Channel Modeling and Quantization Design for 3D NAND Flash Memory
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Related Work
1.2. Contributions
- For the first time, we derive an analytic channel model for 3D NAND MLC flash memory, which considers major sources of errors.
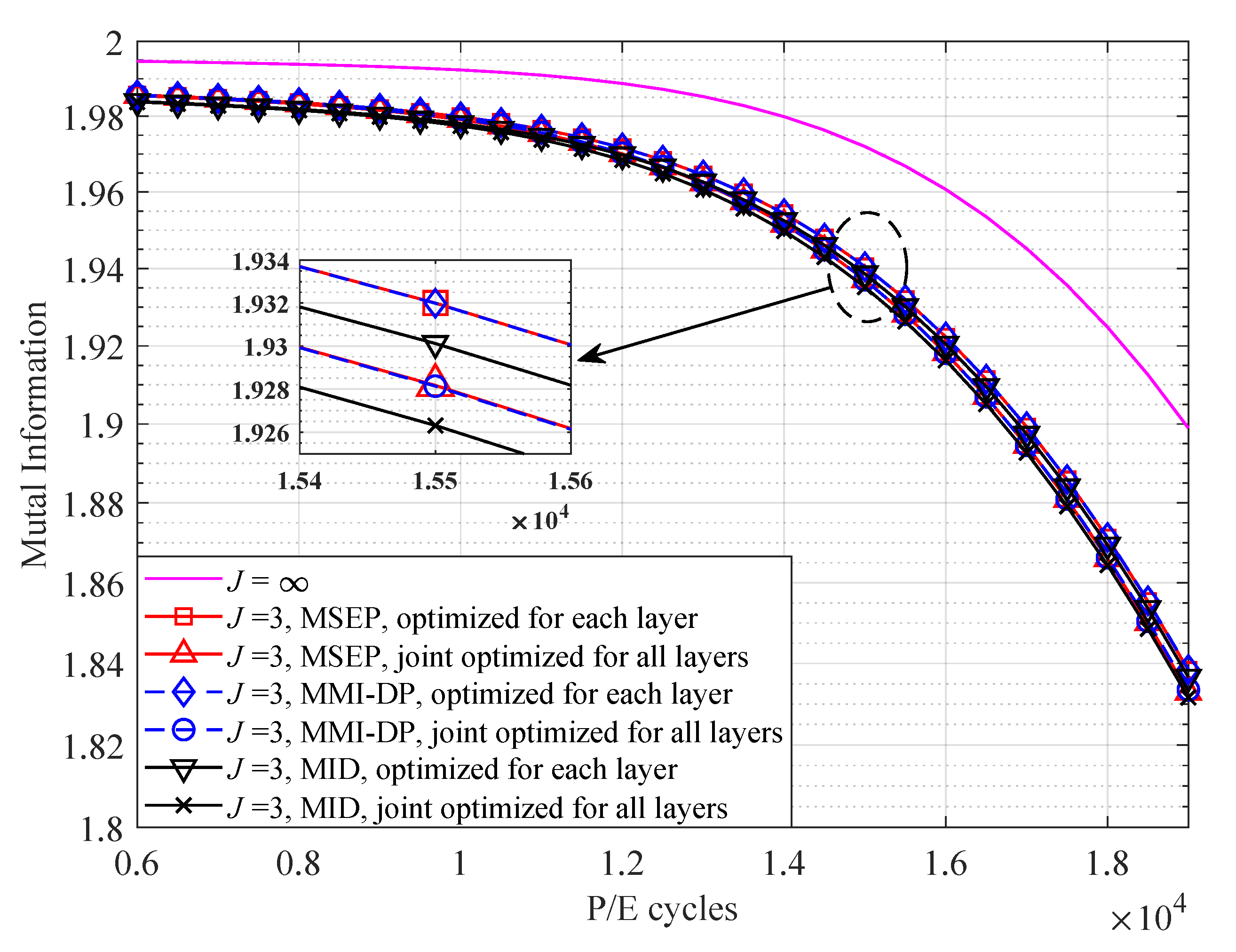
- Rather than optimizing read-voltage thresholds for each layer, we jointly design the quantization for multiple layers of 3D MLC flash memory by MMI. By doing this, the number of total read thresholds for multiple layers can be greatly reduced, such that the storage cost and read latency can be significantly decreased.
- A dynamic programming (DP) algorithm is proposed to optimize read-voltage thresholds for 3D MLC flash memory by MMI of the joint channel.
- To further reduce the complexity of DP algorithm, the 3D MLC flash memory channel is simplified and a MI derivative (MID)-based method is developed to obtain read-voltage thresholds for ECCs with HDD.
