Coarse-Grained Hawkes Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Review of Hawkes Processes
3. Coarse-Grained Hawkes Process
3.1. Motivation
3.2. Definition
3.3. Stationary Process
3.4. Approximation to Hawkes Process
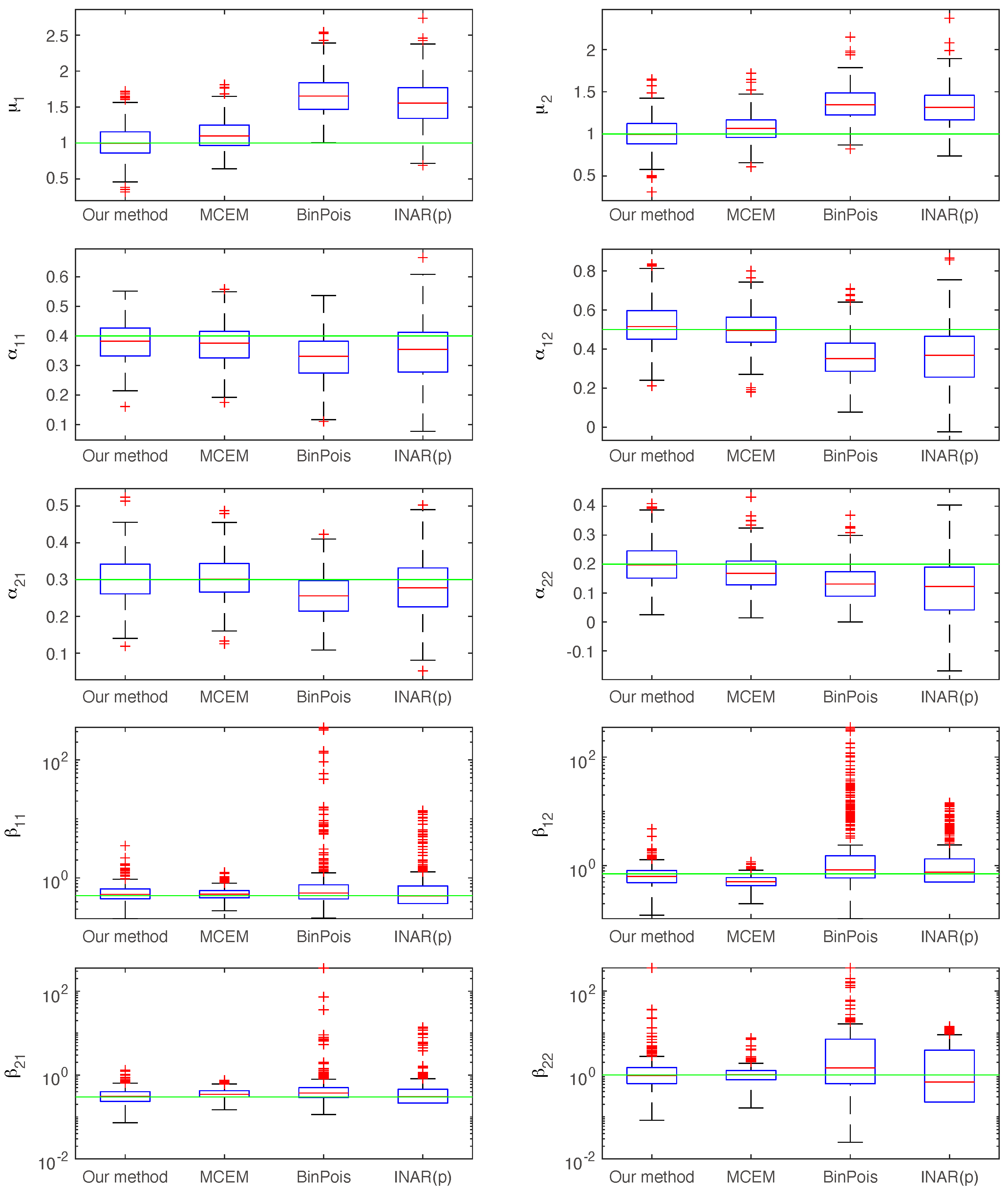
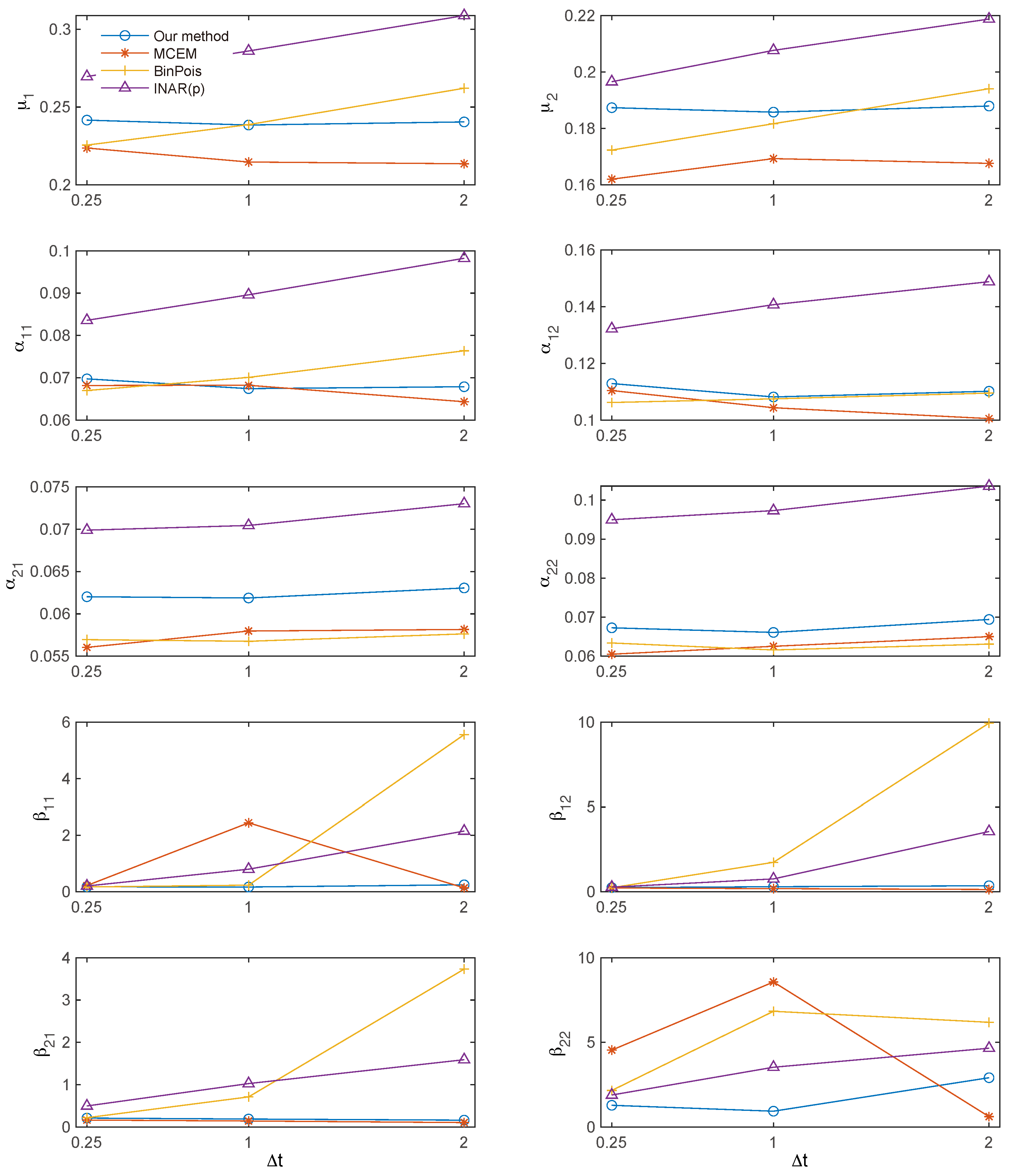
