Efficient Entanglement Swapping in Quantum Networks for Multi-User Scenarios †
Abstract
1. Introduction
- PSES is extended to M-PSES to mitigate resource contention in multi-user concurrent quantum communication and further improve ES efficiency (Section 6).
- We add simulation experiments of M-PSES to demonstrate and discuss its performance improvements in multi-user concurrent quantum communication (Section 7).
- We extend and supplement the content related to PSES, such as explaining the reason for choosing heuristic algorithms to implement PSES (Section 5.4.1), conducting algorithm-level experiments for PSES (Section 5.4.3), and justifying the principle of parallel ES in PSES (Section 5.5).
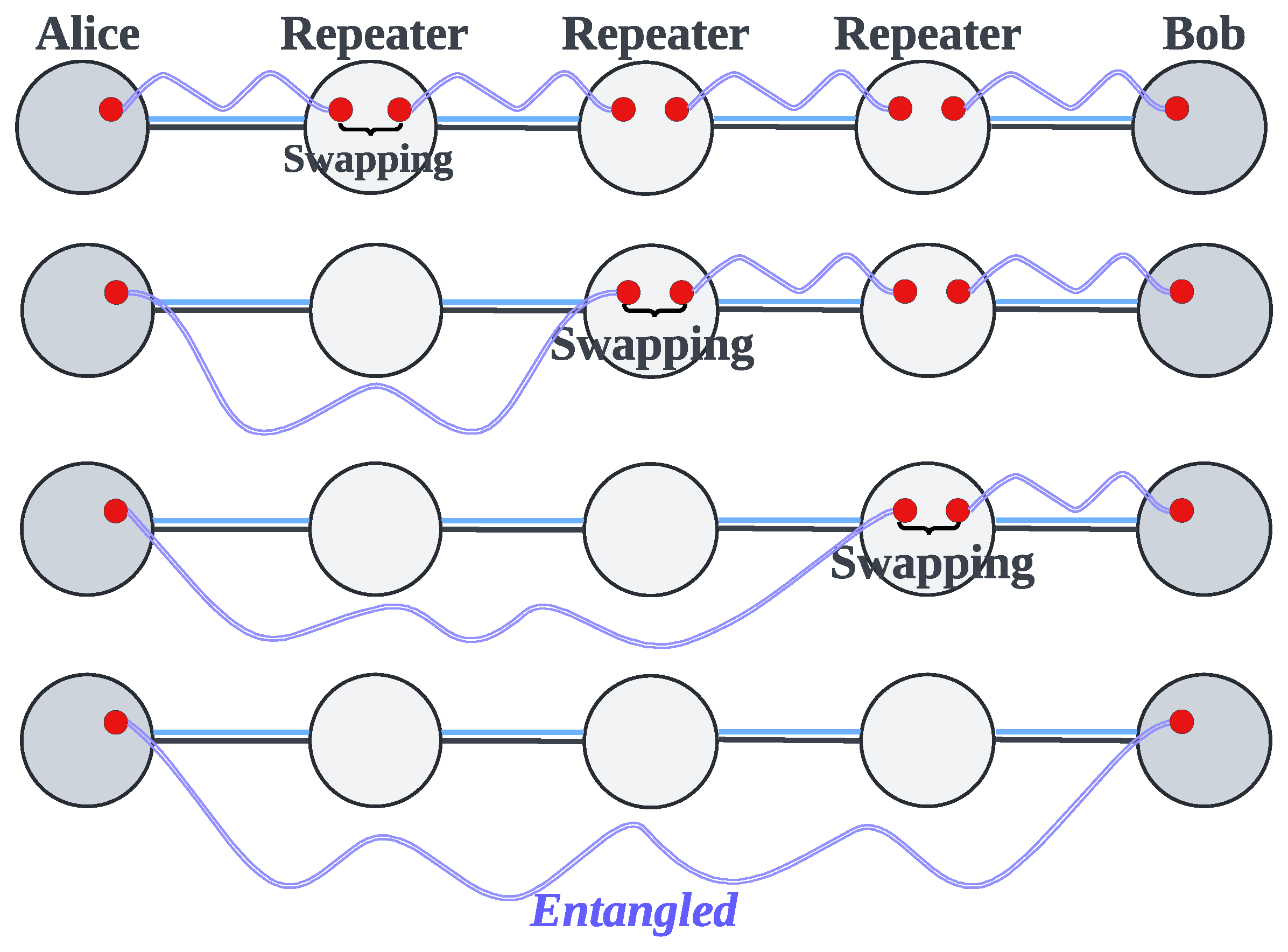
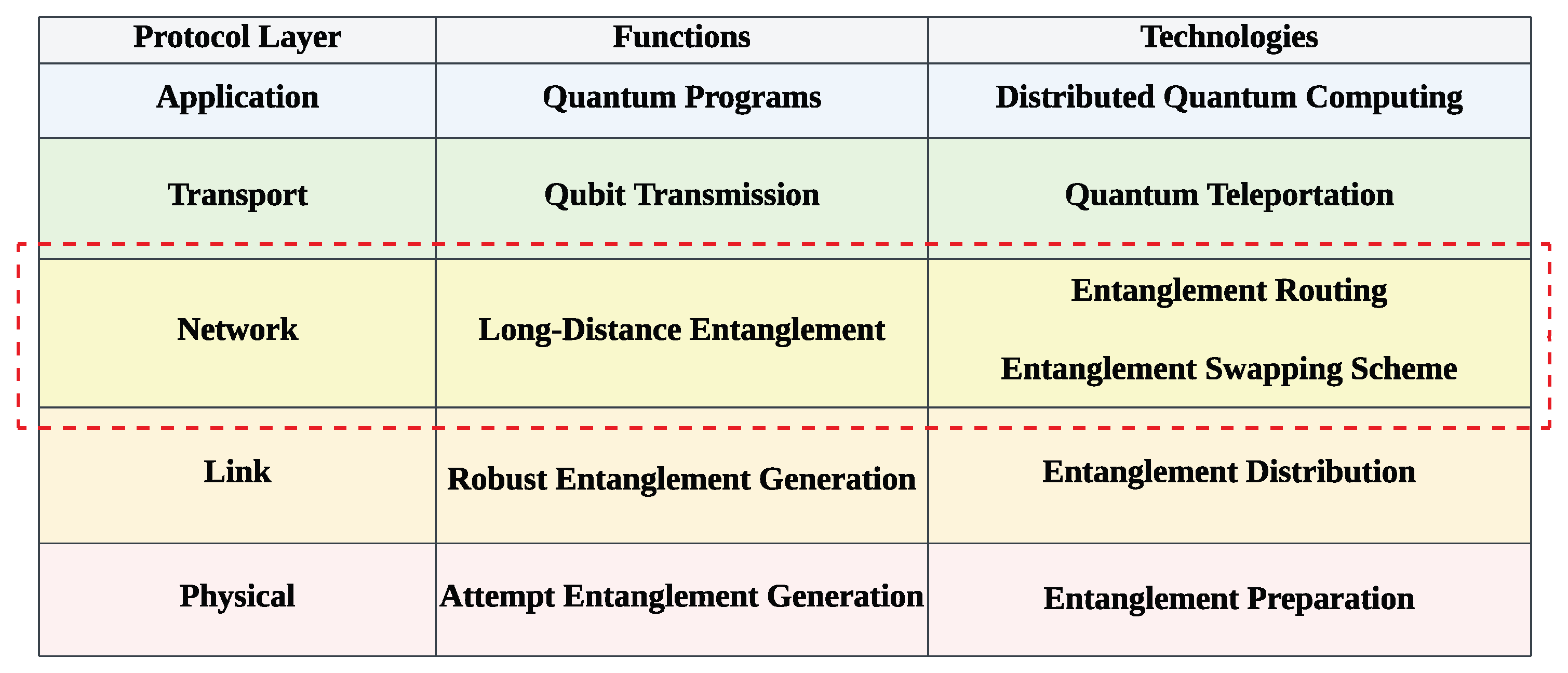
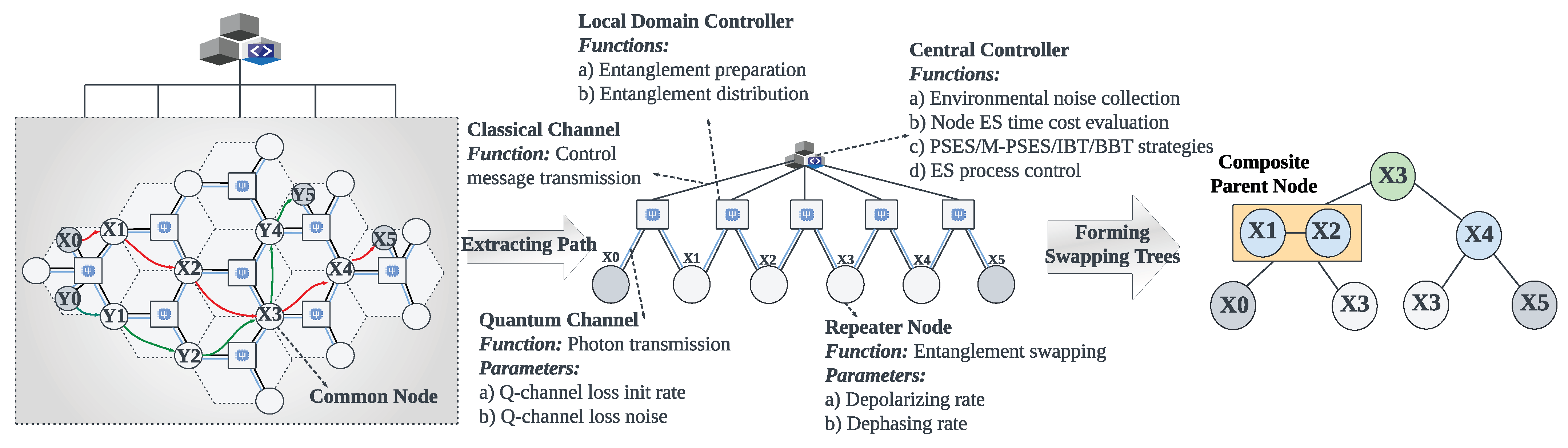
2. Preliminaries and Background
- The depolarizing rate represents the probability that the qubit in quantum memory will depolarize with time.
- The dephasing rate represents the probability that the qubit will dephase with time.
- The Q-channel loss init rate represents the initial probability of a photon being lost upon entry to a quantum channel.
- The Q-channel loss noise represents the noise of the quantum channel, and the unit is dB/km.
