Hydrogen Embrittlement of CrCoNi Medium-Entropy Alloy with Millimeter-Scale Grain Size: An In Situ Hydrogen Charging Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
3. Results
3.1. Microstructure of the CrCoNi MEA
3.2. Tensile Properties
3.3. Fractography
3.4. Deformed Microstructures
4. Discussion
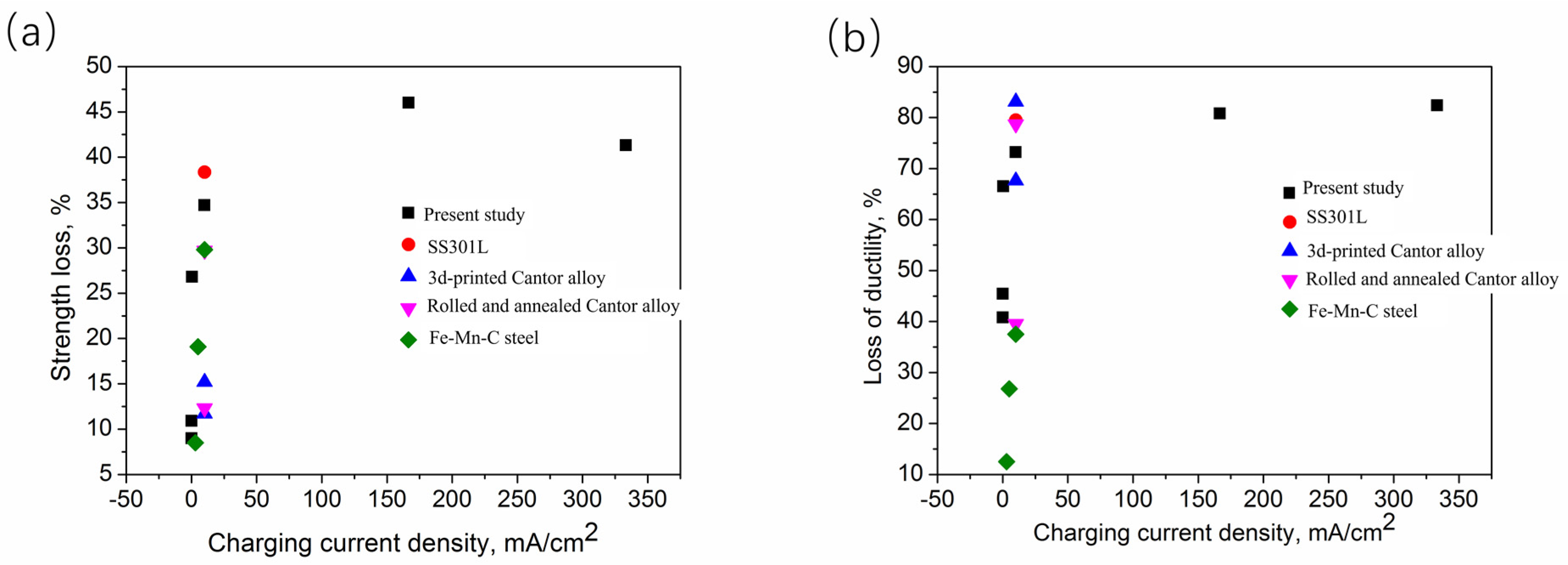
4.1. HE Susceptibility of MEA
4.2. Hydrogen-Assisted Deformation Mechanisms
4.3. Possible Factors Influencing HE of MEA
- Experimental set-ups (pre-charged or in situ charged hydrogen):
- 2.
- Strain rate:
- 3.
