Quantum Computing in Community Detection for Anti-Fraud Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Quantum Computing for Anti-Fraud Applications
1.2. Community Detection Algorithms
1.3. The QUBO Model for Community Detection
1.4. The Numerical Simulation
1.5. The Equivalence Between the QUBO and Ising Models
2. Materials and Methods
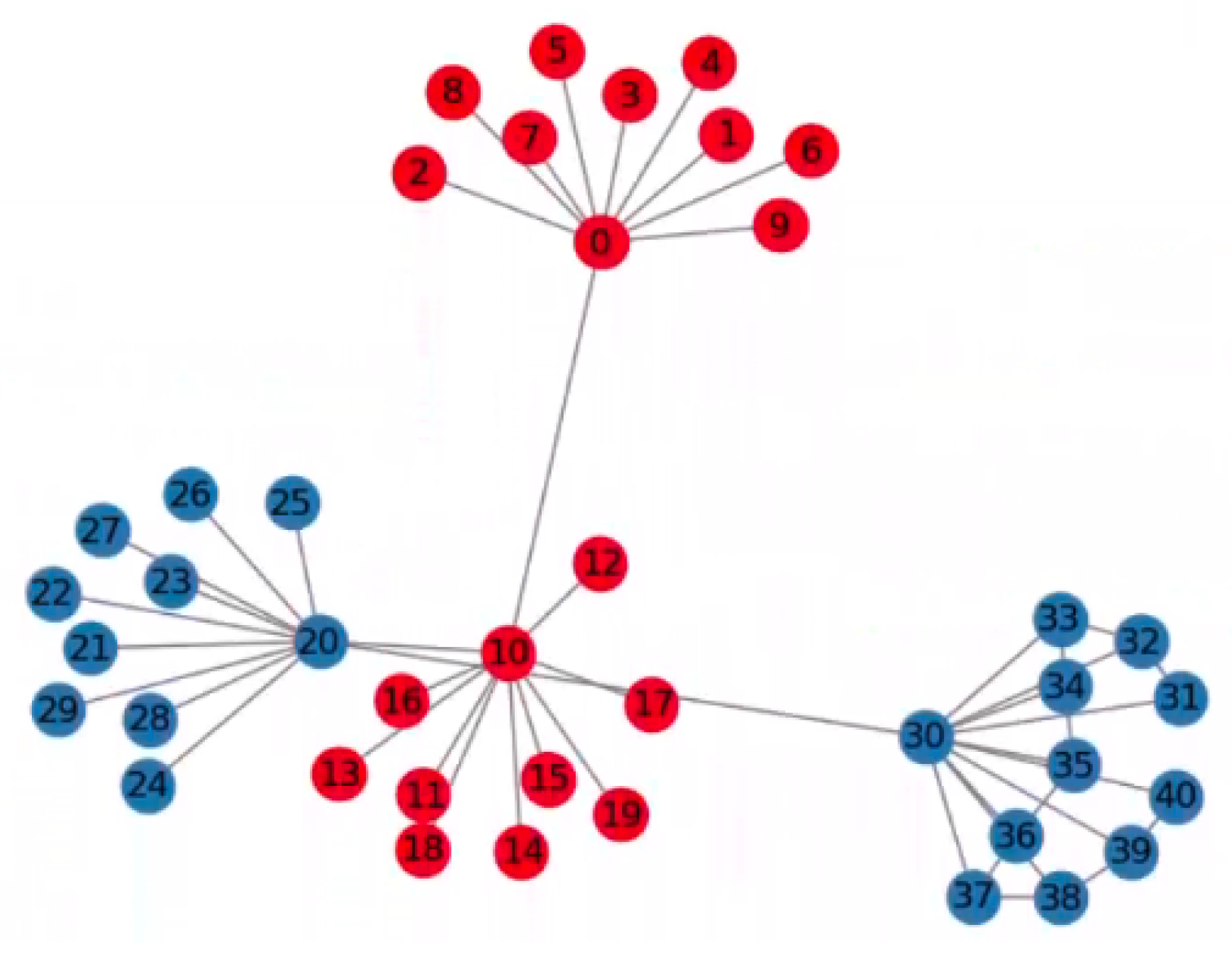
2.1. Graph Formation
2.2. Data Preprocessing
2.3. The CIM Setup
3. Result
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paul, B. The computer as a physical system: A microscopic quantum mechanical Hamiltonian model of computers as represented by Turing machines. J. Stat. Phys. 1980, 22, 563–591. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, B. Quantum mechanical models of Turing machines that dissipate no energy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1982, 48, 1581–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Feynman, R.P. Simulating physics with computers. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 1982, 21, 467–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajagekar, A.; Humble, T.; You, F. Quantum computing based hybrid solution strategies for large-scale discrete-continuous optimization problems. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2020, 132, 106630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, D.E.; Penrose, R. Quantum computational networks. Proc. R. Soc. A 1989, 425, 73–90. [Google Scholar]
- Albash, T.; Lidar, D.A. Adiabatic quantum computation. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2018, 90, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Aihara, K.; Leleu, T.; Kawarabayashi, K.I.; Kako, S.; Fejer, M.; Inoue, K.; Takesue, H. Coherent Ising machines-optical neural networks operating at the quantum limit. NPJ Quant. Inf. 2017, 3, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, J.; Schuman, D.; Benkard, M.; Holger, T.; Sajko, W.; Kölle, M.; Nüßlein, J.; Sünkel, L.; Salomon, O.; Linnhoff-Popien, C. Exploring Unsupervised Anomaly Detection with Quantum Boltzmann Machines in Fraud Detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.04998. [Google Scholar]
- Bikku, T.; Thota, S.; Shanmugasundaram, P. A Novel Quantum Neural Network Approach to Combating Fake Reviews. Int. J. Netw. Distrib. Comput. 2024, 12, 12205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innan, N.; Sawaika, A.; Dhor, A. Financial fraud detection using quantum graph neural networks. Quantum Mach. Intell. 2024, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, A.I.; Faccia, A. Quantum Algorithms: A New Frontier in Financial Crime Prevention. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.18322. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Marandi, A.; Wen, K.; Byer, R.L.; Yamamoto, Y. Coherent Ising machine based on degenerate optical parametric oscillators. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 88, 063853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marandi, A.; Wang, Z.; Takata, K.; Byer, R.L.; Yamamoto, Y. Network of time-multiplexed optical parametric oscillators as a coherent ising machine. Nat. Photon. 