3. Related Work
4. Analysis of Existing Entanglement Swapping Strategies
4.1. Suboptimal Efficiency
4.2. Time Synchronization
4.3. Entanglement Swapping Failure
4.4. Unsuitability for Multi-User Concurrent Quantum Communication
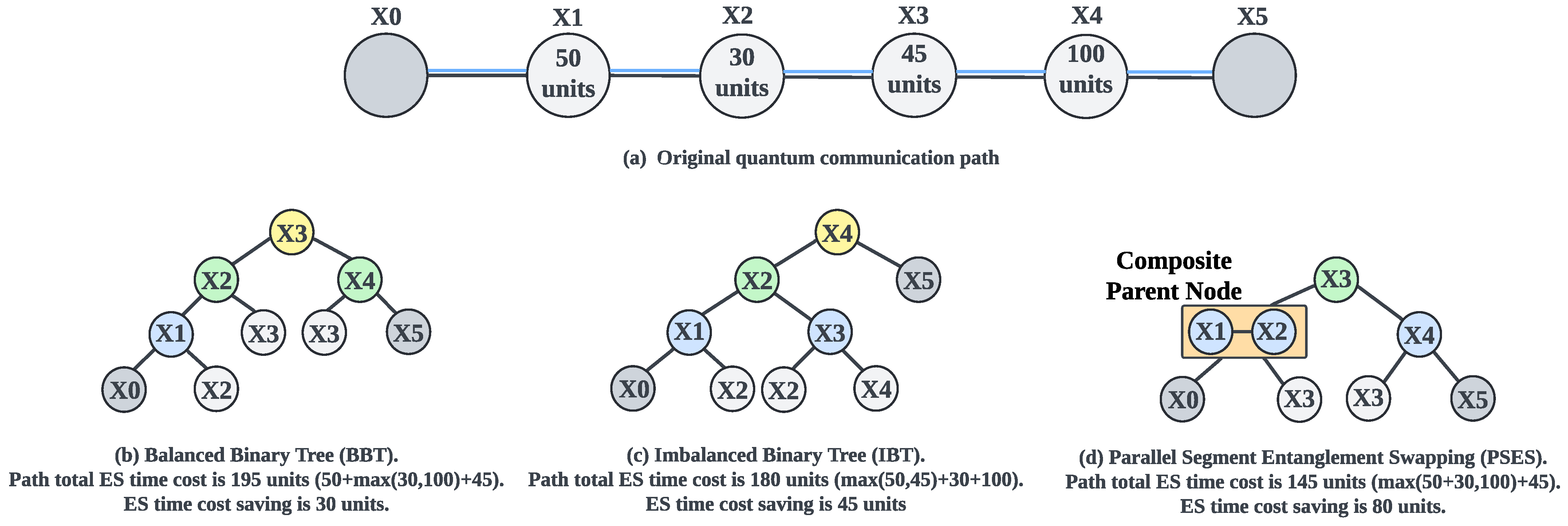
5. The Design of Parallel Segment Entanglement Swapping
5.1. Overview
5.2. Time Cost of Node Entanglement Swapping
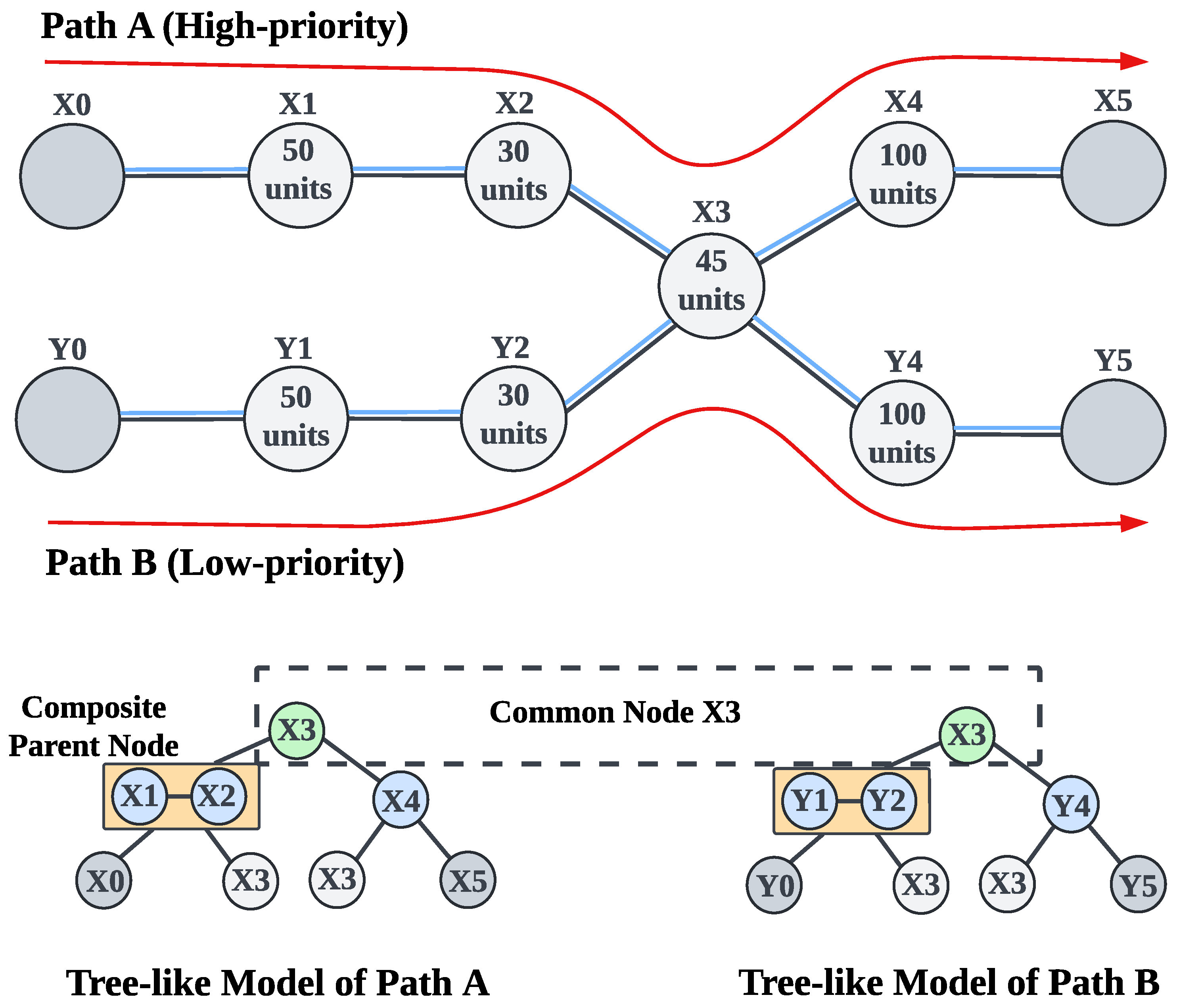
5.3. Tree-like Model
5.4. Algorithms for Generating Tree-like Model
5.4.1. Reasons for Choosing Heuristic Approach
5.4.2. Design of Heuristic Algorithms
| Algorithm 1: Layer Greedy. |
 |
| Algorithm 2: Segment Greedy. |
 |
5.4.3. Assessment of Heuristic Algorithms
5.5. Principle of Performing Parallel Entanglement Swapping
5.6. Time Synchronization and Node Swapping Failure Processing
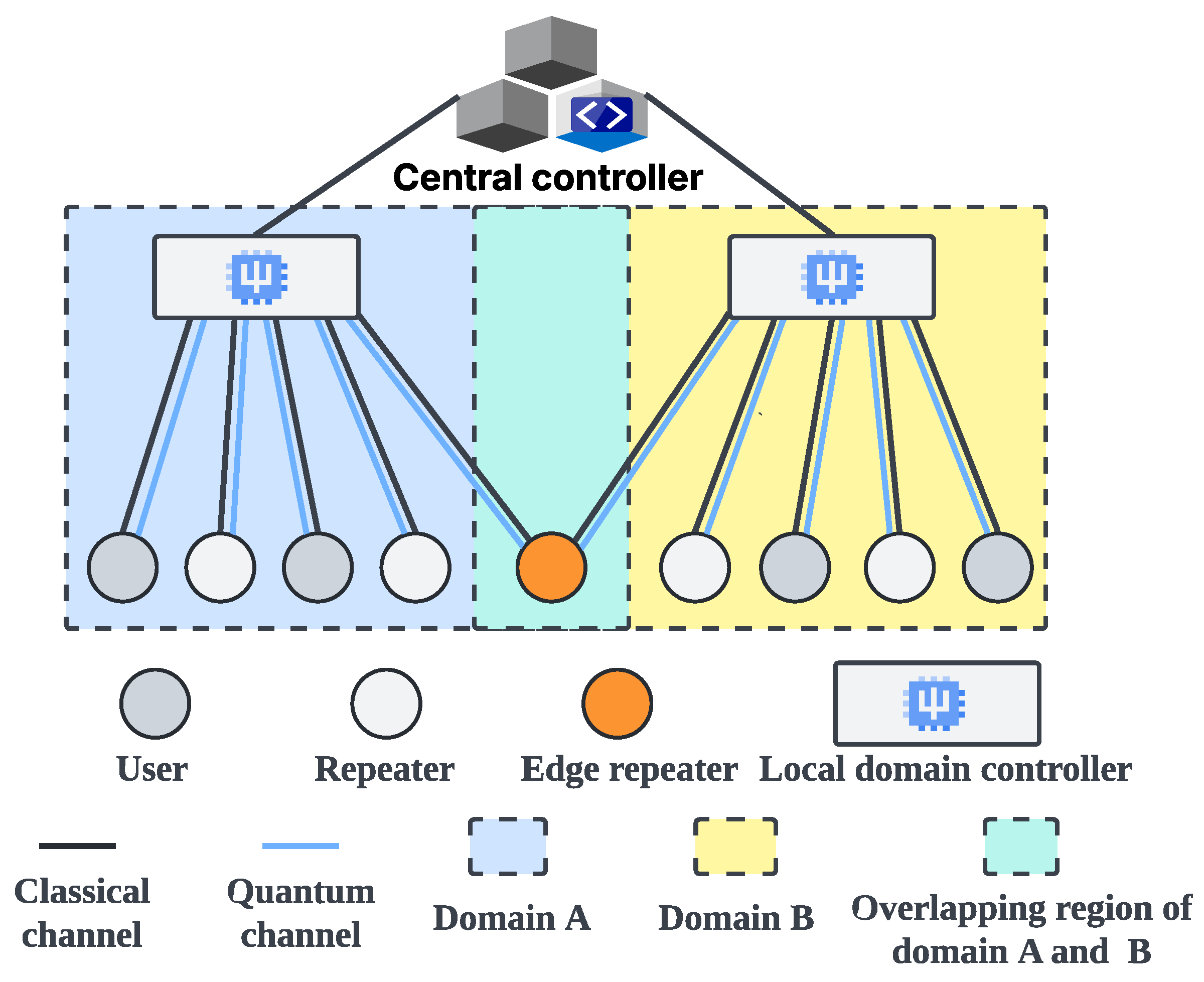
6. Parallel Segment Entanglement Swapping for Multi-User Concurrent Quantum Communication
6.1. Challenges of Resource Contention
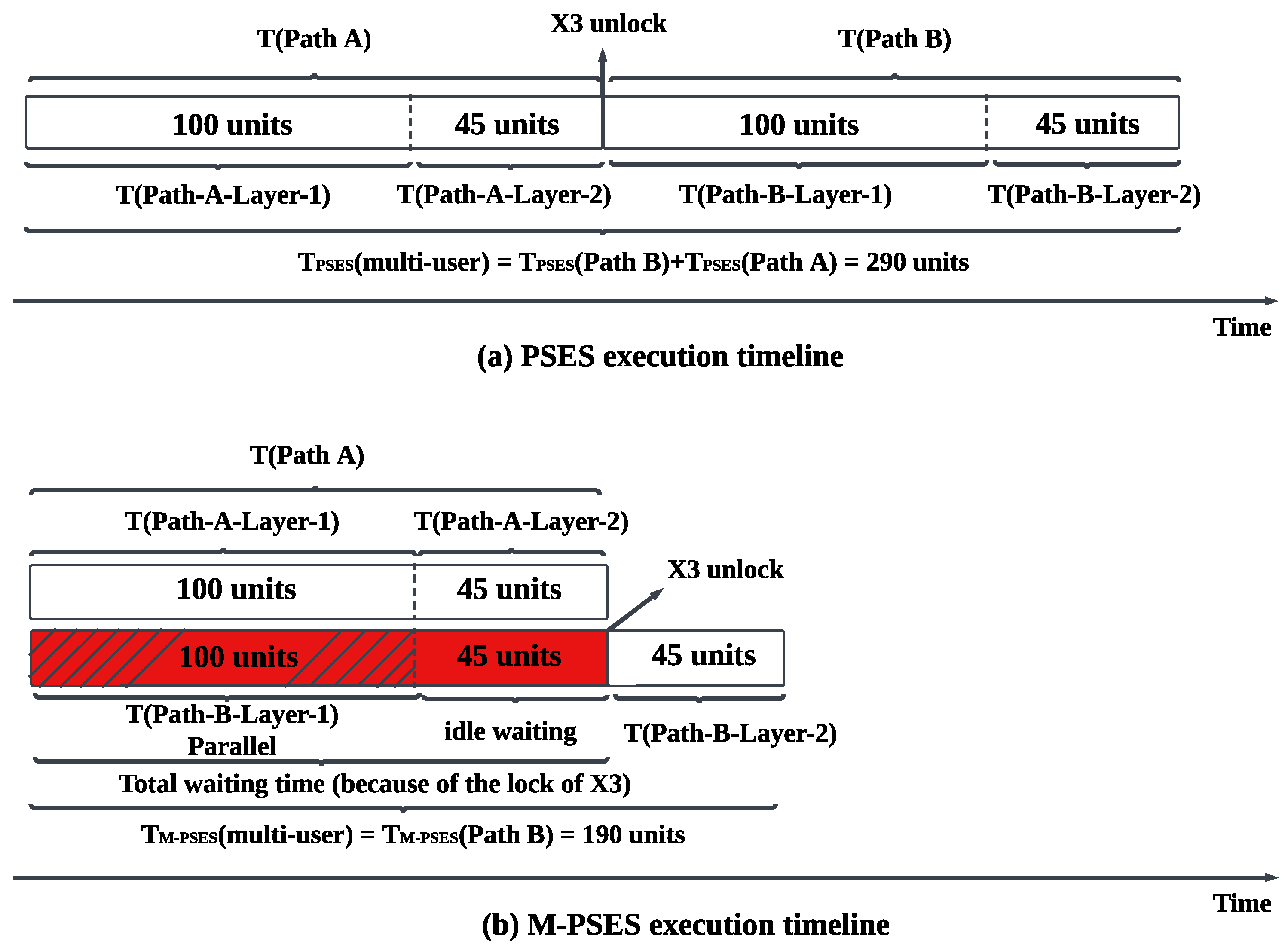
6.2. Design of Multi-User Parallel Segment Entanglement Swapping
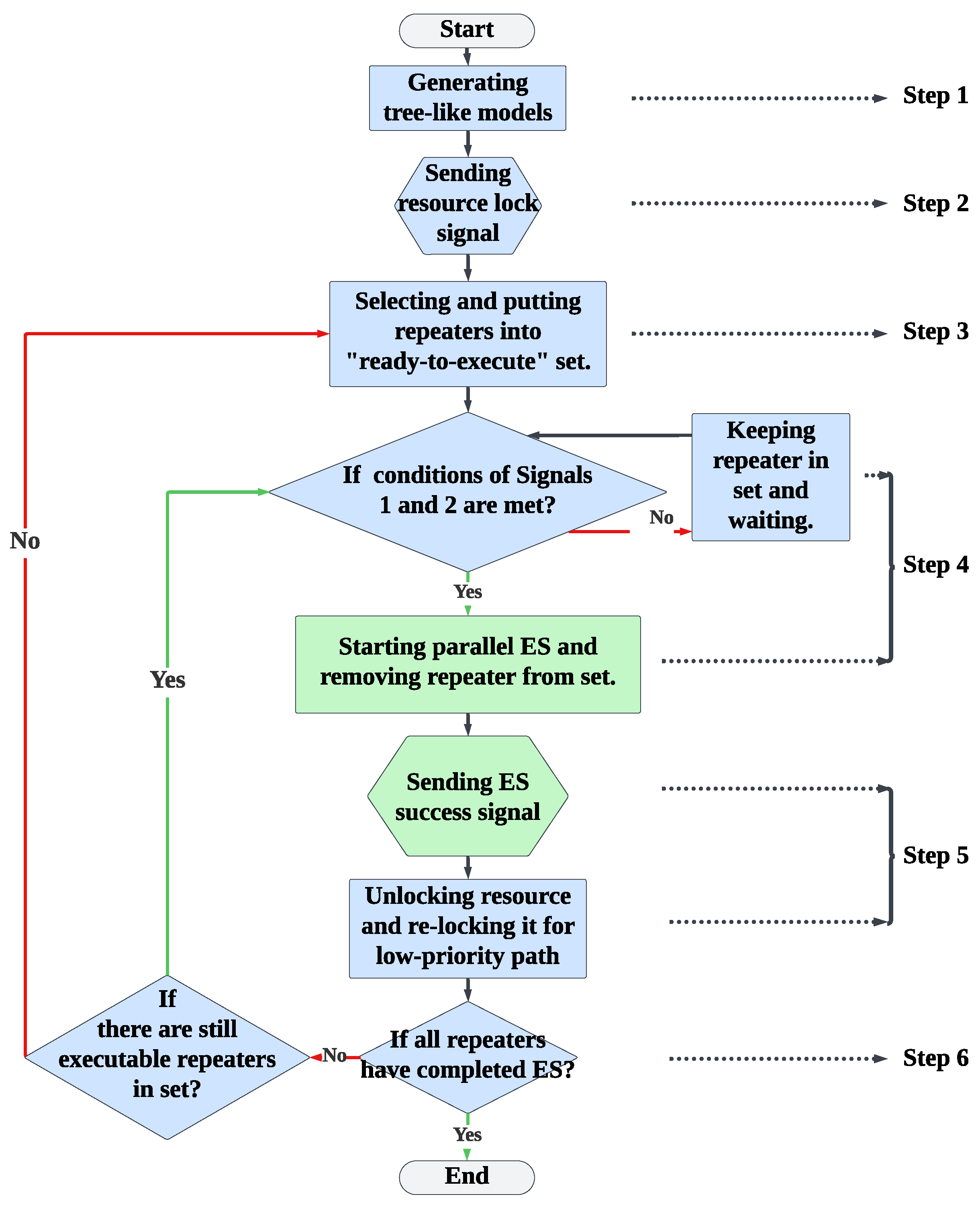
6.3. Implementation of Multi-User Parallel Segment Entanglement Swapping
7. Simulation and Evaluation
7.1. Simulation Environment
7.2. Methodology
7.3. Performance in Point-to-Point Quantum Communication Scenarios
7.4. Performance in Multi-User Concurrent Quantum Communication Scenarios
7.5. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gyongyosi, L.; Imre, S. A survey on quantum computing technology. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2019, 31, 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciapuoti, A.S.; Caleffi, M.; Tafuri, F.; Cataliotti, F.S.; Gherardini, S.; Bianchi, G. Quantum internet: Networking challenges in distributed quantum computing. IEEE Netw. 2019, 34, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, W.; Wehner, S. Towards Large-Scale Quantum Networks. In Proceedings of the Sixth Annual ACM International Conference on Nanoscale Computing and Communication (NANOCOM), Dublin, Ireland, 25–27 September 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Cuomo, D.; Caleffi, M.; Cacciapuoti, A.S. Towards a distributed quantum computing ecosystem. IET Quantum Commun. 