Minimax Bayesian Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Minimax Bayesian Neural Networks
3. Experiments and Results
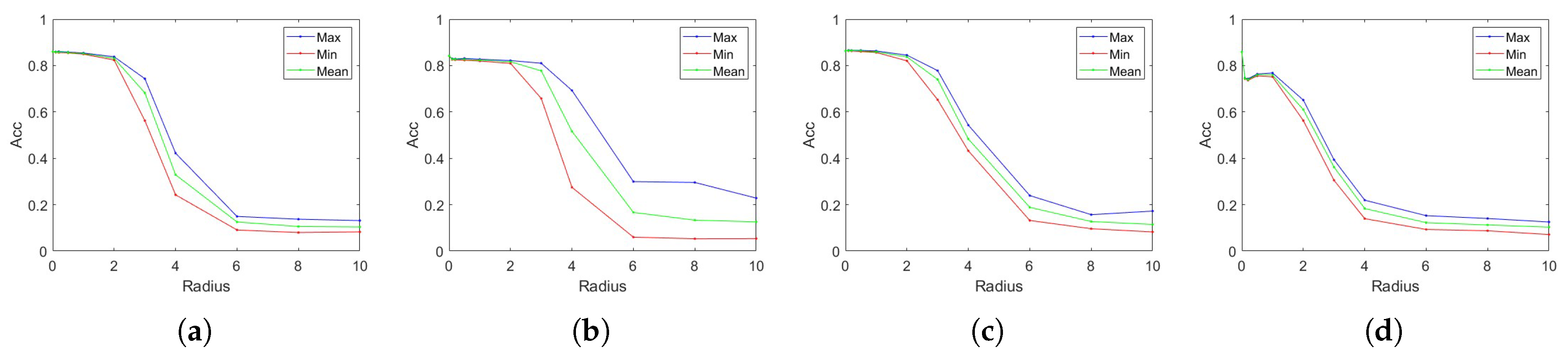
3.1. Main Results
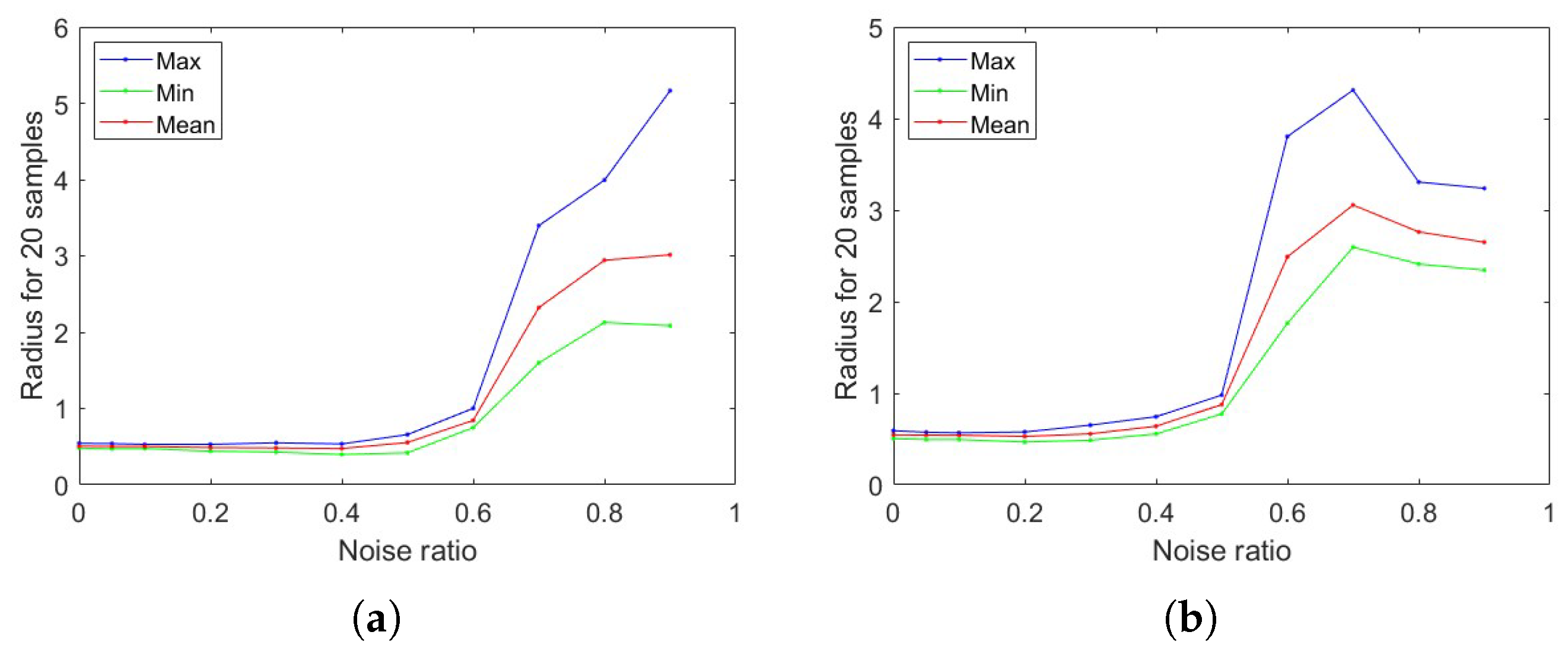
3.2. Noise Perturbation
3.3. Dataset Similarity
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1
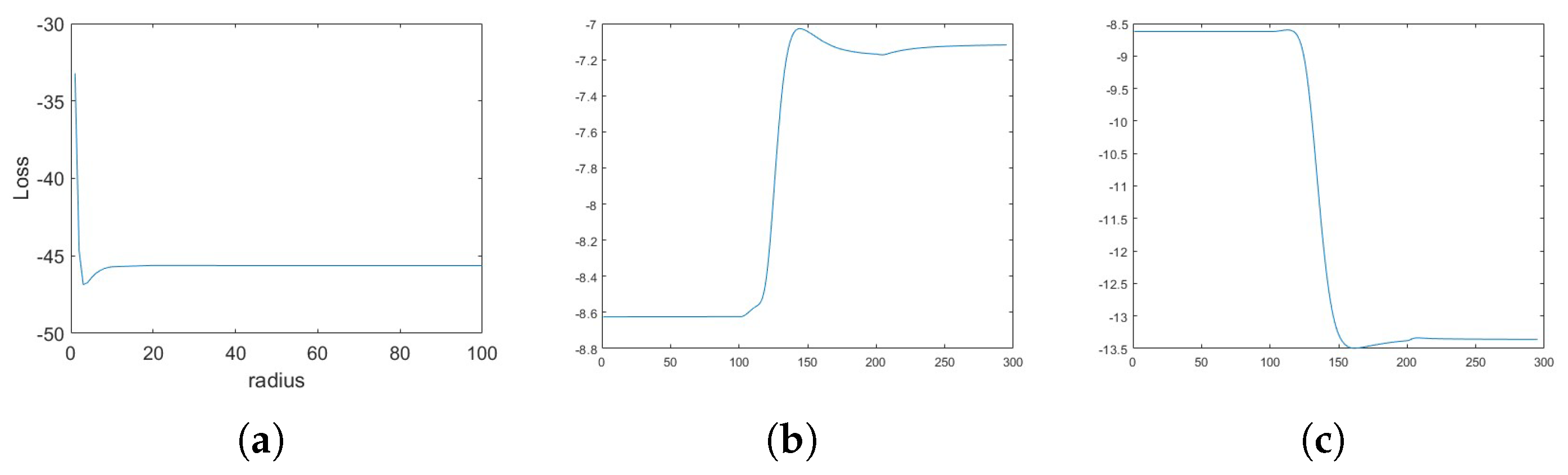
Appendix A.2

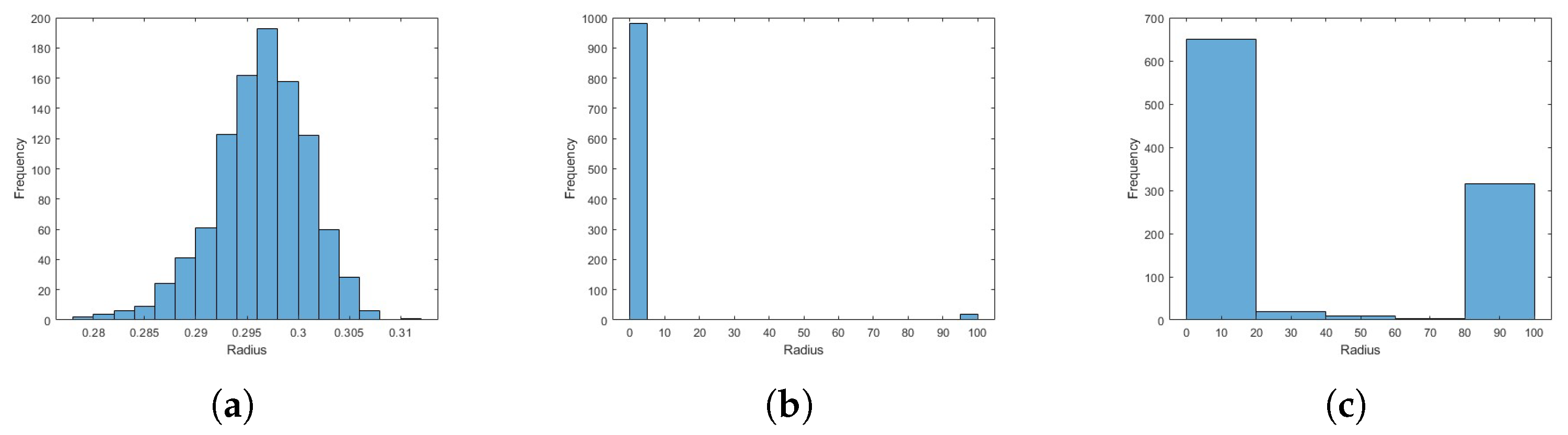
References
- Bi, K.; Xie, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Gu, X.; Tian, Q. Pangu-weather: A 3D high-resolution model for fast and accurate global weather forecast. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.02556. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Song, W.; Fang, L.; Chen, Y.; Ghamisi, P.; Benediktsson, J.A. Deep learning for hyperspectral image classification: An overview. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6690–6709. [Google Scholar]
- Kuruoglu, E.E.; Taylor, A.S. Using Annotations for Summarizing a Document Image and Itemizing the Summary Based on Similar Annotations. US Patent 7,712,028, 4 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hjelm, R.D.; Fedorov, A.; Lavoie-Marchildon, S.; Grewal, K.; Bachman, P.; Trischler, A.; Bengio, Y. Learning deep representations by mutual information estimation and maximization. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.06670. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Chan, K.H.R.; You, C.; Song, C.; Ma, Y. Learning diverse and discriminative representations via the principle of maximal coding rate reduction. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 9422–9434. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Liu, S.; Su, H.; Cao, K.; Zhu, J. Analyzing the noise robustness of deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Visual Analytics Science and Technology (VAST), Berlin, Germany, 21–26 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 60–71. [Google Scholar]
- Fawzi, A.; Moosavi-Dezfooli, S.M.; Frossard, P. The robustness of deep networks: A geometrical perspective. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2017, 34, 50–62. [Google Scholar]
- MacKay, D.J. A practical Bayesian framework for backpropagation networks. Neural Comput. 1992, 4, 448–472. [Google Scholar]
