Quantum Authentication Evolution: Novel Approaches for Securing Quantum Key Distribution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Quantum Cryptography and Quantum Key Distribution
3. QKD Protocols
3.1. BB84 Protocol
3.2. SARG04 Protocol
3.3. Quantum Bit Error Rate
4. Strengthening QKD: Advancing Security through Post-Quantum Cryptography
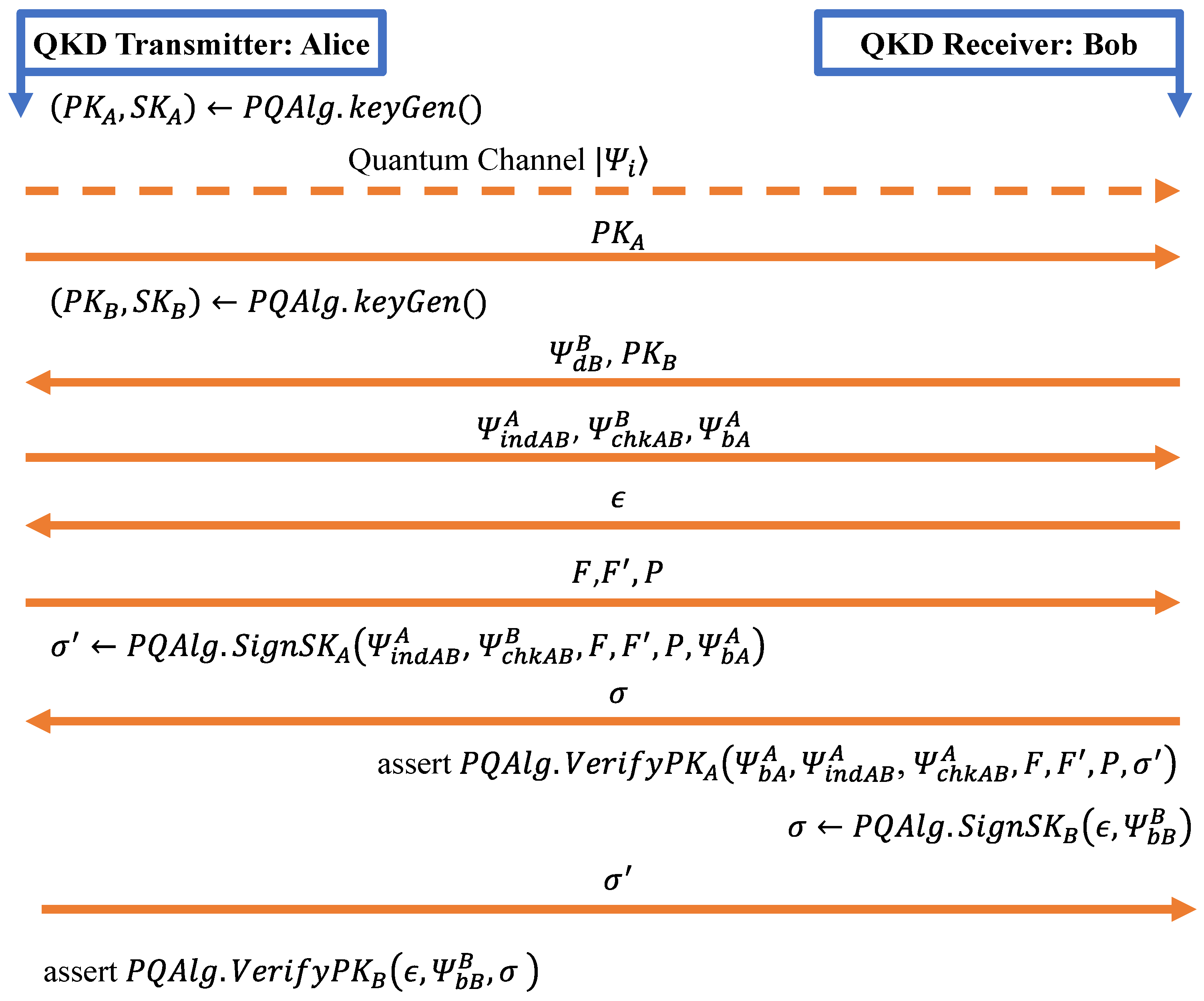
5. QKD Authentication Model Setup and Details
5.1. Mono-Authentication
- is the number of 0 bits in
- is the number of 1 bit in
- is the number of 0 bit in
- is the number of 1 bit in
5.2. Quantum Communication Metrics: QBER, Maximum Corrected Errors, and Overhead
5.3. Compact, Moderate, and Sizable Compartments
5.4. Different Key Rates
6. Outcomes of QKD Mono-Authentication
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grover, L.K. A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search. arXiv 1996, arXiv:quant-ph/9605043. [Google Scholar]
- Shor, P.W. Polynomial-Time Algorithms for Prime Factorization and Discrete Logarithms on a Quantum Computer. SIAM J. Comput. 1997, 26, 1484–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proos, J.; Zalka, C. Shor’s discrete logarithm quantum algorithm for elliptic curves. arXiv 2004, arXiv:quant-ph/0301141. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, S. Universal Quantum Simulators. Sci. New Ser. 1996, 273, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preskill, J. Quantum computing and the entanglement frontier. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1203.5813. [Google Scholar]
- Arute, F.; Arya, K.; Babbush, R.; Bacon, D.; Bardin, J.C.; Barends, R.; Biswas, R.; Boixo, S.; Brandao, F.G.S.L.; Buell, D.A.; et al. Quantum Supremacy using a Programmable Superconducting Processor. Nature 2019, 574, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivest, R.L.; Shamir, A.; Adleman, L. A Method for Obtaining Digital Signatures and Public-Key Cryptosystems; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1978; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, V.S. Use of elliptic curves in cryptography. In Advances in Cryptology-CRYPTO ’85 Proceedings; Williams, H.C., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986; pp. 417–426. [Google Scholar]
- Koblitz, N. Elliptic curve cryptosystems. Math. Comput. 1987, 48, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.H.; Brassard, G. Quantum Cryptography: Public Key Distribution and Coin Tossing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984; pp. 475–480. [Google Scholar]
