Optimal Control of an Electromechanical Energy Harvester
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Energy Harvester Dynamics
3. Global Optimization
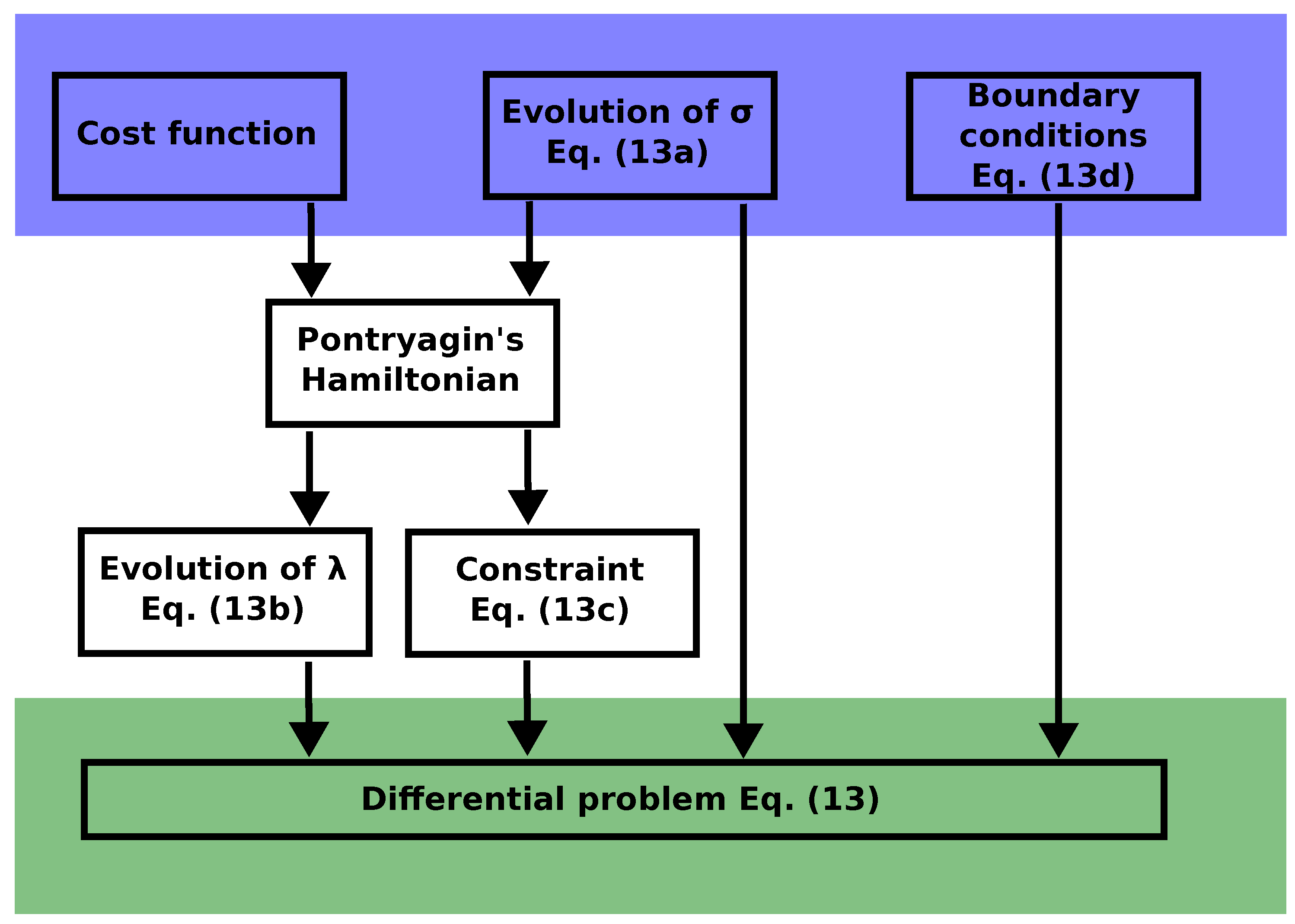
3.1. Pontryagin’s Maximum Principle
3.2. PMP for Affine Dynamics
3.3. Is the Stationary Optimum a Global Optimum?
3.4. A Perturbative Approach to the Solution
4. Results
An Explicit Example: The Case
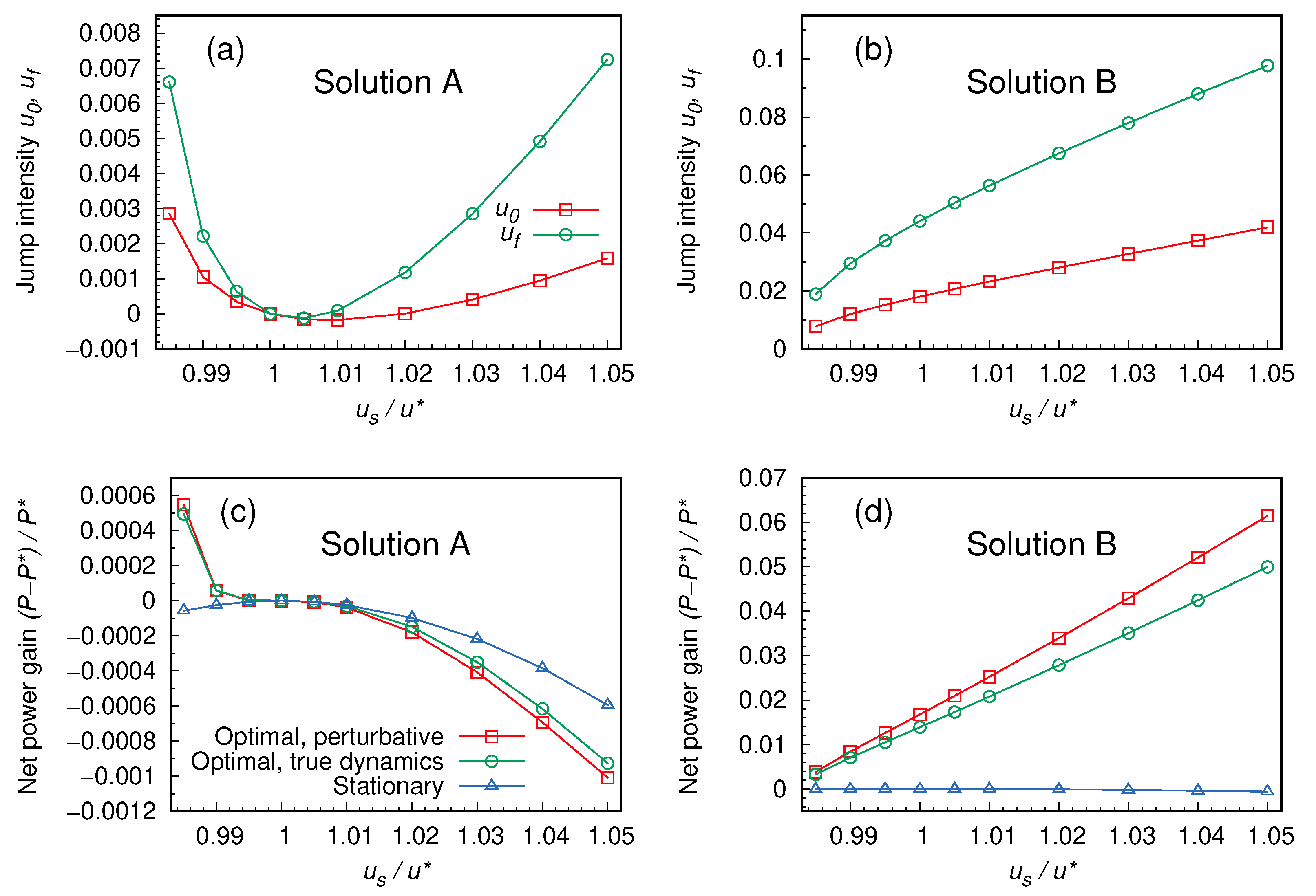
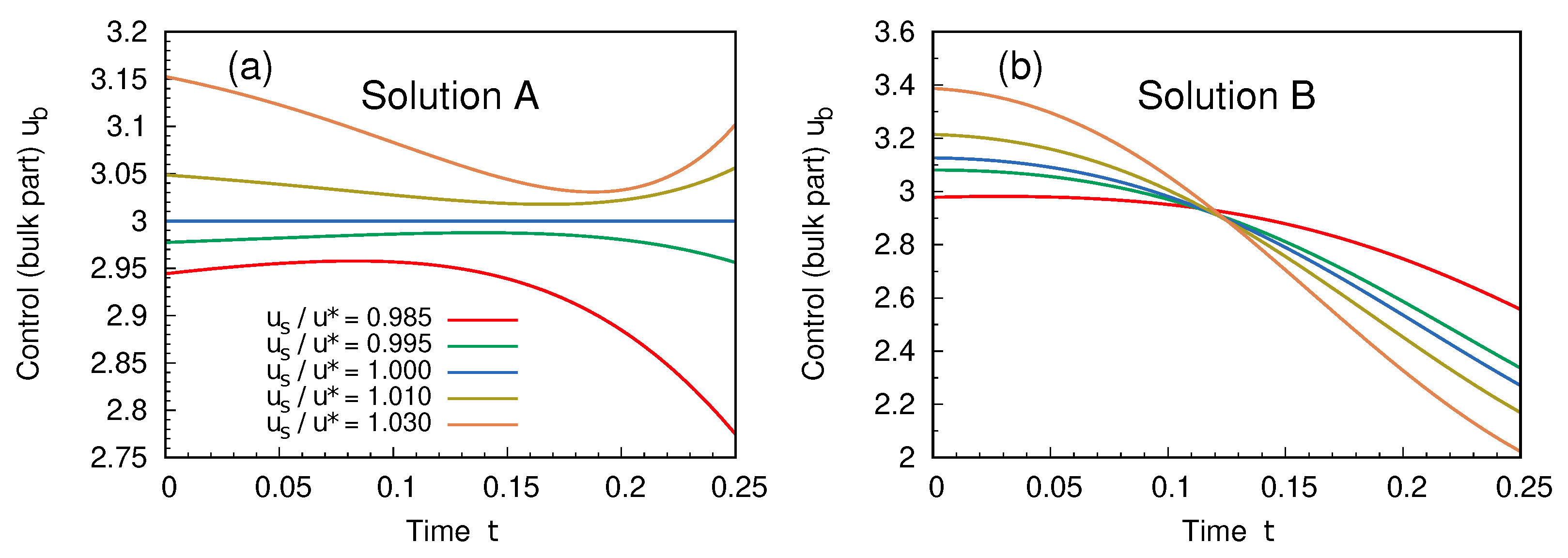
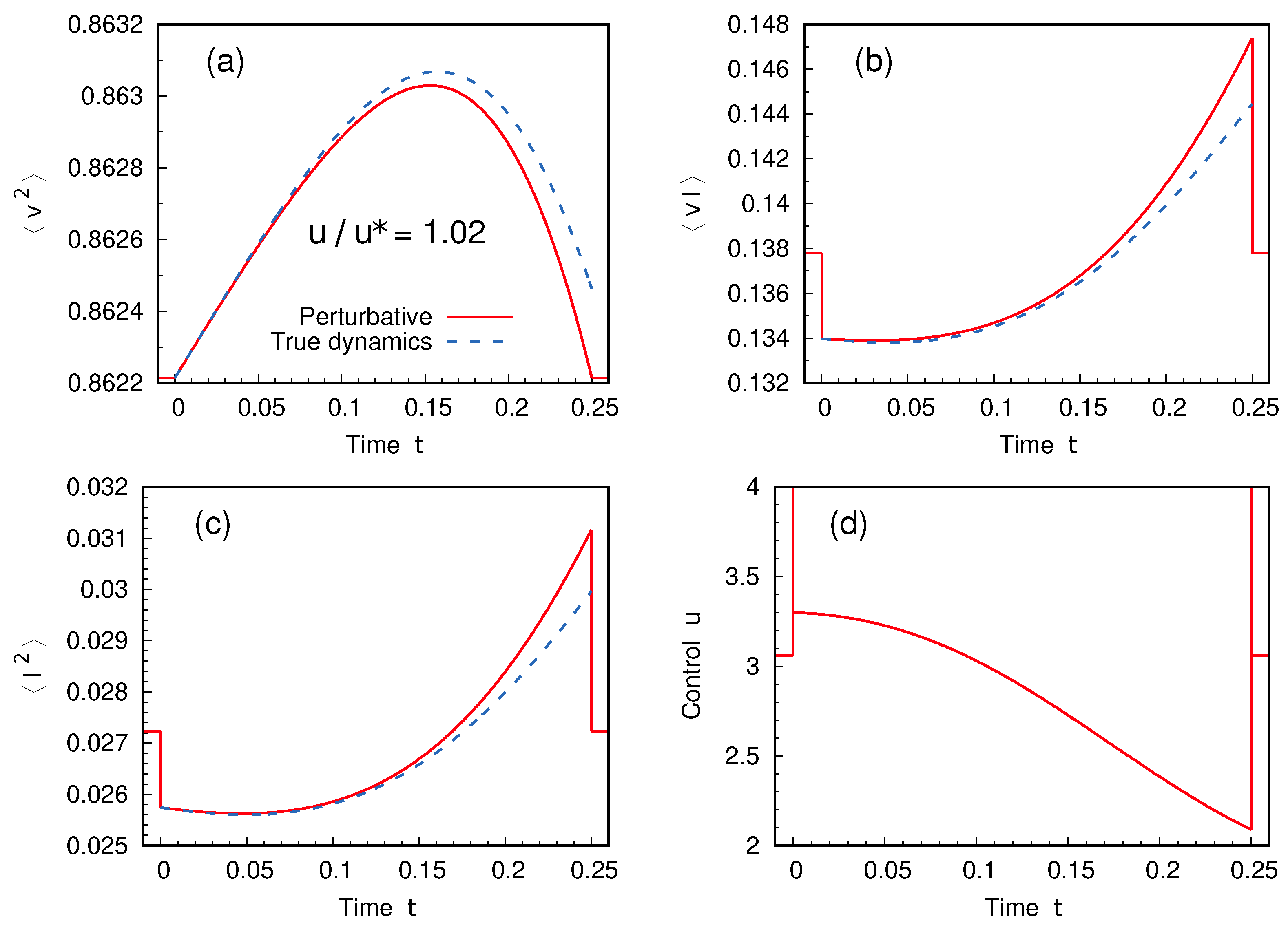
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Energy Harvester Model in Dimensionless Units
- Mass ;
- Time ;
- Length ;
- Current intensity .
| M (kg) | (kg/s) | (N/m) | (N/A) | (H) | () |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.048(5) | 1.80(5) | 18,810(50) | 29.9(5) | 0.124(5) | 227.6(5) |
| 2.67 × 10−2 | 1.60 × 10−3 | 2.58 × 10−3 | 5.44 × 10−4 | 3.22 | 9.66 × 10−2 | 4.74 |
Appendix B. Discontinuous Protocol: Boundary Conditions and Power Extraction
References
- Bellman, R.; Kalaba, R. A mathematical theory of adaptive control processes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1959, 45, 1288–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontryagin, L.S.; Boltyanskii, V.G.; Gamkrelidze, R.V.; Mishchenko, E.F. The Mathematical Theory of Optimal Processes; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Kirk, D.E. Optimal Control Theory: An Introduction; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Guéry-Odelin, D.; Ruschhaupt, A.; Kiely, A.; Torrontegui, E.; Martínez-Garaot, S.; Muga, J.G. Shortcuts to adiabaticity: Concepts, methods, and applications. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2019, 91, 045001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guéry-Odelin, D.; Jarzynski, C.; Plata, C.A.; Prados, A.; Trizac, E. Driving rapidly while remaining in control: Classical shortcuts from Hamiltonian to stochastic dynamics. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2023, 86, 035902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaber, S.; Sivak, D.A. Optimal control in stochastic thermodynamics. J. Phys. Commun. 