Postural Control Adaptations in Trampoline Athletes of Different Competitive Levels: Insights from COP Linear and Nonlinear Measures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Data Processing
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zemková, E.; Kováčiková, Z. Sport-specific training induced adaptations in postural control and their relationship with athletic performance. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1007804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Bando, Y.; Fukui, T.; Maruyama, A.; Sugita, M. Straight Jump Landing Position of Trampoline Gymnasts with Stable Occlusal Balance Reflects Standing Postural Control Function. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wu, D.; Wu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Cui, X.; Zhang, P.; Gao, J.; Fu, Y.; Wang, X. A novel classification method for balance differences in elite versus expert athletes based on composite multiscale complexity index and ranking forests. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0315454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.-W.; Kim, T.; Kim, J.I.; Jeong, Y.; Jang, K.-M.; Kim, J.; Do, J.-H. Development and Application of a Stability Index Estimation Algorithm Based on Machine Learning for Elderly Balance Ability Diagnosis in Daily Life. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kędziorek, J.; Błażkiewicz, M. Nonlinear Measures to Evaluate Upright Postural Stability: A Systematic Review. Entropy 2020, 22, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos, L.; Castaldo, R.; Pecchia, L. On the use of approximate entropy and sample entropy with centre of pressure time-series. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2018, 15, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, L.; Badache, M.; Cale, S.; Behera, L.; Zhang, N. Balance Performance as Observed by Center-of-Pressure Parameter Characteristics in Male Soccer Athletes and Non-Athletes. Sports 2017, 5, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzucka, D.; Kręcisz, K.; Rektor, Z.; Kuczyński, M. Differences in static postural control between top level male volleyball players and non-athletes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trajkovic, N.; Smajla, D.; Kozinc, Ž.; Šarabon, N. Postural Stability in Single-Leg Quiet Stance in Highly Trained Athletes: Sex and Sport Differences. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalska, J.; Zając, R.; Szydło, K.; Gerasimuk, D.; Słomka, K.J.; Juras, G. Biathletes present repeating patterns of postural control to maintain their balance while shooting. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbaş, A.; Marszałek, W.; Drozd, S.; Czarny, W.; Król, P.; Warchoł, K.; Słomka, K.J.; Rzepko, M. The effect of expertise on postural control in elite sport ju-jitsu athletes. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 14, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowska-Maszkowska, B.; Borzucka, D.; Rogowska, A. A comparison of the balance skills, personality, and temperament of elite sports athletes and football players. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2020, 20, 3671–3683. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Landero, L.A.; del Ojo, P.L.; Walker, C.; Floría, P. Static balance performance differs depending on the test, age and specific role played in acrobatic gymnastics. Gait Posture 2021, 90, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omorczyk, J.; Staszkiewicz, R.; Wrzesniewski, K.; Puszczalowska-Lizis, E. Static balance in female artistic gymnasts and non-training girls. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, R.; Behm, D.G.; Chtara, M.; Ben Othman, A.; Chaouachi, A. Comparison of static balance and the role of vision in elite athletes. J. Hum. Kinet. 2014, 41, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Goldberger, A.L.; Peng, C.-K. Multiscale entropy analysis of complex physiologic time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 068102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manor, B.; Lipsitz, L.A.; Wayne, P.M.; Peng, C.-K.; Li, L. Complexity-based measures inform tai chi’s impact on standing postural control in older adults with peripheral neuropathy. Bmc Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N. Quantification of Regularity in RR-Interval Time Series Using Approximate Entropy, Sample Entropy, and Multi-Scale Entropy. Master’s Thesis, New Jersey Institute of Technology, Newark, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzato, A.; Benazzato, M.; Cognolato, M.; Grigoletto, D.; Paoli, A.; Marcolin, G. Different neuromuscular control mechanisms regulate static and dynamic balance: A center-of-pressure analysis in young adults. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2023, 90, 103120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzato, A.; Faggian, S.; Paoli, A.; Marcolin, G. Transfer of balance performance depends on the specificity of balance training. J. Appl. Physiol. 2025, 138, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, O.M.; Missen, K.J.; Tokuno, C.D.; Carpenter, M.G.; Adkin, A.L. Postural threat increases sample entropy of postural control. