Elucidating the Role of the Mixing Entropy in Equilibrated Nanoconfined Reactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Statistical Mechanics Modeling and Computations
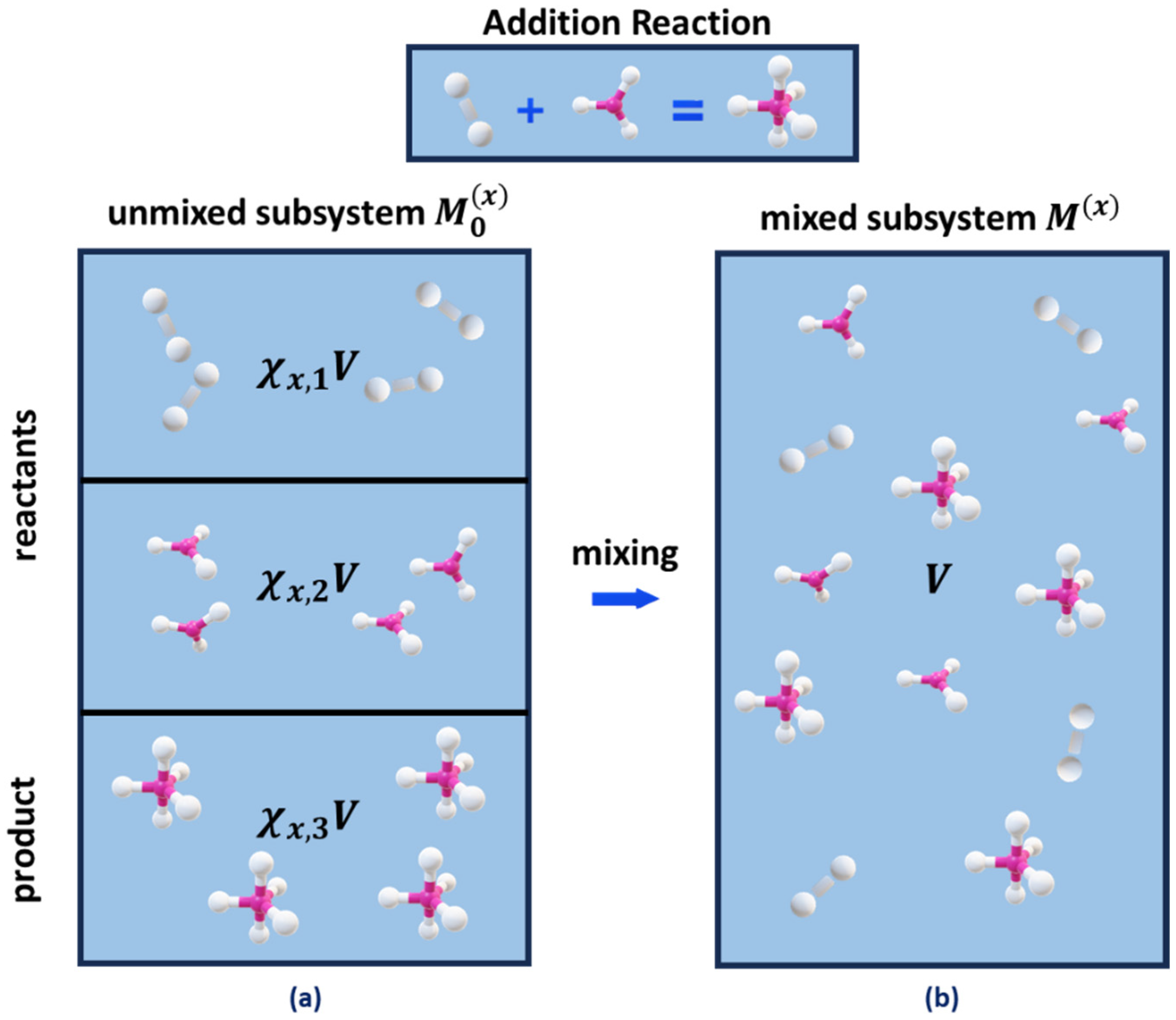
2.1. Nanoconfined Reaction Mixing Entropy
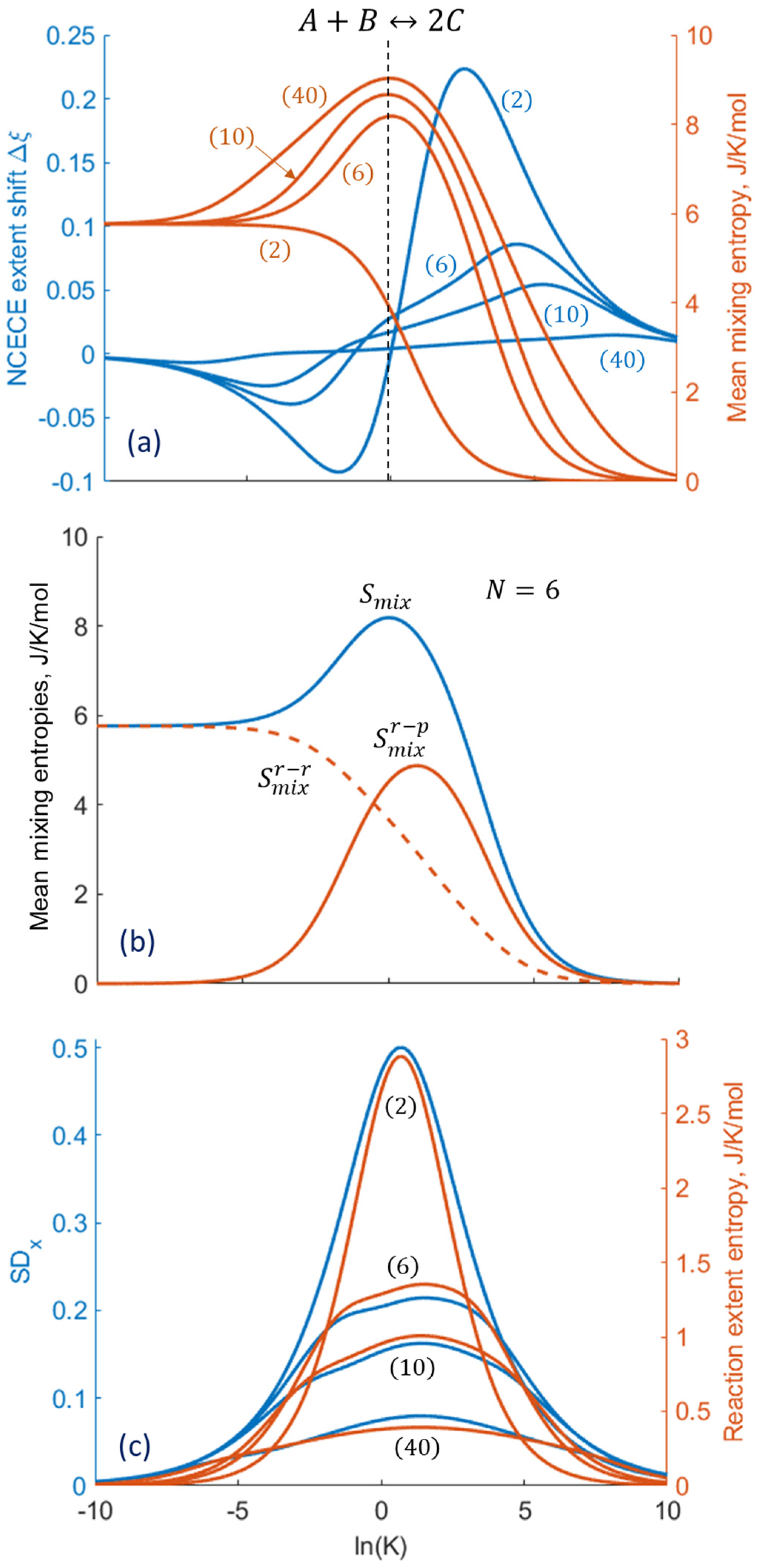
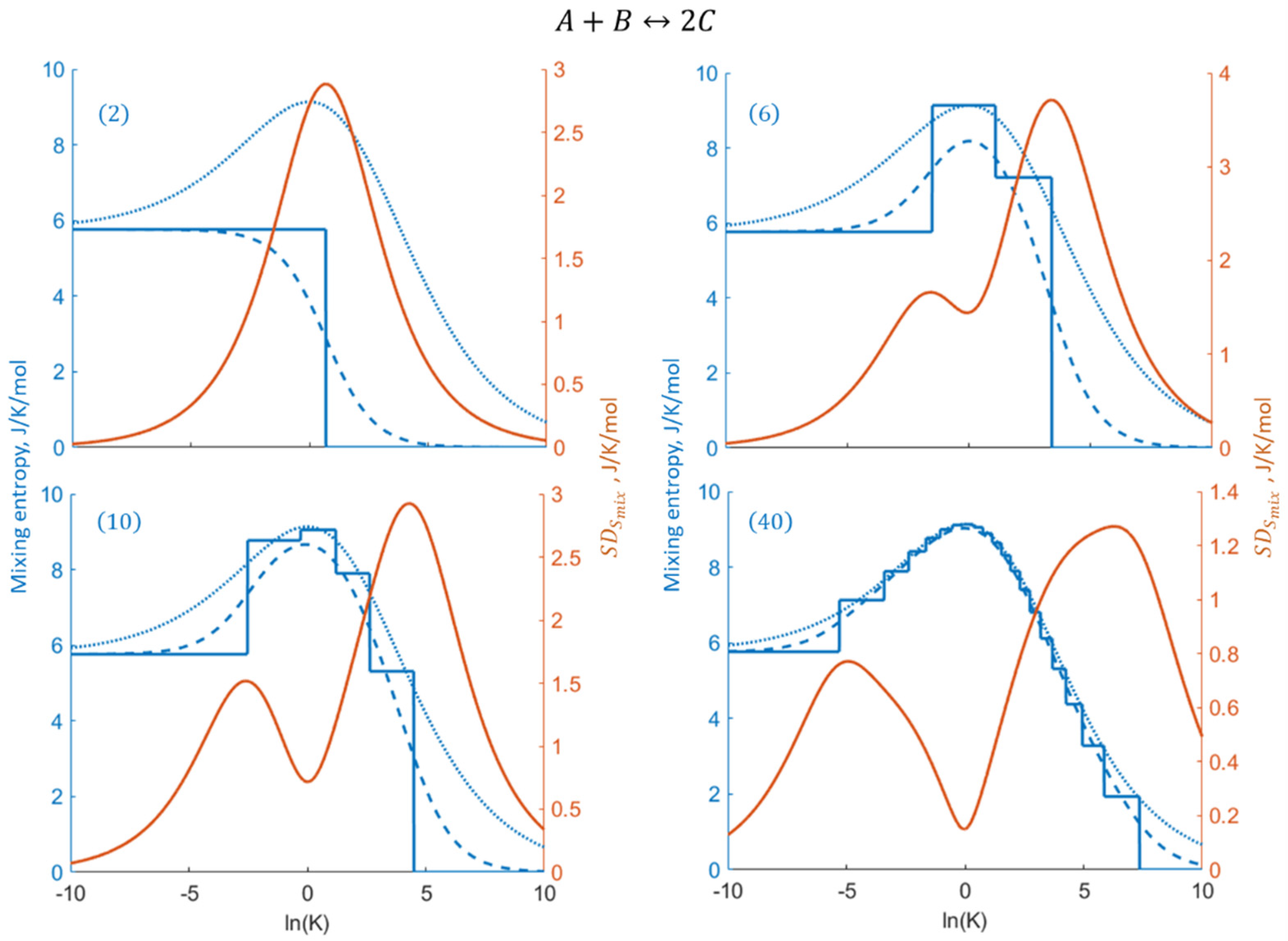
2.2. The General Combination Reaction
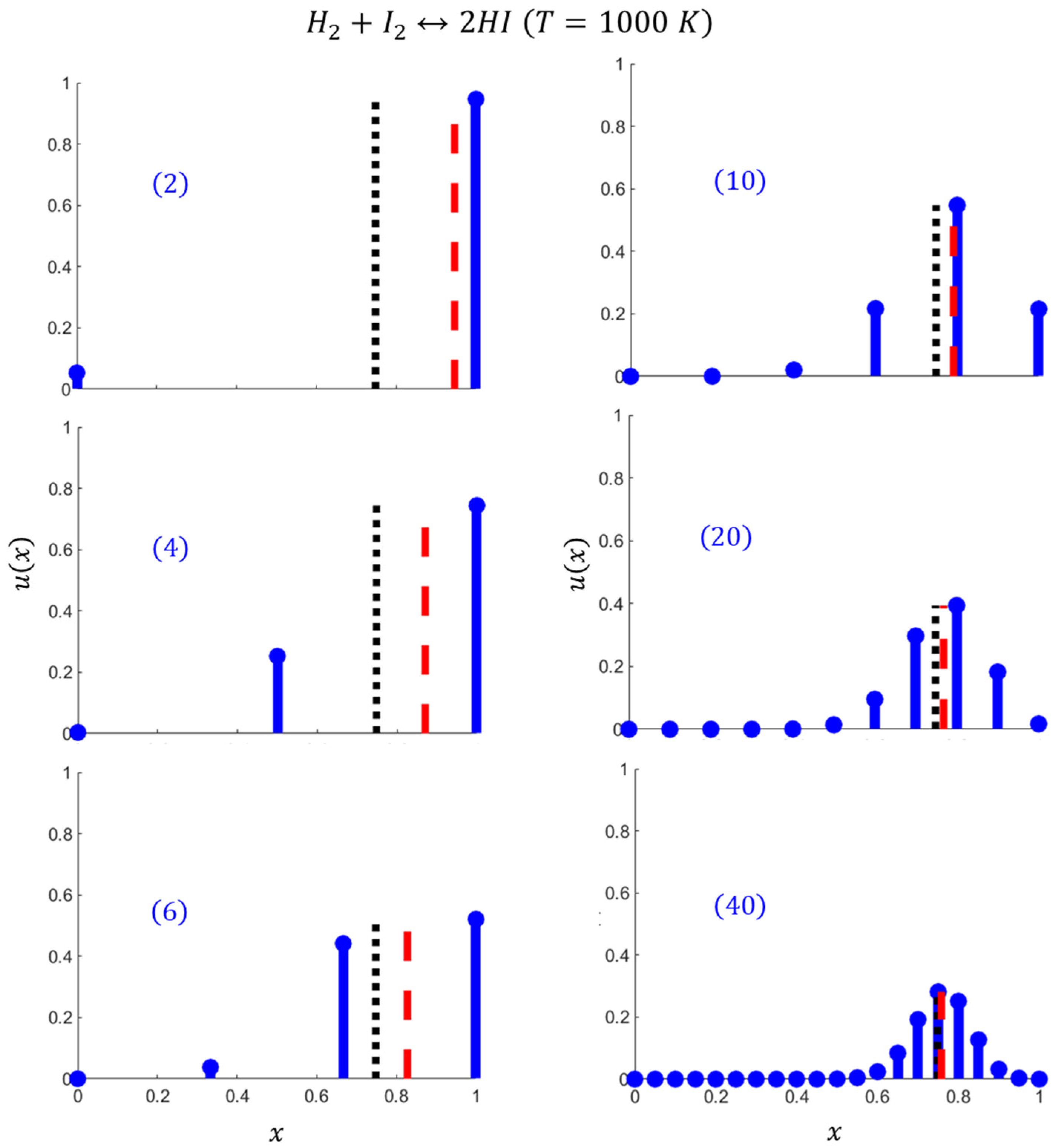
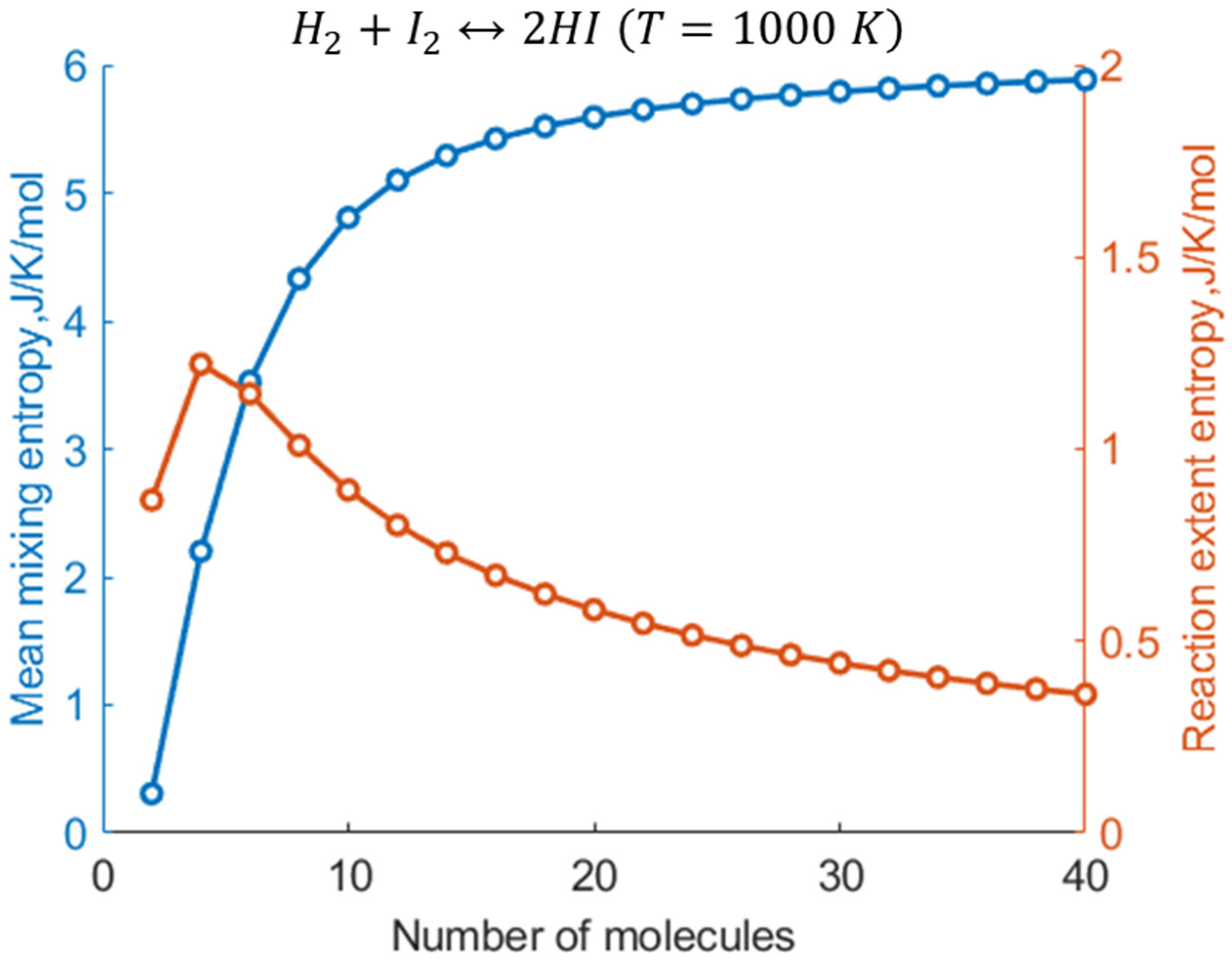
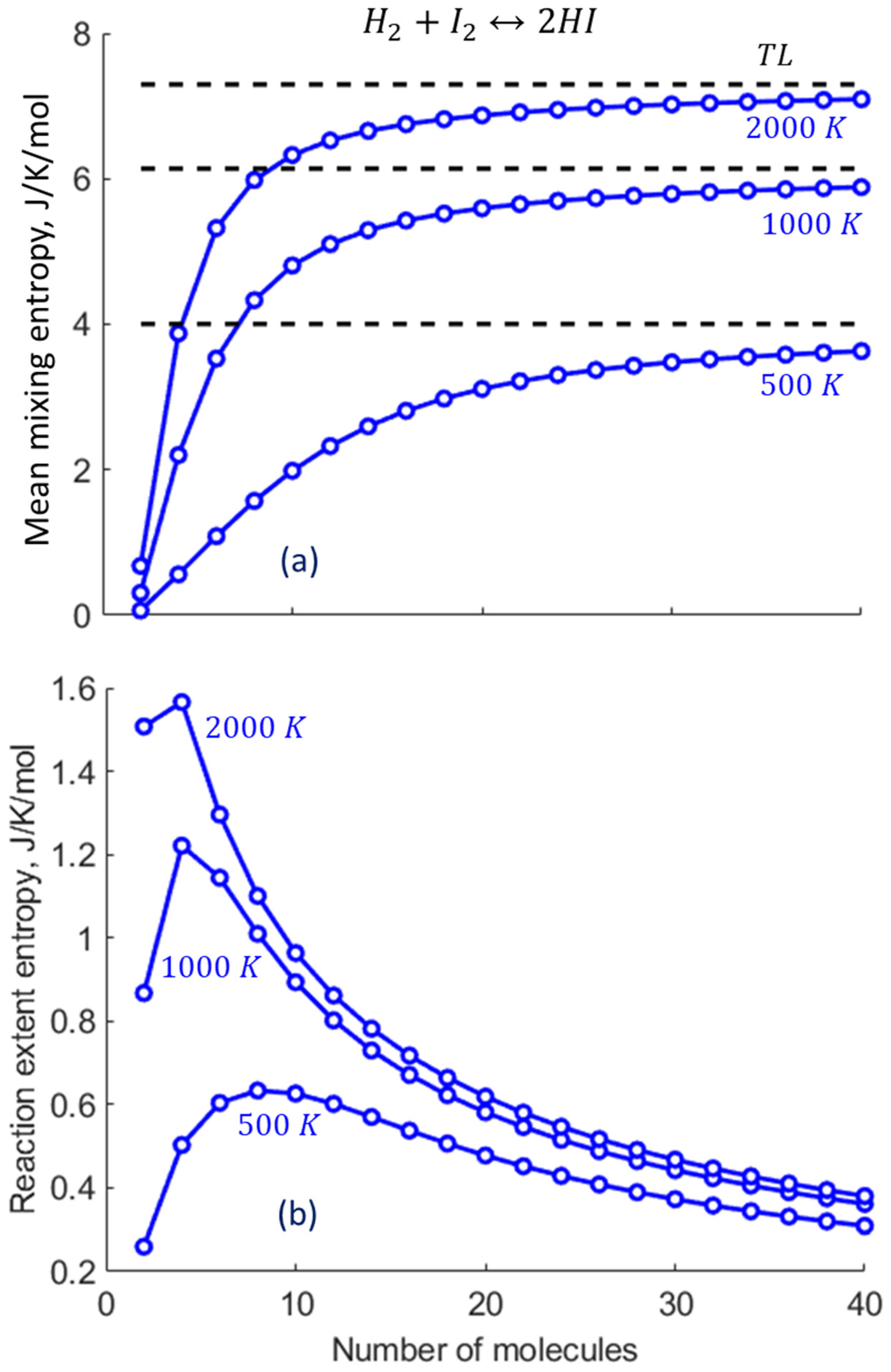
2.3. Specific Example:
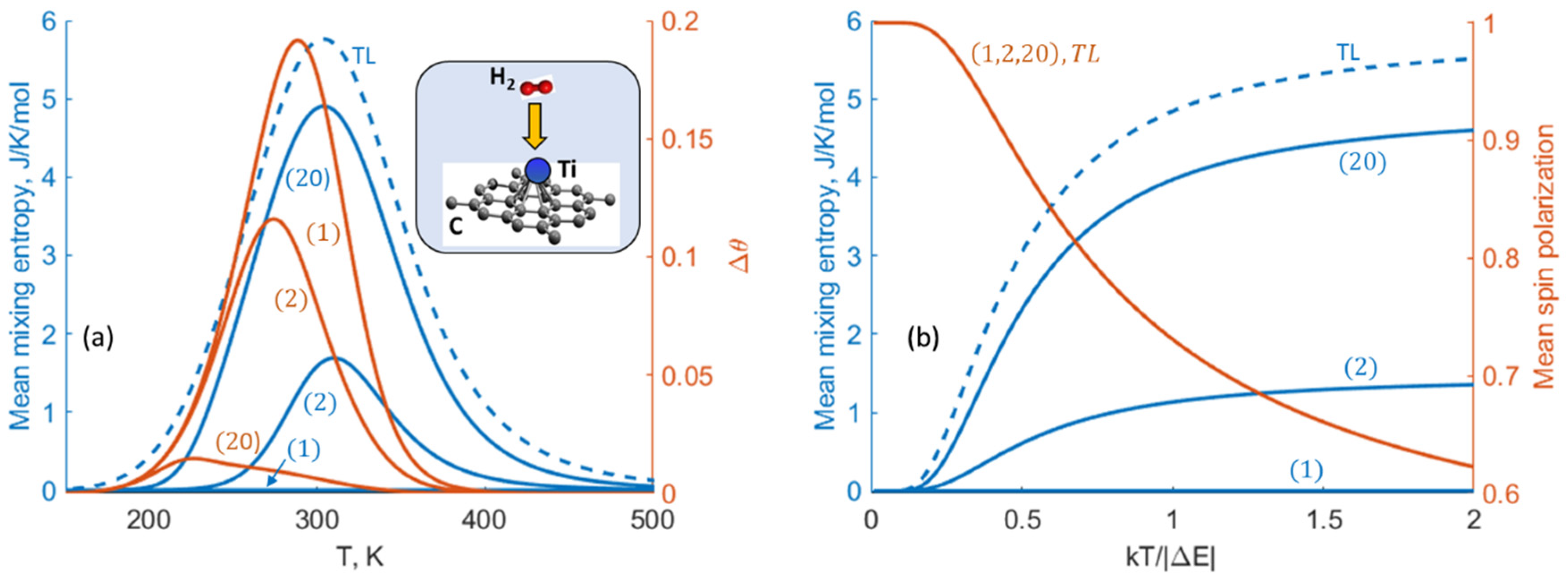
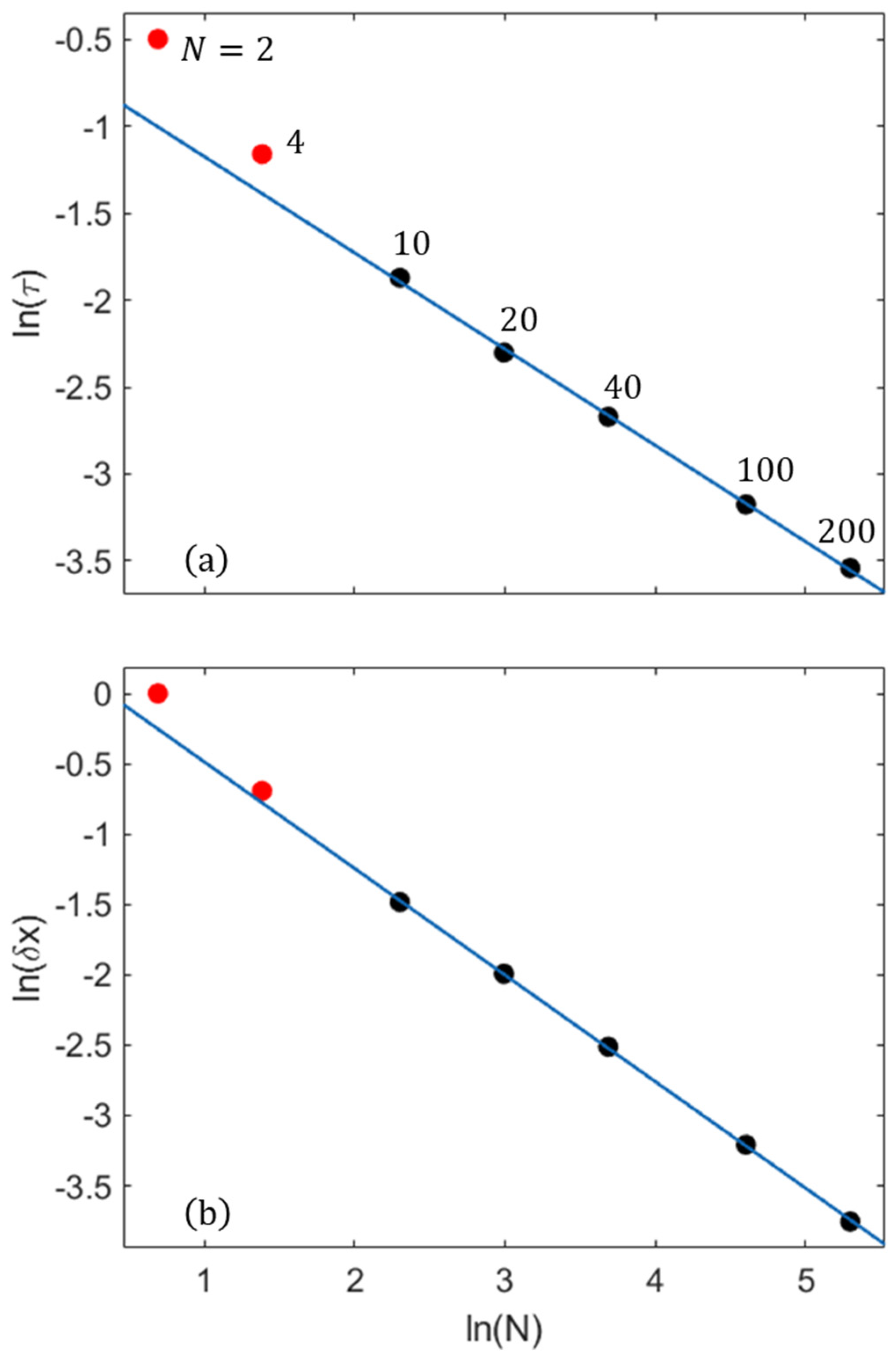
2.4. The Role of the Mixing Entropy in Other Nanosystems
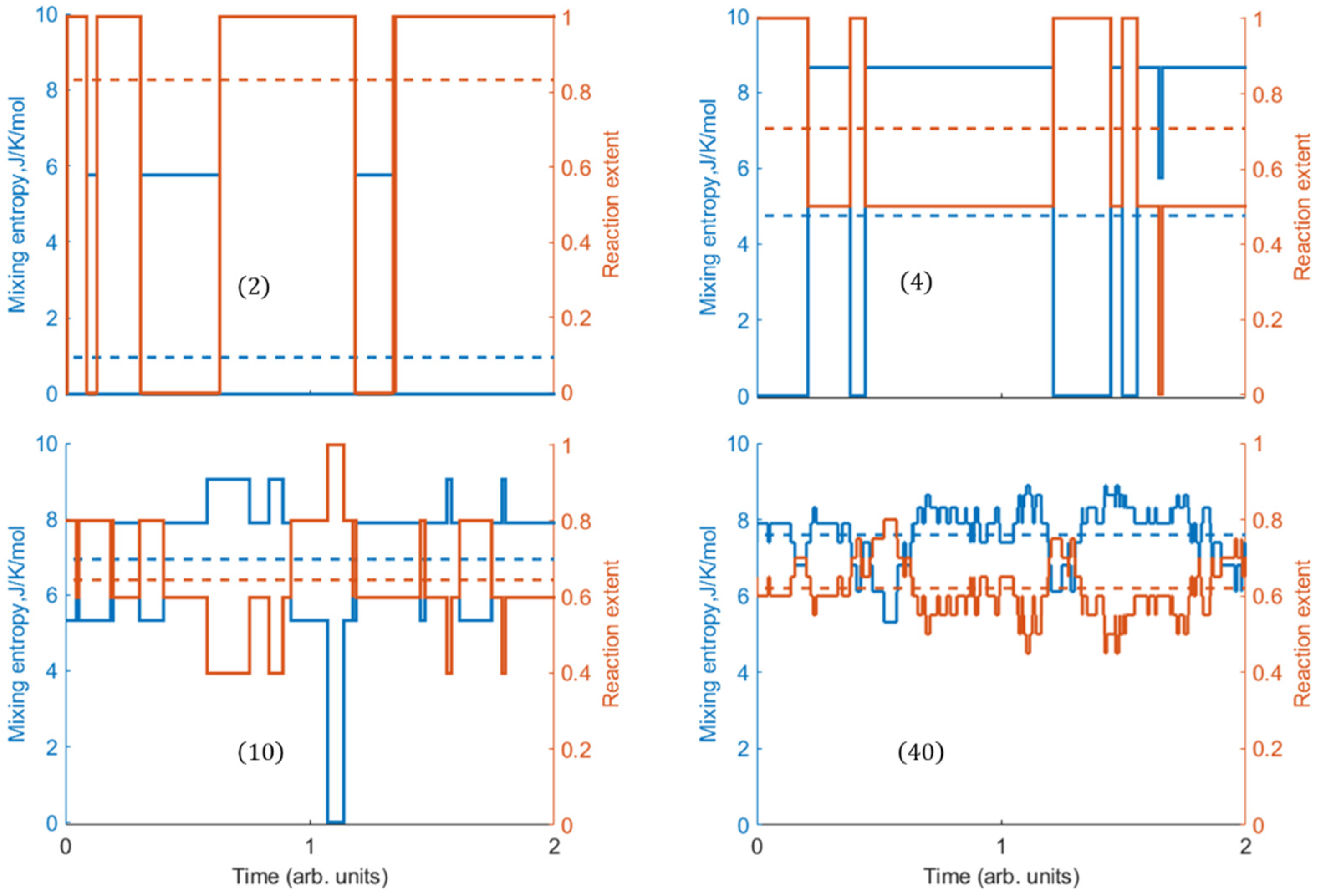
3. Instantaneous Mixing Entropy and Extent in Equilibrated
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Mixing Entropy for a Given Reaction Extent
Appendix A.2. The Relationship Between the Partition Function and the Equilibrium Constant
Appendix A.3. Decomposition of the Total Mixing Entropy into Reactant–Product and Reactant–Reactant Mixing Contributions for the General Reaction
Appendix A.4. Approximation Based on the Gaussian Probability Density
Appendix A.5. Adsorption Under Nanoconfinement