- Ekert, A.K. Quantum cryptography based on bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1991, 67, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, D.J. Introduction to post-quantum cryptography. In Post-Quantum Cryptography; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein, D.J.; Lange, T. Post-quantum cryptography. Nature 2017, 549, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wootters, W.K.; Zurek, W.H. A single quantum cannot be cloned. Nature 1982, 299, 802–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Q.; Lo, H.-K.; Pan, J.-W. Secure quantum key distribution with realistic devices. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2020, 92, 025002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, N.T.; Lim, C.C.W.; Cahall, C.; Kim, J.; Gauthier, D.J. Provably secure and high-rate quantum key distribution with time-bin qudits. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-P.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, W.; Hu, X.-L.; Guan, J.-Y.; Yu, Z.-W.; Xu, H.; Lin, J.; et al. Sending-or-not-sending with independent lasers: Secure twin-field quantum key distribution over 509 km. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 124, 070501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.-T.; Zeng, P.; Liu, H.; Zou, M.; Wu, W.; Tang, Y.-L.; Sheng, Y.-J.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; et al. Implementation of quantum key distribution surpassing the linear rate-transmittance bound. Nat. Photonics 2020, 14, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Li, Y.-H.; Liao, S.-K.; Yang, M.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ren, J.-G.; Cai, W.-Q.; Liu, W.-Y.; Li, S.-L.; et al. Entanglement-based secure quantum cryptography over 1120 kilometres. Nature 2020, 582, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.-K.; Ca, W.-Q.; Handsteiner, J.; Liu, B.; Yin, J.; Zhang, L.; Rauch, D.; Fink, M.; Ren, J.-G.; Liu, W.-Y.; et al. Satellite-relayed intercontinental quantum network. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 030501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shor, P.W. Algorithms for quantum computation: Discrete logarithms and factoring. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Santa Fe, NM, USA, 20–22 November 1994; Goldwasser, S., Ed.; pp. 124–134. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Jordan, S.; Liu, Y.-K.; Moody, D.; Peralta, R.; Perlner, R.; Tone, D.-S. Report on Post-Quantum Cryptography; Technical Report NISTIR 8105; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2016.
- Wang, L.-J.; Zhang, K.-Y.; Wang, J.-Y.; Cheng, J.; Yang, Y.-H.; Tang, S.-B.; Yan, D.; Tang, Y.-L.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Y.; et al. Experimental authentication of quantum key distribution with post-quantum cryptography. NPJ Quantum Inf. 2021, 7, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehner, S.; Elkouss, D.; Hanson, R. Quantum internet: A vision for the road ahead. Science 2018, 362, 9288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleese van Dam, K. From Long-Distance Entanglement to Building a Nationwide Quantum Internet: Report of the DOE Quantum Internet Blueprint Workshop; U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific and Technical Information: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2020.
