Beamspace Spatial Smoothing MUSIC DOA Estimation Method Using Dynamic Metasurface Antenna
Abstract
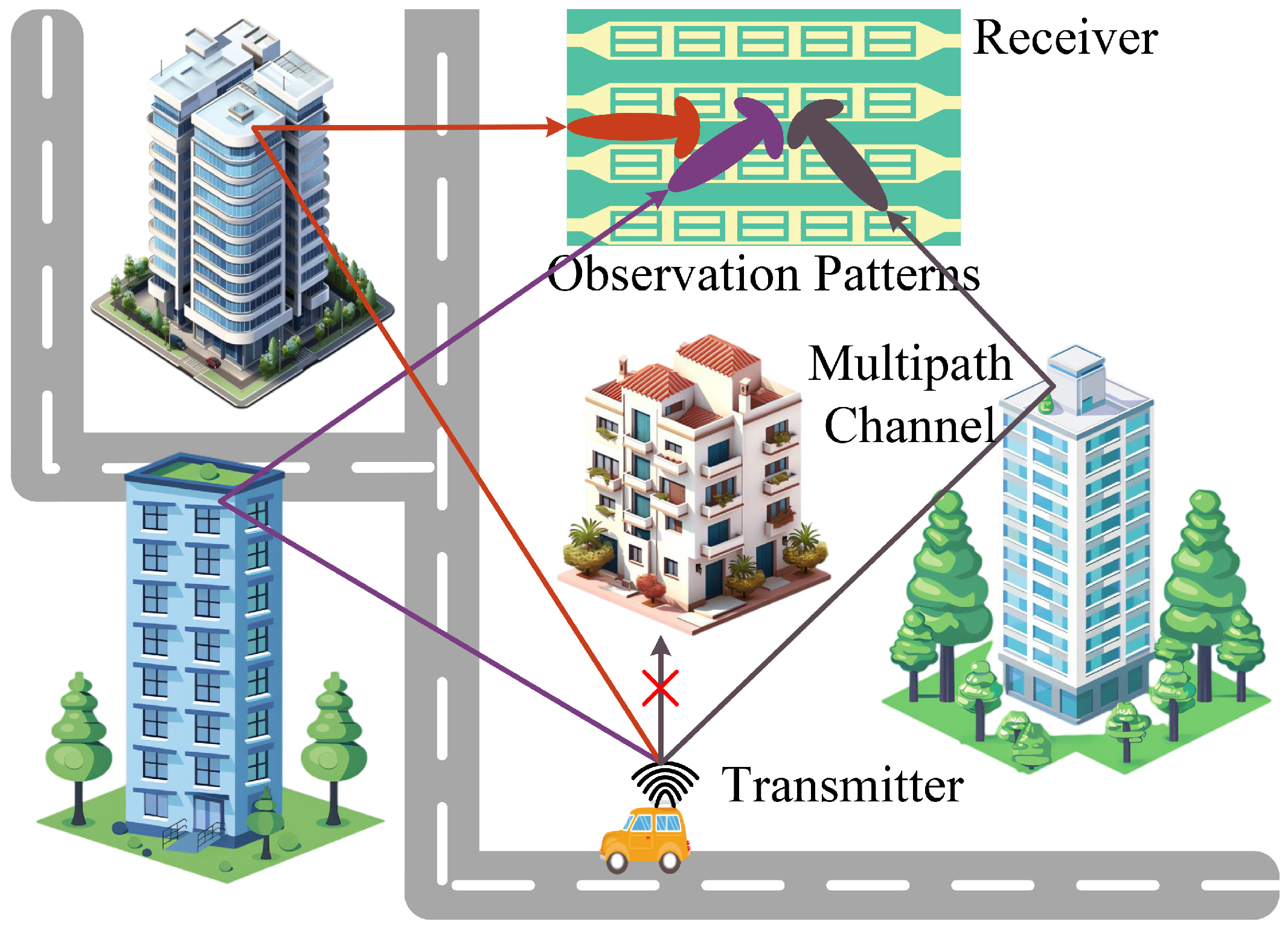
1. Introduction
- We propose a DMA-assisted receiver system model with a single RF chain. Based on this model, we establish a time-division data reception scheme to sequentially capture the received signal data. The observation angle range can be dynamically adjusted using this scheme. Within the adjusted range, the pattern can be rapidly changed during a single pilot symbol period, enabling the reception of signals equivalent to those obtained by a multi-RF chain system.
- To reduce computational complexity and improve the accuracy of the DOA estimation algorithm, we dynamically select the ROI and increase the beam density in the ROI with an appropriate number of beam patterns based on the time-division data reception scheme. Moreover, the BSS-MUSIC algorithm converts 2D DOA estimation into two 1D beamspace MUSIC DOA estimations, which helps to reduce the angular search space. Next, beamspace spatial smoothing effectively utilizes the array aperture to improve the estimation accuracy of the algorithm, achieving multipath signals decorrelation. Finally, the beamspace MUSIC algorithm accurately estimates the DOAs.
- The feasibility of the proposed method is verified through several simulated experiments. The simulation results illustrate that our method offers improved estimation accuracy and reduced computational complexity. Furthermore, it effectively minimizes the required number of RF chains while improving the DOF.