- Neal, R.M. Bayesian Learning for Neural Networks; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012; Volume 118. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Gal, Y.; Ghahramani, Z. Dropout as a Bayesian approximation: Representing model uncertainty in deep learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, New York, NY, USA, 20–22 June 2016; pp. 1050–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Jospin, L.V.; Laga, H.; Boussaid, F.; Buntine, W.; Bennamoun, M. Hands-on Bayesian neural networks—A tutorial for deep learning users. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2022, 17, 29–48. [Google Scholar]
- Blundell, C.; Cornebise, J.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Wierstra, D. Weight uncertainty in neural network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Lille, France, 7–9 July 2015; pp. 1613–1622. [Google Scholar]
- Izmailov, P.; Vikram, S.; Hoffman, M.D.; Wilson, A.G.G. What are Bayesian neural network posteriors really like? In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 4629–4640. [Google Scholar]
- Carbone, G.; Wicker, M.; Laurenti, L.; Patane, A.; Bortolussi, L.; Sanguinetti, G. Robustness of Bayesian neural networks to gradient-based attacks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 15602–15613. [Google Scholar]
- Malinin, A.; Gales, M. Predictive uncertainty estimation via prior networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31, 7047–7058. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, S.L.; Kuruoglu, E.E.; Sun, J.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Y. PAC-Bayes information bottleneck. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.14509. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, J.O. Statistical Decision Theory and Bayesian Analysis; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Neti, C.; Schneider, M.H.; Young, E.D. Maximally fault tolerant neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1992, 3, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deodhare, D.; Vidyasagar, M.; Keethi, S.S. Synthesis of fault-tolerant feedforward neural networks using minimax optimization. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1998, 9, 891–900. [Google Scholar]