2. Channel Modeling of 3D NAND MLC Flash Memory
2.1. 3D NAND Flash Memory Basics
2.2. Channel Modeling
2.2.1. Initial Threshold Voltage Distribution
2.2.2. Program/Erase Cycling Errors
2.2.3. Cell-to-Cell Interference
2.2.4. Early Retention Loss
2.2.5. Layer-to-Layer Process Variation
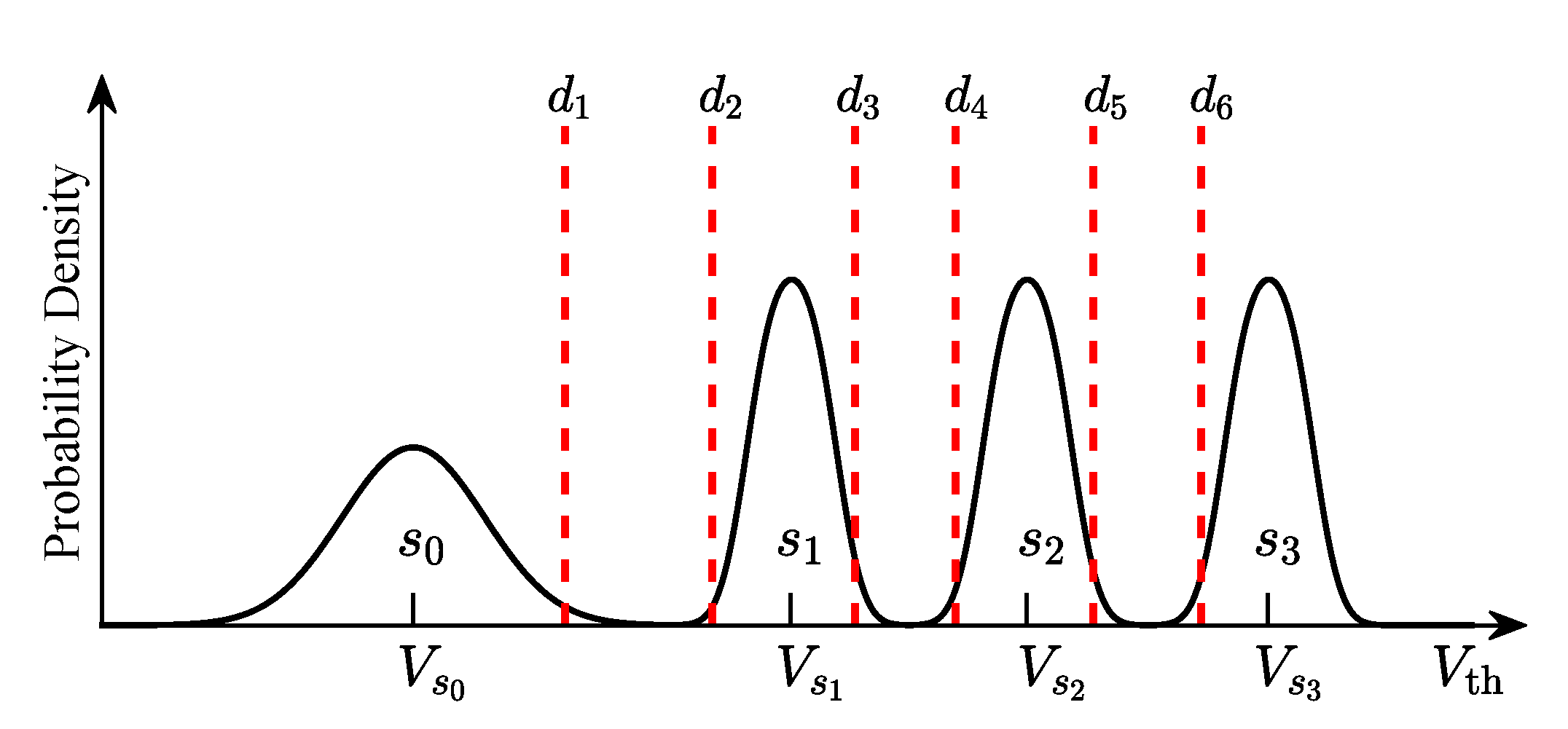