Appendix A.6. Nanoconfined Spin 1/2 System
References
- García-Morales, V.; Cervera, J.; Manzanares, J.A. Nanothermodynamics. In Handbook of Nanophysics. Principles and Methods, 2nd ed.; Sattler, K.D., Ed.; CRC Press Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Bie, C.; Yang, J.; Zeng, X.; Wang, Z.; Sun, X.; Yang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X. Nanoconfinement Effects in Electrocatalysis and Photocatalysis. Small 2025, 21, 2411184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grommet, A.B.; Feller, M.; Klajn, R. Chemical reactivity under nanoconfinement. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, T.; Yoshizawa, M.; Sato, S.; Fujita, M. Minimal Nucleotide Duplex Formation in Water through Enclathration in Self-Assembled Hosts. Nat. Chem. 2009, 1, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Rebek, J. Selectivity in an encapsulated cycloaddition reaction. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 327–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, M.J.; Cohen, A.E. Mass action at the single-molecule level. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 14618–14623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymanski, R.; Sosnowski, S.; Maślanka, Ł. Statistical effects related to low numbers of reacting molecules analyzed for a reversible association reaction A + B = C in ideally dispersed systems: An apparent violation of the law of mass action. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 144, 124112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goch, W.; Bal, W. Stochastic or not? method to predict and quantify the stochastic effects on the association reaction equilibria in nanoscopic systems. J. Phys. Chem. A 2020, 124, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangi, R. Statistical mechanics of dimerizations and its consequences for small systems. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 28804–28813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangi, R. Multimerizations, Aggregation, and Transfer Reactions of Small Numbers of Molecules. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2023, 63, 4383–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangi, R. Breakdown of Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm in Small Closed Systems. Langmuir 2024, 40, 3900–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, M.; Rubinovich, L. Nanochemical Equilibrium Involving a Small Number of Molecules: A Prediction of a Distinct Confinement Effect. