Network Risk Diffusion and Resilience in Emerging Stock Markets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Methodology
3.1. Transfer Entropy and Effective Transfer Entropy
3.2. Network Resilience
4. Results
4.1. Data
4.2. Analysis of Risk Transfer Entropy in Emerging Market Countries
4.3. Analysis of the Risk Correlation Among Emerging Market Countries
4.4. Analysis of the Network Resilience Among Emerging Market Countries
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Country | Stock Index | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|
| China | Shanghai Securities Composite Index | SHCOMP |
| India | BSE SENSEX 30 | SENSEX |
| Brazil | Índice Bovespa | IBOVESPA |
| Russia | Russian Trading System | RTS |
| South Africa | FTSE/JSE Africa Top40 Tradeable Index | FTSE/JSE Top 40 Index |
| Indonesia | Indonesia Jakarta Composite Index | JKSE |
| Argentina | S&P Merval | MERV |
| Mexico | S&P/BMV IPC Index | MXX |
| Turkey | ISE National-100 index | XU100 |
| Saudi Arabia | Tadawul All Share Index | TASI |
| Results of the Parameter of the ETE Function: shuffles = 50, bootstrap = 300 | ||||||||||
| China | India | Brazil | Russia | SouthAfrica | Indonesia | Argentina | Mexico | Turkey | SaudiArabia | |
| China | 0.0000 | 0.0062 | 0.0043 | 0.0040 | 0.0036 | 0.0014 | 0.0000 | 0.0023 | 0.0026 | 0.0004 |
| India | 0.0022 | 0.0000 | 0.0039 | 0.0046 | 0.0039 | 0.0047 | 0.0018 | 0.0034 | 0.0030 | 0.0013 |
| Brazil | 0.0039 | 0.0167 | 0.0000 | 0.0129 | 0.0165 | 0.0152 | 0.0024 | 0.0014 | 0.0076 | 0.0048 |
| Russia | 0.0029 | 0.0035 | 0.0051 | 0.0000 | 0.0032 | 0.0065 | 0.0021 | 0.0036 | 0.0011 | 0.0032 |
| SouthAfrica | 0.0041 | 0.0106 | 0.0049 | 0.0005 | 0.0000 | 0.0051 | 0.0022 | 0.0061 | 0.0013 | 0.0013 |
| Indonesia | 0.0030 | 0.0060 | 0.0047 | 0.0035 | 0.0054 | 0.0000 | 0.0019 | 0.0037 | 0.0034 | 0.0009 |
| Argentina | 0.0044 | 0.0056 | 0.0023 | 0.0029 | 0.0042 | 0.0084 | 0.0000 | 0.0003 | 0.0028 | 0.0012 |
| Mexico | 0.0059 | 0.0166 | 0.0018 | 0.0081 | 0.0137 | 0.0167 | 0.0024 | 0.0000 | 0.0066 | 0.0038 |
| Turkey | 0.0039 | 0.0036 | 0.0036 | 0.0002 | 0.0018 | 0.0066 | 0.0013 | 0.0037 | 0.0000 | 0.0024 |
| SaudiArabia | 0.0018 | 0.0047 | 0.0072 | 0.0047 | 0.0049 | 0.0031 | 0.0003 | 0.0092 | 0.0039 | 0.0000 |
| Results of the Parameter of the ETE Function: shuffles = 100, bootstrap = 100 | ||||||||||
| China | India | Brazil | Russia | SouthAfrica | Indonesia | Argentina | Mexico | Turkey | SaudiArabia | |