2. DMA-Assisted Receiving System Model
3. BSS-MUSIC DOA Estimation Framework Based on DMA
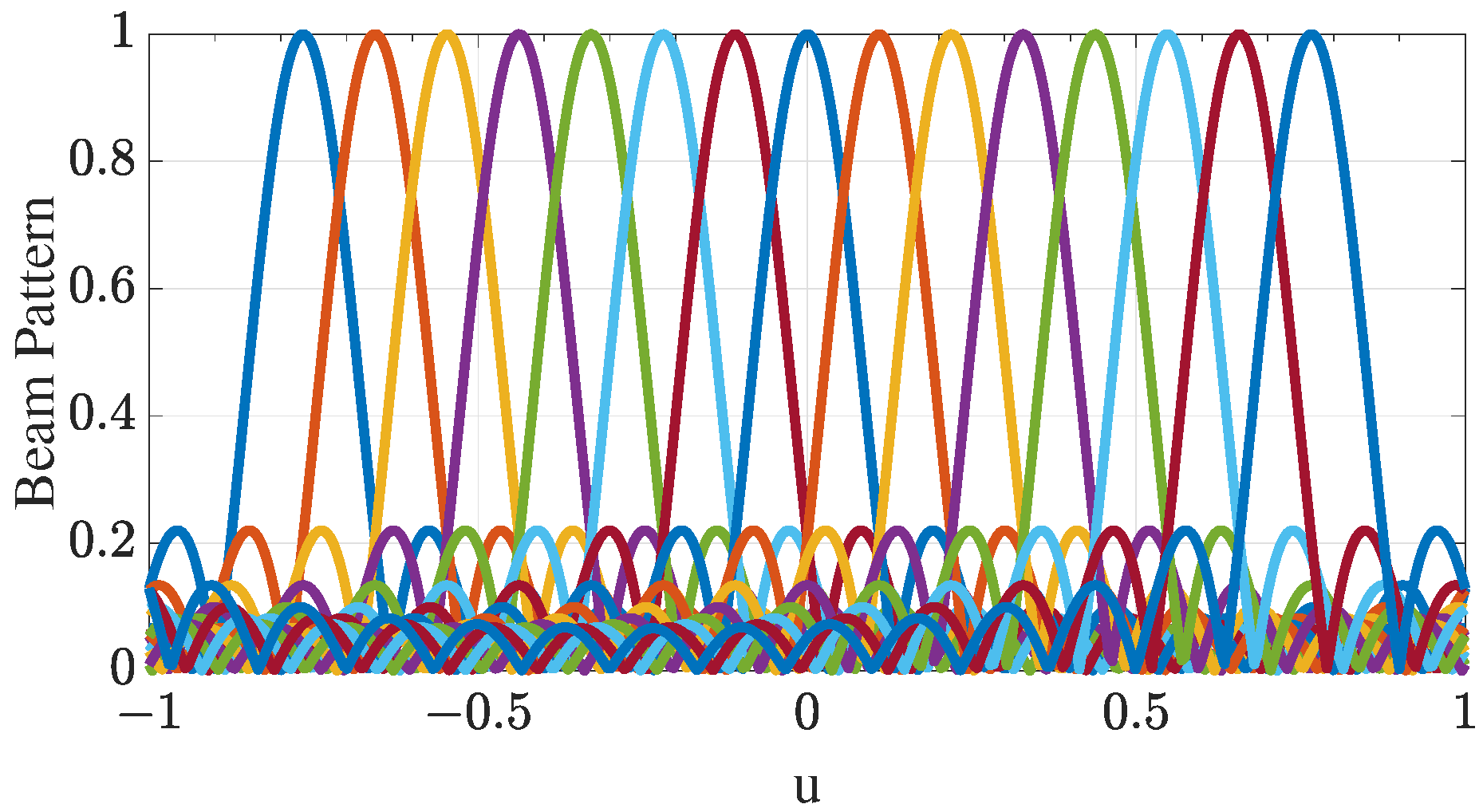
3.1. Design of Time-Division Data Reception Scheme Based on the DFT Algorithm
3.1.1. Implementation of Time-Division Data Reception Scheme Using DMA
3.1.2. Reception of Data Using Time-Division Scheme
3.2. Beamspace Spatial Smoothing Algorithm
3.3. Beamspace MUSIC Algorithm
3.4. Complexity Analysis
4. Simulation Results
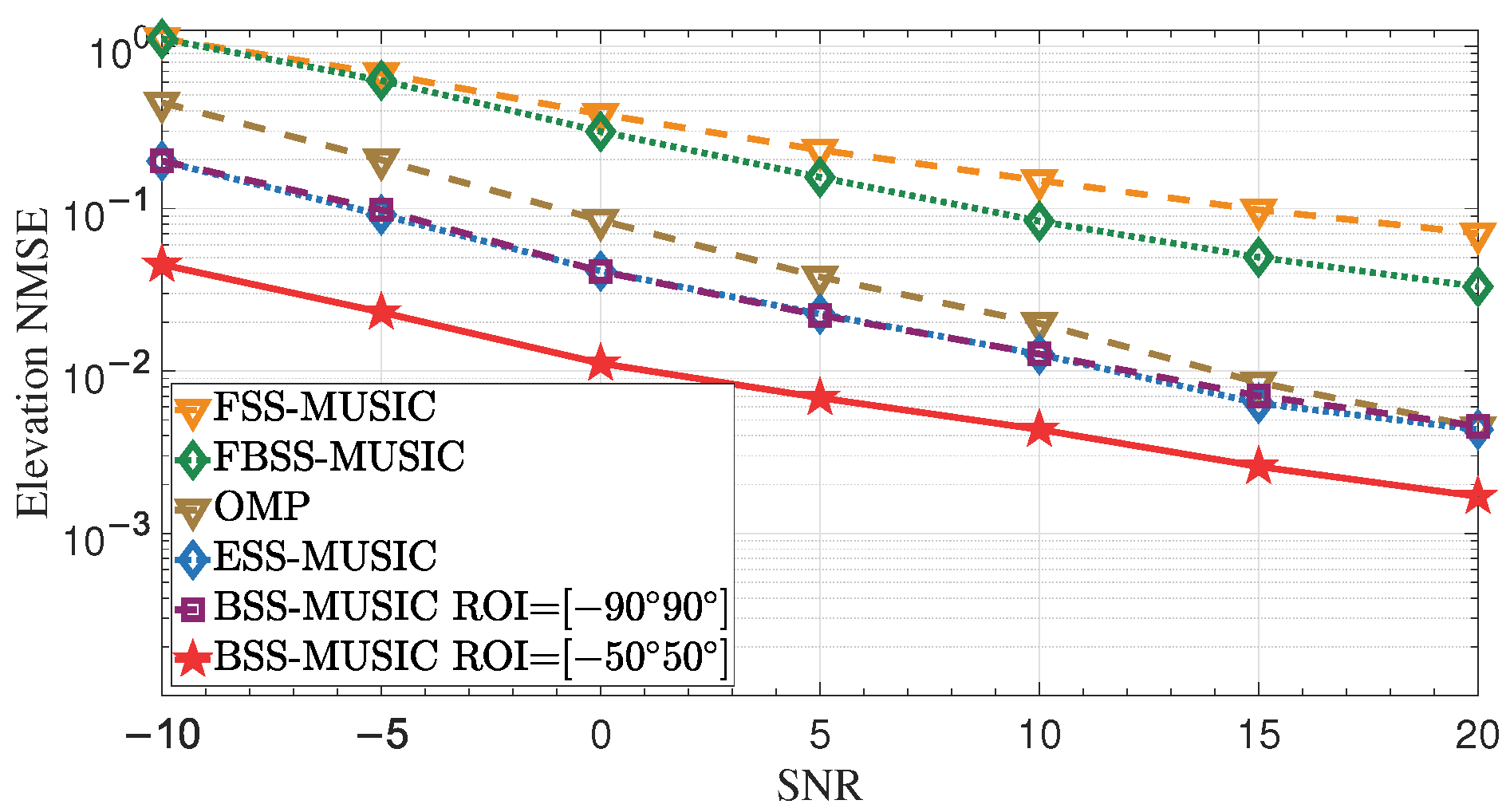
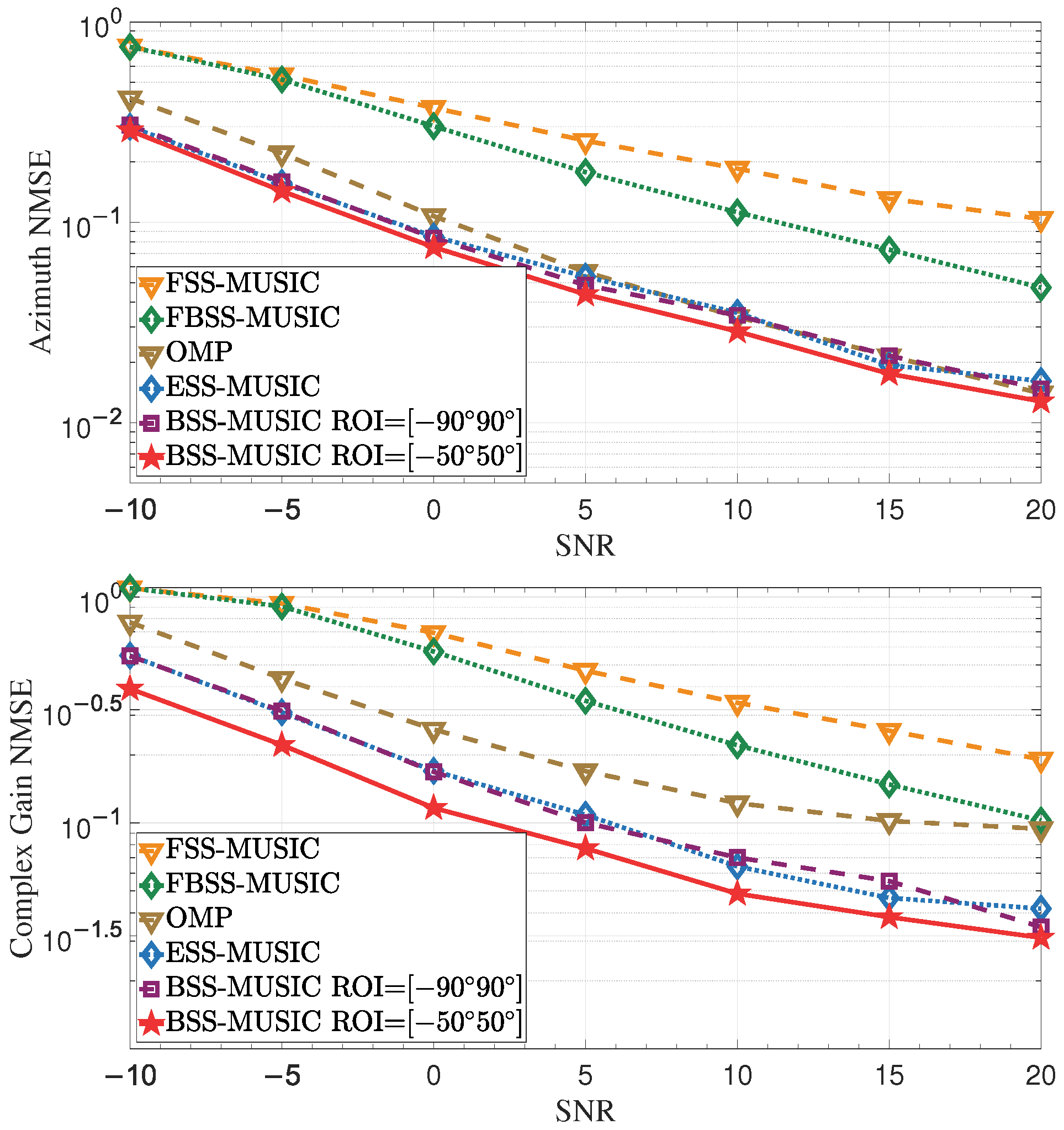
4.1. Impact of SNR
4.1.1. Effect of Increasing Transmit Power
4.1.2. Effect of Increasing Pilot Length
4.1.3. Effect of Increasing Multipaths Number
4.2. Impact of the Array Resolution
4.2.1. Effect of Increasing Number of Elements
4.2.2. Effect of Incident Angle Range
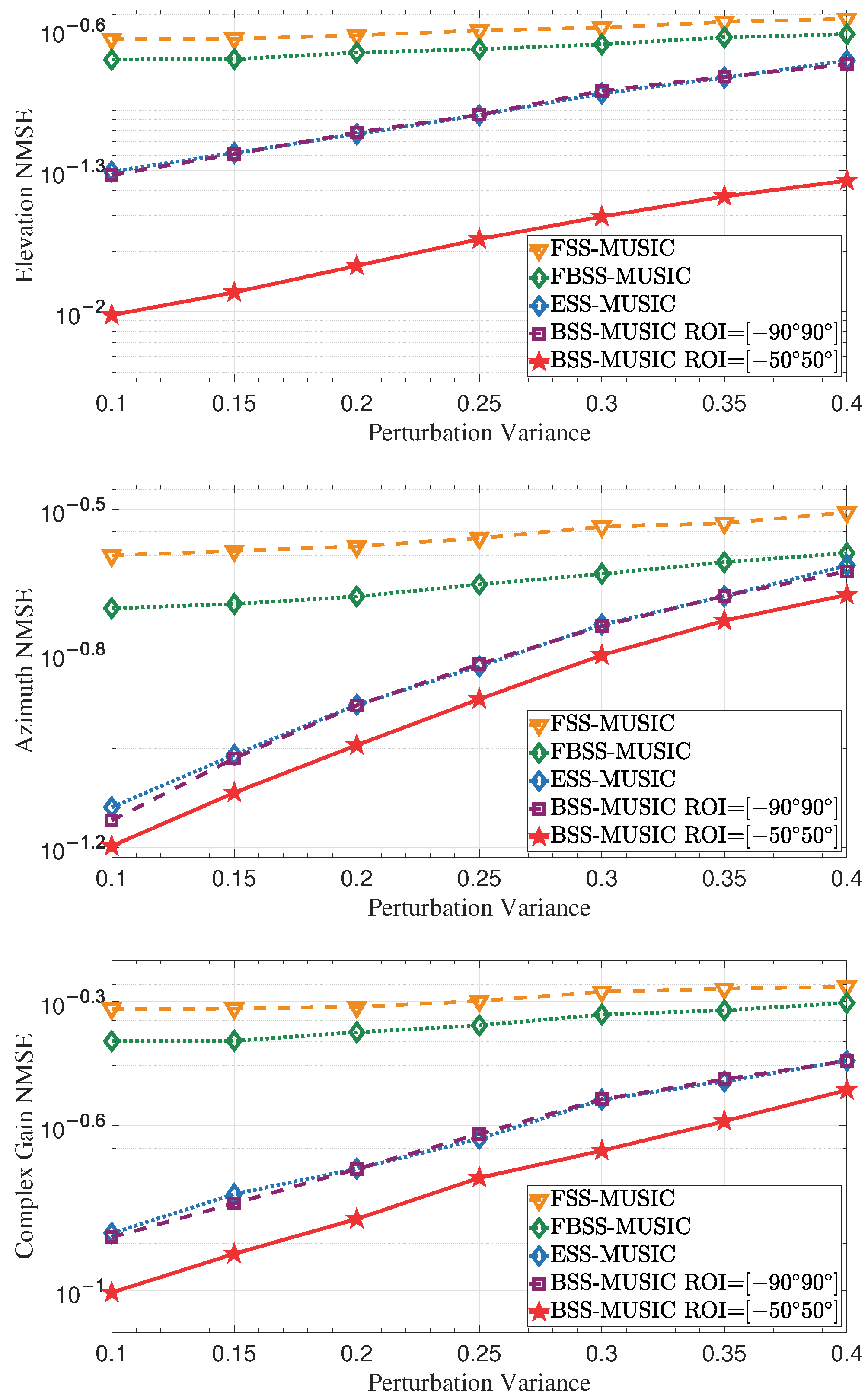
4.3. Impact of Array Element Position Error
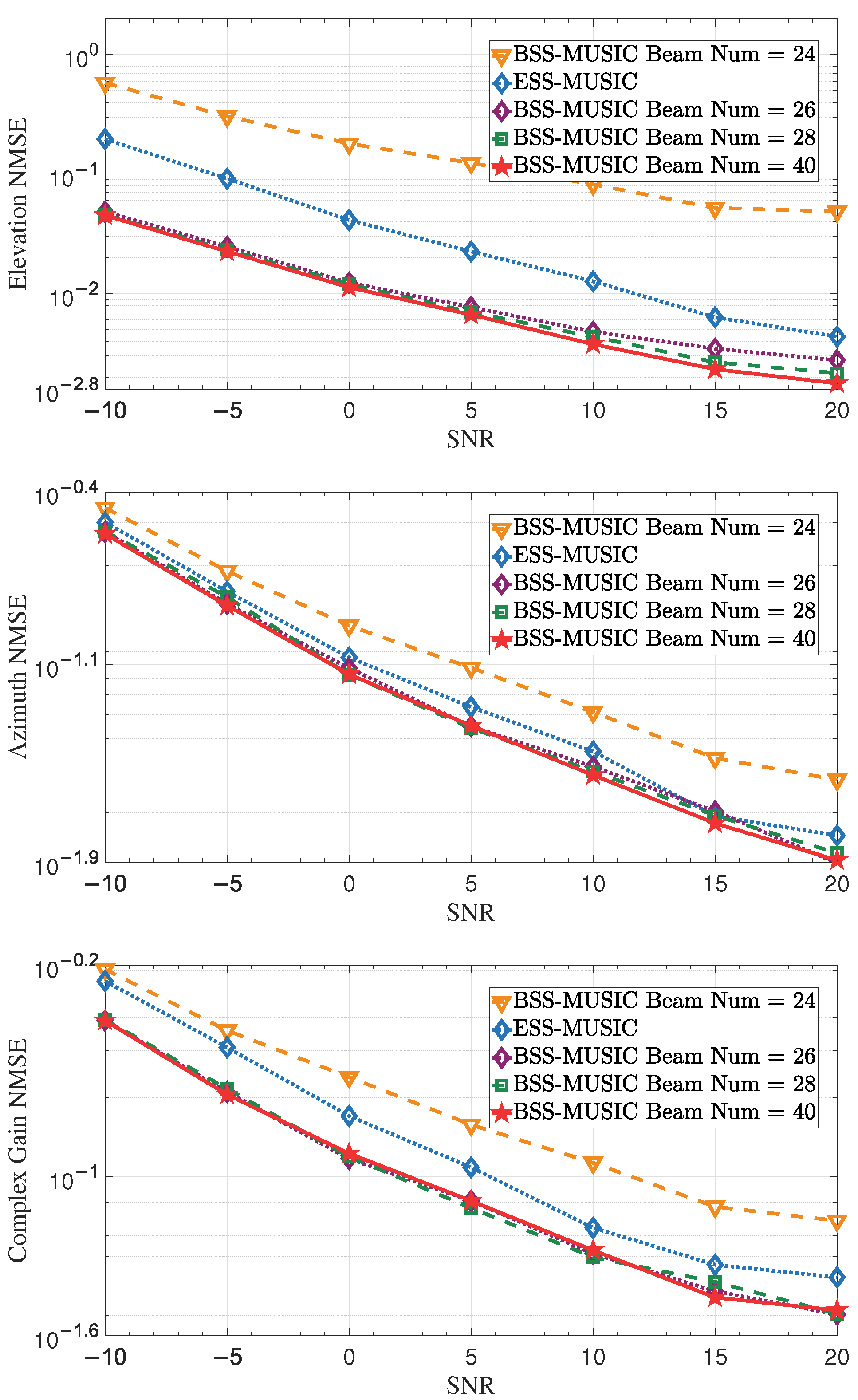
4.4. Effect of Beam Number
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2D | Two-dimensional |
| BSS-MUSIC | Beamspace spatial smoothing multiple signal classification |
| CS | Compressed sensing |
| DMA | Dynamic metasurface antenna |
| DOA | Direction-of-arrival |
| DOF | Degrees of freedom |
| ESS | Element-space spatial smoothing |
| ESPRIT | Estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques |
| FBSS | Forward/backward spatial smoothing |
| FSS | Forward spatial smoothing |
| IQML | Iterative quadratic maximum likelihood |
| ML | Maximum likelihood |
| MODE | Method of direction estimation |
| NMSE | Normalized mean squared error |
| OMP | Orthogonal matching pursuit |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio |
| SS | Spatial smoothing |
| URA | Uniform rectangular arrays |
| WSF | Weighted subspace fitting |
References
- Wang, S.; Nie, K.; He, M.; He, Y. DOA Estimation Aided by Magnitude Measurements. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 12197–12202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, B.; Elnahas, O.; Quan, Z. Efficient DOA Estimation Under Partially Impaired Antenna Array Elements. