Low-Density Parity-Check Decoding Algorithm Based on Symmetric Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We adopt a split optimization strategy to speed up the convergence for the ADMM decoding algorithm in handling non-convex quadratic models. By ensuring the relative independence and stability of each update, we solve the problem of unstable convergence of the ADMM in non-convex problems;
- We propose the S-ADMM decoding algorithm based on penalty terms and derive the algorithm process for the S-ADMM decoding model;
- We establish some contraction properties satisfied by the iterative sequence of the S-ADMM algorithm;
- Simulations demonstrate that the S-ADMM decoding algorithm outperforms the ADMM penalized decoders.
2. Preliminaries
2.1. LDPC Decoding Algorithm Based on ADMM-LP
2.2. ADMM-LP Decoding Algorithm with Penalty Term
3. S-ADMM Decoder
| Algorithm 1 Decoding Algorithm Based on S-ADMM. |
|
4. Algorithm and Contraction Analysis
4.1. Variational Reformulation of Equation (10)
4.2. Some Notation
4.3. Contraction Analysis
5. Simulation Result
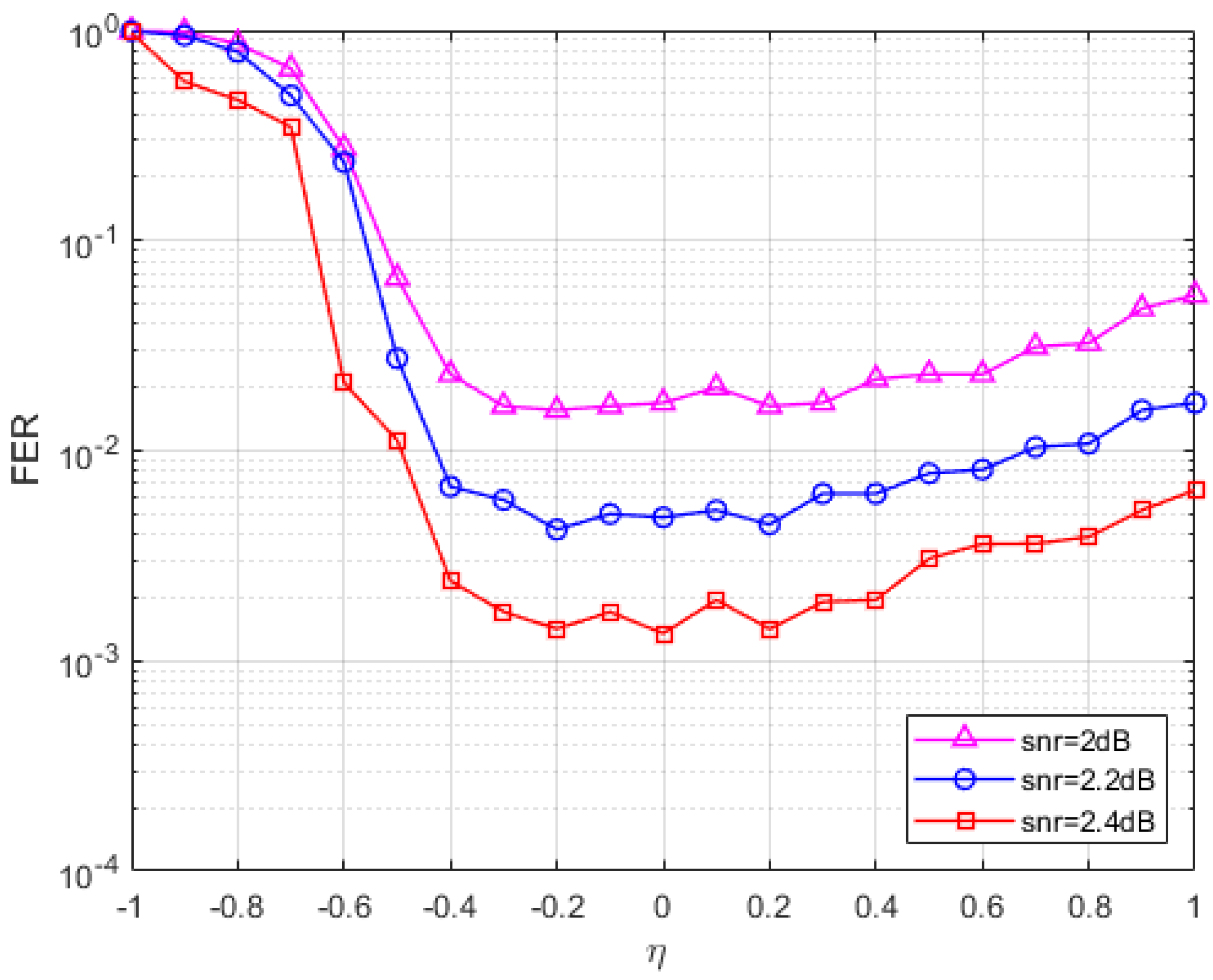
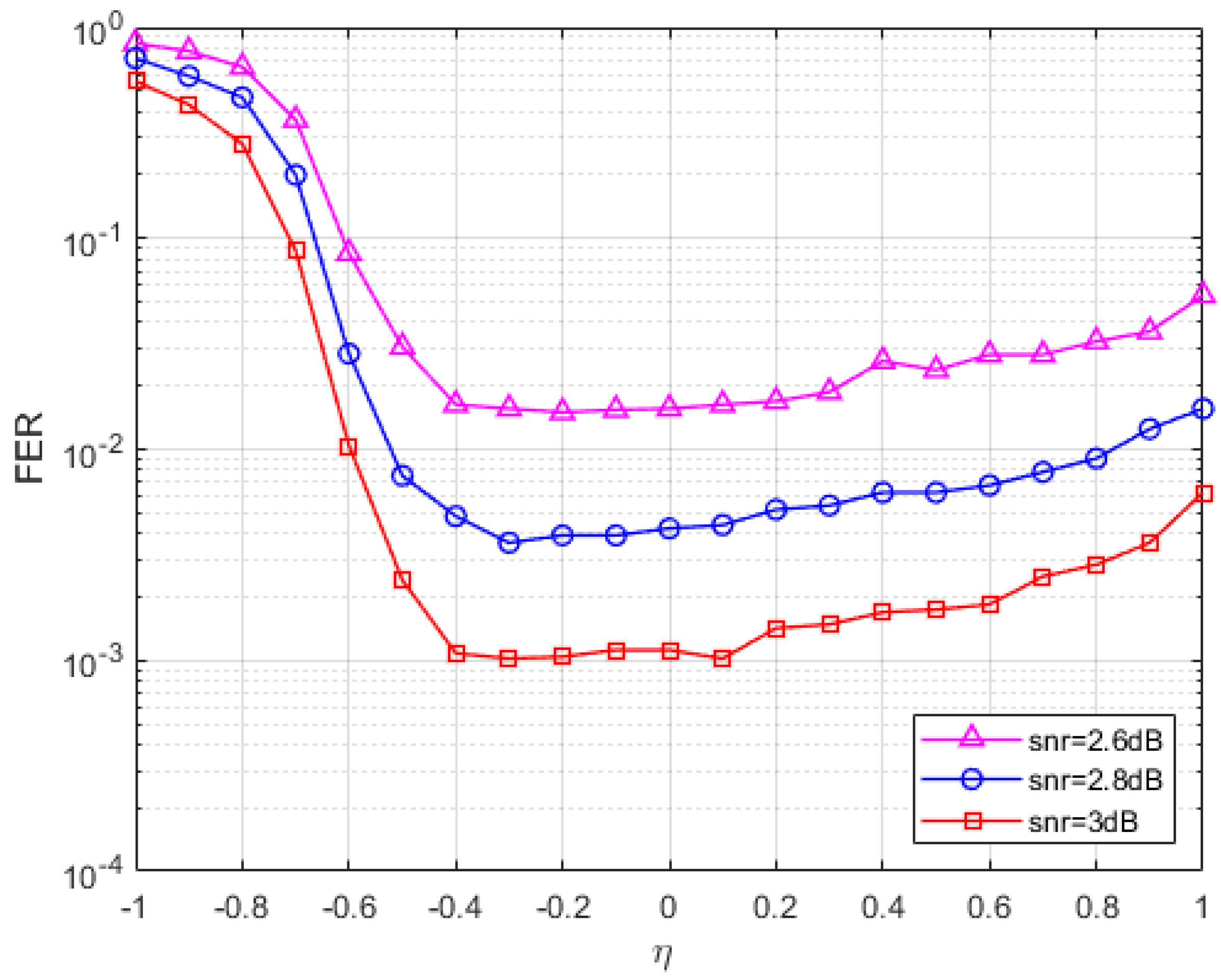
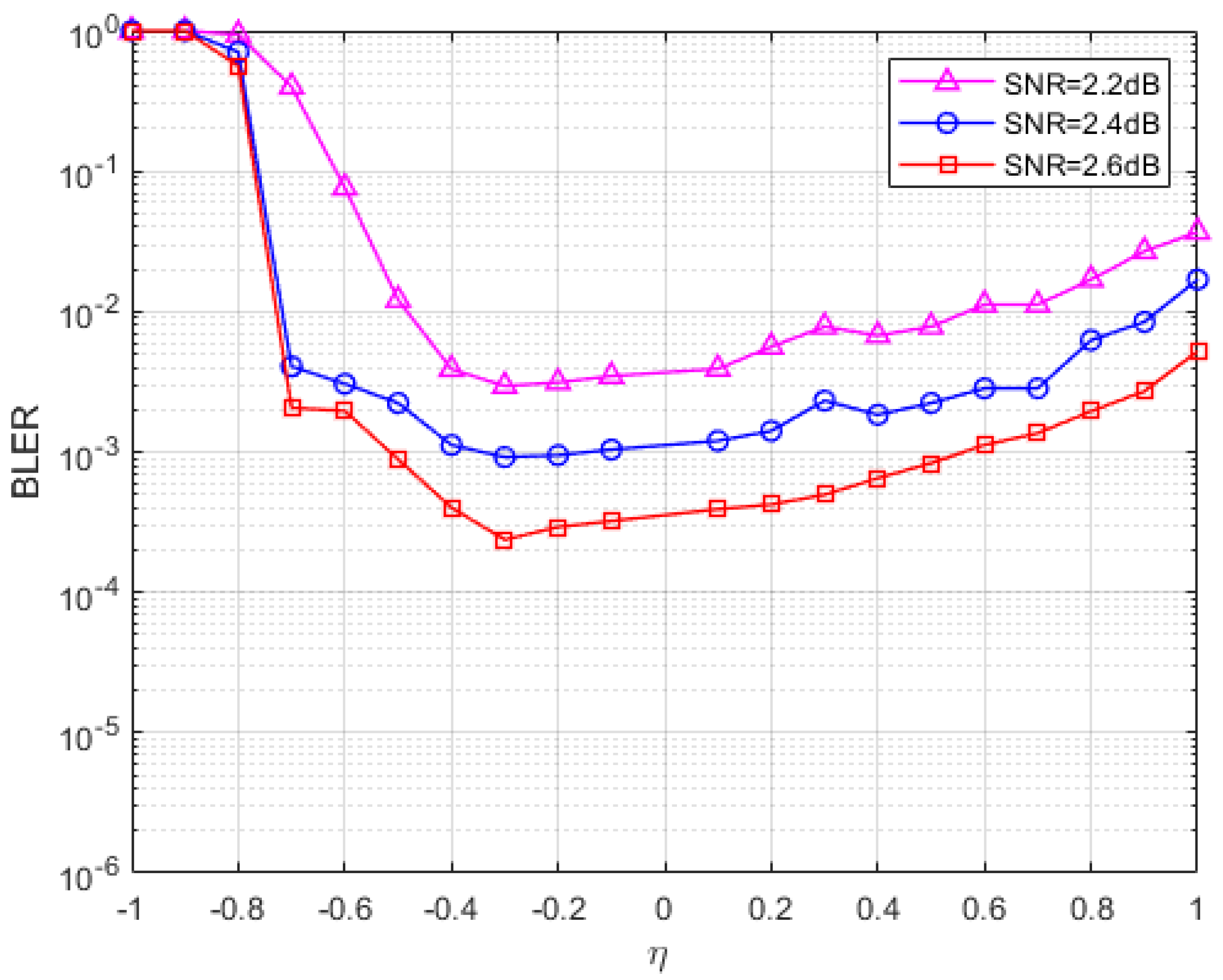
5.1. Parameter Selection
5.2. Performance Analysis
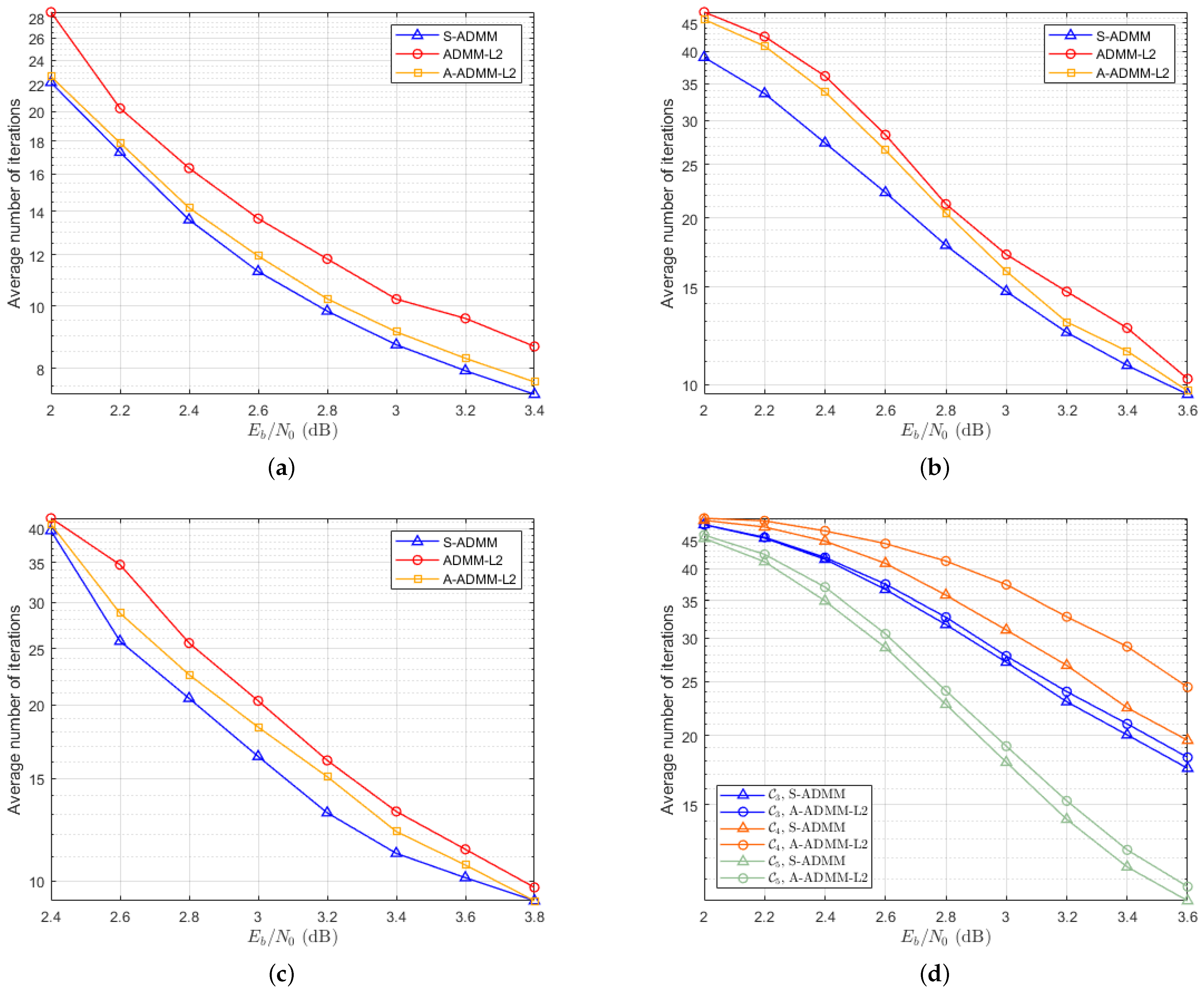
5.3. Average Number of Decoding Iterations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feldman, J.; Wainwright, M.; Karger, D. Using linear programming to Decode Binary linear codes. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2005, 51, 954–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, M.; Dang, S.; Luong, N.C.; Yuen, C.; Nallanathan, A.; Niyato, D. Covert Communications with Enhanced Physical Layer Security in RIS-Assisted Cooperative Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Chen, G.; Hao, W.; Da Costa, D.B.; Nallanathan, A.; Shin, H.; Yuen, C. STAR-RIS Assisted Covert Wireless Communications with Randomly Distributed Blockages. