Road Agglomerate Fog Detection Method Based on the Fusion of SURF and Optical Flow Characteristics from UAV Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
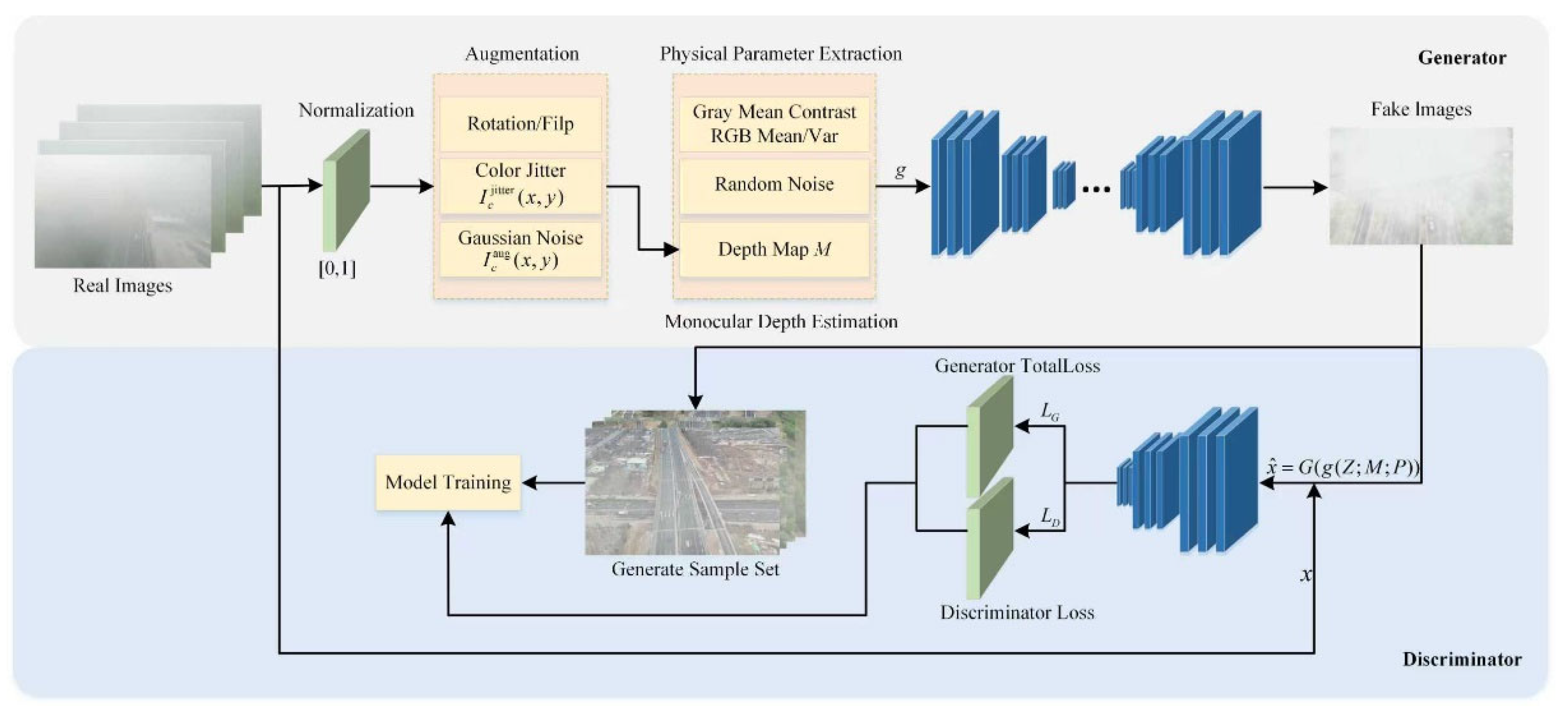
2. Agglomerate Fog Sample Dataset Generation Method Based on GAN
2.1. Generator
2.2. Discriminator
3. Dense Fog Detection Method Based on SURF Feature Extraction and Optical Flow Analysis
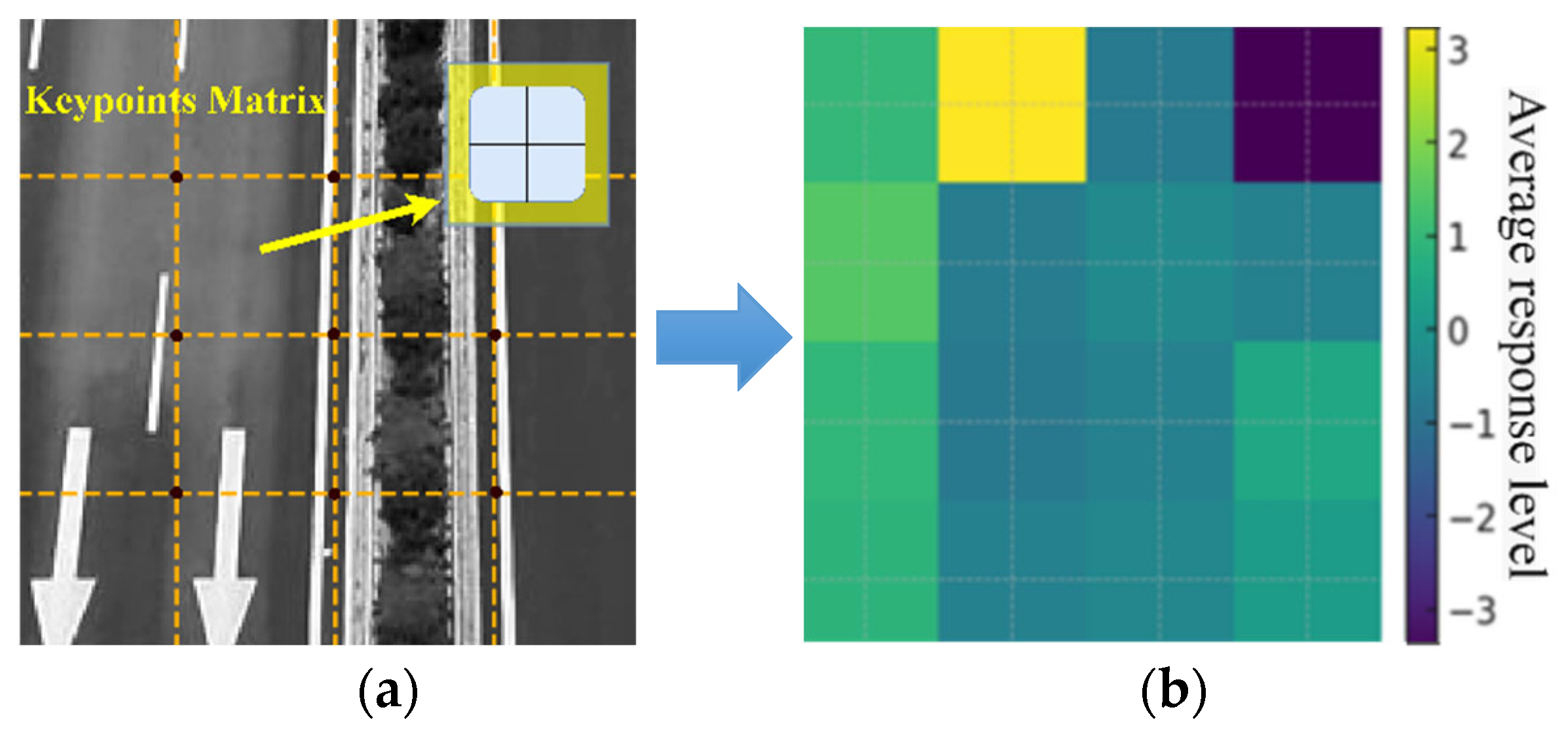
3.1. ROI Division for UAV Perspective
3.2. SURF Extraction of Road Agglomerate Fog
3.3. Optical Flow Analysis of Road Agglomerate Fog
3.4. Bayesian-Based Data Fusion for Agglomerate Fog Detection
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.1. Experimental Conditions
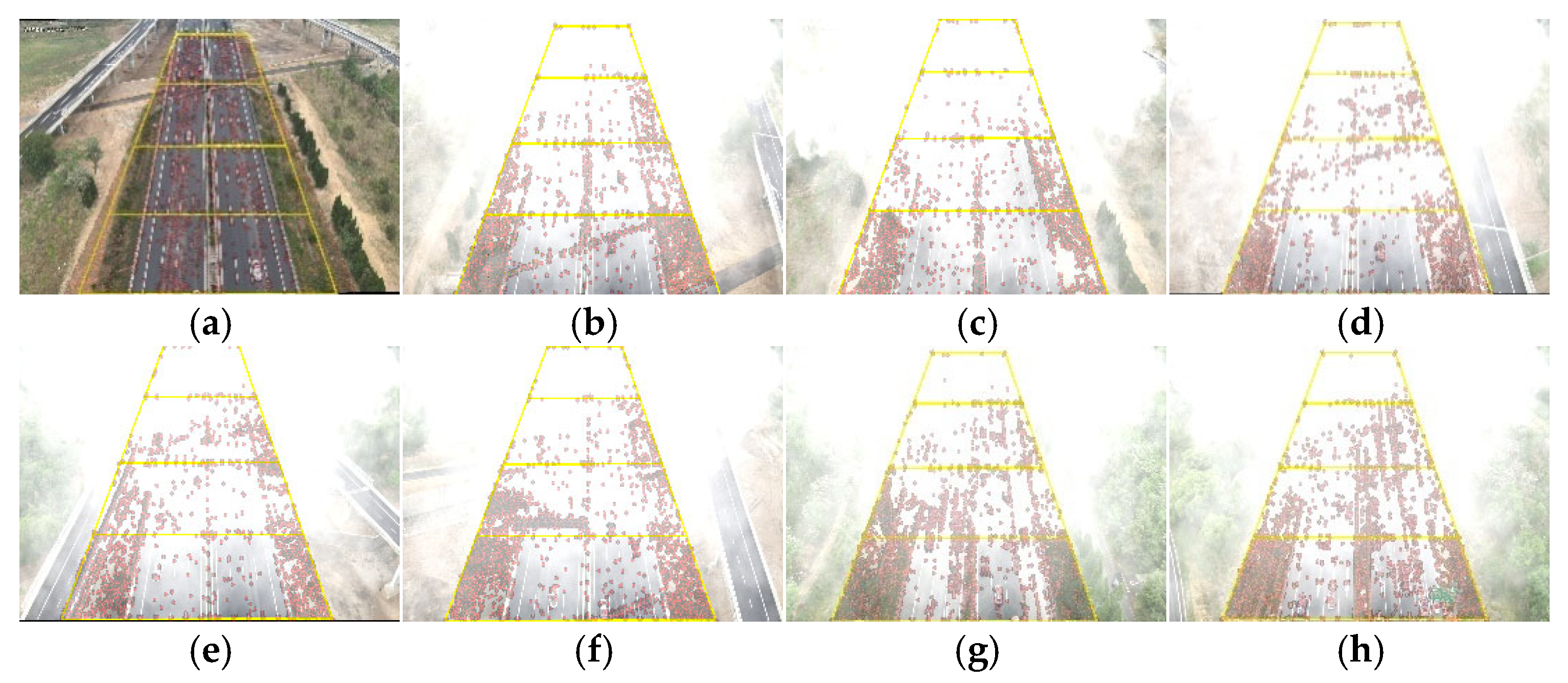
4.2. FogGAN-Based Dataset Generation Results and Analysis
4.3. Agglomerate Fog Detection Results Based on the Fusion of SURF and Optical Flow
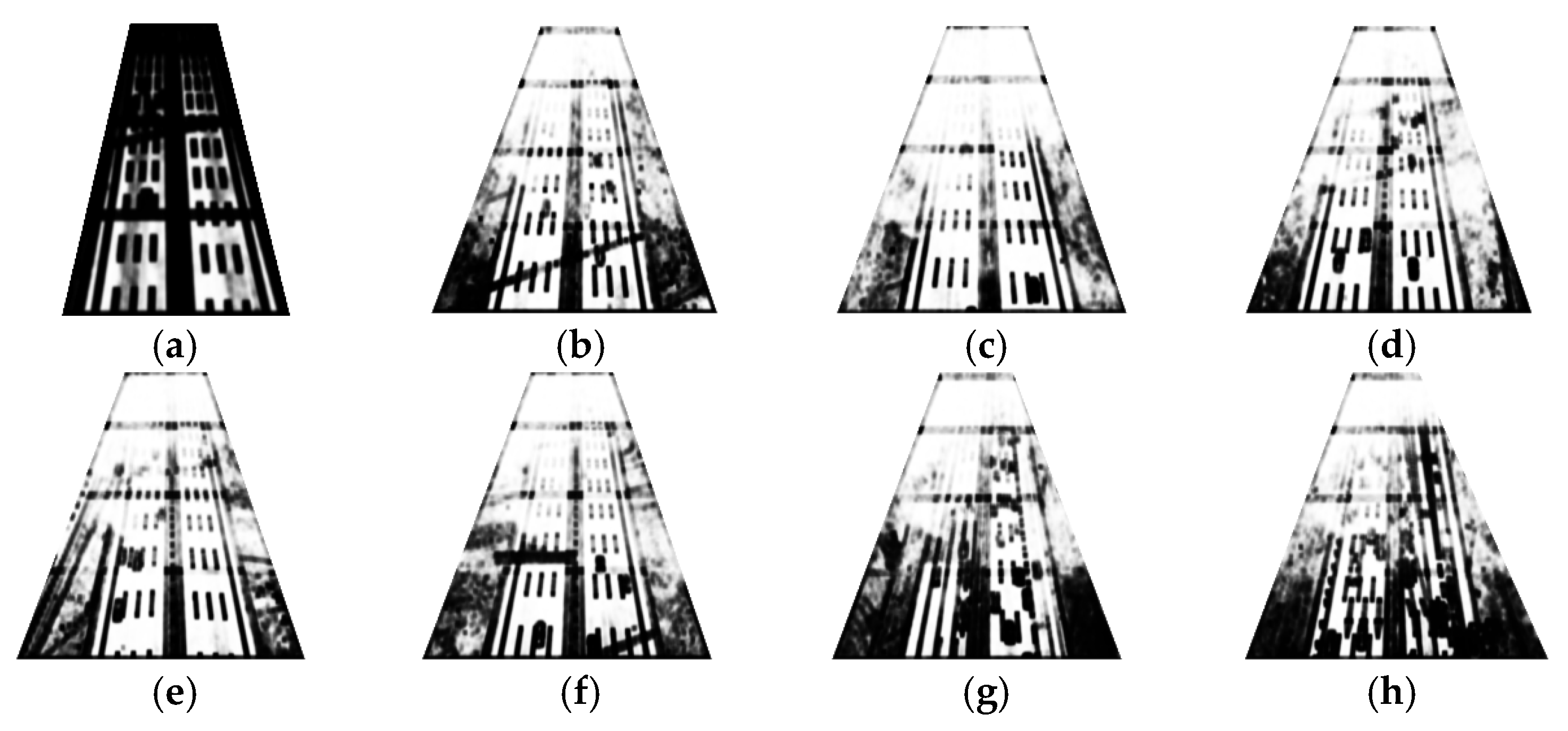
4.3.1. SURF Extraction Results and Analysis
4.3.2. Optical Flow Extraction Results and Analysis
4.3.3. Fusion Method Experimental Results and Analysis
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhen, I.L.; Yuan, A.; Chen, I.Z.; Hai, B.Z.; Chang, M.L.; Zong, J.Z. Research on video monitoring and early warning of expressway fog clusters. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2023, 22, 15408–15417. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Jiang, J.; Yao, Z.; Liu, Y. Nighttime fog and low stratus detection under multi-scene and all lunar phase conditions using S-NPP/VIIRS visible and infrared channels. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 218, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.; Hoos, S.; Sakthivel, T.S.; Babu, B.; Drake, C.; Seal, S. Real-time fog sensing employing roadside traffic cameras using lanthanide-doped upconverting NaYF4 nanomaterials as a contrast piece. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2025, 382, 116131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, M.; Mahdavi, S.; Bullock, T.; Beale, S. Automatic nighttime sea fog detection using GOES-16 imagery. Atmos. Res. 2020, 238, 104712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharatappeh, S.; Neshatfar, S.; Sekeh, S.Y.; Dhiman, V. FogGuard: Guarding YOLO against fog using perceptual loss. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.08939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, A.; Haque, M.R.; Basri, R.; Uddin, M.S. Single image dehazing: An analysis on generative adversarial network. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Netw. Secur. 2024, 24, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, N.; Habib, M.A.; Ahmad, M.; Abbas, Q.; Aldajani, M.B.; Latif, M.A. Efficient and cost-effective vehicle detection in foggy weather for edge/fog-enabled traffic surveillance and collision avoidance systems. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2024, 81, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Liu, Y.; Fan, L.; Fan, J. YOLOv5s-fog: An improved model based on YOLOv5s for object detection in foggy weather scenarios. Sensors 2023, 23, 5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Shi, Z.; Zhu, C. Enhanced multi-scale object detection algorithm for foggy traffic scenarios. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2025, 82, 2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asery, R.; Sunkaria, R.K.; Sharma, L.D.; Kumar, A. Fog detection using GLCM based features and SVM. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Advances in Signal Processing (CASP), Pune, India, 9–11 June 2016; pp. 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Bronte, S.; Bergasa, L.M.; Alcantarilla, P.F. Fog detection system based on computer vision techniques. In Proceedings of the 2009 12th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 4–7 October 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Miclea, R.C.; Ungureanu, V.I.; Sandru, F.D.; Silea, I. Visibility enhancement and fog detection: Solutions presented in recent scientific papers with potential for application to mobile systems. Sensors 2021, 21, 3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Tan, Q.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Nighttime agglomerate fog event detection considering car light glare based on video. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2024, 19, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.M.; Khan, M.N.; Mohamed, A.; Das, A.; Li, L. Automated Real-Time Weather Detection System Using Artificial Intelligence; Wyoming Department