Enhanced CycleGAN Network with Adaptive Dark Channel Prior for Unpaired Single-Image Dehazing
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel unpaired single-image dehazing model is proposed to fuse the dark channel prior and the enhanced CycleGAN.
- An adaptive DCP is designed to rely on the Wave-ViT semantic segmentation model, and it can accurately recover the transmittance and atmospheric light.
- In the enhanced CycleGAN method, the scattering coefficient is obtained from two different approaches in order to generate haze of various thicknesses and uneven distributions. is derived from the atmospheric scattering model, while is randomly sampled.
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Atmospheric Scattering Model
2.2. Dark Channel Prior
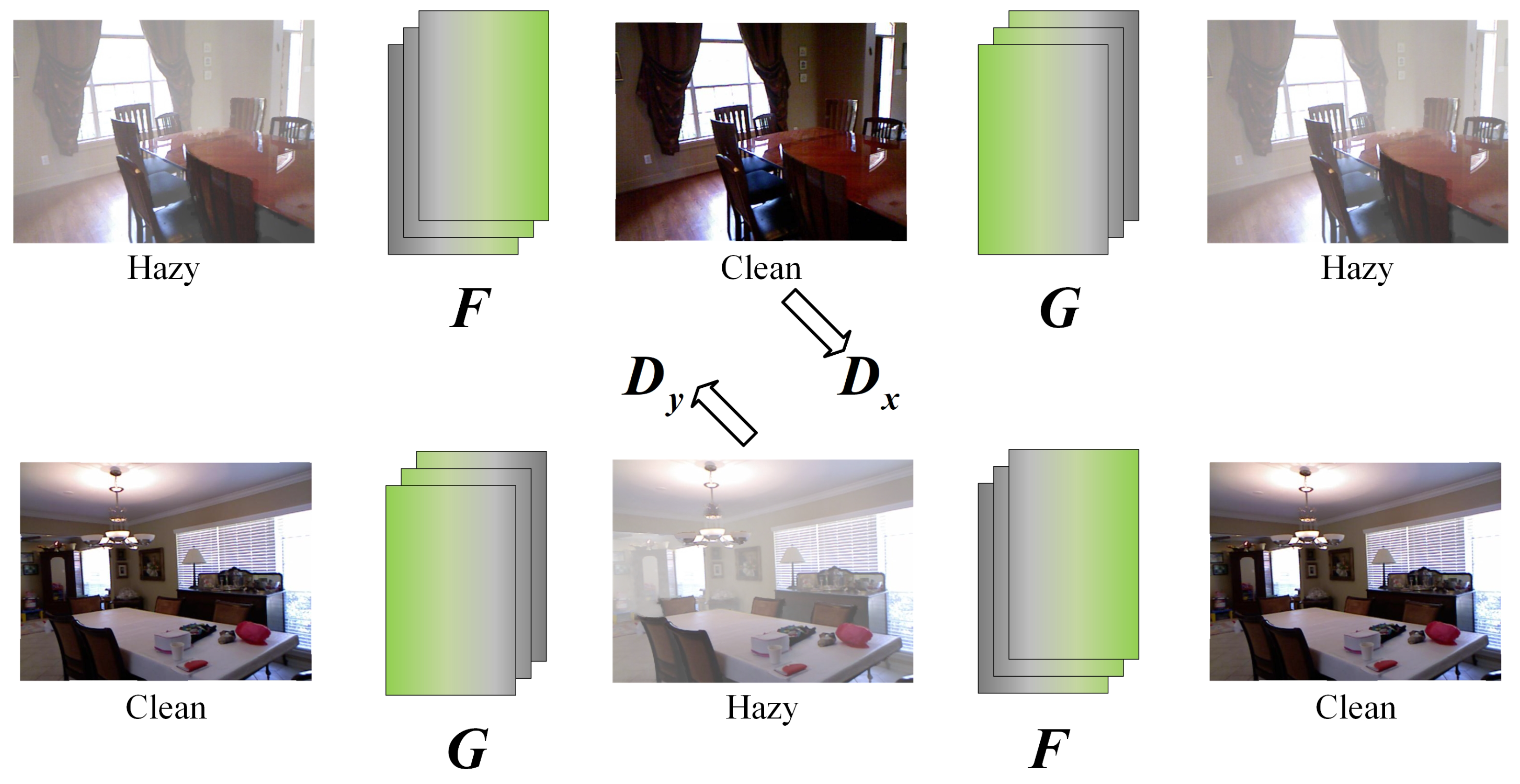
2.3. CycleGAN
3. Proposed Method
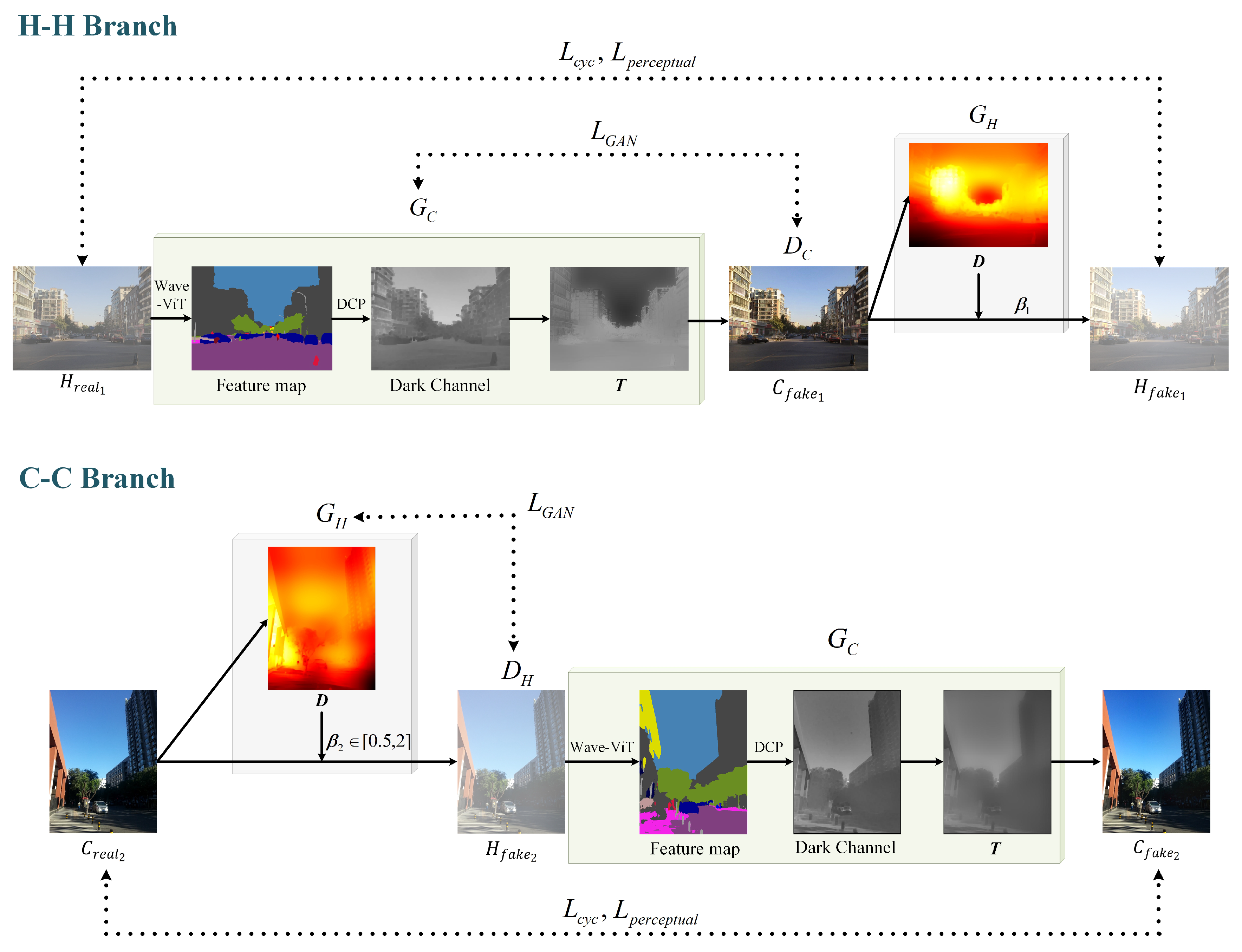
3.1. Network Structure
3.2. Adaptive DCP
3.3. Acquisition of Scattering Coefficient
3.4. Calculation of Losses
4. Experiment
4.1. Experimental Configuration
4.2. Results on Reference and No-Reference Datasets
4.3. Ablation Study
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jobson, D.; Rahman, Z.; Woodell, G. A multi-scale retinex for bridging the gap between color images and the human observation of scenes. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1997, 6, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Liu, Y.; Tan, Z. A fog-removing treatment based on combining high-frequency emphasis filtering and histogram equalization. Key Eng. Mater. 2011, 474, 2198–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Qi, G.; Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wei, H.; Liu, Y. Image dehazing by an artificial image fusion method based on adaptive structure decomposition. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 8062–8072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdran, A. Image dehazing by artificial multiple-exposure image fusion. Signal Process. 