2023, 7, 033001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmiedl, T.; Seifert, U. Optimal Finite-Time Processes In Stochastic Thermodynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 108301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, I.A.; Petrosyan, A.; Guéry-Odelin, D.; Trizac, E.; Ciliberto, S. Engineered swift equilibration of a Brownian particle. Nat. Phys. 2016, 12, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrón, A.; Prados, A.; Plata, C.A. Thermal brachistochrone for harmonically confined Brownian particles. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2022, 137, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Marin, A.; Schmiedl, T.; Seifert, U. Optimal protocols for minimal work processes in underdamped stochastic thermodynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 129, 024114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratore-Ginanneschi, P. On extremals of the entropy production by ‘Langevin–Kramers’ dynamics. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2014, 2014, P05013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratore-Ginanneschi, P.; Schwieger, K. How nanomechanical systems can minimize dissipation. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 90, 060102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldovin, M.; Yedder, I.B.; Plata, C.A.; Raynal, D.; Rondin, L.; Trizac, E.; Prados, A. Optimal control of levitated nanoparticles through finite-stiffness confinement. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.00043. [Google Scholar]
- Plata, C.A.; Prados, A.; Trizac, E.; Guéry-Odelin, D. Taming the Time Evolution in Overdamped Systems: Shortcuts Elaborated from Fast-Forward and Time-Reversed Protocols. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 127, 190605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, J.; Baldovin, M.; Muratore-Ginanneschi, P. Optimal control of underdamped systems: An analytic approach. J. Stat. Phys. 2024, 191, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, J.; Baldovin, M.; Muratore-Ginanneschi, P. Minimal-work protocols for inertial particles in non-harmonic traps. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.15678. [Google Scholar]