2.3. Quantized Model of 3D NAND Flash Memory
3. Quantization Design for 3D NAND Flash Memory
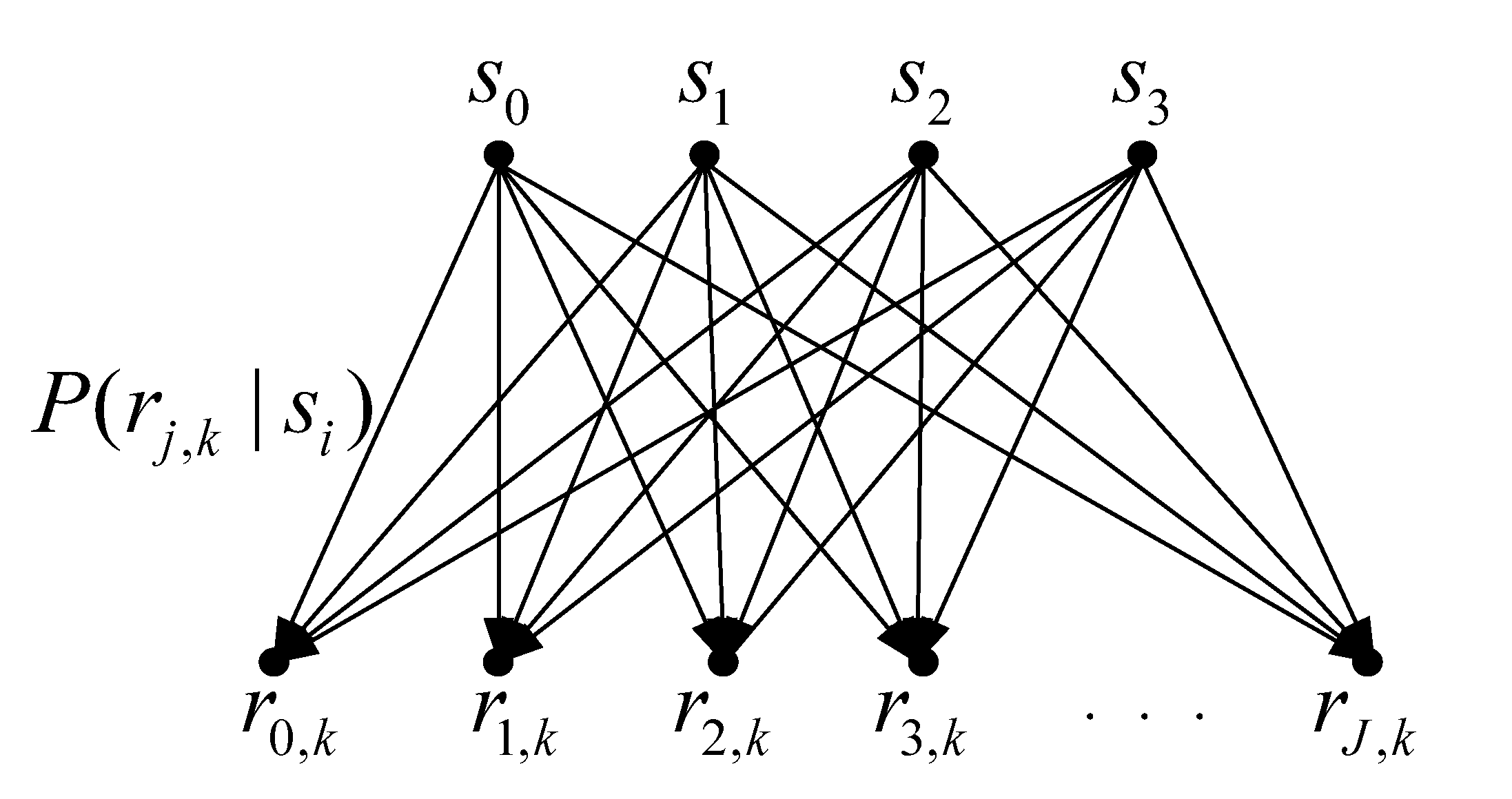
3.1. MI for 3D NAND MLC Flash Memory
3.2. MMI Quantization Design
| Algorithm 1: MMI-DP algorithm for searching optimal read-voltage thresholds in 3D flash memory. |
| Input:J, N, K, , , , . |
Output:.
