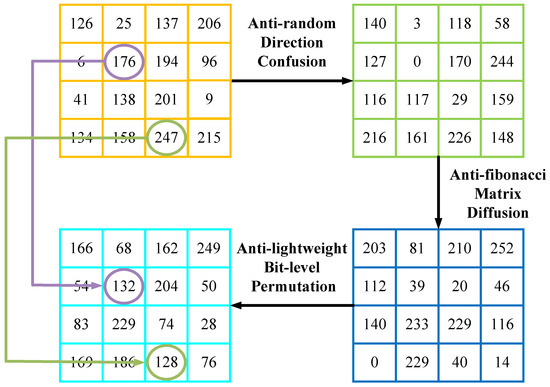
Figure 3.
Single-channel decryption example.
4. Experimental Results and Analysis Discussion
The experimental platform used was a MacBook Pro with MATLAB R2022b laboratory software installed. The device is equipped with a 2.2 GHz quad-core Intel Core i7 processor, 16 GB of RAM, and runs on the Windows 10 operating system. The images presented in this paper are sourced from the USC-SIPI database.
4.1. Histogram Analysis
The histogram illustrates the distribution of each gray level in the image and its corresponding frequency. Generally, the histogram of a plaintext image displays specific statistical patterns, while the histogram of an encrypted image exhibits statistical characteristics similar to a noise distribution. Therefore, effective encryption algorithms can transform the image into a form resembling a noise distribution to conceal the primary information of the image. One plaintext image of each size was selected for histogram testing, as shown in Figure 4. The encrypted image effectively conceals the main information of the plaintext image, preventing attackers from cracking the ciphertext image through statistical analysis.

Figure 4.
Plaintext and ciphertext images and corresponding histograms. (a) Plain-images. (b) Histograms of (a). (c) Encryption results of (a). (d) Histograms of (c). (e) Decryption results of (c).
4.2. The Coefficient of Adjacent Pixels
The objective of image encryption algorithms is to break the correlation between pixels. This prevents attackers from relying on pixel correlation for decryption attempts. This paper uses the ‘Lena’ image as an example to illustrate this process. We randomly selected 3000 pairs of neighboring pixels from the plaintext and ciphertext. Then, we calculated the correlation coefficients of these neighboring pixels in horizontal, vertical, diagonal, and anti-diagonal directions. The scatter plots corresponding to the experiments are displayed in Figure 5, and the results of the correlation analysis are presented in Table 1. The specific calculation formula is as follows:
where and constitute the i-th pair of horizontal, vertical, diagonal or anti-diagonal neighboring pixels, N is the total number of horizontal/vertical/diagonal/anti-diagonal neighboring pixels, is the covariance between pixel values x and y, D(x) and D(y) are the pixel value x and pixel value y mean-square error, and E(x) and E(y) are the expected values of pixel value x and pixel value y, respectively. is the correlation coefficient of pixel values x and y.
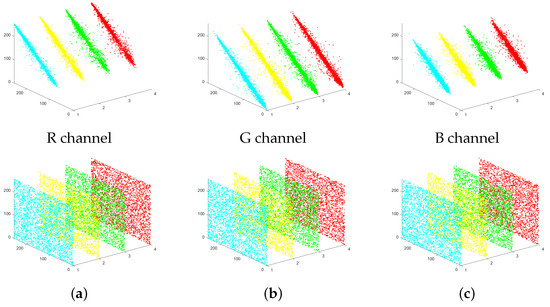
Figure 5.
Adjacent pixels’ correlation of plaintext image and ciphertext image. (a) R channel; (b) G channel; (c) B channel.