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 7991–7996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Hou, Y.T.; Lou, W. A Real-Time Super-Resolution DoA Estimation Algorithm for Automotive Radar Sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 37947–37961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, L.T.; Meng, D.; Dong, M.; Ota, K.; Wang, H. Multi-UAV Cooperative Localization for Marine Targets Based on Weighted Subspace Fitting in SAGIN Environment. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 5708–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Ye, W. Hardware–Algorithm Codesigned Low-Latency and Resource-Efficient OMP Accelerator for DOA Estimation on FPGA. IEEE Trans. VLSI Syst. 2024, 33, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Stoica, P.; Liu, Z.S. Comparative Study of IQML and MODE Direction-of-Arrival Estimators. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1998, 46, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkofer, J.P.; Revach, G.; Shlezinger, N.; Routtenberg, T.; Sloun, R.J.G.v. DA-MUSIC: Data-Driven DoA Estimation via Deep Augmented MUSIC Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 2771–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wen, F.; Liu, J.; Wan, Q. DOA Estimation Under the Existence of Multiple Groups of Coherent Signals with ULA. Electron. Lett. 2017, 53, 562–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V, D.; Balamurugan, K.S.; Villagómez-Galindo, M.; Khandare, A.; Patil, M.; Jaganathan, A. Optimizing Sensor Array DOA Estimation With the Manifold Reconstruction Unitary ESPRIT Algorithm. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2023, 7, 7006804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Zhang, D. Research on DOA Estimation Based on Spatial Smoothing Algorithm and Optimal Smoothing Times. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Data Science and Computer Application, Dalian, China, 29–31 October 2021; pp. 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, X.; Huang, X.; Yang, Y. Direction-of-Arrival Estimation for Coherent Signals Exploiting Moving Coprime Array. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2023, 30, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Sun, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Jin, B. Simplified Spatial Smoothing for DOA Estimation of Coherent Signals. IEEE Trans. Circuits Sys. II-Express Briefs 2023, 70, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, G.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, S. Velocity-Independent 1-D DOA Estimation Method Using Double Parallel Linear Arrays. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2023, 7, 7001004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh-Hoang, M.; Viberg, M.; Pesavento, M. Partial Relaxation Approach: An Eigenvalue-Based DOA Estimator Framework. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 6190–6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Ma, X.; Zhang, R.; Han, Y.; Sheng, W. A Dual-Resolution Unitary ESPRIT Method for DOA Estimation Based on Sparse Co-Prime MIMO Radar. Signal Process. 2023, 202, 108753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wen, X.; QiU, X. A 2D Spatial Smoothing MUSIC Superresolution FMCW SAR Imaging Algorithm1. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 5071–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishin, I.; Fokin, G.; Sevidov, V.; Okuneva, D. Analysis of the Spatial Smoothing Influence on the Perfomance of 2D-MUSIC for Ultra-Dense Networks. In Proceedings of the 2023 Wave Electronics and its Application in Information and Telecommunication Systems (WECONF), St. Petersburg, Russia, 29 May–2 June 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Lee, L.C.; Yang, S.J.; Chen, J.T. A Tree Structure One-Dimensional Based Algorithm for Estimating the Two-Dimensional Direction of Arrivals and Its Performance Analysis. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2008, 56, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertan, A.E.; Ali, M. Spatial and Temporal Smoothing for Covariance Estimation in Super-Resolution Angle Estimation in Automotive Radars. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 8629–8633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, P. A 2-D DOA Estimation Method With Reduced Complexity in Unfolded Coprime L-shaped Array. IEEE Syst. J. 2021, 15, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Wang, W.; Huang, Z.; Huang, P. High-Resolution Angle-of-Arrival and Channel Estimation for mmWave Massive MIMO Systems With Lens Antenna Array. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 12963–12973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.Y.; Wang, X.D.; Zeng, X.Y. Unambiguous Direction-of-Arrival Estimation for Improved Scanning Efficiency in Subarray-Based Hybrid Array. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 7966–7979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.Y.; Wang, W.Z.; Wang, X.D.; Zeng, X.Y. Hardware-Efficient Beamspace Direction-of-Arrival Estimator for Unequal-Sized Subarrays. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express 2022, 69, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C.; Vaidyanathan, P.P. Convolutional Beamspace for Linear Arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2020, 68, 5395–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C.; Vaidyanathan, P.P. Channel Estimation for mmWave Using the Convolutional Beamspace Approach. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2024, 72, 2921–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Huang, K.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, F. An Optimal RIS Design Strategy for Jointly Improving Key Rate and Communication Performance in Quasi-Static Environments. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2023, 12, 1618–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, P.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. A RIS-Based Vehicle DOA Estimation Method With Integrated Sensing and Communication System. IEEE Trans. Int. Trans. Syst. 2024, 25, 5554–5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, P.; Guo, Z.; Ni, D. Low-Cost Beamforming and DOA Estimation Based on One-Bit Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2022, 29, 2397–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Fang, J.; Duan, H.; Li, H. Compressed Channel Estimation for Intelligent Reflecting Surface-Assisted Millimeter Wave Systems. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2020, 27, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liang, Y.C.; Cheng, H.V.; Yu, W. Channel Estimation for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Aided Multi-User mmWave MIMO Systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023, 22, 6853–6869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhang, S. MUSIC Algorithm for IRS-Assisted AOA Estimation. In Proceedings of the VTC2023-Fall, Hong Kong, China, 10–13 October 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlezinger, N.; Alexandropoulos, G.C.; Imani, M.F.; Eldar, Y.C.; Smith, D.R. Dynamic Metasurface Antennas for 6G Extreme Massive MIMO Communications. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2021, 28, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlezinger, N.; Dicker, O.; Eldar, Y.C.; Yoo, I.; Imani, M.F.; Smith, D.R. Dynamic Metasurface Antennas for Uplink Massive MIMO Systems. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2019, 67, 6829–6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shlezinger, N.; Guidi, F.; Dardari, D.; Imani, M.F.; Eldar, Y.C. Beam Focusing for Multi-User MIMO Communications with Dynamic Metasurface Antennas. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 4780–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Lou, Y.; Xu, X.; Yang, J.; Jiang, W.; Huang, K.; Jin, L. Physical-layer Key Generation Based on Multipath Channel Diversity Using Dynamic Metasurface Antennas. China Commun. 2023, 20, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyarsky, M.; Sleasman, T.; Pulido-Mancera, L.; Fromenteze, T.; Pedross-Engel, A.; Watts, C.M.; Imani, M.F.; Reynolds, M.S.; Smith, D.R. Synthetic Aperture Radar with Dynamic Metasurface Antennas: A Conceptual Development. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2017, 34, A22–A36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Jin, L.; Wang, H.; Zhong, Z.; Dai, J. Multi-Stream Signals Separation Based on SPAce-Time-IsOmeric (SPATIO) Array Using Metasurface Antenna. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2024, 67, 122301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Jin, L.; Sun, X.; Xu, X.; Zhong, Z. Multi-Path Separation and Parameter Estimation by Single DMA in Fading Channel. IET Commun. 