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, S.; Liu, X.; Draper, S.C.; Recht, B. Decomposition Methods for Large Scale LP Decoding. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2013, 59, 7870–7886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.; Parikh, N.; Chu, E.; Peleato, B.; Eckstein, J. Distributed Optimization and Statistical Learning via the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 2011, 3, 1–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Draper, S.C. The ADMM Penalized Decoder for LDPC Codes. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2016, 62, 2966–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Mu, J.; He, Y.C.; Chen, C. Efficient ADMM Decoding of LDPC Codes Using Lookup Tables. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2017, 65, 1425–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Jiao, X.; Mu, J. Reduced-Complexity Linear Programming Decoding Based on ADMM for Codes. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2015, 19, 909–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; He, Y.C.; Mu, J. Memory-Reduced Look-Up Tables for Efficient ADMM Decoding of LDPC Codes. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018, 25, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gensheimer, F.; Dietz, T.; Ruzika, S.; Kraft, K.; Wehn, N. A Low-Complexity Projection Algorithm for ADMM-Based LP Decoding. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 10th International Symposium on Turbo Codes Iterative Information Processing (ISTC), Hong Kong, China, 3–7 December 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Banihashemi, A.H. An Iterative Check Polytope Projection Algorithm for ADMM-Based LP Decoding of LDPC Codes. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2018, 22, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Lin, Y.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Q. A Fast Approximate Check Polytope Projection Algorithm for ADMM Decoding of LDPC Codes. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2019, 23, 1520–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Q. Efficient QP-ADMM Decoder for Binary LDPC Codes and Its Performance Analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2020, 68, 503–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wang, X.; Feldman, J. A New Linear Programming Approach to Decoding Linear Block Codes. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2008, 54, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Q.L. A Hybrid Check Polytope Projection Algorithm for ADMM Decoding of LDPC Codes. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadzadeh, A.; Barakatain, M.; Draper, S.C.; Mitra, J. SAPA: Sparse Affine Projection Algorithm in ADMM-LP Decoding of LDPC Codes. In Proceedings of the 2022 17th Canadian Workshop on Information Theory (CWIT), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 5–8 June 2022; pp. 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbabi, I.; Gal, B.L.; Khouja, N.; Tlili, F.; Jego, C. Fast Converging ADMM-Penalized Algorithm for LDPC Decoding. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2016, 20, 648–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; He, P.