of Transportation: Cheyenne, WY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Fu, Z.; Meng, F.; Zhang, L. Confidence-feature fusion: A novel method for fog density estimation in object detection systems. Electronics 2025, 14, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ApinayaPrethi, K.N.; Nithya, S. Fog detection and visibility measurement using SVM. In Proceedings of the 2023 2nd International Conference on Advancements in Electrical, Electronics, Communication, Computing and Automation (ICAECA), Coimbatore, India, 16–17 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Yang, X.; Yuan, G.; Xu, D. ABCNet: A comprehensive highway visibility prediction model based on attention, Bi-LSTM and CNN. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2024, 21, 4397–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.; Zhou, J.; Hong, Z.; Tang, J.; Huang, X. Vehicle recognition and driving information detection with UAV video based on improved YOLOv5-DeepSORT algorithm. Sensors 2025, 25, 2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; An, Y.; Yang, H.; Pan, Y. Real-time vehicle detection and urban traffic behavior analysis based on uav traffic videos on mobile devices. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.16246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baya, C. Lidar from the Skies: A UAV-Based Approach for Efficient Object Detection and Tracking. Master’s Thesis, Missouri University of Science and Technology, Rolla, MO, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Qi, W.; Huang, G.; Zhu, F.; Xiao, Y. Classification guided thick fog removal network for drone imaging: Classifycycle. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 39323–39340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Y. Multi-task learning for uav aerial object detection in foggy weather condition. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Rec. ITU-R BT.601-7; Studio Encoding Parameters of Digital Television for Standard 4:3 and Wide-Screen 16:9 Aspect Ratios. International Telecommunication Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- Bay, H.; Tuytelaars, T.; Van Gool, L. Surf: Speeded up robust features. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 404–417. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, B.D.; Kanade, T. An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 August 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Metz, L.; Chintala, S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.06434. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]






| Category | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental conditions | wind scale | 1–4 F |
| temperature | 10–25 °C | |
| visibility | 4–10 km | |
| UAV configurations | pitching angle | 60° |
| resolution of the camera | 3840 × 2160 Px | |
| frame rate | 30 FPS | |
| locate mode | RTK ± 0.1 m | |
| Flight configurations | height | 100–150 m |
| speed | 15 m/s |
| Method | PSNR (dB) | SSIM | FID |
|---|---|---|---|
| DCGAN | 20.5 | 0.65 | 35.2 |
| CycleGAN Pix2Pix FogGAN | 22.3 23.1 24.1 | 0.70 0.72 0.77 | 30.1 28.4 25.3 |
| Image | ROI(1) | ROI(2) | ROI(3) | ROI(4) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a (no fog) | 2711 | 7.68 × 10−4 | 6012 | 1.06 × 10−3 | 8910 | 1.14 × 10−3 | 9598 | 9.62 × 10−4 |
| b | 117 | 3.31 × 10−5 | 452 | 8.56 × 10−5 | 1411 | 2.01 × 10−4 | 3996 | 4.56 × 10−4 |
| c | 72 | 2.04 × 10−5 | 239 | 4.53 × 10−5 | 1024 | 1.46 × 10−4 | 1585 | 1.81 × 10−4 |
| d | 135 | 3.82 × 10−5 | 467 | 8.84 × 10−5 | 577 | 8.21 × 10−5 | 1552 | 1.77 × 10−4 |
| e | 93 | 2.63 × 10−5 | 670 | 1.27 × 10−4 | 957 | 1.36 × 10−4 | 1847 | 2.11 × 10−4 |
| f | 94 | 2.66 × 10−5 | 403 | 7.63 × 10−5 | 1884 | 2.68 × 10−4 | 2218 | 2.53 × 10−4 |
| g | 138 | 3.90 × 10−5 | 452 | 8.56 × 10−5 | 2000 | 2.84 × 10−4 | 5406 | 6.16 × 10−4 |
| h | 149 | 4.21 × 10−5 | 756 | 1.43 × 10−4 | 1622 | 2.31 × 10−4 | 3881 | 4.43 × 10−4 |
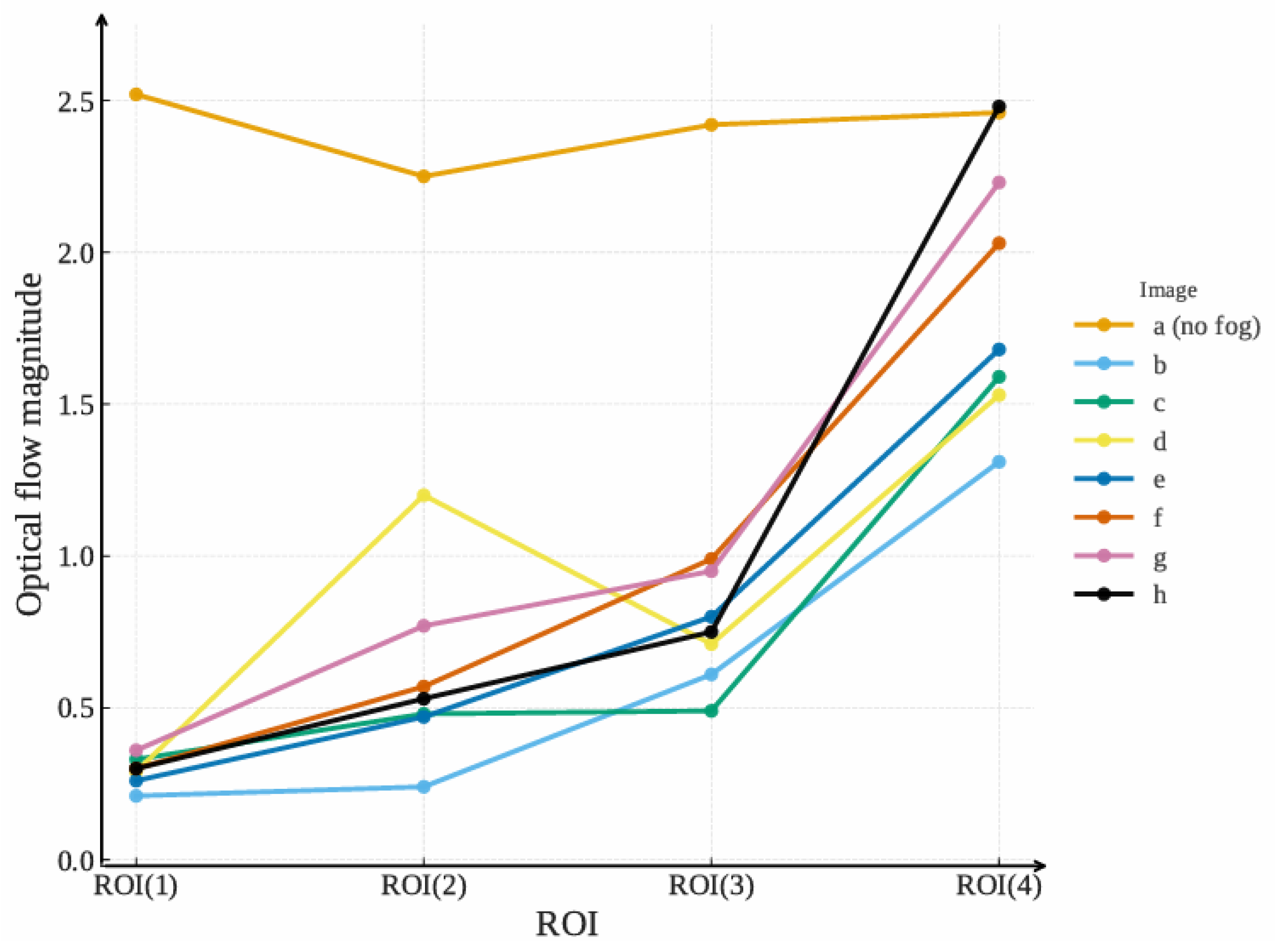
| Image | ROI(1) | ROI(2) | ROI(3) | ROI(4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a (no fog) | 2.52 | 2.25 | 2.42 | 2.46 |
| b | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.61 | 1.31 |
| c | 0.33 | 0.48 | 0.49 | 1.59 |
| d | 0.29 | 1.20 | 0.71 | 1.53 |
| e | 0.26 | 0.47 | 0.80 | 1.68 |
| f | 0.30 | 0.57 | 0.99 | 2.03 |
| g | 0.36 | 0.77 | 0.95 | 2.23 |
| h | 0.30 | 0.53 | 0.75 | 2.48 |
| Method | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| SURF-based method | 0.82 | 0.75 | 0.78 |
| Optical flow-based method Fusion of SURF and optical flow method | 0.79 0.88 | 0.78 0.85 | 0.76 0.82 |