- Baldassarri, A.; Puglisi, A.; Sesta, L. Engineered swift equilibration of a Brownian gyrator. Phys. Rev. E 2020, 102, 030105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos, S.A.; Monter, S.; Ginot, F.; Bechinger, C. Universal symmetry of optimal control at the microscale. Phys. Rev. X 2024, 14, 021032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruyne, B.; Mori, F. Resetting in stochastic optimal control. Phys. Rev. Res. 2023, 5, 013122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goerlich, R.; Keidar, T.D.; Roichman, Y. Resetting as a swift equilibration protocol in an anharmonic potential. Phys. Rev. Res. 2024, 6, 033162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Raju, V.; Mahadevan, L. Optimal transport and control of active drops. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2121985119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldovin, M.; Guéry-Odelin, D.; Trizac, E. Control of Active Brownian Particles: An Exact Solution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2023, 131, 118302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, L.K.; Proesmans, K.; Fodor, E. Active Matter under Control: Insights from Response Theory. Phys. Rev. X 2024, 14, 011012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Millan, R.; Schüttler, J.; Cates, M.E.; Loos, S.A. Optimal closed-loop control of active particles and a minimal information engine. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.18542. [Google Scholar]
- Prados, A. Optimizing the relaxation route with optimal control. Phys. Rev. Res. 2021, 3, 023128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Pino, N.; Prados, A. Optimal control of uniformly heated granular fluids in linear response. Entropy 2022, 24, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plati, A.; Petri, A.; Baldovin, M. Control of friction: Shortcuts and optimization for the rate- and state-variable equation. Eur. J. Mech.