Passive Continuous Variable Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution Predictable with Machine Learning in Oceanic Turbulence
Abstract
1. Introduction
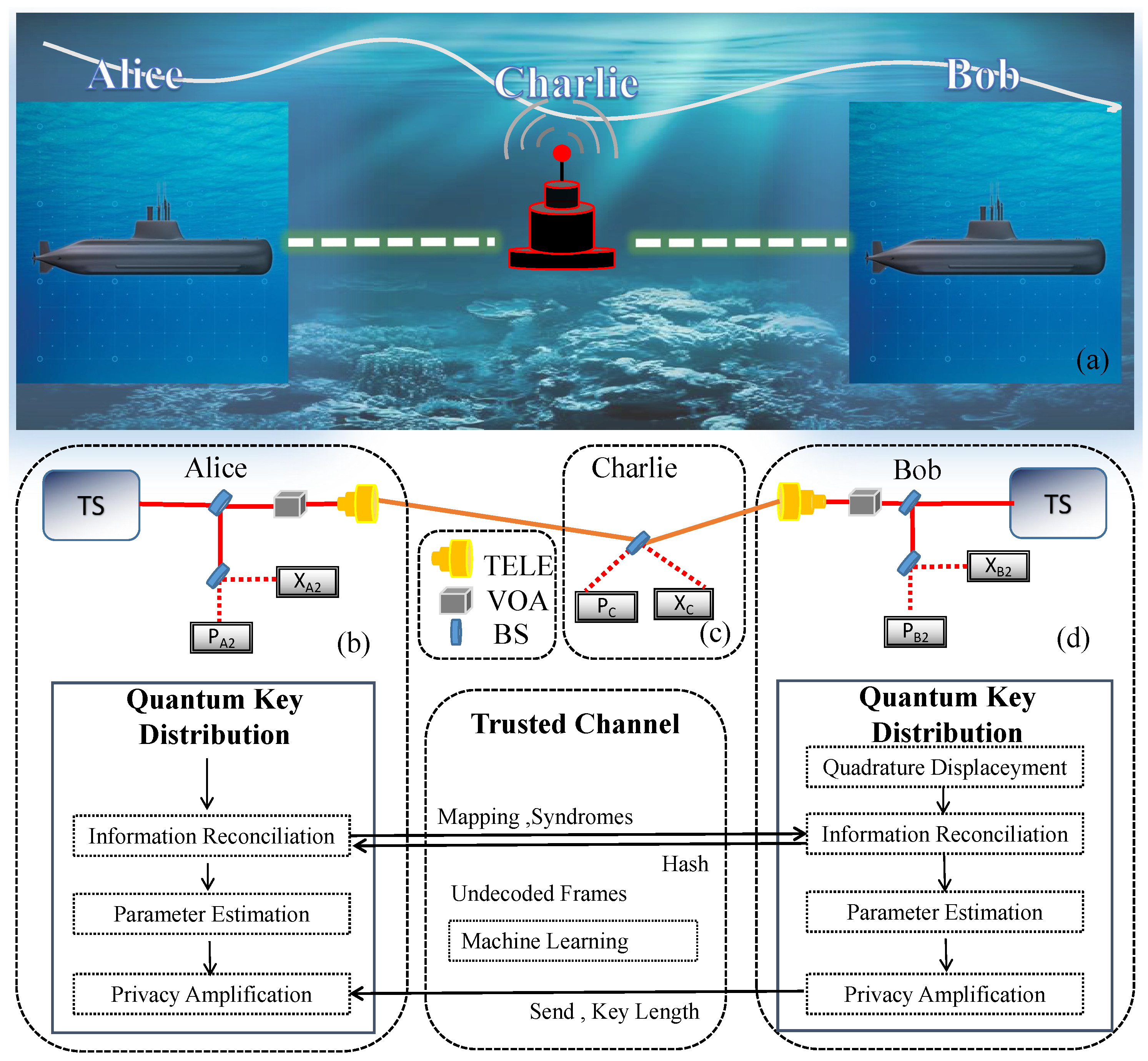
2. CV-MDI QKD with Passive State Preparation
3. Transmittance Prediction with Machine Learning
3.1. Optical Propagation Characteristics of the Oceanic Turbulence Channel
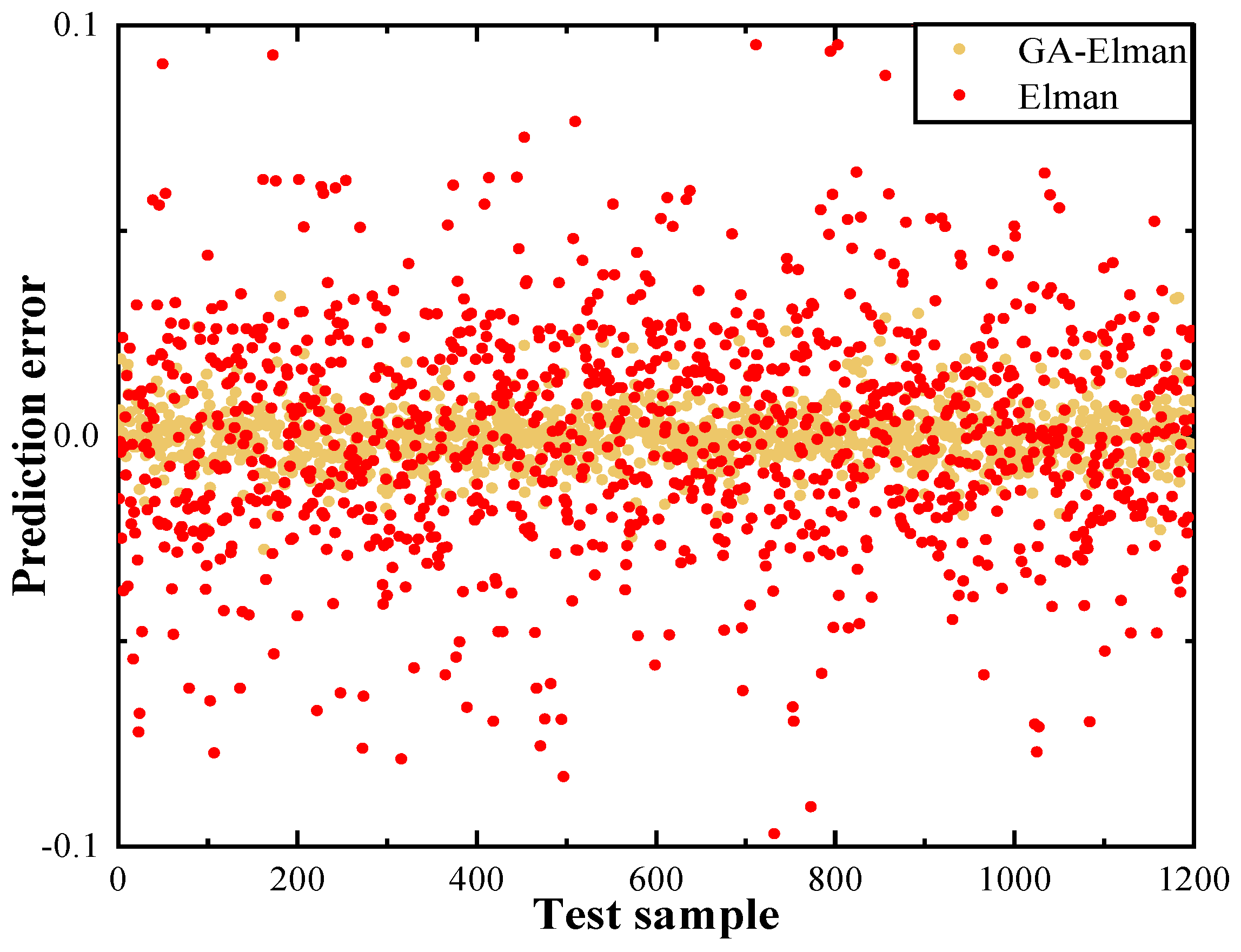
3.2. Transmittance Prediction of Seawater Channel
4. Security Analysis
4.1. Secret Key Rate in Asymptotic Scenarios
4.2. Secret Key Rate in the Finite-Size Case
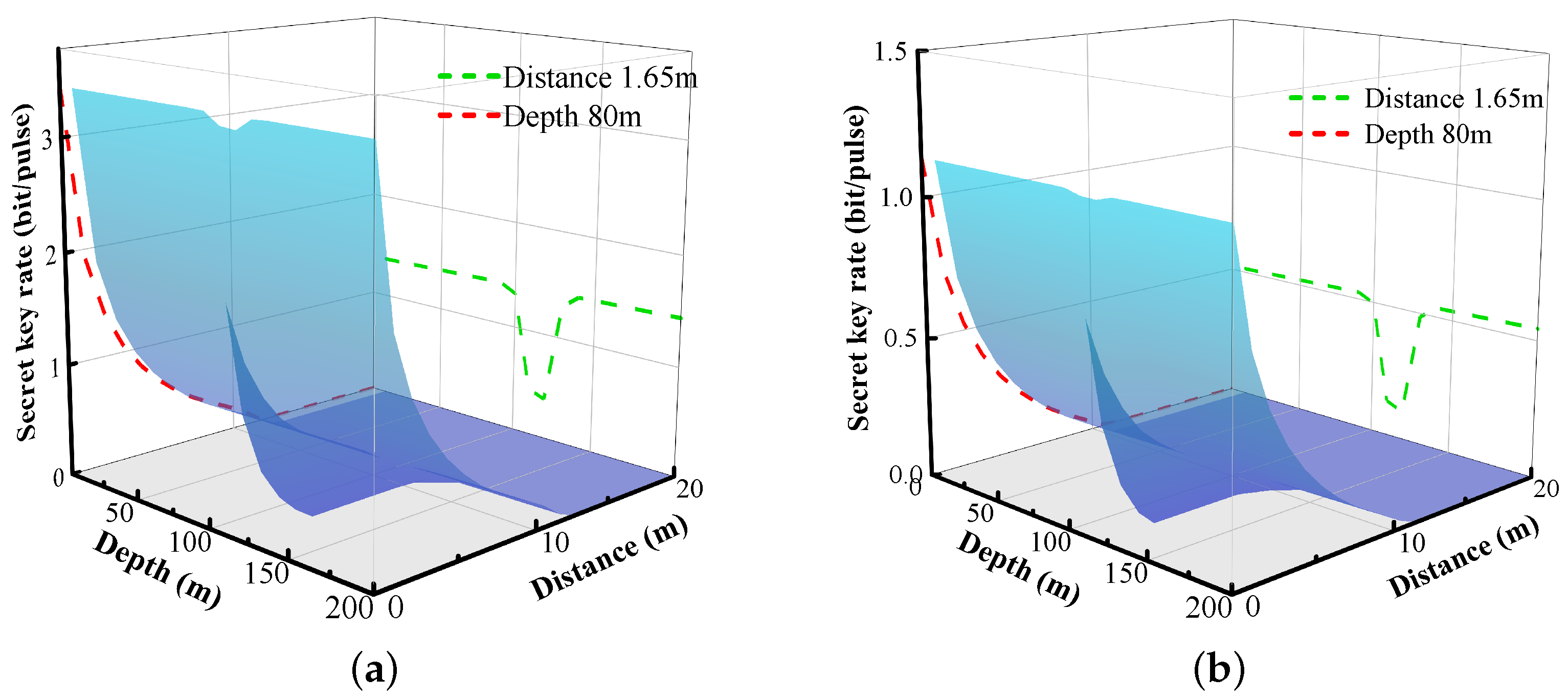
5. Simulation Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. The Seawater Chlorophyll Model
| Meaning of the Variates | Parameter | |
|---|---|---|
| The absorption coefficient of chlorophyll a at wavelength | ||
| The loss of light propagation in pure water | ||
| The fulvic acid’s absorption coefficient | ||
| The fulvic acid’s exponential coefficient | ||
| The wavelength | 532 nm | |
| The humic acid’s absorption of coefficient | ||
| The humic acid’s exponential coefficient | ||
| The surface’s background chlorophyll content | ||
| s | The vertical gradient of concentration | |
| h | The total chlorophyll a above the background levels | 11.87 mg |
| The depth of the deep chlorophyll maximum | 115.4 m | |
| The maximum chlorophyll concentration at the chlorophyll maximum layer | ||
| The scattering coefficient of small particulate matter | ||
| The scattering coefficient of large particulate matter | ||
| The scattering coefficient of the pure water | ||
| d | The depth of ocean |
References
- Weedbrook, C.; Pirandola, S.; García-Patrón, R.; Cerf, N.J.; Ralph, T.C.; Shapiro, J.H.; Lloyd, S. Gaussian quantum information. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2012, 84, 621–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirandola, S.; Andersen, U.L.; Banchi, L.; Berta, M.; Bunandar, D.; Colbeck, R.; Englund, D.; Gehring, T.; Lupo, C.; Ottaviani, C.; et al. Advances in quantum cryptography. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2020, 12, 1012–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirandola, S.; Ottaviani, C.; Spedalieri, G.; Weedbrook, C.; Braunstein, S.L.; Lloyd, S.; Gehring, T.; Jacobsen, C.S.; Andersen, U.L. High-rate measurement-device-independent quantum cryptography. Nat. Photonics 2015, 9, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Xu, F.; Peng, X.; Guo, H. Continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 