| China | 0.0000 | 0.0062 | 0.0044 | 0.0040 | 0.0036 | 0.0012 | 0.0000 | 0.0022 | 0.0025 | 0.0004 |
| India | 0.0023 | 0.0000 | 0.0039 | 0.0046 | 0.0038 | 0.0047 | 0.0018 | 0.0034 | 0.0031 | 0.0014 |
| Brazil | 0.0038 | 0.0166 | 0.0000 | 0.0129 | 0.0166 | 0.0152 | 0.0024 | 0.0014 | 0.0077 | 0.0049 |
| Russia | 0.0030 | 0.0036 | 0.0051 | 0.0000 | 0.0032 | 0.0064 | 0.0020 | 0.0036 | 0.0012 | 0.0030 |
| SouthAfrica | 0.0039 | 0.0106 | 0.0051 | 0.0007 | 0.0000 | 0.0050 | 0.0022 | 0.0062 | 0.0014 | 0.0013 |
| Indonesia | 0.0030 | 0.0061 | 0.0049 | 0.0035 | 0.0054 | 0.0000 | 0.0020 | 0.0038 | 0.0035 | 0.0010 |
| Argentina | 0.0043 | 0.0056 | 0.0023 | 0.0029 | 0.0043 | 0.0085 | 0.0000 | 0.0003 | 0.0028 | 0.0011 |
| Mexico | 0.0059 | 0.0167 | 0.0017 | 0.0080 | 0.0137 | 0.0169 | 0.0026 | 0.0000 | 0.0066 | 0.0038 |
| Turkey | 0.0041 | 0.0037 | 0.0036 | 0.0003 | 0.0019 | 0.0067 | 0.0015 | 0.0037 | 0.0000 | 0.0024 |
| SaudiArabia | 0.0018 | 0.0048 | 0.0070 | 0.0047 | 0.0048 | 0.0033 | 0.0002 | 0.0091 | 0.0038 | 0.0000 |
References
- Hautsch, N.; Schaumburg, J.; Schienle, M. Financial Network Systemic Risk Contributions. Rev. Financ. 2015, 19, 685–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diebold, F.X.; Yılmaz, K. On the Network Topology of Variance Decompositions: Measuring the Connectedness of Financial Firms. J. Econom. 2014, 182, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, K.J.; Warnock, F.E. Capital Flow Waves: Surges, Stops, Flight, and Retrenchment. J. Int. Econ. 2012, 88, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korbel, J.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, B. Transfer entropy between communities in complex financial networks. Entropy 2019, 21, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahnert, T.; Georg, C. Information Contagion and Systemic Risk. J. Financ. Stab. 2018, 35, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, T. Measuring Information Transfer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, R.V.L. Transmission of Information 1. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1928, 7, 535–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschinski, R.; Kantz, H. Analysing the Information Flow between Financial Time Series: An Improved Estimator for Transfer Entropy. Eur. Phys. J.-Condens. Matter Complex Syst. 2002, 30, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jizba, P.; Kleinert, H.; Shefaat, M. Rényi’s Information Transfer between Financial Time Series. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2012, 391, 2971–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Shang, P. Comparison of Transfer Entropy Methods for Financial Time Series. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2017, 482, 772–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Bouri, E.; Roubaud, D.; Kristoufek, L. Information Interdependence among Energy, Cryptocurrency and Major Commodity Markets. Energy Econ. 2019, 81, 1042–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, C.S. Resilience and Stability of Ecological Systems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1973, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, R.; Jeong, H.; Barabási, A.-L. Error and Attack Tolerance of Complex Networks. Nature 2000, 406, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorogovtsev, S.N.; Mendes, J.F.F. Evolution of Networks. Adv. Phys. 2002, 51, 1079–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, M.; Golub, B.; Jackson, M.O. Financial Networks and Contagion. Am. Econ. Rev. 2014, 104, 3115–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, H.; Cont, R.; Minca, A. Resilience to Contagion in Financial Networks. Math. Financ. 2016, 26, 329–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, P.; Kapadia, S. Contagion in Financial Networks. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2010, 466, 2401–2423. [Google Scholar]
- Haldane, A.G.; May, R.M. Systemic Risk in Banking Ecosystems. Nature 2011, 469, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefano, B.; Michelangelo, P.; Rahul, K.; Paolo, T.; Guido, C. Debtrank: Too Central to Fail? Financial Networks, the Fed and Systemic Risk. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 541. [Google Scholar]
- Adrian, T.; Brunnermeier, M.K. CoVaR. Am. Econ. Rev. 2016, 106, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueti, R.; Cinelli, M.; Ferraro, G.; Iovanella, A. Financial Interbanking Networks Resilience under Shocks Propagation. Ann. Oper. Res. 2023, 330, 389–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, E.H.; Mantegna, R.N. An Introduction to Econophysics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Moro, E.; Frank, M.R.; Pentland, A.; Rutherford, A.; Cebrian, M.; Rahwan, I. Universal Resilience Patterns in Labor Markets. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Huang, Z.