|
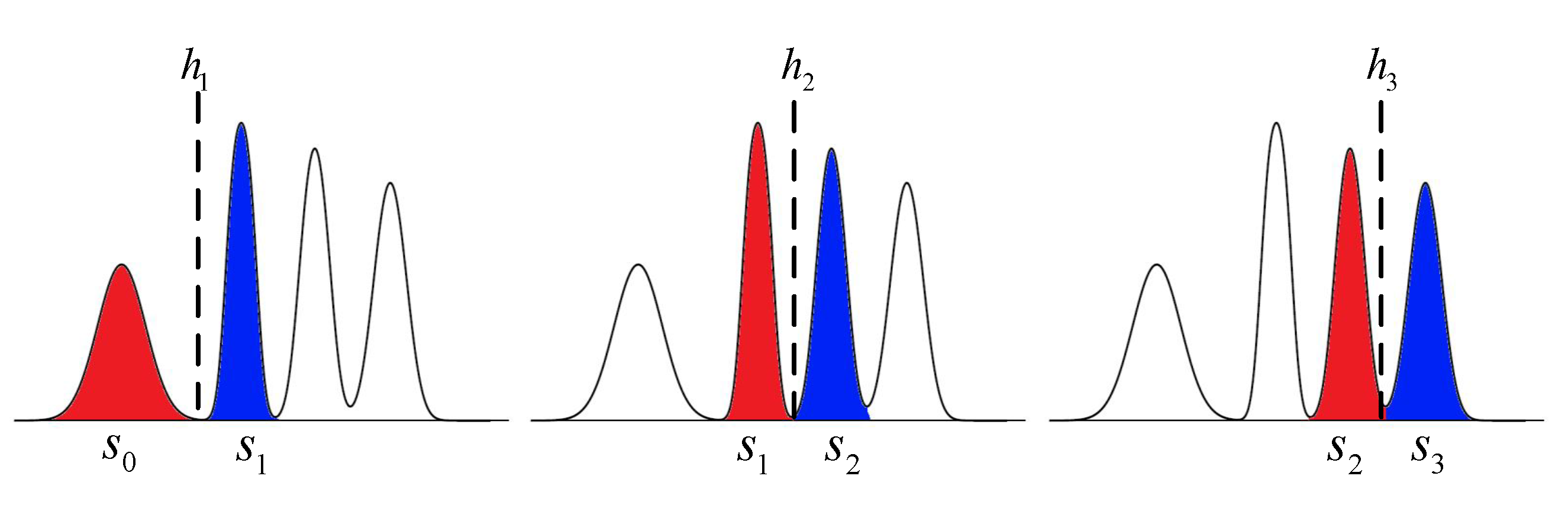
3.3. Read Thresholds Design for Hard Decision Decoding
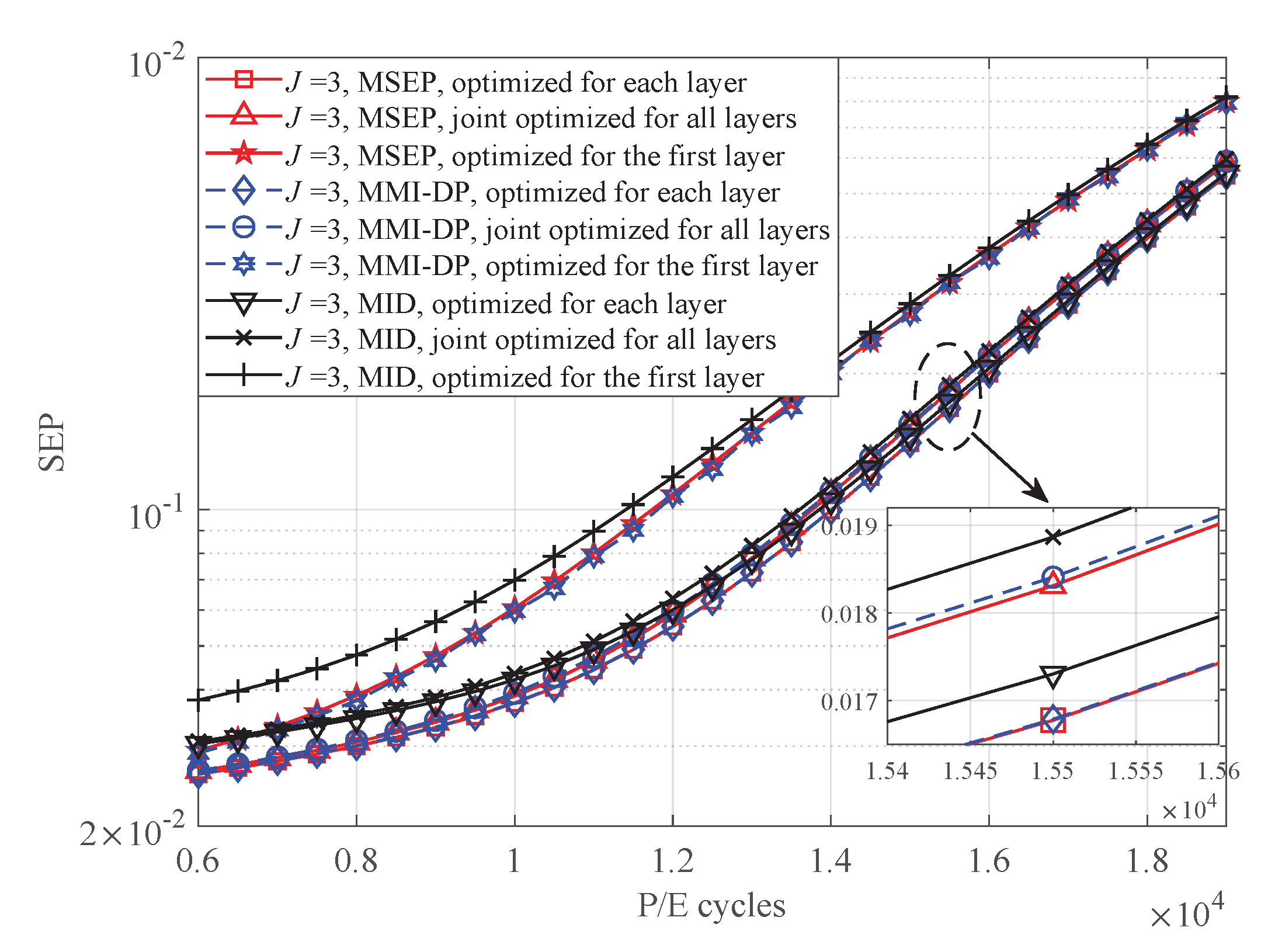
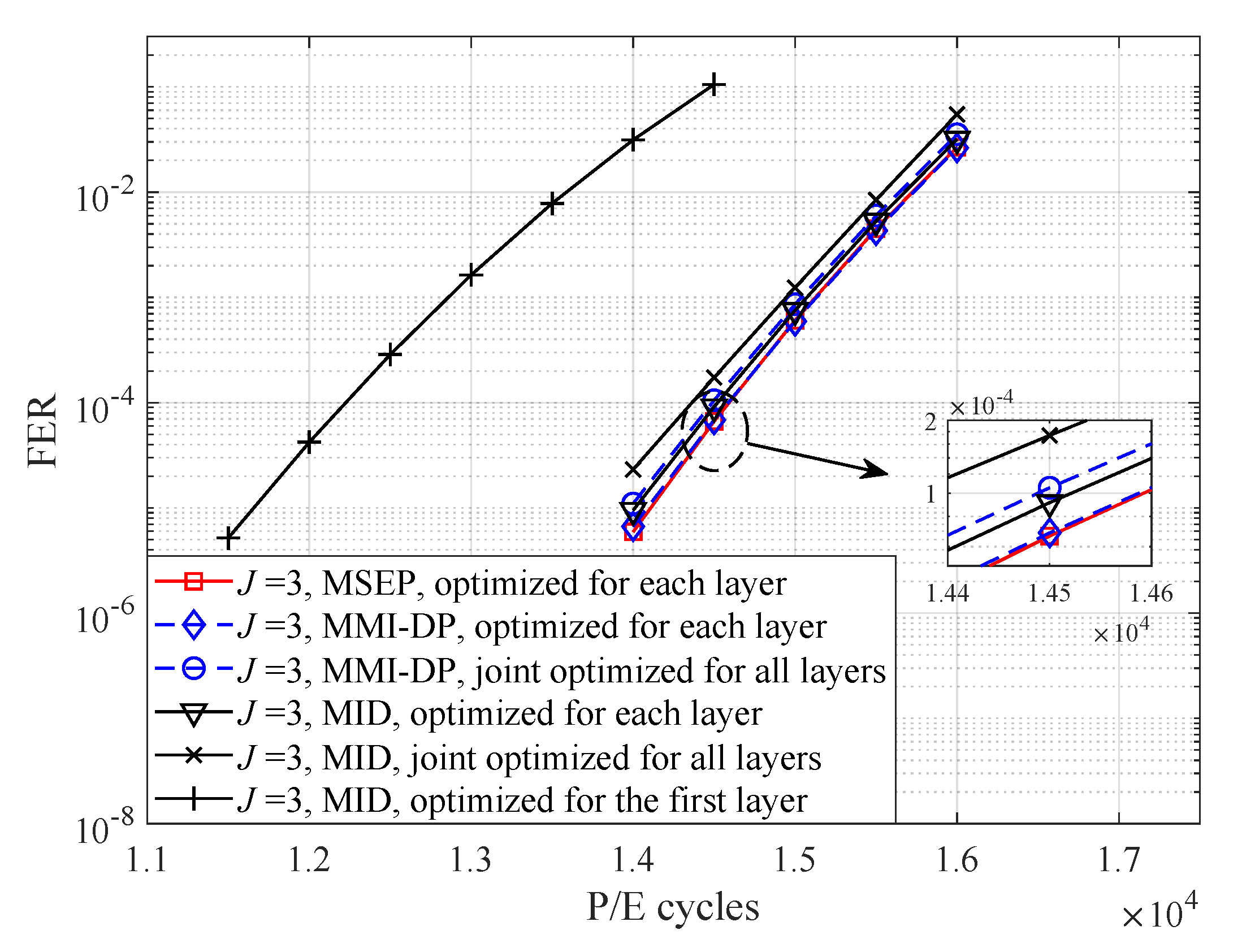
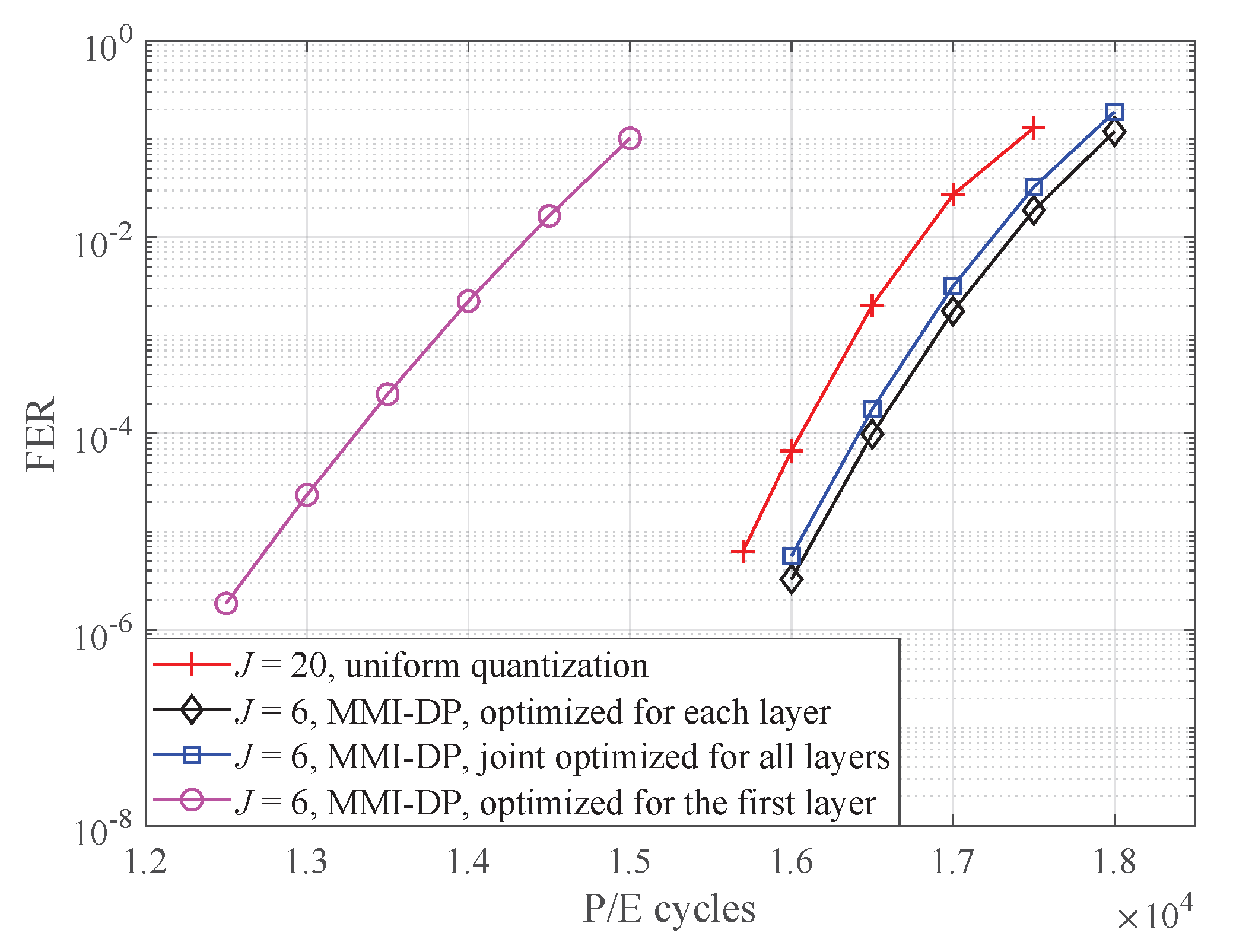
4. Numerical and Simulation Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Derivation of Equation (uid68)
References
- Kim, K. Future memory technology: Challenges and opportunities. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on VLSI Technology, Systems and Applications, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 21–23 April 2008; pp. 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, G.; Xie, N.; Zhang, T. On the use of soft-decision error-correction codes in NAND flash memory. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 2011, 58, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Haratsch, E.F. Noise modeling and capacity analysis for NAND flash memories. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, Honolulu, HI, USA, 29 June–4 July 2014; pp. 2262–2266. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Ghose, S.; Cai, Y.; Haratsch, E.F.; Mutlu, O. HeatWatch: Improving 3D NAND Flash Memory Device Reliability by Exploiting Self-Recovery and Temperature Awareness. In Proceeding of the IEEE International Symposium on High Performance Computer Architecture, Vienna, Austria, 24–28 February 2018; pp. 504–517. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Tan, J.; Mao, R.; Li, T. Temperature-aware persistent data management for LSM-tree on 3-D NAND flash memory. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2020, 39, 4611–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Mao, R. PVSensing: A Process-Variation-Aware Space Allocation Strategy for 3D NAND Flash Memory. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2021, 42, 1302–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, L.; Mao, R. P-Alloc: Process-variation tolerant reliability management for 3D charge-trapping flash memory. ACM Trans. Embed. Comput. Syst. 2017, 16, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheloni, R. 3D Flash Memories; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Ghose, S.; Cai, Y.; Haratsch, E.F.; Mutlu, O. Improving 3D NAND flash memory