Stochastic Gradient Descent for Kernel-Based Maximum Correntropy Criterion
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (a)
- This work establishes the theoretical foundations for SGD applied to MCC. Some important convergence properties are provided, in which the role of the robustness parameter is presented.
- (b)
- We introduce the Polyak–Łojasiewicz (PL) condition to derive the explicit convergence rates of algorithm (4). A global linear convergence rate is achieved when the step size is chosen properly.
2. Main Results
- (a)
- The generalization error is uniformly bounded. More precisely, there is some constant C, such that
- (b)
- There is some constant , such that
- (a)
- If for any , then
- (b)
- If , then
- (a)
- If and , then
- (b)
- If and , then
- (c)
- If there exists some , such that for any , , then
3. Discussions
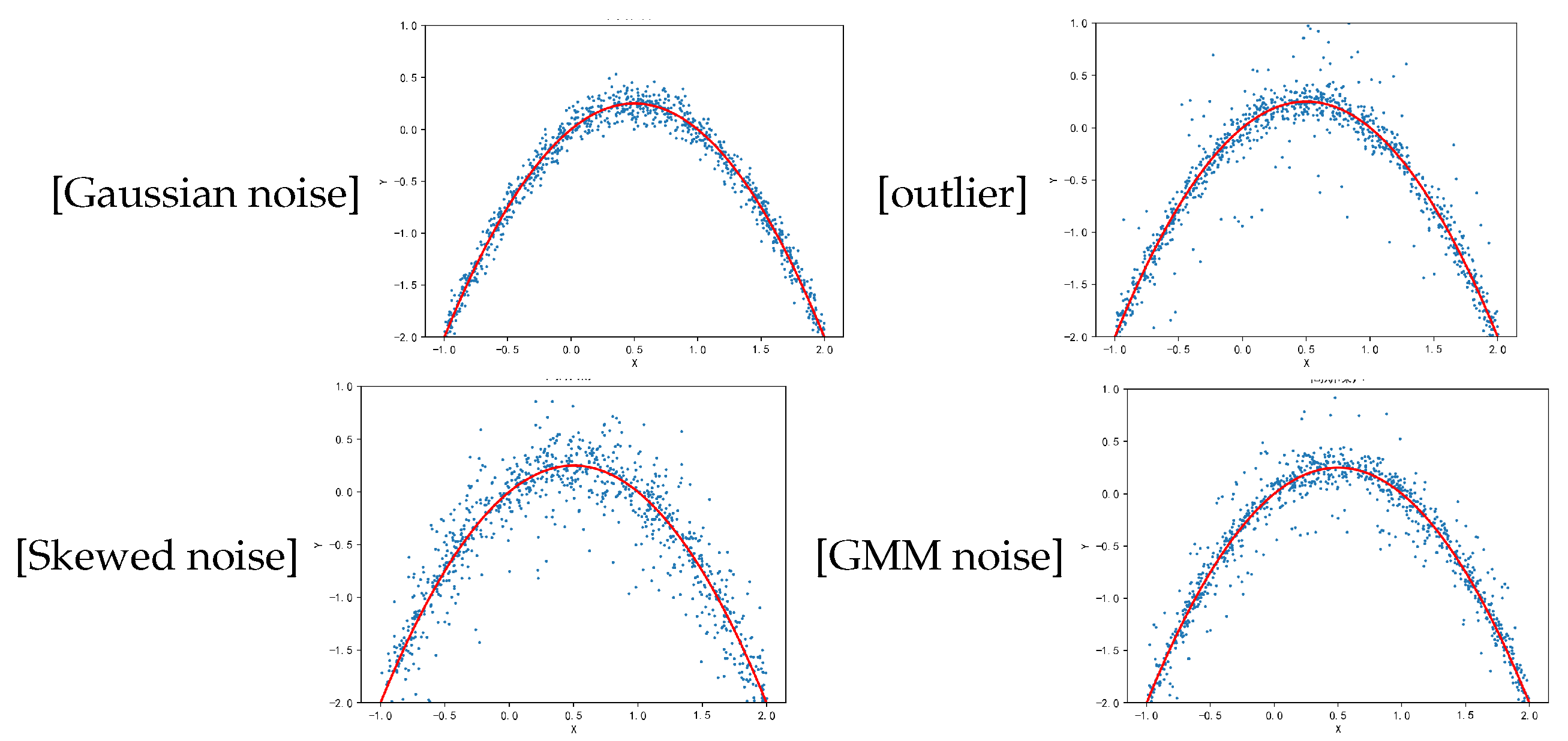
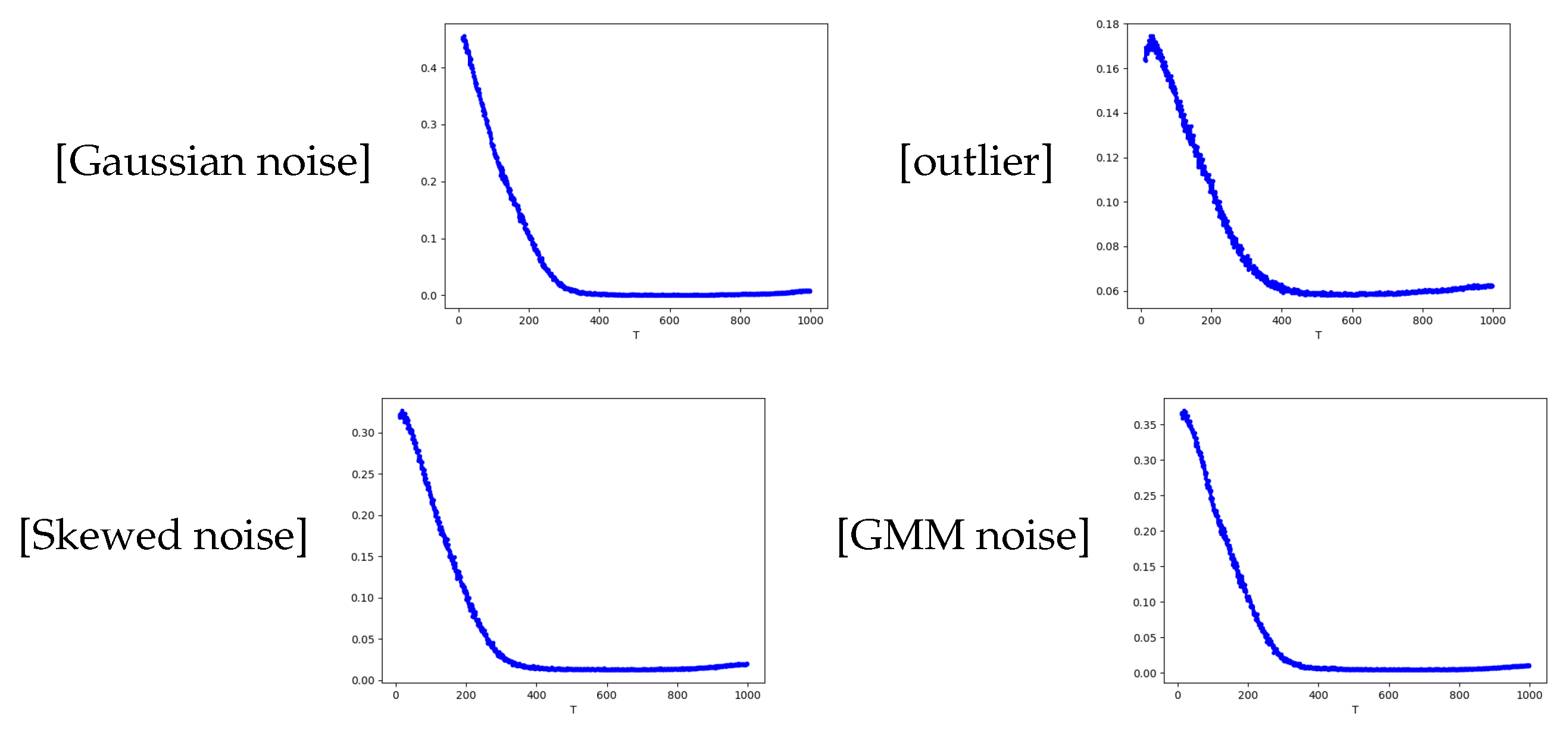
4. Simulation Validation
- Gaussion noise: ∼
- outlier noise: noise ∼, noise ∼
- skewed noise: , where
- GMM noise: noise ∼, noise is generated by the following density probability
5. Proofs
6. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, B.; Xing, L.; Liang, J.; Zheng, N.; Principe, J.C. Steady-state mean-square error analysis for adaptive filtering under the maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2014, 21, 880–884. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Shen, L.; Chen, B. An efficient parameter optimization of maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2023, 30, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhao, H.; Zakharov, Y. An improved variable kernel width for maximum correntropy criterion algorithm. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2020, 67, 1339–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, L.; Shi, L.; Zhu, G.; Yang, X. Euclidean direction search algorithm based on maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2023, 30, 1032–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Principe, J.C. Information Theoretic Learning: Renyi’s Entropy and Kernel Perspectives; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Pokharel, P.P.; Principe, J.C. Correntropy: Properties and Applications in Non-Gaussian Signal Processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2007, 55, 5286–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Huang, X.; Shi, L.; Yang, Y.; Suykens, J.A. Learning with the Maximum Correntropy Criterion Induced Losses for Regression. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2015, 16, 993–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, C.; Xiang, S.; Zhu, F. Robust Hyperspectral Unmixing with Correntropy-Based Metric. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 4027–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Y. Kernel-based sparse regression with the correntropy-induced loss. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 2018, 44, 144–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Zheng, W.; Hu, B. Maximum Correntropy Criterion for Robust Face Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 1561–1576. [Google Scholar]