2014, 8, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, P.L.; Marandi, A.; Haribara, Y.; Hamerly, R.; Langrock, C.; Tamate, S.; Inagaki, T.; Takesue, H.; Utsunomiya, S. A fully programmable 100-spin coherent Ising machine with all-to-all connections. Science 2016, 354, 614–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, T.; Haribara, Y.; Igarashi, K.; Sonobe, T.; Tamate, S.; Honjo, T.; Marandi, A.; McMahon, P.L.; Umeki, T.; Enbutsu, K. A coherent Ising machine for 2000-node optimization problems. Science 2016, 354, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honjo, T.; Sonobe, T.; Inaba, K.; Inagaki, T.; Ikuta, T.; Yamada, Y.; Kazama, T.; Enbutsu, K.; Umeki, T.; Kasahara, R.; et al. 100,000-spin coherent Ising machine. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, 0952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Fan, C.-R.; Liu, L.; Wen, K.; Wang, C. Speed-up coherent Ising machine with a spiking neural network. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 3676–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Liu, L.; Song, J.-Y.; Wen, K.; Wang, C. Recent progress on coherent computation based on quantum squeezing. AAPPS Bull. 2023, 33, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aonishi, T.; Mimura, K.; Okada, M.; Yamamoto, Y. L0 regularization-based compressed sensing with quantum-classical hybrid approach. Quant. Sci. Technol. 2022, 7, 035013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takabatake, K.; Yanagisawa, K.; Akiyama, Y. Solving generalized polyomino puzzles using the Ising model. Entropy 2022, 24, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Cai, D.; Jia, B.; Cao, C.; Ma, Y.; Wei, H.; Wen, K.; Qian, L. Optical experimental solution for the multiway number partitioning problem and its application to computing power scheduling. Sci. Chin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 2023, 66, 290313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Pan, C.; Hou, S.; Lu, X.; Cui, C.; Wen, J.; Xu, J.; Cao, C.; Ma, Y.; et al. Quantum computing for MIMO beam selection problem: Model and optical experimental solution. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.12389. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Yang, C.; Wen, K.; Wu, W.; Guo, Y. Quantum computing for several AGV scheduling models. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, J.; Su, J.; Li, T.; Cao, C.; Ma, Y.; Wei, H.; Huang, Z.; Qian, L.; Wen, K.; Zhang, J.; et al. Encoding molecular docking for quantum computers. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2023, 19, 9018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, D.; Wen, Q.; Qin, S.; Gao, F. A quantum federated learning framework for classical clients. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 2024, 67, 250311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, J.; Song, Y.; Qin, S.; Wen, Q.; Gao, F. An efficient quantum proactive incremental learning algorithm. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 2025, 68, 210313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Zhang, T.; Jing, Z.; Wu, K.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Bu, W.; Zheng, K.; Kang, J.; et al. A scalable universal Ising machine based on interaction-centric storage and compute-in-memory. Nat. Electron. 2024, 7, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Louvain | SA (14-bit) | SA (8-bit) | CIM (14-bit) | CIM (8-bit) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| modularity (median) | 0.7062 | 0.5898 | 0.5253 | 0.6828 | 0.7088 |