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1179237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofré Lizama, L.E.; He, X.; Kalincik, T.; Galea, M.P.; Panisset, M.G. Sample Entropy Improves Assessment of Postural Control in Early-Stage Multiple Sclerosis. Sensors 2024, 24, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilmes, E.; de Ruiter, C.J.; Beers, L.G.; de Koning, L.; Brink, M.S.; Savelsbergh, G.J. New training load metrics in field hockey using inertial measurement units. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2023, 23, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraiva, M.; Vilas-Boas, J.P.; Castro, M.A. Postural Control and Muscle Activity during Dual-Task in Young Adults. Behav. Sci. 2024, 14, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Zhang, Z.; Bao, J.; Zhu, X.; Tan, Y.; Xia, X.; Zhang, Q.; Hao, Y. Influences of cognitive load on center of pressure trajectory of young male adults with excess weight during gait initiation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 11, 1297068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozzi, S.; Honeine, J.-L.; Do, M.-C.; Schieppati, M. Leg muscle activity during tandem stance and the control of body balance in the frontal plane. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2013, 124, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Martel, V.; Santuz, A.; Ekizos, A.; Arampatzis, A. Neuromuscular organisation and robustness of postural control in the presence of perturbations. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mademli, L.; Mavridi, D.; Bohm, S.; Patikas, D.A.; Santuz, A.; Arampatzis, A. Standing on unstable surface challenges postural control of tracking tasks and modulates neuromuscular adjustments specific to task complexity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, T.; Visser, A.; Havers, T.; Büchel, D.; Baumeister, J. Dynamic modulations of effective brain connectivity associated with postural instability during multi-joint compound movement on compliant surface. Exp. Brain Res. 2025, 243, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.S.B.; Murray, N.G.; Powell, D.W. Athletes who train on unstable compared to stable surfaces exhibit unique postural control strategies in response to balance perturbations. J. Sport Health Sci. 2016, 5, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richman, J.S.; Randall, M.J. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, H2039–H2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhang, F.; Lewis, K.; Song, Q.; Li, L. The Impact of Hoffmann Reflex on Standing Postural Control Complexity in the Elderly with Impaired Plantar Sensation. Entropy 2023, 25, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical power Analysis for the Behavioral sciences. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1989, 14, 499–500. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, K.J.; Zaback, M.; Tokuno, C.D.; Carpenter, M.G.; Adkin, A.L. Exploring the relationship between threat-related changes in anxiety, attention focus, and postural control. Psychol. Res. 2019, 83, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, T.; Fisher, B.E.; Hortobágyi, T.; Salem, G.J. Increasing mediolateral standing sway is associated with increasing corticospinal excitability, and decreasing M1 inhibition and facilitation. Gait Posture 2018, 60, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, M.; Paszkiel, S.; Vilas-Boas, J.P.; Castro, M.A. Influence of Cognitive Task Difficulty in Postural Control and Hemodynamic Response in the Prefrontal Cortex during Static Postural Standing. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholewicki, J.; Polzhofer, G.; Radebold, A. Postural control of trunk during unstable sitting. J. Biomech. 2000, 33, 1733–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, A.M. Analysis of postural sway using entropy measures of signal complexity. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2000, 38, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanaugh, J.T.; Mercer, V.S.; Stergiou, N. Approximate entropy detects the effect of a secondary cognitive task on postural control in healthy young adults: A methodological report. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2007, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donker, S.F.; Roerdink, M.; Greven, A.J.; Beek, P.J. Regularity of center-of-pressure trajectories depends on the amount of attention invested in postural control. Exp. Brain Res. 2007, 181, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.; Wei, Q.; Shieh, J.-S.; Fourcade, P.; Isableu, B.; Majed, L. Sample entropy, univariate, and multivariate multi-scale entropy in comparison with classical postural sway parameters in young healthy adults. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busa, M.A.; van Emmerik, R.E.A. Multiscale entropy: A tool for understanding the complexity of postural control. J. Sport Health Sci. 2016, 5, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, S.; Sepehri, N.; Wu, C.; Szturm, T. Sample entropy of human gait center of pressure displacement: A systematic methodological analysis. Entropy 2018, 20, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.; Zhou, M.; Mao, M.; Yang, J. The static balance ability on soft and hard support surfaces in older adults with mild cognitive impairment. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0295569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubetzky, A.V.; Harel, D.; Lubetzky, E. On the effects of signal processing on sample entropy for postural control. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
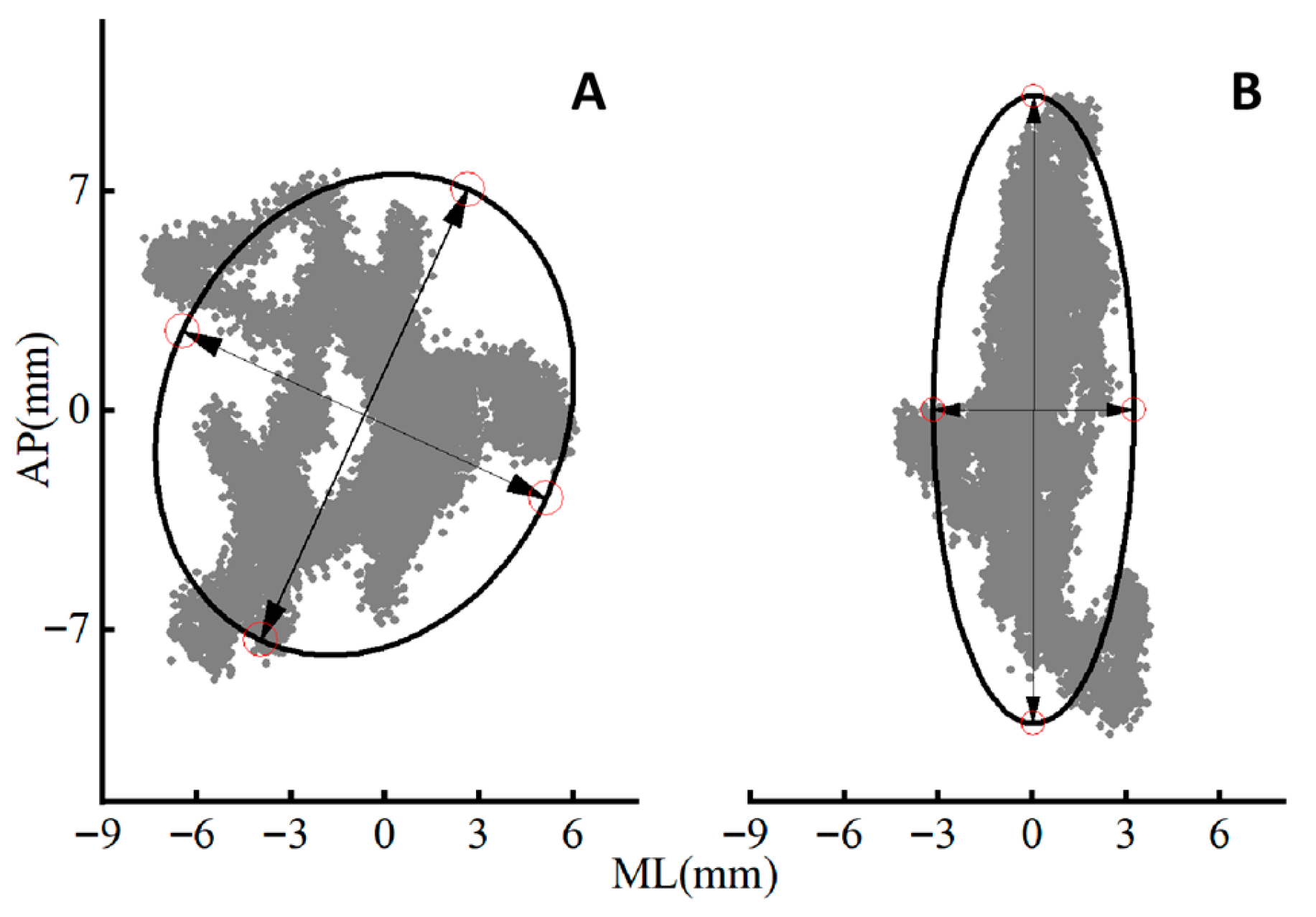
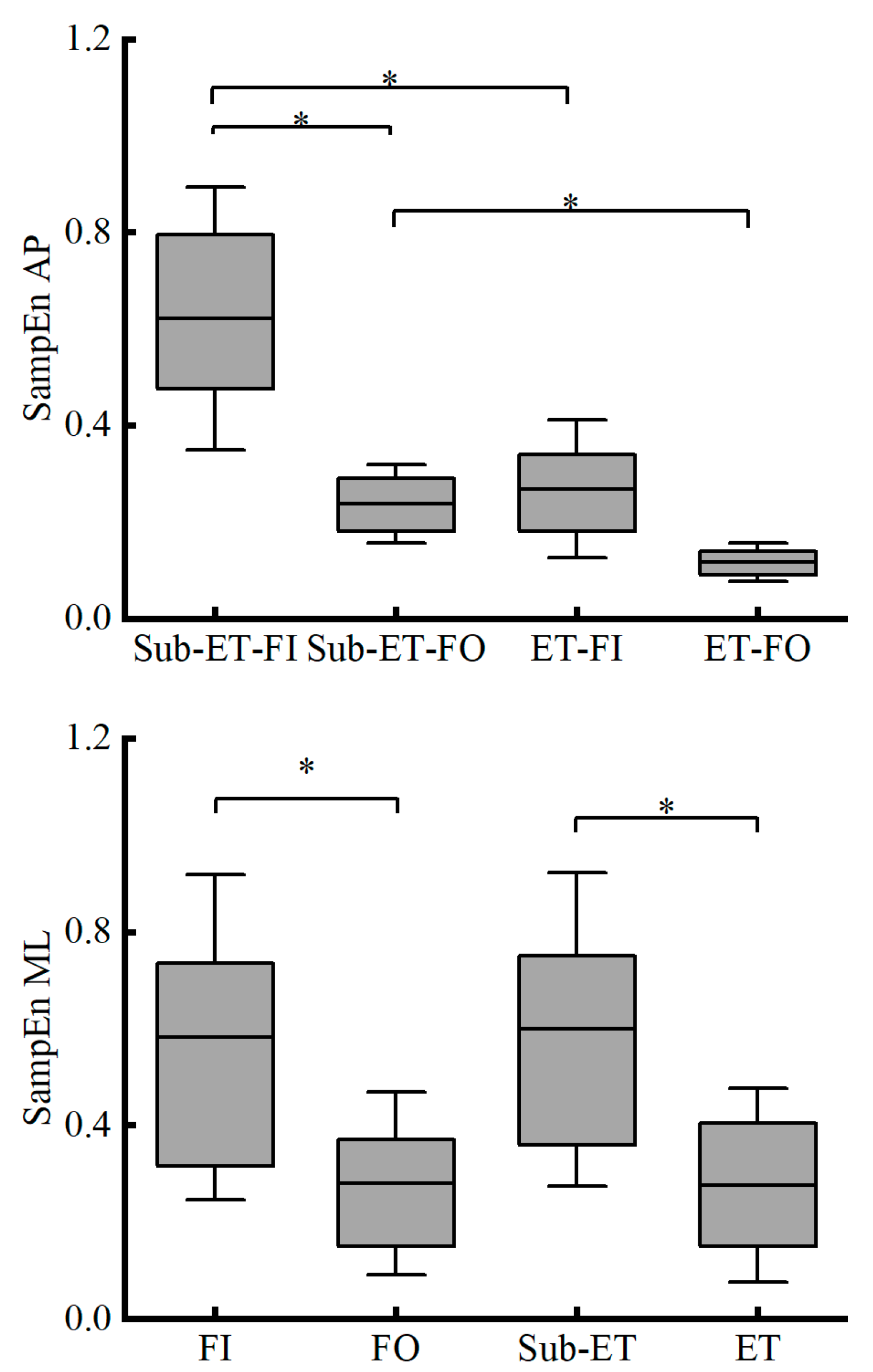
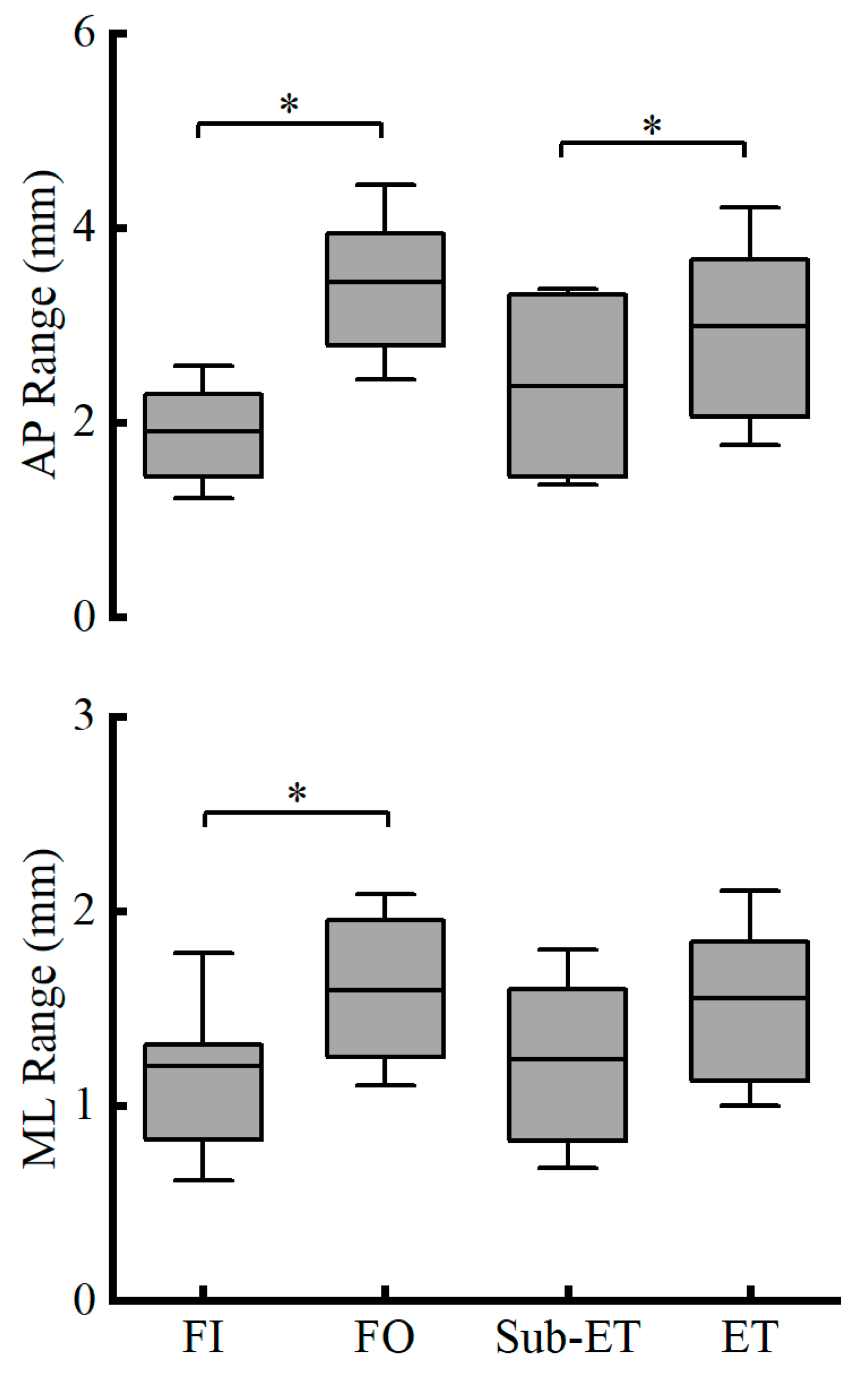
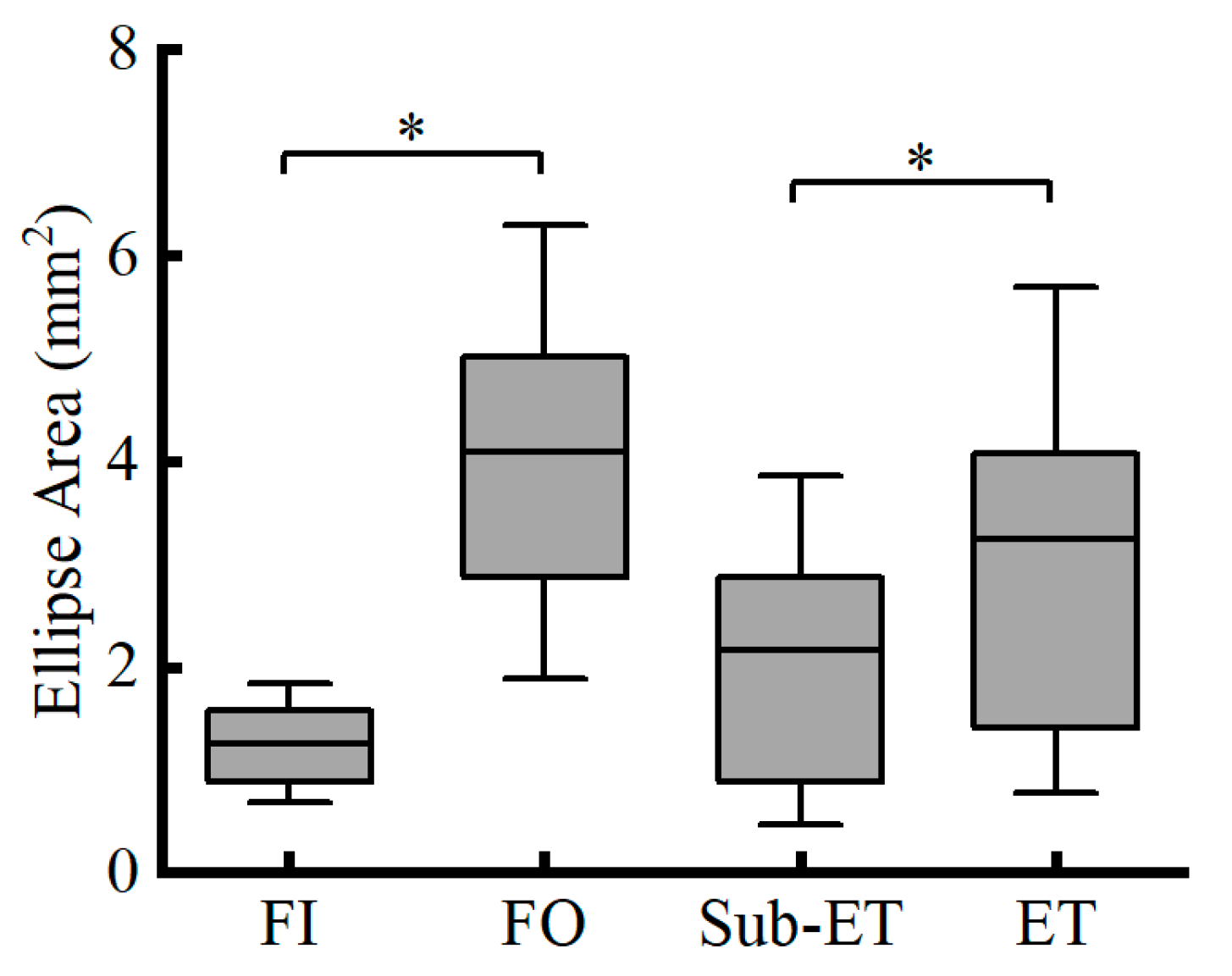
| COP Parameters | Group | FI | FO | F Value | Competitive Level | Surface Condition | Competitive Level * Surface Condition | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | Partial η2 | p | Partial η2 | p | Partial η2 | |||||
| SampEn-ML | Sub-ET | 0.73 ± 0.27 | 0.40 ± 0.20 | F1,21 = 1.848 | 0.001 * | 0.419 | <0.001 * | 0.650 | 0.188 | 0.081 |
| ET | 0.38 ± 0.23 | 0.17 ± 0.08 | ||||||||
| SampEn-AP | Sub-ET | 0.62 ± 0.27 | 0.24 ± 0.08 | F1,21 = 6.304 | - | - | - | - | 0.010 * | 0.277 |
| ET | 0.24 ± 0.11 | 0.12 ± 0.04 | ||||||||
| ML Range (mm) | Sub-ET | 0.99 ± 0.4 | 1.49 ± 0.59 | F1,20 = 0.034 | 0.240 | 0.068 | <0.001 * | 0.660 | 0.856 | 0.002 |
| ET | 1.17 ± 0.34 | 1.71 ± 0.32 | ||||||||
| AP Range (mm) | Sub-ET | 1.53 ± 0.4 | 3.04 ± 0.69 | F1,21 < 0.001 | 0.007 * | 0.302 | <0.001 * | 0.650 | 0.996 | <0.001 |
| ET | 2.24 ± 0.73 | 3.74 ± 1.16 | ||||||||
| Ellipse Area (mm2) | Sub-ET | 1.01 ± 0.52 | 3.3 ± 1.71 | F1,20 = 2.312 | 0.013 * | 0.271 | <0.001 * | 0.610 | 0.144 | 0.104 |
| ET | 1.72 ± 0.86 | 5.72 ± 3.2 | ||||||||
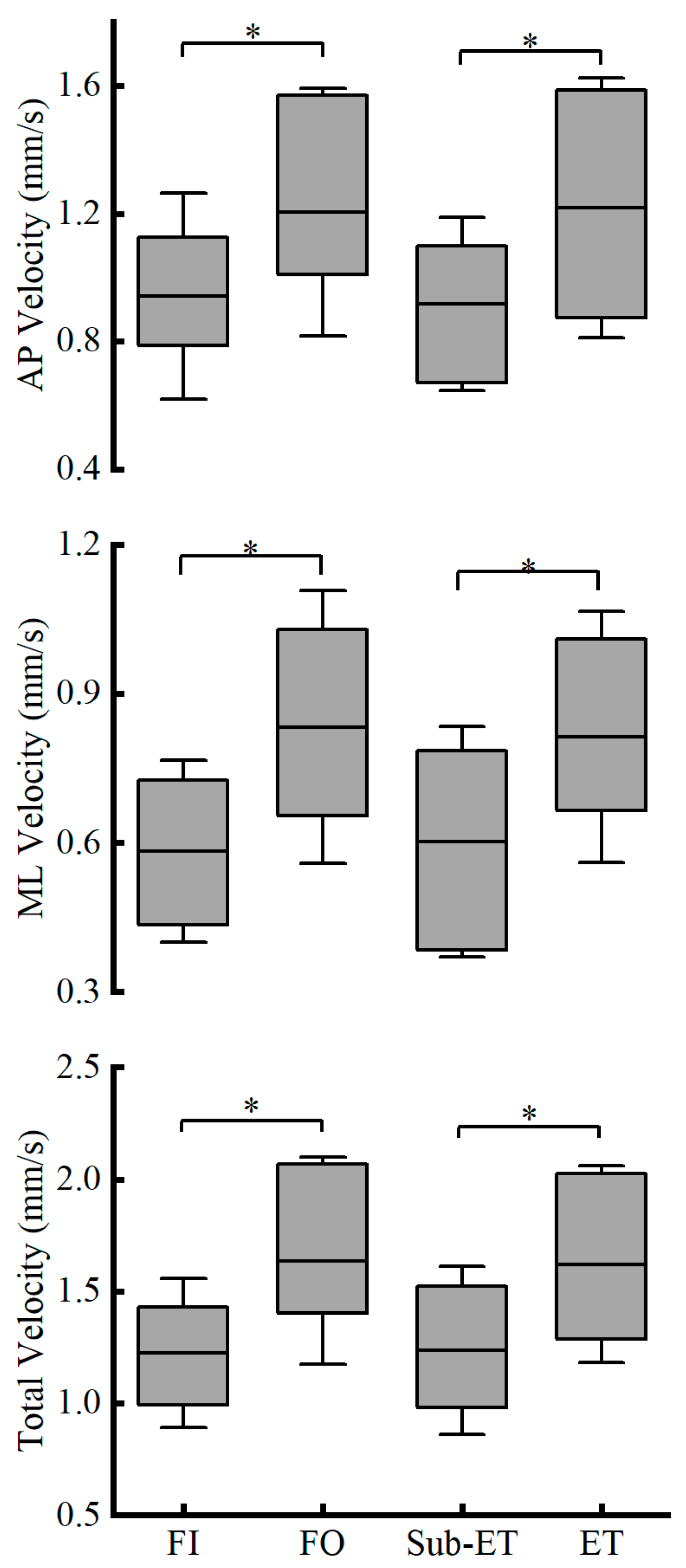
