Further Exploration of an Upper Bound for Kemeny’s Constant
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. A Family of Biregular Graphs with Diameter 2
2.1. Construction
2.2. Tightness of the Upper Bound
2.3. Some Examples
3. Graphs with Diameter 2 for Which Is Not Tight
3.1. Bimodal Graphs with Diameter 2 for Which Equation (4) Is Not Tight
3.2. Non-Biregular Graphs with Diameter 2
4. Regular Graphs
5. Complexity for the Computation of
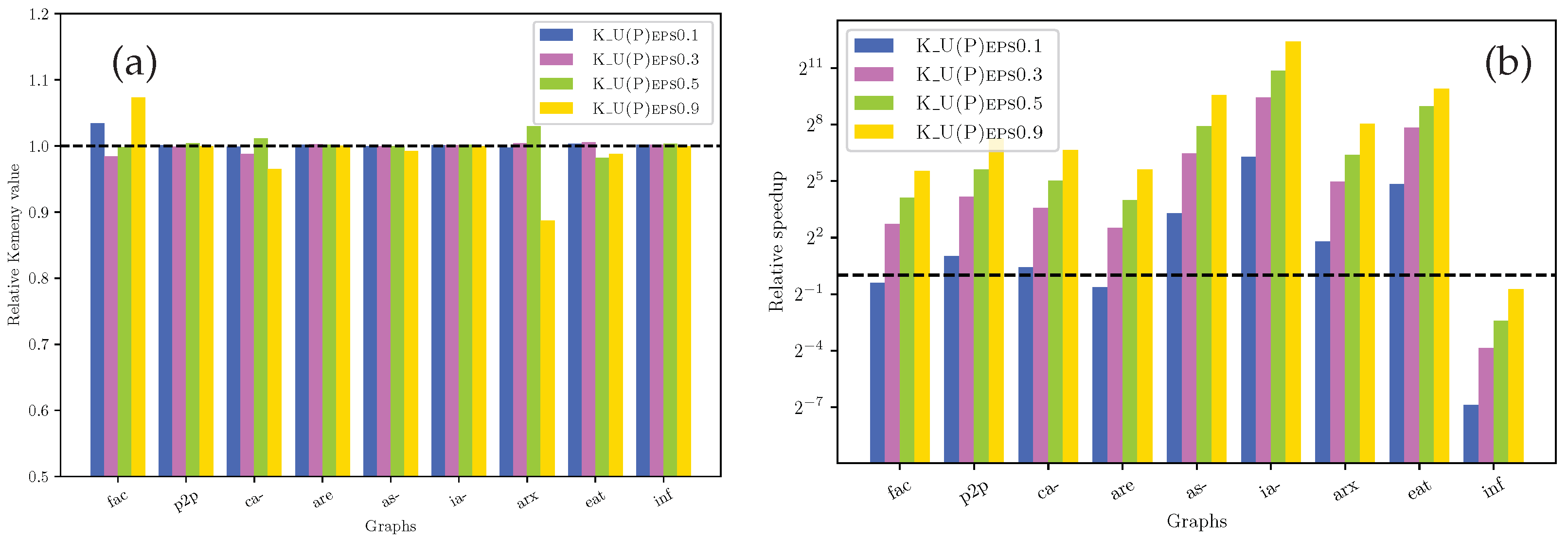
6. Analysis of Some Large Real-World Networks
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kemeny, J.G.; Snell, J.L. Finite Markov Chains; D. Van Nostrand: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Lovász, L. Random Walks on Graphs: A Survey. In Paul Erdös is Eighty; Bolyai Society, Mathematical Studies: Keszthely, Hungary, 1993; Volume 2, pp. 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Palacios, J.L.; Renom, J.M. Bounds for the Kirchhoff index of regular graphs via the spectra of their random walks. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2010, 110, 1637–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dubbeldam, J.L.A.; Van Mieghem, P. Kemeny’s constant and the effective graph resistance. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 2017, 535, 231–244. [Google Scholar]
- Noh, J.D.; Rieger, H. Random Walks on Complex Networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 118701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levene, M.; Loizou, G. Kemeny’s Constant and the Random Surfer. Am. Math. Mon. 2002, 109, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J. Mixing times with applications to perturbed Markov chains. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 2006, 417, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.J. The role of Kemeny’s constant in properties of Markov chains. Commun. Stat.-Theory Methods 2014, 43, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkland, S.; Zeng, Z. Kemeny’s Constant and an Analogue of Braess’ Paradox for Trees. Electron. J. Linear Algebra 2016, 31, 444–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Cover, J.A.T. Elements of Information Theory; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Altafini, D.; Bini, D.A.; Cutini, V.; Meini, B.; Poloni, F. An edge centrality measure based on the Kemeny constant. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.06459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, S.; Dudkina, E.; Bin, M.; Crisostomi, E.; Ferraro, P.; Murray-Smith, R.; Parisini, T.; Stone, L.; Shorten, R. Kemeny-based testing for COVID-19. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.niallmadden.ie/ILAS-2022.pdf (accessed on 2 December 2024).