| modularity (max) | 0.7089 | 0.7038 | 0.6967 | 0.7089 | 0.7089 |
| time-to-solution in milliseconds (median) | 35.474 | 2,414,001.600 | 269,003.000 | 1.860 | 0.263 |
| time-to-solution in milliseconds (min) | 24.517 | 104,872.000 | 259,830.332 | 0.367 | 0.093 |
| success rate | 1.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 15.0% | 32.0% |
| fraud probability of the high-risk community | 14.4% | 14.0% | 14.3% | 14.4% | 14.4% |
| recall rate of fraud accounts | 68.4% | 63.2% | 68.4% | 68.4% | 68.4% |
| ID | Node Count | Fraudulent Accounts | Fraud Probability | Recall Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 61 | 1 | 0.016393 | 0.052632 |
| 1 | 80 | 5 | 0.062500 | 0.263158 |
| 2 | 77 | 0 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 3 | 90 | 13 | 0.144444 | 0.684211 |
| Total | 308 | 19 | 0.061688 | 1.000000 |
| ID | Node Count | Fraudulent Accounts | Fraud Probability | Recall Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 61 | 1 | 0.016393 | 0.052632 |
| 1 | 90 | 13 | 0.144444 | 0.684211 |
| 2 | 80 | 5 | 0.062500 | 0.263158 |
| 3 | 77 | 0 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| Total | 308 | 19 | 0.061688 | 1.000000 |
| ID | Node Count | Fraudulent Accounts | Fraud Probability | Recall Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 76 | 4 | 0.052632 | 0.210526 |
| 1 | 78 | 1 | 0.012821 | 0.052632 |
| 2 | 91 | 13 | 0.142857 | 0.684211 |
| 3 | 63 | 1 | 0.015873 | 0.052632 |
| Total | 308 | 19 | 0.061688 | 1.000000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Ju, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Cao, X.; Ma, Y.; et al. Quantum Computing in Community Detection for Anti-Fraud Applications. Entropy 2024, 26, 1026. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26121026
Wang Y, Yang X, Ju C, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Xu Q, Wang Y, Gao X, Cao X, Ma Y, et al. Quantum Computing in Community Detection for Anti-Fraud Applications. Entropy. 2024; 26(12):1026. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26121026
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yanbo (Justin), Xuan Yang, Chao Ju, Yue Zhang, Jun Zhang, Qi Xu, Yiduo Wang, Xinkai Gao, Xiaofeng Cao, Yin Ma, and et al. 2024. "Quantum Computing in Community Detection for Anti-Fraud Applications" Entropy 26, no. 12: 1026. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26121026
APA StyleWang, Y., Yang, X., Ju, C., Zhang, Y., Zhang, J., Xu, Q., Wang, Y., Gao, X., Cao, X., Ma, Y., & Wu, J. (2024). Quantum Computing in Community Detection for Anti-Fraud Applications. Entropy, 26(12), 1026. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26121026