2022, 16, 1475–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, K.; Xu, X.; Lan, T. Coherent DOA Estimation Using Dynamic Metasurface Antenna Working in Space Isomeric Mode. In Proceedings of the 2022 2nd International Conference on Computer Science, Electronic Information Engineering and Intelligent Control Technology (CEI), Nanjing, China, 23–25 September 2022; pp. 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Sima, B.; Xi, F.; Wu, W.; Liu, Z. Super-Resolution DOA Estimation Using Dynamic Metasurface Antenna. In Proceedings of the 2020 14th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Copenhagen, Denmark, 15–20 March 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beit-On, H.; Shlomo, T.; Rafaely, B. Weighted Frequency Smoothing for Enhanced Speaker Localization. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2023, 31, 2090–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, M.Z.; Mir, T. Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-Aided Wireless Communications: An Overview. Intell. Converg. Netw. 2022, 3, 33–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.C.; Lee, J.H.; Chen, Y.M. Estimating Two-Dimensional Angles of Arrival in Coherent Source Environment. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1989, 37, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R.; Yurduseven, O.; Mancera, L.P.; Bowen, P. Analysis of a Waveguide-Fed Metasurface Antenna. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2017, 8, 054048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, T.L.; Carvalho, E.D. An Optimal Channel Estimation Scheme for Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces Based on a Minimum Variance Unbiased Estimator. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 5000–5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, M.; Adve, R. Channel Estimation for Dynamic Metasurface Antennas. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2024, 23, 5832–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, X.; Heng, W. Millimeter-Wave Channel Estimation Based on 2-D Beamspace MUSIC Method. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2017, 16, 5384–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoltowski, M.D.; Kautz, G.M.; Silverstein, S.D. Beamspace Root-MUSIC. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1993, 41, 344–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, B.; Wang, X. Efficient DOA Estimation Method for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces Aided UAV Swarm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trees, H.L.V. Optimum Array Processing (Part IV of Detection, Estimation, and Modulation Theory); John Wiley and Sons Incorporated: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]



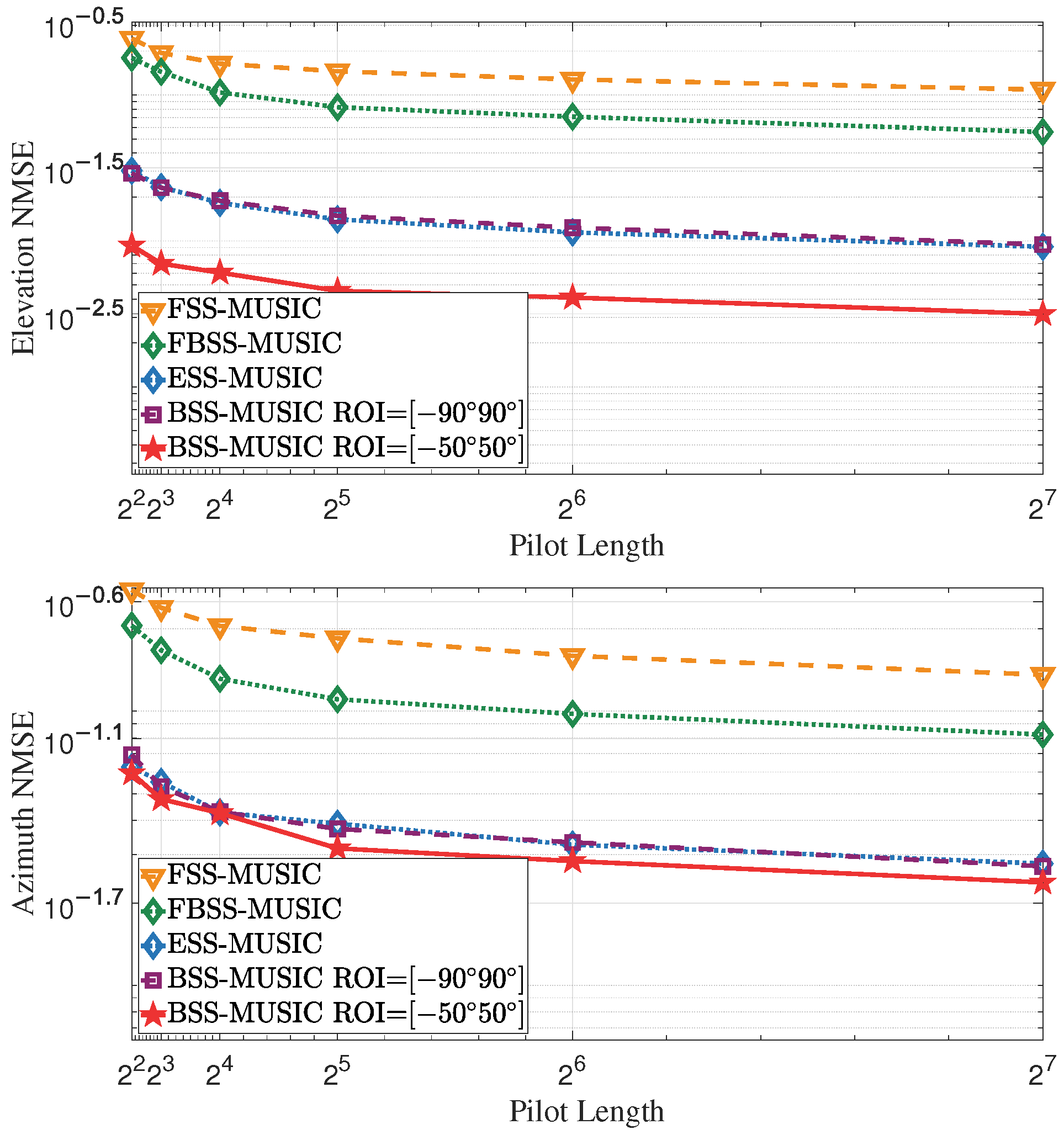
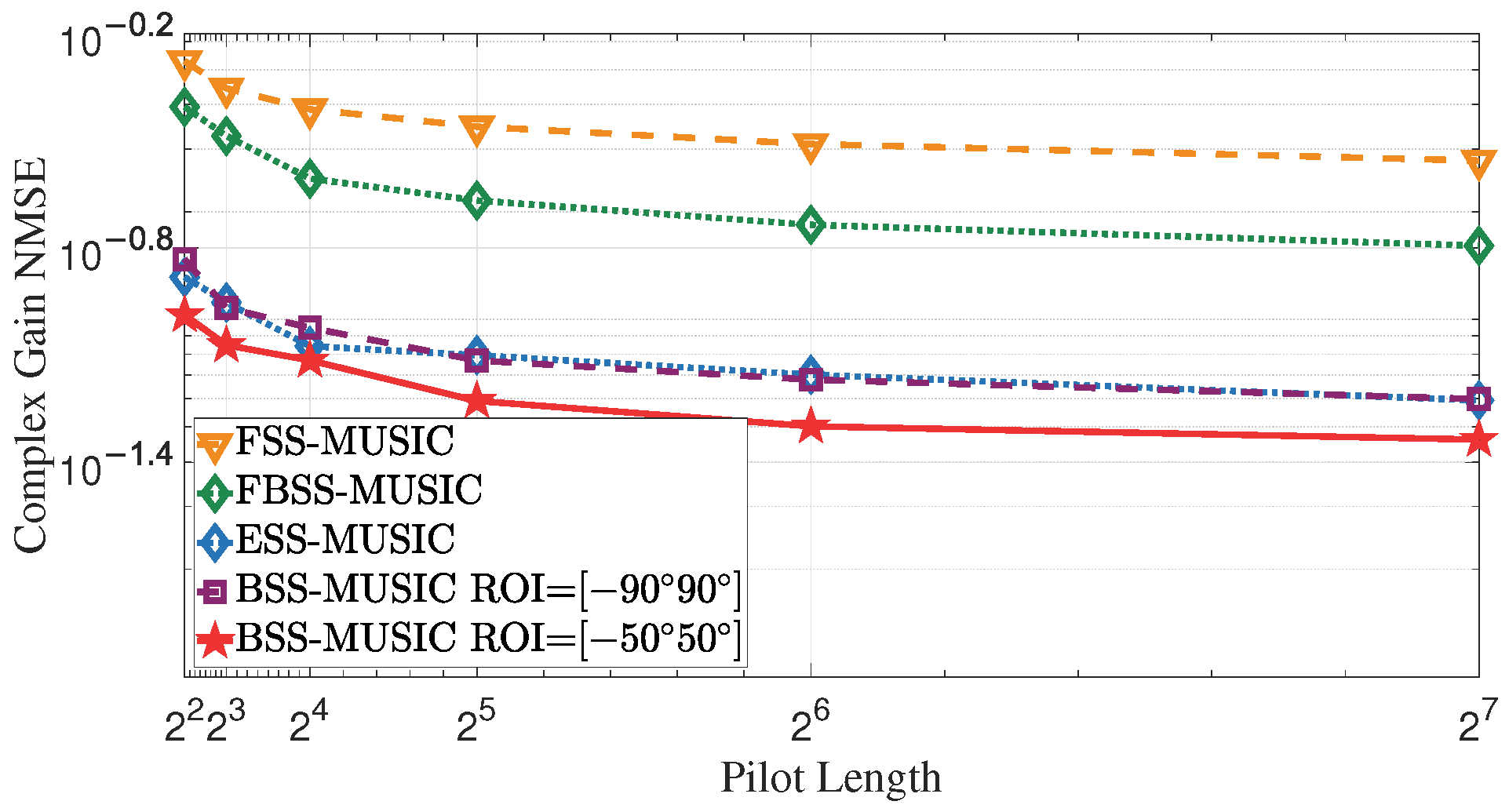
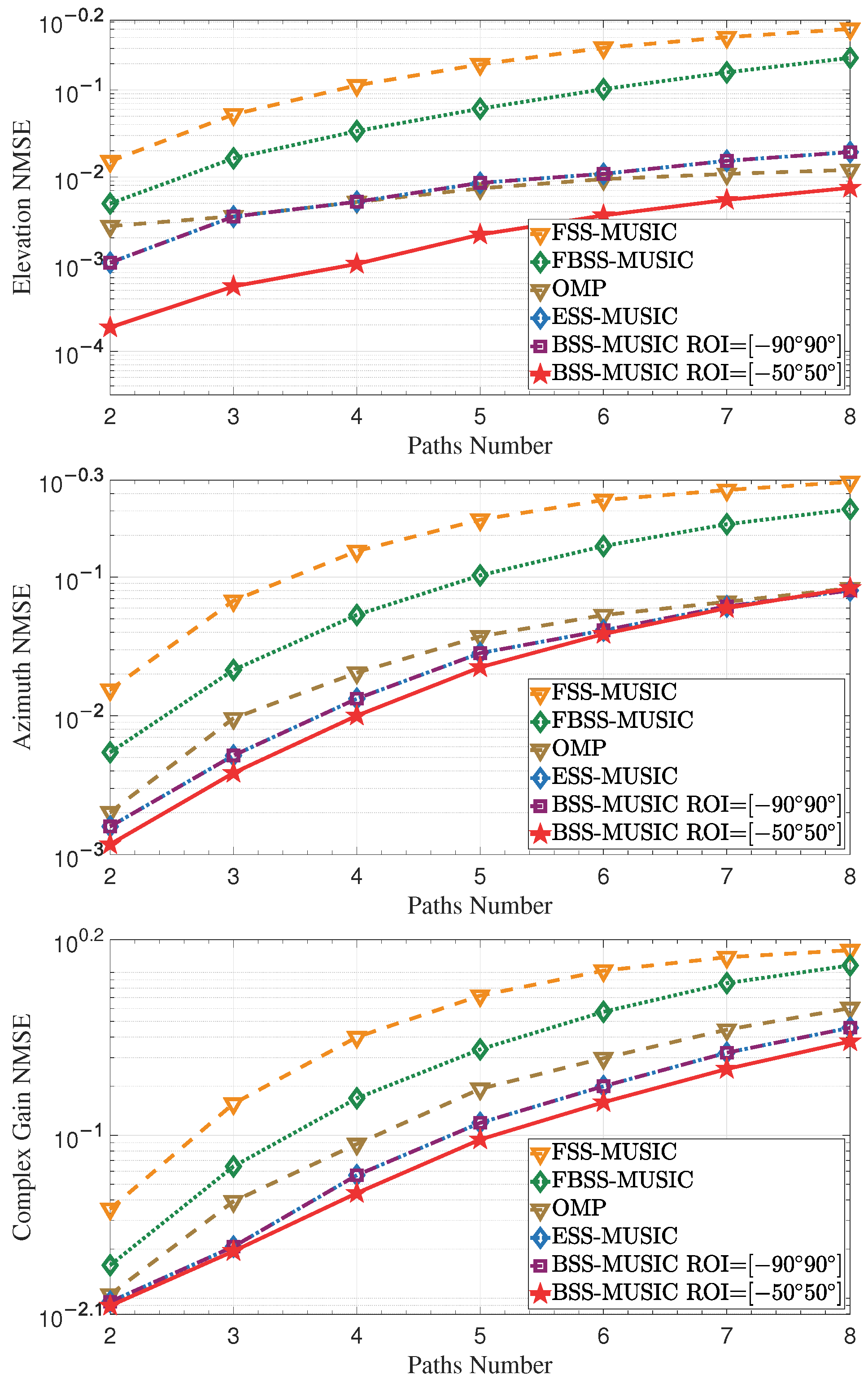

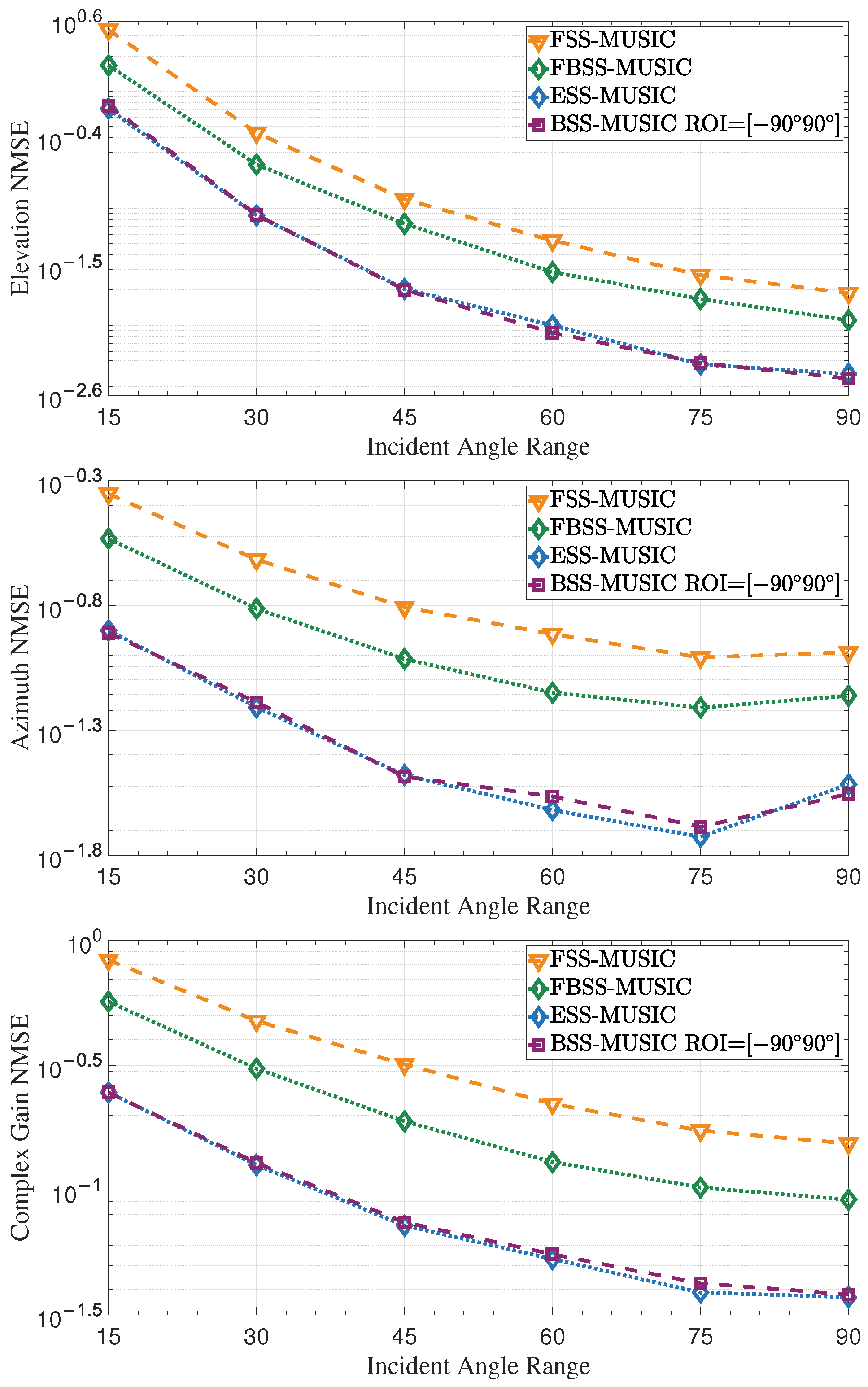
| Parameter Type | Parameter Value |
|---|---|
| Number of Microstrips M | 32 |
| Number of Elements N | 32 |
| Element Spacing | |
| Number of Desired Signal | 3 |
| Number of Snapshots | 32 |
| Elevation Range | |
| Azimuth Range | |
| Monte-Carlo | 10,000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, L.; Jin, L.; Huang, K.; Xiao, S.; Lou, Y.; Chen, Y. Beamspace Spatial Smoothing MUSIC DOA Estimation Method Using Dynamic Metasurface Antenna. Entropy 2025, 27, 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040335
Hou L, Jin L, Huang K, Xiao S, Lou Y, Chen Y. Beamspace Spatial Smoothing MUSIC DOA Estimation Method Using Dynamic Metasurface Antenna. Entropy. 2025; 27(4):335. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040335
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Lilong, Liang Jin, Kaizhi Huang, Shuaifang Xiao, Yangming Lou, and Yajun Chen. 2025. "Beamspace Spatial Smoothing MUSIC DOA Estimation Method Using Dynamic Metasurface Antenna" Entropy 27, no. 4: 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040335
APA StyleHou, L., Jin, L., Huang, K., Xiao, S., Lou, Y., & Chen, Y. (2025). Beamspace Spatial Smoothing MUSIC DOA Estimation Method Using Dynamic Metasurface Antenna. Entropy, 27(4), 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27040335