- Duddu, V.; Rao, D.V.; Balas, V.E. Adversarial fault tolerant training for deep neural networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.03103. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, X.; Tong, S.; Li, M.; Wu, Z.; Psenka, M.; Chan, K.H.R.; Zhai, P.; Yu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Shum, H.Y.; et al. Ctrl: Closed-loop transcription to an LDR via minimaxing rate reduction. Entropy 2022, 24, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioffe, S. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1502.03167. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y. The MNIST Database of Handwritten Digits. 1998. Available online: http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/ (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- Xiao, H.; Rasul, K.; Vollgraf, R. Fashion-mnist: A novel image dataset for benchmarking machine learning algorithms. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.07747. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Hinton, G. Learning Multiple Layers of Features from Tiny Images; University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y. Convolutional networks for images, speech, and time series. Handb. Brain Theory Neural Netw. 1995, 3361, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, G.; Wang, H.; Bell, D.; Bi, Y.; Greer, K. KNN model-based approach in classification. In On The Move to Meaningful Internet Systems 2003: CoopIS, DOA, and ODBASE: OTM Confederated International Conferences, CoopIS, DOA, and ODBASE 2003, Catania, Sicily, Italy, 3–7 November 2003; Proceedings; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 986–996. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, O.; Kramer, O. Scikit-learn. Mach. Learn. Evol. Strateg. 2016, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 8026–8037. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.; Li, Y.; Srikant, R. Enhancing the reliability of out-of-distribution image detection in neural networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.02690. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhoti, J.; Kirsch, A.; van Amersfoort, J.; Torr, P.H.; Gal, Y. Deep deterministic uncertainty: A new simple baseline. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17 June–24 June 2023; pp. 24384–24394. [Google Scholar]