-G.; Seager, T.P.; Lin, W.; Grebogi, C.; Hastings, A.; Lai, Y.-C. Predicting Tipping Points in Mutualistic Networks through Dimension Reduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E639–E647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, D.; Aharony, A. Introduction to Percolation Theory; Taylor & Francis: Oxfordshire, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nagariya, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Baral, M.M.; Chittipaka, V. Analyzing Blockchain-Based Supply Chain Resilience Strategies: Resource-Based Perspective. Int. J. Product. Perform. Manag. 2024, 73, 1088–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Duan, D.; Xiao, R. A novel dimension reduction method with information entropy to evaluate network resilience. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2023, 620, 128727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumöhl, E.; Bouri, E.; Shahzad, S.J.H.; Výrost, T. Measuring systemic risk in the global banking sector: A cross-quantilogram network approach. Econ. Model. 2022, 109, 105775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, L.; Barrett, A.B.; Seth, A.K. Granger causality and transfer entropy are equivalent for Gaussian variables. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 238701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzioutziou, A.; Xenidis, Y. Information entropy-driven recovery strategies for systems’ resilience. In Bridge Maintenance, Safety, Management, Digitalization and Sustainability; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 3286–3294. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, C.; Zhong, G.-Y.; Li, J.-C. Dynamic correlation and risk resonance among industries of Chinese stock market: New evidence from time-frequency domain and complex network perspectives. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2023, 614, 128558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Désirée, K.; Winasti, W.; Tournois, F.; Mertens, H.; van Merode, F. Quantifying the resilience of a healthcare system: Entropy and network science perspectives. Entropy 2023, 26, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. A resilience analysis method for distributed system based on complex network. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Unmanned Systems (ICUS), Beijing, China, 15–17 October 2021; pp. 238–243. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Mostafavi, A. Network dynamics of community resilience and recovery: New frontier in disaster research. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2025, 123, 105489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Su, B.; Guo, M.; Wang, J. Exploring R&D network resilience under risk propagation: An organizational learning perspective. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2024, 273, 109266. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, B.; Holmér, L.; Smith, K.M.; Johnson, M.M.; Swain, A.; Stolp, L.; Teufel, A.I.; Kleppe, A.S. A computational exploration of resilience and evolvability of protein-protein interaction networks. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, S.; Panda, P. Spillovers and Financial Integration in Emerging Markets: Analysis of BRICS Economies within a VAR-BEKK Framework. Int. J. Financ. Econ. 2021, 26, 493–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boorman, J. The Impact of the Financial Crisis on Emerging Market Economies: The Transmission Mechanism, Policy Response and Lessons. Glob. Meet. Emerg. Mark. Forum 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, P. Macroeconomic Shock, Financial Risk Transmission and Governance Response to Major Public Emergencies. J. Manag. World 2020, 36, 13–35. [Google Scholar]
- Belaid, F.; Ben Amar, A.; Goutte, S.; Guesmi, K. Emerging and Advanced Economies Markets Behaviour during the COVID-19 Crisis Era. Int. J. Financ. Econ. 2023, 28, 1563–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensi, W.; Hkiri, B.; Al-Yahyaee, K.H.; Kang, S.H. Analyzing Time-Frequency Co-Movements across Gold and Oil Prices with BRICS Stock Markets: A VaR Based on Wavelet Approach. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2018, 54, 74–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunnermeier, M.K. Deciphering the Liquidity and Credit Crunch 2007–2008. J. Econ. Perspect. 2009, 23, 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorton, G.; Metrick, A. Securitized Banking and the Run on Repo. J. Financ. Econ. 2012, 104, 425–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.B.; Williams, J.C. A Black Swan in the Money Market. Am. Econ. J. Macroecon. 2009, 1, 58–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Ren, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, J.; Xiao, Y.; Jia, Z.; Guo, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, C.; Jiang, S.; et al. Heightened Innate Immune Responses in the Respiratory Tract of COVID-19 Patients. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, M.U.G.; Yang, C.; Gutierrez, B.; Wu, C.; Klein, B.; Pigott, D.M.; Open COVID-19 Data Working Group; Du Plessis, L.; Faria, N.R.; Li, R.; et al. The Effect of Human Mobility and Control Measures on the COVID-19 Epidemic in China. Science 2020, 368, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, T.; Angrist, N.; Goldszmidt, R.; Kira, B.; Petherick, A.; Phillips, T.; Webster, S.; Cameron-Blake, E.; Hallas, L.; Majumdar, S. A Global Panel Database of Pandemic Policies (Oxford COVID-19 Government Response Tracker). Nat. Hum. Behav. 2021, 5, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kose, A.; Prasad, M.E.S.; Terrones, M.E. How Does Globalization Affect the Synchronization of Business Cycles? Am. Econ. Rev. 2003, 93, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaert, G.; Harvey, C.R.; Lundblad, C. Does Financial Liberalization Spur Growth? J. Financ. Econ. 2005, 77, 3–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.R.; Bloom, N.; Davis, S.J.; Terry, S.J. Covid-Induced Economic Uncertainty. Natl. Bur. Econ. Res. 2020, w26983. [Google Scholar]
- Fahlenbrach, R.; Rageth, K.; Stulz, R.M. How Valuable Is Financial Flexibility When Revenue Stops? Evidence from the COVID-19 Crisis. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2021, 34, 5474–5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, G.C. Crisis and Responses: The Federal Reserve in the Early Stages of the Financial Crisis. J. Econ. Perspect. 2009, 23, 51–75. [Google Scholar]
- Verschuur, J.; Koks, E.E.; Hall, J.W. Observed Impacts of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Global Trade. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2021, 5, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charmantier, A.; McCleery, R.H.; Cole, L.R.; Perrins, C.; Kruuk, L.E.B.; Sheldon, B.C. Adaptive Phenotypic Plasticity in Response to Climate Change in a Wild Bird Population. Science 2008, 320, 800–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, T.A.; Gruber, D.A.; Sutcliffe, K.M.; Shepherd, D.A.; Zhao, E.Y. Organizational Response to Adversity: Fusing Crisis Management and Resilience Research Streams. Acad. Manag. Ann. 2017, 11, 733–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, H.; Yan, T.; Hatton, M.; Fowler, J.; Kull, T.J.; Sisk, L. When Complexity Meets Complexity: COVID-19-Induced Supply Chain Disruptions and Strategy Portfolio Efficiency. J. Oper. Manag. 