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Q. Node-Wise Scheduling Algorithm of ADMM Decoding Based on Line Segment Projection. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2022, 26, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Wei, H.; Mu, J.; Chen, C. Improved ADMM Penalized Decoder for Irregular Low-Density Parity-Check Codes. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2015, 19, 913–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Mu, J.; Jiao, X.; Wang, Z. Improved Penalty Functions of ADMM Penalized Decoder for LDPC Codes. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2017, 21, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Banihashemi, A.H. ADMM Check Node Penalized Decoders for LDPC Codes. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021, 69, 3528–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Wang, H.; Lin, J.; Liu, Y. Parameter-Free ℓp -Box Decoding of LDPC Codes. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2018, 22, 1318–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhao, M.M.; Zhao, M.J.; Lei, M. A PDD Decoder for Binary Linear Codes With Neural Check Polytope Projection. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2020, 9, 1715–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhu, J.; Wen, Z. Decoding LDPC Codes by Using Negative Proximal Regularization. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2023, 71, 3835–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasson, M.; Draper, S.C. Hardware based projection onto the parity polytope and probability simplex. In Proceedings of the 2015 49th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 8–11 November 2015; pp. 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, X. A strictly contractive peaceman–rachford splitting method for convex programming. SIAM J. Optim. 2014, 24, 1011–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchinei, F.; Pang, J.S. Finite-Dimensional Variational Inequalities and Complementarity Problems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]

| Step | Number of Operations | Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | n | - |
| 2 | m | - |
| 3 | - | |
| 6 | ||
| 9 | ||
| 10 | ||
| 11 |
| Algorithm | S-ADMM | A-ADMM- | Comparison of Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Update of x | Same, both have linear complexity. | ||
| Update of z | The projection algorithms used are all from reference [25], with the same complexity. | ||
| Update of | S-ADMM has an additional dual update, but it is only a linear operation and the actual cost can be ignored. | ||
| Average number of iterations | Less (Due to the two-stage balance adjustment, oscillation is suppressed.) | Many, due to the single update direction being prone to oscillation. | Symmetrical design balances the adjustment direction of dual variables and accelerates convergence. |
| Convergence stability | Theorem 1 guarantees strict monotonic convergence. | Relying on the convergence of the traditional ADMM may lead to local oscillations. | S-ADMM suppresses oscillations and reduces ineffective iterations. |
| Code | Symbol | Rate | Column Redistribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| (576,288) | {2,3,6} | ||
| (648,216) | {2,3,4,6,8} | ||
| (1,152,288) | {2,3,6} | ||
| 320 | {1,2,3,4,5,7,8} | ||
| 320 | {1,2,3,4,5,7,8,10,11} | ||
| 320 | {1,2,3,4,5} |
| Decoding Algorithm | A-ADMM- | S-ADMM |