2018, 149, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wei, H.; Hu, G.; Li, Y.; Qi, G.; Mazur, N. A novel fast single image dehazing algorithm based on artificial multiexposure image fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 70, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattal, R. Single Image Dehazing. ACM Trans. Graph. 2008, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Sun, J.; Tang, X. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 33, 2341–2353. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Mai, J.; Shao, L. A fast single image haze removal algorithm using color attenuation prior. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 3522–3533. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, D. Non-local image dehazing. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1674–1682. [Google Scholar]
- Mccartney, E.J. Optics of the atmosphere: Scattering by molecules and particles. Phys. Bull. 1977, 28, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yuan, X.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y. Fast image dehazing method based on linear transformation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2017, 19, 1142–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.B.; Xu, X.M.; Jia, K.; Qing, C.M.; Tao, D.C. Dehazenet: An end-to-end system for single image haze removal. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 5187–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Patel, V.M. Densely connected pyramid dehazing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3194–3203. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Peng, X.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Feng, D. Aod-net: All-in-one dehazing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4770–4778. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; He, M.; FAN, A. Gated context aggregation network for image dehazing and deraining. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 7–11 January 2019; pp. 1375–1383. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Pan, J.; Li, Z.; Tang, J. Single image dehazing via conditional generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8202–8211. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, J.; Xie, Y. Enhanced pix2pix dehazing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 8160–8168. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Shi, Z.; Chen, J. Griddehazenet: Attention-based multi-scale network for image dehazing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 7314–7323. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.; Wang, Z.; Bai, Y.; Xie, X.; Jia, H. FFA-Net: Feature fusion attention network for single image dehazing. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 11908–11915. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Gou, Y.; Liu, J.Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, J.T.; Peng, X. Zero-shot image dehazing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 8457–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, L.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, Y. RefineDNet: A weakly supervised refinement framework for single image dehazing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 3391–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhuo, L.; Kuang, L.; Yu, T. USID-Net: Unsupervised single image dehazing network via disentangled representations. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Zhang, R.; Xu, L.; Liu, G.; Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q. U2D2 Net: Unsupervised Unified Image Dehazing and Denoising Network for Single Hazy Image Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Park, T.; Isola, P. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Engin, D.; Genc, A.; Ekenel, H.K. Cycledehaze: Enhanced cyclegan for single image dehazing. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 825–833. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y. Dehaze-AGGAN: Unpaired Remote Sensing Image Dehazing Using Enhanced Attention-Guide Generative Adversarial Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2022, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, R.; Zhang, L.; Guo, X.; Tao, D. Self-augmented Unpaired Image Dehazing via Density and Depth Decomposition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 2037–2046. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, C.T. Single Image Dehazing Based on Superpixel Segmentation Combined with Dark-Bright Channels. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2020, 57, 161023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; He, B.; Wu, Q. Single image dehazing based on dark channel prior and energy minimization. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2017, 25, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.; Kun, S.; Agyekum, K.O. A fast single-image dehazing algorithm based on dark channel prior and rayleigh scattering. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 73330–73339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Luo, H.; Hui, B.; Chang, Z. Haze removal using scale adaptive dark channel prior. Infrared Laser Eng. 2016, 45, 928002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Song, M. Single image dehazing algorithm based on sky segmentation and optimal transmission maps. Vis. Comput. 2023, 39, 997–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Qiu, J.; Tang, J. Single Image Dehazing Using Adaptive Sky Segmentation. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2021, 16, 1209–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hou, X.; Duan, J.; Qiu, G. End-to-end single image fog removal using enhanced cycle consistent adversarial networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 7819–7833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Hwang, J.N.; Gao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Jiang, X.; Huang, B. Dd-cyclegan: Unpaired image dehazing via double-discriminator cycle-consistent generative adversarial network. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2019, 82, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Pan, Y.; Li, Y.; Ngo, C.W.; Mei, T. Wave-vit: Unifying wavelet and transformers for visual representation learning. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision-ECCV 2022: 17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 328–345. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Ren, W.; Fu, D.; Tao, D.; Feng, D.; Zeng, W.; Wang, Z. Benchmarking singleimage dehazing and beyond. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 492–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancuti, C.O.; Ancuti, C.; Timofte, R.; Vleeschouwer, C.D. O-HAZE: A Dehazing Benchmark with Real Hazy and Haze-Free Outdoor Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18-22 June 2018; pp. 754–762. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, L.; Huang, S.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, S.; Yang, Y. Evaluation of defogging: A real-world benchmark dataset, a new criterion and baselines. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Shanghai, China, 8–12 July 2019; pp. 1840–1845. [Google Scholar]
- Fattal, R. Dehazing using color-lines. ACM Trans. Graph. 2014, 34, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O. The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 586–595. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, A.; Soundararajan, R.; Bovik, A.C. Making a “completely blind” image quality analyzer. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2012, 20, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
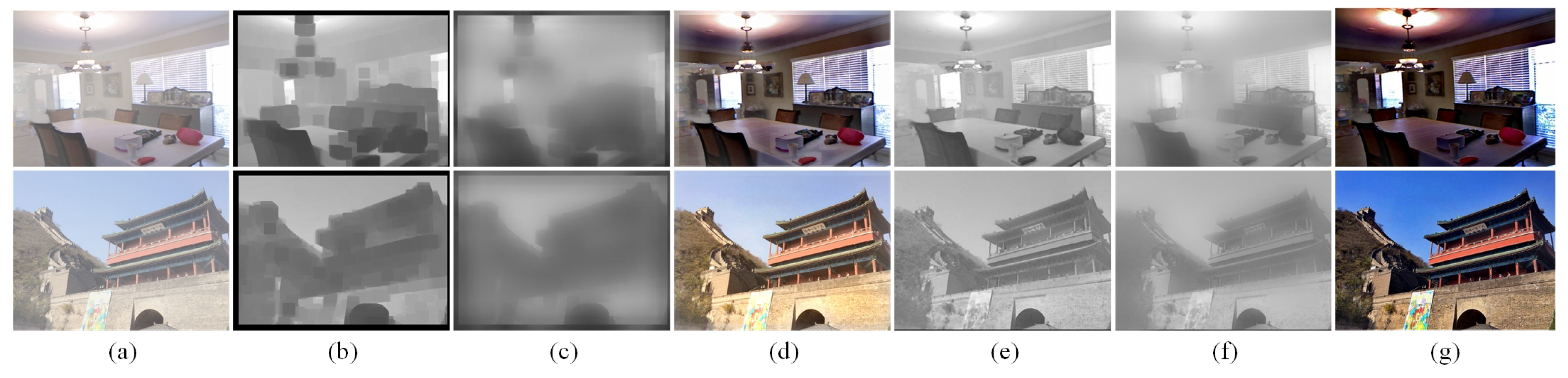
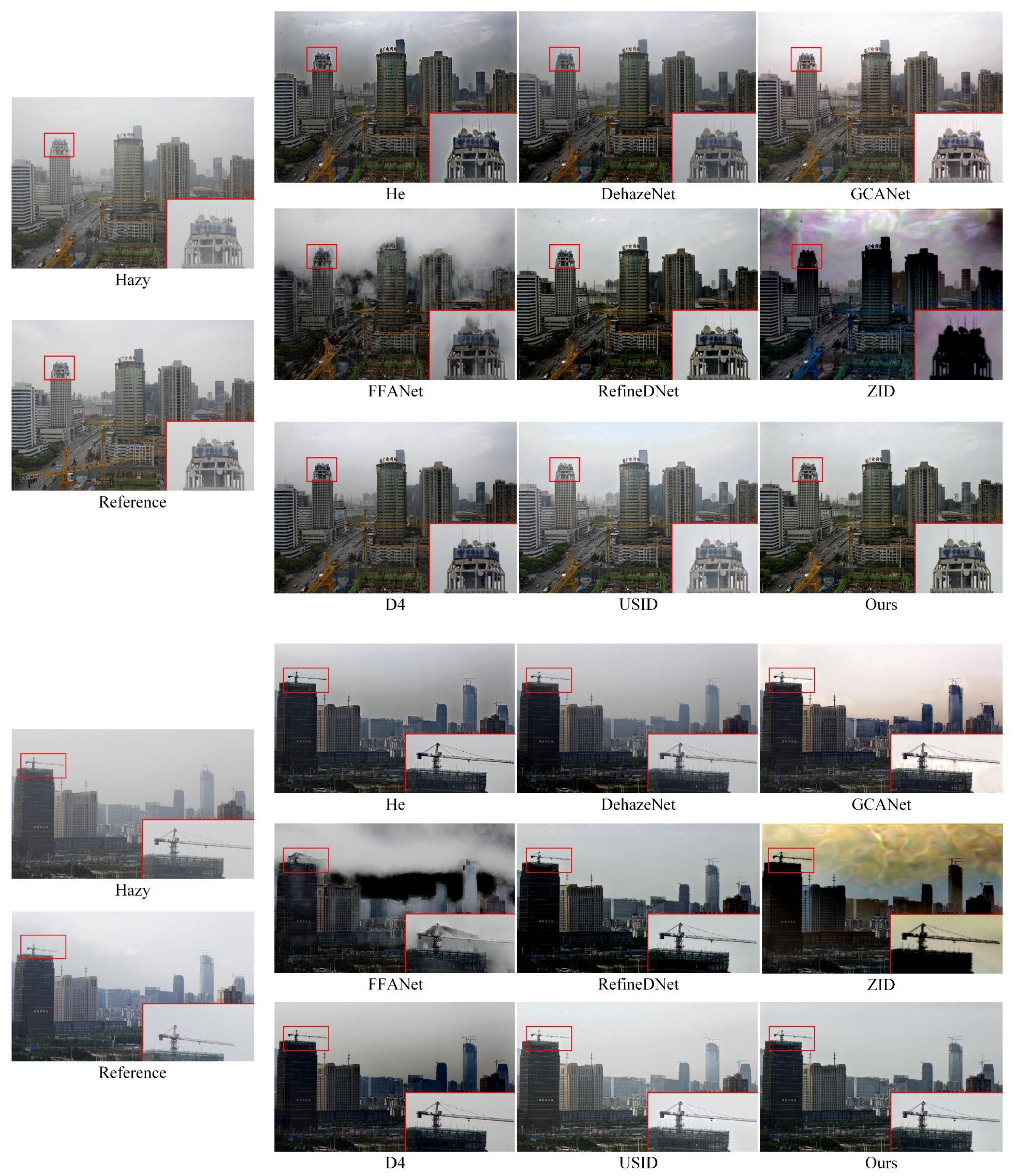








| Type | Methods | SOTS-Indoor | SOTS-Outdoor | O-HAZE | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR↑ | SSIM↑ | LPIPS↓ | PSNR↑ | SSIM↑ | LPIPS↓ | PSNR↑ | SSIM↑ | LPIPS↓ | ||
| Prior | DCP [7] | 16.61 | 0.855 | 0.225 | 19.41 | 0.861 | 0.122 | 12.32 | 0.516 | 0.473 |
| Supervised | DehazeNet [12] | 19.82 | 0.821 | 0.186 | 24.75 | 0.927 | 0.065 | 16.47 | 0.624 | 0.229 |
| GCANet [15] | 30.23 | 0.975 | 0.161 | 24.36 | 0.894 | 0.115 | 18.51 | 0.693 | 0.332 | |
| FFANet [19] | 21.23 | 0.835 | 0.173 | 18.36 | 0.829 | 0.170 | ||||
| Unsupervised | RefineDNet [21] | 25.06 | 0.929 | 0.199 | 23.58 | 0.914 | 0.047 | 19.27 | 0.853 | 0.152 |
| ZID [20] | 17.26 | 0.801 | 0.244 | 12.19 | 0.614 | 0.396 | 9.82 | 0.437 | 0.528 | |
| D4 [27] | 25.40 | 0.934 | 0.207 | 25.75 | 0.936 | 0.035 | 19.90 | 0.844 | 0.147 | |
| USID [22] | 20.09 | 0.873 | 0.218 | 24.97 | 0.930 | 0.044 | 20.12 | 0.862 | 0.140 | |
| Ours | 25.98 | 0.941 | 0.157 | |||||||