| ML Velocity (mm/s) | Sub-ET | 0.49 ± 0.14 | 0.71 ± 0.26 | F1,22 = 0.598 | 0.010 * | 0.267 | <0.001 * | 0.608 | 0.448 | 0.026 |
| ET | 0.67 ± 0.18 | 0.95 ± 0.24 | ||||||||
| AP Velocity (mm/s) | Sub-ET | 0.84 ± 0.24 | 1.05 ± 0.3 | F1,22 = 0.865 | 0.012 * | 0.255 | 0.001 * | 0.395 | 0.362 | 0.038 |
| ET | 1.04 ± 0.32 | 1.39 ± 0.34 | ||||||||
| Total Velocity (mm/s) | Sub-ET | 1.07 ± 0.26 | 1.4 ± 0.41 | F1,22 = 0.929 | 0.003 * | 0.327 | <0.001 * | 0.512 | 0.345 | 0.041 |
| ET | 1.38 ± 0.33 | 1.87 ± 0.4 | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, M.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, X.; Qu, F.; Mao, W.; Li, L. Postural Control Adaptations in Trampoline Athletes of Different Competitive Levels: Insights from COP Linear and Nonlinear Measures. Entropy 2025, 27, 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27121181
Sun M, Zhang F, Zhou X, Qu F, Mao W, Li L. Postural Control Adaptations in Trampoline Athletes of Different Competitive Levels: Insights from COP Linear and Nonlinear Measures. Entropy. 2025; 27(12):1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27121181
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Mengzi, Fangtong Zhang, Xinglong Zhou, Feng Qu, Wenhui Mao, and Li Li. 2025. "Postural Control Adaptations in Trampoline Athletes of Different Competitive Levels: Insights from COP Linear and Nonlinear Measures" Entropy 27, no. 12: 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27121181
APA StyleSun, M., Zhang, F., Zhou, X., Qu, F., Mao, W., & Li, L. (2025). Postural Control Adaptations in Trampoline Athletes of Different Competitive Levels: Insights from COP Linear and Nonlinear Measures. Entropy, 27(12), 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27121181