- Lewis, A.M.; Travagnin, M. A Secure Quantum Communications Infrastructure for Europe: Technical Background for a Policy Vision; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Yin, Z.-Q.; He, D.-Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, R.-Q.; Ye, P.; Zhou, Y.; Fan-Yuan, G.-J.; Wang, F.-X.; Zhu, Y.-G.; et al. Twin-field quantum key distribution over 830-km fibre. Nat. Photonics 2022, 16, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.L.; Plews, A.; Takahashi, R.; Doi, K.; Tam, W.; Sharpe, A.W.; Dixon, A.R.; Lavelle, E.; Dynes, J.F.; Murakami, A.; et al. 10-Mb/s Quantum Key Distribution. J. Light. Technol. 2018, 36, 3427–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado, A.; Lopez, V.; Lopez, D.; Peev, M.; Poppe, A.; Pastor, A.; Folgueira, J.; Martin, V. The Engineering of Software-Defined Quantum Key Distribution Networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2019, 57, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FG QIT4N (Focus Group on Quantum Information Technology for Networks). Standardization Outlook and Technology Maturity: Quantum Key Distribution Network; ITU-T: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Travagnin, M.; Lewis, A.M. Quantum Key Distribution In-Field Implementations; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. Communication theory of secrecy systems. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1949, 28, 656–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarani, V.; Acin, A.; Ribordy, G.; Gisin, N. Quantum cryptography protocols robust against photon number splitting attacks for weak laser pulse implementations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 057901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekert, A.K. Quantum cryptography and Bell’s theorem. In Quantum Measurements in Optics; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 413–418. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, C.H.; Brassard, G.; Mermin, N.D. Quantum cryptography without Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 68, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ecker, S.; Pseiner, J.; Piris, J.; Bohmann, M. Advances in entanglement-based qkd for space applications. In Proceedings of the SPIE, International Conference on Space Optics-ICSO, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 3–7 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, C.H. Quantum cryptography using any two nonorthogonal states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 68, 3121–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruß, D. Optimal eavesdropping in quantum cryptography with six states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 81, 3018–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.