2020, 1, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meter, R.; Satoh, R.; Benchasattabuse, N.; Teramoto, K.; Matsuo, T.; Hajdušek, M.; Satoh, T.; Nagayama, S.; Suzuki, S. A quantum internet architecture. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Quantum Computing and Engineering (QCE), Broomfield, Colorado, USA, 18–23 September 2022; pp. 341–352. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Xue, K.; Li, J.; Yu, N.; Liu, J.; Wei, D.S.; Sun, Q.; Lu, J. Building a large-scale and wide-area quantum internet based on an OSI-alike model. China Commun. 2021, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Zhang, D.; Loke, S.W.; Lin, S.; Lu, L. Building a Hierarchical Architecture and Communication Model for the Quantum Internet. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2024, 42, 1919–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, S.D.; Kok, P. Efficient high-fidelity quantum computation using matter qubits and linear optics. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 71, 060310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, E.T.; Benjamin, S.C. Measurement-based entanglement under conditions of extreme photon loss. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 130502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Qian, C. Concurrent entanglement routing for quantum networks: Model and designs. In Proceedings of the the Annual Conference of the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication on the Applications, Technologies, Architectures, and Protocols for Computer Communication (SIGCOMM), Virtual Event, USA, 10–14 August 2020; pp. 62–75. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg, A.; Skrzypczyk, M.; Coopmans, T.; Wubben, L.; Rozpundefineddek, F.; Pompili, M.; Stolk, A.; Pawełczak, P.; Knegjens, R.; de Oliveira Filho, J.; et al. A link layer protocol for quantum networks. In Proceedings of the the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication (SIGCOMM), Beijing, China, 19–23 August 2019; pp. 159–173. [Google Scholar]