3.5. Parameter Estimation Method
| Algorithm 1 Estimation procedure for Hawkes processes |
|
4. Numerical Experiments
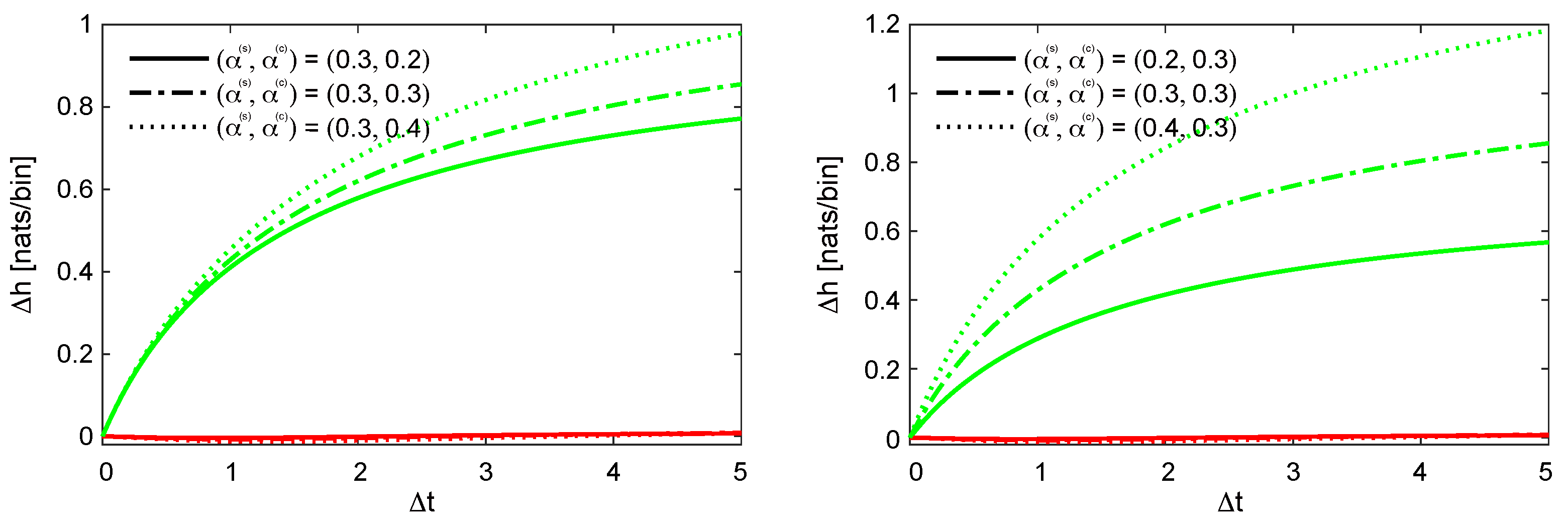
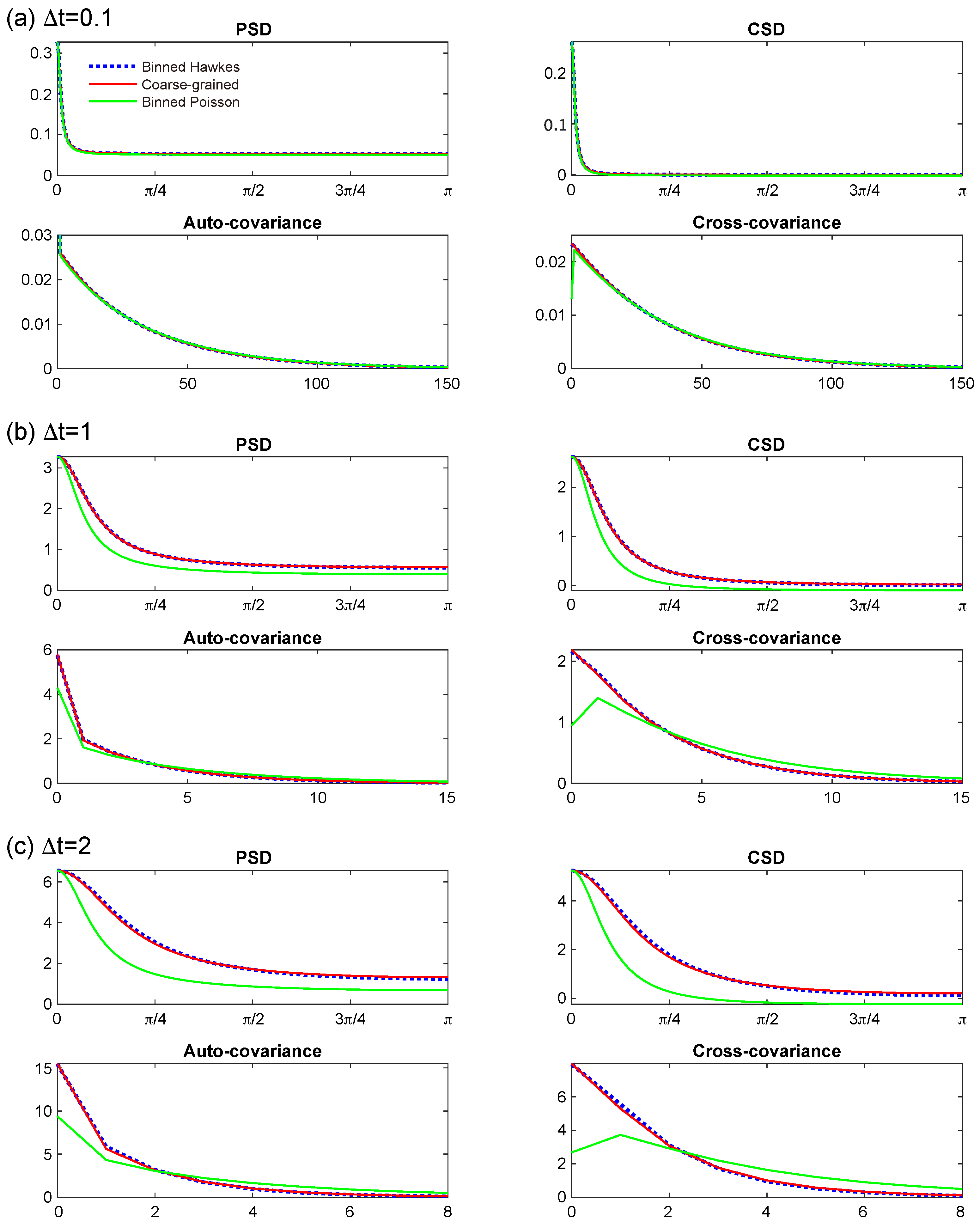
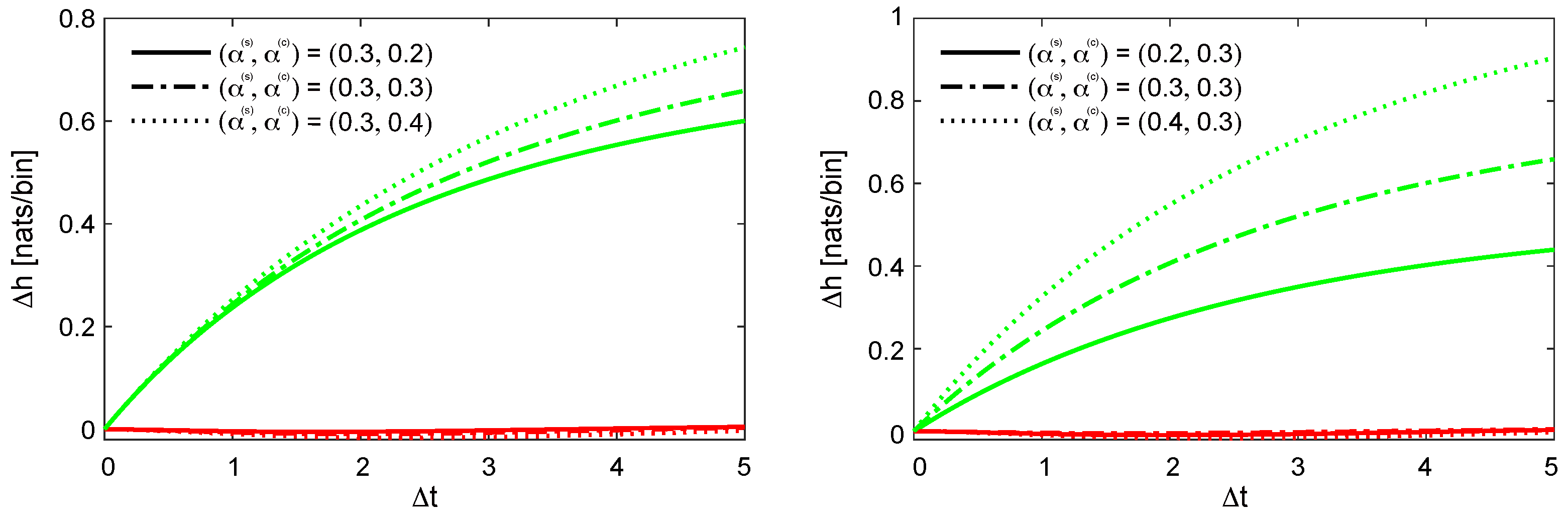
4.1. Assessment of Second-Order Characteristics
4.2. Parameter Estimation
4.3. Choice of Parametric Form of Excitation Kernel
5. Discussion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Proofs
Appendix A.1. Proof of Lemma 1
Appendix A.2. Derivation of (12) and (13)
Appendix A.3. Proof of Lemma 2
Appendix A.4. Ar(∞) and MA(∞) Representations
Appendix A.5. Proof of Theorem 1
Appendix A.6. Proof of Theorem 2
Appendix B. Second-Order Properties of the Stationary Hawkes Process
- Spectral Density Matrix of the Stationary Hawkes Process:where denotes the Fourier transform of the excitation kernel matrix, andrepresents the stationary (mean) intensity.