-K.; Ma, X.; Chen, K. Decoy state quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 230504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-B. Beating the photon-number-splitting attack in practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 230503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Qi, B.; Zhao, Y.; Lo, H.-K. Practical decoy state for quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 72, 012326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.-K.; Cai, W.-Q.; Liu, W.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Ren, J.-G.; Yin, J.; Shen, Q.; Cao, Y.; Li, Z.-P.; et al. Satellite-to-ground quantum key distribution. Nature 2017, 549, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Cao, Y.; Li, Y.-H.; Liao, S.-K.; Zhang, L.; Ren, J.-G.; Cai, W.-Q.; Liu, W.-Y.; Li, B.; Dai, H.; et al. Satellite-based entanglement distribution over 1200 kilometers. Science 2017, 356, 1140–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.-L.; Chen, T.-Y.; Yu, Z.-W.; Liu, H.; You, L.-X.; Zhou, Y.-H.; Chen, S.-J.; Mao, Y.; Huang, M.-Q.; Zhang, W.-J.; et al. Measurement device- independent quantum key distribution over a 404 km optical fiber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117, 190501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boaron, A.; Boso, G.; Rusca, D.; Vulliez, C.; Autebert, C.; Caloz, M.; Perrenoud, M.; Gras, G.; Bussières, F.; Li, M.-J.; et al. Secure quantum key distribution over 421 km of optical fiber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 190502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesner, S. Conjugate coding. ACM Sigact News 1983, 15, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhu, Q.; Li, S.; Ansari, I.S.; Yu, S. On the Performance of Mixed FSO UWOC Dual-Hop Transmission Systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 2041–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branciard, C.; Gisin, N.; Kraus, B.; Scarani, V. Security of two quantum cryptography protocols using the same four qubit states. Phys. Rev. A Gen. Phys. 2005, 72, 032301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koashi, M. Security of quantum key distribution with discrete rotational symmetry. arXiv 2005, arXiv:quant-ph/0507154. [Google Scholar]