Table 1.
Neighboring pixel correlation values for plaintext and ciphertext image in different directions.
The findings demonstrate that our encryption algorithm successfully minimizes the correlation between pixels, rendering it almost undetectable in the ciphertext. This provides strong evidence that our proposed encryption algorithm is highly secure.
4.3. Differential Attack Analysis
To evaluate the robustness of the proposed image encryption algorithm against differential attacks, we analyze three key metrics: the Number of Pixels Change Rate (NPCR), the Unified Average Changing Intensity (UACI), and the Bit-level Average Change Intensity (BACI). These metrics are commonly used to measure the sensitivity of the ciphertext to small changes in the plaintext and help determine whether the encryption scheme can effectively resist differential cryptanalysis.
NPCR measures the percentage of pixels that change value when a single pixel in the plaintext is altered. A higher NPCR value indicates stronger diffusion characteristics in the encryption algorithm. NPCR is computed as follows:
where is the image size, and is defined as follows:
Here, and denote the encrypted images generated from two plaintexts differing by a single pixel.
UACI evaluates the average intensity of differences between the ciphertexts, defined by the following:
A higher UACI value indicates better resistance to differential attacks by ensuring greater changes in pixel intensity.
BACI extends UACI to the bit level, capturing average bit-wise changes between two ciphertexts:
where calculates the number of differing bits between corresponding pixel values.
The experiments were conducted by encrypting images of three different sizes, where a single pixel in the plaintext was modified and the corresponding encrypted outputs were compared. The results are listed in Table 4 and Table 2, and the NPCR visualization comparison results are listed in Figure 6, Figure 7, and Figure 8, respectively. The consistently high NPCR, UACI, and BACI values across different resolutions validate the proposed algorithm’s strong resistance against differential attacks.

Table 2.
Comparison of NPCR values between different algorithms.
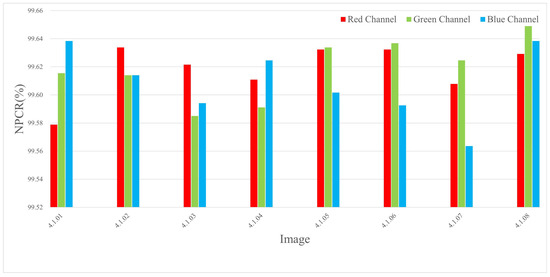
Figure 6.
The NPCR test values for different channels of 256 × 256 size image.

Figure 7.
The NPCR test values for different channels of 512 × 512 size image.
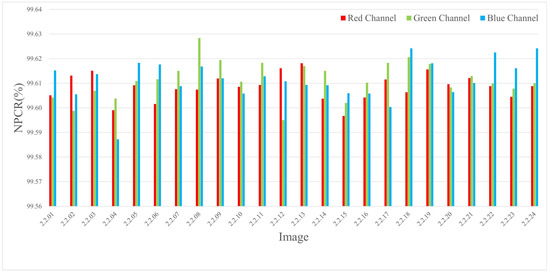
Figure 8.
The NPCR test values for different channels of 1024 × 1024 size image.
4.4. Image Quality Analysis
Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR) and Structural Similarity (SSIM) are frequently used to evaluate the quality of encryption in image processing. PSNR includes Mean Square Error (MSE) as a component, which is defined as follows:
where MSE represents the mean square error between the plaintext image X and the ciphertext image Y, with H and W representing the height and width of the image, respectively. Q denotes the pixel level of the image.
SSIM is a measure of the similarity between two images, defined as follows:
where and denote the mean values of image X and Y, respectively. The standard deviation of image X and Y are denoted by and , respectively. L represents the dynamic range of pixel values.
Equations (22) and (23) are used to calculate the values of MSE, PSNR, and SSIM. Additionally, to ensure generality, several images were selected to test the encryption module. The encrypted images should have a PSNR of less than 10 dB and an SSIM value close to 0. Table 4 and Table 3 details the results of the tests. The experimental results demonstrate the excellent encryption performance of our algorithm.

Table 3.
Comparison of information entropy between different algorithms.
4.5. Information Entropy Analysis
In image encryption, information entropy serves as a vital measure, representing the extent of uncertainty linked to image data and commonly serving to assess the randomness within the system. A higher information entropy value suggests enhanced uncertainty and diminished visibility of image data, indicating better encryption efficacy of the algorithm. To illustrate, a contrast was drawn between the information entropy of the initial and encrypted images. For the information source m, the information entropy can be calculated using the following equation:
where L is the total number of symbols and denotes the probability of the symbols. From Table 4, we can see that the experimental results are close to 8, so the proposed algorithm has good information entropy properties.