| Models | f (MNIST) | Closed-Loop | f (FMNIST) | Closed-Loop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| test 1 | 96.28% | 96.57% | 85.82% | 86.09% |
| test 2 | 96.43% | 96.40% | 85.79% | 86.24% |
| test 3 () | 96.70% | 96.82% | 86.21% | 86.81% |
| test 4 () | 96.73% | 97.25% | 86.09% | 86.71% |
| r (Test 4, 20 Samples) | Max | Min | Mean | Variance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 97.01% | 96.93% | 96.97% | 5.0 × |
| 0.2 | 97.07% | 96.9% | 96.96% | 1.5 × |
| 0.5 | 97.03% | 96.84% | 96.93% | 2.6 × |
| 1 | 96.95% | 96.65% | 96.81% | 7.1 × |
| 2 | 96.38% | 95.18% | 95.82% | 9.8 × |
| 3 | 92.21% | 78.3% | 84.78% | 1.7 × |
| 4 | 62.99% | 26.33% | 40.83% | 9.7 × |
| 6 | 17.88% | 10.45% | 13.33% | 5.0 × |
| 8 | 14.54% | 8.22% | 10.84% | 1.8 × |
| 10 | 11.93% | 7.91% | 10.29% | 1.2 × |
| r (, 20 Samples) | Max | Min | Mean | Variance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNIST | 0.544 | 0.481 | 0.507 | 3.1 × |
| FMNIST | 1.768 | 1.186 | 1.473 | 1.8 × |
| CIFAR-10 (channel 1) | 3.134 | 1.999 | 2.639 | 1.0 × |
| Gaussian | 3.751 | 1.778 | 2.661 | 3.1 × |
| Laplace | 5.637 | 2.902 | 3.800 | 4.9 × |
| Cauchy | 5.807 | 4.188 | 4.942 | 1.9 × |
| r (, 20 Samples) | Max | Min | Mean | Variance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FMNIST | 0.591 | 0.503 | 0.546 | 5.4 × |
| MNIST | 1.904 | 1.479 | 1.671 | 1.6 × |
| CIFAR-10 (channel 1) | 2.599 | 2.155 | 2.458 | 1.2 × |
| Gaussian | 3.220 | 2.189 | 2.560 | 7.6 × |
| Laplace | 4.129 | 2.852 | 3.487 | 9.4 × |
| Cauchy | 5.851 | 4.121 | 4.723 | 1.6 × |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, J.; Kuruoglu, E.E. Minimax Bayesian Neural Networks. Entropy 2025, 27, 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040340
Hong J, Kuruoglu EE. Minimax Bayesian Neural Networks. Entropy. 2025; 27(4):340. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040340
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Junping, and Ercan Engin Kuruoglu. 2025. "Minimax Bayesian Neural Networks" Entropy 27, no. 4: 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040340
APA StyleHong, J., & Kuruoglu, E. E. (2025). Minimax Bayesian Neural Networks. Entropy, 27(4), 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040340