—A/Solids 2025, 111, 105550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Kaur, R.; Singh, D. Energy harvesting in wireless sensor networks: A taxonomic survey. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 118–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halvorsen, E. Energy harvesters driven by broadband random vibrations. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2008, 17, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, L.; Lo Schiavo, A.; Sarracino, A.; Vitelli, M. Stochastic thermodynamics of a piezoelectric energy harvester model. Entropy 2021, 23, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, L.; Baldassarri, A.; Lo Schiavo, A.; Sarracino, A.; Vitelli, M. Inference of Time-Reversal Asymmetry from Time Series in a Piezoelectric Energy Harvester. Symmetry 2023, 16, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanfelice, A.; Costanzo, L.; Lo Schiavo, A.; Sarracino, A.; Vitelli, M. Stochastic Model for a Piezoelectric Energy Harvester Driven by Broadband Vibrations. Entropy 2024, 26, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, L.; Lo Schiavo, A.; Sarracino, A.; Vitelli, M. Stochastic Thermodynamics of an Electromagnetic Energy Harvester. Entropy 2022, 24, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clementi, G.; Cottone, F.; Di Michele, A.; Gammaitoni, L.; Mattarelli, M.; Perna, G.; López-Suárez, M.; Baglio, S.; Trigona, C.; Neri, I. Review on innovative piezoelectric materials for mechanical energy harvesting. Energies 2022, 15, 6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, H. Unify energy harvesting and vibration control functions in randomly excited structures with electromagnetic devices. J. Eng. Mech. 2019, 145, 04018115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astumian, R.D.; Bier, M. Fluctuation driven ratchets: Molecular motors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 72, 1766–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, P.; Hänggi, P. Introduction to the physics of Brownian motors. Appl. Phys. A 2002, 75, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnoli, A.; Petri, A.; Dalton, F.; Pontuale, G.; Gradenigo, G.; Sarracino, A.; Puglisi, A. Brownian