- Padamvathi, V.; Vardhan, B.V.; Krishna, A.V.N. Quantum cryptography and quantum key distribution protocols: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 6th International Conference on Advanced Computing (IACC), Bhimavaram, India, 27–28 February 2016; pp. 556–562. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, M.; Aziz, K. A survey of quantum key distribution protocols. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Frontiers of Information Technology, Abbottabad, Pakistan, 16–18 December 2009; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Fung, C.-H.F.; Tamaki, K.; Lo, H.-K. On the performance of two protocols: SARG04 and BB84. arXiv 2005, arXiv:quant-ph/0510025. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Li, W.; Shen, Y.; Yu, Y.; Han, X.; Zeng, H.; Cai, M.; Qian, T.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; et al. Experimental investigation of quantum key distribution over a water channel. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 3902–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekert, A.; Christandl, M.; Renner, R. A Generic Security Proof for Quantum Key Distribution; Hardvard Edu: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fung, C.-H.F.; Ma, X.; Chau, H.F. Practical issues in quantum-key-distribution post-processing. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 81, 012318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiktenko, E.O.; Malyshev, A.O.; Gavreev, M.A.; Bozhedarov, A.A.; Pozhar, N.O.; Anufriev, M.N.; Fedorov, A.K. Lightweight authentication for quantum key distribution. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2020, 66, 6354–6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, M.; Stebila, D.; Ustaoglu, B. Quantum Key Distribution in the Classical Authenticated Key Exchange Framework. In Proceedings of the Post-Quantum Cryptography: 5th International Workshop, PQCrypto 2013, Limoges, France, 4–7 June 2013; Proceedings 5. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 7932. [Google Scholar]
- Ducas, L.; Kiltz, E.; Lepoint, T.; Lyubashevsky, V.; Schwabe, P.; Seiler, G.; Stehlé, D. Crystals-DILITHIUM: A lattice-based digital signature scheme. IACR Trans. Cryptogr. Hardw. Embed. Syst. 2018, 1, 238–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducs, L.; Lyubashevsky, V.; Prest, T. Efficient Identity-Based Encryption over Ntru Lattices; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 8874. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Schmidt, D. RAINBOW, a New Multivariable Polynomial Signature Scheme; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 3531, pp. 164–175. [Google Scholar]
- Aumasson, J.-P.; Bernstein, D.J.; Beullens, W.; Dobraunig, C.; Eichlseder, M.; Fluhrer, S.; Gazdag, S.-L.; Hülsing, A.; Kampanakis, P.; Kölbl, S.; et al. SPHINCS: Practical Stateless Hash-Based Signatures; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volueme 9056. [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe, P.; Stebila, D.; Wiggers, T. More efficient post-quantum KEMTLS with pre-distributed public keys. In Proceedings of the 26th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security (ESORICS), Darmstadt, Germany, 4–8 October 2021; Bertino, E., Shulman, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar]