2025, 71, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenico, M.D.; Baronchelli, A. The Fragility of Decentralised Trustless Socio-Technical Systems. EPJ Data Sci. 2019, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acemoglu, D.; Ozdaglar, A.; Tahbaz-Salehi, A. Systemic Risk and Stability in Financial Networks. Am. Econ. Rev. 2015, 105, 564–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetzsche, D.A.; Buckley, R.P.; Barberis, J.N.; Arner, D.W. Regulating a revolution: From regulatory sandboxes to smart regulation. Fordham J. Corp. Financ. Law 2017, 23, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenbaum, M.S.; Rebelo, S.; Trabandt, M. The macroeconomics of epidemics. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2021, 34, 5149–5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Barzel, B.; Barabási, A. Universal Resilience Patterns in Complex Networks. Nature 2016, 530, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



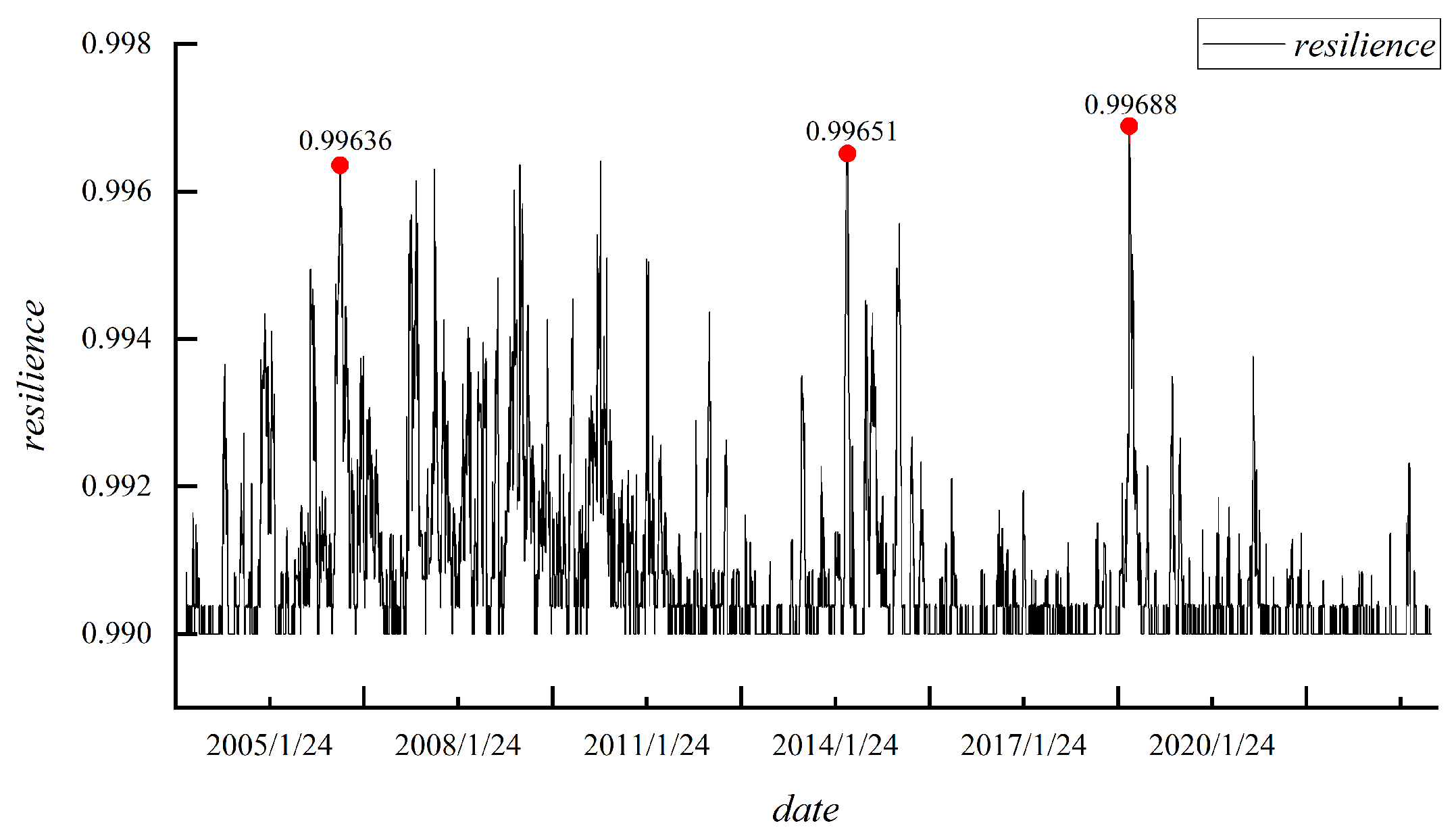
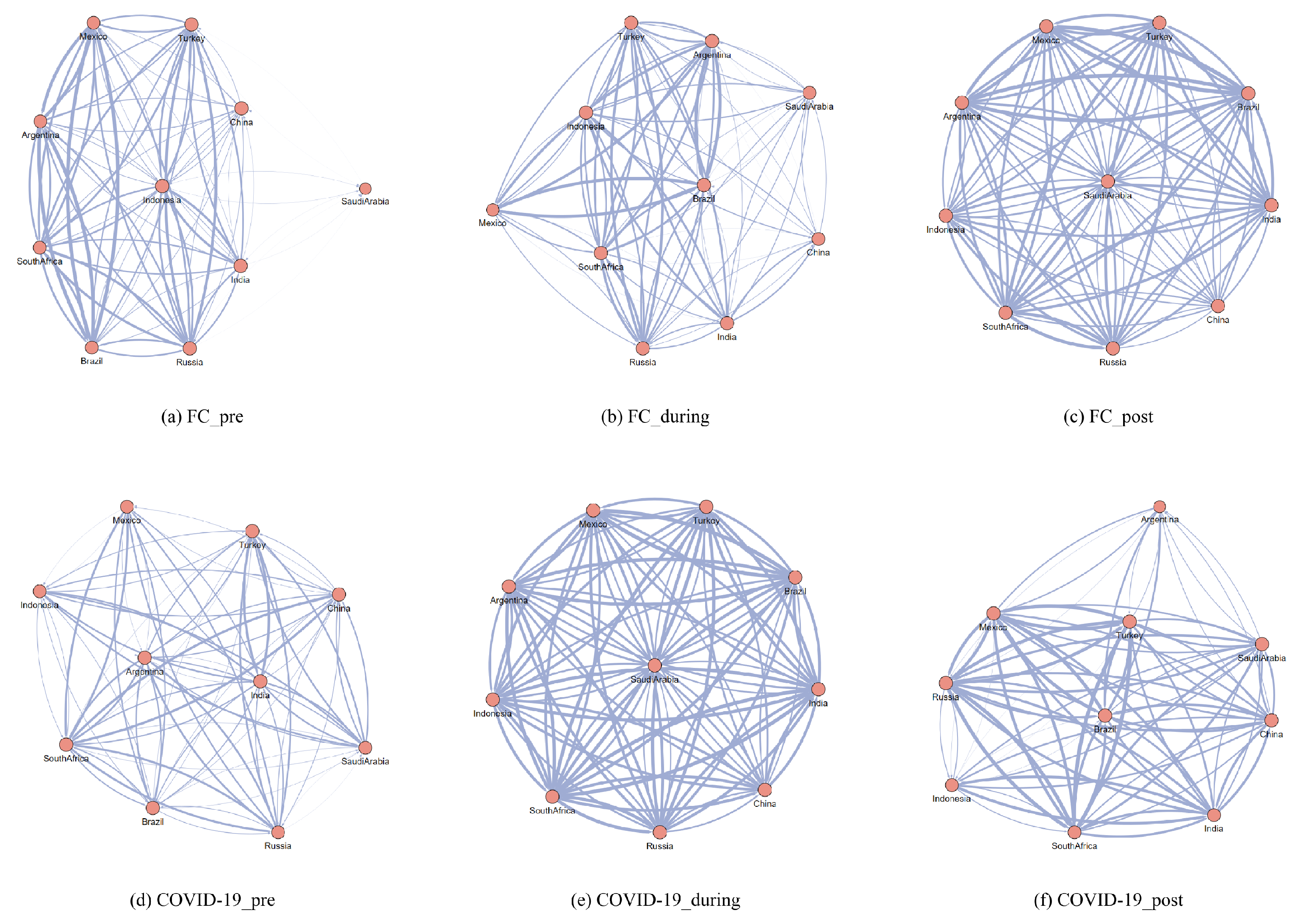
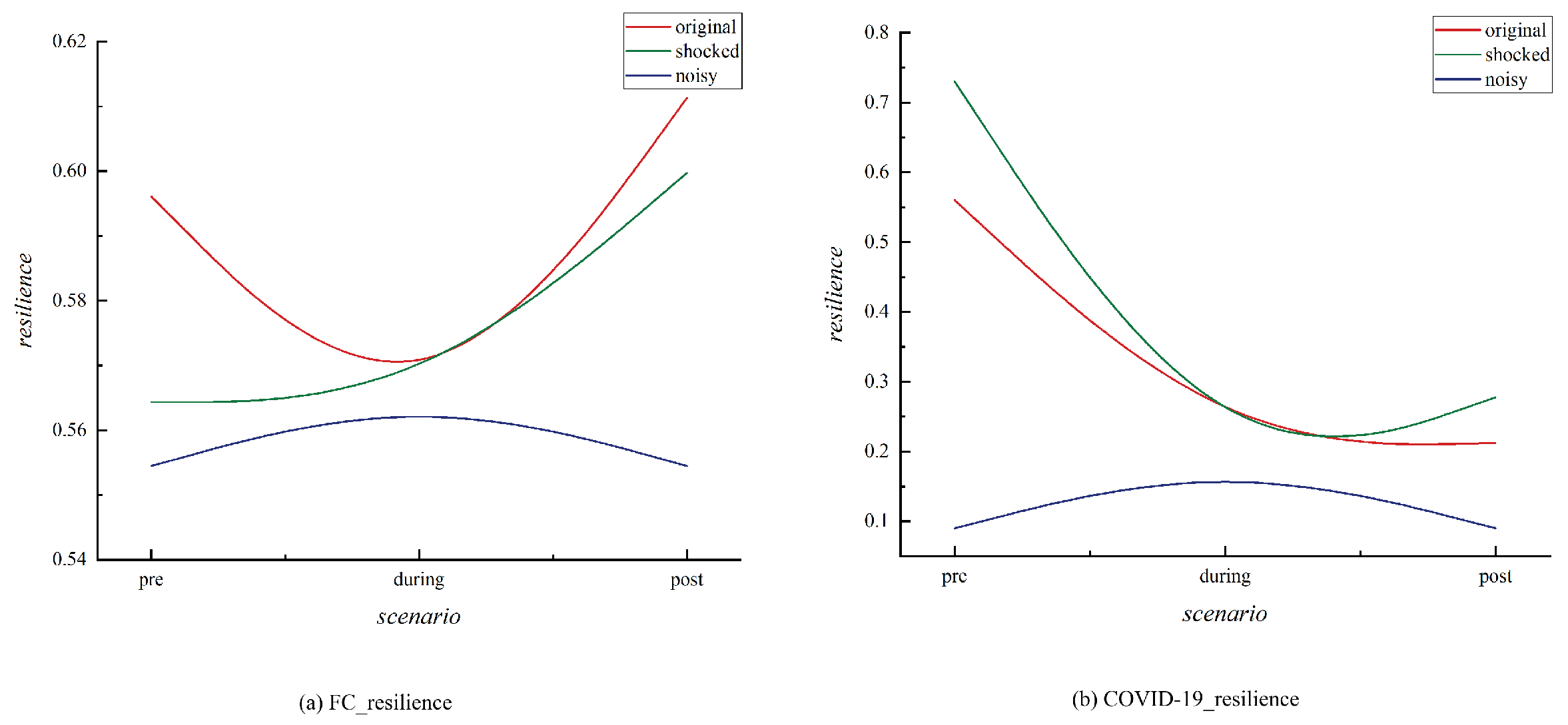
| Country | China | India | Brazil | Russia | South Africa | Indonesia | Argentina | Mexico | Turkey | Saudi Arabia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | 0 | 0.0062 | 0.0045 | 0.0040 | 0.0035 | 0.0011 | 0.0000 | 0.0021 | 0.0025 | 0.0004 |
| India | 0.0023 | 0 | 0.0041 | 0.0044 | 0.0037 | 0.0046 | 0.0019 | 0.0036 | 0.0032 | 0.0015 |
| Brazil | 0.0038 | 0.0165 | 0 | 0.0130 | 0.0164 | 0.0156 | 0.0025 | 0.0016 | 0.0076 | 0.0047 |
| Russia | 0.0030 | 0.0035 | 0.0051 | 0 | 0.0031 | 0.0064 | 0.0020 | 0.0037 | 0.0011 | 0.0032 |
| South Africa | 0.0039 | 0.0106 | 0.0052 | 0.0009 | 0 | 0.0049 | 0.0023 | 0.0061 | 0.0014 | 0.0012 |
| Indonesia | 0.0029 | 0.0061 | 0.0047 | 0.0033 | 0.0052 | 0 | 0.0019 | 0.0038 | 0.0033 | 0.0009 |
| Argentina | 0.0044 | 0.0055 | 0.0022 | 0.0030 | 0.0043 | 0.0083 | 0 | 0.0004 | 0.0028 | 0.0011 |
| Mexico | 0.0059 | 0.0165 | 0.0018 | 0.0079 | 0.0135 | 0.0169 | 0.0026 | 0 | 0.0066 | 0.0039 |
| Turkey | 0.0040 | 0.0037 | 0.0037 | 0.0004 | 0.0018 | 0.0070 | 0.0014 | 0.0035 | 0 | 0.0024 |
| Saudi Arabia | 0.0020 | 0.0049 | 0.0072 | 0.0049 | 0.0051 | 0.0032 | 0.0002 | 0.0094 | 0.0038 | 0 |
| Country | Export Risk Driver | Input Risk Driver |
|---|---|---|
| China | India (0.0062) | Mexico (0.0059) |