Table 4.
Results of the proposed encryption system: NPCR, UACI, BACI, MSE, PSNR, SSIM, information entropy.
4.6. Key Space Analysis
Cryptography experts emphasize that to effectively resist brute-force attacks, the key length of chaotic encryption systems should be no less than 128 bits. In the chaotic system used in this paper [55], the key space is defined as
which comprises a total of 55 key parameters, including the nominal system parameters of the non-degenerate hyper-chaotic system, parameters of the feedback controller, initial conditions of four distinct key types, and the SHA-2 hash value.
Based on experimental analysis, the effective key lengths are as follows: the nominal system parameters provide a key space of approximately , the feedback controller parameters contribute around , the initial chaotic values account for roughly , and the SHA-2 hash value itself corresponds to a key length of . Summing these components yields a total key length of
4.7. Analysis of Plaintext Sensitivity
The sensitivity of plaintext refers to the extent of ciphertext changes observed when operating on the pixels of plaintext. Insufficient sensitivity of plaintext in encryption algorithms can increase the risk of leakage, and plaintext sensitivity plays an important role in enhancing the algorithm’s ability to resist plaintext attacks. In this section, four pixels of plaintext images are randomly selected and the encryption effects of the original image and the processed plaintext image are compared, with the results shown in Table 5. The experimental results using images of different sizes are shown in Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11. From the experimental data, it can be seen that the algorithm proposed in this research has good plaintext sensitivity.

Table 5.
Plaintext sensitivity analysis of different images.
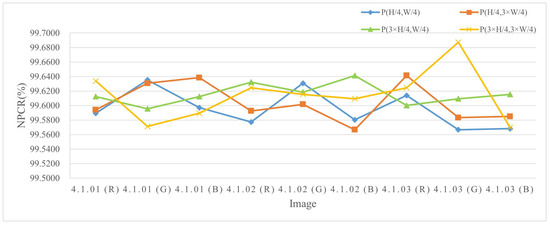
Figure 9.
Plaintext sensitivity test results for images of size 256 × 256.

Figure 10.
Plaintext sensitivity test results for images of size 512 × 512.

Figure 11.
Plaintext sensitivity test results for images of size 1024 × 1024.
4.8. Theoretical Security Analysis of Fibonacci Diffusion
4.8.1. Effective Nonlinearity Through Dynamic Matrix Diffusion
The proposed diffusion mechanism utilizes a block-wise transformation:
where is a pixel block, and is a Fibonacci Q-matrix of power n (as defined in Equation (8)). Although the transformation is linear per block, the use of a dynamically changing matrix —with indices determined by the chaotic matrix —induces system-level nonlinearity.
Two key cryptographic properties are introduced:
- Exponential Amplification: Elements of follow the Fibonacci recurrence , with growth rate , where . As n increases, even minor differences in are exponentially amplified.
- Path Confusion: The dynamic index , derived from a chaotic sequence , assigns a unique matrix to each block, disrupting any attempt at consistent linear modeling across the image.
The scheme therefore achieves confusion in Shannon’s sense, while retaining invertibility via (Equation (9)).
4.8.2. Resistance to Differential Cryptanalysis
Let be a one-pixel input difference, with . The output difference is as follows:
We approximate the expected Hamming weight of as follows:
This implies that at least bits are expected to change on average. Given , the minimum expected bit change satisfies the following:
This theoretical bound corroborates the empirical values reported in Section 4.3, confirming robustness against differential attacks.
4.8.3. Key Sensitivity Analysis
Assuming a one-step tampering of the chaotic index, i.e., , the deviation in the transformation matrix is quantified by the Frobenius norm:
For , . This yields a pixel change probability approximated by an exponential decay model:
This estimation reflects the high diffusion sensitivity to minor key variations. Since is derived from via the following:
recovering n requires inversion of the chaotic map, which for a 128-bit key space implies a brute-force complexity of , ensuring resistance against chosen-plaintext attacks.
4.8.4. Resistance to Algebraic Attacks
The Fibonacci recurrence introduces algebraic structure, which may suggest susceptibility to equation-solving attacks. However, the encryption structure effectively prevents this by the following:
- Each block generates four linear equations but includes six unknowns: four matrix entries of and two plaintext variables.
- The chaotic index n differs per block, preventing consistent coefficient reuse and eliminating possibilities of system-wide equation alignment.
- The modular reduction operation () introduces nonlinear discontinuities (wrap-around effects), further complicating algebraic inference.
Hence, any system of equations derived from known-plaintext attacks becomes underdetermined, nonuniform, and nonlinear, rendering algebraic cryptanalysis infeasible in practice.
4.9. Cryptanalysis of the Proposed Encryption Algorithm
To evaluate the robustness of the proposed Fibonacci-chaos encryption scheme against chosen-plaintext attacks (CPA), we conducted a targeted cryptanalysis experiment based on our previous cryptanalytic research framework [52,53,54]. In a CPA scenario, an adversary can arbitrarily select plaintext images and obtain their corresponding ciphertexts, which is particularly effective in revealing structural weaknesses in diffusion mechanisms. Our methodology employs uniform-color test images—known to expose deterministic patterns in Fibonacci-based diffusion systems.
Four monochromatic images of size were generated with all pixel values set to the following:
- 170 (10101010): Probes alternating bit patterns.
- 255 (11111111): Evaluates all-one input handling.
We encrypted the uniform-color test images using the proposed algorithm. As shown in Figure 12, the resulting ciphertext images exhibit snow-like randomness, with no visible patterns or structural biases, indicating strong confusion and diffusion effects. Experimental results affirm that the proposed scheme withstands chosen-plaintext attacks.