- Pant, M.; Krovi, H.; Towsley, D.; Tassiulas, L.; Jiang, L.; Basu, P.; Englund, D.; Guha, S. Routing entanglement in the quantum internet. Npj Quantum Inf. 2019, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.C.; Cheng, X.; Sarihan, M.C.; Wong, C.W. Recent advances in high-dimensional quantum frequency combs. Newton 2025, 1, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwmeester, D.; Pan, J.W.; Mattle, K.; Eibl, M.; Weinfurter, H.; Zeilinger, A. Experimental quantum teleportation. Nature 1997, 390, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.W.; Bouwmeester, D.; Weinfurter, H.; Zeilinger, A. Experimental entanglement swapping: Entangling photons that never interacted. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Loke, S.W.; Zhang, D. Parallel Segment Entanglement Swapping. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Quantum Communications, Networking, and Computing (QCNC), Kanazawa, Japan, 1–3 July 2024; pp. 271–279. [Google Scholar]
- Coopmans, T.; Knegjens, R.; Dahlberg, A.; Maier, D.; Nijsten, L.; de Oliveira Filho, J.; Papendrecht, M.; Rabbie, J.; Rozpedek, F.; Skrzypczyk, M.; et al. Netsquid, a network simulator for quantum information using discrete events. Commun. Phys. 2021, 4, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Example of Entanglement Swapping in Repeater Chain. 2021. Available online: https://docs.netsquid.org/latest-release/learn_examples/learn.examples.repeater_chain.html (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Werner, R.F. Quantum states with Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen correlations admitting a hidden-variable model. Phys. Rev. A 1989, 40, 4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briegel, H.J.; Dür, W.; Cirac, J.I.; Zoller, P. Quantum repeaters: The role of imperfect local operations in quantum communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 81, 5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.M.; Lukin, M.D.; Cirac, J.I.; Zoller, P. Long-distance quantum communication with atomic ensembles and linear optics. Nature 2001, 414, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangouard, N.; Simon, C.; De Riedmatten, H.; Gisin, N. Quantum repeaters based on atomic ensembles and linear optics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2011, 83, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Peng, T.; Win, M.Z. Optimal remote entanglement distribution. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2020, 38, 540–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderibaneh, M.; Zhan, C.; Gupta, H.; Ramakrishnan, C. Efficient quantum network communication using optimized entanglement swapping trees. IEEE Trans. Quantum Eng. 2022, 3, 4100420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, N.; Saglamyurek, E.; Mallahzadeh, H.; Slater, J.A.; George, M.; Ricken, R.; Hedges, M.P.; Oblak, D.; Simon, C.; Sohler, W.; et al. Spectral multiplexing for scalable quantum photonics using an atomic frequency comb quantum memory and feed-forward control. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 053603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Towsley, D. Entanglement swapping for repeater chains with finite memory sizes. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.10994. [Google Scholar]
- Shchukin, E.; Schmidt, F.; van Loock, P. Waiting time in quantum repeaters with probabilistic entanglement swapping. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 100, 032322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Humble, T.S.; Danageozian, A. Adaptive mitigation of time-varying quantum noise. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Quantum Computing and Engineering (QCE), Bellevue, WA, USA, 17–22 September 2023; pp. 99–110. [Google Scholar]
- Etxezarreta Martinez, J.; Fuentes, P.; Crespo, P.; Garcia-Frias, J. Time-varying quantum channel models for superconducting qubits. Npj Quantum Inf. 2021, 7, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, W.; Wehner, S.; Van Meter, R.; Rijsman, B.; Cacciapuoti, A.; Caleffi, M.; Nagayama, S. RFC 9340: Architectural Principles for a Quantum Internet; RFC Editor: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangouard, N.; Dubessy, R.; Simon, C. Quantum repeaters based on single trapped ions. Phys. Rev. A 2009, 79, 042340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimian, S.; Tavassoly, M.; Ghasemi, M. Multistage entanglement swapping using superconducting qubits in the absence and presence of dissipative environment without Bell state measurement. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Source Code of PSES and M-PSES. 2025. Available online: https://github.com/HeLabFzu/PSES_and_M-PSES (accessed on 27 April 2025).
- Huang, Z.; Lai, H.; Wan, L. An Advanced Collaborative Routing Algorithm for Optimizing Entanglement and Resource Efficiency in Quantum Networks. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2025, 64, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xue, K.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Li, R.; Yu, N.; Sun, Q.; Lu, J. REDP: Reliable Entanglement Distribution Protocol Design for Large-Scale Quantum Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2024, 42, 1723–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jia, Z. On Optimum Entanglement Purification Scheduling in Quantum Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2024, 42, 1779–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidharan, S.; Li, L.; Kim, J.; Lütkenhaus, N.; Lukin, M.D.; Jiang, L. Optimal architectures for long distance quantum communication. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, W.J.; Stephens, A.M.; Devitt, S.J.; Harrison, K.A.; Nemoto, K. Quantum communication without the necessity of quantum memories. Nat. Photonics 2012, 6, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borregaard, J.; Pichler, H.; Schröder, T.; Lukin, M.D.; Lodahl, P.; Sørensen, A.S. One-way quantum repeater based on near-deterministic photon-emitter interfaces. Phys. Rev. X 2020, 10, 021071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, S.W. From Distributed Quantum Computing to Quantum Internet Computing: An Introduction, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Victoria, Australia, 2023; pp. 165–171. [Google Scholar]