| India | Indonesia (0.0046) | Mexico (0.0165), Brazil (0.0165) |
| Brazil | India (0.0165) | Saudi Arabia (0.0072) |
| Russia | Indonesia (0.0064) | Brazil (0.0130) |
| South Africa | India (0.0106) | Brazil (0.0164) |
| Indonesia | India (0.0061) | Mexico (0.0169) |
| Argentina | Indonesia (0.0083) | Mexico (0.0026) |
| Mexico | Indonesia (0.0169) | Saudi Arabia (0.0094) |
| Turkey | Indonesia (0.0070) | Brazil (0.0076) |
| Saudi Arabia | Mexico (0.0094) | Brazil (0.0047) |
| Variable | TO | FROM | NET |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | 0.0243 | 0.0322 | −0.0079 |
| India | 0.0293 | 0.0735 | −0.0442 |
| Brazil | 0.0817 | 0.0383 | 0.0433 |
| Russia | 0.0311 | 0.0419 | −0.0107 |
| South Africa | 0.0365 | 0.0567 | −0.0202 |
| Indonesia | 0.0321 | 0.0681 | −0.0359 |
| Argentina | 0.0320 | 0.0148 | 0.0173 |
| Mexico | 0.0754 | 0.0342 | 0.0412 |
| Turkey | 0.0279 | 0.0323 | −0.0044 |
| Saudi Arabia | 0.0408 | 0.0192 | 0.0216 |
| Event | Time | Days | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 Financial Crisis | 1 July 2006–9 August 2007 | 769 (Risk Build-up) | Brunnermeier (2009) [42] |
| 10 August 2007–15 September 2008 | 402 (Outbreak of Crisis) | Gorton & Metrick (2012) [43] | |
| 16 September 2008–9 March 2009 | 175 (Policy Response) | Taylor & Williams (2009) [44] | |
| COVID-19 | 1 December 2019–23 January 2020 | 54 (Initial Virus Spread) | Zhou et al. (2020) [45] |
| 24 January 2020–24 March 2020 | 60 (Global Spread and Market Collapse) | Kraemer et al. (2020) [46] | |
| 25 March 2020–1 May 2020 | 36 (Policy Intervention) | Hale et al. (2021) [47] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.-C.; Xu, Y.-Z.; Tao, C. Network Risk Diffusion and Resilience in Emerging Stock Markets. Entropy 2025, 27, 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27050533
Li J-C, Xu Y-Z, Tao C. Network Risk Diffusion and Resilience in Emerging Stock Markets. Entropy. 2025; 27(5):533. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27050533
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jiang-Cheng, Yi-Zhen Xu, and Chen Tao. 2025. "Network Risk Diffusion and Resilience in Emerging Stock Markets" Entropy 27, no. 5: 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27050533
APA StyleLi, J.-C., Xu, Y.-Z., & Tao, C. (2025). Network Risk Diffusion and Resilience in Emerging Stock Markets. Entropy, 27(5), 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27050533