- Breen, J.; Crisostomi, E.; Kim, S. Kemeny’s constant for a graph with bridges. Discret. Appl. Math. 2022, 322, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bini, D.A.; Durastante, F.; Kim, S.; Meini, B. On Kemeny’s constant and stochastic complement. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 2024, 703, 137–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, F. A note on the irregularity of graphs. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 1992, 161, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooij, R.E.; Dubbeldam, J.L. Kemeny’s constant for several families of graphs and real-world networks. Discret. Appl. Math. 2020, 285, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooij, R.E. On generalized windmill graphs. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 2019, 565, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devriendt, K.; Martin-Gutierrez, S.; Lambiotte, R. Variance and Covariance of Distributions on Graphs. SIAM Rev. 2022, 64, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godsil, C.; Royle, G.F. Algebraic Graph Theory; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Scheinermann, E.; Ullman, D. Fractional Graph Theory: A Rational Approach; Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Van Mieghem, P. Graph Spectra for Complex Networks; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Palacios, J.L.; Renom, J. Broder and Karlin’s formula for hitting times and the Kirchhoff Index. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2011, 111, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquelin, M.; Lin, L.; Yang, C. PSelInv—A distributed memory parallel algorithm for selected inversion: The non-symmetric case. Parallel Comput. 2018, 74, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, M.F. A stochastic estimator of the trace of the influence matrix for Laplacian smoothing splines. J. Commun. Statist. Simula. 1990, 19, 433–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekas, C.; Kokiopoulou, E.; Saad, Y. An Estimator for the Diagonal of a Matrix. Appl. Numer. Math. 2007, 57, 1214–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angriman, E.; Predari, M.; van der Grinten, A.; Meyerhenke, H. Approximation of the Diagonal of a Laplacian’s Pseudoinverse for Complex Network Analysis. In Proceedings of the ESA. Schloss Dagstuhl-Leibniz-Zentrum für Informatik, Pisa, Italy, 7–9 September 2020; LIPIcs. Volume 173, pp. 6:1–6:24. [Google Scholar]
- Bollobás, B. Modern Graph Theory; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, M. Networks, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Paige, C. Accuracy and effectiveness of the Lanczos algorithm for the symmetric eigenproblem. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 1980, 34, 235–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudt, C.L.; Sazonovs, A.; Meyerhenke, H. NetworKit: A tool suite for large-scale complex network analysis. Netw. Sci. 2016, 4, 508–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angriman, E.; van der Grinten, A.; von Looz, M.; Meyerhenke, H.; Nöllenburg, M.; Predari, M.; Tzovas, C. Guidelines for experimental algorithmics: A case study in network analysis. Algorithms 2019, 12, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskovec, J. Stanford Network Analysis Package (SNAP). Available online: https://snap.stanford.edu/ (accessed on 2 December 2024).
- Rossi, R.A.; Ahmed, N.K. The Network Data Repository with Interactive Graph Analytics and Visualization. In Proceedings of the AAAI, Austin, TX, USA, 25–30 January 2015. [Google Scholar]




| Graph | Type | ID | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| inf-power | infrastructure | inf | 4 K | 6 K |
| facebook-ego-combined | social | fac | 4 K | 8.8 K |
| p2p-Gnutella04 | internet | p2p | 10 K | 39 K |
| ca-HepPh | collaboration | ca- | 11 K | 117 K |
| arxiv-astro-ph | collaboration | arx | 17 K | 196 K |
| eat | words | eat | 23 K | 297 K |
| arenas-pgp | infrastructure | are | 24 K | 10 K |
| as-caida20071105 | internet | as- | 26 K | 53 K |
| ia-email-EU | communication | ia- | 32 K | 54.4 K |
| loc-brightkite | social | lob | 57 K | 213 K |
| soc-Slashdot0902 | social | soc | 82 K | 504 K |
| flickr | images | fli | 106 K | 2.31 M |
| livemocha | social | liv | 104 K | 2.19 M |
| loc-gowalla-edges | social | log | 196 K | 950 K |
| web-NotreDame | web | web | 325 K | 1.09 M |
| citeseer | citation | cit | 365 K | 1.72 M |
| Graph | Time (h:min:s) | |
|---|---|---|
| lob | 80,903 | 48.83 s |
| soc | 96,102 | 50.87 s |
| fli | 122,185 | 1 min:38.11 s |
| liv | 120,525 | 37.07 s |
| log | 271,577 | 5 min:10.77 s |
| web | 1,009,760 | 1 h:11 min:19.36 s |
| cit | 508,244 | 1 h:16 min:11.51 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kooij, R.E.; Dubbeldam, J.L.A. Further Exploration of an Upper Bound for Kemeny’s Constant. Entropy 2025, 27, 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040384
Kooij RE, Dubbeldam JLA. Further Exploration of an Upper Bound for Kemeny’s Constant. Entropy. 2025; 27(4):384. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040384
Chicago/Turabian StyleKooij, Robert E., and Johan L. A. Dubbeldam. 2025. "Further Exploration of an Upper Bound for Kemeny’s Constant" Entropy 27, no. 4: 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040384
APA StyleKooij, R. E., & Dubbeldam, J. L. A. (2025). Further Exploration of an Upper Bound for Kemeny’s Constant. Entropy, 27(4), 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040384