- Rozpedek, F.; Schiet, T.; Thinh, L.P.; Elkouss, D.; Doherty, A.C.; Wehner, S. Optimizing practical entanglement distillation. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 97, 062333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roffe, J. Quantum error correction: An introductory guide. Contemp. Phys. 2019, 60, 226–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Heuristic Method | Optimization Method | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Algorithm | Layer Greedy | Segment Greedy | Dynamic Programming [24] |
| Principle | Find the optimal layer solution | Find the optimal segment solution | Find the optimal tree solution |
| Problem Size (Granularity) | Middle (Layer level) | Small (Segment level) | Big (Tree level) |
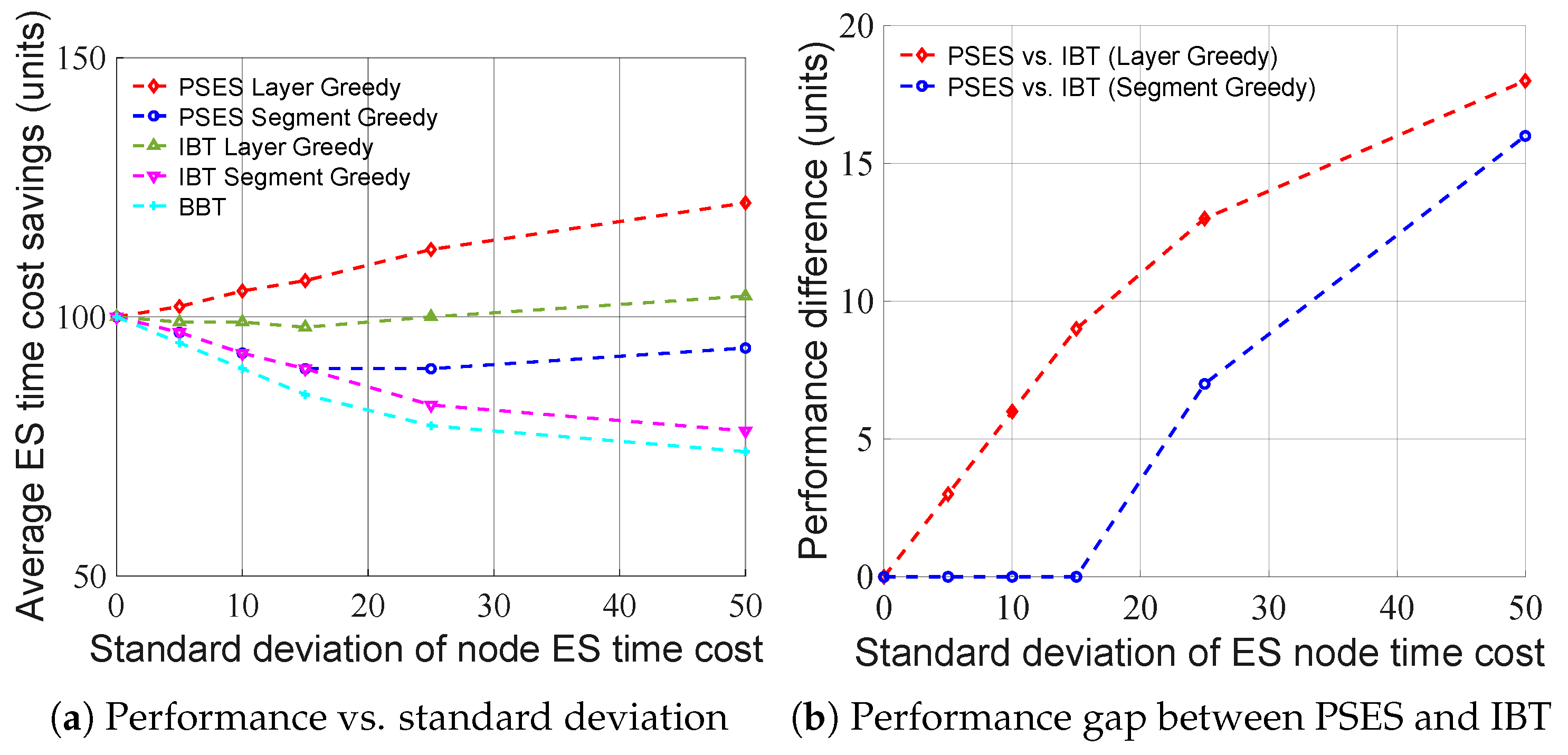
| Performance | Middle (see Figure 6 and Figure 7) | Low (see Figure 6 and Figure 7) | High [24] |
| Time Cost | Middle (see Figure 8) | Low (see Figure 8) | Huge [24] |
| Short-Path Scenarios (Hops ≤ 7) | Long-Path Scenarios (Hops > 7) | |
|---|---|---|
| Best-fit scheme | PSES Layer Greedy | PSES Segment Greedy |
| Reason |
Best performance (Figure 6 and Figure 7); s-level algorithm time cost (Figure 8) | Acceptable performance (Figure 6 and Figure 7); s-level algorithm time cost, regardless of hops (Figure 8) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, B.; Loke, S.W.; Lu, L.; Zhang, D. Efficient Entanglement Swapping in Quantum Networks for Multi-User Scenarios. Entropy 2025, 27, 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060615
He B, Loke SW, Lu L, Zhang D. Efficient Entanglement Swapping in Quantum Networks for Multi-User Scenarios. Entropy. 2025; 27(6):615. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060615
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Binjie, Seng W. Loke, Luke Lu, and Dong Zhang. 2025. "Efficient Entanglement Swapping in Quantum Networks for Multi-User Scenarios" Entropy 27, no. 6: 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060615
APA StyleHe, B., Loke, S. W., Lu, L., & Zhang, D. (2025). Efficient Entanglement Swapping in Quantum Networks for Multi-User Scenarios. Entropy, 27(6), 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060615