- Microstructures:
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, Z.; Yan, S.; Chen, H.; Gou, G. Unprecedented combination of strength and ductility in laser welded NiCoCr medium entropy alloy joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 803, 140501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yuan, X.; Huang, H.; Wen, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wu, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Short-range ordering and its effects on mechanical properties of high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 62, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Qin, Q.H.; Zhong, Z. On the real-time atomistic deformation of nano twinned CrCoFeNi high entropy alloy. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 385705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, E.P.; Curtin, W.A.; Tasan, C.C. High entropy alloys: A focused review of mechanical properties and deformation mechanisms. Acta Mater. 2020, 188, 435–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, E.P.; Raabe, D.; Ritchie, R.O. High-entropy alloys. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Fu, X.; Chen, D.; Chen, S.; Gu, L.; Wei, F.; Bei, H.; Gao, Y.; et al. Tuning element distribution, structure and properties by composition in high-entropy alloys. Nature 2019, 574, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Y.; Nie, Y.; Yan, S. Small-scale mechanical properties and deformation mechanisms of a laser welded CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy joint. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 855, 143959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, Z.; Fu, Y.; Tian, J. High strength-ductility synergy in a laser welded dissimilar joint of CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy and stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 840, 142854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gludovatz, B.; Hohenwarter, A.; Catoor, D.; Chang, E.H.; George, E.P.; Ritchie, R.O. A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications. Science 2014, 345, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.; Fu, X.; Chen, D.; Bei, H.; Gludovatz, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; George, E.P.