89, 052301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauerer, W.; Silberhorn, C. Quantum key distribution with passive decoy state selection. Phys. Rev. A 2007, 75, 050305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Koashi, M.; Imoto, N. Simple and efficient quantum key distribution with parametric down-conversion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 180503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, S.; Yin, Z.-Q.; Xu, F.-X.; Wu, X.-W.; Dong, C.-H.; Li, H.-W.; Guo, G.-C.; Han, Z.-F. Practical non-Poissonian light source for passive decoy state quantum key distribution. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 3393–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curty, M.; Ma, X.; Lo, H.-K.; Lütkenhaus, N. Passive sources for the Bennett-Brassard. quantum-key-distribution protocol with practical signals. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 82, 052325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.-H.; Tang, G.-Z.; Li, C.-Y.; Liang, L.-M. Experimental demonstration of passive-decoy-state quantum key distribution with two independent lasers. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 94, 032324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Evans, P.G.; Grice, W.P. Passive state preparation in the Gaussian-modulated coherent-states quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 97, 012317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Wang, T.; Chen, R.; Wang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, G. Experimental continuous-variable quantum key distribution using a thermal source. New J. Phys. 2021, 23, 113028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Gunther, H.; Evans, P.G.; Williams, B.P.; Camacho, R.M.; Peters, N.A. Experimental passive-state preparation for continuous-variable quantum communications. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2020, 13, 054065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mao, Y.; Wu, X.; Guo, Y. Security Analysis of a Passive Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution by Considering Finite-Size Effect. Entropy 2022, 23, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.