| Security Bits | DILITHIUM | SPHINCS+ | FALCON | RAINBOW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 128 | DILITHIUM 2 | SPHINCS-128f-simple | FALCON 512 | RAINBOW IIIc-classic |
| 192 | DILITHIUM 3 | SPHINCS-192f-simple | - | RAINBOW Vc-classic |
| 256 | DILITHIUM 5 | SPHINCS-256f-simple | FALCON 1024 | - |
| Post-Quantum Algorithm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Security Bits | Size in Bytes | DILITHIUM | SPHINCS+ | FALCON | RAINBOW |
| 128 | SK | 2544 | 64 | 1281 | 626,048 |
| PK | 1312 | 32 | 897 | 882,080 | |
| Sig | 2420 | 16,972 | 659 | 164 | |
| 192 | SK | 4016 | 96 | - | 1,408,736 |
| PK | 1952 | 48 | - | 1,930,600 | |
| Sig | 3293 | 35,664 | - | 212 | |
| 256 | SK | 4880 | 128 | 2305 | - |
| PK | 2592 | 64 | 1793 | - | |
| Sig | 4595 | 49,216 | 1276 | - | |
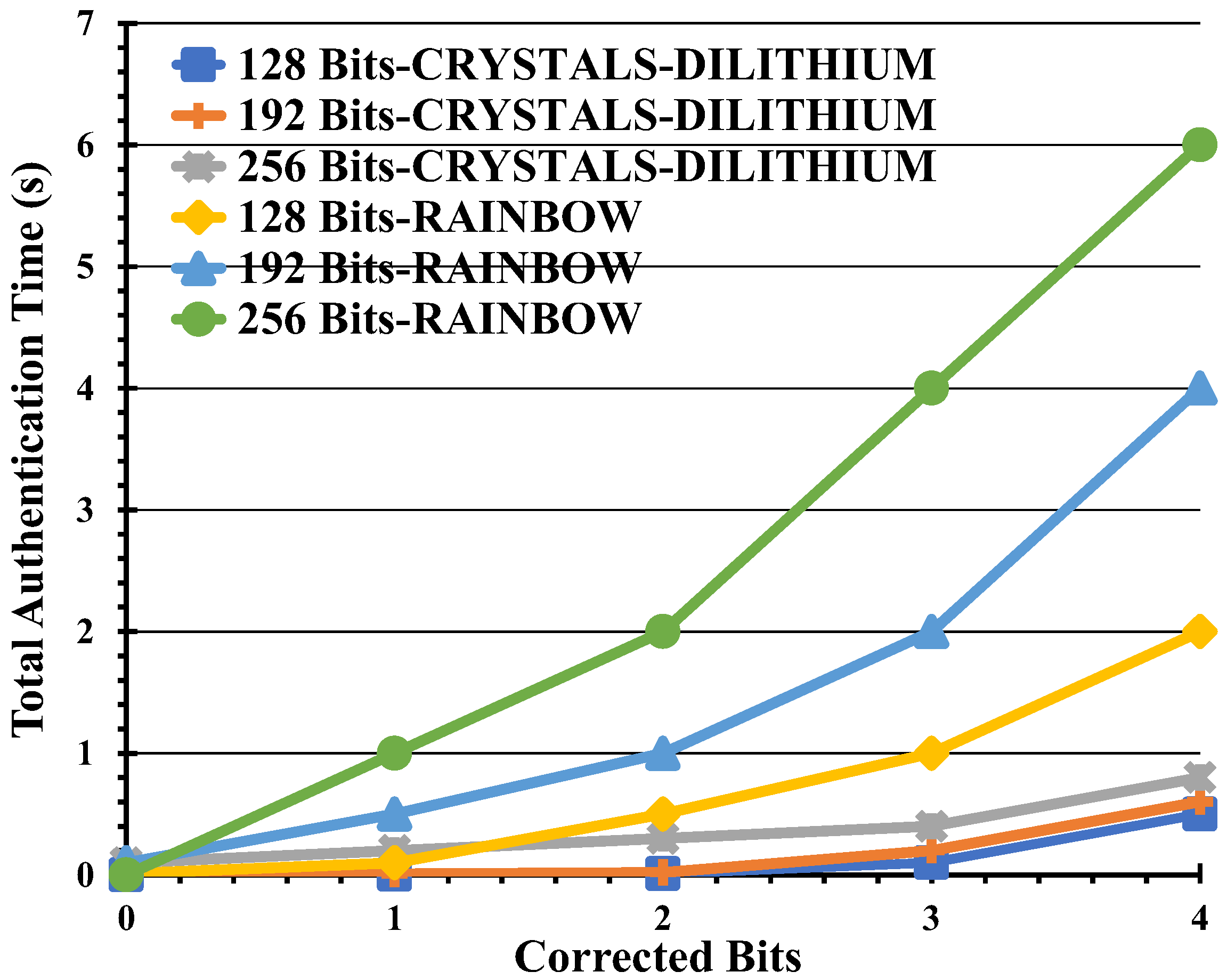
| Maximum Corrected Bits | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Secuirty Bits | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 128 | ≈0.005 s (1 h) | ≈0.022 s (129 h) | ≈0.95 s (8257 h) | ≈40 s (691,000 h) |
| 192 | ≈0.006 s (1 h) | ≈0.036 s (193 h) | ≈3.5 s (18,529 h) | ≈188 s (2,341,089 h) |
| 256 | ≈0.007 s (1 h) | ≈8 s (32,897 h) | ≈8 s (32,897 h) | ≈581 s (5,559,937 h) |
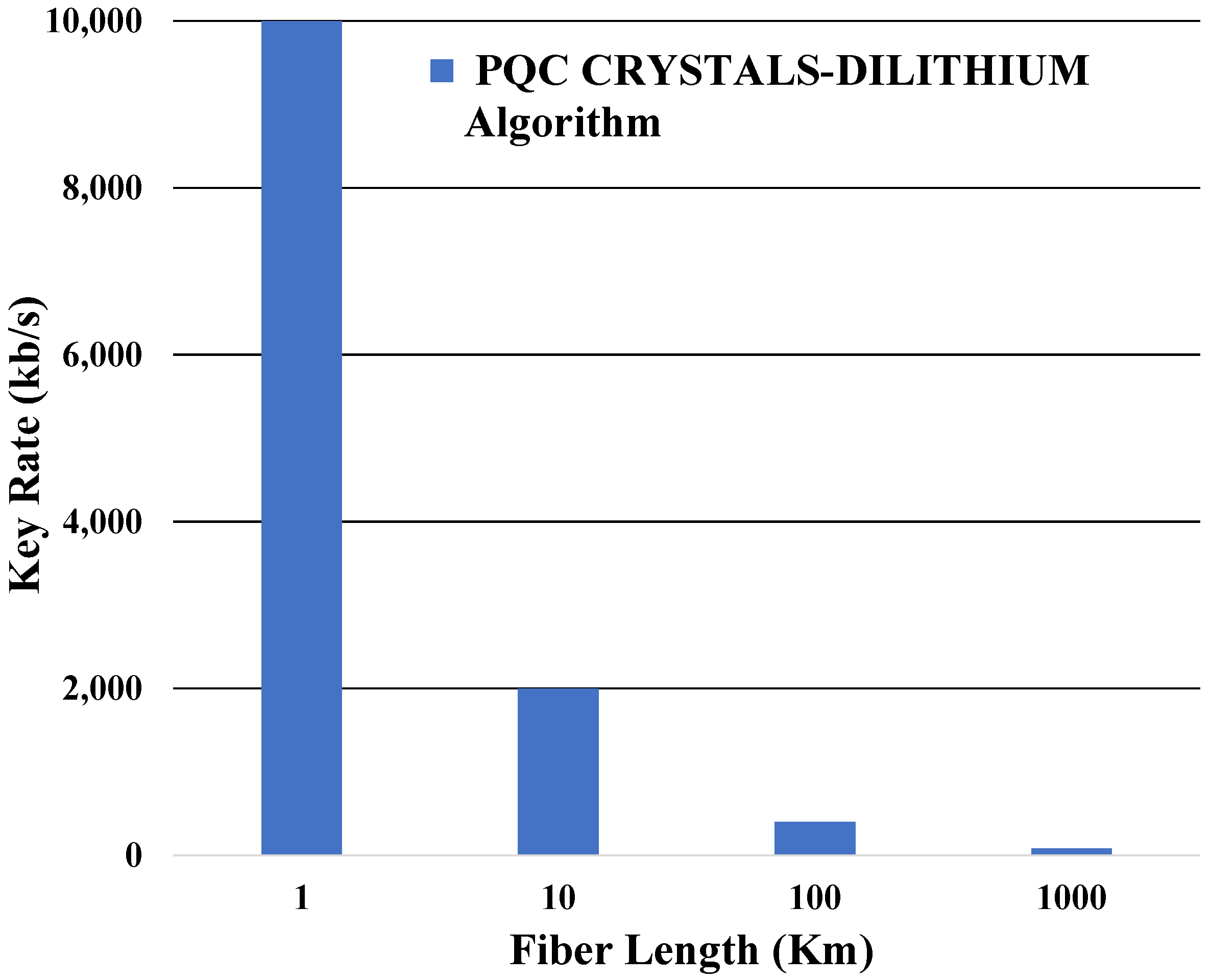
| Post-Quantum Algorithms | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Secuirty Bits | Key Rate (kb/s) | CRYSTALS-DILITHIUM Time (s) | RAINBOW Time (s) |
| 128 | 100 | 0.0011 | 0.11 |
| 192 | 1000 | 0.0024 | 0.14 |
| 256 | 10,000 | 0.0088 | 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Termos, H. Quantum Authentication Evolution: Novel Approaches for Securing Quantum Key Distribution. Entropy 2024, 26, 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26060447
Termos H. Quantum Authentication Evolution: Novel Approaches for Securing Quantum Key Distribution. Entropy. 2024; 26(6):447. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26060447
Chicago/Turabian StyleTermos, Hassan. 2024. "Quantum Authentication Evolution: Novel Approaches for Securing Quantum Key Distribution" Entropy 26, no. 6: 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26060447
APA StyleTermos, H. (2024). Quantum Authentication Evolution: Novel Approaches for Securing Quantum Key Distribution. Entropy, 26(6), 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26060447