| Method | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Processing Time (ms/Image) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XGBoost-based method | 0.78 | 0.74 | 0.76 | 140 |
| Survey informed fusion method Fusion of SURF and optical flow method | 0.80 0.88 | 0.76 0.85 | 0.78 0.82 | 135 180 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, F.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Jing, M.; Gong, X. Road Agglomerate Fog Detection Method Based on the Fusion of SURF and Optical Flow Characteristics from UAV Perspective. Entropy 2025, 27, 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27111156
Guo F, Liu H, Zhang M, Jing M, Gong X. Road Agglomerate Fog Detection Method Based on the Fusion of SURF and Optical Flow Characteristics from UAV Perspective. Entropy. 2025; 27(11):1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27111156
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Fuyang, Haiqing Liu, Mengmeng Zhang, Mengyuan Jing, and Xiaolong Gong. 2025. "Road Agglomerate Fog Detection Method Based on the Fusion of SURF and Optical Flow Characteristics from UAV Perspective" Entropy 27, no. 11: 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27111156
APA StyleGuo, F., Liu, H., Zhang, M., Jing, M., & Gong, X. (2025). Road Agglomerate Fog Detection Method Based on the Fusion of SURF and Optical Flow Characteristics from UAV Perspective. Entropy, 27(11), 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27111156