-Q.; Mao, Y.; Zhong, H.; Huang, D.; Guo, Y. Hybrid linear amplifier-involved detection for continuous variable quantum key distribution with thermal states. Chin. Phys. B 2020, 29, 050309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Huang, P.; Ma, H.; Wang, T.; Zeng, G. Passive-state preparation in continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2019, 52, 135502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Li, S.; Xu, Z. Experimental underwater quantum key distribution. Opt. Express 2019, 29, 8725–8736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiskett, P.A.; Lamb, R.A. Underwater optical communications with a single photon-counting system. Adv. Photon Count. Tech. VIII 2014, 9114, 113–127. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.-Q.; Yan, Z.-Q.; Gao, J.; Li, Z.-M.; Zhou, H.; Dou, J.-P.; Jin, X.-M. Decoy-state quantum key distribution over a long-distance high-loss air-water channel. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2021, 15, 024060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xie, C.; Huang, P.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, D.; Zeng, G. Channel-parameter estimation for satellite-to-submarine continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 97, 052326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Ding, H.; Wang, Q. Implementation of Machine Learning in Quantum Key Distributions. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 25, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Wang, Q. Predicting optimal parameters with random forest for quantum key distribution. Quantum Inf. Process. 2020, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, C.; Bai, J.; Xue, Y.; Fu, Y.; Yin, H.; Chen, Z. Neural network-based prediction of the secret-key rate of quantum key distribution. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadian, M.; Ruiz, M.; Comellas, J.; Velasco, L. Cost-Effective ML-Powered Polarization-Encoded Quantum Key Distribution. J. Light. Technol. 2023, 13, 4119–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frédéric, G.; Gilles, V.A.; Jérôme, W.; Rosa, B.; Nicolas, C.; Philippe, J.G. Quantum key distribution using gaussian-modulated coherent states. Nature 2003, 6920, 238–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Mao, Y.; Ruan, X.; Guo, Y. Security of quantum communications in oceanic turbulence. Phys. Rev. A 2021, 104, 052613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haltrin, V.I.; Kattawar, G.W. Effects of Raman Scattering and Fluorescence on Apparent Optical Properties of Seawater; Texas A&M University: College Station, TX, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Yentsch, C.S. The