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, T.; et al. Real-time nanoscale observation of deformation mechanisms in CrCoNi-based medium- to high-entropy alloys at cryogenic temperatures. Mater. Today 2019, 25, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Li, Z.; Raabe, D. Hydrogen enhances strength and ductility of an equiatomic high-entropy alloy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Lu, W.; Fang, X.; Ponge, D.; Li, Z.; Raabe, D. Beating hydrogen with its own weapon: Nano-twin gradients enhance embrittlement resistance of a high-entropy alloy. Mater. Today 2018, 21, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lee, D.-H.; Seok, M.-Y.; Lee, J.-A.; Phaniraj, M.P.; Suh, J.-Y.; Ha, H.-Y.; Kim, J.-Y.; Ramamurty, U.; Jang, J.-I. Resistance of CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy to gaseous hydrogen embrittlement. Scr. Mater. 2017, 135, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichii, K.; Koyama, M.; Tasan, C.C.; Tsuzaki, K. Comparative study of hydrogen embrittlement in stable and metastable high-entropy alloys. Scr. Mater. 2018, 150, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygren, K.E.; Bertsch, K.M.; Wang, S.; Bei, H.; Nagao, A.; Robertson, I.M. Hydrogen embrittlement in compositionally complex FeNiCoCrMn FCC solid solution alloy. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2018, 22, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.H.; Yang, B.J.; Chen, M.; Gou, G.Q.; Chen, H. Effect of recrystallization annealing treatment on the hydrogen embrittlement behavior of equimolar CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 6970–6978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Dai, L.H. Strong resistance to hydrogen embrittlement of high-entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 736, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygren, K.E.; Wang, S.; Bertsch, K.M.; Bei, H.; Nagao, A.; Robertson, I.M. Hydrogen embrittlement of the equi-molar FeNiCoCr alloy. Acta Mater. 