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3543–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinovich, L.; Polak, M. The intrinsic role of nanoconfinement in chemical equilibrium: Evidence from DNA hybridization. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2247–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinovich, L.; Polak, M. Unraveling the Distinct Relationship between the Extent of a Nanoconfined Reaction and the Equilibrium Constant. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 125, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Naim, A. Entropy and the Second Law: Interpretation and Misss-Interpretationsss; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 2012; pp. 1–294. [Google Scholar]
- Atkins, P.; de Paula, J. Physical Chemistry, 9th ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 1–972. [Google Scholar]
- Shultz, M.J. Why Equilibrium? Understanding the Role of Entropy of Mixing. J. Chem. Educ. 1999, 76, 1391–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, T.L. Thermodynamics of Small Systems; Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 1–210. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Broeck, C. Stochastic thermodynamics: A brief introduction. In Physics of Complex Colloids; Bechinger, C., Sciortino, F., Ziherl, P., Eds.; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 155–193. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, M. Stochastic thermodynamics under coarse graining. Phys. Rev. E-Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2012, 85, 041125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reguera, D.; Rubi, J.M.; Vilar, J.M.G. The mesoscopic dynamics of thermodynamic systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 21502–21515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnell, S.K.; Vlugt, T.J.; Simon, J.M.; Bedeaux, D.; Kjelstrup, S. Thermodynamics of a small system in a μT reservoir. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2011, 504, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekking, F.M.; Kraaikamp, C.; Lopuhaa, H.P.; Meester, L.E. A Modern Introduction to Probability and Statistics: Understanding Why and How; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 1–486. [Google Scholar]