influence of phytoplankton pigments on the colour of sea water. Deep. Sea Res. 1953 1960, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elman, J.L. Finding Structure in Time. Cogn. Sci. 1990, 2, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, Y.; Hou, S. A novel optimized GA–Elman neural network algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ruan, X.; Zuo, Z.; Guo, Y. Improving the discretely modulated underwater continuous-variable quantum key distribution with heralded hybrid linear amplifier. Phys. Scr. 2021, 6, 065103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaviani, C.; Spedalieri, G.; Braunstein, S.L.; Pirandola, S. A Continuous-variable quantum cryptography with an untrusted relay: Detailed security analysis of the symmetric configuration. Phys. Rev. A 2015, 91, 022320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, L.; Usenko, C.V.; Filip, R. Long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution with efficient channel estimation. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 6, 062310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirandola, O.S. Finite-size analysis of measurement-device-independent quantum cryptography with continuous variables. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 96, 4aPta1. [Google Scholar]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, J.; Wu, H.; Guo, Y. Passive Continuous Variable Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution Predictable with Machine Learning in Oceanic Turbulence. Entropy 2024, 26, 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26030207
Yi J, Wu H, Guo Y. Passive Continuous Variable Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution Predictable with Machine Learning in Oceanic Turbulence. Entropy. 2024; 26(3):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26030207
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Jianmin, Hao Wu, and Ying Guo. 2024. "Passive Continuous Variable Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution Predictable with Machine Learning in Oceanic Turbulence" Entropy 26, no. 3: 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26030207
APA StyleYi, J., Wu, H., & Guo, Y. (2024). Passive Continuous Variable Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution Predictable with Machine Learning in Oceanic Turbulence. Entropy, 26(3), 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26030207