2018, 157, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, D.; Li, Z.; Deng, Y.; Barnoush, A. Hydrogen susceptibility of an interstitial equimolar high-entropy alloy revealed by in-situ electrochemical microcantilever bending test. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Pradeep, K.G.; Deng, Y.; Raabe, D.; Tasan, C.C. Metastable high-entropy dual-phase alloys overcome the strength-ductility trade-off. Nature 2016, 534, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Parish, C.M.; Bei, H. Nano-twin mediated plasticity in carbon-containing FeNiCoCrMn high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 647, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Li, Z.; Lu, W.; Ponge, D.; Raabe, D. Hydrogen embrittlement of an interstitial equimolar high-entropy alloy. Corros. Sci. 2018, 136, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astafurova, E.G.; Panchenko, M.Y.; Reunova, K.A.; Mikhno, A.S.; Moskvina, V.A.; Melnikov, E.V.; Astafurov, S.V.; Maier, H.J. The effect of nitrogen alloying on hydrogen-assisted plastic deformation and fracture in FeMnNiCoCr high-entropy alloys. Scr. Mater. 2021, 194, 113642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Yang, B.; Gan, K.; Yan, D.; Li, Z.; Gou, G.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z. Improving the hydrogen embrittlement resistance of a selective laser melted high-entropy alloy via modifying the cellular structures. Corros. Sci. 2021, 190, 109695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, M.; Ichii, K.; Tsuzaki, K. Grain refinement effect on hydrogen embrittlement resistance of an equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 17163–17167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Bei, H.; Pharr, G.M.; George, E.P. Temperature dependence of the mechanical properties of equiatomic solid solution alloys with face-centered cubic crystal structures. Acta Mater. 