- McQuarrie, D.A. Statistical Mechanics; Harper & Row: Manhattan, NY, USA, 1976; pp. 1–641. [Google Scholar]
- Rubinovich, L.; Polak, M. Remarkable nanoconfinement effects on equilibrated reactions: Statistical-mechanics modeling focused on Ir dimerization beneath surface sites in Pd–Ir nanoparticles. Top. Catal. 2018, 61, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, R.L.; Henry, J.M.; Anderson, J.B. Molecular dynamics of the hydrogen iodide and hydrogen-iodine exchange reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 1140–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, M.; Rubinovich, L. Adsorption under Nanoconfinement: A Theoretical-Computational Study Revealing Significant Enhancement Beyond the Langmuirian Levels. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 19600–19605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, H.; Gil, A.; Frapper, G. Trends in the Hydrogen Activation and Storage by Adsorbed 3d Transition Metal Atoms onto Graphene and Nanotube Surfaces: A DFT Study and Molecular Orbital Analysis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 5506–5522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, D.T. Exact Stochastic Simulation of Coupled Chemical-Reactions. J. Phys. Chem. 1977, 81, 2340–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, D.T. Stochastic Simulation of Chemical Kinetics. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2007, 58, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touchette, H. The large deviation approach to statistical mechanics. Phys. Rep. 2009, 478, 1–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, E.; Nicholls, D.; Browning, N.D.; de Jonge, N. High temporal-resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy using sparse-serpentine scan pathways. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, Y. Attosecond electron-beam technology: A review of recent progress. Microscopy 2023, 72, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Z.; Wang, W.Y.; Qiao, L.; Fu, Y.Z.; Ge, X.C.; Zhao, K.; Zhanghao, K.; Guan, M.L.; Chen, X.; Li, M.Q.; et al. Ultra-high spatio-temporal resolution imaging with parallel acquisition-readout structured illumination microscopy (PAR-SIM). Light Sci. Appl. 2024, 13, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baez, J.C.; Fong, B. Quantum Techniques for Studying Equilibrium in Reaction Networks. J. Complex Netw. 2015, 3, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruijn, N.G. Asymptotic Methods in Analysis; North-Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1958; pp. 1–200. [Google Scholar]
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Elements of Information Theory, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 1–774. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rubinovich, L.; Polak, M. Elucidating the Role of the Mixing Entropy in Equilibrated Nanoconfined Reactions. Entropy 2025, 27, 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060564
Rubinovich L, Polak M. Elucidating the Role of the Mixing Entropy in Equilibrated Nanoconfined Reactions. Entropy. 2025; 27(6):564. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060564
Chicago/Turabian StyleRubinovich, Leonid, and Micha Polak. 2025. "Elucidating the Role of the Mixing Entropy in Equilibrated Nanoconfined Reactions" Entropy 27, no. 6: 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060564
APA StyleRubinovich, L., & Polak, M. (2025). Elucidating the Role of the Mixing Entropy in Equilibrated Nanoconfined Reactions. Entropy, 27(6), 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060564