|---|---|---|
| 5.11368 | 0.00001 | |
| 1.00586 | 1.90024 | |
| 0.30138 | 5.42336 | |
| 3.29866 | 4.15607 |
| Decoding Algorithm | A-ADMM- | S-ADMM |
|---|---|---|
| 0.12794 | 0.06876 | |
| 0.76466 | 1.13234 | |
| 1.90017 | 1.60122 | |
| 2.94728 | 5.29668 | |
| 6.16048 | 6.44272 | |
| 3.60323 | 3.17501 |
| Decoding Algorithm | A-ADMM- | S-ADMM |
|---|---|---|
| 0.00001 | 0.00290 | |
| 0.00001 | 0.00001 | |
| 1.45949 | 1.53340 | |
| 0.00001 | 4.09405 | |
| 2.56477 | 2.17151 | |
| 6.49895 | 3.05173 | |
| 10.14689 | 7.49879 | |
| 9.48708 | 5.93976 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Chen, A.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, B.; Li, H.; Xu, H. Low-Density Parity-Check Decoding Algorithm Based on Symmetric Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers. Entropy 2025, 27, 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040404
Zhang J, Chen A, Zhang Y, Ji B, Li H, Xu H. Low-Density Parity-Check Decoding Algorithm Based on Symmetric Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers. Entropy. 2025; 27(4):404. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040404
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ji, Anmin Chen, Ying Zhang, Baofeng Ji, Huaan Li, and Hengzhou Xu. 2025. "Low-Density Parity-Check Decoding Algorithm Based on Symmetric Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers" Entropy 27, no. 4: 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040404
APA StyleZhang, J., Chen, A., Zhang, Y., Ji, B., Li, H., & Xu, H. (2025). Low-Density Parity-Check Decoding Algorithm Based on Symmetric Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers. Entropy, 27(4), 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040404