- Bessa, R.J.; Miranda, V.; Gama, J. Entropy and Correntropy Against Minimum Square Error in Offline and Online Three-Day Ahead Wind Power Forecasting. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2009, 24, 1657–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H.; Principe, J.C. Maximum correntropy Kalman filter. Automatica 2017, 76, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Correntropy kernel learning for nonlinear system identification with outliers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 53, 5248–5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Park, I.; Principe, J.C. An information theoretic approach of designing sparse kernel adaptive filters. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2009, 20, 1950–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heravi, A.R.; Hodtani, G.A. A new correntropy-based conjugate gradient backpropagation algorithm for improving training in neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 16, 6252–6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Dang, L.; Chen, B.; Duan, S.; Wang, L.; Tse, C.K. Random fourier filters under maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2018, 65, 3390–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X.; Ma, W.; Chen, B. Kernel recursive maximum correntropy. Signal Process. 2015, 117, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Duan, S.; Wang, L.; Tan, H. Quantized kernel maximum correntropy and its mean square convergence analysis. Digit. Signal Process. 2017, 63, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.; Shi, W.; Wang, S. Robust multikernel maximum correntropy filters. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2020, 67, 1159–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Chen, B.; Príncipe, J.C. Kernel adaptive filtering with maximum correntropy criterion. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, San Jose, CA, USA, 31 July–5 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, K.; Iu, H.H.; Wang, S. Kernel correntropy conjugate gradient algorithms based on half-quadratic optimization. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 51, 5497–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T. Solving large scale linear prediction problems using stochastic gradient descent algorithms. In Proceedings of the Twenty-First International Conference on Machine Learning, Banff, AB, Canada, 4–8 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, D.; Lin, M.; Zhang, C. On the Generalization Ability of Online Gradient Descent Algorithm Under the Quadratic Growth Condition. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 29, 5008–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Y.; Zhou, D.X. Unregularized Online Learning Algorithms with General Loss Functions. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 2017, 42, 224–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronszajn, N. Theory of reproducing kernels. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 1950, 68, 337–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Fan, J.; Suykens, J.A.K. A Statistical Learning Approach to Modal Regression. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Ying, Y. Learning with correntropy-induced losses for regression with mixture of symmetric stable noise. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 2020, 48, 795–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadimi, S.; Lan, G. Stochastic First- and Zeroth-order Methods for Nonconvex Stochastic Programming. Siam J. Optim. 2013, 23, 2341–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Roth, S.; Black, M.J. Secrets of Optical Flow Estimation and Their Principles. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Hu, T.; Shi, L. Gradient Descent for Robust Kernel-based Regression. Inverse Probl. 