Figure 12.
Cryptanalysis of the proposed encryption algorithm.
4.10. Run Time Analysis
To evaluate the computational efficiency of the proposed image encryption scheme, we conducted experiments on a PC equipped with an AMD 5950X processor, 128 GB RAM, and 8TB storage, using MATLAB R2025a. The experiments involved repeatedly encrypting standard RGB images of sizes 256 × 256 × 3 and 512 × 512 × 3, with the average execution time calculated over multiple iterations. The results are summarized in Table 6, which compares the proposed method against several recent schemes, including AES and state-of-the-art algorithms from 2024 and 2025. As demonstrated in Table 6, the proposed method significantly outperforms conventional encryption standards like AES in computational speed. These results clearly indicate that the proposed scheme is not only secure and effective but also highly efficient, making it suitable for real-time image encryption applications.

Table 6.
Comparison of time with different algorithms.
5. Conclusions
This paper proposes an image security communication enhancement scheme based on Fibonacci interleaved diffusion and non-degenerate discrete chaos. The scheme utilizes a hash function to extract the hash characteristic values of the plaintext image, generates an initial perturbation key-driven chaotic system to produce an initial pseudo-random sequence, and then applies a lightweight bit-level scrambling to the input image. The intermediate ciphertext image is then subjected to diffusion and random permutation using the Fibonacci Q matrix, resulting in the final ciphertext image. Throughout the encryption process, a plaintext correlation mechanism is employed. Consequently, due to the feedback loop of the plaintext, the algorithm is capable of resisting known-plaintext and chosen-plaintext attacks. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed algorithm exhibits high security and robustness, with strong resistance to various cryptographic attacks. Consequently, the image encryption algorithm proposed in this paper represents a preferred security communication technology solution, with broad prospects for applications such as secure transmission of multimedia information in big data environments.
Author Contributions
Z.X. is mainly responsible for the supervision and leadership of the planning and implementation of scientific research activities. Z.X. and W.X. are mainly responsible for the research design and code writing and article writing. Y.L. and W.C. are mainly responsible for literature search and format proofreading. Z.Y. and X.C. are mainly responsible for Latex typesetting and drawing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- Lai, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L. Image encryption using memristive hyperchaos. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 22863–22881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xie, E.Y.; Li, C. Periodicity Analysis of Logistic Map over Ring Z3n. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2023, 33, 2350063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, C.; Ou, B. Cryptanalysis of an image block encryption algorithm based on chaotic maps. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2020, 54, 102566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Zhang, C.; Xia, J.; Liang, X.; Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, G. Chaotic 4D Modulation with Intrusion Detection for Secure Data Centers. J. Light. Technol. 2025, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Wang, Y.; Gan, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y. Preserving privacy while revealing thumbnail for content-based encrypted image retrieval in the cloud. Inf. Sci. 2022, 604, 115–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Gong, X.; Li, H.; Wang, S. Differential cryptanalysis of image cipher using block-based scrambling and image filtering. Inf. Sci. 2021, 554, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Fu, J.; Gan, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y. An image encryption scheme based on multi-objective optimization and block compressed sensing. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 108, 2671–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, O.; Erkan, U.; Toktas, A.; Gao, S. PSO-based image encryption scheme using modular integrated logistic exponential map. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 237, 121452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toktas, A.; Erkan, U.; Gao, S.; Pak, C. A robust bit-level image encryption based on Bessel map. Appl. Math. Comput. 2024, 462, 128340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Wu, R.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Tang, X. New image encryption algorithm based on hyperchaotic 3D-IHAL and a hybrid cryptosystem. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 27826–27843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Ye, X.; Zhou, S.; Gao, S.; Shi, Y. A secure image protection algorithm by steganography and encryption using the 2D-TSCC. Chin. Phys. B 2021, 30, 110501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ma, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Gao, S. Image Steganography in Color Conversion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2024, 71, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Huang, H.; Qi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, Y. Joint Coverless Steganography and Image Transformation for Covert Communication of Secret Messages. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2024, 11, 2951–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Teng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Si, R.; Liu, P. Mutil-medical image encryption by a new spatiotemporal chaos model and DNA new computing for information security. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 235, 121090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Xie, Z.; Wu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Feng, W. Exploring the future application of UAVs: Face image privacy protection scheme based on chaos and DNA cryptography. J. King Saud Univ.—Comput. Inf. Sci. 2023, 36, 101871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, S. Image encryption algorithm based on the matrix semi-tensor product with a compound secret key produced by a Boolean network. Inf. Sci. 2020, 539, 195–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wu, R.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Tang, X. EFR-CSTP: Encryption for face recognition based on the chaos and semi-tensor product theory. Inf. Sci. 2022, 621, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, S. A chaotic image encryption algorithm based on a counting system and the semi-tensor product. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 80, 10301–10322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Iu, H.; Zhang, H. Image encryption algorithm based on the dynamic RNA computing and a new chaotic map. Integration 2024, 101, 102336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikas; Parhi, D.R. Chaos-based optimal path planning of humanoid robot using hybridized regression-gravity search algorithm in static and dynamic terrains. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 140, 110236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Iu, H.H.C.; Mou, J.; Erkan, U.; Liu, J.; Wu, R.; Tang, X. Temporal action segmentation for video encryption. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 183, 114958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, R.; Liang, J.; Liu, R. Cryptanalysis and improvement of a reversible data-hiding scheme in encrypted images by redundant space transfer. Inf. Sci. 2021, 545, 188–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ahmad, M.; Woźniak, M. Exploiting robust quadratic polynomial hyperchaotic map and pixel fusion strategy for efficient image encryption. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 246, 123190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Iu, H.H.C.; Wang, M.; Jiang, D.; El-latif, A.; Wu, R.; Tang, X. Design, Hardware Implementation, and Application in Video Encryption of the 2D Memristive Cubic Map. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 21807–21815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wu, R.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Tang, X. Asynchronous Updating Boolean Network Encryption Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 4388–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, Q.; Ling, B.; Pun, C.M.; Huang, G.; Yuan, X.; Zhong, G.; Ayouni, S.; Chen, J. DPPAD-IE: Dynamic Polyhedra Permutating and Arnold Diffusing Medical Image Encryption Using 2D Cross Gaussian Hyperchaotic Map. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2025; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Lam, C.T.; Yuan, X.; Im, S.K.; Machado, P. MMQW: Multi-Modal Quantum Watermarking Scheme. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2024, 19, 5181–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Dai, W.; Wu, S.; Li, G. Application of two general Memristor models in chaotic systems. In Memristors—The Fourth Fundamental Circuit Element—Theory, Device, and Applications; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Li, G.; Xu, X.; Song, X.; Wu, S. Multistable dynamics and attractors self-reproducing in a new hyperchaotic complex Lü system. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2023, 33, 093112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.; Liu, H.; Li, G.; Xu, X.; Gu, Y. A general method for generating multi-scroll and multi-wing chaotic systems and its implementation of attractor reproduction. Phys. Scr. 2023, 98, 085232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Li, G.; Xu, W.; Zhong, H.; Xu, X. A compressive sensing encryption scheme for dual color images based on discrete memristor map and Rubik’s cube scramble. Optik 2023, 286, 170991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, G.; Xu, W.; Xu, X.; Zhong, H. Modelling and dynamic analysis of a novel seven-dimensional Hamilton conservative hyperchaotic systems with wide range of parameter. Phys. Scr. 2023, 98, 055218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Lin, Y.; Liu, T.; Wen, H. Face privacy protection scheme by security-enhanced encryption structure and nonlinear dynamics. iScience 2024, 27, 110768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, Q.; He, S.; Zhang, Y. What is the lowest cost to calculate the Lyapunov exponents from fractional differential equations? Nonlinear Dyn. 2025, 113, 14825–14871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Zhang, C.; Liang, X.; Xia, J.; Lin, Y.; Lin, Y. Intrusion Detection-Embedded Chaotic Encryption via Hybrid Modulation for Data Center Interconnects. Opt. Lett. 2025, 50, 4450–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Iu, H.H.; Erkan, U.; Şimşek, C.; Toktas, A.; Cao, Y.; Wu, R.; Mou, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, C. A 3D Memristive Cubic Map with Dual Discrete Memristors: Design, Implementation, and Application in Image Encryption. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2025; early access. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, W.; Zhang, C.; Liang, X.; Lin, Y.; Xia, J.; Li, Y. A Novel Secure Key Stream Generator Based on Chaotic Multi-State Cellular Automata. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Xie, Z.; Chen, T.; Cheng, X.; Wen, H. Image privacy protection scheme based on high-quality reconstruction DCT compression and nonlinear dynamics. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 257, 124891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. Image data security using Quasigroup combined with Fibonacci Q-transformation. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2021, 61, 102941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, C.; Dhara, B.C.; Umer, S.; Asari, V. An Efficient and Secure Method of Plaintext-Based Image Encryption Using Fibonacci and Tribonacci Transformations. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 48421–48440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouarroudj, R.; Souami, F.; Zohra Bellala, F.; Zerrouki, N. A reversible fragile watermarking technique using fourier transform and Fibonacci Q-matrix for medical image authentication. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 92, 105967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Lin, Y.; Xie, Z.; Liu, T. Chaos-based block permutation and dynamic sequence multiplexing for video encryption. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Bao, L.; Chen, C.P. A new 1D chaotic system for image encryption. Signal Process. 2014, 97, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Tang, Z.; Gan, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y. SE-NDEND: A novel symmetric watermarking framework with neural network-based chaotic encryption for Internet of Medical Things. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 90, 105877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Zhang, C.; Liang, X.; Luo, Y.; Wang, X.; Qiu, K. Chaotic phase noise-like encryption based on geometric shaping for coherent data center interconnections. Opt. Express 2023, 32, 1595–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Lin, D.; Feng, B.; Lü, J.; Hao, F. Cryptanalysis of a Chaotic Image Encryption Algorithm Based on Information Entropy. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 75834–75842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, E.Y.; Li, C.; Yu, S.; Lu, J. On the cryptanalysis of Fridrich’s chaotic image encryption scheme. Signal Process. 2016, 132, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Lin, Y.; Li, Q.; Xing, Z.; Yuan, X. Lightweight Image Encryption Algorithm Using 4D-NDS: Compound Dynamic Diffusion and Single-Round Efficiency. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 74652–74662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yin, Y.; Erkan, U.; Toktas, A.; Zhang, Y. Novel hyperchaotic system: Implementation to audio encryption. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2025, 193, 116088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhao, R.; Wen, W.; Zhu, Y. RAPP: Reversible Privacy Preservation for Various Face Attributes. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2023, 18, 3074–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, X.; Yuan, X. Privacy Image Secrecy Scheme Based on Chaos-Driven Fractal Sorting Matrix and Fibonacci Q-Matrix. Vis. Comput. 2025, 41, 6931–6941. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, H.; Lin, Y. Cryptanalysis of an image encryption algorithm using quantum chaotic map and DNA coding. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 237, 121514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Lin, Y.; Feng, Z. Cryptanalyzing a bit-level image encryption algorithm based on chaotic maps. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2024, 51, 101634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Lin, Y. Cryptanalyzing an image cipher using multiple chaos and DNA operations. J. King Saud Univ.—Comput. Inf. Sci. 2023, 35, 101612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Liu, Z.; Lai, H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Liao, Y.; Ma, L.; et al. Secure DNA-Coding Image Optical Communication Using Non-Degenerate Hyperchaos and Dynamic Secret-Key. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, H.; Ding, W. VSDHS-CIEA: Color image encryption algorithm based on novel variable-structure discrete hyperchaotic system and cross-plane confusion strategy. Inf. Sci. 2024, 665, 120332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Lan, Z.; Sun, K.; Xu, W. A simple color image encryption algorithm based on a discrete memristive hyperchaotic map and time-controllable operation. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 165, 109543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, H. An image encryption algorithm based on a compound-coupled chaotic system. Digit. Signal Process. 2023, 146, 104367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Fu, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, P. Batch image encryption using cross image permutation and diffusion. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2024, 80, 103686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Xu, X.; Jiang, Z.H.; Meng, D.; Sun, K. An image encryption scheme without additional key transmission based on an N-dimensional closed-loop coupled triangular wave model. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 185, 115039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Teng, L.; Zhou, W.; Yan, X.; Xia, Z.; Zhou, S. A new 2D cross hyperchaotic Sine-modulation-Logistic map and its application in bit-level image encryption. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 261, 125328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Tao, Z.; Erkan, U.; Toktas, A.; Iu, H.H.C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Multidimensional chaotic signals generation using deep learning and its application in image encryption. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 156, 111017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).