Ratchet in a Thermal Bath Driven by Coulomb Friction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 120601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manacorda, A.; Puglisi, A.; Sarracino, A. Coulomb Friction Driving Brownian Motors. Commun. Theor. Phys. 2014, 62, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tarlie, M.B.; Astumian, R.D. Optimal modulation of a Brownian ratchet and enhanced sensitivity to a weak external force. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2039–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.J.; Dinis, L.; Parrondo, J.M.R. Feedback Control in a Collective Flashing Ratchet. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 040603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkowski, P.R.; DeWeese, M.R. Optimal control of overdamped systems. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 92, 032117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammaitoni, L.; Vocca, H.; Neri, I.; Travasso, F.; Orfei, F. Vibration energy harvesting: Linear and nonlinear oscillator approaches. In Sustainable Energy Harvesting Technologies-Past, Present and Future; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; pp. 171–190. [Google Scholar]
- Cottone, F.; Vocca, H.; Gammaitoni, L. Nonlinear energy harvesting. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 080601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Jin, Y. Stochastic optimal control of a tri-stable energy harvester with the P-SSHI circuit under colored noise. Eur. Phys. J. B 2024, 97, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Jin, Y. Stochastic optimal control of a coupled tri-stable energy harvester under correlated colored noises. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 6993–7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.M.; El-Borai, M.M.; El-Sayed, W.; Elbadrawi, A. Null Controllability of Hilfer Fractional Stochastic Differential Inclusions. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.M.; El-Borai, M.M.; El-Sayed, W.G.; Elbadrawi, A.Y. Fractional Stochastic Evolution Inclusions with Control on the Boundary. Symmetry 2023, 15, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberzon, D. Calculus of Variations and Optimal Control Theory: A Concise Introduction; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner, C. Stochastic Methods; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Muratore-Ginanneschi, P.; Schwieger, K. An application of Pontryagin’s principle to Brownian particle engineered equilibration. Entropy 2017, 19, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frobenius, F. Ueber lineare Substitutionen und bilineare Formen. J. Reine Angew. Math. (Crelles J.) 1878, 1878, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, S. Linear Algebra; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Brenes, A.; Morel, A.; Juillard, J.; Lefeuvre, E.; Badel, A. Maximum power point of piezoelectric energy harvesters: A review of optimality condition for electrical tuning. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 033001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellman, R. Dynamic programming and stochastic control processes. Inf. Control 1958, 1, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lucente, D.; Manacorda, A.; Plati, A.; Sarracino, A.; Baldovin, M. Optimal Control of an Electromechanical Energy Harvester. Entropy 2025, 27, 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27030268
Lucente D, Manacorda A, Plati A, Sarracino A, Baldovin M. Optimal Control of an Electromechanical Energy Harvester. Entropy. 2025; 27(3):268. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27030268
Chicago/Turabian StyleLucente, Dario, Alessandro Manacorda, Andrea Plati, Alessandro Sarracino, and Marco Baldovin. 2025. "Optimal Control of an Electromechanical Energy Harvester" Entropy 27, no. 3: 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27030268
APA StyleLucente, D., Manacorda, A., Plati, A., Sarracino, A., & Baldovin, M. (2025). Optimal Control of an Electromechanical Energy Harvester. Entropy, 27(3), 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27030268