- Expected Value of the Binned Stationary Hawkes Process:
- Spectral Density Matrix of the Binned Stationary Hawkes Process:
Appendix C. Power-Law Distribution


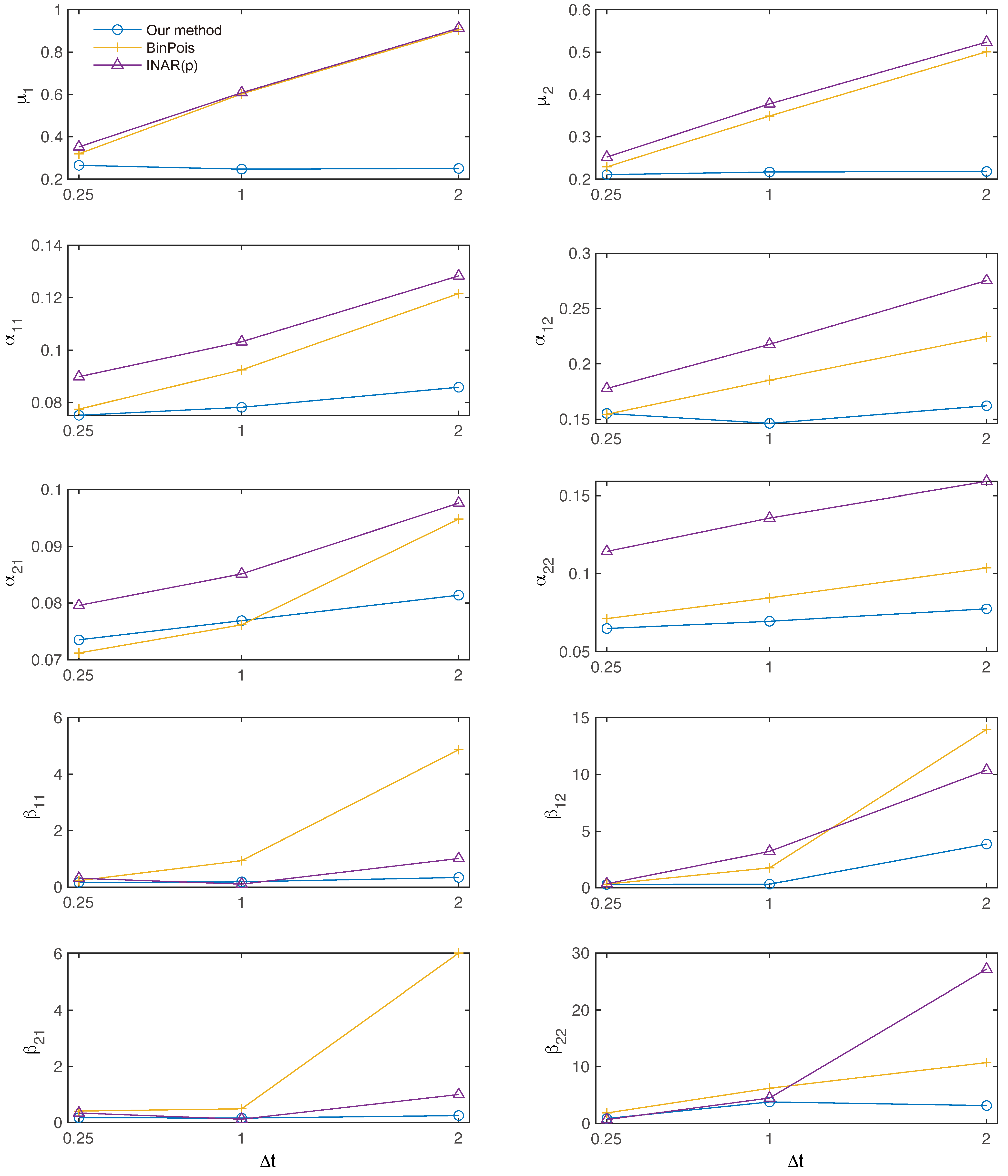


References
- Hawkes, A.G. Spectra of some self-exciting and mutually exciting point processes. Biometrika 1971, 58, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, A.G. Point spectra of some mutually exciting point processes. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1971, 33, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, L. Cluster models for earthquakes: Regional comparisons. J. Int. Assoc. Math. Geol. 1976, 8, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, Y. Statistical models for earthquake occurrences and residual analysis for point processes. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1988, 83, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chornoboy, E.S.; Schramm, L.P.; Karr, A.F. Maximum likelihood identification of neural point process systems. Biol. Cybern. 1988, 59, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernice, V.; Staude, B.; Cardanobile, S.; Rotter, S. How structure determines correlations in neuronal networks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 7, e1002059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynaud-Bouret, P.; Schbath, S. Adaptive estimation for Hawkes processes; application to genome analysis. Ann. Stat. 2010, 38, 2781–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacry, E.; Mastromatteo, I.; Muzy, J.F. Hawkes processes in finance. Mark. Microstruct. Liq. 2015, 1, 1550005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, A.G. Hawkes processes and their applications to finance: A review. Quant. Financ. 2018, 18, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, E.W.; Short, M.B.; Schoenberg, F.P.; Coronges, K.D.; Bertozzi, A.L. Modeling E-mail Networks and Inferring Leadership Using Self-Exciting Point Processes. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2016, 111, 564–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, R.; Lambiotte, R. TiDeH: Time-dependent Hawkes process for predicting retweet dynamics. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, Cologne, Germany, 17–20 May 2016; Volume 10, pp. 191–200. [Google Scholar]
- Koyama, S.; Shinomoto, S. Statistical physics of discovering exogenous and endogenous factors in a chain of events. Phys. Rev. Res. 2020, 2, 043358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohler, G.; Short, M.B.; Brantingham, P.J.; Schoenberg, F.P.; Tita, G.E. Self-Exciting Point Process Modeling of Crime. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2011, 106, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Mateu, J. A semiparametric spatiotemporal Hawkes-type point process model with periodic background for crime data. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A (Stat. Soc.) 2019, 182, 919–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.; Mohler, G.; Brantingham, P.J.; Bertozzi, A.L. Self-exciting point process models of civilian deaths in Iraq. Secur. J. 2012, 25, 244–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalair, K.; Connaughton, C.; Loro, P.A.D. A non-parametric Hawkes process model of primary and secondary accidents on a UK smart motorway. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C (Appl. Stat.) 2021, 70, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, M. Hawkes and INAR(∞) processes. Stoch. Processes Their Appl. 2016, 126, 2494–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, M. An estimation procedure for the Hawkes process. Quant. Financ. 2017, 17, 571–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlomovich, L.; Cohen, E.A.K.; Adams, N.; Patel, L. Parameter estimation of binned Hawkes processes. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2022, 31, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlomovich, L.; Cohen, E.A.K.; Adams, N. A parameter estimation method for multivariate binned Hawkes processes. Stat. Comput. 2022, 32, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Kwan, T.K.J.; Stindl, T. Estimating the Hawkes Process From a Discretely Observed Sample Path. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheysson, F.; Lang, G. Spectral estimation of Hawkes processes from count data. Ann. Stat. 2022, 50, 1722–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley, D.; Vere-Jones, D. An Introduction to the Theory of Point Processes Volume II: General Theory and Structure, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mark, B.; Raskutti, G.; Willett, R. Network estimation from point process data. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2019, 65, 2953–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlomovich, L. MATLAB Code for Multivariate Implementation of Aggregated Hawkes Parameter Estimation. Available online: https://github.com/lshlomovich/MCEM_Multivariate_Hawkes (accessed on 11 February 2025).
- Durbin, J.; Koopman, S. Time Series Analysis by State Space Methods; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa, G. Introduction to Time Series Modeling; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bacry, E.; Dayri, K.; Muzy, J.F. Non-parametric kernel estimation for symmetric Hawkes processes. Application to high frequency financial data. Eur. Phys. J. B 2012, 85, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacry, E.; Muzy, J.F. First- and second-order statistics characterization of Hawkes processes and non-parametric estimation. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2016, 62, 2184–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koyama, S. Coarse-Grained Hawkes Processes. Entropy 2025, 27, 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060555
Koyama S. Coarse-Grained Hawkes Processes. Entropy. 2025; 27(6):555. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060555
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoyama, Shinsuke. 2025. "Coarse-Grained Hawkes Processes" Entropy 27, no. 6: 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060555
APA StyleKoyama, S. (2025). Coarse-Grained Hawkes Processes. Entropy, 27(6), 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060555