2018, 34, 065009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Hu, T.; Li, G.; Tang, K. Stochastic Gradient Descent for Nonconvex Learning Without Bounded Gradient Assumptions. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 31, 4394–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, H.; Nutini, J.; Schmidt, M. Linear Convergence of Gradient and Proximal-Gradient Methods Under the Polyak-Lojasiewicz Condition. In Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases: European Conference; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Polyak, B.T. Gradient methods for the minimisation of functionals. USSR Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 1963, 3, 864–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, M.N.; Pardalos, P.M.; Principe, J.C. On the optimization properties of the correntropic loss function in data analysis. Optim. Lett. 2014, 8, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y. New insights into learning with correntropy-based regression. Neural Comput. 2021, 33, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Hu, T. Online gradient descent for kernel-based maximum correntropy criterion. Entropy 2019, 21, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, Y.; Zhou, D. Online regularized classification algorithm. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 4775–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, L.J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Duchi, J.; Hazan, E.; Singer, Y. Adaptive subgradient methods for online learning and stochastic optimization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2121–2159. [Google Scholar]
- Tieleman, T.; Hinton, G. RMSProp: Divide the gradient by a running average of its recent magnitude. Coursera Neural Netw. Mach. Learn. 2012, 4, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Reddi, S.J.; Kale, S.; Kumar, S. On the convergence of Adam and beyond. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, T. Kernel-based maximum correntropy criterion with gradient descent method. Commun. Pure Appl. Anal. 2020, 19, 4159–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinwart, I.; Christmann, A. Support Vector Machines; Springer Science and Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, T.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, D.-X. Distributed kernel gradient descent algorithm for minimum error entropy principle. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 2020, 49, 229–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Wang, B.; Peng, C.; Yin, H. Stochastic Gradient Descent for Kernel-Based Maximum Correntropy Criterion. Entropy 2024, 26, 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26121104
Li T, Wang B, Peng C, Yin H. Stochastic Gradient Descent for Kernel-Based Maximum Correntropy Criterion. Entropy. 2024; 26(12):1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26121104
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tiankai, Baobin Wang, Chaoquan Peng, and Hong Yin. 2024. "Stochastic Gradient Descent for Kernel-Based Maximum Correntropy Criterion" Entropy 26, no. 12: 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26121104
APA StyleLi, T., Wang, B., Peng, C., & Yin, H. (2024). Stochastic Gradient Descent for Kernel-Based Maximum Correntropy Criterion. Entropy, 26(12), 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26121104