| Type | Methods | Number of Parameters | Runtime (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prior | DCP [7] | - | 0.2930 |
| Supervised | DehazeNet [12] | 1.6200 | |
| GCANet [15] | 0.9275 | ||
| FFANet [19] | 1.3418 | ||
| Unsupervised | RefineDNet [21] | 0.7053 | |
| ZID [20] | 57.3681 | ||
| D4 [27] | 0.0579 | ||
| USID [22] | 0.0432 | ||
| Ours | 0.0656 |
| Type | Methods | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prior | DCP [7] | 7.2658 | 7.4342 | 9.3858 |
| Supervised | DehazeNet [12] | 7.2945 | 7.0627 | 7.7306 |
| GCANet [15] | 7.3098 | 6.4246 | 6.9544 | |
| FFANet [19] | 7.1056 | 7.1901 | 7.3398 | |
| Unsupervised | RefineDNet [21] | 7.0903 | 7.9750 | 6.8427 |
| ZID [20] | 7.2770 | 5.1849 | 12.4221 | |
| D4 [27] | 7.2251 | 7.4858 | 7.1425 | |
| USID [22] | 7.3560 | 8.0217 | 7.0951 | |
| Ours |
| Methods | SOTS-Indoor | SOTS-Outdoor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR↑ | SSIM↑ | LPIPS↓ | PSNR↑ | SSIM↑ | LPIPS↓ | |
| Model A | 21.60 | 0.872 | 0.209 | 22.78 | 0.904 | 0.046 |
| Model B | 24.22 | 0.921 | 0.166 | 24.19 | 0.916 | 0.043 |
| Model C | 23.09 | 0.919 | 0.173 | 24.48 | 0.925 | 0.037 |
| ADCP-CycleGAN | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; He, F.; Guo, J.; Wang, Z. Enhanced CycleGAN Network with Adaptive Dark Channel Prior for Unpaired Single-Image Dehazing. Entropy 2023, 25, 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25060856
Xu Y, Zhang H, He F, Guo J, Wang Z. Enhanced CycleGAN Network with Adaptive Dark Channel Prior for Unpaired Single-Image Dehazing. Entropy. 2023; 25(6):856. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25060856
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yijun, Hanzhi Zhang, Fuliang He, Jiachi Guo, and Zichen Wang. 2023. "Enhanced CycleGAN Network with Adaptive Dark Channel Prior for Unpaired Single-Image Dehazing" Entropy 25, no. 6: 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25060856
APA StyleXu, Y., Zhang, H., He, F., Guo, J., & Wang, Z. (2023). Enhanced CycleGAN Network with Adaptive Dark Channel Prior for Unpaired Single-Image Dehazing. Entropy, 25(6), 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25060856