2014, 81, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplanche, G.; Kostka, A.; Reinhart, C.; Hunfeld, J.; Eggeler, G.; George, E.P. Reasons for the superior mechanical properties of medium-entropy CrCoNi compared to high-entropy CrMnFeCoNi. Acta Mater. 2017, 128, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sheng, H.; Wang, Z.; Gludovatz, B.; Zhang, Z.; George, E.P.; Yu, Q.; Mao, S.X.; Ritchie, R.O. Dislocation mechanisms and 3D twin architectures generate exceptional strength-ductility-toughness combination in CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gludovatz, B.; Hohenwarter, A.; Thurston, K.V.; Bei, H.; Wu, Z.; George, E.P.; Ritchie, R.O. Exceptional damage-tolerance of a medium-entropy alloy CrCoNi at cryogenic temperatures. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhou, L.; Wang, C.; Jiang, P.; Yuan, F.; Ma, E.; Wu, X. High impact toughness of CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy at liquid-helium temperature. Scr. Mater. 2019, 172, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhao, S.; Ding, J.; Chong, Y.; Jia, T.; Ophus, C.; Asta, M.; Ritchie, R.O.; Minor, A.M. Short-range order and its impact on the CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy. Nature 2020, 581, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.X.; Zhao, S.; Jin, K.; Xue, H.; Velisa, G.; Bei, H.; Huang, R.; Ko, J.Y.P.; Pagan, D.C.; Neuefeind, J.C.; et al. Local structure and short-range order in a NiCoCr solid solution alloy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 118, 205501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundararajan, C.K.; Luo, H.; Raabe, D.; Li, Z. Hydrogen resistance of a 1 GPa strong equiatomic CoCrNi medium entropy alloy. Corros. Sci. 2020, 167, 108510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhou, H.; Xing, B.