lifetime by tolerating early retention loss and process variation. Proc. ACM Meas. Anal. Comput. Syst. 2018, 2, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Gong, P.; Chen, T.; Michael, J.; Li, S. Modelling and characterization of NAND flash memory channels. Measurement 2015, 70, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Du, G.; Lun, Z.; Chen, W.; Liu, X. Modeling of program Vth distribution for 3-D TLC NAND flash memory. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2019, 62, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, Y.; Kim, M.; Chun, M.; Park, J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J. Exploiting process similarity of 3D flash memory for high performance SSDs. In Proceedings of the Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture, New York, NY, USA, 12–16 October 2019; pp. 211–223. [Google Scholar]
- Papandreou, N.; Pozidis, H.; Parnell, T.; Ioannou, N.; Pletka, R.; Tomic, S.; Breen, P.; Tressler, G.; Fry, A.; Fisher, T. Characterization and analysis of bit errors in 3D TLC NAND flash memory. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium, Monterey, CA, USA, 31 March–4 April 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, B.; Jang, S.H.; Yoon, J.; Lee, J.; Jeon, M.; Lee, Y.; Han, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.M.; Kim, D.H.; et al. Comprehensive evaluation of early retention (fast charge loss within a few seconds) characteristics in tube-type 3-D NAND flash memory. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology, Honolulu, HI, USA, 14–16 June 2016; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Gallager, R. Low-density parity-check codes. IRE Trans. Inf. Theory 1962, 8, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, W.; Xiong, S. Adapting layer RBERs variations of 3D flash memories via multi-granularity progressive LDPC reading. In Proceedings of the Annual Design Automation Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2–6 June 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, F.; Yu, Q.; Liu, W.; Cui, L.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, C. BeLDPC: Bit errors aware adaptive rate LDPC codes for 3D TLC NAND flash memory. In Proceedings of the Design, Automation and Test in Europe Conference and Exhibition, Grenoble, France, 9–13 March 2020; pp. 302–305. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Vakilinia, K.; Chen, T.; Courtade, T.; Dong, G.; Zhang, T. Enhanced precision through multiple reads for LDPC decoding in flash memories. IEEE J. Sel. Areas. Commun. 2014, 32, 880–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Wu, F.; Zhang, M.; Lu, Z.; Wan, J.; Xie, C. RBER-aware lifetime prediction scheme for 3D-TLC NAND flash memory. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 44696–44708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Hsieh, J. Differential Evolution Algorithm with Asymmetric Coding for Solving the Reliability Problem of 3D-TLC CT Flash-Memory Storage Systems. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr Circuits Syst. 2021, 41, 2863–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, C.; Guan, Y.; Cai, K. Read and write voltage signal optimization for multi-level-cell (MLC) NAND flash memory. IEEE Trans. Comm. 2016, 64, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; He, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Huo, Z. LIAD: A Method for Extending the Effective Time of 3D TLC NAND Flash Hard Decision. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr Circuits Syst. 2022, 42, 1705–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleato, B.; Agarwal, R.; Cioffi, J.; Qin, M.; Siegel, P. Adaptive read thresholds for NAND flash. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2015, 63, 3069–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wei, K.; Kong, L.; Shi, L.; Mei, Z.; Li, J.; Cai, K. DNN-aided read-voltage threshold optimization for MLC flash memory with finite block length. IET Commun. 2022, 16, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Z.; Cai, K.; Shi, L. Information theoretic bounds based channel quantization design for emerging memories. In Proceedings of the IEEE Information Theory Workshop, Guangzhou, China, 25–29 November 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Ye, M.; Cui, Y.; Shi, L.; Li, X.; Kuo, T.W.; Xue, C.J. Shaving retries with sentinels for fast read over high-density 3D flash. In Proceedings of the Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture, Athens, Greece, 9–13 March 2020; pp. 483–495. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Shi, L.; Cui, Y.; Xue, C. Exploiting asymmetric errors for LDPC decoding optimization on 3D NAND flash memory. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2020, 69, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, F.; Yu, Q.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Xie, C. Exploiting error characteristic to optimize read voltage for 3-D NAND flash memory. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2020, 67, 5490–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Moon, J. Characterization of Inter-Cell Interference in 3D NAND Flash Memory. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 2021, 68, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wu, F.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, M.; Yang, C.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xie, C. Modeling of threshold voltage distribution in 3d nand flash memory. In Proceedings of the Design, Automation and Test in Europe Conference and Exhibition, Grenoble, France, 1–5 February 2021; pp. 1729–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Bez, R.; Camerlenghi, E.; Modelli, A.; Visconti, A. Introduction to flash memory. Proc. IEEE 2003, 91, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Ghose, S.; Haratsch, E.; Luo, Y.; Mutlu, O. Error characterization, mitigation, and recovery in flash-memory-based solid-state drives. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 1666–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, K.; Suh, B.; Lim, Y.; Kim, J.; Choi, Y.; Koh, Y.; Lee, S.; Kwon, S.; Choi, B.; Yum, J.; et al. A 3.3 V 32 Mb NAND flash memory with incremental step pulse programming scheme. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1995, 30, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, J.; Yuan, W.; Yang, L. Improving 3D NAND SSD read performance by parallelizing read-retry. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2022, 42, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Li, S.; Zhang, T. Using data postcompensation and predistortion to tolerate cell-to-cell interference in MLC NAND flash memory. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 2010, 57, 2718–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, C.; Guan, Y.; Cai, K. Decision-directed retention-failure recovery with channel update for MLC NAND flash memory. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 2018, 65, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Xie, N.; Zhang, T. Enabling NAND flash memory use soft-decision error correction codes at minimal read latency overhead. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 2013, 60, 2412–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ash, R.B. Information Theory; Courier Corporation: Chicago, IL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Cai, K.; Song, W.; Mei, Z. Dynamic programming for sequential deterministic quantization of discrete memoryless channels. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021, 69, 3638–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable A | Variable A | Variable B | Variable B | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.74 | −67.27 | 0 | −0.028 | 1.94 | ||||
| −0.4 | 106.47 | 0 | 0 | 0.0075 | ||||
| −0.7 | 183.58 | 0 | 0 | −0.0447 | ||||
| −1.2 | 252.85 | 0 | 0 | −0.0308 | ||||
| −0.1 | 14.01 | 0 | −0.0048 | 0.185 | ||||
| 0.0098 | 8.2 | 0 | −0.0045 | 0.153 | ||||
| 0.0098 | 9.65 | −0.037 | ||||||
| 0.014 | 9.83 | −0.0034 | 0.0129 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Mei, Z.; Li, J.; Shu, F.; He, X.; Kong, L. Channel Modeling and Quantization Design for 3D NAND Flash Memory. Entropy 2023, 25, 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25070965
Wang C, Mei Z, Li J, Shu F, He X, Kong L. Channel Modeling and Quantization Design for 3D NAND Flash Memory. Entropy. 2023; 25(7):965. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25070965
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Cheng, Zhen Mei, Jun Li, Feng Shu, Xuan He, and Lingjun Kong. 2023. "Channel Modeling and Quantization Design for 3D NAND Flash Memory" Entropy 25, no. 7: 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25070965
APA StyleWang, C., Mei, Z., Li, J., Shu, F., He, X., & Kong, L. (2023). Channel Modeling and Quantization Design for 3D NAND Flash Memory. Entropy, 25(7), 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25070965