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Qin, Q.H. Crystal plasticity in fusion zone of a hybrid laser welded Al alloys joint: From nanoscale to macroscale. Mater. Des. 2018, 160, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Qin, Q.H.; Chen, H.; Zhong, Z. Hybrid laser welding of dissimilar aluminum alloys: Welding processing, microstructure, properties and modelling. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 56, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Ma, C.; Chen, H. Modifying microstructures and mechanical properties of laser-arc welded joints of dissimilar advanced aluminum alloys. Mater. Charact. 2020, 164, 110331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Chen, H.; Ma, C.; Nie, Y.; Wang, X.; Qin, Q.H. Local corrosion behaviour of hybrid laser-MIG welded Al–Zn–Mg alloy joints. Mater. Des. 2015, 88, 1353–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slone, C.E.; Chakraborty, S.; Miao, J.; George, E.P.; Mills, M.J.; Niezgoda, S.R. Influence of deformation induced nanoscale twinning and FCC-HCP transformation on hardening and texture development in medium-entropy CrCoNi alloy. Acta Mater. 2018, 158, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.H.; Yang, B.J.; Shan, M.L.; Li, T.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Ma, C.P.; Zhang, X.; Gou, G.Q.; Wang, Z.R.; Gao, W. Hydrogen embrittlement behavior of SUS301L-MT stainless steel laser-arc hybrid welded joint localized zones. Corros. Sci. 2020, 164, 108337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, M.; Akiyama, E.; Tsuzaki, K. Effect of hydrogen content on the embrittlement in a Fe–Mn–C twinning-induced plasticity steel. Corros. Sci. 2012, 59, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, M.; Akiyama, E.; Tsuzaki, K.; Raabe, D. Hydrogen-assisted failure in a twinning-induced plasticity steel studied under in situ hydrogen charging by electron channeling contrast imaging. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 4607–4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.; Koyama, M.; Ajito, S.; Akiyama, E. Strain rate sensitivity of hydrogen-assisted ε-martensitic transformation and associated hydrogen embrittlement in high-Mn steel. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 27221–27233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuğluca, I.B.; Koyama, M.; Shimomura, Y.; Bal, B.; Canadinc, D.; Akiyama, E.; Tsuzaki, K. Lowering Strain Rate Simultaneously Enhances Carbon- and Hydrogen-Induced Mechanical Degradation in an Fe-33Mn-1.1C Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2019, 50, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.-S.; Kang, J.-H.; Kim, S.-J. Effect of grain size on hydrogen embrittlement in stable austenitic high-Mn TWIP and high-N stainless steels. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 25076–25090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

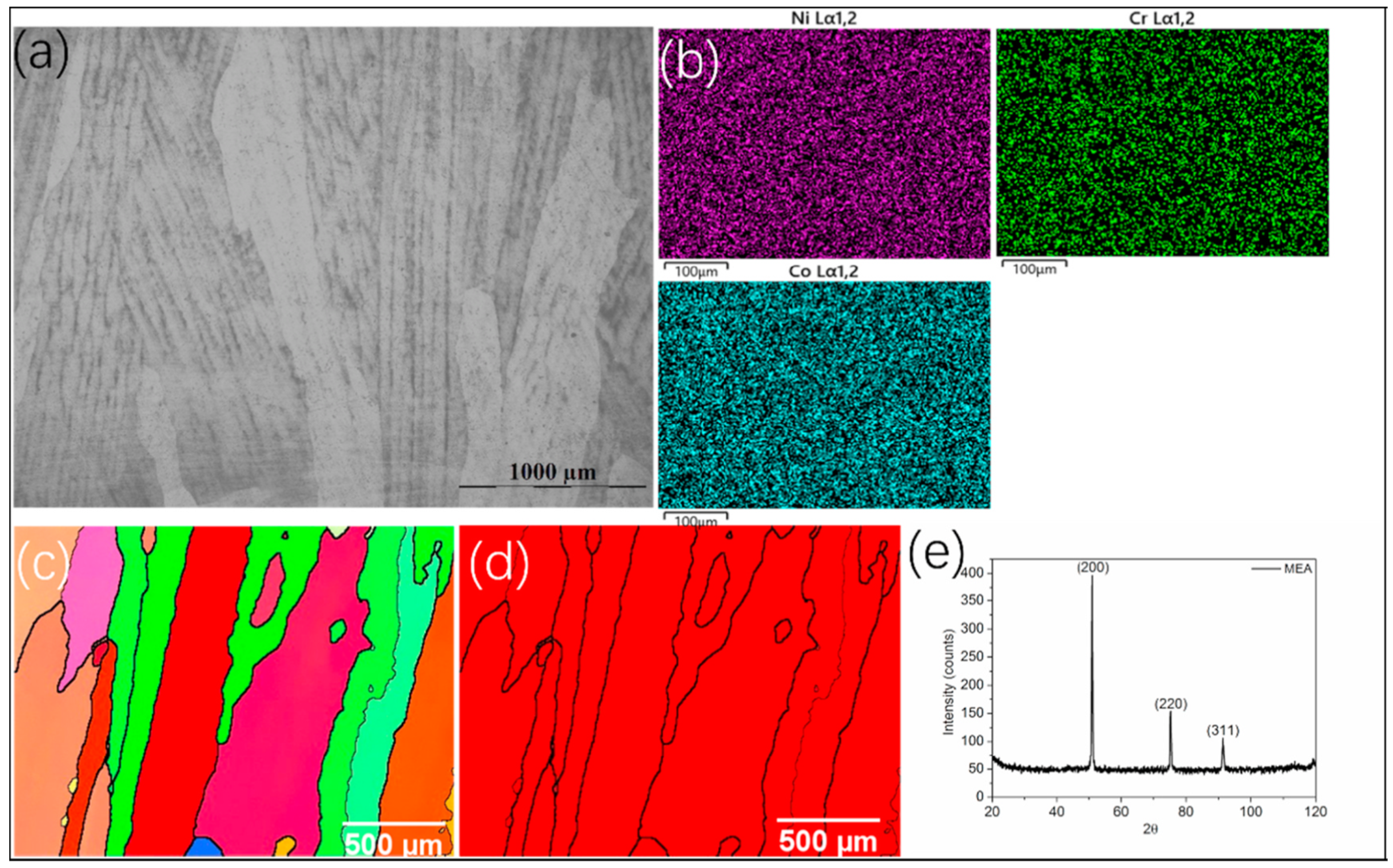
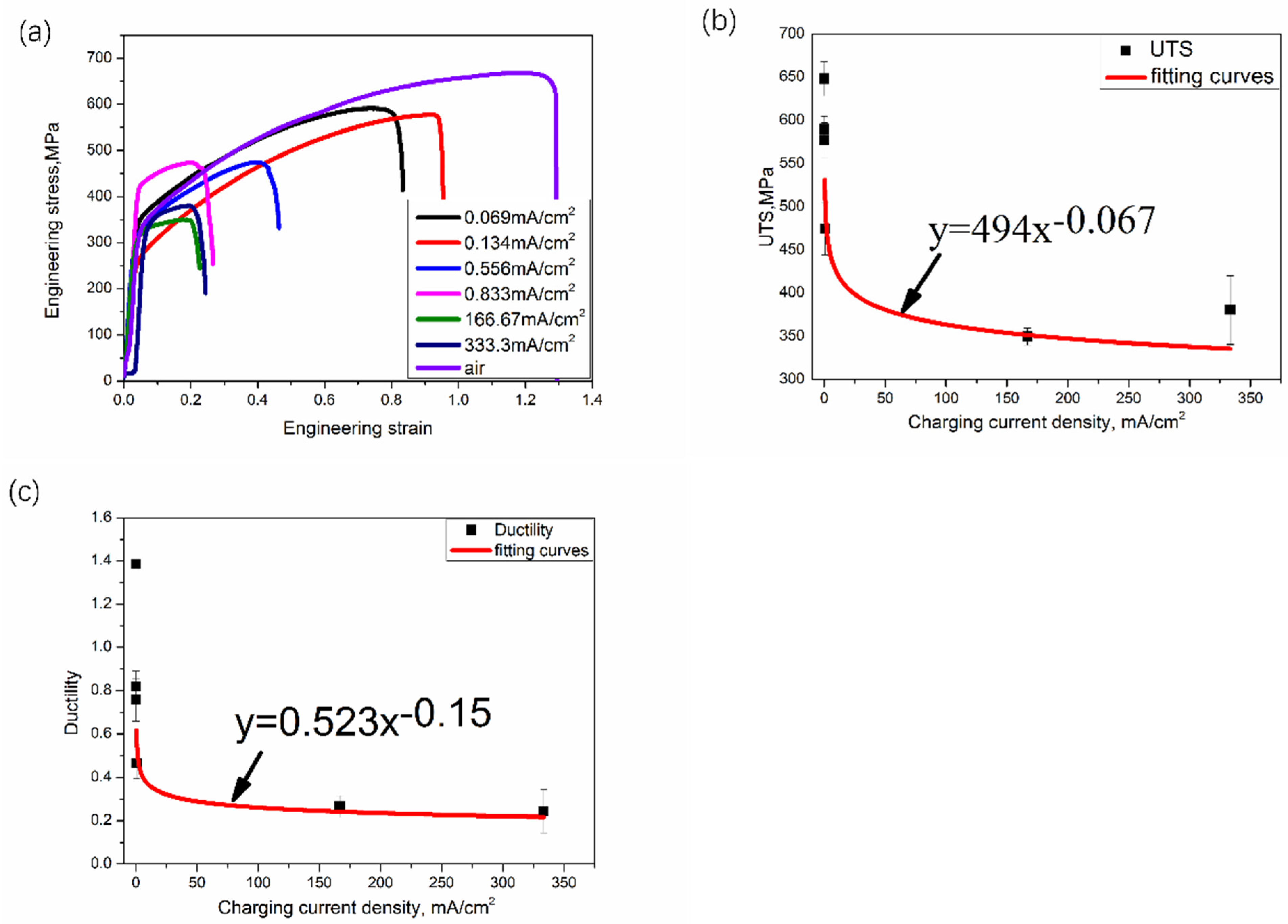

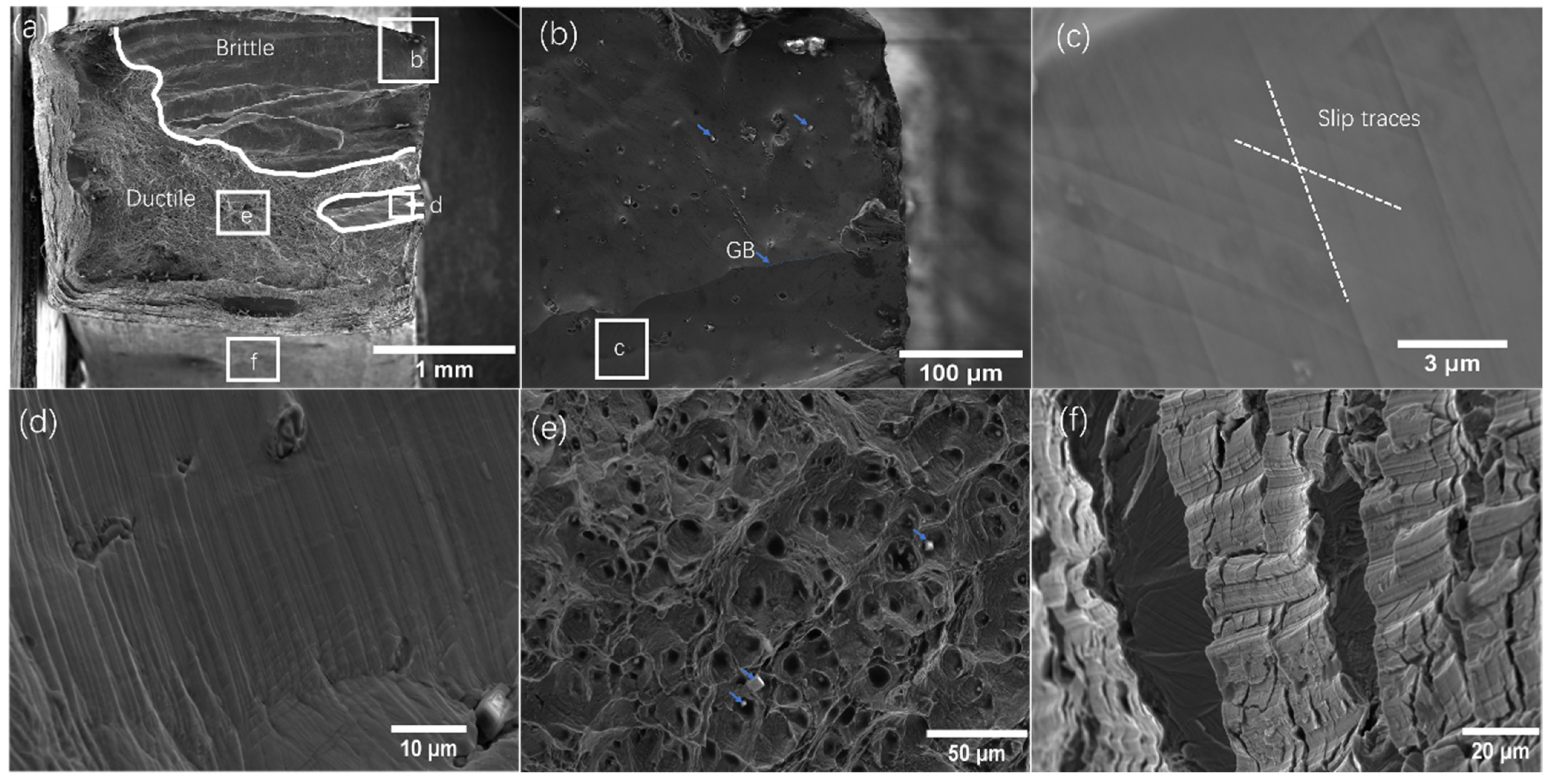


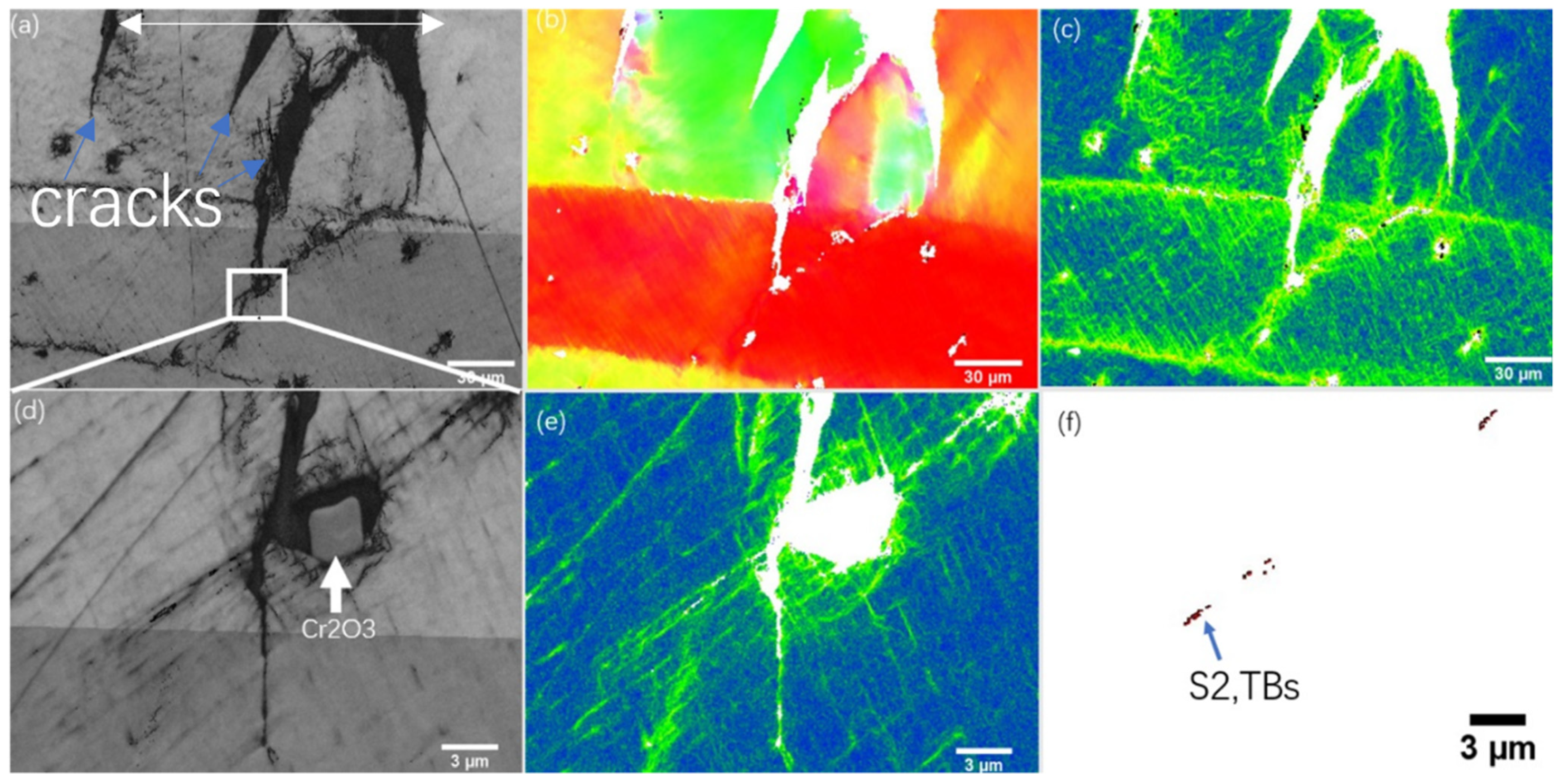

| Elements | wt. % | at. % |
|---|---|---|
| Ni | 31.87 | 30.60 |
| Co | 34.84 | 34.84 |
| Cr | 33.29 | 36.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, S.; He, X.; Zhu, Z. Hydrogen Embrittlement of CrCoNi Medium-Entropy Alloy with Millimeter-Scale Grain Size: An In Situ Hydrogen Charging Study. Entropy 2023, 25, 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25040673
Yan S, He X, Zhu Z. Hydrogen Embrittlement of CrCoNi Medium-Entropy Alloy with Millimeter-Scale Grain Size: An In Situ Hydrogen Charging Study. Entropy. 2023; 25(4):673. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25040673
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Shaohua, Xipei He, and Zhongyin Zhu. 2023. "Hydrogen Embrittlement of CrCoNi Medium-Entropy Alloy with Millimeter-Scale Grain Size: An In Situ Hydrogen Charging Study" Entropy 25, no. 4: 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25040673
APA StyleYan, S., He, X., & Zhu, Z. (2023). Hydrogen Embrittlement of CrCoNi Medium-Entropy Alloy with Millimeter-Scale Grain Size: An In Situ Hydrogen Charging Study. Entropy, 25(4), 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25040673




